lecture 5 intraspecific population regulation
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
exponential growth model equation
dN/dt = (b-d)N = rN
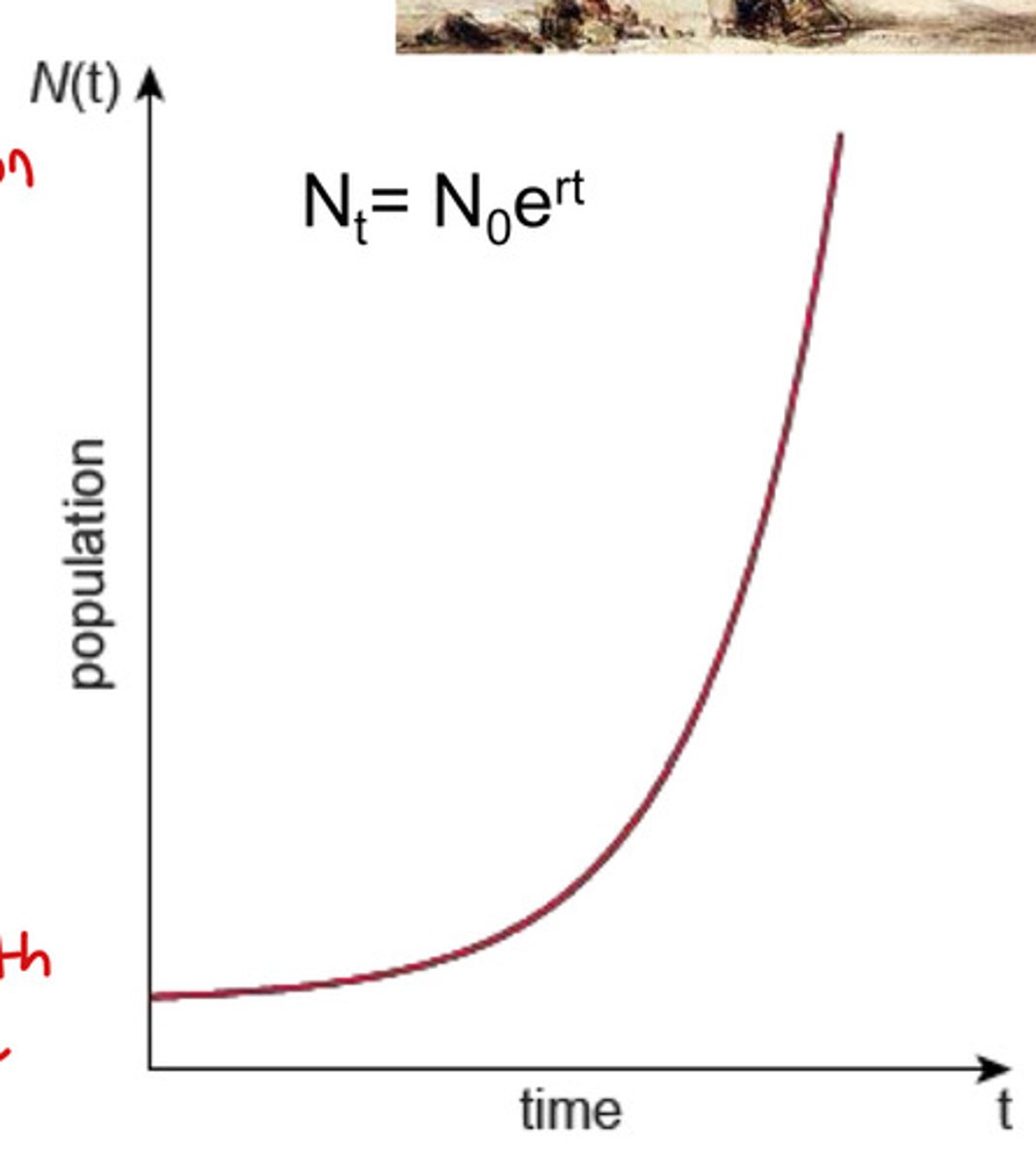
what are the assumptions of the exponential growth model?
