L2 P1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/117
Earn XP
Last updated 8:41 AM on 1/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
1
New cards
3rd
TAXONOMICAL CLASSIFICATION OF FLAGELLATES:
kingdom: protista -- it is the __ kingdom in the organism world
kingdom: protista -- it is the __ kingdom in the organism world
2
New cards
Sarcomastigophora
mastigophora
mastigophora
TAXONOMICAL CLASSIFICATION OF FLAGELLATES:
kingdom: protista
Phylum: ___
subphylum: ___
kingdom: protista
Phylum: ___
subphylum: ___
3
New cards
phytomastigophora and zoomastigophora
TAXONOMICAL CLASSIFICATION OF FLAGELLATES:
kingdom: protista
Phylum: sarcomastigophora
subphylum: mastigophora
class: what are the 2 types which are classified into 2 based on the presence or absence of plastids
kingdom: protista
Phylum: sarcomastigophora
subphylum: mastigophora
class: what are the 2 types which are classified into 2 based on the presence or absence of plastids
4
New cards
chromatophores or plastids
TAXONOMICAL CLASSIFICATION OF FLAGELLATES:
kingdom: protista
Phylum: sarcomastigophora
subphylum: mastigophora
class: phytomastigophora has __
kingdom: protista
Phylum: sarcomastigophora
subphylum: mastigophora
class: phytomastigophora has __
5
New cards
does not have chromatophores or plastid
TAXONOMICAL CLASSIFICATION OF FLAGELLATES:
kingdom: protista
Phylum: sarcomastigophora
subphylum: mastigophora
class: phytomastigophora has plastid or chromatophores while **zoomastigophora __**
kingdom: protista
Phylum: sarcomastigophora
subphylum: mastigophora
class: phytomastigophora has plastid or chromatophores while **zoomastigophora __**
6
New cards
plastids
___ are organelles in which photosynthesis occurs and can also be found in plants and algae, however the function of plastids in obligate intracellular parasites has not been established.
7
New cards
chromatophores
___ - they are cytoplasmic structures that give color and pigment to your cytoplasm.
8
New cards
* bodonida
* tetramitida
* hexamitida
* trichomonadida
* trypanosomatida
* tetramitida
* hexamitida
* trichomonadida
* trypanosomatida
TAXONOMICAL CLASSIFICATION OF FLAGELLATES:
kingdom: protista
Phylum: sarcomastigophora
subphylum: mastigophora
class: zoomastigophora and phytomastigophora
order:?? enumerate
kingdom: protista
Phylum: sarcomastigophora
subphylum: mastigophora
class: zoomastigophora and phytomastigophora
order:?? enumerate
9
New cards
2
TAXONOMICAL CLASSIFICATION OF FLAGELLATES:
kingdom: protista
Phylum: sarcomastigophora
subphylum: mastigophora
class: zoomastigophora and phytomastigophora
order: **Bodonida has __ flagella**
kingdom: protista
Phylum: sarcomastigophora
subphylum: mastigophora
class: zoomastigophora and phytomastigophora
order: **Bodonida has __ flagella**
10
New cards
tetramitida - 3 flagella
hexamitida - 6 or 8 flagella
Trichomonadida - 3 to 5 flagella
trypanosomatida - single flagellum
hexamitida - 6 or 8 flagella
Trichomonadida - 3 to 5 flagella
trypanosomatida - single flagellum
TAXONOMICAL CLASSIFICATION OF FLAGELLATES:
kingdom: protista
Phylum: sarcomastigophora
subphylum: mastigophora
class: zoomastigophora and phytomastigophora
order:
* Bodonida has 2 flagella
* **Tetramitida has __ flagella**
* **Hexamitida has __ flagella**
* **Trichomonatida has __ flagella**
* **Trypanosomatida has __ flagellum**
kingdom: protista
Phylum: sarcomastigophora
subphylum: mastigophora
class: zoomastigophora and phytomastigophora
order:
* Bodonida has 2 flagella
* **Tetramitida has __ flagella**
* **Hexamitida has __ flagella**
* **Trichomonatida has __ flagella**
* **Trypanosomatida has __ flagellum**
11
New cards
bodonidae
INTESTINAL (DIGESTIVE AND UROGENITAL) FLAGELLATES: IDENTIFY THE FAMILY:
* Usually has 2 flagella: 1 is directed anteriorly, the other is posteriorly & trailing both arising from a blepharoplast in front of the nucleus.
