The tongue and no
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
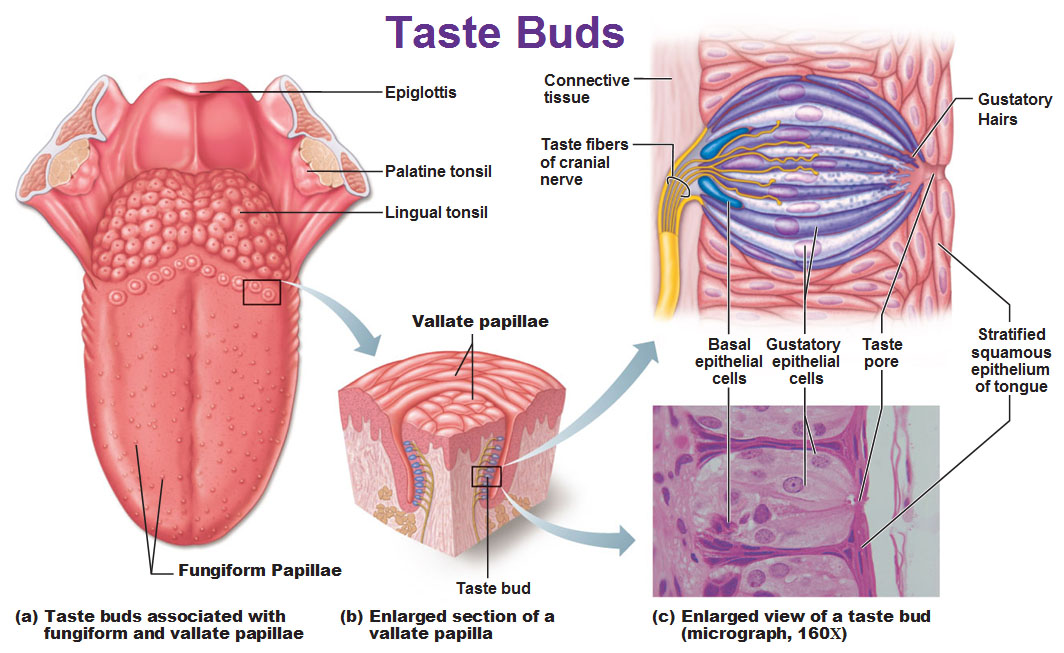
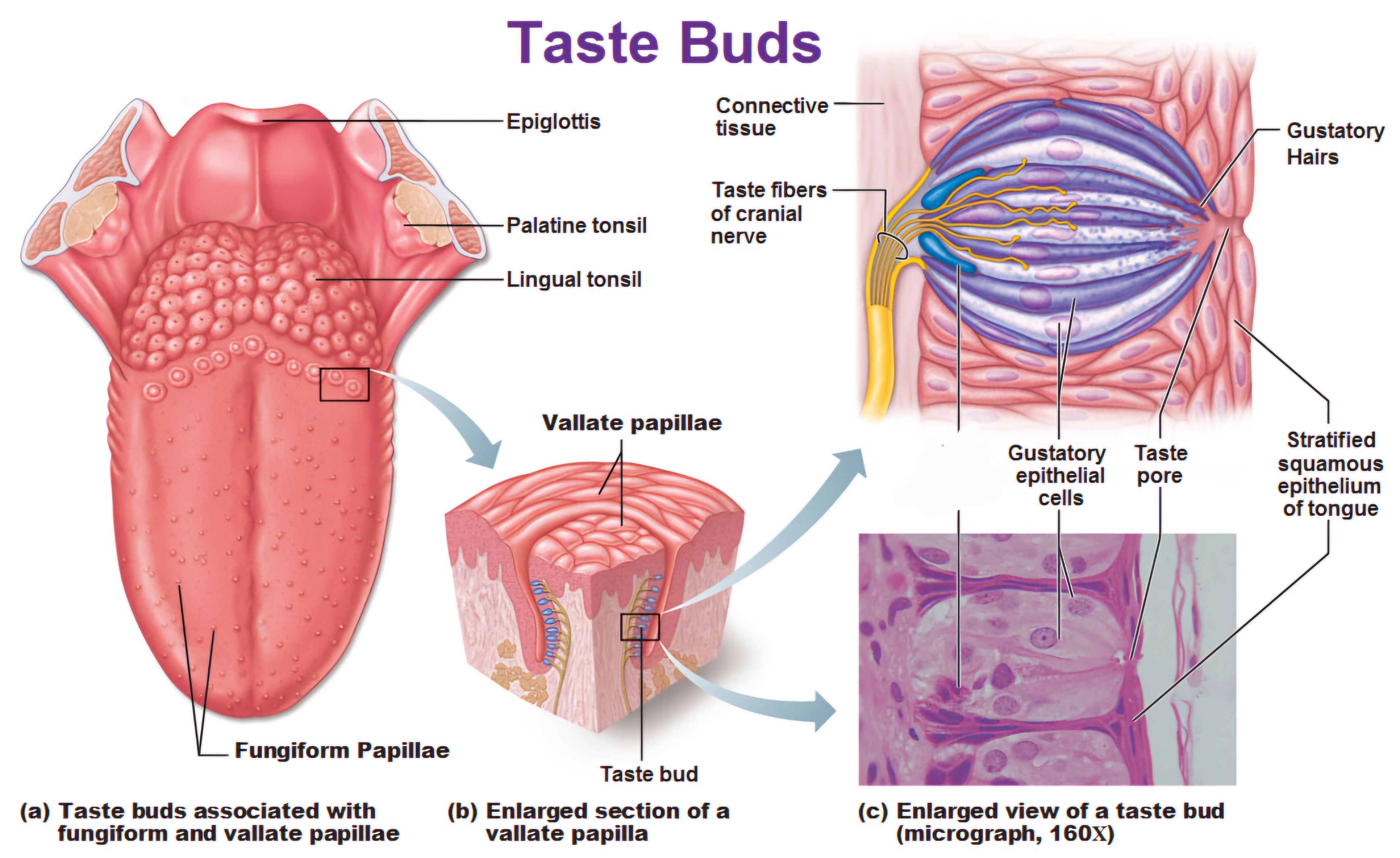
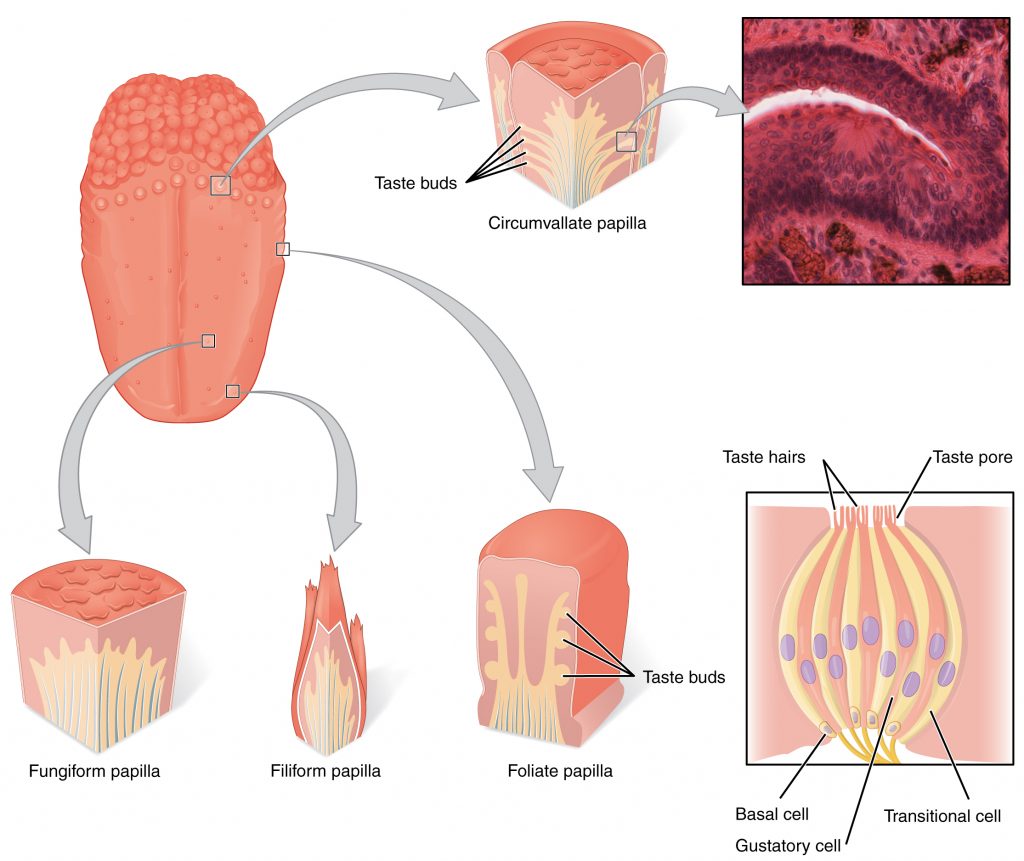
The tongue's anatomy includes several cell types within taste buds, which are located on the surface in structures called papillae. Taste buds