Kemiske reaktioner
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
AlBr3 (Lewis syre) - Lewis acid, promoter for electrophilic aromatic sub
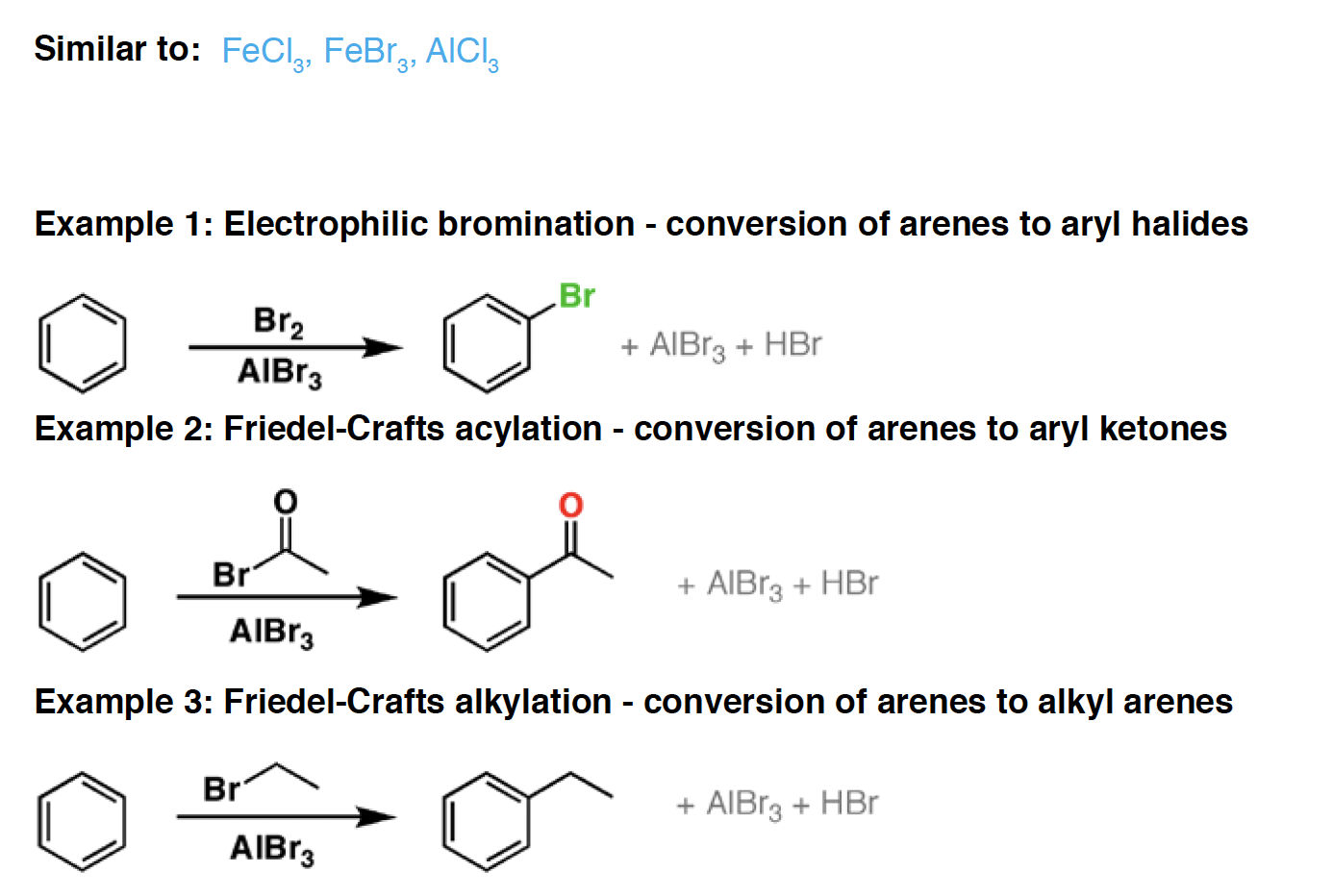
AlCl3 (Lewis syre) Aluminum chloride is a strong Lewis acid. It can be used to catalyze the chlorination of aromatic compounds, as well as Friedel-Crafts reactions
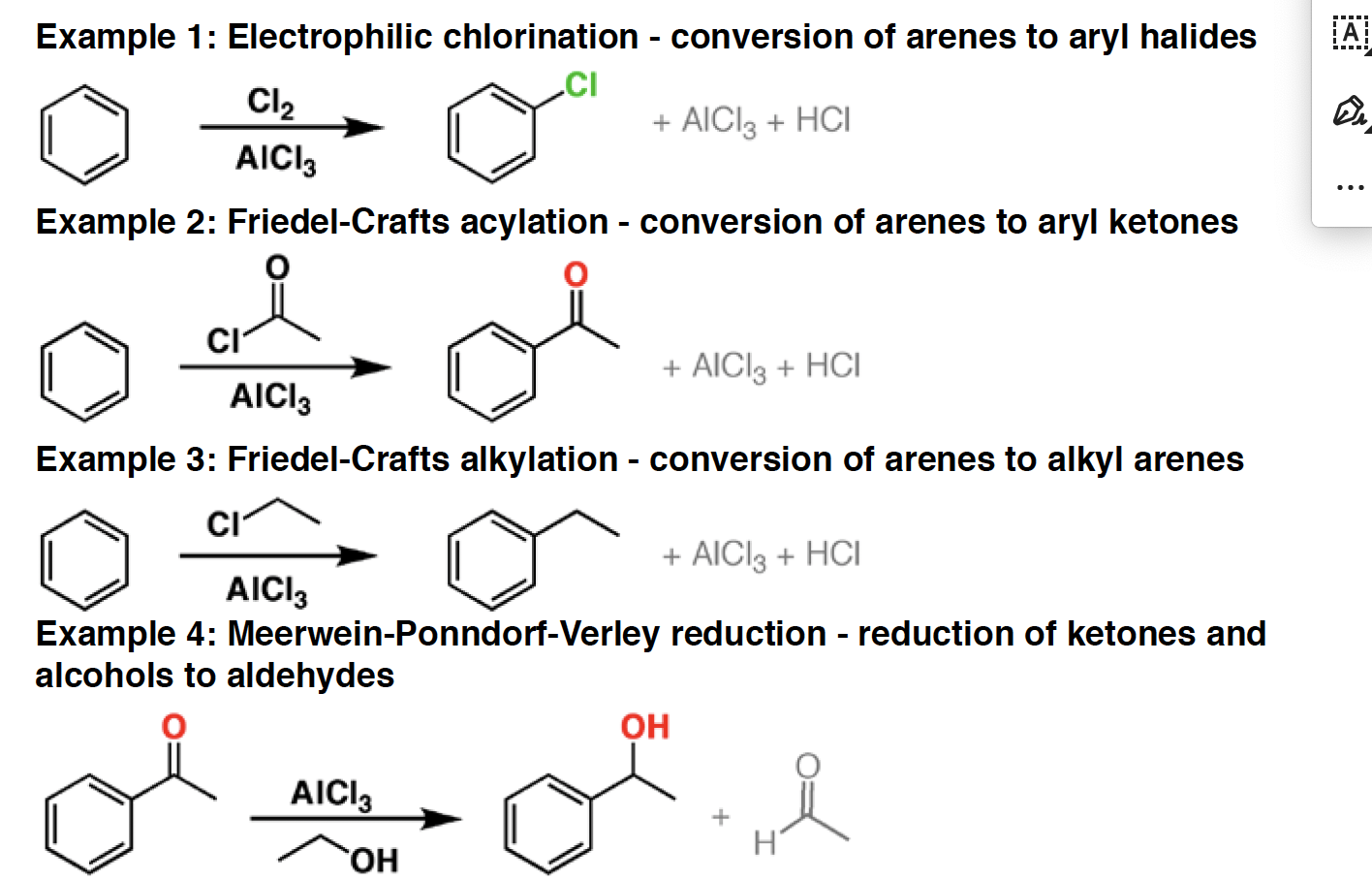
BH3 - Borane is used for the hydroboration of alkenes and alkynes
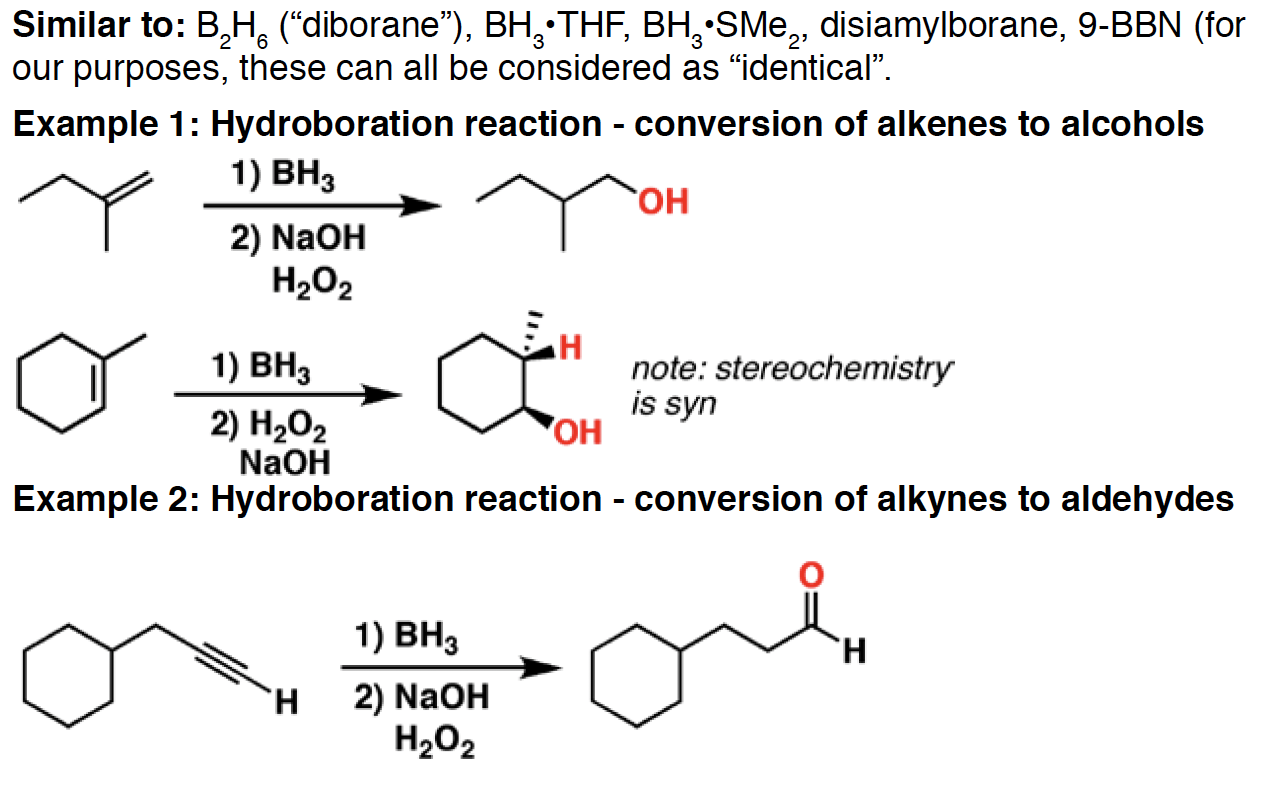
Br2 - Bromine will react with alkenes, alkynes, aromatics, enols, and enolates, producing brominated compounds. In the presence of light, bromine will also replace hydrogen atoms in alkanes. Finally, bromine is also used to promote the Hoffmann rearrangement of amides to amines
DIBAL - Strong, bulky reducing agent. It is most useful for the reduction of esters to aldehydes: unlike LiAlH4 , it will not reduce the aldehyde further unless an extra equivalent is added. It will also reduce other carbonyl compounds such as amides, aldehydes, ketones, and nitriles.