* Usually has 2 flagella: 1 is directed anteriorly, the other is posteriorly & trailing both arising from a blepharoplast in front of the nucleus.
12
New cards
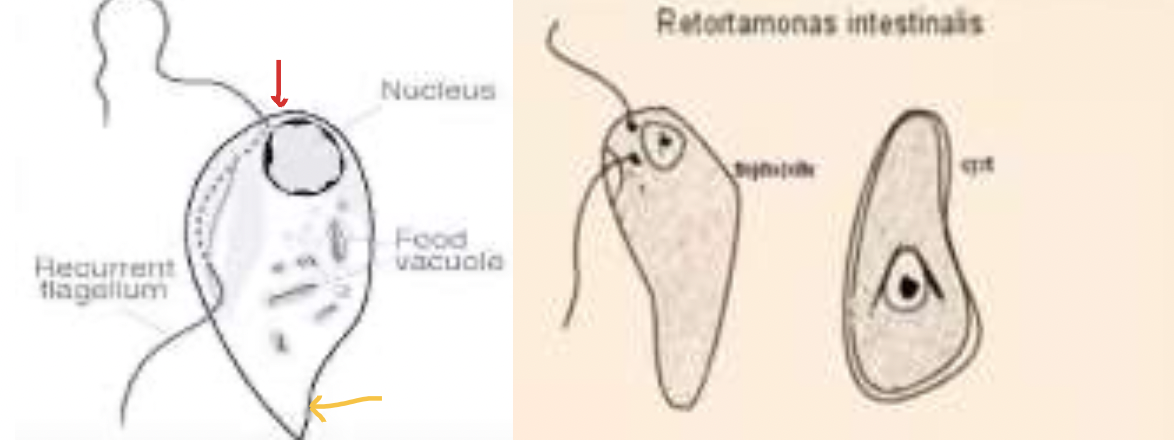
retortamonas intestinalis
INTESTINAL (DIGESTIVE AND UROGENITAL) FLAGELLATES: give 1 member under the family of bodonidae
13
New cards
retortamonas intestinalis
INTESTINAL (DIGESTIVE AND UROGENITAL) FLAGELLATES: IDENTIFY THE MEMBER: bodonidae
* Most important member
* Non-pathogenic but opportunistic
* Only harmful in immunocompromised patients
* Most important member
* Non-pathogenic but opportunistic
* Only harmful in immunocompromised patients
14
New cards
BODONIDAE; Retortamonas intestinalis
IDENTIFY THE FAMILY AND MEMBER
15
New cards
BODONIDAE; Retortamonas intestinalis
IDENTIFY THE FAMILY AND MEMBER:
* In total, the posterior part also contains a small version of a flagella
* Has 3; but the most prominent feature is found in the interior portion (the trailing one)
* Flagella is for the locomotion of the parasite
* In total, the posterior part also contains a small version of a flagella
* Has 3; but the most prominent feature is found in the interior portion (the trailing one)
* Flagella is for the locomotion of the parasite
16
New cards
TETRAMITIDAE
INTESTINAL (DIGESTIVE AND UROGENITAL) FLAGELLATES: IDENTIFY THE FAMILY:
* 3 anterior flagella, with 4th trailing flagellum
* Lack an axostyle or other axial organelles
* 3 anterior flagella, with 4th trailing flagellum
* Lack an axostyle or other axial organelles
17
New cards
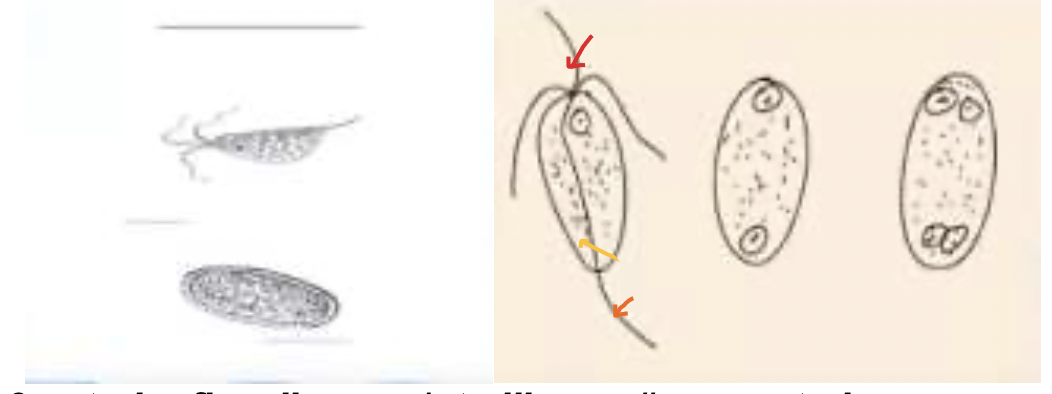
Enteromonas hominis
name 1 member under tetramitidae
18
New cards
tetramitidae, Enteromonas hominis, there are 3 anterior flagellum, trailing, and a posterior flagellum
identify the family and the member:
also identify the flagellum located
also identify the flagellum located
19
New cards
Chilomastigidae
INTESTINAL (DIGESTIVE AND UROGENITAL) FLAGELLATES: IDENTIFY THE FAMILY:
* 3 anteriorly directed free flagella, 4th delicate flagellum lying within a cytosomal cleft
* Pear-shaped cysts with clear visible cytosome
* 3 anteriorly directed free flagella, 4th delicate flagellum lying within a cytosomal cleft
