AP Gov Unit 2 Review
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/66
Earn XP
Last updated 6:01 AM on 1/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
1
New cards
Pork barrel spending
When members of Congress spend government money on specific projects intended to benefit their home districts. (aka earmarks)
2
New cards
Majority-minority district
A district in which voters of minority ethnicity constitute an electoral majority within the electoral district.
3
New cards
Speaker of the House
The leader of the house of Reps, chosen by an election of its members.
4
New cards
House majority leader
Second in command to the speaker of the house.
5
New cards
House minority leader
The head of the party with the second highest number of seats in Congress, chosen by the party’s members.
6
New cards
House rules committee
A Committee that determines when a bill will be subject to debate and vote on the House floor, how long the debate will last, and whether amendments will be allowed on the floor.
7
New cards
Entitlement program
A program that provides benefits for those who qualify for them by law.
8
New cards
Trustee role
Members of Congress who make decisions based on their knowledge and judgment.
9
New cards
Politico role
Members of Congress who balance their choices with the interest of their constituents and parties in making decisions.
10
New cards
Delegate role
Members of Congress who carry out constituents’ wishes.
11
New cards
Oversight
Efforts by Congress to ensure that executive branch agencies, bureaus, and cabinet depts, as well as their officials are acting legally and in accordance with congressional goals.
12
New cards
Apportionment
The process of determining the number of representatives for each state.
13
New cards
Incumbency advantage
Institutional advantages held by those already in office who are trying to fend off challengers in an election.
14
New cards
Filibuster
A tactic through which an individual senator may use the right of unlimited debate to delay a motion or postpone action on a piece of legislation.
15
New cards
Hold
A delay placed on legislation by a senator who objects to a bill.
16
New cards
Mandatory spending
Spending required by existing laws that is “locked in” the budget. Ex: entitlement programs like Social Security and Medicare.
17
New cards
Discretionary spending
Spending for programs and policies at the discretion of Congress and the president.
18
New cards
Logrolling
Trading of votes on legislation by members of Congress to get their earmarks passed into legislation.
19
New cards
Redistricting
States’ redrawing of boundaries of electoral districts following each census.
20
New cards
Cloture vote
A procedure through which senators can end a filibuster and proceed to action, provided 60 senators agree to it.
21
New cards
Divided government
Control of the presidency and one or both chambers of Congress split between the two major parties.
22
New cards
Constituency
A body of voters in a given area who elect a representative or senator.
23
New cards
Gerrymandering
The intentional use of redistricting to benefit a specific interest or group of voters.
24
New cards
Veto
The power of a president to reject a bill passed by Congress, sending it back to the originating branch with objections.
25
New cards
Executive Branch
The branch of government charged with putting the nation's laws into effect
26
New cards
Formal Powers
Powers expressly granted in the constitution.
27
New cards
Informal powers
Powers not laid out in the Constitution but used to carry out presidential duties.
28
New cards
State of the Union Adress
The annual speech from the president to Congress updating that branch on the state national affairs.
29
New cards
Veto
Formal rejection by the president of a bill that has passed both houses of Congress.
30
New cards
Pocket Veto
An informal veto caused when the president chooses not to sign a bill within ten days, during a time when Congress has adjourned at the end of a session.
31
New cards
Pardon power
Presidential authority to release individuals convicted of a crime from legal consequences and set aside punishment for a crime.
32
New cards
Executive privilege
A right claimed by presidents to keep certain conversations, records, and transcripts confidential from outside scrutiny, especially that of Congress.
33
New cards
Executive Order
Policy directives issued by presidents that do not require congressional approval.
34
New cards
Executive agreement
An agreement between the president and another nation that does not have the same durability as a treaty but does not require Senate ratification.
35
New cards
War Powers Resolution
A law passed over President Nixon's veto that restricts the power of the president to maintain troops in combat for more than sixty days without congressional authorization.
36
New cards
Impeachment
The process of removing a president from office, with articles of impeachment issued by a majority vote in the House of Reps, followed by a trial in the Senate, with a 2/3 vote necessary to convict and remove.