1. infinite resources
2. constant birth and death rate
what do the terms in the exponential growth model mean?
dN/dt = (b-d)N = rN
dN/dt = instantaneous rate of change in population size ("growth rate")
r = intrinsic rate of increase
b = birth rate
d = death rate
N = population size
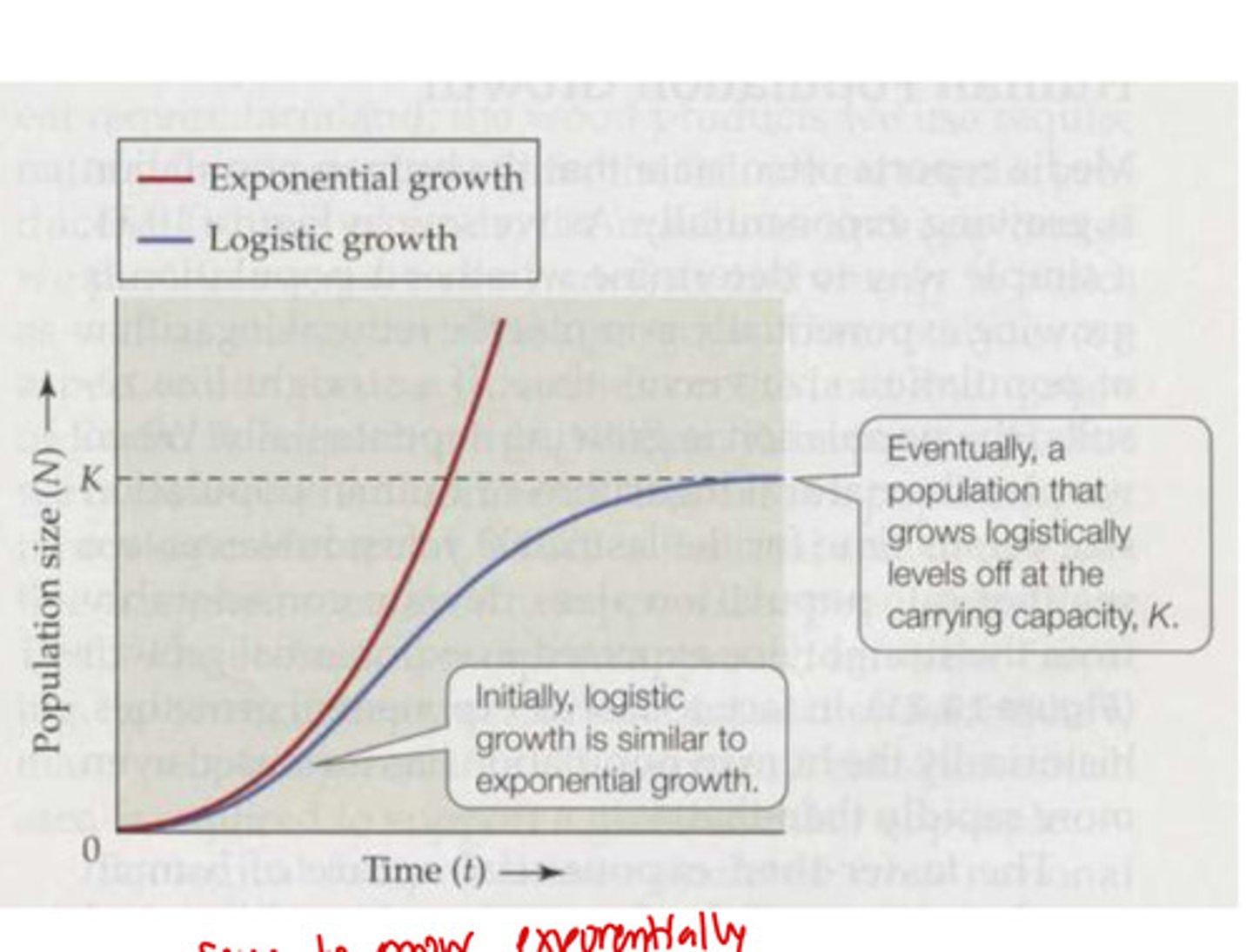
intraspecific population regulation
population growth is limited in natural populations because as population density increases, demand for limited resources increases, which increases competition
- limitations are imposed on population growth by other members of the same species (birth and death rate are not constant)
as population size (N) increases, what does the population experience?
increased mortality
decreased fecundity
actual birth rate formula
b = b0 - aN
d0 term meaning
minimum death rate
b0 term meaning
maximum birth rate under ideal conditions
when b > d what is happening to the population?
growing
when b = d what is happening to the population?
stable
when b < d what is happening to the population?
decaying
actual death rate formula
d = d0 + cN
what does slope c mean? slope a?