* Pear-shaped cysts with clear visible cytosome
20
New cards
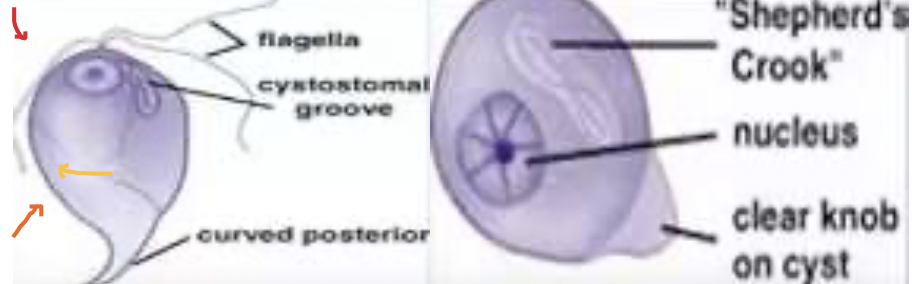
Chilomastix mesnili
give one member under chilomastigidae
21
New cards
3 anterior flagellum, 4th delicate flagellum (shorter and curved), axostyle (spine of organism)
IDENTIFY THE FAMILY AND THE MEMBER: also find the flagellum and their location
22
New cards
axostyle
what is known as the spine of organism
23
New cards
5 flagella (3 anterior, 4th delicate, 1 posterior)
in total, how many flagellum are there in Chilomastix mesnili (member of Chilomastigidae)
24
New cards
HEXAMITIDAE
INTESTINAL (DIGESTIVE AND UROGENITAL) FLAGELLATES: IDENTIFY THE FAMILY:
* Have 2 nuclei lying side by side in the same transverse plane, 6 to 8 (3 to 4 pairs) flagella in bilateral symmetry
* Usually, there are 6 flagella
* Have 2 nuclei lying side by side in the same transverse plane, 6 to 8 (3 to 4 pairs) flagella in bilateral symmetry
* Usually, there are 6 flagella
25
New cards
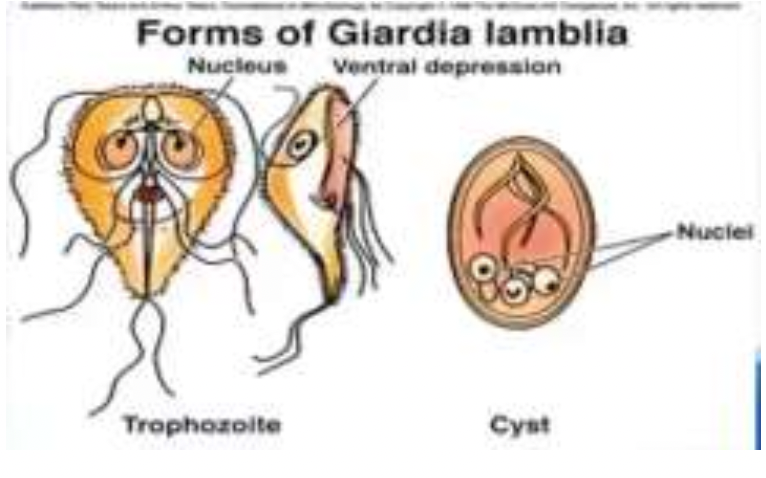
Giardia lamblia
give one member under hexamitidae
26
New cards
Hexamitidae, Giardia lamblia
IDENTIFY THE FAMILY AND MEMBER:
* Described to be **bilateral symmetry** (whatever parts or structures that is found in the right side, can also be seen in the left side)
* Described to be **bilateral symmetry** (whatever parts or structures that is found in the right side, can also be seen in the left side)
27
New cards
Hexamitidae; Giardia lamblia
IDENTIFY THE FAMILY AND MEMBER:
28
New cards
Trichomonadidae
INTESTINAL (DIGESTIVE AND UROGENITAL) FLAGELLATES: IDENTIFY THE FAMILY:
* Have 4 anterior flagella
* Have cytosome with 3 to have free flagella
* Additional flagellum on the margin of an undulating
membrane
* Axostyle protrudes through the posterior end of the body
* Have 4 anterior flagella
* Have cytosome with 3 to have free flagella
* Additional flagellum on the margin of an undulating
membrane
* Axostyle protrudes through the posterior end of the body
29
New cards
Trichomonas vaginalis; Dientamoeba fragilis
name the members under trichomonadidae
30
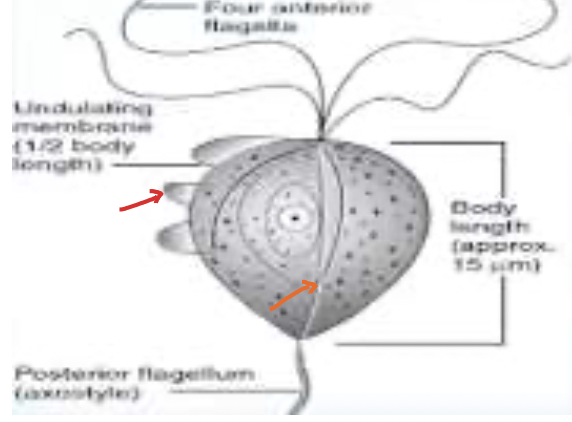
New cards
