V Physics - Astrophysics
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Orbit of: Comets
Shape is very elliptical
Around the star
Orbit of: Moons
More circular in shape
Around their planet
Orbit of: Planets
More circular
Around the star
Equation linking: orbital speed, orbital radius and time period
v = 2πr/T
How are stars classified by their colour?
Blue stars are the hottest
In the middle is white and yellow
Red stars are the coolest

Star Life Cycle Step 1
Protostar:
Hydrogen dust clouds contract into a ball due to gravitational attraction
As density and pressure increase, temperature starts to increase
Star Life Cycle Step 2
Main Sequence Star:
The star fuses hydrogen into helium
Inwards gravitational attraction balance by outwards radiation and pressure
A star spends most of its life as a main sequence star
Star Life Cycle Step 3 - High Mass Stars
Red Supergiant (Bigger than Red Giant):
The star begins to run out of hydrogen
Inwards gravitation attraction is stronger than outwards radiation pressure, causing the star to contract
As the star contracts, the temperature increases and the remaining hydrogen in the outer layers begin to fuse, causing the star to expand and hence cool.
Star Life Cycle Step 4 - High Mass Stars
Supernova:
The gravitational collapse of a high mass star is so fast and violent that a shockwave bounces off the core
This explosion is called a supernova
Star Life Cycle Step 4 - High Mass Stars (Way 1)
Neutron Star:
The gravitational attraction is so strong that electrons and protons are pushed together to form neutrons
Star Life Cycle Step 4 - High Mass Stars (Way 2)
Black Hole:
Gravitational collapse is so strong that all matter gets crushed into a single, infinitely dense point
Star Life Cycle Step 3 - Low Mass Stars
Red Giant:
The star begins to run out of hydrogen
Inwards gravitation attraction is stronger than outwards radiation pressure, causing the star to contract
As the star contracts, the temperature increases and the remaining hydrogen in the outer layers begin to fuse, causing the star to expand and hence cool.
Star Life Cycle Step 4 - Low Mass Stars
White Dwarf:
A low mass star will not have enough gravitational attraction to heat up the centre of the star to fuse the built-up carbon.
The outer layers have been blown away and will make up the building blocks of planets in millions of years, called a planetary nebula
Absolute Magnitude Scale
-10 → +15 : bright → dim
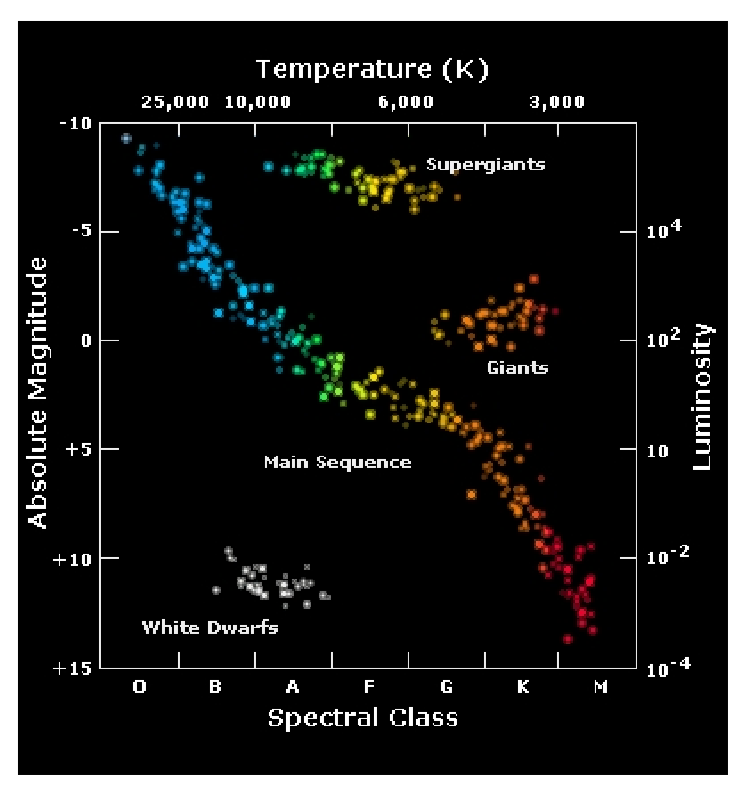
Hertzsprung-Russell diagram
Red Shift
Astronomers have discovered that, in general, the further away a galaxy is, the more red-shifted its light is. This means that the further away the galaxies are, the faster they are moving. Red-shift data provides evidence that the Universe, including space itself, is expanding.
Cosmic Background Radiation (CMBR)
Empty space is full of electromagnetic waves of microwave wavelength
Universe started very hot and as it expanded it cooled
At the very hot temperatures, protons and neutrons were able to fuse
When the temperature dropped, hydrogen and helium gas were formed. This is when raw material of stars was made.
When neutral atoms were formed, all the high energy gamma rays were free to propagate rather than constantly colliding with particles and the universe became transparent.
As it continued to expand, the gamma rays became stretched out - so much that they became microwaves: finding these leftover microwaves supports the Big Bang theory.
Equation linking: change in wavelength, wavelength, velocity of a galaxy and the speed of light
change in wavelength / reference wavelength = velocity of a galaxy / speed of light
Speed of Light
3×10^8