c = slope of death rate
a = slope of birth rate
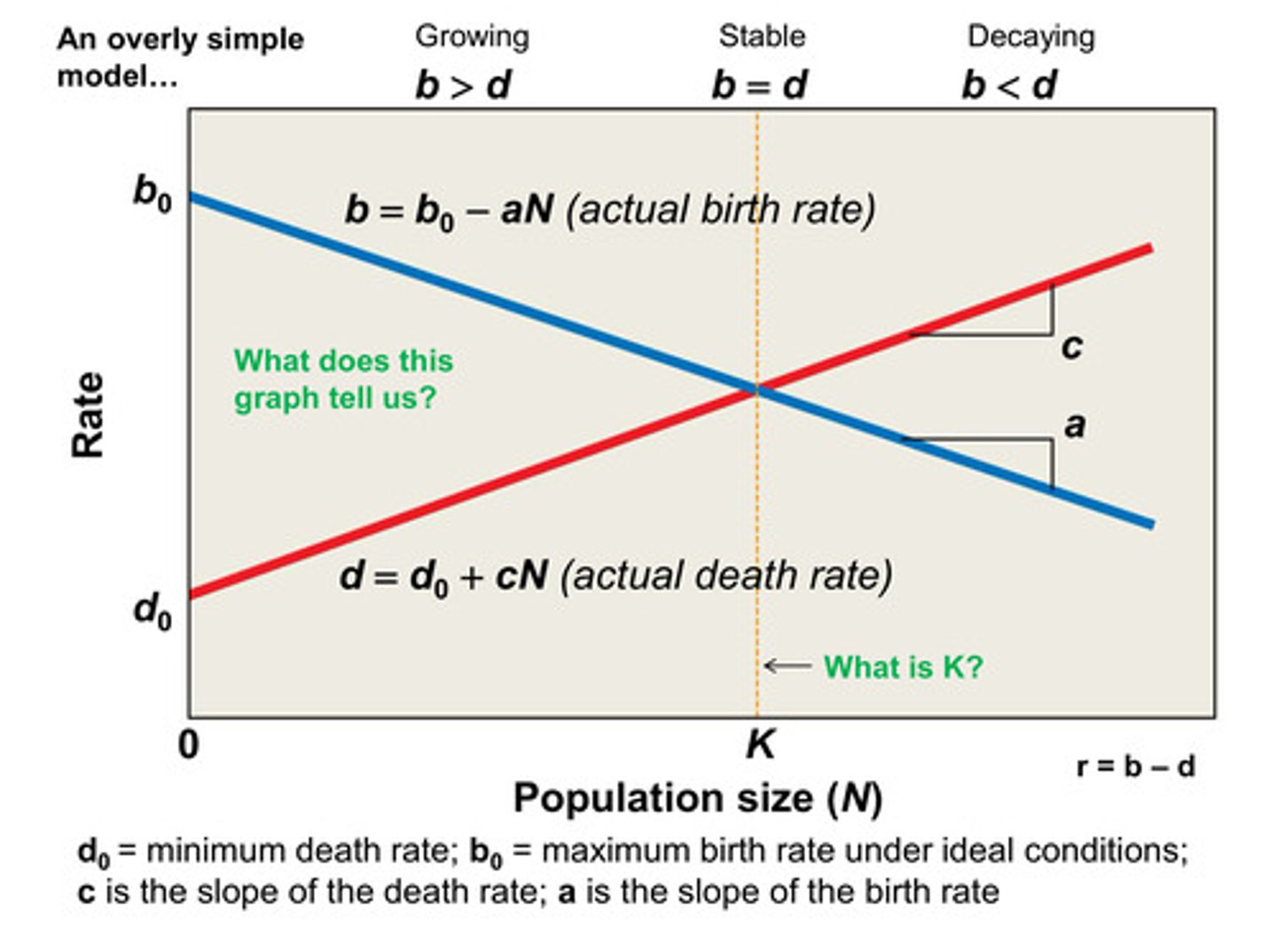
exponential population growth model including variation of birth and death rate as population changes
dN/dt = [(b0 - aN) - (d0 + cN)] x N
What happens as N increases according to this formula? dN/dt = [(b0 - aN) - (d0 + cN)] x N
as N increases, the birth rate declines and death rate increases, resulting in a slowing of population growth
K term meaning
carrying capacity
carrying capacity
the population size at which birth rate is equal to death rate is the maximum sustainable size in the current environment
maximum sustainable population size for a prevailing environment; can change