Trichomonadidae; Trichomonas vaginalis; Dientamoeba fragilis; red arrow is **Undulating flagellum** while the orange at the middle is the **Axostyle**
IDENTIFY THE FAMILY & MEMBER as well as name the arrows pointed
31
New cards
Trypanosomatidae
BLOOD AND TISSUE FLAGELLATES: IDENTIFY THE FAMILY:
* Single flagellum which arises from a nucleus and kinetoplast (composed of Blepharoplast & Parabasal body)
* Single flagellum which arises from a nucleus and kinetoplast (composed of Blepharoplast & Parabasal body)
32
New cards
* trypanosomes & Leishmania
name the members under trypanosomatidae
33
New cards
Trypanosomes & Leishmania
Trypanosomatidae: they are members who are medically important
34
New cards
Trypanosomes
Trypanosomatidae: ____ blood parasites/ flagellates
35
New cards
leishmania
Trypanosomatidae: ___ are tissue flagellates
36
New cards
Blepharoplast and Parabasal body
trypanosomatidae contains **kinetoplast** which are made of ??
37
New cards
true
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS: T/F: **Motion** is by **flagella**. The flagellum arises from kinetoplast. The kinetoplast is composed of the **blepharoplast** and the **parabasal body**.
38
New cards
Blepharoplast
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS: ___ protein structure that serves as the base of the flagella; site for nucleation (production of the nucleus and microtubules)
39
New cards
Parabasal body
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS: ___ - similar to Golgi bodies in plants; serve as intracellular structure membranes which glycosylation and packaging of secretive proteins take place.
40
New cards
true
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS: T/F: **Vesicular nucleus** with **central karyosome**.
* Some flagella have granulated nucleus but they are mononucleated
* Some flagella have granulated nucleus but they are mononucleated
41
New cards
binary fission
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS:
* Reproduction is by longitudinal ___.
* Asexual method; therefore, there are no male and female flagella.
* Reproduction is by longitudinal ___.
* Asexual method; therefore, there are no male and female flagella.
