AP CHEMISTRY EVERYTHING!!
1/442
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
443 Terms
How to find average atomic mass using mass spectrometry
Calculate the weighted average for atomic mass of the naturally occurring isotopes, usually found in a graph
How much does one mole of gas occupy at STP
22.4L, Moles =(Liters) / (22.4L/mol)
How to calculate percent composition of an element in a compound
Count the number of atoms of each element present
Then, multiply number of atoms by atomic mass
Then, add up masses of ind. elements to get whole molar mass
Finally, divide each ind. molar mass by total molar mass and multiply by q00% to get percent composition
How to find empirical formula
Assume 100 g sample, convert % of element to grams
Convert grams of each element to moles
Divide each mole by the lowest of the values
This number is the subscript on each element!
(if you don’t get whole numbers multiply all numbers by number needed to make whole (.33×3, .5×2, etc))
How to find molecular formula
Take total molar mass of empirical formula
Divide given molar mass over the empirical mass to find the ratio
Multiply subscripts by this ratio number
Positively charged nucleus attracts __________
negatively charged electrons
Electrons have a lower PE and are ore stable when ______
closer to nucleus
Electrons CANNOT exist _______ (where?)
between energy levels (must be 1 OR 2,not inbetween)
What does Coulomb’s law tell us?
As the magnitude, or value, of the charges (q1 and q2) increases in the numerator, the force between them increases, since electrons all have the same charge, only protons affect this, and therefore, there is more attraction for nuclei with more protons
Distance between the charges is in the denominator, so there is a smaller force when farther apart, and electrons closer to the nucleus are more attracted
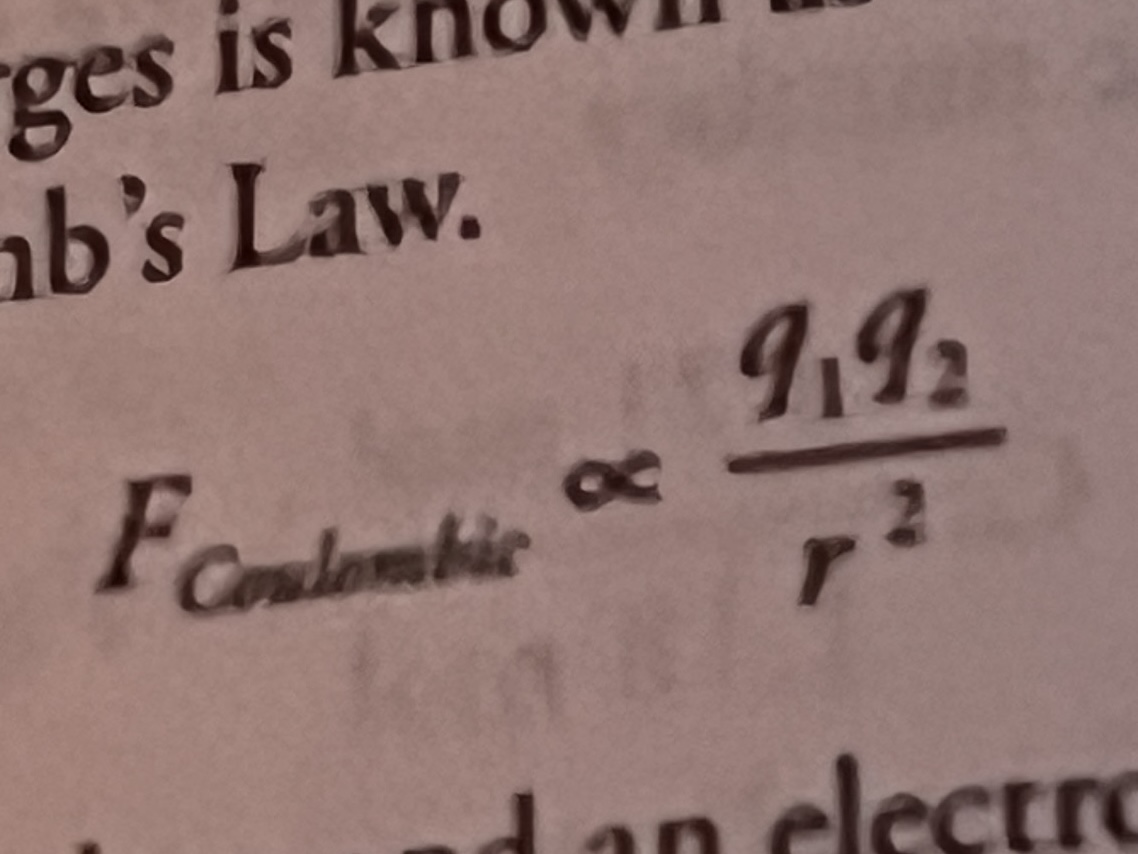
What is ionization energy
How much energy needs to be added in order to overcome the electrostatic energy, or the energy required to remove most loosely held electron. can have 1st, 2nd, 3rd, etc ionization energy, which increase as you go (takes more energy to take more)
Where is ionization energy the highest
Upper right (where attraction is strongest)
Why would a subsequent IE be MUCH higher than the first
Because there is a LARGE spike in IE anytime electrons are removed from a full subshell
WHat is photoelectron spectrum
Graph showing relative IE and therefore can tell you electron configuration
Peaks in the same group correspond to ejection of electrons in ______
same energy level
Same energy level electrons still have slightly different binding energies because of _____
different subshell shapes
First subshell
s-subshell, one orbital, 2 electrons
Second subshell
p-subshell, 3 orbitals, 6 electrons
How many electrons can one orbital hold
2 electrons
Aufbau principle
Electrons will completely occupy lowest orbitals first (1s before 2s)
Pauli Exclusion Principle
2 electrons per orbital and they MUST have opposite spins
Hund’s Rule
Electrons will occupy each orbital once BEFORE pairing up (only up arrows , then add down arrows one at a time)
What are ions, anions, cations
Ion-atoms that have gained or lost electrons
Anion-negative charge (added e-)
Cation-positive charge (lost e-)
Transition metals lose what before d orbitals