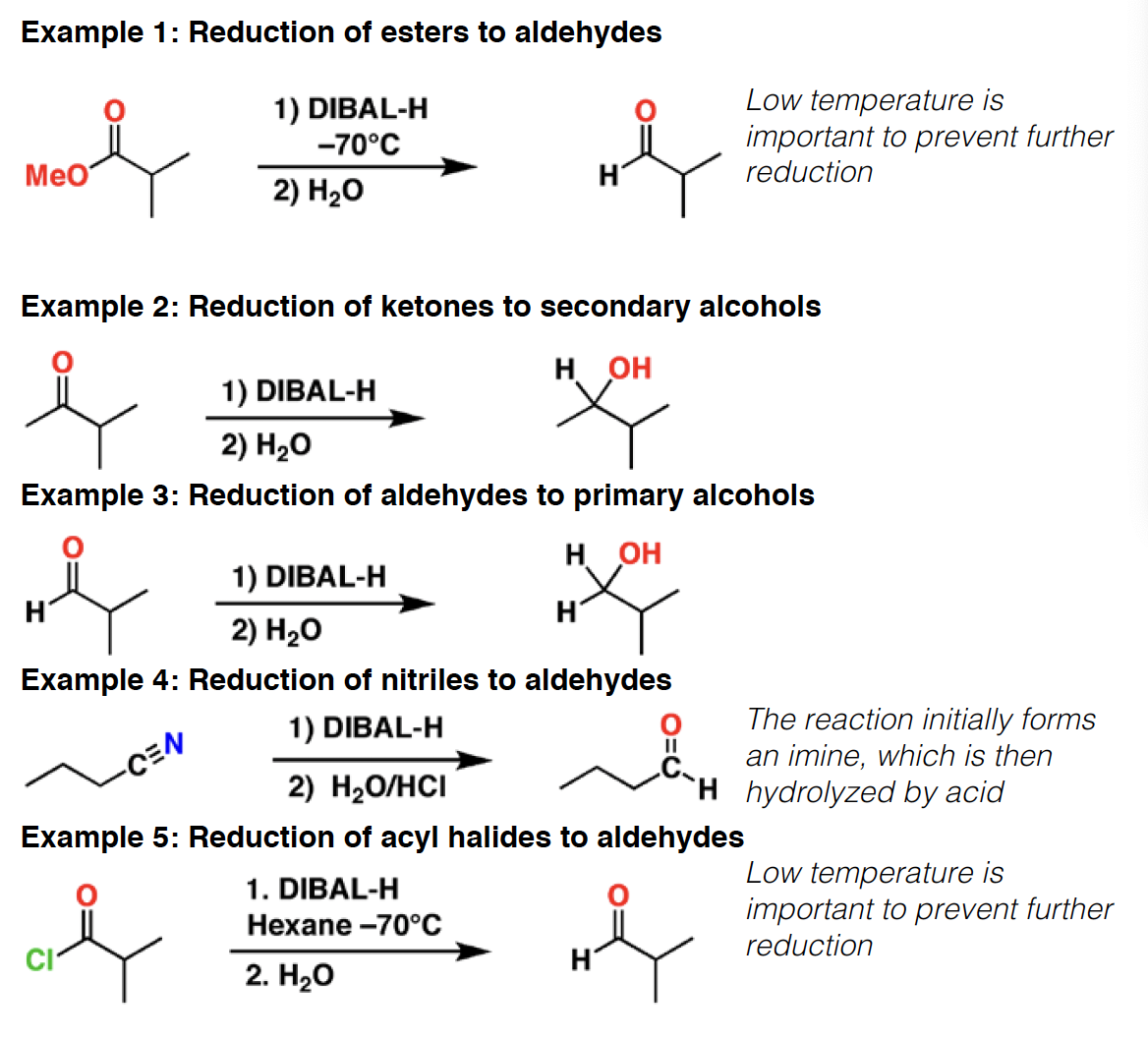
DMP - Dess-Martin periodinane is an oxidizing agent. It will oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes without going to the carboxylic acid (similar to PCC). It will also oxidize secondary alcohols to ketones.
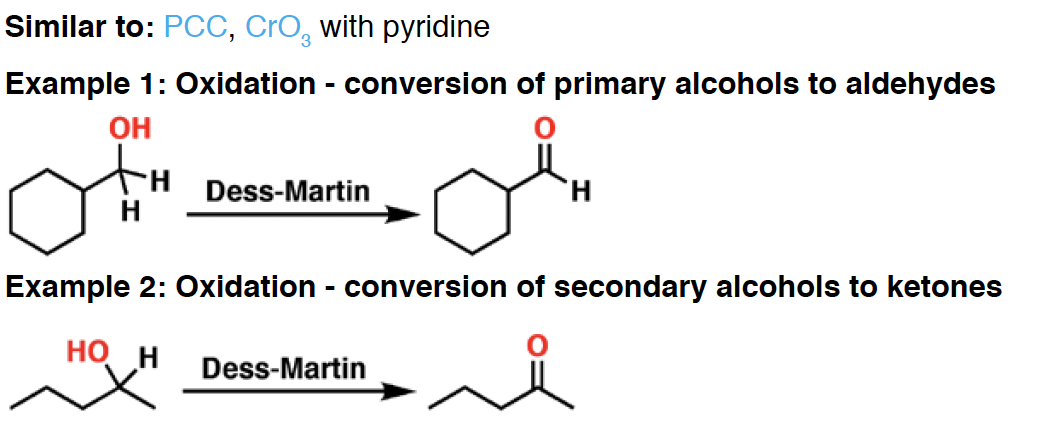
DMS - Used in the “reductive workup” of ozonolysis, to reduce the ozonide that is formed. DMS is oxidized to dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) in the process.
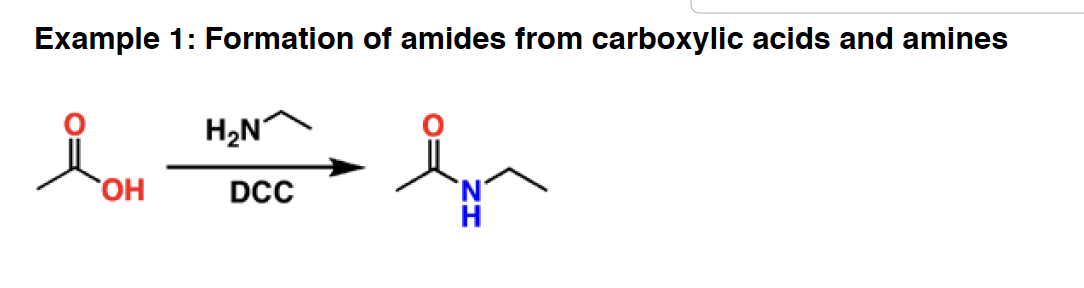
DCC - DCC is primarily used for the synthesis of amides from amines and carboxylic acids. It is, essentially, a dehydration reagent (removes water
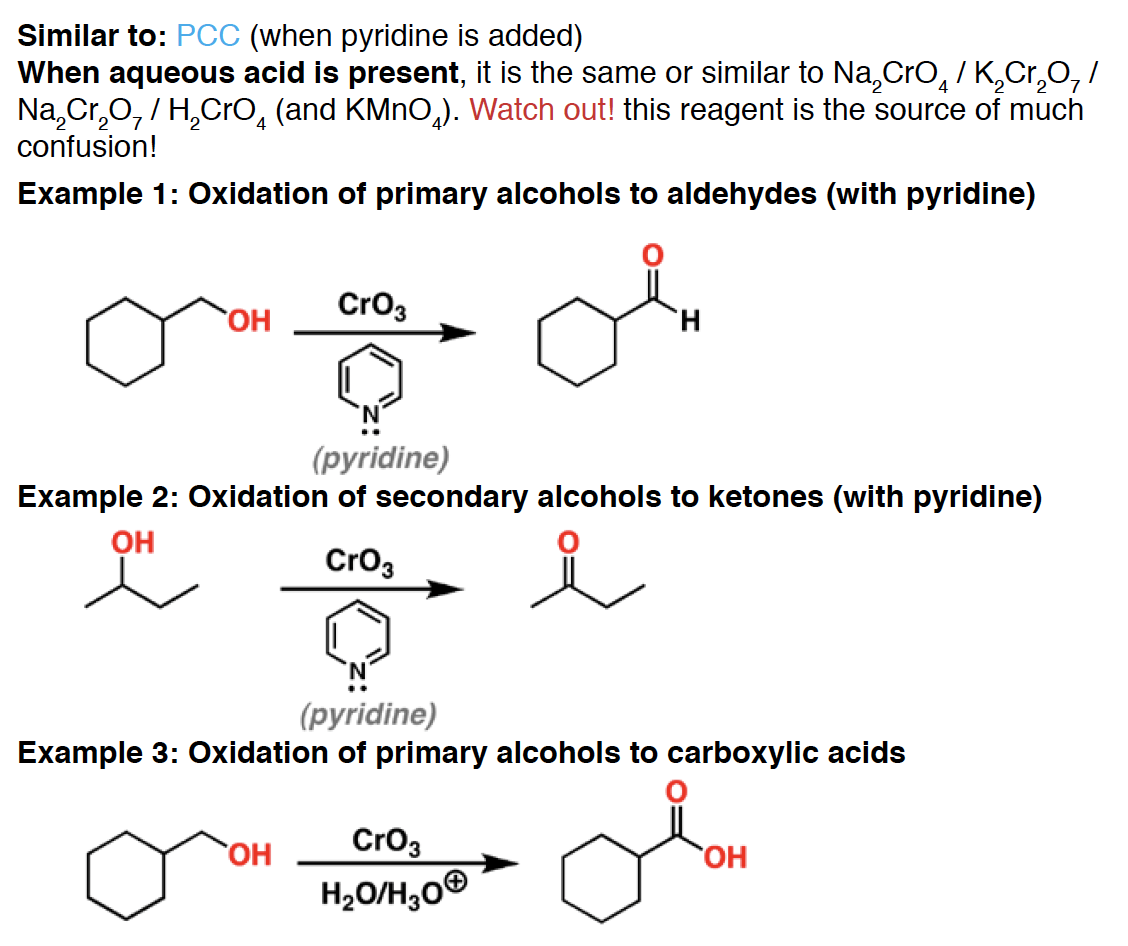
CrO3 - is an oxidant. When pyridine is present, it is a mild oxidant that will oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes. However, if water and acid are present, the aldehyde will be oxidized further the the carboxylic acid.
