bio9
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
The Central Dogma of Biology states that _ is _ _, which is then _ into _. (Word bank: Translated, Transcribed, Protein, RNA, DNA)
DNA, transcribed, RNA, translated, protein
It plays a structural role in ribosomes and helps drive chemical reactions.
rRNA
It is the copy made from DNA that provides the template for protein synthesis during
translation.
mRNA
It reads the mRNA during translation and brings amino acids.
tRNA
This organelle is where the DNA is stored.
Nucleus
This organelle is responsible for protein production.
Ribosome
Name the nucleotide base that is used instead of thymine in an RNA strand.
Uracil
DNA and RNA are read in groups of three nucleotides, which codes for a specific amino
acid, and are called
codons
What’s the purpose of protein synthesis?
Trait development (DNA becoming reality)
Polypeptide=
protein
amino acid=
building block of life
tRNA
carries amino acids to ribosome and matches theme to coded mRNA message
rRNA
Forms important part of both subunits of the ribosome
mRNA
carries instructions for polypeptide synthesis from nucleus to ribosomes in cytoplasm
Only RNA
1 strand, Base Uracil, A-U, Sugar is ribose, found in cytoplasm, “Working copy”
Only DNA
2 strands, base thymine, A-T, stays in nucleus, sugar is deoxyribose, “master copy”
Both DNA and RNA
Contains nucleic acids, A,C,G, sugar phosphate backbone
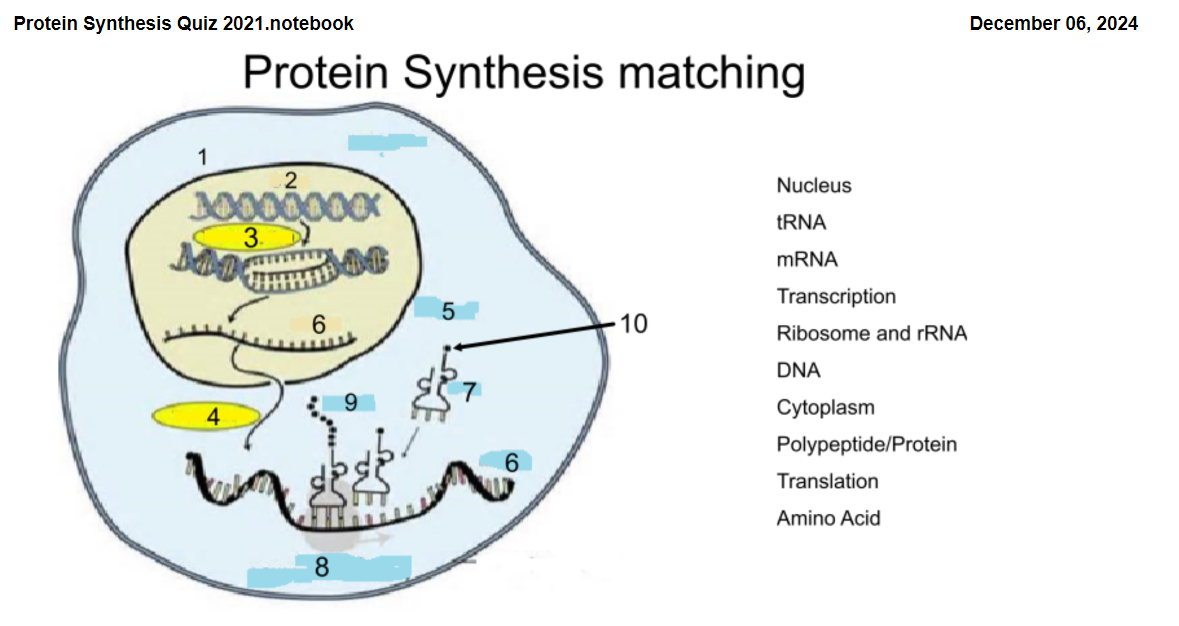
1
Nucleus
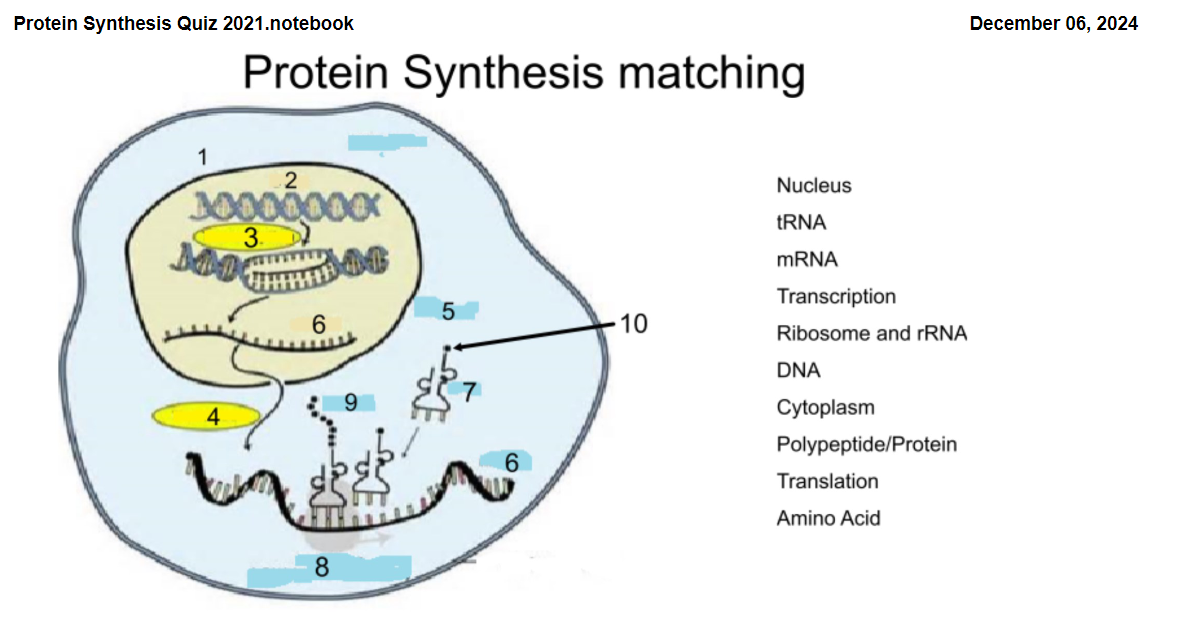
2
DNA
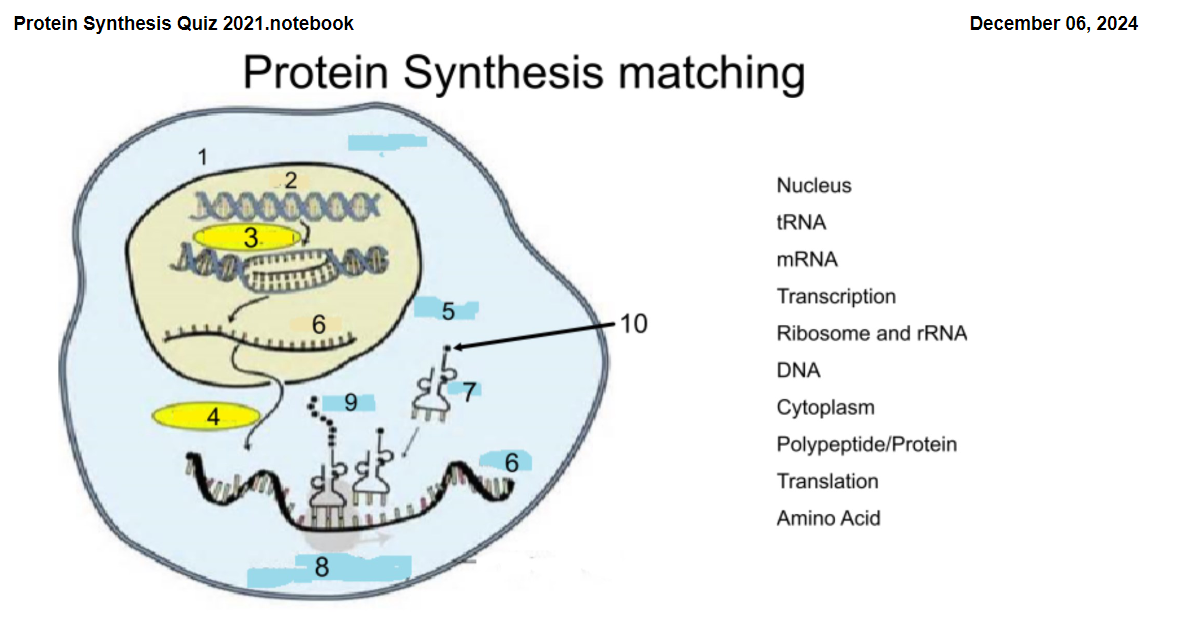
3
Transcription
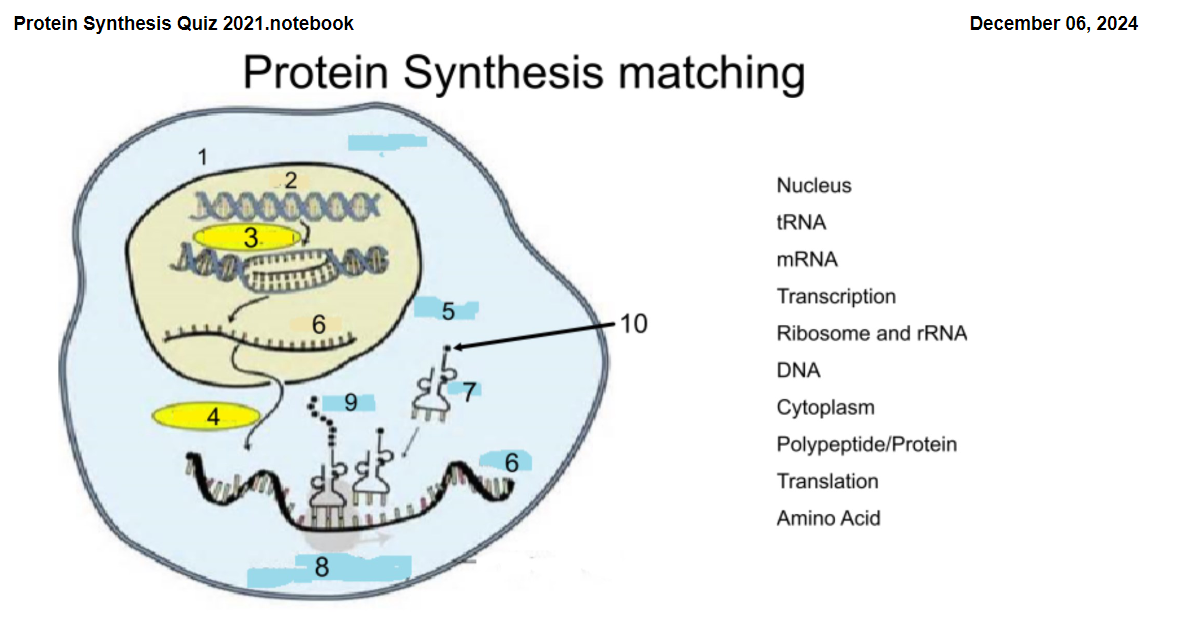
4
Translation
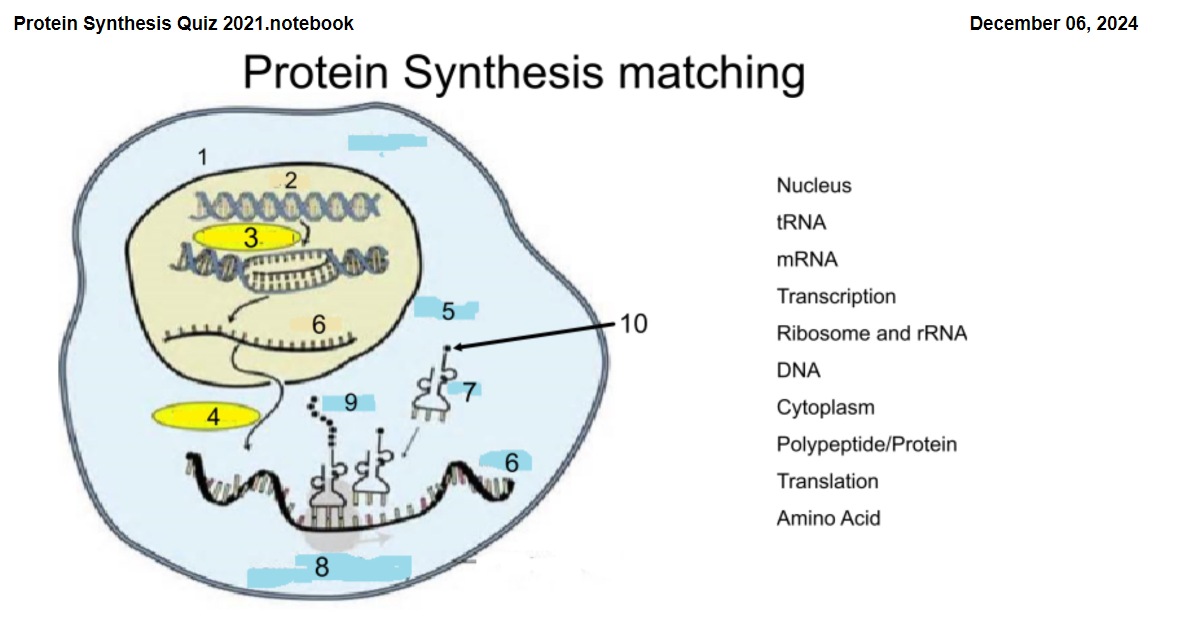