carrying capacity formula
K = (b0 - d0) / (a + c)
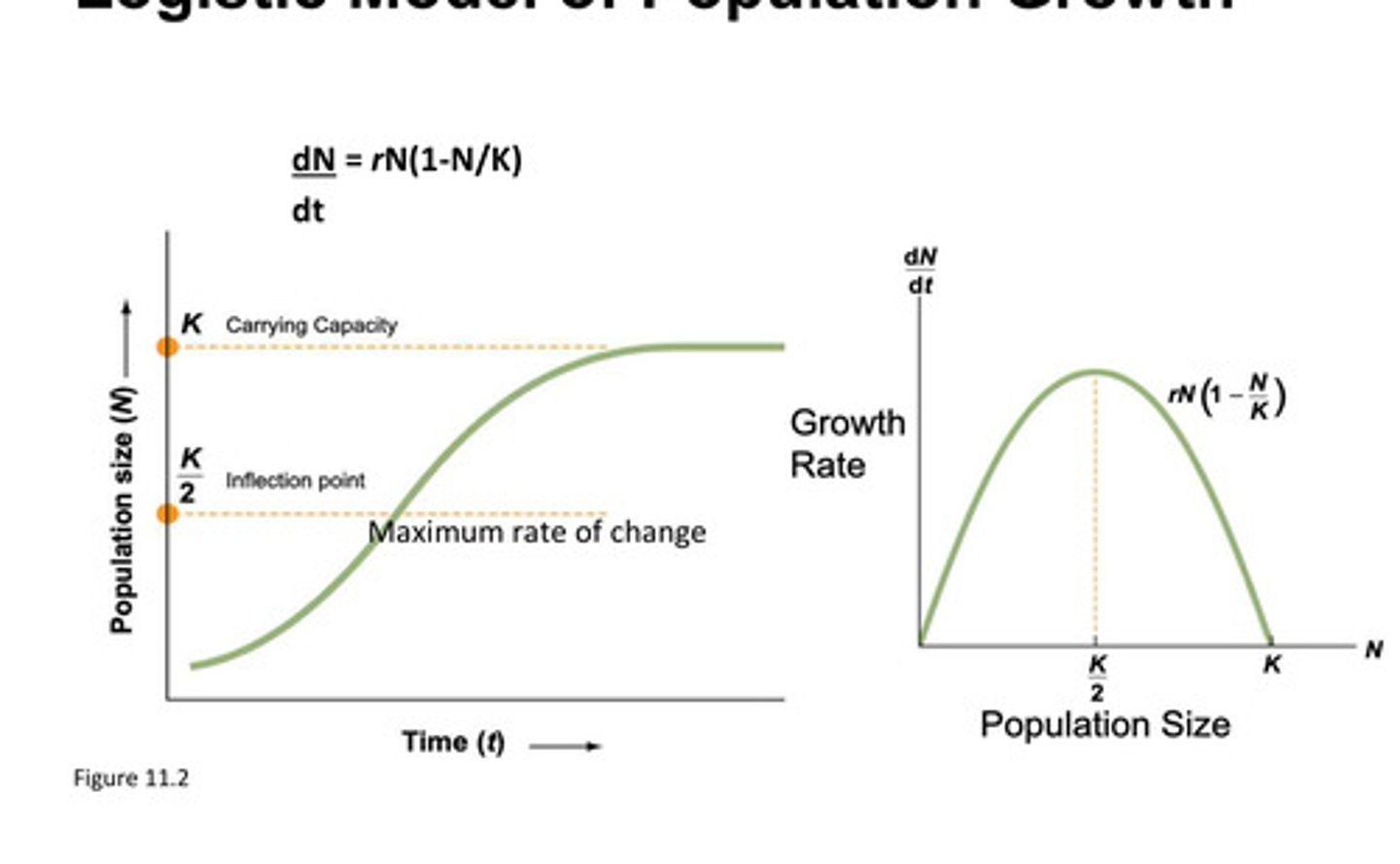
logistic model of population growth forumala
dN/dt = rN * (1 - N/K)
what does the rN term in the logistic model of population growth stand for?
exponential growth
- r is defined as a constant = b0 - d0
what does the (1 - N/K) term stand for in the logistic model of population growth?
slowing of population growth; reduction of population growth as the population approaches carrying capacity
what happens when N << K?
N/K approaches 1
close to exponential growth
what happens when N = K?
N/K is equal to 0
close to zero growth
what happens when N >> K?
