bio 16 Inheritance
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/56
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
1
New cards
meaning of haploid (n)
\-a cell that possesses one complete set of chromosomes
2
New cards
meaning of diploid (2n)
\-a cell that possesses two complete sets of chromosomes ( 2n, where n = the number of chromosomes)
3
New cards
what is meant by homologous pairs of chromosomes
pairs of chromosomes in a diploid cell that have the same structure and the same genes at the same loci.
Each member of the homologous pair is provided by each parent
Each member of the homologous pair is provided by each parent
4
New cards
explain the need for a reduction division during meiosis in the production of gametes
\n reduce / halve, chromosome number ; \n retain diploid number at fertilisation ; \n prevent chromosome number doubling each generation ; \n ref to variation ; A ref. to meiosis crossing over / independent assortment
5
New cards
(i) Explain the term F1 generation.
1 (first) generation of offspring (from parental cross) ;
2 (parents are) homozygous / true bred / pure bred / pure breeding ;
3 F1 generation will be heterozygous ;
2 (parents are) homozygous / true bred / pure bred / pure breeding ;
3 F1 generation will be heterozygous ;
6
New cards
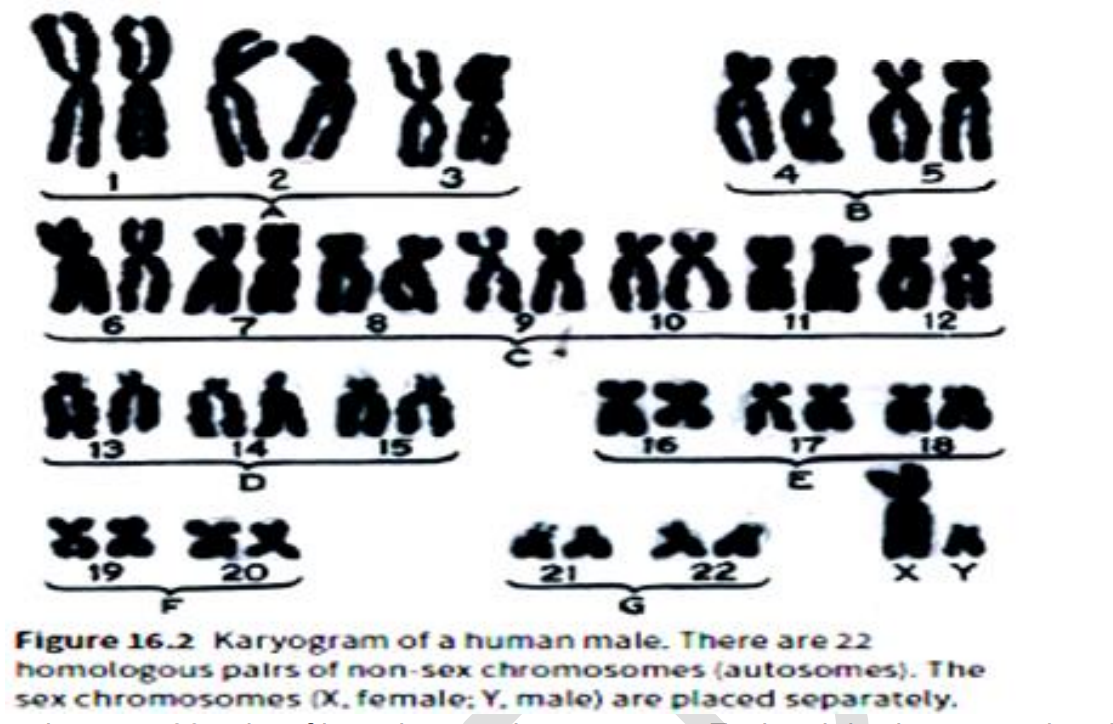
what is a Karyogram
photograph or diagram of a set of chromosomes from an individual
(non-matching X and Y- chromosomes are called sex- chromosomes but all the other chromosomes are called autosomes)
(non-matching X and Y- chromosomes are called sex- chromosomes but all the other chromosomes are called autosomes)
7
New cards
what is an allele
different versions/forms of a gene
8
New cards
2 parts of meiosis
\-meiosis I and meiosis II
9
New cards
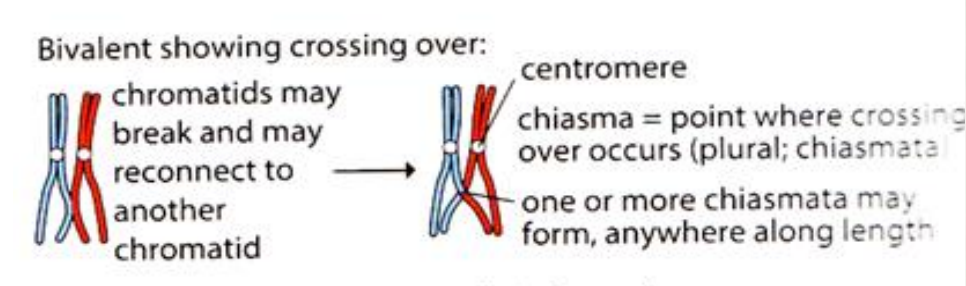
describe the steps of prophase 1
\- Homologous chromosomes shorten and thicken (condensation) and come together in their homologous pairs. Each pair is called a bivalent. This process is called synapsis.
\-centrosomes move to opposite ends of nucleus.
\-crossing over between non-sister chromatids of a pair of homologous chromosomes (bivalent) at chiasmata
\-the nucleolus disappears and the nuclear envelope breaks up
\-spindle produced
\-centrosomes move to opposite ends of nucleus.