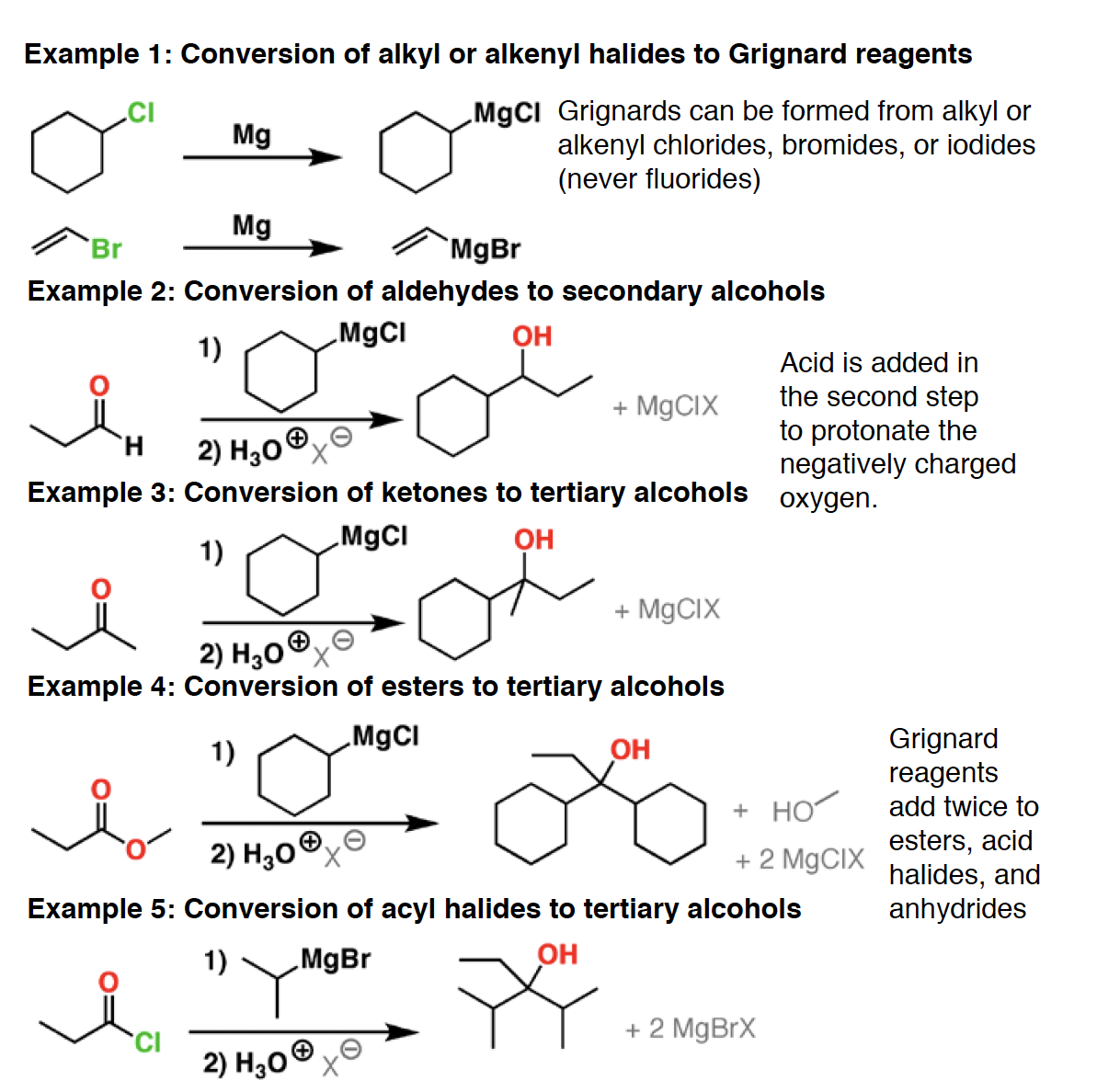
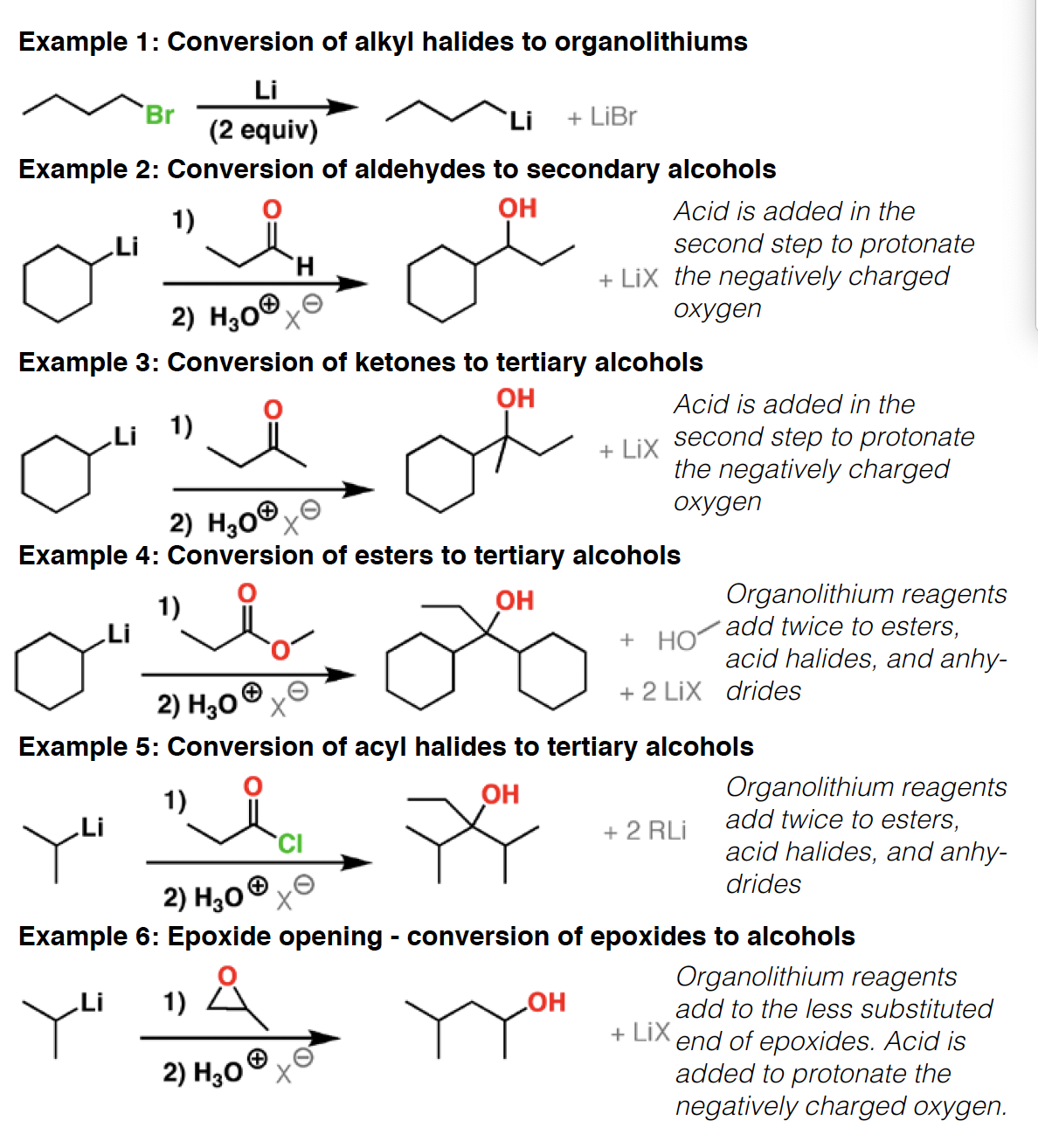
Grignard R-Mg-X, hvor X er et halid. - Extremely good nucleophile, reacts with electrophiles such ascarbonyl compounds (aldehydes, ketones, esters, carbon dioxide, etc.) and epoxides.
In addition Grignard reagents are very strong bases and will react with acidic hydrogens.
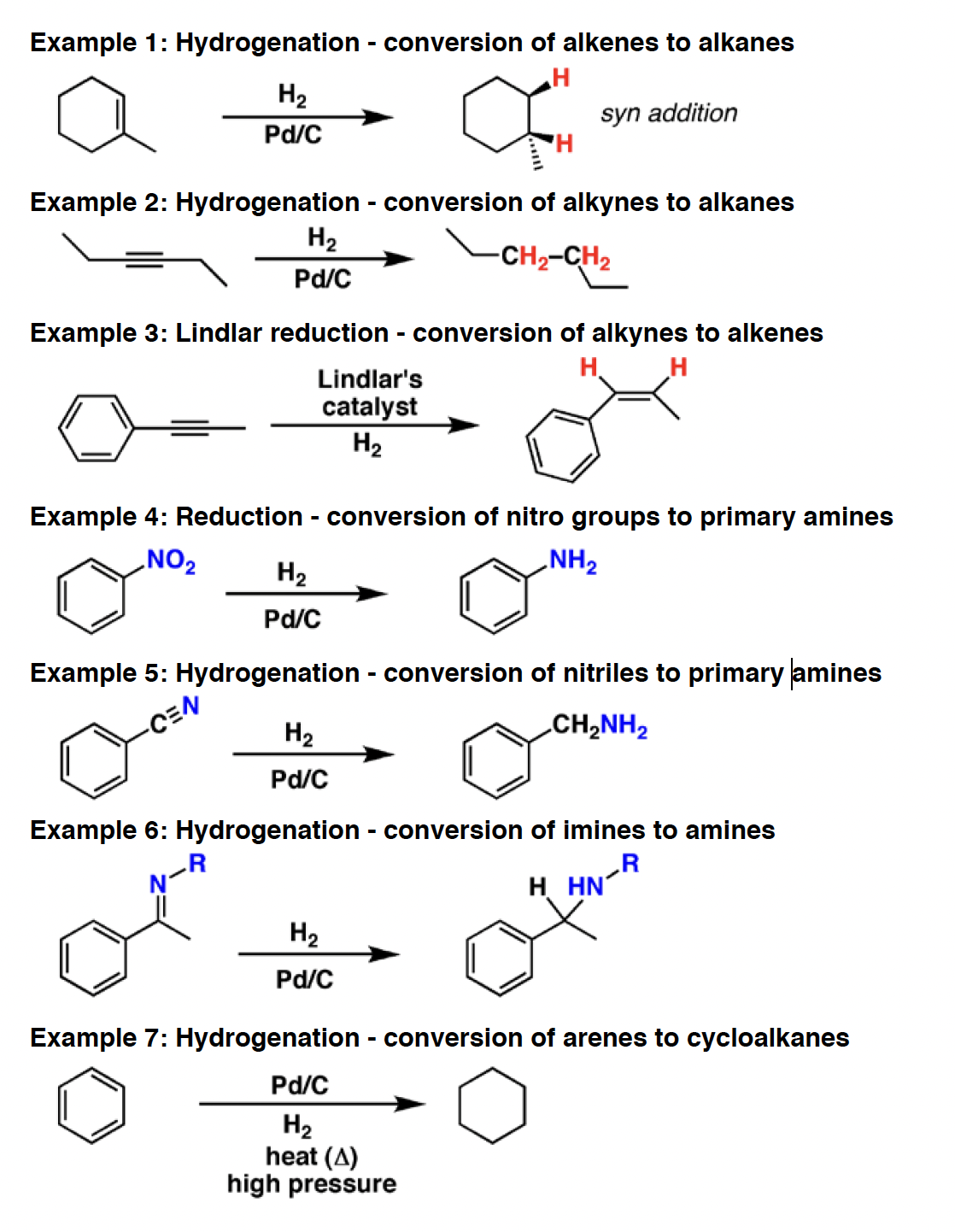
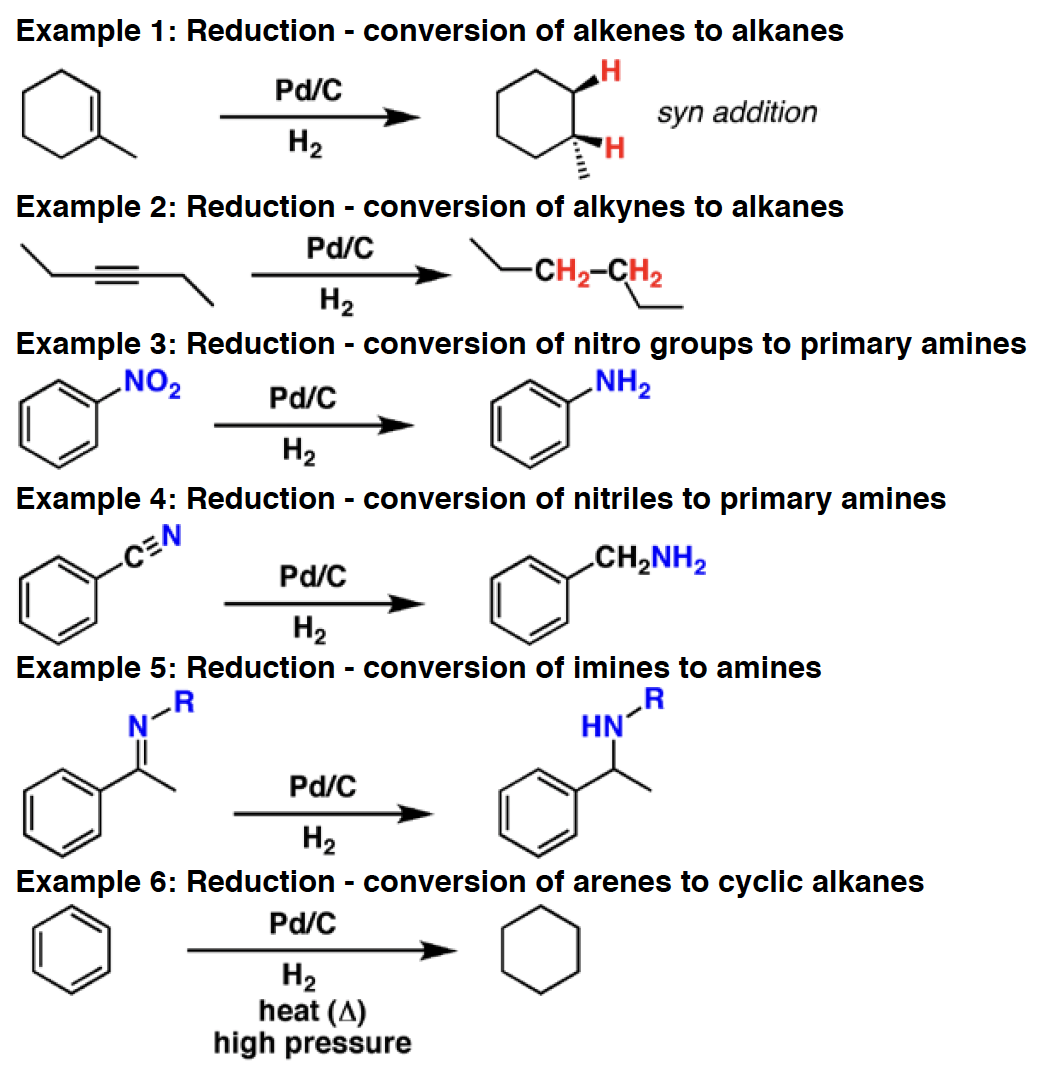