N/K is negative
growth is negative
logistic growth in a population graph
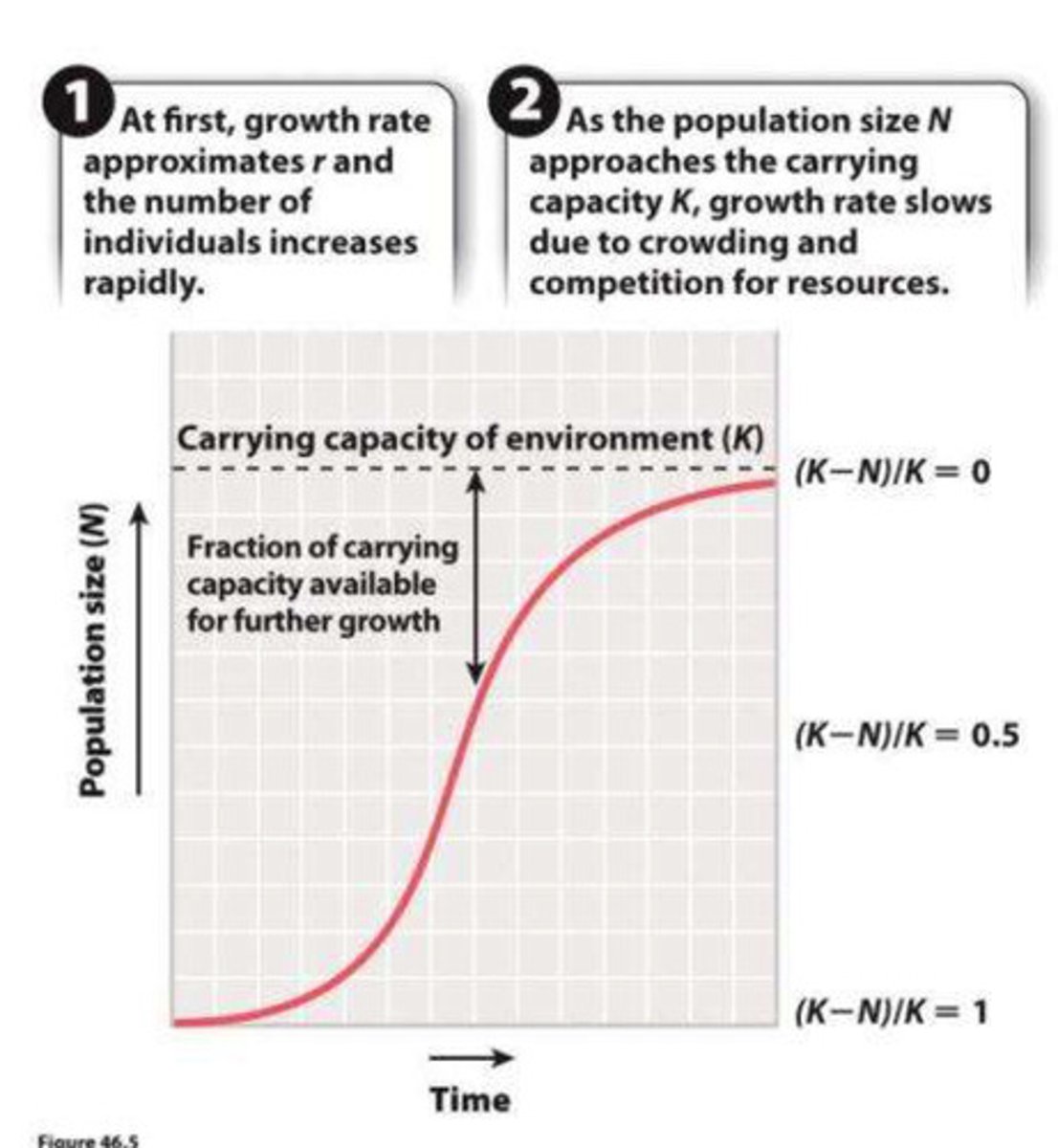
As N approaches K there is increased ______________ for limited resources
As N approaches K there is increased intraspecific competition for limited resources
labeled logistic growth in population graph
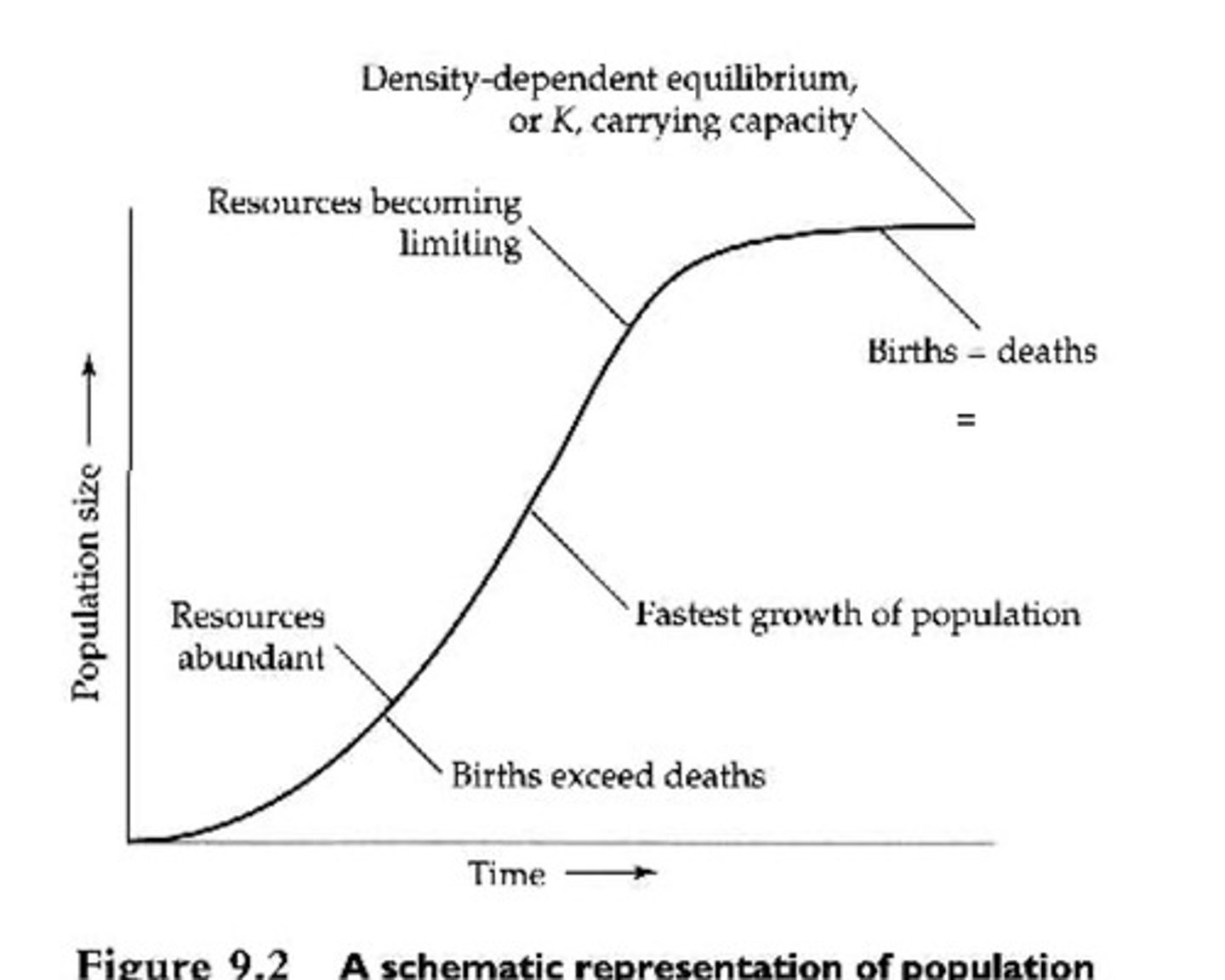
what happens if you go above the carrying capacity line?
the population overshot and got too large, so now it declines to go back to carrying capacity
K/2 term meaning
inflection point
what is the human carrying capacity?
1.5 billion people
density independent factors
factors not related to population density can influence birth and death rates within a population; are usually random
- examples: extreme weather events, flood, drought
density independent factors are associate to what kind of species?
r selected species
density dependent factors
things like competition for resources, disease, territoriality, intrinsic factors (physiological), predation, parasitism
density dependent factors are associated to what kind of species?
k selected species
density dependent mortality
as population density increases, the rate of mortality increases
density dependent fecundity
as population density increases, the rate of fecundity decreases
density dependent population regulation
- competition is density dependent
- competition generally slows growth and development, raises mortality rates, and reduces fecundity
- high density is stressful and can trigger hormonal changes that suppress growth, curtail reproduction, delay sexual activity, suppress the immune system
idea of sustainable yield
yield should not exceed the ability of natural population growth to replace harvested individuals
- manage population at intermediate population sizes
- take only those individuals that would naturally be lost to mortality
how is maximum sustainable yield achieved?
by managing populations at a level where maximum growth occurs
- in the case of the logistic model, this occurs at a population size N = K/2