\-crossing over between non-sister chromatids of a pair of homologous chromosomes (bivalent) at chiasmata
\-the nucleolus disappears and the nuclear envelope breaks up
\-spindle produced
10
New cards
steps of Metaphase I:
\-The bivalents arrange themselves randomly on the equator of the spindle with each of a pair of homologous chromosomes facing opposite poles.
\-Centromeres are attached to the spindle.
\-Centromeres are attached to the spindle.
11
New cards
steps of Anaphase I:

12
New cards
steps of Telophase I:
\-in animal cells a nuclear envelope and nucleolus reforms around the chromosomes at each pole
\-Microtubules pull two sides of the cell surface membrane and cell becomes narrower towards its center to give two separate cells (cytokinesis)
\-Microtubules pull two sides of the cell surface membrane and cell becomes narrower towards its center to give two separate cells (cytokinesis)
13
New cards
Difference in meiosis1 in plants and animals
\-In most plant cells there is no telophase I and the cell goes directly into metaphase II.
14
New cards
describe the steps of meiosis 2
Prophase II: -Nuclear envelope and nucleolus disappear -Chromosomes shorten and thicken and spindle fibers reform. -Centrosomes and centrioles replicate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
Metaphase II: -Chromosomes line up separately across equator of the spindle.
Anaphase II: -Centromeres split and the sister chromatids separate each other and are pulled to opposite poles by spindle fibers.
Telophase II: -Four daughter cells are formed. -Each cell has the haploid number of chromosomes.
Metaphase II: -Chromosomes line up separately across equator of the spindle.
Anaphase II: -Centromeres split and the sister chromatids separate each other and are pulled to opposite poles by spindle fibers.
Telophase II: -Four daughter cells are formed. -Each cell has the haploid number of chromosomes.
15
New cards
Explain how meiosis and fertilisation can result in genetic variation amongst offspring

16
New cards
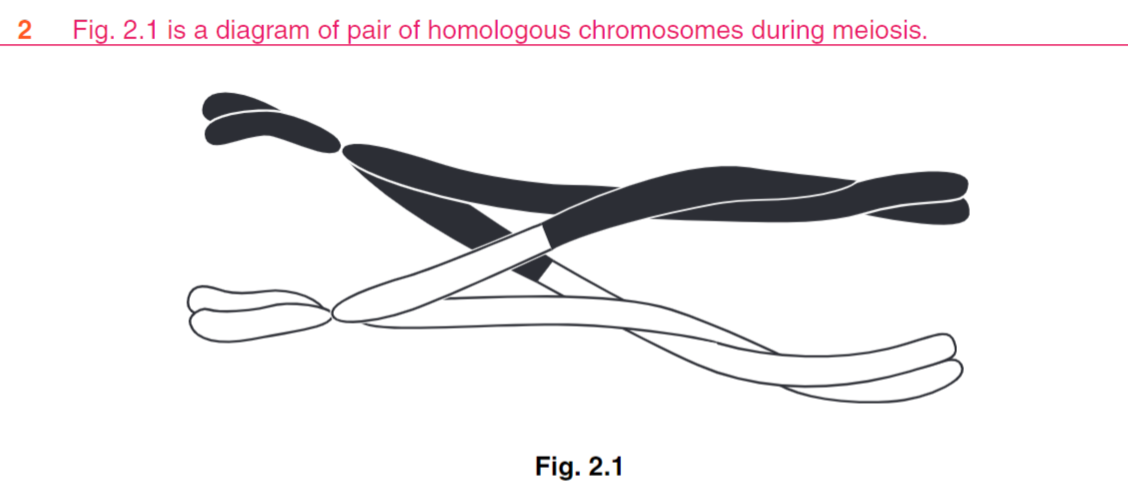
(ii) Describe how crossing over produces genetic variation in a population.
\

17
New cards
define gene
a length of DNA that codes for the production of a polypeptide molecule
18
New cards
define genotype and phenotype
Genotype: the genetic makeup of an organism and describes the alleles that an organism contains
Phenotype: the observable characteristics of an organism.
Phenotype: the observable characteristics of an organism.
19
New cards
define homozygous and heterozygous
If the allele on each of the chromosomes is the same then the organism is called homozygous for the characteristic.
heterozygous means having two different alleles of a gene
heterozygous means having two different alleles of a gene
20
New cards
Define the terms dominant and recessive.
dominant – allele always has effect on phenotype / allele expressed in homozygote and heterozygote / allele always expressed ;
\
recessive – allele only has effect on phenotype if dominant allele absent / only expressed in homozygote ;
\
recessive – allele only has effect on phenotype if dominant allele absent / only expressed in homozygote ;
21
New cards
define Codominant alleles
when two different alleles are present in the genotype and both have an effect on the phenotype of a heterozygous organism
phenotype of heterozygote different from either homozygote
phenotype of heterozygote different from either homozygote
22
New cards
what are F1 and F2 generations
\-The F1 generation is the offspring resulting from a cross between an organism with a homozygous dominant genotype, and one with a homozygous recessive genotype. -The F2 generation is the offspring resulting from a cross between two F1 (heterozygous) organisms.