higher level s orbitals electrons first (4s BEFORE 3d)
Periodic Trends: Electrons are attracted to ____ in nucleus, attraction increases with what
Electrons are attracted to protons in the nucleus, Closer an electron=more attraction, More protons in nucleus=stronger attraction
Period Trends: Why do valence electrons not experience full charge (Z) of the nucleus?
Because inner core electrons shield and repel them from nucleus, they experience Zeff which is less than Z
Valence electrons on the ______ of the PT are more strongly attracted than those on the _____
Valence electrons on the RIGHT of the PT are more strongly attracted than those on the LEFT (added valence don’t shield, so added protons increase)
Valence electrons toward the ____ of PT are more attracted than those on the _____
Valence electrons toward the TOP of PT are more attracted than those on the BOTTOM (more shielding and more distance)
Where are valence electrons of an atom more attracted to nuclei?
TOP RIGHT
Atomic radius increases ____ and ____
down and left (right is more tight attracted and top has less shielding)
Cations are ___ than corresponding atom
Anions are ___ than corresponding atom
Cations-SMALLER (more p than e, so more attraction)
Anions-LARGER (more e, more repulsion)
Electronegativity (EN) is
How strongly an atom attracts valence electrons in a covalent bond with other atoms
Electronegativity increases ____ and ______
UPWARD AND RIGHT, parallels the attraction to their own electrons, more protons and less shielding=more attraction
IE increases ____ and _____
UPWARD AND RIGHT, more protons and less shielding=more attraction
What is electron affinity
Likelihood to gain and electron, and change in energy when a gas phaser atom does gain an electron
Electron Affinity increases ____ and ______ on PT
UPWARDS AND RIGHT, similar (not same) to EN, how much an atom can attract an electron, more attraction, less shielding
Where does the energy (as heat) flow in a system for an endothermic process? What is the sign on ΔH? What does the temperature feel like?
Heat flows INTO the system, it absorbs energy, therefore the ΔH gets a + sign (the heat within the system goes up because it absorbs energy), because it is absorbing heat from the surroundings it feels colder because the heat from the surroundings (your hand) is being absorbed and the surroundings lose energy and heat and feels colder.
Where does the energy (as heat) flow in a system for an exothermic process? What is the sign on ΔH? What does the temperature feel like?
Heat flows OUT of the system, it releases energy, therefore the ΔH gets a - sign (the heat within the system goes down because it loses energy), because it is releasing energy into the surroundings it feels warmer because the heat from the system is being released into the surroundings (your hands) and the surroundings gain energy and heat and feel warmer.
in an endothermic reaction (absorbing energy) the product in a reaction has…energy
MORE energy
in an exothermic reaction (releasing energy) the product in a reaction has…energy
LESS energy
Equation for ΔE
ΔE = q + w
in ΔE = q + w, q represents
Heat
in ΔE = q + w, w is…
work
in ΔE = q + w, ΔE is the…
change in the system’s (internal) energy
Units for all of this in ΔE = q+w, the units are
J or kJ
in ΔE = q+w, + q or - q means..