contain taste receptor cells, basal cells, and supporting cells
Tongue

also known as taste receptor cells, are the sensory receptor cells within taste buds that detect taste
Gustatory cells

also known as sustentacular cells or glia-like cells, are present within taste buds on the tongue and play a crucial role in the structure and function of these sensory organs
Supporting cell
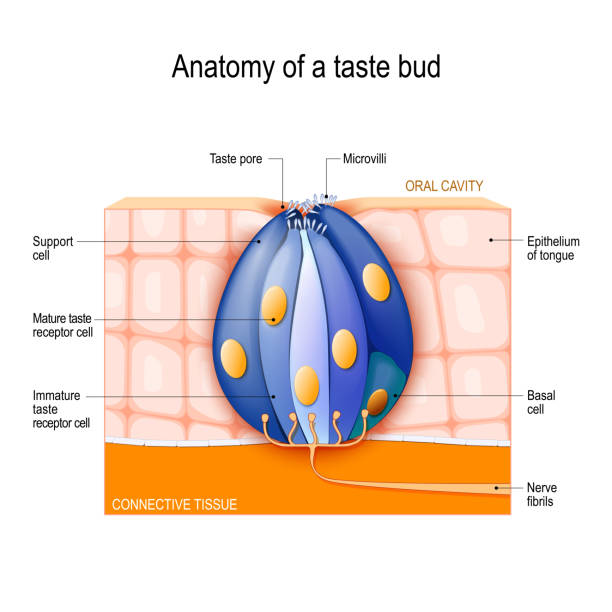
stem cells that differentiate into mature taste receptor cells within taste buds
Basal cell
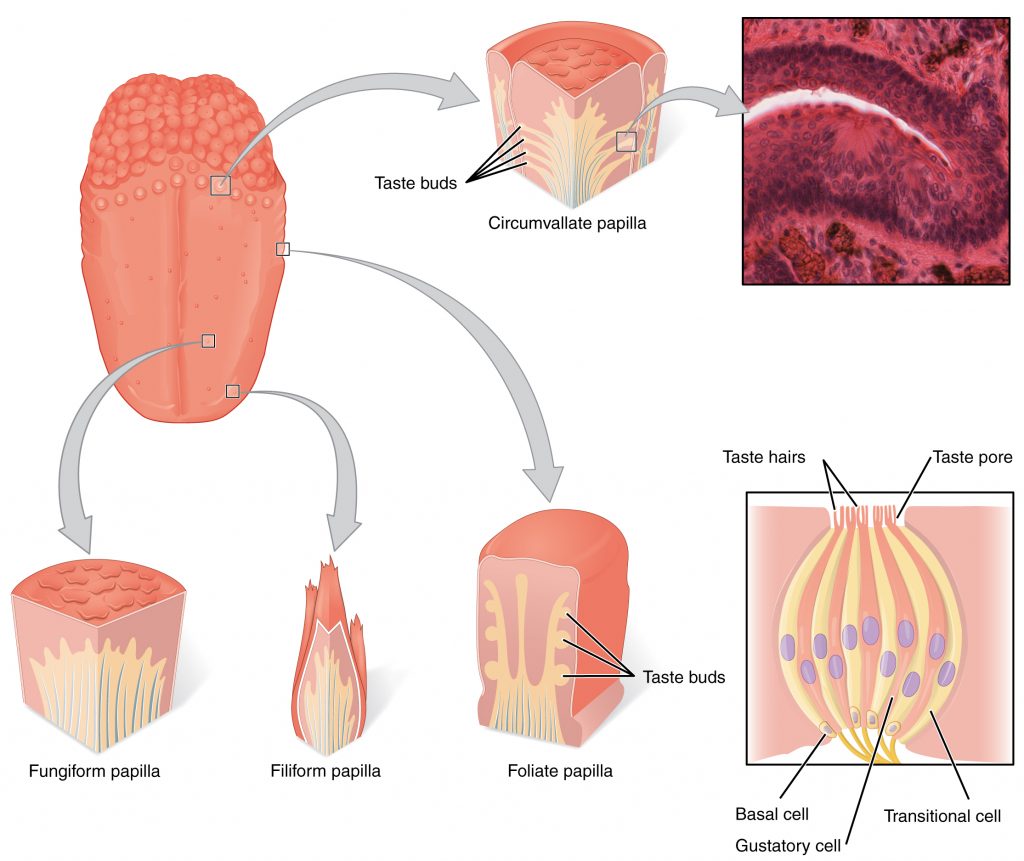
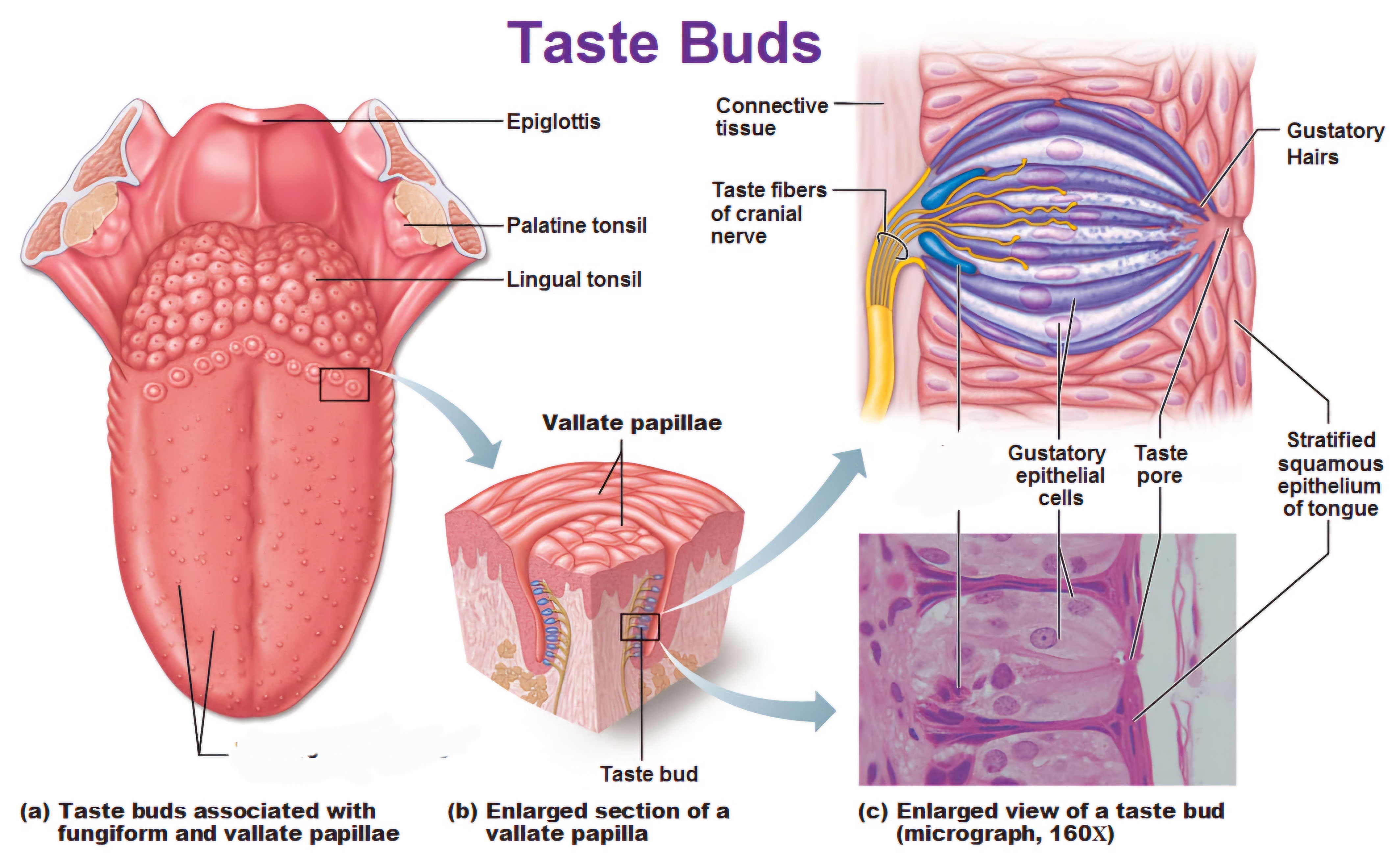
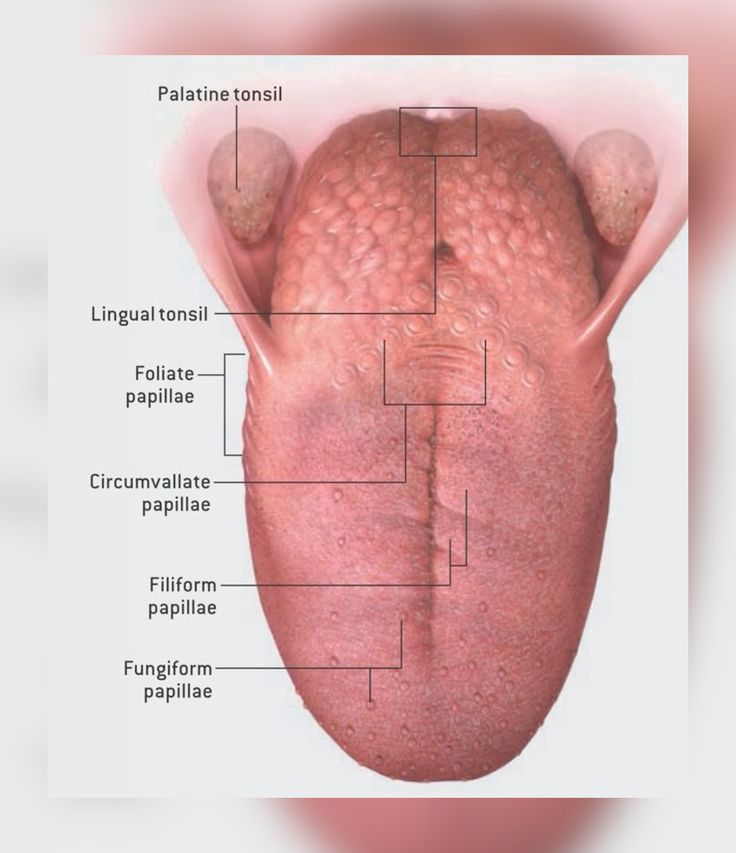