23
New cards

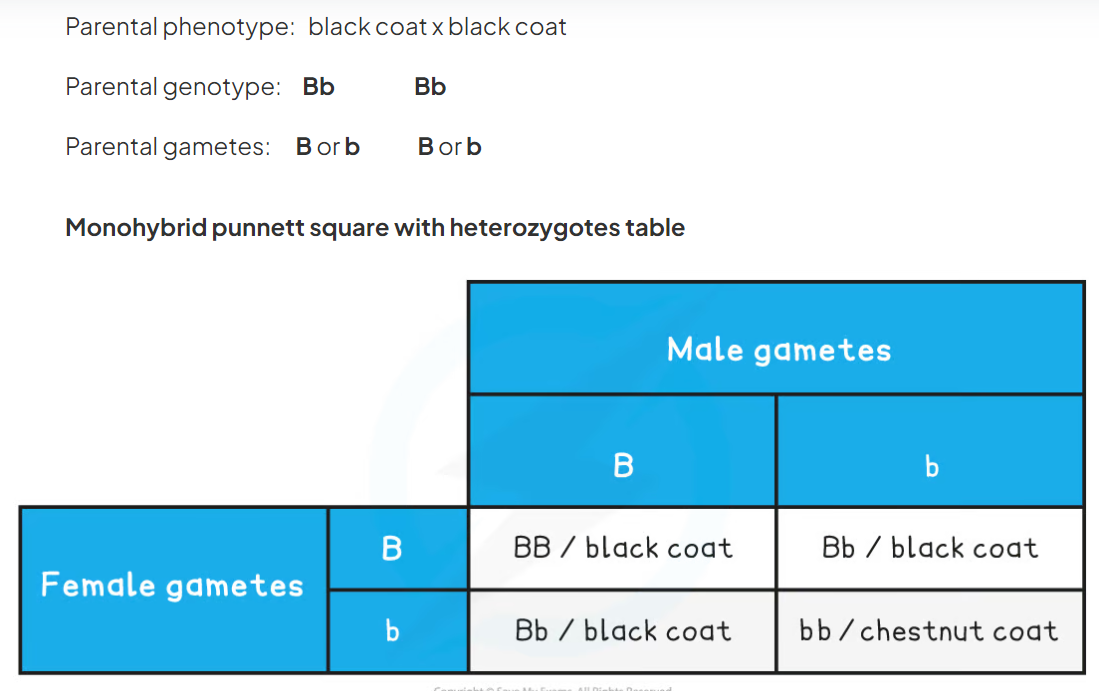
24
New cards
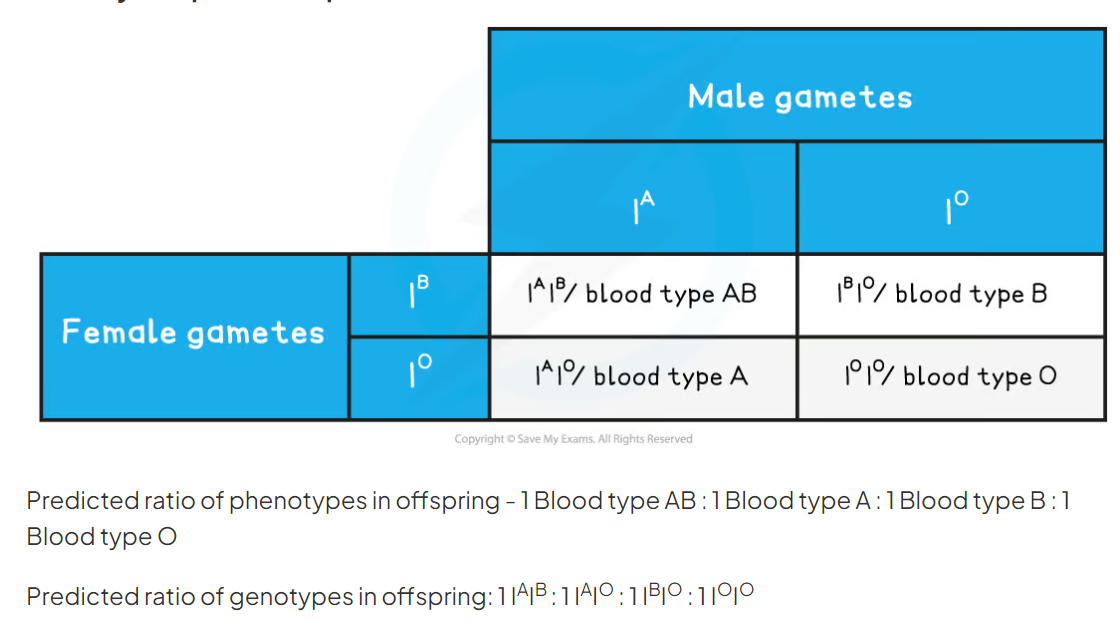
Punnet square showing the inheritance of flower colour in snapdragons showing codominance
red x pink
red x pink
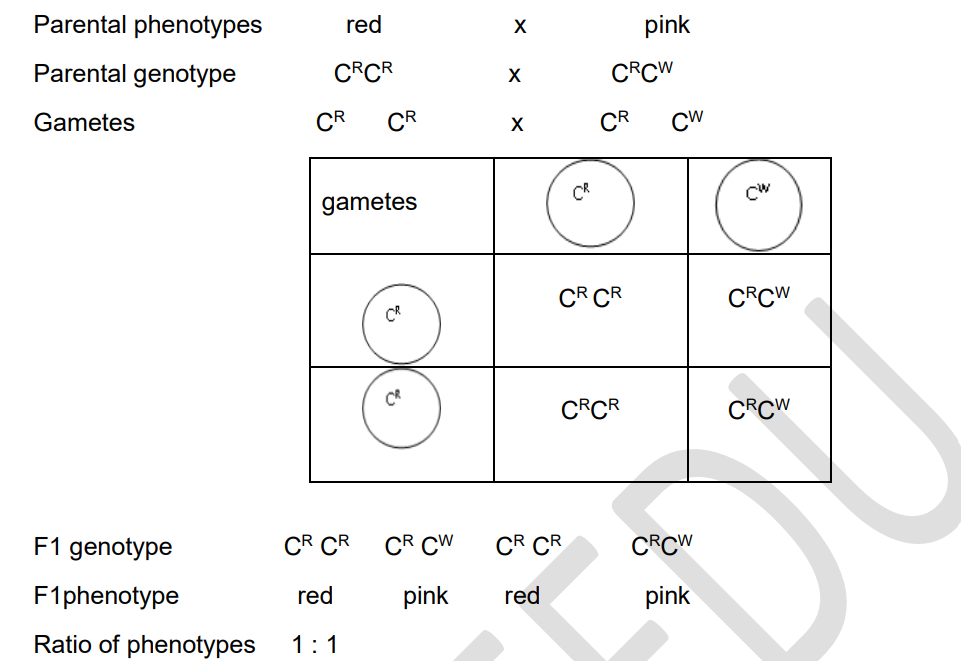
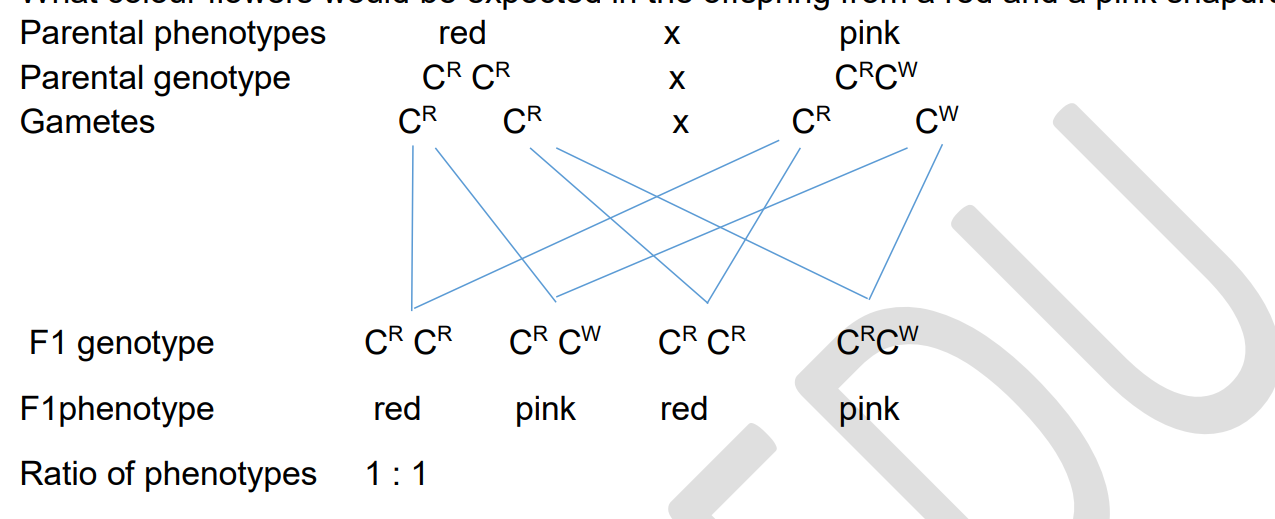
25
New cards
Genetic diagram showing the inheritance of flower colour in snapdragons showing codominance
red x pink
red x pink
26
New cards
how are genotypes represnted when codominance is involved
genotypes are represented using a capital letter for the gene and superscript letters for the alleles (eg. IAIA)
27
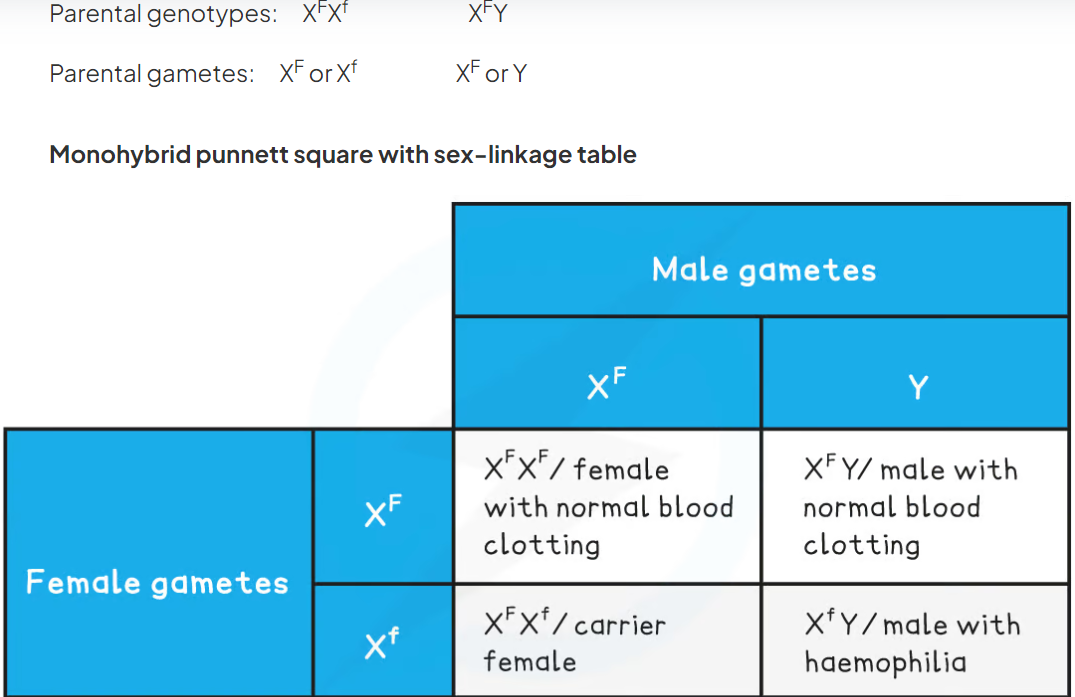