37
New cards
Persuasion power
An informal tool used by the President to persuade members of Congress to support their policy initiatives.
38
New cards
Bully pulpit
Presidential appeals to the public to pressure other branches of govt. to support their policies.
39
New cards
Going public
A tactic through which presidents read out directly to the American people with the hope that the people will put pressure on their reps/senators to press for the president's policy goals.
40
New cards
Executive office of the president
A collection of offices within the White House organization designed mainly to provide info to the president.
41
New cards
Federalist No. 70
Argues in favor of the unitary executive. According to Alexander Hamilton, a unitary executive is necessary to ensure accountability in government.
42
New cards
Original jurisdiction
The authority of a court to hear a case first, which includes the finding of facts in the case.
43
New cards
Appellate jurisdiction
The authority of a court to hear review decisions made by lower courts in that system.
44
New cards
Federalist No. 78
Argument by Hamilton that the federal judiciary would be unlikely to infringe upon rights and liberties but would serve as a check on the other two branches.
45
New cards
Marbury v. Madison
The Supreme Court decision that established judicial review over federal laws. (1803)
46
New cards
Criminal law
A category of law covering actions that harm the community.
47
New cards
Civil law
A category of law covering cases involving private rights and relationships between individuals and groups.
48
New cards
Federal district courts
The lowest level of the federal judicial; these courts usually have original jurisdiction in cases that cases that start at the federal level.
49
New cards
Federal circuit courts
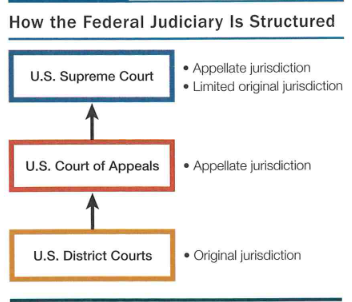
The federal court system has three main levels: district courts (the trial court), circuit courts which are the first level of appeal, and the Supreme Court of the United States.
50
New cards
Precedent
A judicial decision that guides future courts in handling similar cases.
51
New cards
Stare decisis
The practice of letting a previous legal decision stand.
52
New cards
Majority opinion
A binding Supreme Court opinion, which serves as precedent for future cases.
53
New cards
Dissenting opinion
An opinion that disagrees with the majority opinion and does not serve as precedent.
54
New cards
Concurring opinion
An opinion that agrees with the majority decision, offering different or additional reasoning, that does not serve as precedent.
55
New cards
Judicial restraint
A philosophy of constitutional interpretation that justices should be cautious in overturning laws.
56
New cards
Judicial activism
A philosophy of constitutional interpretation that justices should wield the power of judicial review, sometimes creating bold new policies.
57
New cards
Federal Bureaucracy
The departments and agencies within the executive branch that carry out the laws of the nation.
58
New cards
Bureaucrat
An official employed within a government bureaucracy.
59
New cards
Patronage
Filing of administrative positions as a reward for support, rather than merit.
60
New cards
Pendleton act
An act of Congress that created the first US civil service commissions to draw up and enforce rules on hiring, promoting, and tenure of office within the civil service. (aka Civil Service Reform Act of 1883)
61
New cards
Merit system
A system of hiring and promotion based on competitive testing results, education, and other qualifications rather than politics and personal connections.
62
New cards
Iron triangle
Coordinated and mutually beneficial activities of the bureaucracy, Congress, and interest groups to achieve shared political goals.
63
New cards
Issue network
Webs of influence between interest groups, policymakers, and policy advocates.
64
New cards
Bureaucratic discretion
The power to decide how a law is implemented and to decide what Congress meant when it passed a law.
65
New cards
Regulation
The process through which the federal bureaucracy makes rules that have the force of law, to carry out the laws passed by Congress.
66
New cards
Implementation
The bureaucracy’s role in putting into action laws that Congress has passed.
67
New cards
Sunset laws
A legal provision that provides for the automatic termination of a government program, agency, or law on a certain date unless the legislature affirmatively acts to renew it.