H2 - Hydrogen gas is used for the reduction of alkenes, alkynes, and many other species with multiple bonds, in concert with catalysts such as Pd/C and Pt.
H+
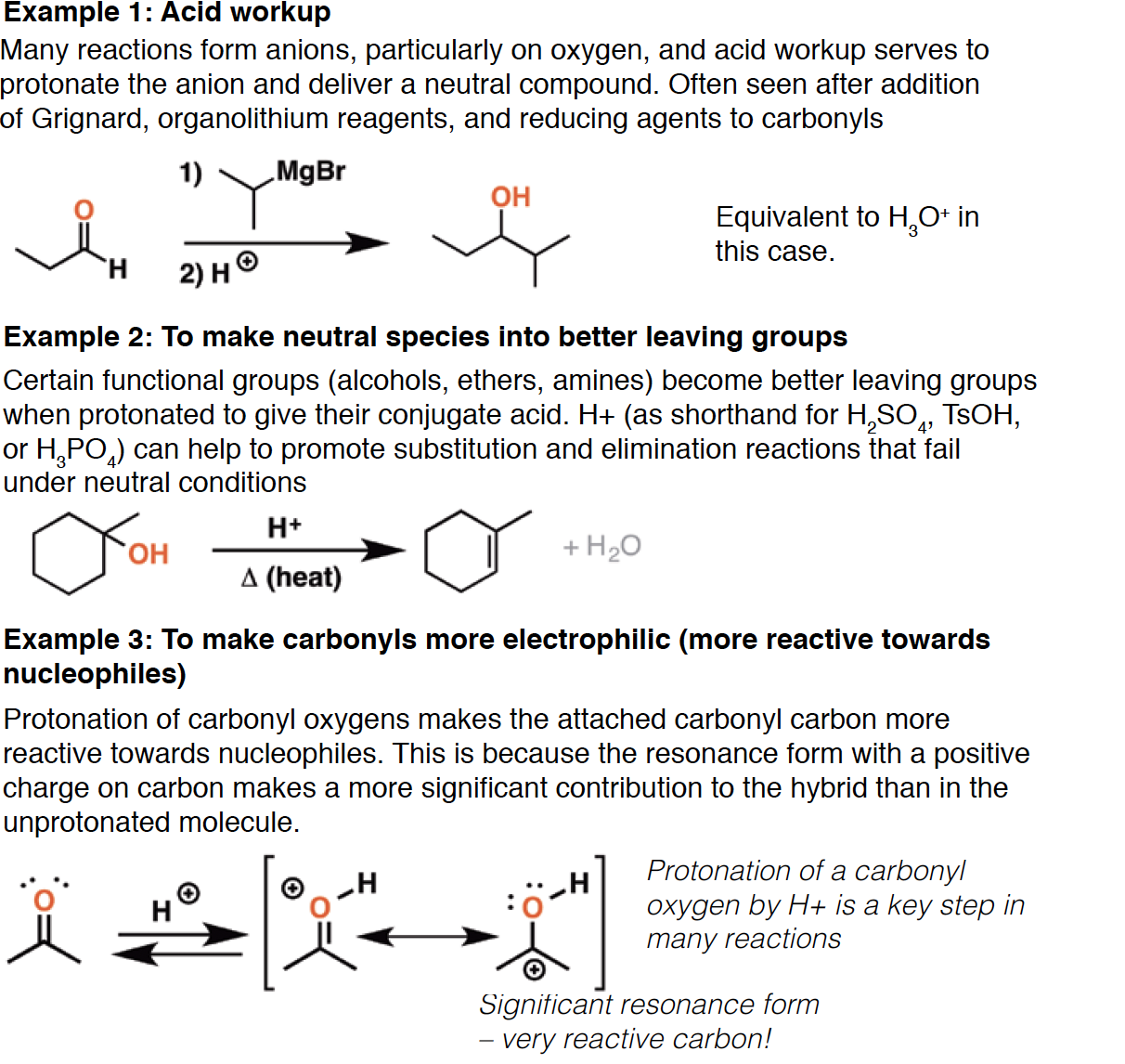
H3O+ - Equivalent to: H2O/H2SO4, H2O/H3PO4
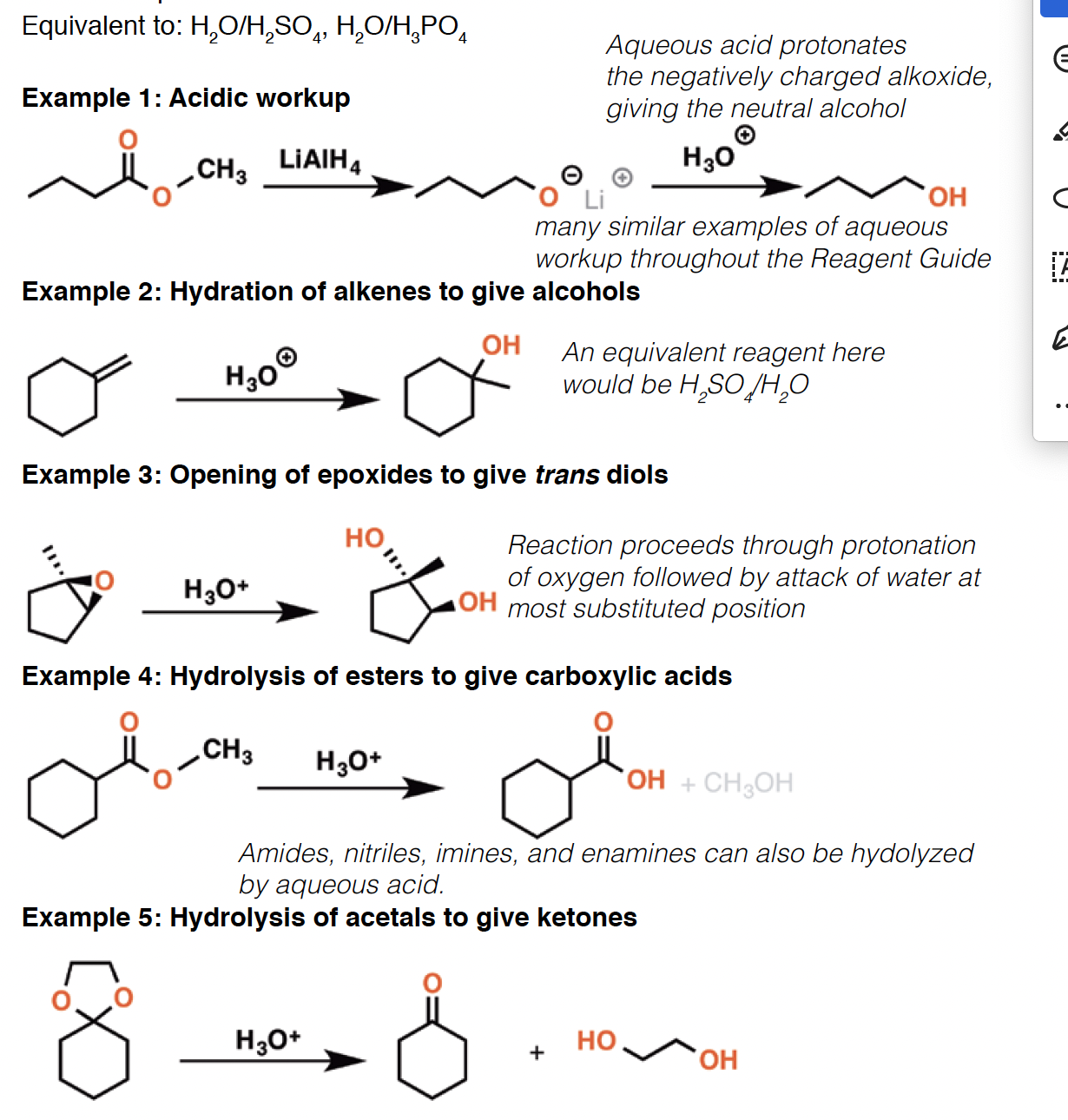
HBr - Hydrobromic acid is a strong acid. It can add to compounds with multiple bonds such as alkenes and alkynes. It can also react with primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols to form alkyl bromides.