New cards
punnet square showing haemophilia as an example of sex linkage. dominant F allele which codes for normal factor VIII and the recessive f allele which results in a lack of factor VIII (found on the X chromosome)
carrier female x normal male
carrier female x normal male
28
New cards

29
New cards

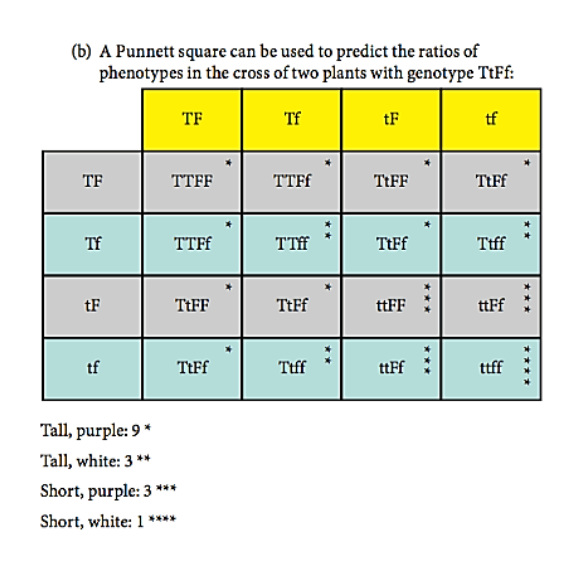
30
New cards
what is autosomal linkage
(autosomal) not a sex chromosome ; \n (linkage) genes on the same chromosome / alleles inherited together ;
31
New cards
representing autosomally linked genes in diagrams
To help keep track of linked alleles in a genetic diagram, you can bracket each linkage group eg. (EA)(EA) and not EEAA