+q means the system gains heat, -q means the system loses heat
in ΔE = q+w, ±w means…
+w means work is done ON the system
-w means work is done BY the system
in ΔE = q+w, +\- ΔE means…
+ΔE means net GAIN of energy by the system (endothermic)
-ΔE mean net LOSS of energy by the system (exothermic)
What is H, what does it mean when ΔH is ±
H is enthalpy (heat flow)
+ΔH is endothermic (heat flow increases by absorbing)
-ΔH is exothermic (heat flow decreases or is released
heat capacity of a substance.. equation and units?
C = heat absorbed (ΔH) / increase in temp (Δt)
units are J/°C
What is specific heat capacity
the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1°C
can be designated by symbol s Cp or c
What does a high/low specific heat capacity mean for a substance
a substance with a high specific heat capacity requires a lot of energy to heat up BUT will retain the energy longer and result in a smaller ΔT (ex. water)
a substance with a low specific heat capacity heats up quickly and cools down quickly resulting in a larger ΔT (ex. most metals)
equation for K
K = °C + 273
change in 1°C means what for K
means there is a change in 1K
Δ1°C = Δ1K
molar heat capacity
amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 mol of a substance by 1°C
units: J/mol*°C or J/mol*K
to find energy/heat flow (ΔH) use the equation..
m*c*Δt
MCATTTTTT
what do variables mean in mcat
m=mass in grams
c=specific heat capacity
Δt = change in temp (Tfinal-Tinitial)
When one substance is added to another an important assumption is that…
ALL of the heat transfers from substance a to substance b
heat lost by substance a = heat gained by substance b
using the previous assumption, because the HEAT FLOW between the two is equal (all is transferred, and ΔH is heat flow, and ΔH is mcat then you can use the equation ____
mcΔt=mcΔt
Important note: when performing calculations using this Δt has to be POSITIVE on both sides of the equation (so Tfinal and Tinital will have to be opposite on one side or the other)
Steps for Hess’ Law
To calculate the ΔH for overall reaction rearrange the equations to have the correct coefficients or flip the equations to cancel out substances until you have the reaction you want, if you flip them make the ΔH negative or multiply them by the coefficients and add the ΔHs
ΔHf° is ..?
the change in enthalpy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of a compound from its elements. All substances are in their standard states (a precisely defined reference state) 1 atm for gases, 25°C, 1M for solutions
this is NOT the same as STP
to calculate ΔHrxn° =
[∑n*ΔHf°products] - [∑n*ΔHf°reactants]
∑=the sum of and n=moles (ie coefficient from balanced equation)
Ways to calculate ΔHrxn
Hess’s Law
ΔH bonds broken - ΔH bonds formed
[∑n*ΔHf°products]-[∑n*ΔHf°reactants]
ΔH = mcAt
S is ____
entropy, a measure of how dispersed (=randomized) (ordered) the energy of a system is
a reaction is said to be spontaneous if…
it occurs without outside intervention
this could happen fast or slow, it happens without intervention
also could be called thermodynamically favorable
More ordered means…
low energy dispersal, low entropy
-S = less spontaneous
More disordered means:
high energy dispersal;high entropy
+s = more spontaneous
A state in which a given amount is more highly dispersed (or randomized) has MORE entropy than a state in which the same energy is more highly ____
concentrated
dispersed is more random than concentrated
Examples of entropy increases:
increase in temperature
vaporization (becoming gas), melting
mixing of substances
expansion of a gas
increase in volume
What is positional probability
the greater number of available positions, the greater the entropy (more disorder and greater energy dispersal)
more positions is more disorder because there are more choices for ways for the thing to orient move and be dispersed
Second law of thermodynamics
in any spontaneous process there is always an increase in the entropy of the universe
ΔSuniverse = ΔSsystem + ΔSsurrounding
if ΔSuniverse is + then it is a spontaneous process
to predict the sign of ΔS you…
see which side of eqn has (in this order) more mols gas, if same then more mols of any substance, if same then more positions
more in products is +, more in reactants is -
look at the reaction equation gas is more disorder because it is more dispersed more mols in reactants/products means more positions/disorder gas takes priority over mol value so if the products has more gas or more mols then S is + because there is more disorder in the products, and vice versa: S is - if the reactants are more disordered
3rd law of thermodynamics
the entropy of a perfect crystal at 0K is ZERO
(remember that all molecular motion ceases at 0K)