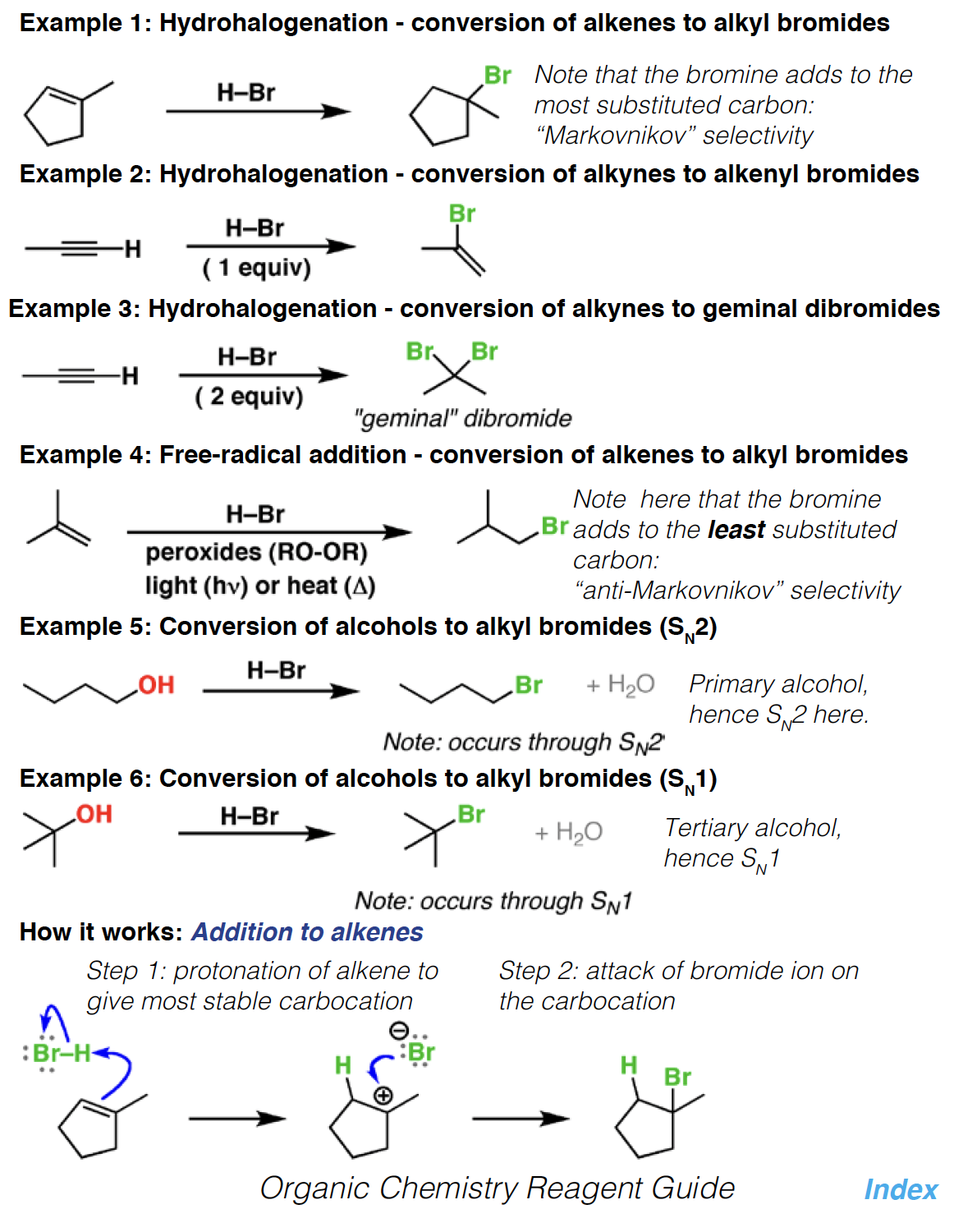
Hg(OAc)2 - Mercuric acetate is a useful reagent for the oxymercuration of alkenes and alkynes. It makes double bonds more reactive towards nucleophilic attack by nucleophiles such as water and alcohols.
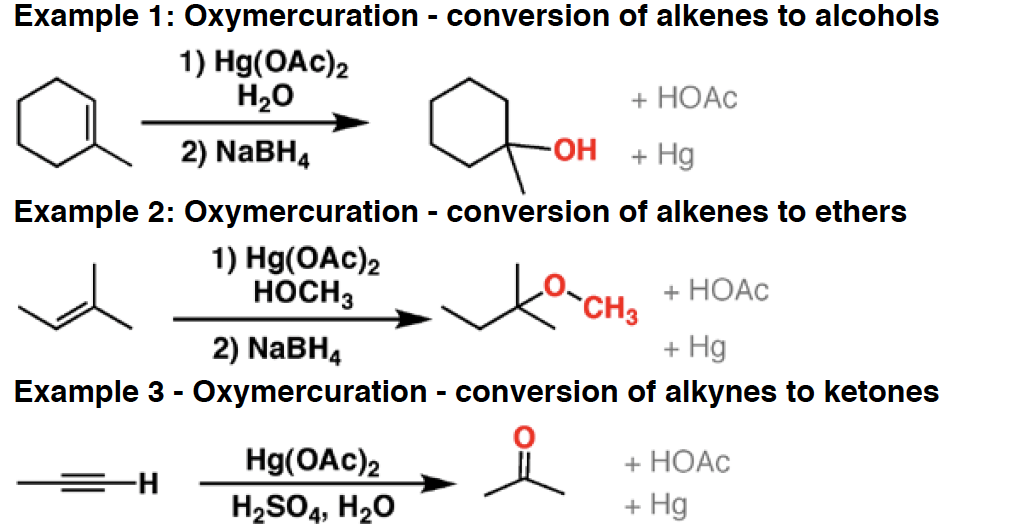
HNO3 - A strong acid, HNO3 is used as a reagent in the addition of NO2 to aromatic compounds (“nitration”). It will also oxidize primary alcohols and aldehydes to carboxylic acids.
H2O2 - Hydrogen peroxide is used as an oxidant in the hydroboration of alkenes and alkynes, converting the C–B bond into a C–O bond. It is also used in the oxidative workup of ozonolysis, converting aldehydes into carboxylic acids
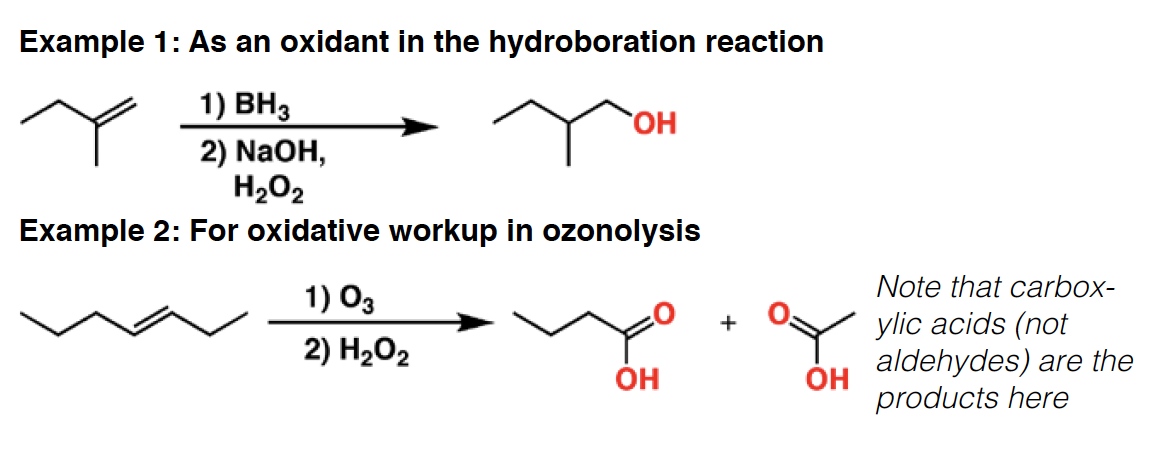
H2SO4 - Sulfuric acid is a strong acid (pKa –3.0). It is particularly useful for elimination reactions since its conjugatebase [HSO4–] is a very poor nucleophile. It finds use in many other reactions as a general strong acid.
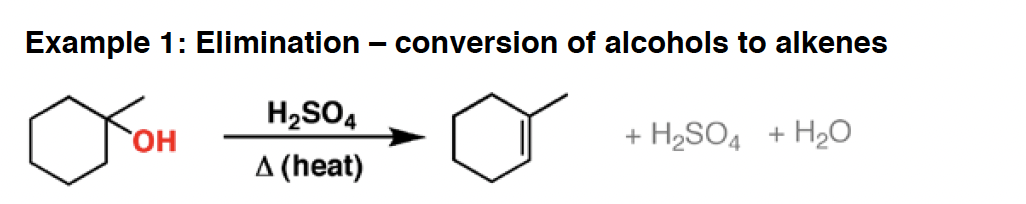
KMnO4 - This strong oxidizing agent will oxidize primary alcohols (and aldehydes) to carboxylic acids, secondary alcohols to ketones, form diols from alkenes, and oxidatively cleave carbon-carbon bonds. It will also oxidize C-H bonds adjacent to aromatic rings.