mushroom-shaped taste buds on the tongue that help detect sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami flavors
Tongue mucosa: fungiform papillae
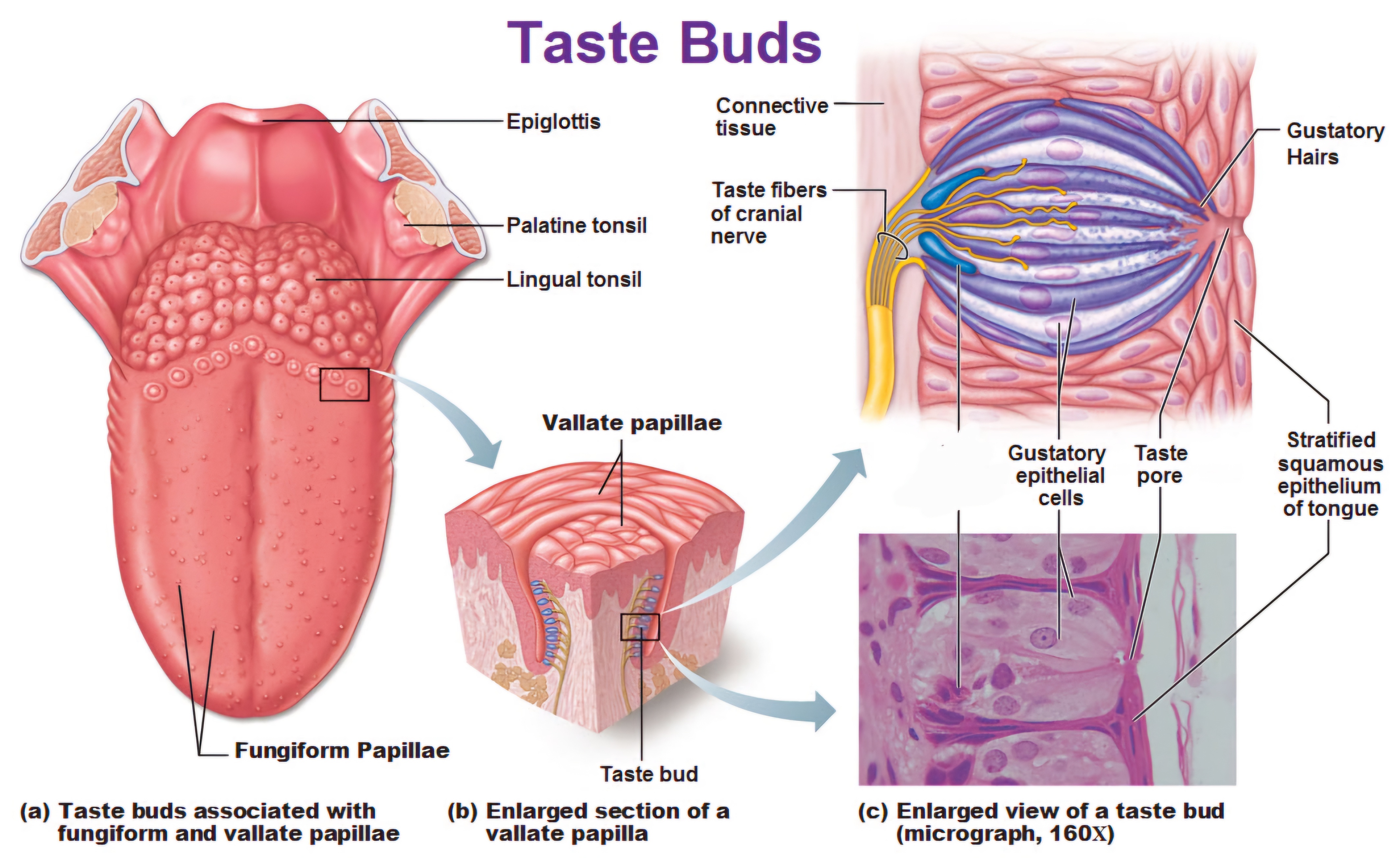

are large, dome-shaped structures located at the back of the tongue. They are arranged in a V-shaped row immediately in front of the foramen cecum and sulcus terminalis.
