Anemia Part 2
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Anemia: Hb concentration in the blood is below a defined level,
resulting in a reduced oxygen-carrying capacity of RBCs
for men vs for women
Hb <13 g/dL; for women Hb <12 g/dL
causes of anemia
mechanism for the decrease in Hb concentration
kinetic approach
causes of anemia
alterations in RBC size and reticulocyte response
morphological approach
Kinetic Approach
Nutrient deficiency
•Disorders of bone
marrow
•Suppression of bone
marrow
•Low levels of trophic
hormones
decrease RBC production
Kinetic Approach
Nutrient deficiency
•Disorders of bone
marrow
•Suppression of bone
marrow
•Low levels of trophic
hormones
increase RBC destruction
kinetic approach
Obvious bleeding
•Occult bleeding
•Induced bleeding
•Surgical procedure
•Use of anticoagulants
blood loss
Morphological approach
•Reduced iron
availability
•Disorders of heme
synthesis
•Reduced globin
production
microcytic mcv<80 fl
Morphological approach
•Hemorrhage
•Anemia of chronic
disease
•Hemolytic anemia
normocytic mcv 80-100 fl
Morphological approach
Reticulocytosis
•Abnormal nucleic acid
methabolisms
•Abnormal RBC
maturation
•EtOH abuse
•Liver disease
•Hypothyroidism
macrocytic mcv >100 fl
symptoms of ____
Most patients are asymptomatic
Physical examination
Laboratory evaluation
Symptoms:
• decrease O2 delivery to tissues:
• Dyspnea, fatigue, palpitations
• Severe: lethargy, confusion, arrhythmia, MI
• Acute blood loss:
• Dizziness, lethargy, hypotension, shock
anemia
nutritional deficiencies of _____ are common causes of anemia
iron, vitamin B12, or folic acid

some causes include increase deman, increase loss, or decrease intake
Iron deficiency anemia
Laboratory finding for anemia
____ are increase
______ are decreased
TIBC (increase) vs Hgb MCV Serum Iron, Serum Ferritin (decreased)
Management of iron deficiency anemia: correct underlying cause and reverse parameters
maintenance dose: pregnant vs lactating
27mg vs 10 mg
Management of iron deficiency anemia: correct underlying cause and reverse parameters
maintenance dose: supplement
18mg/day
Management of iron deficiency anemia: correct underlying cause and reverse parameters
therapeutic dose
100-200 mg/day
Iron come from diet
______ increase iron absorption
gastric and ascorbic acid (200mg VitC per 30mg Fe)
Iron come from diet
______ decrease iron absorption
calcium and tea
treatment reccs for iron def in Jane?
Ferrous Sulfate 325 mg qd
administer oral iron on _____ because food can reduce absorption
empty stomach
anatacids, H, RA, PPI, Ca can ____
inhibit iron abosorption
Vit C or orange juice can ____
increase iron absorption
Failure of oral iron → inability to absorb oral iron
malabsorptive state
Failure of oral iron → worsening of
underlying disease, poorly absorbed and ineffective
Inflammatory bowel disease
Failure of oral iron → amount absorbed not sufficient to replete
Heavy blood loss and gastric bypass
Failure of oral iron→ unable to fully utilize oral iron
Dialysis/cancer patients on erythropoiesisstimulating agents
iron toxicity
____ associated with sever iron overload = liver/heart failure
hemochromatosis
iron toxicity
____ to treat iron overload
chelation therapy
Folic acid deficiency anemia aka “Megaloblastic anemia”
folic acid = folate = vitamin B9
________________ is storage site of folic acid → limited space
liver
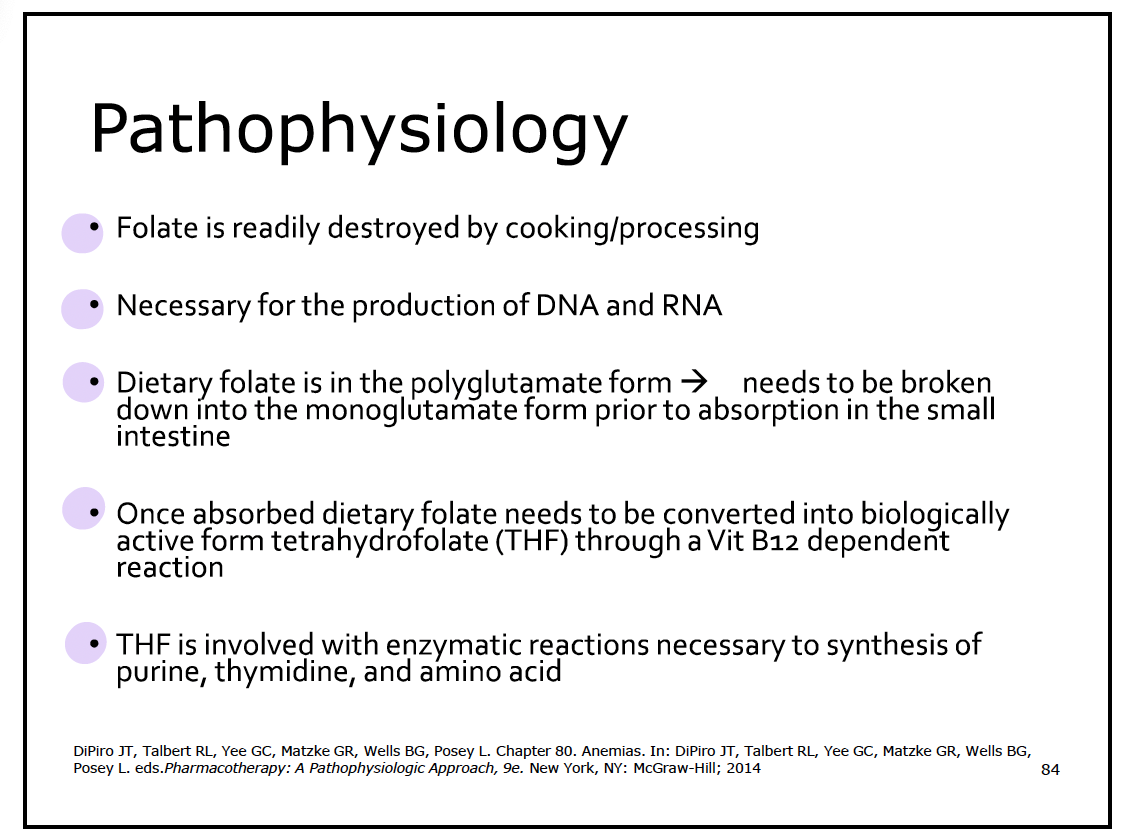