42
New cards
1. SIMPLE LIFE CYCLE
2. COMPLEX LIFE CYCLE
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS:
Complex life cycles include alternation of hosts.
WHAT ARE THE TWO TYPES OF LIFE CYCLES IN FLAGELLATES
Complex life cycles include alternation of hosts.
WHAT ARE THE TWO TYPES OF LIFE CYCLES IN FLAGELLATES
43
New cards
SIMPLE LIFE CYCLE
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS: THE TWO TYPES OF LIFE CYCLES IN FLAGELLATES:
* ___ - urogenital and intestinal flagellates
* ___ - urogenital and intestinal flagellates
44
New cards
COMPLEX LIFE CYCLE
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS: THE TWO TYPES OF LIFE CYCLES IN FLAGELLATES:
* ___ - tissue and blood flagellates
* ___ - tissue and blood flagellates
45
New cards
Intermediate hosts
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS: ___ commonly serve as vectors, which transport developing parasites from one definitive host to another.
46
New cards
DEFINITIVE HOST
“the organism harbors the sexual portion of the parasite”
47
New cards
a. Trypanosoma
B. Leishmania
B. Leishmania
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS:
* Their transmission requires a biological vector.
* Parasitical species parasites of tissues and blood are??
* Their transmission requires a biological vector.
* Parasitical species parasites of tissues and blood are??
48
New cards
TRUE
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS: T/F: Their transmission **does not require** a biological vector.
49
New cards
Free-living
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS:
* SPECIES LIVING IN THE DIGESTIVE TRACT AND GENITALS ARE:
* ___ flagellates.
* __ in the digestive tract and genetals
* Can survive in the environment even outside the
body of the host
* SPECIES LIVING IN THE DIGESTIVE TRACT AND GENITALS ARE:
* ___ flagellates.
* __ in the digestive tract and genetals
* Can survive in the environment even outside the
body of the host
50
New cards
a. Giardia lamblia
b. Trichomonas vaginalis
c. Trichomonas hominis
b. Trichomonas vaginalis
c. Trichomonas hominis
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS:
examples under transmission does not require a biological vector
examples under transmission does not require a biological vector
51
New cards
C. Giardia lamblia
GROUPS OF PARASITES WITH MEDICAL & PUBLIC HEALTH IMPORTANCE: THE FF ARE **NON-PATHOGENIC** EXCEPT:
A. Chilomastix mesnili
B. Dientamoeba fragilis
C. Giardia lamblia \n D. Trichomonas hominis
A. Chilomastix mesnili
B. Dientamoeba fragilis
C. Giardia lamblia \n D. Trichomonas hominis
52
New cards
B. Trichomonas vaginalis
GROUPS OF PARASITES WITH MEDICAL & PUBLIC HEALTH IMPORTANCE: THE FF ARE **PATHOGENIC**:
A. Trichomonas tenax
B. Trichomonas vaginalis
C. Retortamonas intestinalis
D. Enteromonas hominis
A. Trichomonas tenax
B. Trichomonas vaginalis
C. Retortamonas intestinalis
D. Enteromonas hominis
53
New cards
TRUE
DIFFERENTIATING FLAGELLATES: T/F: Flagellates are one of the **smallest parasites** under the microscope.
54
New cards
* ANTERIOR FLAGELLA
* UNDULATING MEMBRANE
* NUCLEUS
* UNDULATING MEMBRANE
* NUCLEUS
IN DIFFERENTIATING FLAGELLATES, YOU WILL NEED TO OBSERVE THE PRESENCE OF??
55
New cards
MOVEMENT
In dealing with flagellates in the laboratory, observe first the ___
56
New cards
presence of the nucleus
To differentiate a contaminant from a real parasite, take note of the ___.
57
New cards
The development of trophozoite and cyst.
There are only 2 stages in the life cycle of flagellates. What are they??