32
New cards

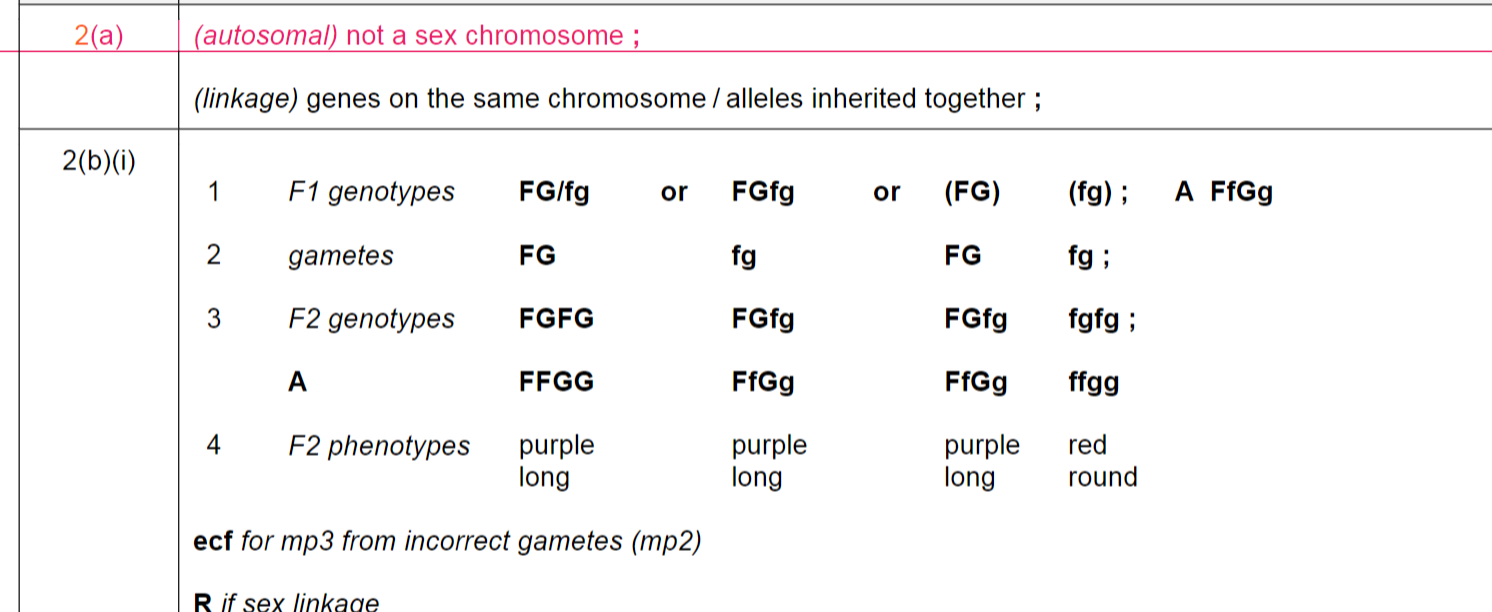
33
New cards
what is epistasis
A gene interaction, where one gene interferes with expression of another gene is known as epistasis (opposite of codominance) PS go over ppqs bb
34
New cards
Test crosses
\-Test cross is genetic cross used to know if an individual displaying a dominant trait is homozygous or heterozygous for a particular allele. This involves crossing the dominant organism with a homozygous recessive organism
\-in a dihybrid test cross, the unknown genotype is crossed with an individual with a double homozygous recessive genotype.
