APHG - Unit 1 Vocab Flashcards - *Thinking Geographically*
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1.1 - 1.7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Cartographer
A person who makes maps
Relative Distance
Distance in relation to other things
Relative Location
Location in relation to other places or areas
Absolute distance
The exact distance between places
Absolute location
The exact location of a place (coordinates, address, ect.)
Large-scale map
A detailed
Medium-scale map
An entire state
Large-scale map
All of U.S
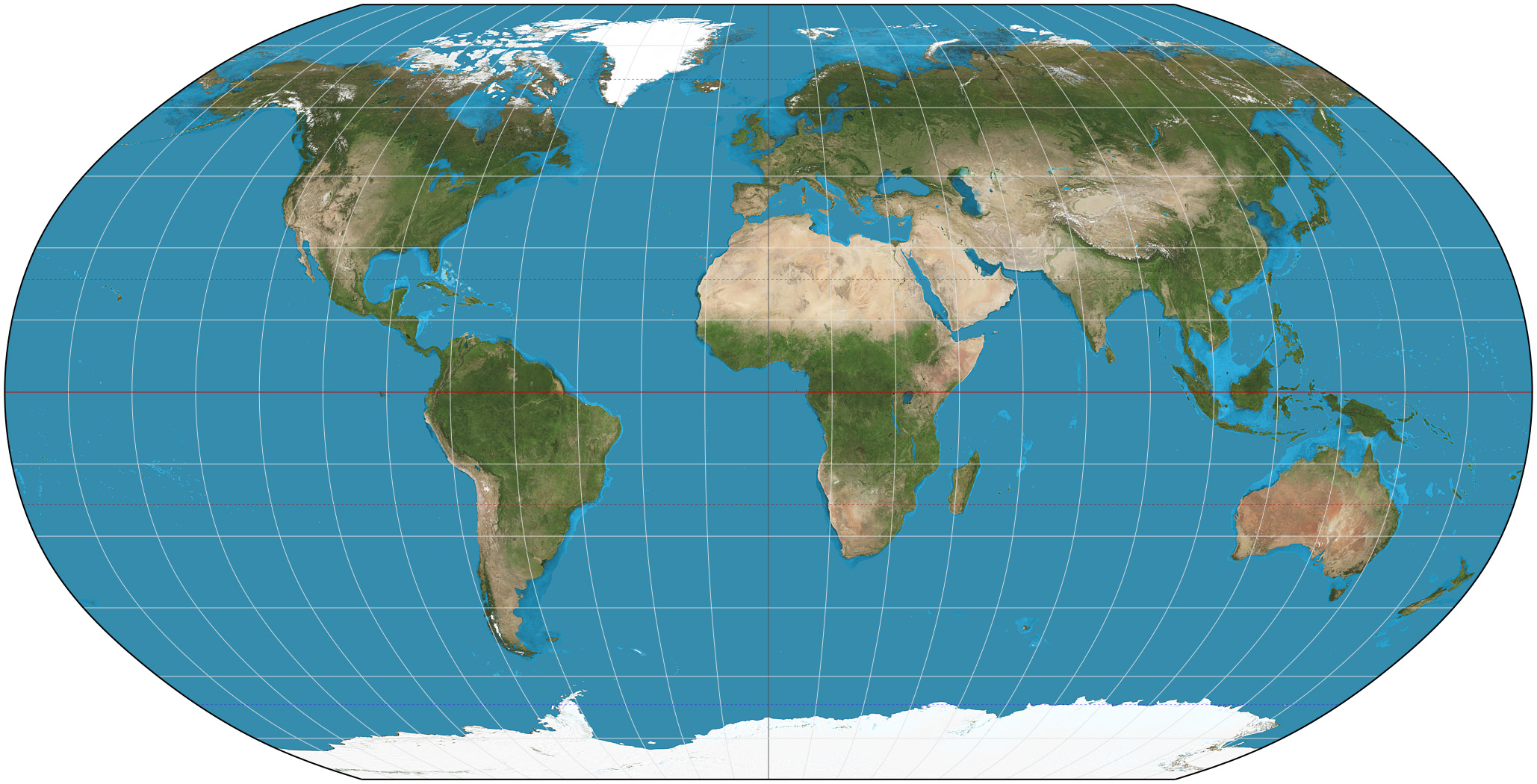
Robinson Projection
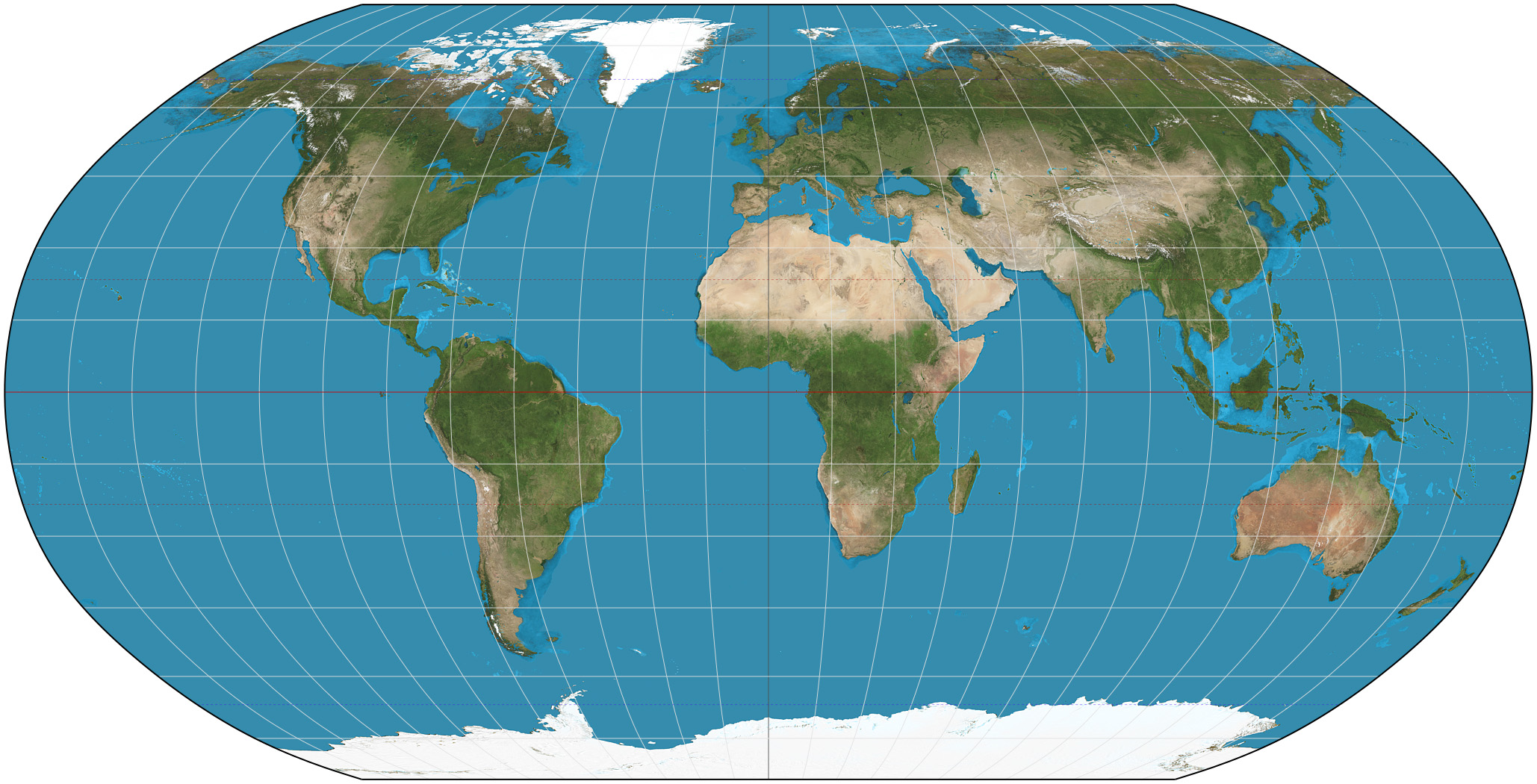
Mercator Projection
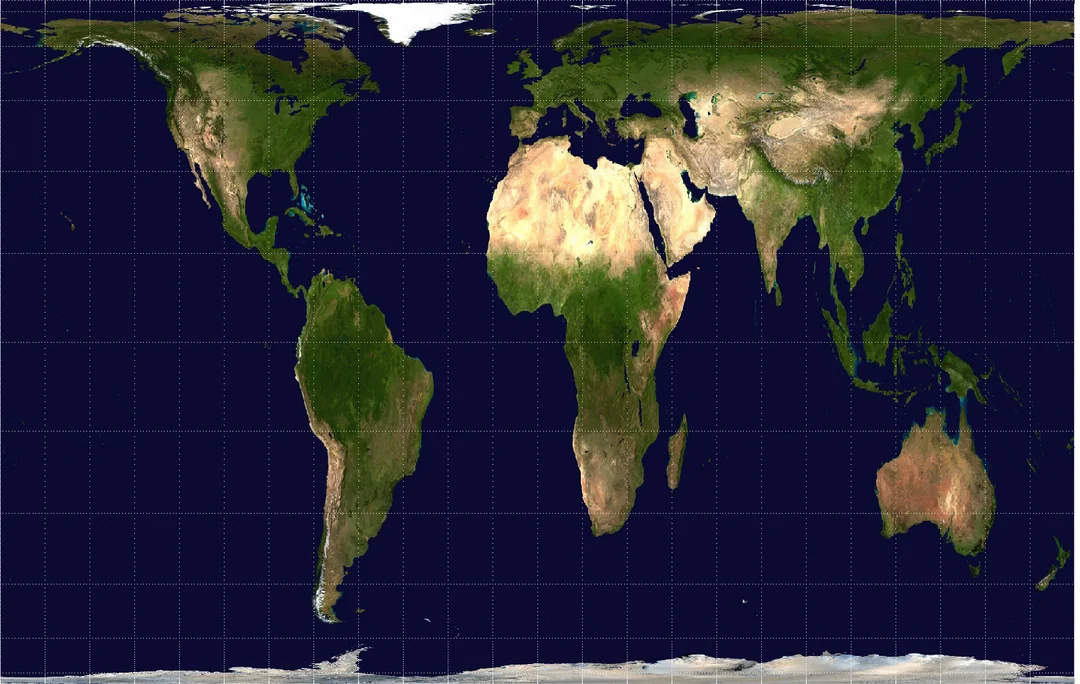
Gall-Peters Projection
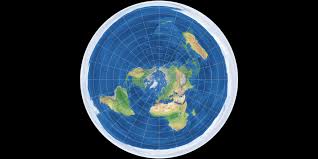
Azimuthal Projection
Reference Map
Maps with generalized sources of geographic data that focus on location
Thematic Map
Maps that have a theme or specific purpose and focus on the relationship among geographic data
Isoline Map
Lines that connect data points used to show particular characteristics of data
Graduated Symbols Map
Differently sized symbols used to indicate quantitative data
Cartogram Map
Show relative size of an area based on a particular attribute
Dot Map
Dots show specific observations or events, like crimes, births, and deaths
Choropleth Map
Uses colors and shading to represent categories of data
Quantative
relating to, measuring, or measured by the quantity of something