58
New cards
cyst
___ are the inactive form; just like cells; round or oval in shape
59
New cards
Chilomastix mesnili
identify the parasite:
60
New cards
* **common name** - none
* **geographical distribution** - Cosmopolitan
* **pathogenesis -** Nonpathogenic but opportunistic
* **Habitat** - Colon
* **geographical distribution** - Cosmopolitan
* **pathogenesis -** Nonpathogenic but opportunistic
* **Habitat** - Colon
chilomastix mesnili: identify the ff:
* common name
* geographical distribution
* pathogenesis
* Habitat
* common name
* geographical distribution
* pathogenesis
* Habitat
61
New cards
* **Intermediate host** - none
* **Reservoir host** - none
* **Infected form** - Mature Cyst
* **Mode of infection** - Ingestion
* **Reservoir host** - none
* **Infected form** - Mature Cyst
* **Mode of infection** - Ingestion
chilomastix mesnili: identify the ff:
* Intermediate host
* Reservoir host
* Infected form
* Mode of infection
* Intermediate host
* Reservoir host
* Infected form
* Mode of infection
62
New cards
* **mode of entry** - mouth
* **laboratory indication** - Direct Fecal Smear (Wet & Stained)
* **specimen source** - Feces
* **laboratory indication** - Direct Fecal Smear (Wet & Stained)
* **specimen source** - Feces
chilomastix mesnili: identify the ff:
* mode of entry
* laboratory indication
* specimen source
* mode of entry
* laboratory indication
* specimen source
63
New cards
Chilomastix Mesnili Trophozoite
identify :
64
New cards
* **size** - 6-24 micometer/microns
* **shape** - pyriform; Asymmetrical; with a longitudinal spiral torsion
* **nucleus** - one (mononucleated); relatively big; large nucleus to cytoplasm ratio; usually found in the anterior portion of the organism, by the cytoplasm, centrally located karyosome
* **shape** - pyriform; Asymmetrical; with a longitudinal spiral torsion
* **nucleus** - one (mononucleated); relatively big; large nucleus to cytoplasm ratio; usually found in the anterior portion of the organism, by the cytoplasm, centrally located karyosome
Chilomastix Mesnili Trophozoite: Identify the ff:
* size
* shape
* nucleus
* size
* shape
* nucleus
65
New cards
**flagella:**
* **external -** 2; anterior
* **internal -** 1; cytostomal
* **kinetosomes -** anterior; connected by microfibrils
**Chromosomal groove:** prominent; near the anterior end; hour glass shape
**Cytostomal Fibril:** support along each side of the cytostomal groove
* **external -** 2; anterior
* **internal -** 1; cytostomal
* **kinetosomes -** anterior; connected by microfibrils
**Chromosomal groove:** prominent; near the anterior end; hour glass shape
**Cytostomal Fibril:** support along each side of the cytostomal groove
Chilomastix Mesnili Trophozoite: Identify the ff:
CYTOPLASM:
**flagella:**
* **external -**
* **internal -**
* **kinetosomes -**
**Chromosomal groove:**
**Cytostomal Fibril:**
CYTOPLASM:
**flagella:**
* **external -**
* **internal -**
* **kinetosomes -**
**Chromosomal groove:**
**Cytostomal Fibril:**
66
New cards
**mobility** - stiff and rotary
Chilomastix Mesnili Trophozoite:
* mobility
* mobility
67
New cards
Chilomastix Mesnili cyst
identify:

68
New cards
* **size** - 6-10 microns/micrometer
* **shape -** prominent lemon-shape, ovoid
* **nucleus** - one
* **cytoplasm** - remnants of flagella, kinetosomes, and cytostomal groove (hour-glass shape); hyaline anterior nipple
* **shape -** prominent lemon-shape, ovoid
* **nucleus** - one
* **cytoplasm** - remnants of flagella, kinetosomes, and cytostomal groove (hour-glass shape); hyaline anterior nipple
Chilomastix Mesnili cyst: identify the ff:
* **size**
* **shape**
* **nucleus**
* **cytoplasm**
* **size**
* **shape**
* **nucleus**
* **cytoplasm**
69
New cards
cytoplasm of chilomastix mesnili cyst
* remnants of flagella, kinetosomes, and cytostomal groove (hour-glass shape); hyaline anterior nipple
70
New cards
* infective stage
* Diagnostic stage
* Diagnostic stage
LIFE CYCLE OF CHILOMASTIX MESNILI: what are the 2 different roles/stages
71
New cards
infective stage
LIFE CYCLE OF CHILOMASTIX MESNILI:
* Stage that causes infection to humans.
* Stage being ingested by humans.
* Stage that causes infection to humans.
* Stage being ingested by humans.