Circumvallate papillae
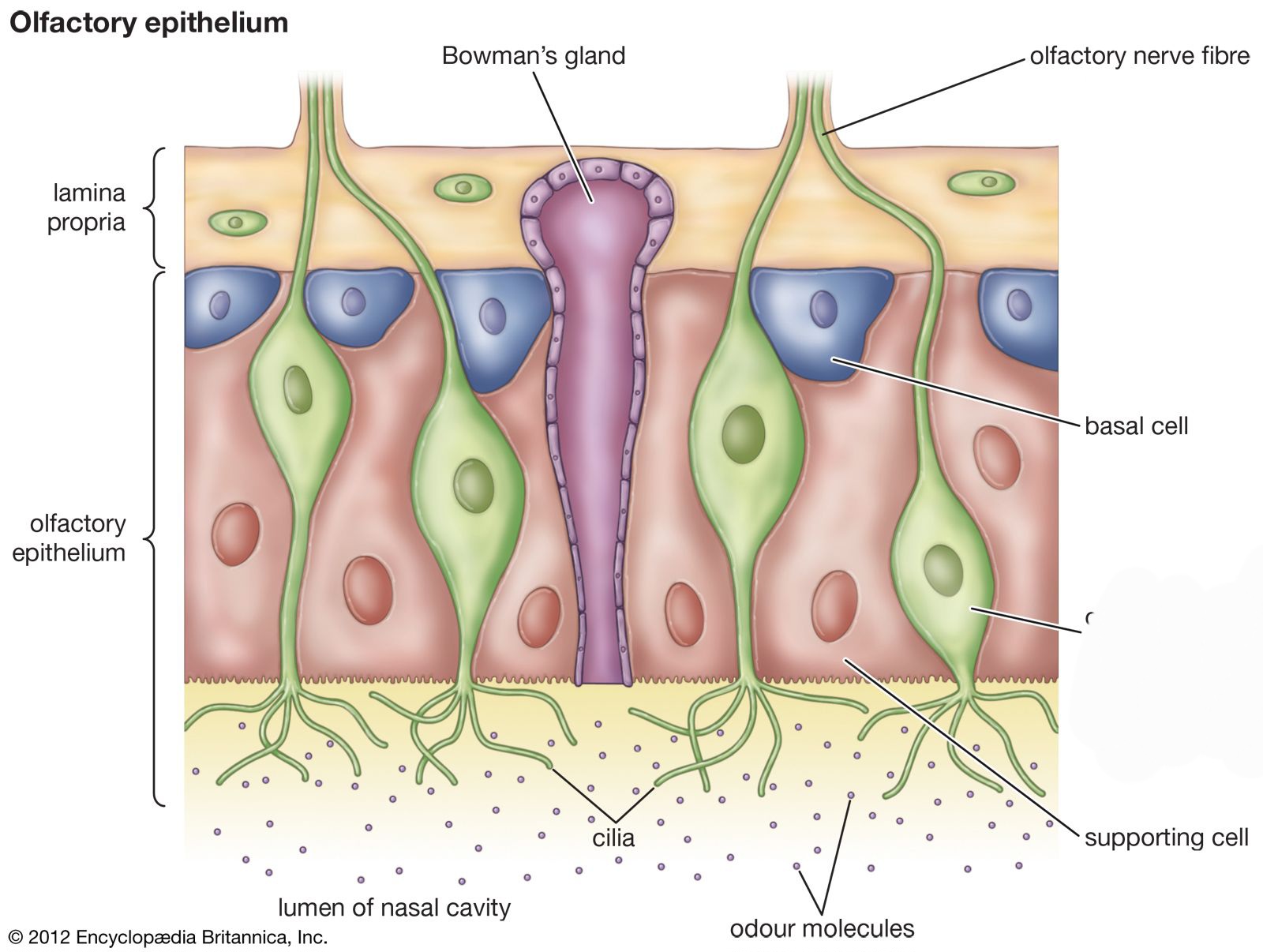
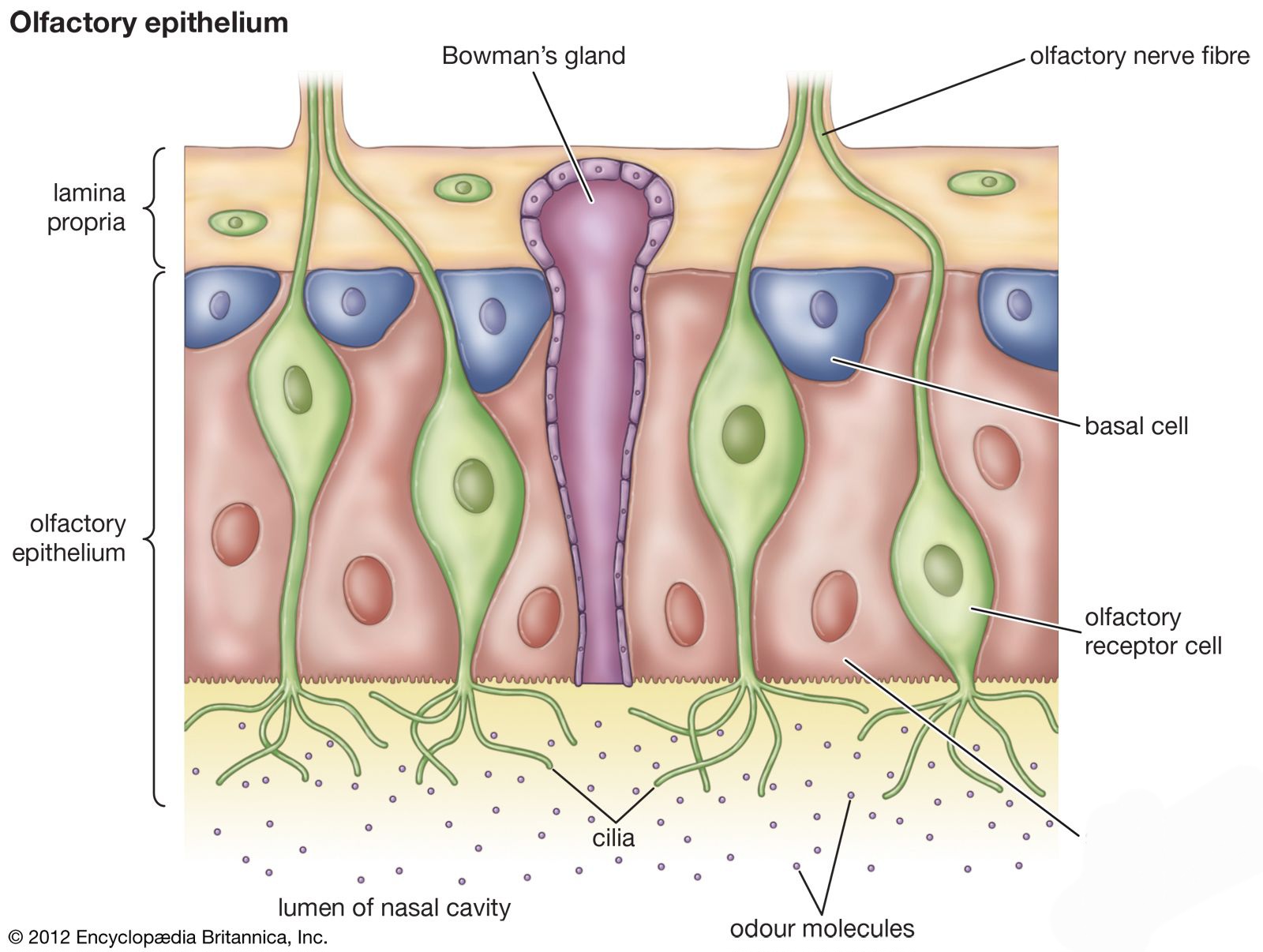
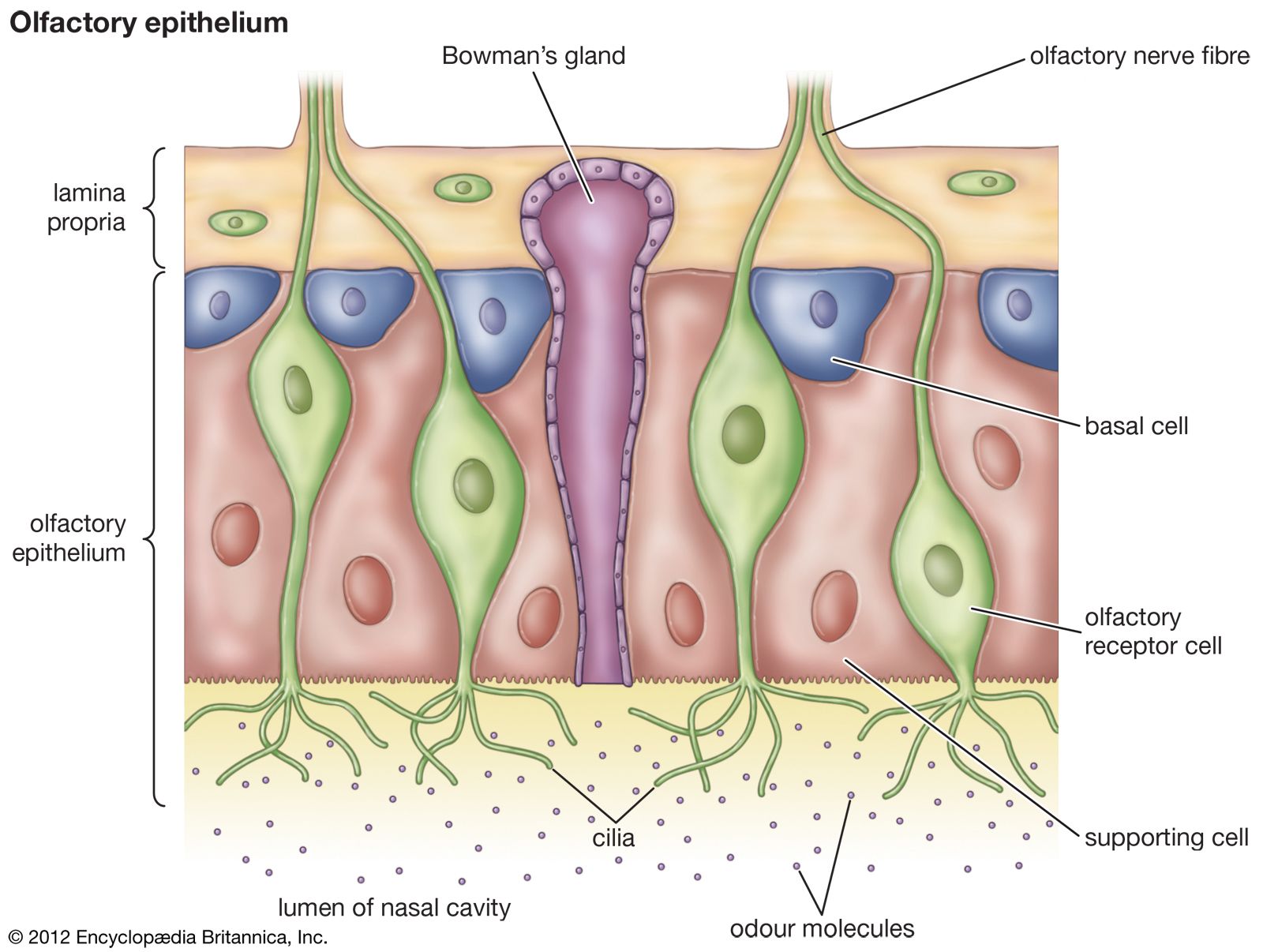
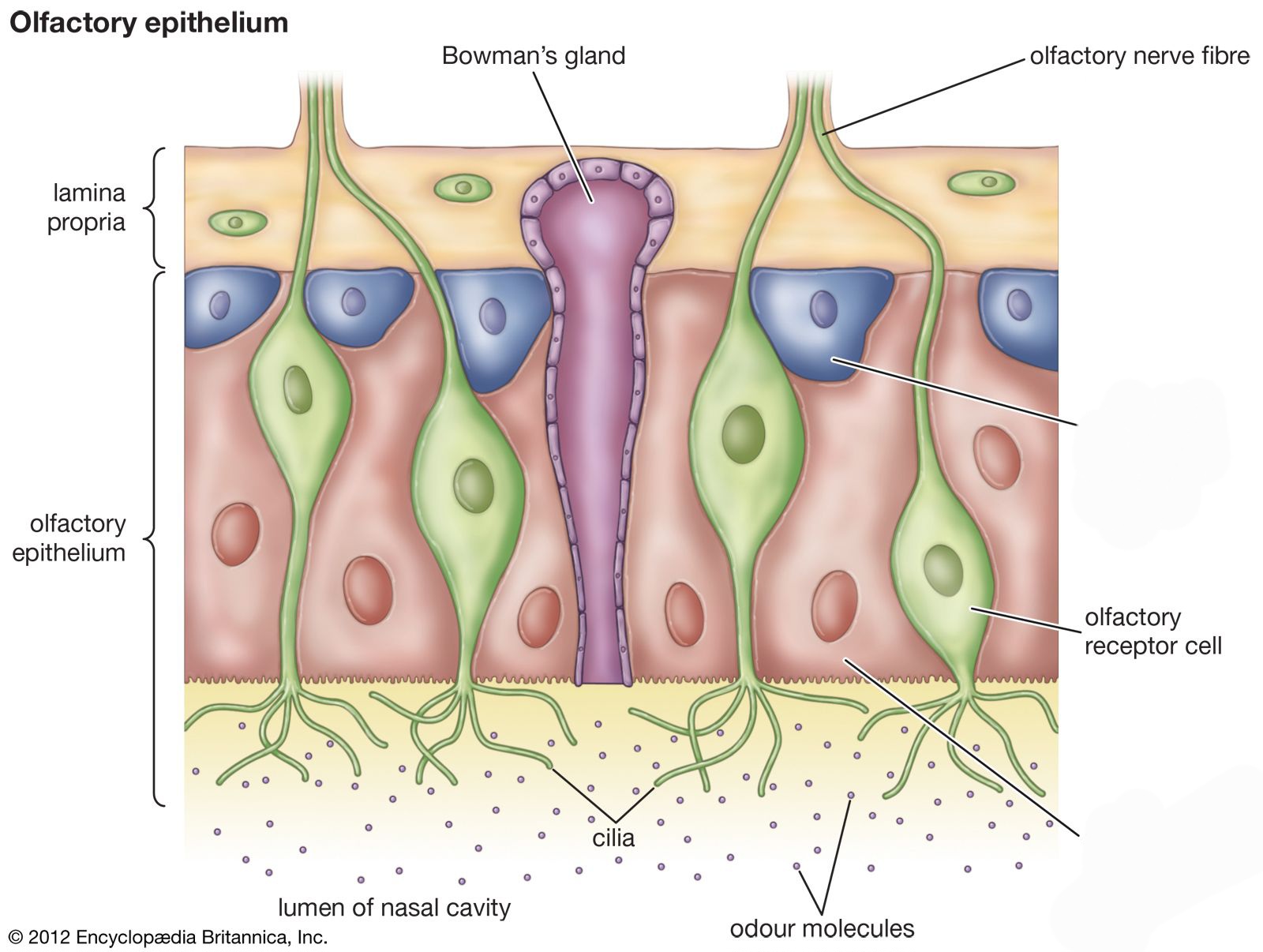