Folic Acid is essential for DNA synthesis and red blood cell formation. A deficiency can lead to _____ characterized by the presence of large, immature red blood cells.
megaloblastic anemia
Folic Acid Deficiency Etiology (what causes the deficiencies)
inadequate intake, increased need, impaired metabolism, malabsorption
Medication interfering with folic acid metabolism
weak inhibitor of dihydrofolate reductase
trimethoprim
Medication interfering with folic acid metabolism
blocks folate absorption and increase utilization
phenytoin
Medication interfering with folic acid metabolism
inhibit dihydrofolate reductase
methotrexate
Medication interfering with folic acid metabolism
used for treatment of malaria and toxoplasmosis
inhibits parasitic dihydrofolate reductase
pyrimethamine
Symptom of ____
Usually asymptomatic
• GI symptoms
• Nausea/vomiting/ abdominal pain especially after a meal
• Weight loss
• Sore tongue or pain when swallowing
• Stomatitis
folic acid deficiency
Folic Acid Deficiency Lab
____ increase
____ decrease
MCV (increase) vs RBC, HgB, Reticulocytes, Serum Folate (decrease)
maintenance dose of folic acid
_____ in adults
400 mg
maintenence dose of folic acid in pregnant vs lactating
500 mcg vs 600 mcg
therapeutic dose of folic acid: including pregnant who are considered deficient
____
1 mg/day
therapeutic dose of folic acid: women who previously had babies with neural tube defects
____
4 mg/day
therapeutic dose of folic acid: deficiency due to malabsoprtion
1-5 mg/day
vernacular “megaloblastic anemia”
risk increase with age
large storage in liver → will take years to develop
neurological damage is progressive and may be pernament
Vitamin B12 Deficiency Anemia

____ Etiology
Inadequate intake → rare
Malabsorption → most common
Loss of intrinsic factor
GI disorders
Competition for B12
Drug interactions and effects
Inadequate utilization
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Medication interfering with Vitamin B12
____ → impaired release of B12 from food due to absence of gastric acid secretions
prolong use of PPIs and H2RA
Medication interfering with Vitamin B12
____ → reduce B12 absorption due to calcium-dependent ileal membrane antagonism
can be reversed with supplemental calcium
Metformin
Symptoms:
• Pica: Eating ice for something with no nutritional value.
may also be caused by severe blood loss, which can present as dizziness, lethargy, hypotension, or shock (in acute blood loss), or as occult (hidden) bleeding, such as a gastric intestinal bleed or bleeding ulcer from NSAID use
Iron Deficiency Anemia (IDA)
Symptoms:
may present with GI symptoms.
• Sore tongue or pain when swallowing.
• Stomatitis.
• Nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain, especially after a meal.
• Weight loss.
Folic Acid Deficiency Anemia
Symptoms:
Neurological symptoms:
◦ Numbness .
◦ Weakness .
◦ Impaired memory .
◦ Tingling on the arm or leg → paresthesias
poor brain developement in children.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency Anemia
Lab finding for Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia
increase ____
decrease ____
MCV (increase) vs RBC, HgB, Reticulocyte, Serum B12 decrease
Vitamin B12 RDA (recommended daily allowance)
adults
pregnant/lactating females
2mcg/day vs 2.6 mcg/day
Vitamin B12 therapeutic dose
oral ___
Im/SubQ ____
1000-2000 mcg/day vs 1000 mcg daily/week, weekly/1month, maintenance monthly