72
New cards
diagnostic stage
LIFE CYCLE OF CHILOMASTIX MESNILI:
* Stage that you can identify in the laboratory using the specimen.
* Stage that you can identify in the laboratory using the specimen.
73
New cards
* **mode of infection:** ingestion of contaminated food or drinks
* **portal of entry:** mouth
* **final habitat:** large intestine
* **portal of entry:** mouth
* **final habitat:** large intestine
Chilomastix mesnili:
* mode of infection:
* portal of entry:
* final habitat:
* mode of infection:
* portal of entry:
* final habitat:
74
New cards
cyst
cyst or trophozoite:
* under the stained smear, the remnant of the flagella in the cytoplasm and the nucleus is very prominent
* under the stained smear, the remnant of the flagella in the cytoplasm and the nucleus is very prominent
75
New cards
Trophozoite
cyst or trophozoite:
* The anterior flagella and the posterior flagellum
* The anterior flagella and the posterior flagellum
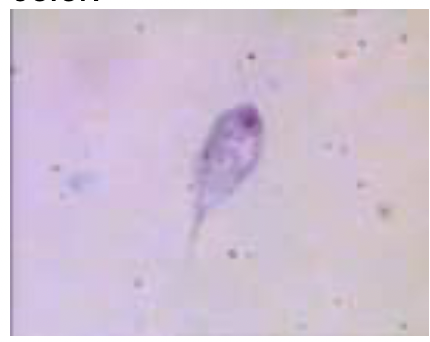
76
New cards
* Cercomonas hominis var. A
* Chylomastix hominis
* Chylomastix hominis
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: what are the synonyms of chilomastix mesnili
77
New cards
Davaine (1854)
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION:
* **Cercomonas hominis var. A** is from ___ in (year) ?
* **Cercomonas hominis var. A** is from ___ in (year) ?
78
New cards
von Prowazek & Werner (1914)
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION:
* Chylomastix hominis is by ____ (year)??
* Chylomastix hominis is by ____ (year)??
79
New cards
* Davaine (1854)
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: Chilomastix Mesnili:
it was discovered by __
it was discovered by __
80
New cards
Wenyon (1910)
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: Chilomastix Mesnili:
* accurately described by ____
* accurately described by ____
81
New cards
Alexieff
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: Chilomastix Mesnili:
named by ___ into C. mesnili (1912)
named by ___ into C. mesnili (1912)
82
New cards
C. mesnili
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: Chilomastix Mesnili:
it was named by Alexieff into __ (1912)
it was named by Alexieff into __ (1912)
83
New cards
True
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: Chilomastix Mesnili:
T/F: they are prevalent in **warm countries** (hence its presence in the philippines)
T/F: they are prevalent in **warm countries** (hence its presence in the philippines)
84
New cards
Iodine, Giemsa, Mayer’s hematoxylin
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: Chilomastix Mesnili:
what are the stain used for smear
what are the stain used for smear
85
New cards
Wet mount preparation
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: Chilomastix Mesnili:
identify the stain used:
* unstained, refractile components under the microscope
identify the stain used:
* unstained, refractile components under the microscope

86
New cards
Iodine Stain
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: Chilomastix Mesnili:
identify the stain used:
* brownish in color
identify the stain used:
* brownish in color
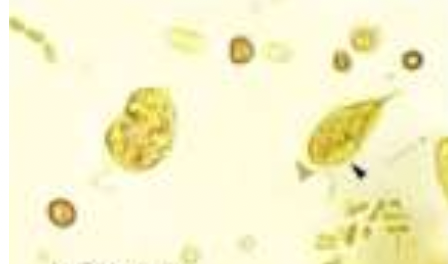
87
New cards
Giemsa stain
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: Chilomastix Mesnili:
identify the stain used:
* purple to violet in color
identify the stain used:
* purple to violet in color
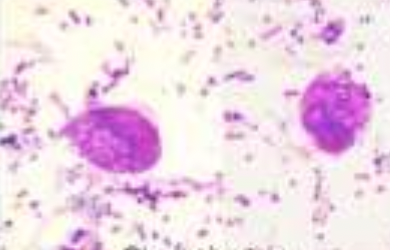
88
New cards
