neonatal/msk exam review guide
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
why ICH common in preterm infants
low birth weight
<34 wks
fragile & not developed blood vessels
US appearance of ganglion cyst
cystic (simple) on wrist
when does ant. fontanelle close
9-15 mnths
another name for mastoid fontanelle
posterolateral fontanelle
where is largest part of choroid plexus located
lateral ventricle
leukomalacia definition
CNS dysfunction bc hypoxic ischemia or infection
white matter softens
leukomalacia presents…
limp & pale at birth
seizures
hypotonia
poor prognosis
neurological deficits
IVH grade 0
no hemorrhage
IVH grade I
(SEH) blood only in germinal matrix
IVH grade II
(w/out dilation) SEH breaks thru ependymal into ventricle
IVH grade III
(w/ dilation) motor problems & mental retardation
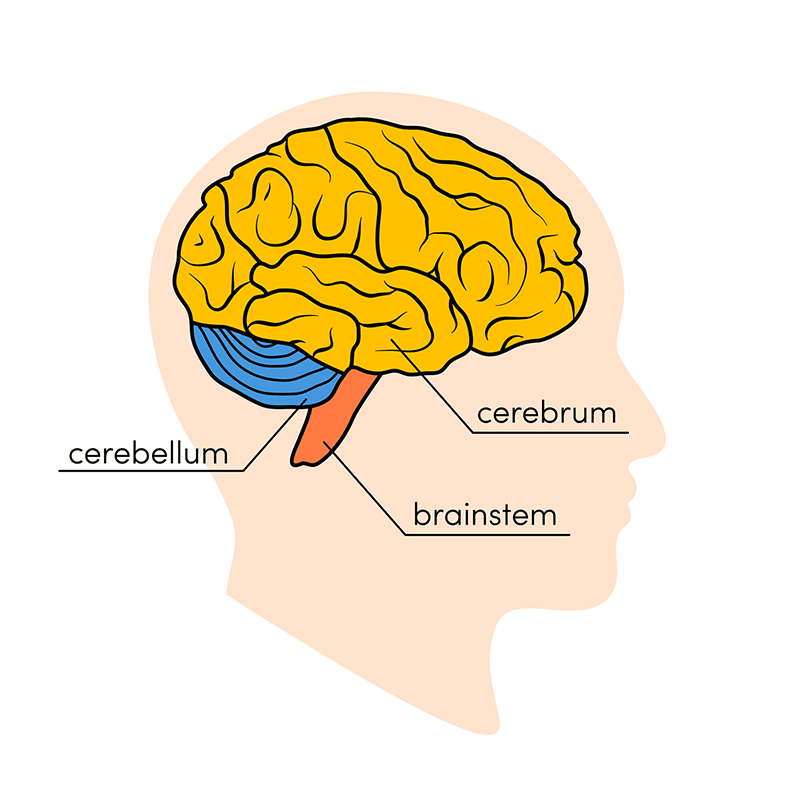
3 segments of the brain
cerebrum
cerebellum
brain stem
most common neonatal congenital infection
cytomegalovirus cmv
hydrocephalus
dilation of ventricle bc CSF obstruction
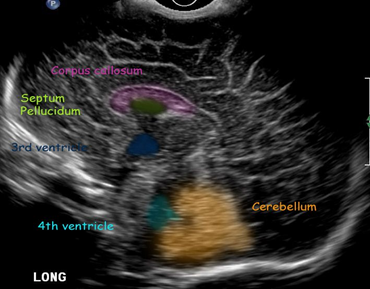
SAG neonatal head
corpus collosum
4th ventricle
cavum septum pellucidum (anechoic)
3rd ventricle
cerebellum
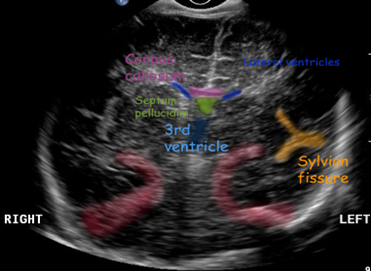
COR neonatal head image
frontal horns of lateral ventricle *always in image*
sylvian fissure (bright spot)
cavum septum pellucidum
what lumbosacral anomaly is indication for neonatal spine US
sacral dimple/pilonidal sinus
skin anomalies (hair, dimple, pigment)
until when is spinal US helpful on newborns
<6 mnths bc post. spinous process not yet ossified
US appearance of spinal canal
anechoic
spinal dysraphism
inadequate neural tube fusion
open-spinal dysraphism (neural tissue exposed to skin)
closed-spinal dysraphism (neural tissue covered by skin)
myelocele
myelomeningocele
OSD
herniated meninges
herniated meninges & nerve roots
tethered cord
CSD
low, thick filum terminal; below L3
diastomyelia
CSD
seperation of spinal cord into two; thoracolumbar
dorsal dermal sinus
CSD
thin, epithelial tract from skin to spinal canal; deep midline dimple
sacral dimple/pilonidal sinus
CSD
m.c. reason for neonatal spinal US; dimple w/ tract
spinal lipoma
CSD
fat & connective tissue connected w/ spinal cord; skin covered back mass; lumbar
terminal myelocystocele
CSD
skin covered, fluid filled, lumbar mass; CSF accumulation; omphalocele
where does conus medullaris terminate when tethered
L3 or below