🔺S° can be calculated with…
[∑n*ΔSf°products] - [∑n*ΔSf°reactants]
ΔS° is in terms of
J/K
Free energy ( G ) is…
maximum amount of of energy that is available, lets us compare the relative tendency of a reaction to occur IE
a measure of spontaneity factoring in H AND S
-ΔG means
spontaneous process
+ΔG means
non spontaneous process
0ΔG means
equilibrium, NO free energy change, no energy is released or gained or changed, it just stays the same
First method for calculating ΔG
ΔG=ΔH-TΔS
method two for finding ΔG
Hess’s law, adding several reactions together, manipulating the sign or coeffiecents and doing the same for G
Third method for finding ΔG
(Σn*ΔGf°products)-(Σn*ΔGf°reactants)
To find the boiling or melting point you should
set ΔG equal to 0 which is the boiling/melting point and when the process isnt spontaneous or not spontaneous
To find at what temperature the system is spontaneous you can either
find the boiling point (set G to 0 solve for T) (ex 333K) and plug in one above or below that number (334) and see the sign on ΔG and you know if it spontaneous above or below the equilibrium point (333) then look at the signs on ΔH and ΔS (table with ± H and S), if it is spontaneous at high temps, it will be temps above your boiling point (above 333K), and vice versa (low temps, below 333K). if it’s all or no temps, you don’t need to know boiling point or anything yk already what it is from that
+ΔS is (favorable or not favorable)
FAVORABLE (more entropy/disorder and nature is “lazy” and likes less order, more thermodynamically favorable)
-ΔS is (favorable/not)
NOT FAVORABLE (less entropy/more order, it takes more energy to be ordered and nature is lazy)
-ΔH is (favorable or not)
FAVORABLE (exothermic, releasing energy and is more stable which is better)
+ΔH is (favorable or not)
NOT FAVORABLE (endothermic, gains energy, takes effort to gain energy ADN becomes less stable at higher energy states)
+ΔS and -ΔH means
spontaneous at ALL temps (both favorable, ΔG is -, because according to ΔG=ΔH-TΔS, the TΔS remains negative with a positive S being multiplied, and when -H subtracts a negative it will ALWAYS be negative aka spontaneous)
+ΔS and +ΔH means
spontaneous at HIGH temps (because you are subtracting ΔH-TΔS, TΔS has to be larger than ΔH in order to result in a negative (spontaneous) answer, and in order to make it larger, T (temp) has to be high)
-ΔS and -ΔH means
spontaneous at LOW temps (if ΔS is negative TΔS will end up being positive, so in order to result in a negative (spontaneous) answer you have to add something to -ΔH that is smaller so it doesnt become positive, in order to + something smaller, T has to be lower) (and a really low -T means that you will still be subtracting TΔS and it will be spontaneous at this low temp)
-ΔS and +ΔH
Spontaneous at NO temps (both are unfavorable and according to ΔG=ΔH-TΔS, if ΔS is negative you will end up adding TΔS, and since ΔH is positive when you add to a positive, it will always be positive (nonspontaneous))
To answer questions about whether something is spontaneous, if you are given values for ΔH and ΔS AND are given a temp use..
ΔG=ΔH-TΔS and look at the sign on ΔG
To answer questions about what temps or whether something is spontaneous, if you are given values for ΔH and ΔS ONLY use..
“When ΔG=0 (equilibrium) then T=ΔH/ΔS and you can find the temp at which it is at equilibrium and then use the signs on ΔH and ΔS to determine if it is spontaneous above or below that temp (or spontaneous always/never)
Strong electrolytes (SE) are substances that
break apart (dissociate) completely in water
Molarity (M) =
Mols of solute (substance being dissolved) / Liters of solution (solute+solvent)
when can you use M=mols/Liters
in a solution problem when you are given mols or grams (and can convert to mols)
Equation to use for solution chemistry when NOT given grams or mols
(M1)(V1)=(M2)(V2)
To calculate the concentration of all ions present in a solution…
Find the molarity (M) and then using the chemical equation multiply the molarity by the coeffiecients in the eqn
IMPORTANT SOLUBILITY RULE: all Na+ K+ NH4+and NO3- salts are
ALWAYS soluble in water. they will never form the precipitate in a reaction and will be aqueous (aq), meaning the other product is normally the precipitate (if there is one)
Steps for stoich of precipitation reactions
us the solubility rule to write the balanced eqn
identify given and find
convert moles of reactants using molarity eqn (M=mol/L)
determine mole-to-mole ratio using balanced eqn
convert to desired units
(basically the same but you use M=mols/L instead of molar mass to convert volume to moles, this is written as value of molarity/1 liter because in M=mol/L if L is 1 then mols=M)