specialized nerve cells located in the nasal cavity that play a crucial role in the sense of smell.
Olfactory receptor cells
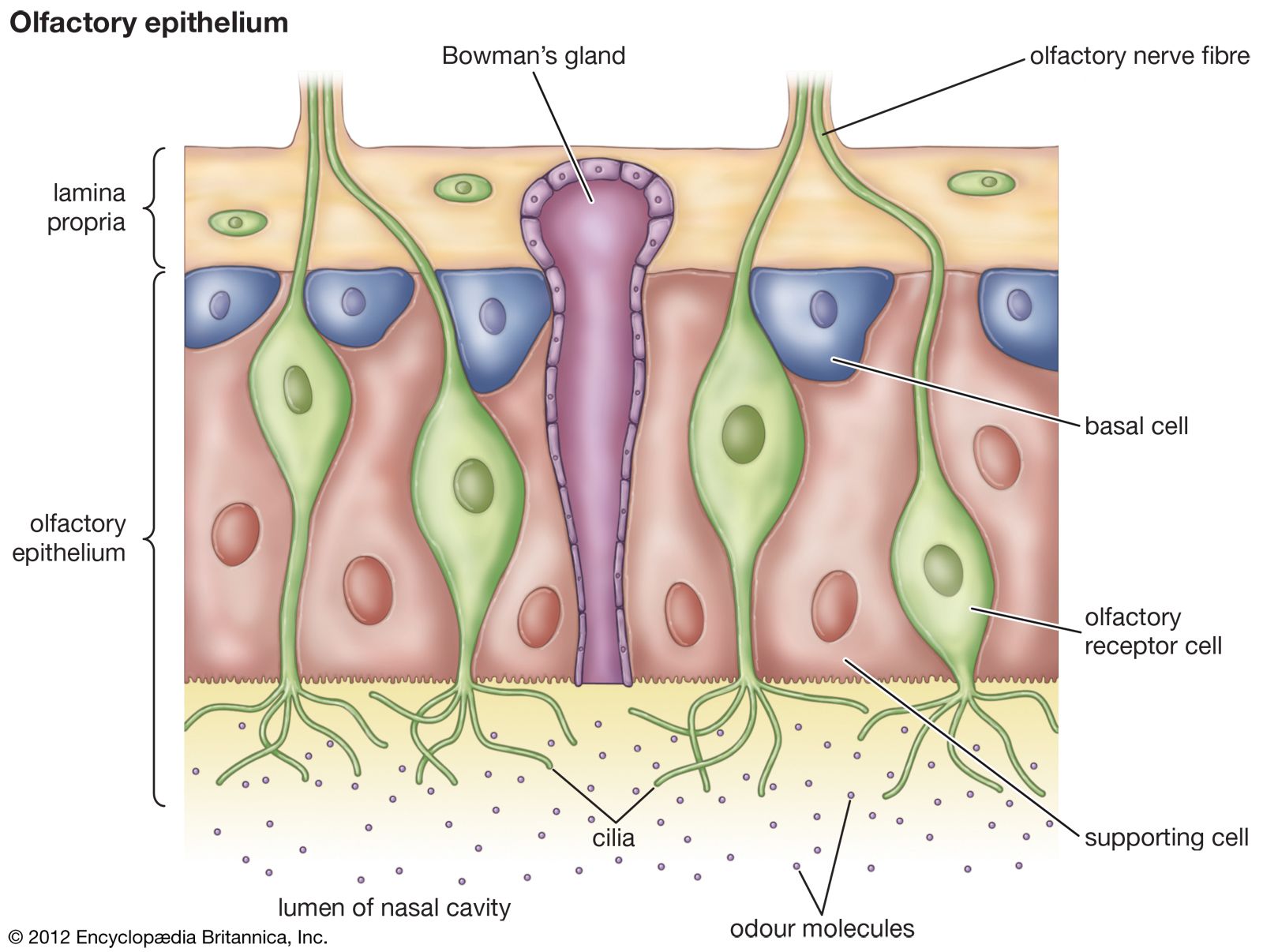