Mayer’s hematoxylin
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: Chilomastix Mesnili:
identify the stain used:
* Grayish-charcoaled color in brown background
identify the stain used:
* Grayish-charcoaled color in brown background
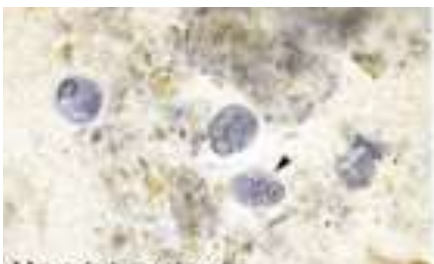
89
New cards
Dientamoeba Fragilis
IDENTIFY:
90
New cards
* **common name -** None
* **geographical distribution -** Costmopolitan
* **pathogenesis** - Nonpathogenic by opportunistic
* **Habitat** - lumen of caecum and upper colon
* **geographical distribution -** Costmopolitan
* **pathogenesis** - Nonpathogenic by opportunistic
* **Habitat** - lumen of caecum and upper colon
Dientamoeba Fragilisi: identify the ff:
* common name
* geographical distribution
* pathogenesis
* Habitat
* common name
* geographical distribution
* pathogenesis
* Habitat
91
New cards
diarrhea, abdominal pain, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and weight loss
Dientamoeba Flagilis:
* pathogenesis: what are the symptoms that have been associated with this infection
* pathogenesis: what are the symptoms that have been associated with this infection
92
New cards
* **Intermediate host** - none
* **Reservoir host** - none
* **Infected form** - mature trophozoites
* **Mode of infection** **-** ingestion of contaminated food/drinks (w/ mature trophozoites), fecal - oral route, via Helminth eggs such as Ascaris spp., and Enterobius spp.
* **Reservoir host** - none
* **Infected form** - mature trophozoites
* **Mode of infection** **-** ingestion of contaminated food/drinks (w/ mature trophozoites), fecal - oral route, via Helminth eggs such as Ascaris spp., and Enterobius spp.
dientamoeba fragilis: identify the ff:
* Intermediate host
* Reservoir host
* Infected form
* Mode of infection
* Intermediate host
* Reservoir host
* Infected form
* Mode of infection
93
New cards
* **portal of entry** - mouth
* **laboratory identification** - Direct Fecal Smear (Wet & Stained)
* **specimen source** - Feces
* **laboratory identification** - Direct Fecal Smear (Wet & Stained)
* **specimen source** - Feces
dientamoeba fragilis: identify the ff:
* portal of entry
* laboratory identification
* specimen source
* portal of entry
* laboratory identification
* specimen source
94
New cards
trophozoite
Dientamoeba fragilis has only 1 stage of development, which is??
95
New cards
Dientamoeba Fragilis Trophozoite
is is Similar to Active Amoeba trophozoite
96
New cards
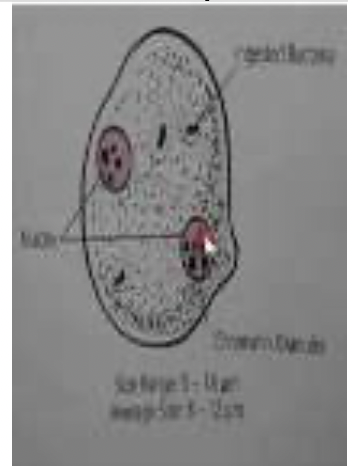
Dientamoeba fragilis Trophozoite
identify:
97
New cards
* **size** -
* small: 3-22um
* Narrow size: 5-12 um
* small: 3-22um
* Narrow size: 5-12 um
Dientamoeba fragilis Trophozoite: identify:
* size
* size
98
New cards
* Rounded but also elongated, sometimes pointed at one end or racket-shaped
Dientamoeba fragilis Trophozoite: identify:
* shape
* shape
99
New cards
nucleus of dientamoeba fragilis trophozoite
identify:
* Can be Mononucleated or Binucleated, Rosette-shape, Has large central chromatin karyosome with 4(tetrad like) discrete granules
* Can be Mononucleated or Binucleated, Rosette-shape, Has large central chromatin karyosome with 4(tetrad like) discrete granules
100
New cards
cytoplasm of dientamoeba fragilis trophozoite
identify:
* May contain food vacuoles with bacteria, flagella extend from the cell wall and resembles like pseudopods
* May contain food vacuoles with bacteria, flagella extend from the cell wall and resembles like pseudopods