\-in a dihybrid test cross, the unknown genotype is crossed with an individual with a double homozygous recessive genotype.
35
New cards
using a chi squared table rules
-If the calculated χ2 value is greater than or equal to the critical value (probability value read from the table), then there is a significant difference between our observed results and expected results
-If the calculated χ 2 value is less than the critical value, then there is no significant difference between the observed and expected data
-If the calculated χ 2 value is less than the critical value, then there is no significant difference between the observed and expected data
36
New cards
what enzyme does the TYR gene code for
tyrosinase
37
New cards
role of tyrosinase
1. amino acid tyrosine → DOPA
2. DOPA → dopaquinone
3. Dopaquinone is converted to melanin
4. absence of melanin → albinism
38
New cards
what does HBB gene code for
β-globin polypeptide
39
New cards
steps for developing sickle cell anemia
1. single base substitution CTC → CAC
2. mRNA transcript codes for valine (GUG) rather than glutamic acid (GAG) (glutamic acid → valine)
3. Hydrophobic side chain for valine (non polar) causes RBC’s to have crescent shape, unable to transport oxygen and stick to each other blocking capillaries
4. homozygous individual with two abnormal alleles for the *HBB* gene produces only sickle cell haemoglobin
40
New cards
what does F8 gene code for
factor VIII (X- linked gene)
41
New cards
how is haemophilia develop
* dominant allele, H, producing normal factor VIII, and the recessive one, h, resulting in a lack of factor VIII
* The recessive allele causes haemophilia, in which the blood fails to clot properly
* gene for haemophilia is on the X chromosome, so females have 2 copies and Males have 1 copy
* The recessive allele causes haemophilia, in which the blood fails to clot properly
* gene for haemophilia is on the X chromosome, so females have 2 copies and Males have 1 copy
42
New cards
genetic diagram showing cross between normal man and haemophilia-carrier woman
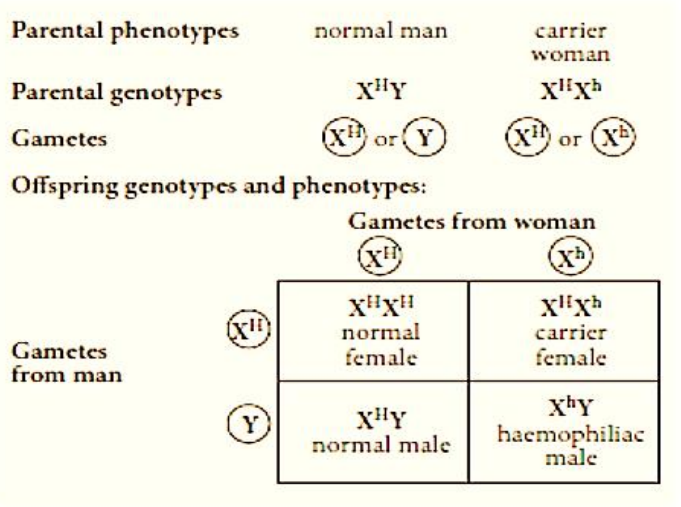
43
New cards
what does the HTT gene code for
huntingtin
44
New cards
development of Huntington’s disease
1. Mutation of HTT gene → many (40-100) repeats of sequence CAG (glutamine amino acid)
2. mutated allele is dominant over normal allele
3. symptoms only show after 30+ years and causes neurological degeneration