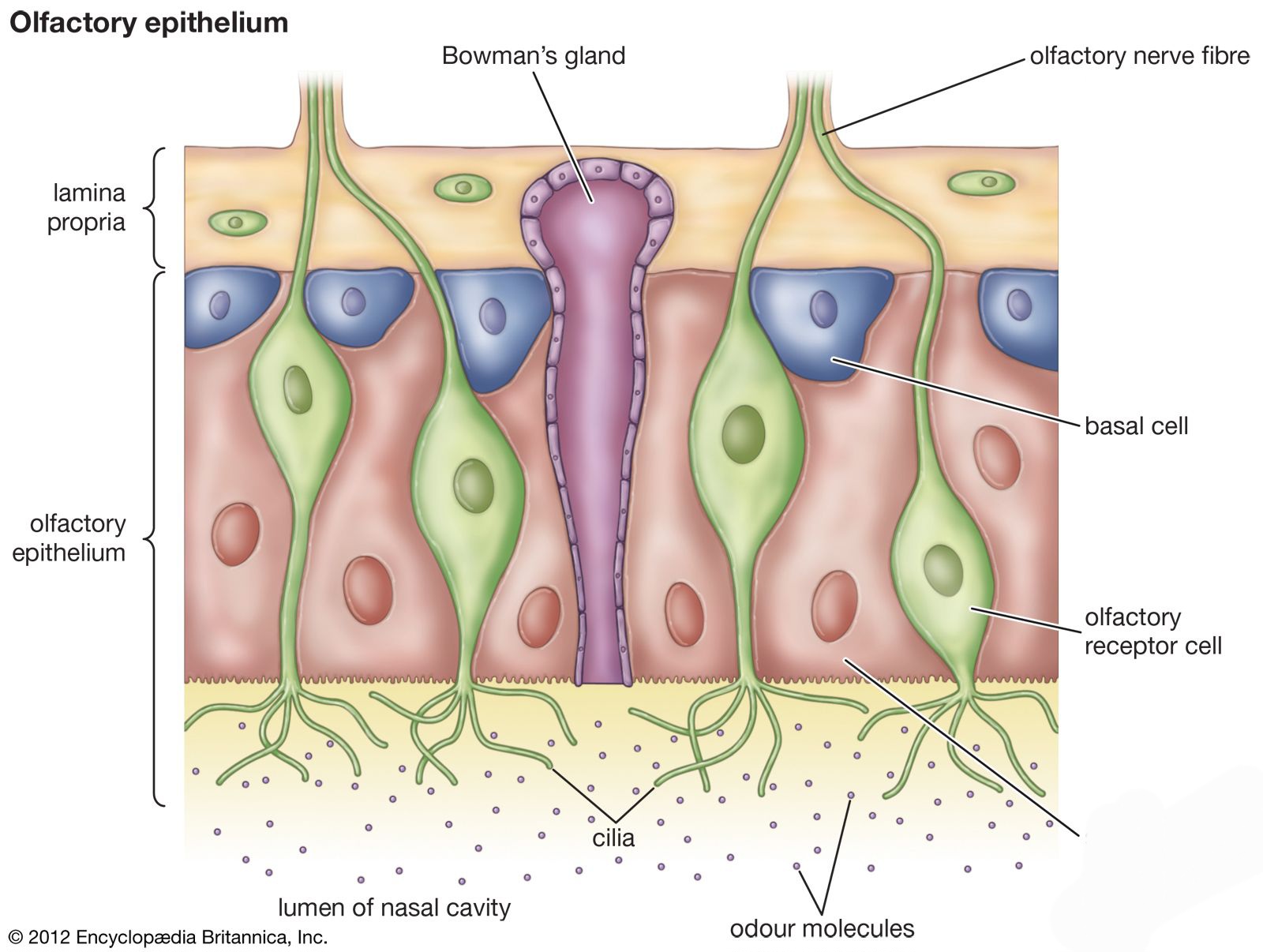
also known as sustentacular cells, are non-neuronal cells that play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and functionality of the olfactory epithelium.
Supporting cells
a type of skin cell found in the basal cell layer, which is the deepest layer of the epidermis (the outer layer of skin)
Nose- basal cell