transducer for neonatal spine
8-15 mhz; high frequency; linear/sector
where does diastomyelia occur
thoracolumbar
dorsal dermal sinus
thin, epithelial lined tract that passes from skin to spinal canal; CSD; lumbosacral; deep midline dimple
most common methods for DDH
clinical assessment
sonography
types of hip displacement
instability
subluxation
dislocation
normal value of hip displacement
alpha >60°
scanning planes for femoral head
COR, neutral: how well femoral head is in acetabulum (>50%)
COR, flexion: same as COR but hold hip at 90°; w/ stress
TRANS, flexion: rotate probe 90°; flexed femur at 90°; w/ stress (look for ‘U’)
hip effusion
swelling of hip joint bc increased synovial fluid around joint
pain, limping, no weight bearing, fever
DDH risk factors
breech
family history
cultural swaddle
abnormal physical
female
1st pregnancy
oligohydramnios in utero
high birth weight
bursa definition
closed connective & synovial sacs w small amount of fluid
what does bursa do
gliding at high friction points
bursa US appearance
small, hypoechoic, flat sac; hyperechoic wall; fluid
most common joint injury
ankle (complex diarthrosis joint)
plantar fasciitis
inflammation of plantar fascia (>4mm)
thick, medial, central, & lateral cords
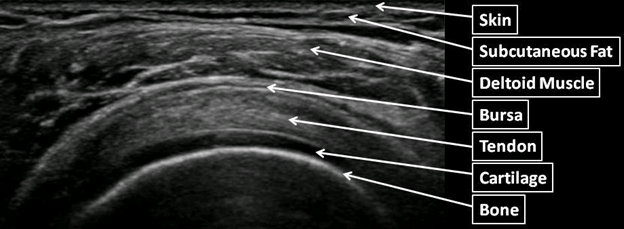
msk image
skin
fat
muscle
tendon
what shares insertion point with supraspinatus at tendon
infraspinatus
what is elevated with rotator cuff imaging
subscapular nerves (C5, C6, C7)
suprascapular nerves (C4, C5, C6)
minor rotator cuff tear criteria
subdeltoid bursal effusion
major rotator cuff tear criteria
focal, nonvisualized cuff
localized absence of cuff
abnormal echogenicity
periosteum US appearance
thin, bright line parallel to cortex of bone
tendons
bone to muscle
flexion & extension
type II collagen & water
ligaments
bone to bone
stability & strength
type I collagen & water
‘basket weave’
muscle
smooth, cardiac, skeletal
contract & extend
US sees mostly skeletal muscle
fibers...fascicles…muscle group…endomysium…perimysium…epimysium (muscle to bone)
what is a sign of full thickness tear
complete tendon interruption
compartment syndrome
compression of blood vessels & nerves stops blood flow to that compartment
what nerve is compressed w/ carpal tunnel
median nerve
retinaculum
band of thick, deep fascia around tendons to hold them in place
anisotropy
change in properties of structure when evaluated in different directions