Qualative
relating to, measuring, or measured by the quality of something
Census
an official court or survey of a population, typically recording various details
GIS - Geographic Info Systems
visualizes geographic and spatial data to understand patterns here
Topography
the arrangement of the natural and artificial physical features of an area
Remote Sensing
gathering info about the Earth's physical characteristics from a distance
Global Positioning System (GPS)
a net work of satellites orbiting the earth to send signals
Physical Geography
the study of natural processes and distribution of features in an enviroment
Human Geography
the study of events and processes that have shaped how humans use earth
Spatial Perspective
refers to where something occurs
Ecological perspective
the relationship between living things and their environment
Location
the position of a point or object occupies on earth
Place
related to but different from location, an area
Site
refers to a places absolute location and physical characteristics
Situation
refers to a places location in relation to other places or its surrounding features
Space
refers to the area between two or more things in Earth's surface
Distributed
the way something is spread out or arranged across a specific area
Density
the number of things (people, animals, or objects) in a specific area
Pattern
how things are arranged in a particular space
Spatial Concepts
location, place, space, flows pattern, distance, decay, and time space compression
Human Environment Interaction (HEI)
how human interact with the environment
Environmental Determinism
the study of how the physical environment (natural environment) shapes human culture
Sustainability
the balance between meeting human needs in the present and ensuring future generation can meet their own needs through responsible resource management
Scale
how distance on a map compass to distance on the ground
Region
an area of Earth's surface with certain characteristics
Formal Region
an area that has one or more shared traits (The Rocky Moutains)
Functional Region
an area organized by its function around a focal point or the center of an interest or activity (cities)
Node
the focus of the region (downtown)
6 Types of Land Use
Residential (homes, apartments)
Recreational (parks, camp grounds)
Transportation (airports, bus stations, roads)
Agricultural (farms, ranches)
Industrial (factories, businesses)
Commercial (malls, restaurants)
Scales of Analysis
Global (entire world)
Regional (specific to one area - general)
National (specific to a nation)
Local or Sub-national (specific info / lots of detail)
Small scale map
generalized + less detail (zoomed out)
Large scale map
more detailed (zoomed in)
Scale of analysis
How data is shown on a map
Perceptual Region
A region based on perception or human ideas, thoughts, or opinions