45
New cards
cross between one parent with huntingtons disease and one without
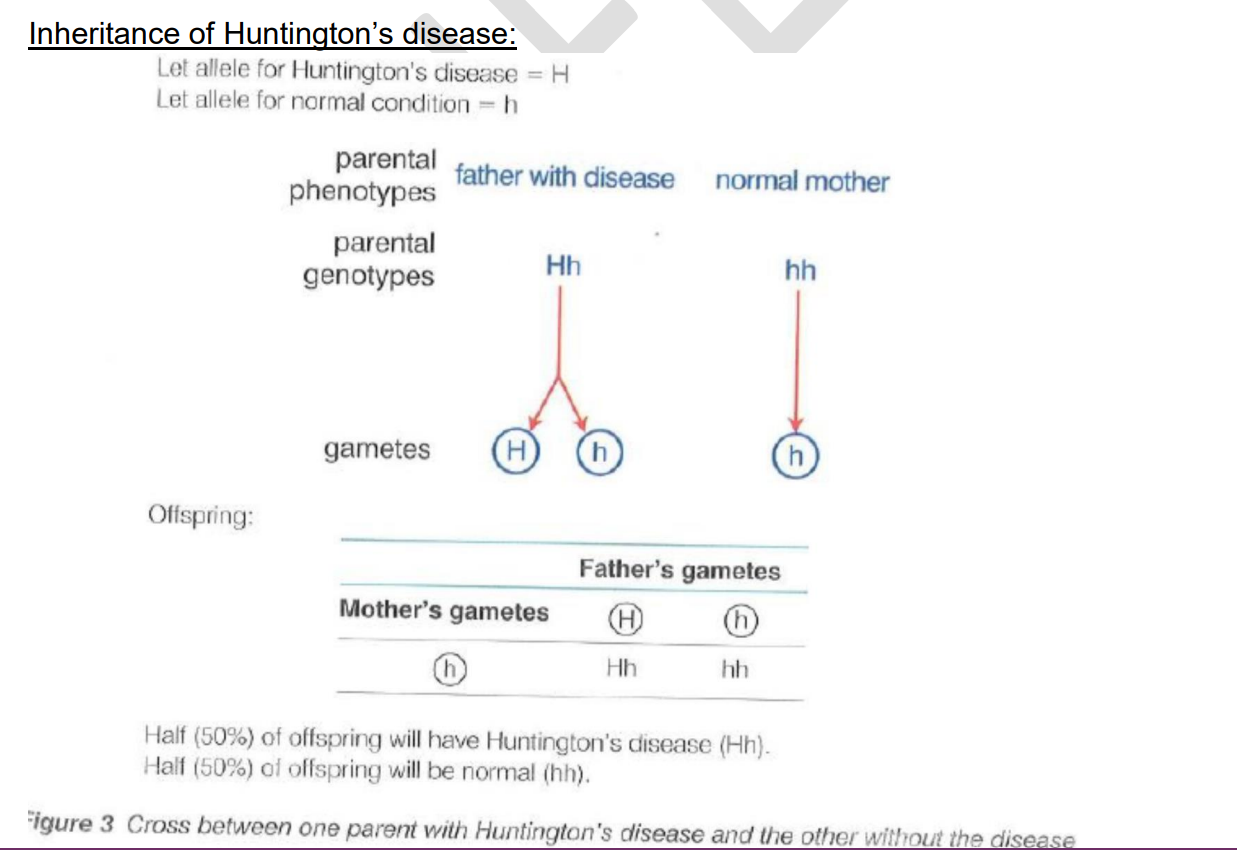
46
New cards
explain the role of gibberellin in stem elongation
* tallness has two alleles; dominant, Le and recessive, le
* dominant allele regulates the synthesis of an enzyme in a pathway that produces an active form of gibberellin,GA1 (inactive → active)
* Active gibberellin stimulates cell division and cell elongation in the stem
* A substitution mutation in this gene (le) causes alanine → threonine near active site, producing a non-functional enzyme. Homozygous plants, lele, are genetically dwarf
* dominant allele regulates the synthesis of an enzyme in a pathway that produces an active form of gibberellin,GA1 (inactive → active)
* Active gibberellin stimulates cell division and cell elongation in the stem
* A substitution mutation in this gene (le) causes alanine → threonine near active site, producing a non-functional enzyme. Homozygous plants, lele, are genetically dwarf
47
New cards
describe the differences between structural genes and regulatory genes
structural genes code for a proteins that have a **function within a cell (**enzymes, haemoglobin, keratin, collagen)
Regulatory genes code for proteins that regulate/control the expression of other genes (transcription factors)
Regulatory genes code for proteins that regulate/control the expression of other genes (transcription factors)
48
New cards
describe the differences between repressible enzymes and inducible enzymes
* **Inducible** enzymes are only synthesized when their substrate (inducer) is present. Substrate switches on gene that codes for these enzymes
\
* **Repressible** enzymes are synthesized as normal until a **repressor protein** binds to an operator
\
* **Repressible** enzymes are synthesized as normal until a **repressor protein** binds to an operator
49
New cards

1 promoter
2 operator
3 lac Z / β-galactosidase gene
4 lac Y / lactose permease gene ; ;
2 operator
3 lac Z / β-galactosidase gene
4 lac Y / lactose permease gene ; ;
50
New cards

3(b)(ii) any three from:
1 repressor (protein) not bound to, lactose / allolactose ;
2 repressor binds to operator ;
3 RNA polymerase cannot move to, operator / (structural) genes ;
4 no / prevents, transcription (of genes) / formation of mRNA ;
3
3(b)(iii) any one from:
proteins / enzymes, made, all the time / when not needed / too much / in excess / in uncontrolled fashion ;
