Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
What are neurons
cells that receive information and transmit it to other cells
What are the parts of a neuron
Dendrites - receive information from previous neuron
Cell body - processes said information
Axon - Carries the information from the cell body to the axon terminals
Axon terminals - passes on the information to the next cell
Myelin sheath - a fatty substance that covers the axons and speeds up the propagation of information
Nodes of Ranvier - interruptions in the myelin sheath of the axon
What are the 3 types of neurons
Motor neurons - soma in the spine
- receives excitation from other cell
- conducts impulses to muscles or glands
Sensory neuron - is specialized at one end to be very sensitive to a specific type of stimulation
Inter neurons - connects the sensory and the motor neurons
what are dendritic spines
they are short outgrowths that increase the surface area available for synapses
In people with schizophrenia, they often have a lot of dendritic spines, this can lead to them experiencing things that don’t exist, as they often have impulses that don’t exist.
What are the 2 directions in which a neuron can be labeled
Afferent neuron- brings info into a structure
Efferent neuron - brings info out of a structure
What are glial cells
cells in the nervous system, that don’t carry impulses as far as neurons do.
Astrocytes
star shaped glial cells that wrap around the synapses, and helps in passing chemicals back and forth between neurons and the blood
Microglia
they help in removing waste materials, pathogens, and dead or dying neurons from the brain
Oligodendrocytes
help in building the myelin sheath that surrounds the neurons in the CNS
Schwann cells
helps in building the myelin sheath in the PNS
Radial Glia
guide the migration of neurons during embryonic development. They later differentiate into the other neural cells when development is complete
What is the blood brain barrier
mechanism that excludes most chemicals from the brain
What are the 3 cells that make up the bbb?
Endothelial cells
Pericytes
Astrocytes
What are the 3 mechanisms used in the bbb
Physical → the endothelial cells are held tgt by tight jns that act as physical barrier
Transport → They control the movement of anything with the help of certain transporters
→ There are 2 types of transporters efflux transporters [use cellular energy to move things that have passively diffused against their conc gradient, usually located on the blood side of the bbb] and
→ nutrient transporters [facilitate the transport of nutrients(glucose) and amino acids, down their conc gradient and into the brain]
Metabolic → the barrier contains a bunch of enzymes that metabolize and inactivate a bunch of neurotransmitters, drugs and toxins, preventing them from entering the brain
Why is the bbb not used for other organs also
It is such a good defense that it does not allow for the transport of neccesary materials [glucose and amino acids].
The brain has special transport mechanisms for these materials that are not found in the other parts of the body.
What are the circumventricular organs
They are the organs that are around the midline of the ventricular system and do not have the bbb
eg. the pituitary gland in the brain needs access to blood to monitor hormone levels, and thus has access
How can you make drugs cross the bbb
make them lipid soluble
deliver them direct to the cerebral spinal fluid
use vasoactive compounds
repress the efflux transporters to prevent the drug from being put back into the blood
hack the nutrient transporters to move the drugs
What provides energy for the brain
Glucose, and large amounts of it cross the bbb
Thought the brain is only 2% of the body’s weight it uses 20% of the O2 and 25% of the glucose
What vitamin is needed for the brain to actually use glucose
Vitamin B1, thiamine
Local neuons
neurons without an axon
Electrical gradient
the difference between the levels electrical charges in and out the cell [-70mV at rest, called resting potential]
cellular conditions at rest
Na+ is more outside the cell and is in more quantity making the outside relatively +ve
K+ is more inside the cell and is in less quantity making the inside relatively -ve
Na+ channels are closed
K+ channels are closed
NaK [3 Na out and 2 K in] pump is active and moves ions that have passively diffused against their conc gradients
Voltage gated channels
channels that need the cell membrane to reach a certain voltage to open
Ligand gated channels
Are triggered when a certain chemical attaches to them
Mechanically gated channels
open in response to physical forces [change in length or pressure]
Graded potential
a membrane potential that varies in magnitude based on the intensity of the stimulus
causes the membrane to move away from resting potential
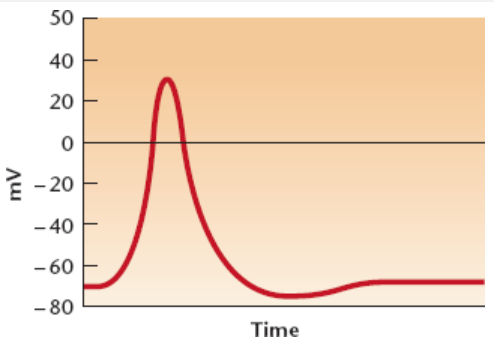
List the 3 phases of this graph and their respective voltages
Rest = -70mV
Threshold = -55mV
Peak = 30mV
Hyperpolarization = below -70mV
All about the action potential
Transcript in the ppt
Hyperpolarization
increased polarization of the membrane
depolarization
reduced polarization
threshold
minimum polarization for all or none action potential
All or nothing law
principle that amplitude and the velocity of an action potential are independent of the stimulus that initiated it
every depolarization post threshold produces the same resulting action potential
Propogation
transmission of an action potential down an axon
Saltatory conduction
the jumping of potentials from node to node
Absolute refractory period
membrane is unable to produce another action potential
Relative refractory period
period after arp, where the membrane requires a stronger than usual stimulus for an action potential
local anesthetic
drug that attaches to na channels preventing propogation of action potentials