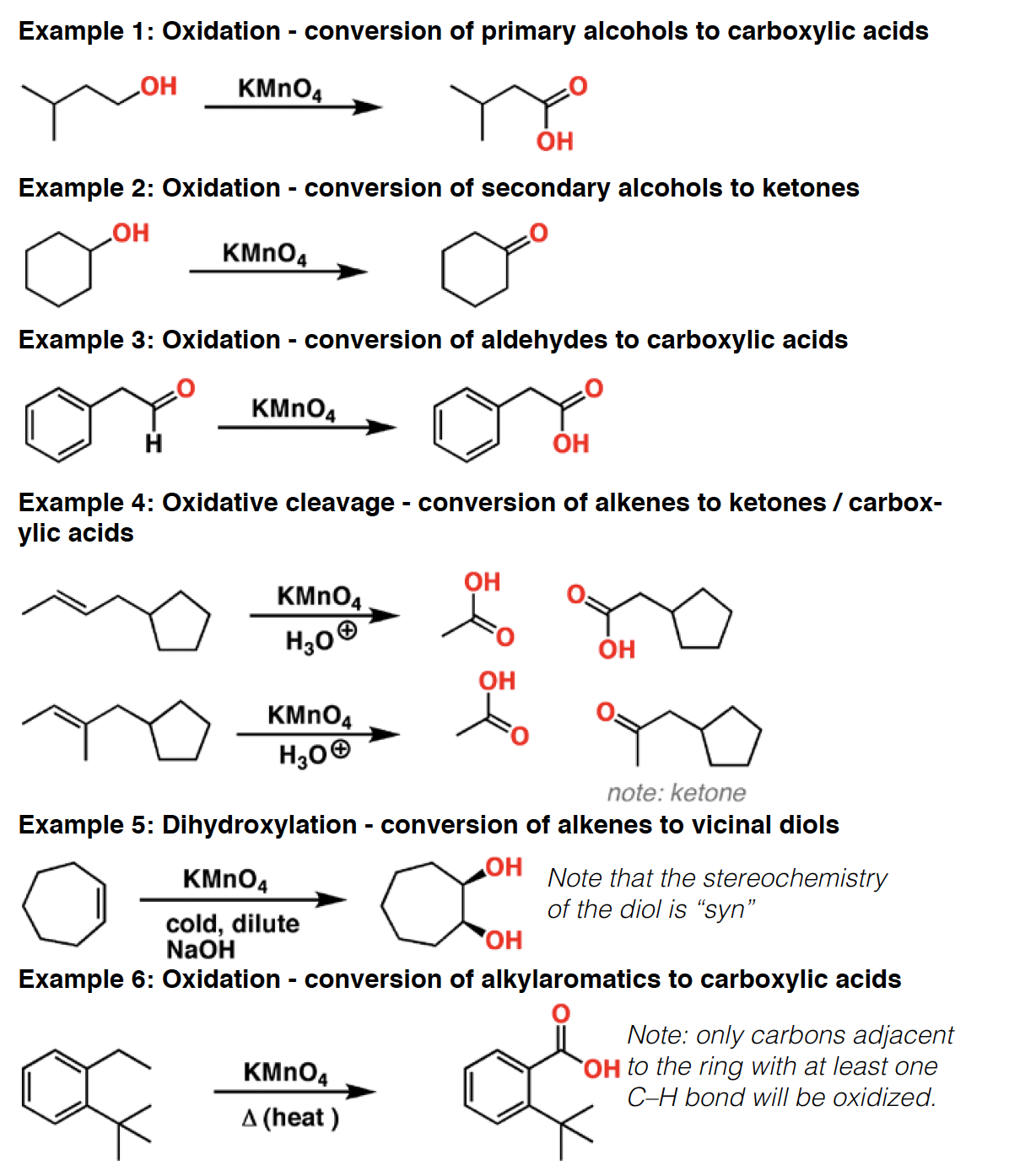
KOt-Bu - Potassium t-butoxide is a strong, sterically hindered base.The prototypical “bulky base”, it is useful in elimination reactions for forming the less substituted “non-Zaitsev” [sometimes called “Hofmann”] alkene product
LDA - LDA is a strong, bulky, non-nucleophilic base. It is the reagent
of choice for selectively removing a proton from the least hindered carbon next to a
ketone. It can also be used to form the “Hofmann” product in elimination reactions.
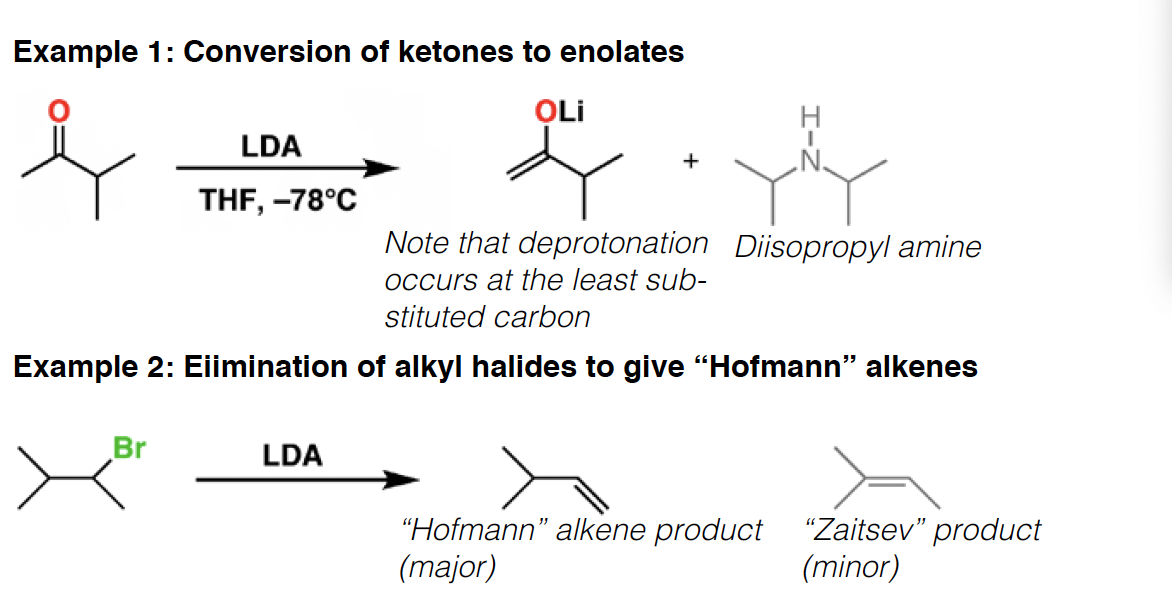
Lindlar’s catalyst - Lindlar’s catalyst is a poisoned palladium metal catalyst that performs partial hydrogenations of alkynes in the presence of hydrogen gas (H2). It always gives the cis alkene, in contrast to Na/NH3 which gives trans.
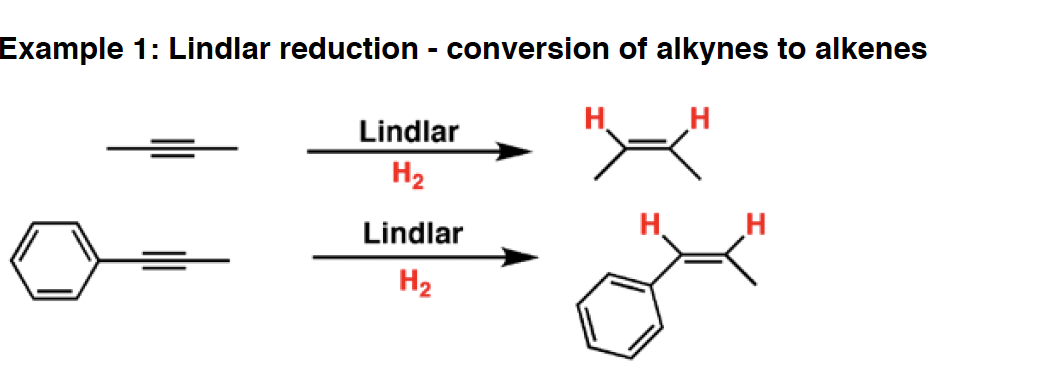
LiAlH4 - Lithium aluminum hydride is a very strong reducing agent. It will reduce aldehydes, ketones, esters and carboxylic acids to alcohols, amides and nitriles to amines, and open epoxides to give alcohols
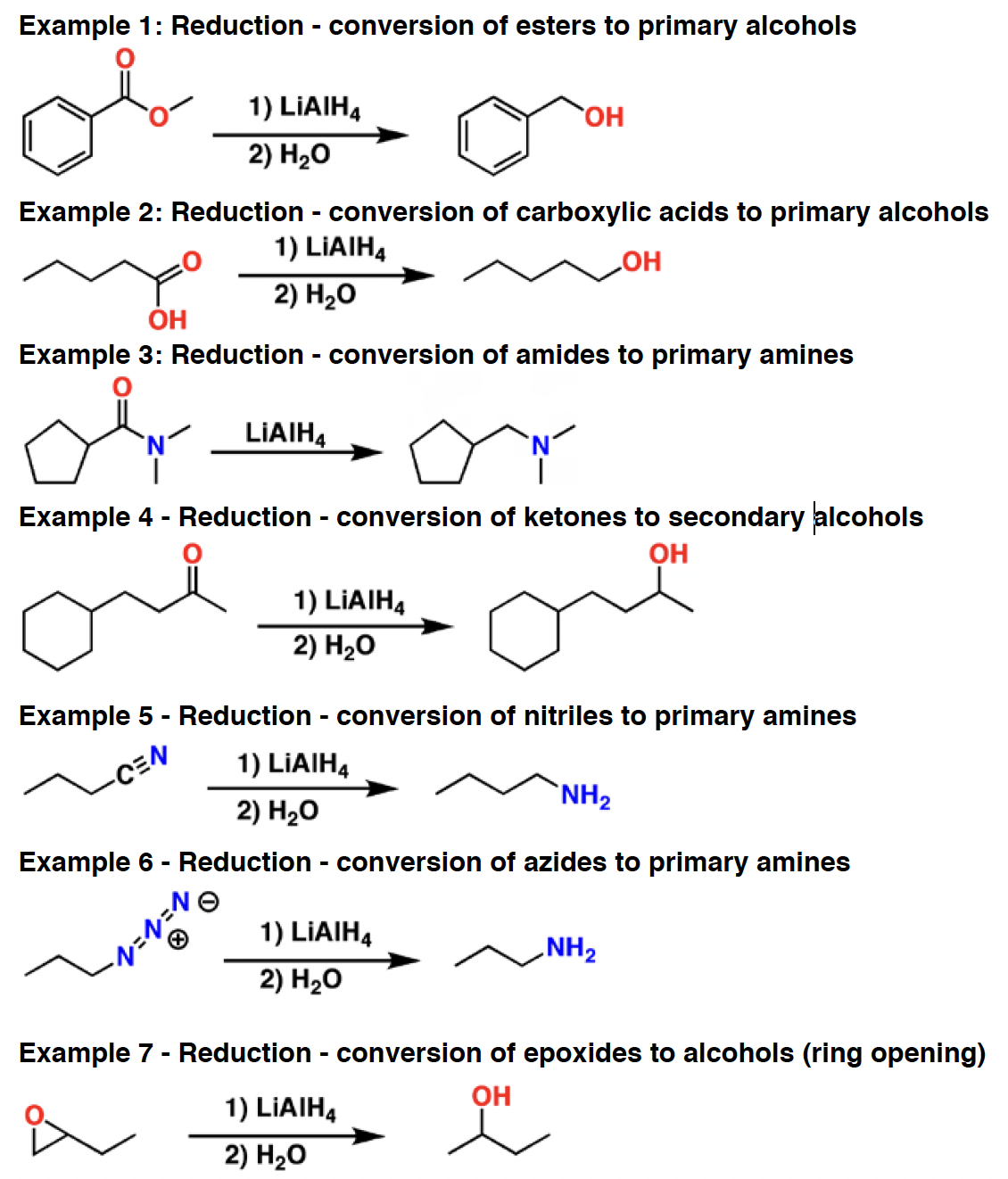
m-CPBA - is an oxidizing agent. It sees use in two main ways. First, it is used to transform alkenes into epoxides. Secondly, it will react with ketones to form esters in the Baeyer-Villiger reaction.
NaN3 - Sodium azide is a good nucleophile that readily participates in SN2 reactions. Alternatively the sodium or lithium salt of azide ion can be used, but sodium is the most common
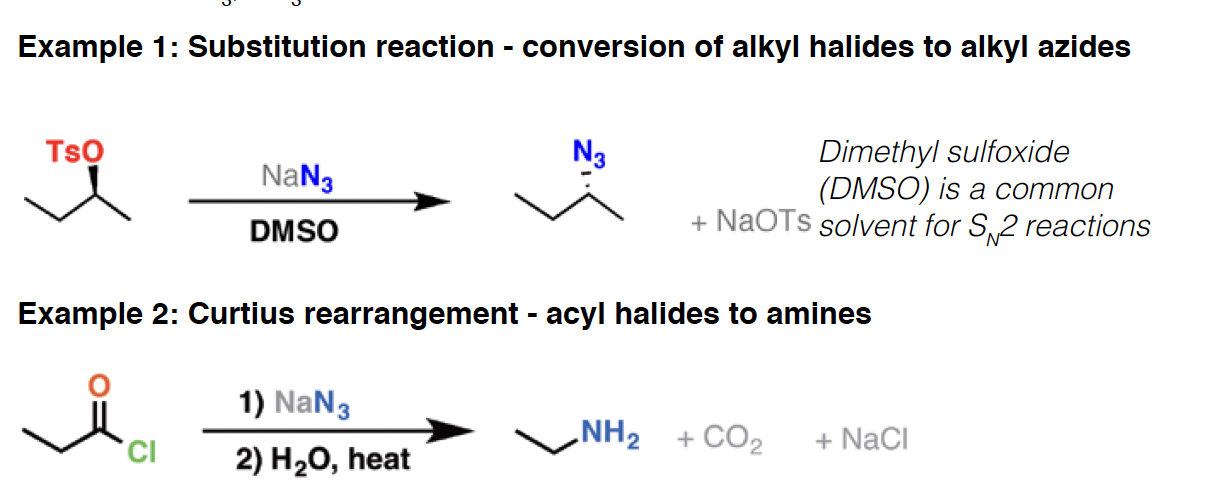
NaBH4 - Sodium borohydride is a reagent mainly used for the reduction of ketones and aldehydes (it will also reduce acid halides). It is also used in the oxymercuration of alkenes, to replace mercury with H.