5
Cytoplasm
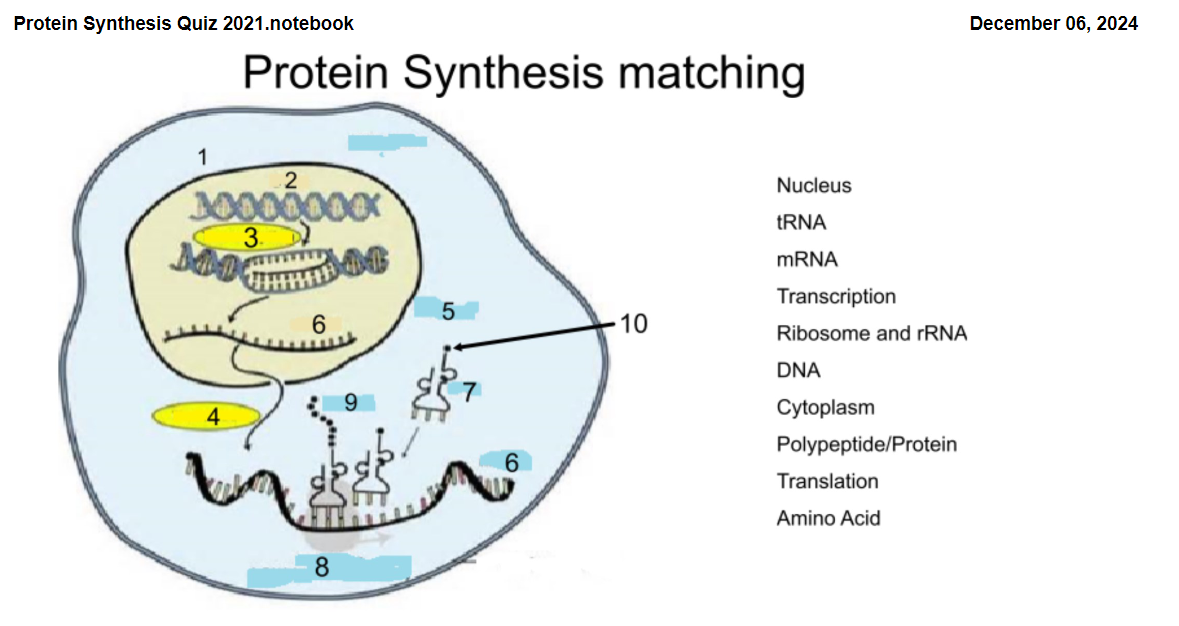
6
mRNA
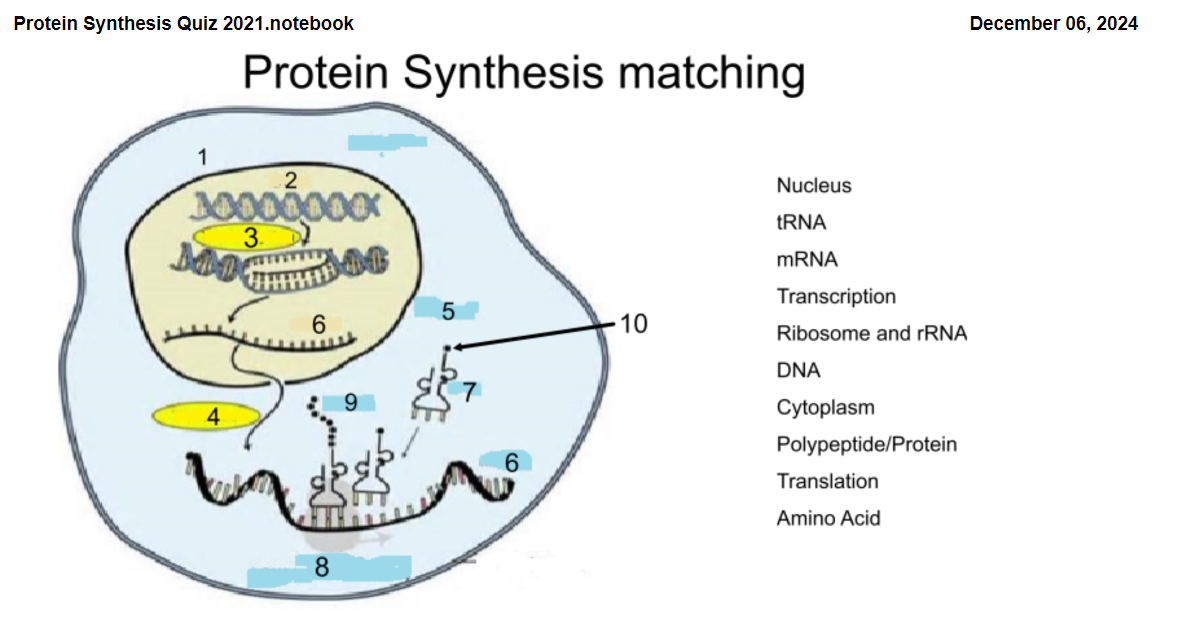
7
tRNA
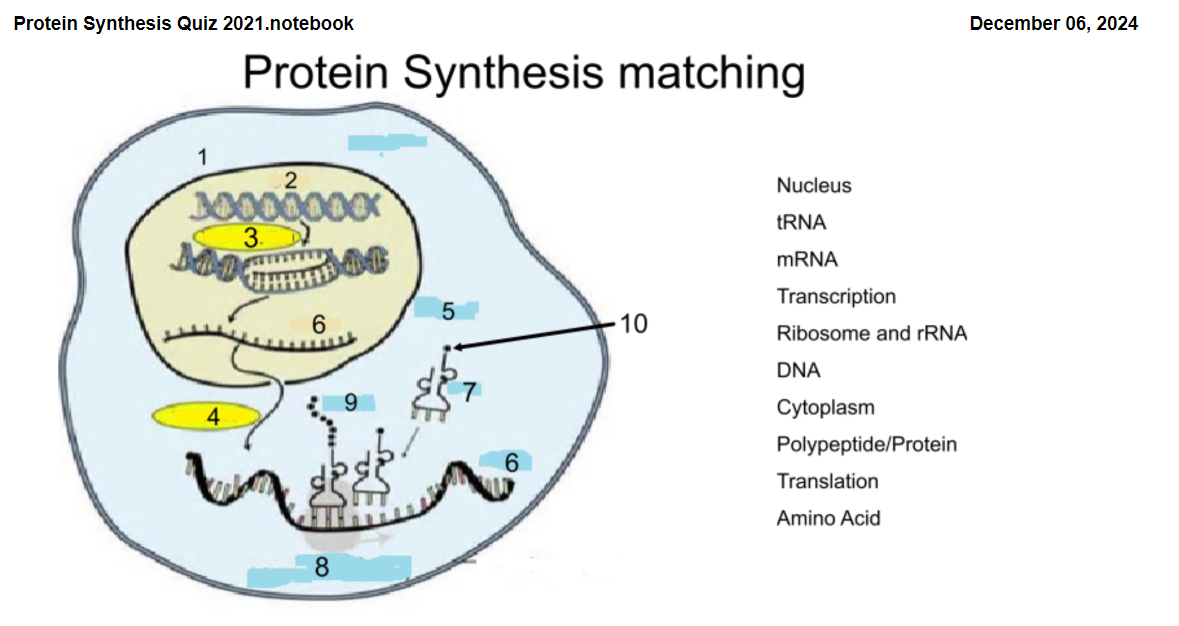
8
Ribosome and rRNA
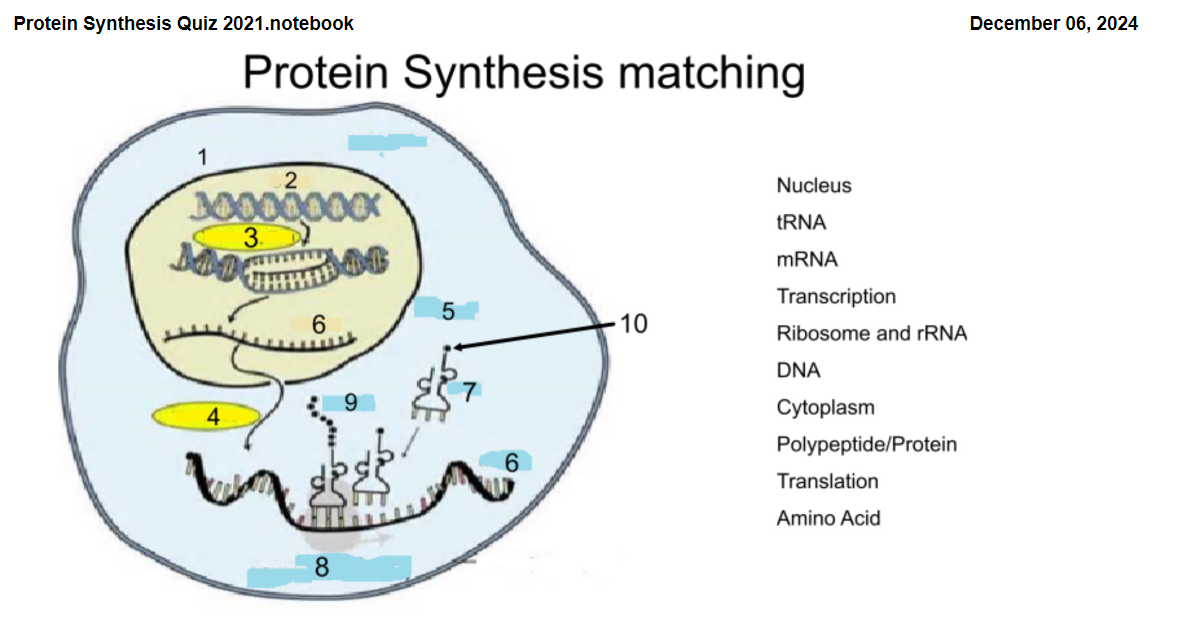
9
Polypeptide/Protein
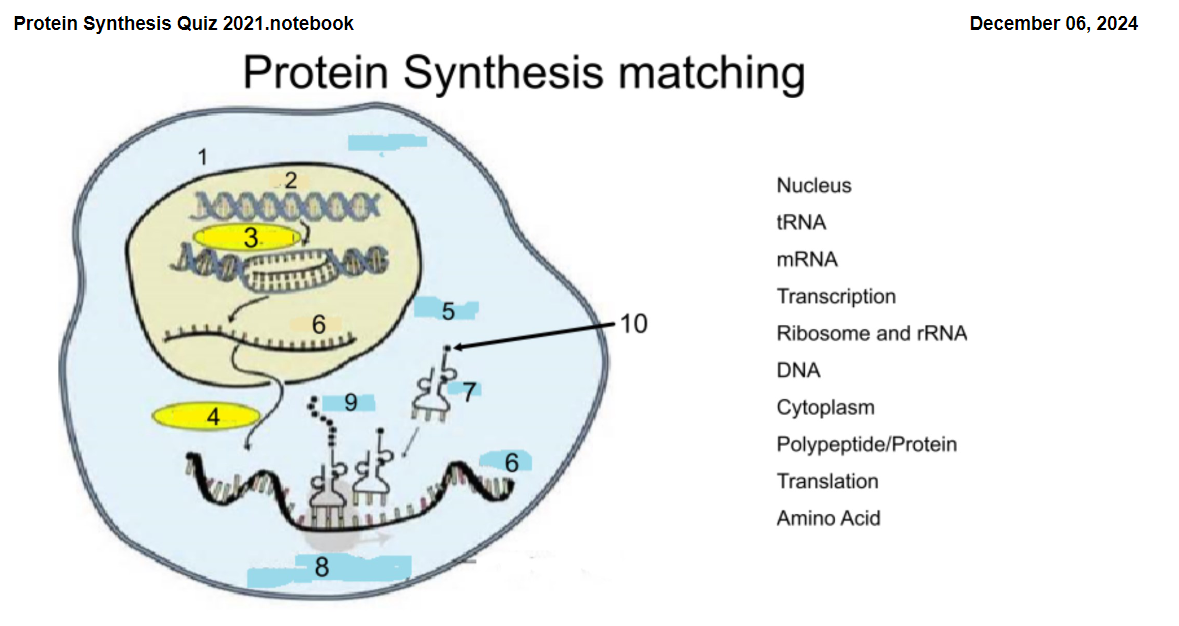
10
Amino Acid
Mutation
Change in genetic material
The development of traits is affected by 2 things
DNA, environment
Factors in the environment that cause mutations are called…
Mutagens
Examples of mutagens
drugs, radiation, carcinogens, toxins
#1 cause of mutation is…
DNA replication
Gene mutations involving a change in one or a few nucleotides are known as _ because they occur at a single point in the DNA sequence
point mutations
Point mutations include…
substitutions, insertions, and deletions
Frameshift mutation is caused by either _ or _ and it is shift in the codons causing a misreading of the genetic information (shift of the reading frame of the genetic message)
insertion, deletion
Transcription
The synthesis of RNA from a DNA template, where the code in the DNA is converted into a complementary RNA code.
Translation
The synthesis of a protein from an mRNA template, where the code in the mRNA is converted into an amino acid sequence in a protein