waste of, amino acids / ATP / nucleotides ;
decrease growth ;
1 repressor (protein) not bound to, lactose / allolactose ;
2 repressor binds to operator ;
3 RNA polymerase cannot move to, operator / (structural) genes ;
4 no / prevents, transcription (of genes) / formation of mRNA ;
3
3(b)(iii) any one from:
proteins / enzymes, made, all the time / when not needed / too much / in excess / in uncontrolled fashion ;
waste of, amino acids / ATP / nucleotides ;
decrease growth ;
51
New cards
β-galactosidase – any one of: \n digests / hydrolyses, lactose to, monomers / glucose + galactose ; \n converts / isomerises, lactose to allolactose ; \n lactose permease \n increases / allows, lactose uptake / lactose entry / permeability (of cell) to lactose ;
52
New cards
why does lac repressor protein have 2 active sites (allosteric)
* When it binds to the operator it **prevents the transcription** of the structural genes as RNA polymerase cannot attach to the promoter
* When it binds to lactose the shape of the repressor protein distorts and it can **no longer bind to the operator**
* When it binds to lactose the shape of the repressor protein distorts and it can **no longer bind to the operator**
53
New cards
what is a promoter gene
portion of DNA to which the enzyme RNA polymerase becomes attached to in order to begin the process of transcription
54
New cards
Describe the genetic control of protein production in a prokaryote using the lac operon

55
New cards
diagram showing functioning of lac operon in presence and absence of lactose
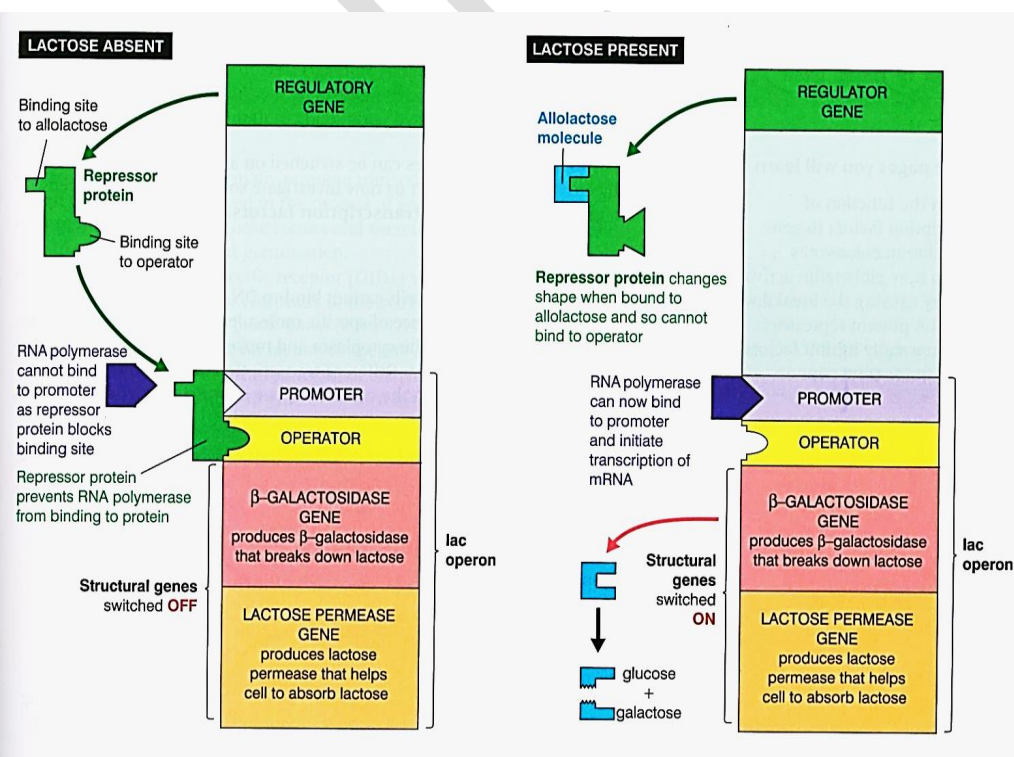
56
New cards
what is a transcription factor
transcription factors are proteins that bind to DNA and are involved in the control of gene expression in eukaryotes by decreasing or increasing the rate of transcription
57
New cards
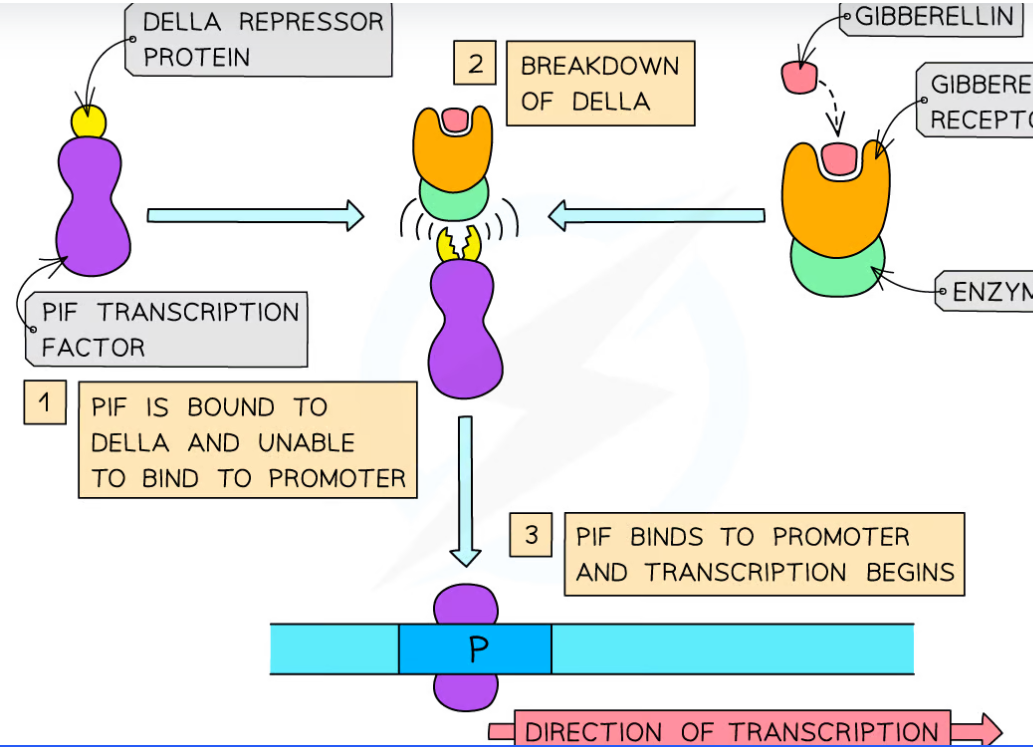
explain how gibberellin activates genes in plants
1 idea that DELLA proteins prevent the activation of genes ;
2 gibberellin binds to receptors ;
3 causes breakdown of DELLA proteins ;
4 (so) transcription / gene expression / gene activation / mRNA synthesis, can occur ;
5 AVP ; e.g. ref. to transcription factors / PIF
2 gibberellin binds to receptors ;
3 causes breakdown of DELLA proteins ;
4 (so) transcription / gene expression / gene activation / mRNA synthesis, can occur ;
5 AVP ; e.g. ref. to transcription factors / PIF