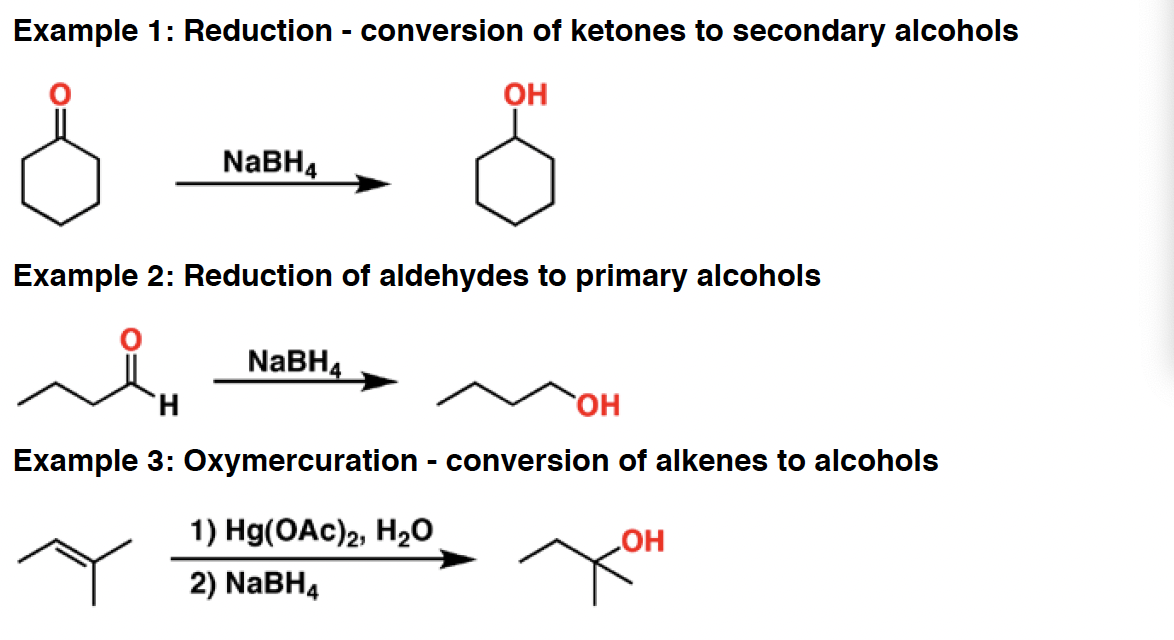
NaH - Sodium hydride is a strong base and a poor nucleophile. It isuseful for deprotonating alcohols and alkynes, among others. One advantage of using NaH is that the byproduct is H2, a gas which does not further interfere with the reaction.
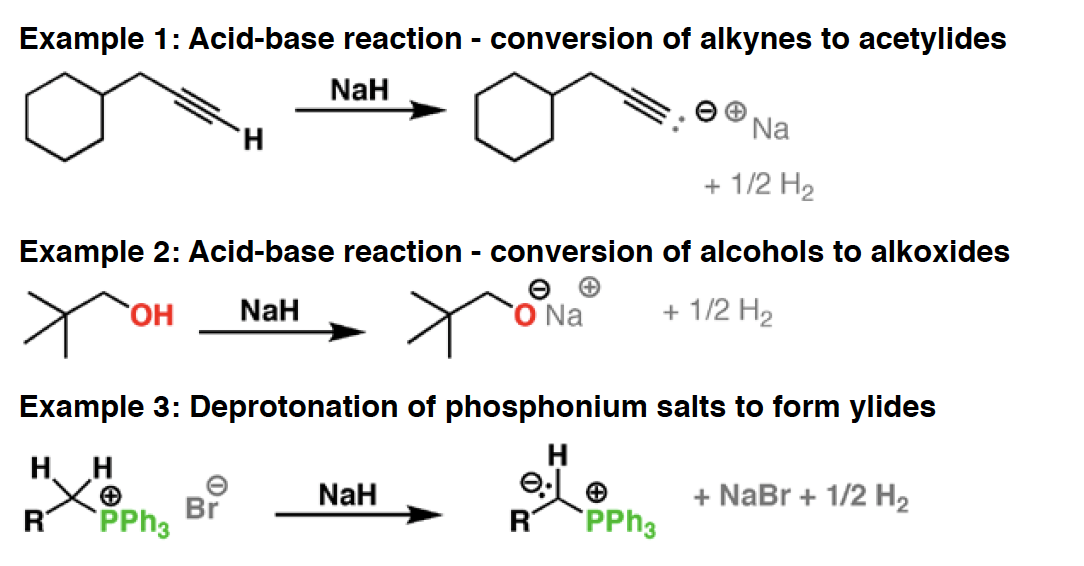
NaOH - Hydroxide ion (often encountered as NaOH or KOH) is a strong base and good nucleophile. It is impossible to mention all of its applications here but a few of its crucial reactions are highlighted.
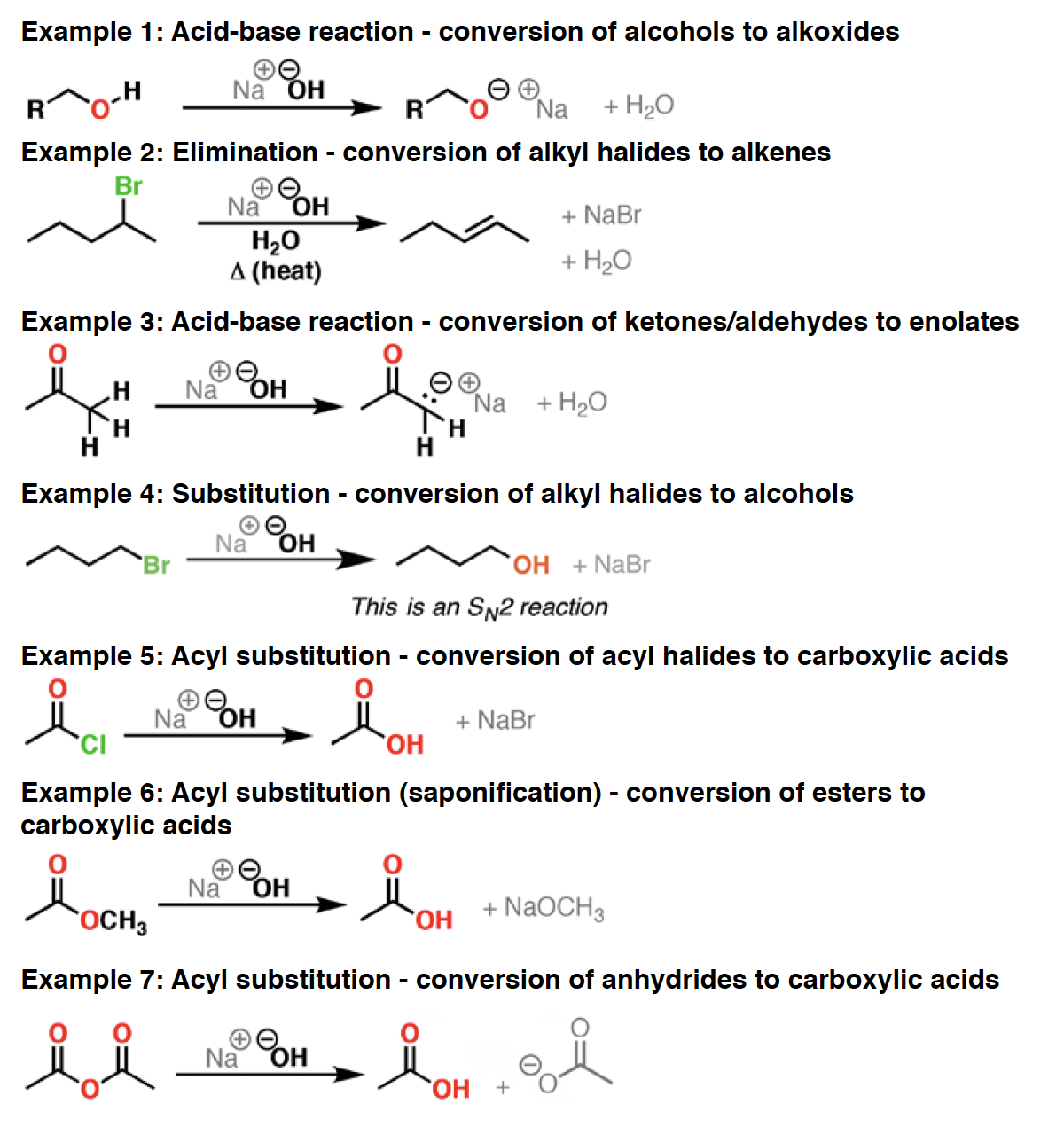
NaOEt - Strong base and good nucleophile. Most often seen as a base for promoting elimination reactions (E2). Can also be used as a nucleophile in SN2 reactions, particularly if the alkyl halide is primary. The conjugate base of ethanol. Not really a “reagent”, per se, but gets so much use that it deserves its own entry
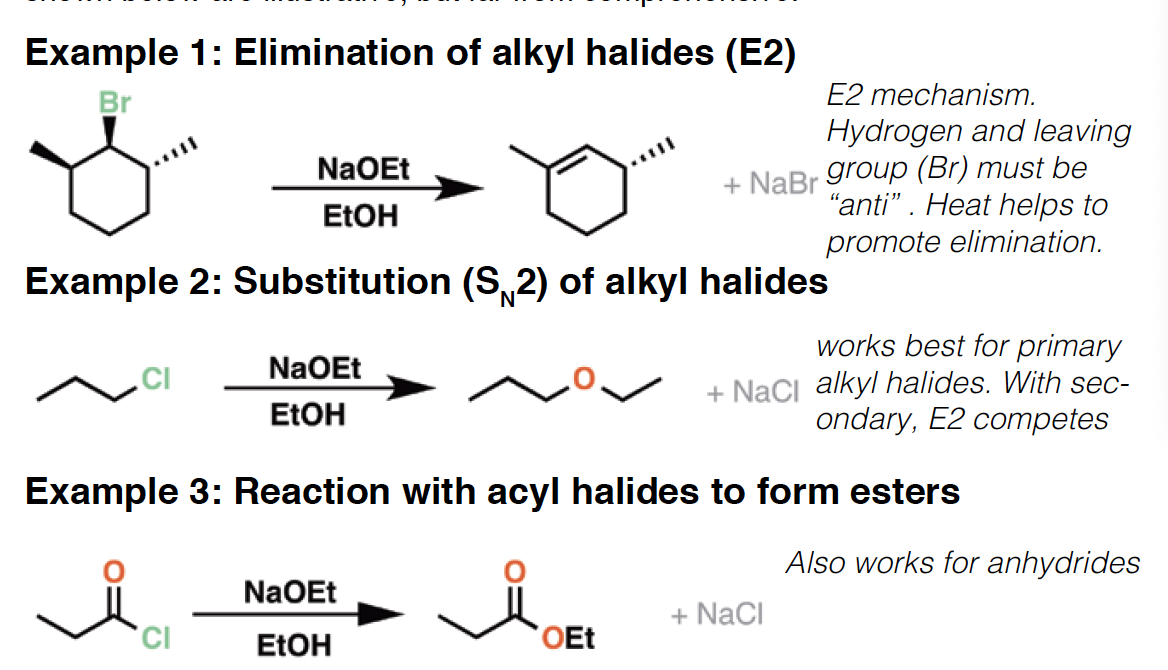
NBS - NBS is a source of reactive, electrophilic bromine. It is often used for allylic bromination and in formation of halohydrins from alkenes. Since it is a crystalline solid it is more convenient to use than liquid elemental Br2
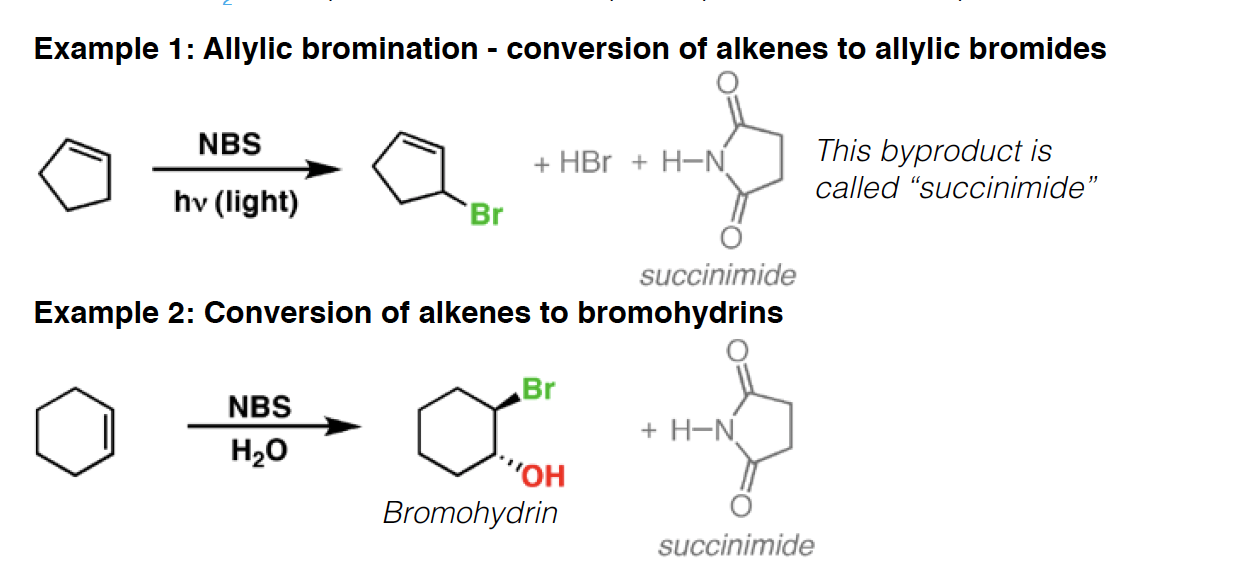
NH3 - Ammonia is a base and a nucleophile. It is often used as a solvent in reactions involving lithium (Li), sodium (Na), and potassium (K).
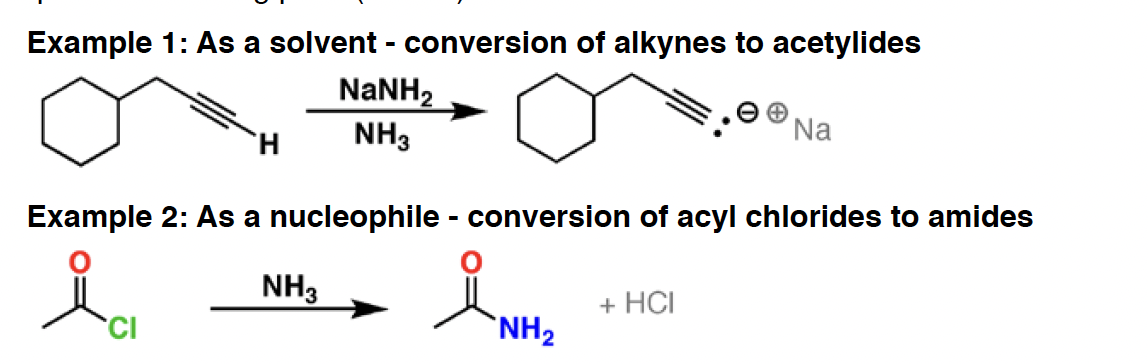
NH2NH2 - Hydrazine is a good reductant and nucleophile. It is used in the Wolff-Kishner reaction, a means of converting ketones to alkanes. It is also used in the final step of the Gabriel amine synthesis to liberate the free amine.
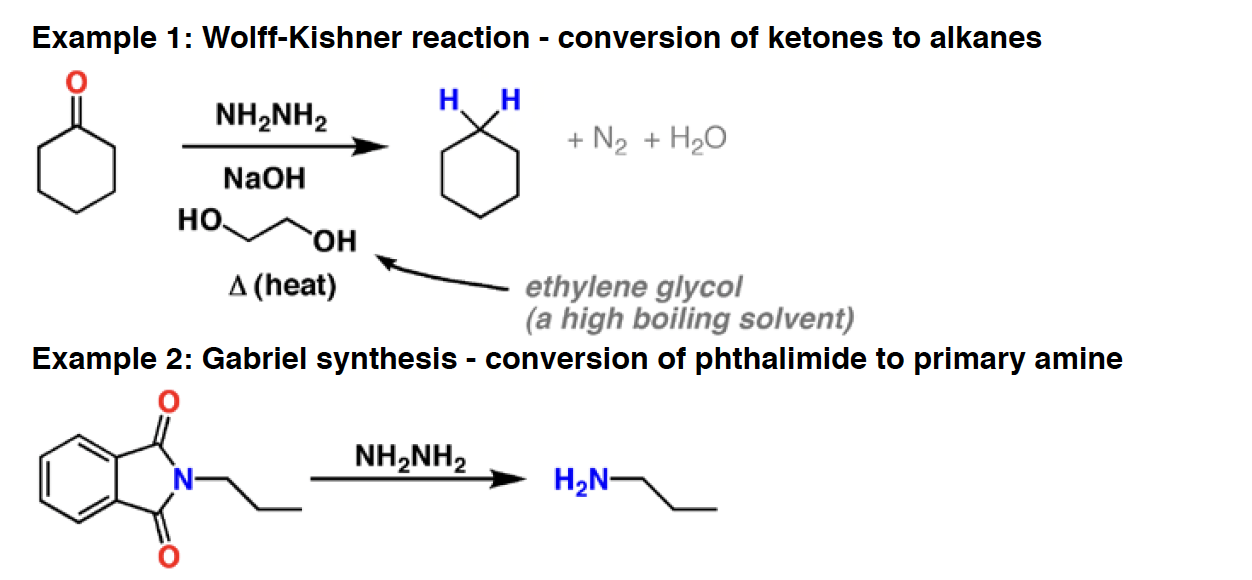
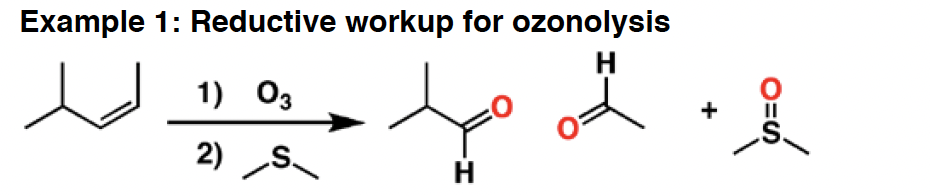
O3 - Ozone is an oxidizing agent. It will cleave alkenes and alkynes to give carbonyl compounds, in a reaction called “oxidative cleavage”. The products formed can be dependent on the type of workup used. Reductive workup preserves aldehydes, whereas oxidative workup will oxidize any aldehydes to carboxylic acids.
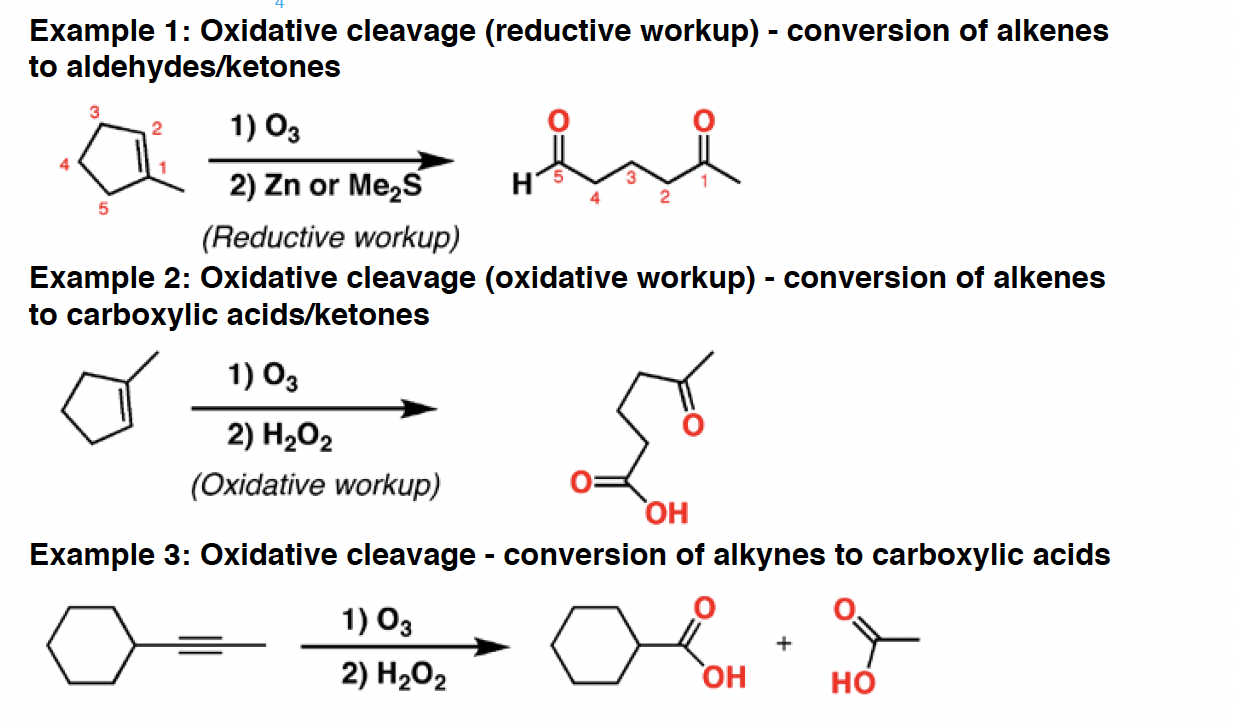
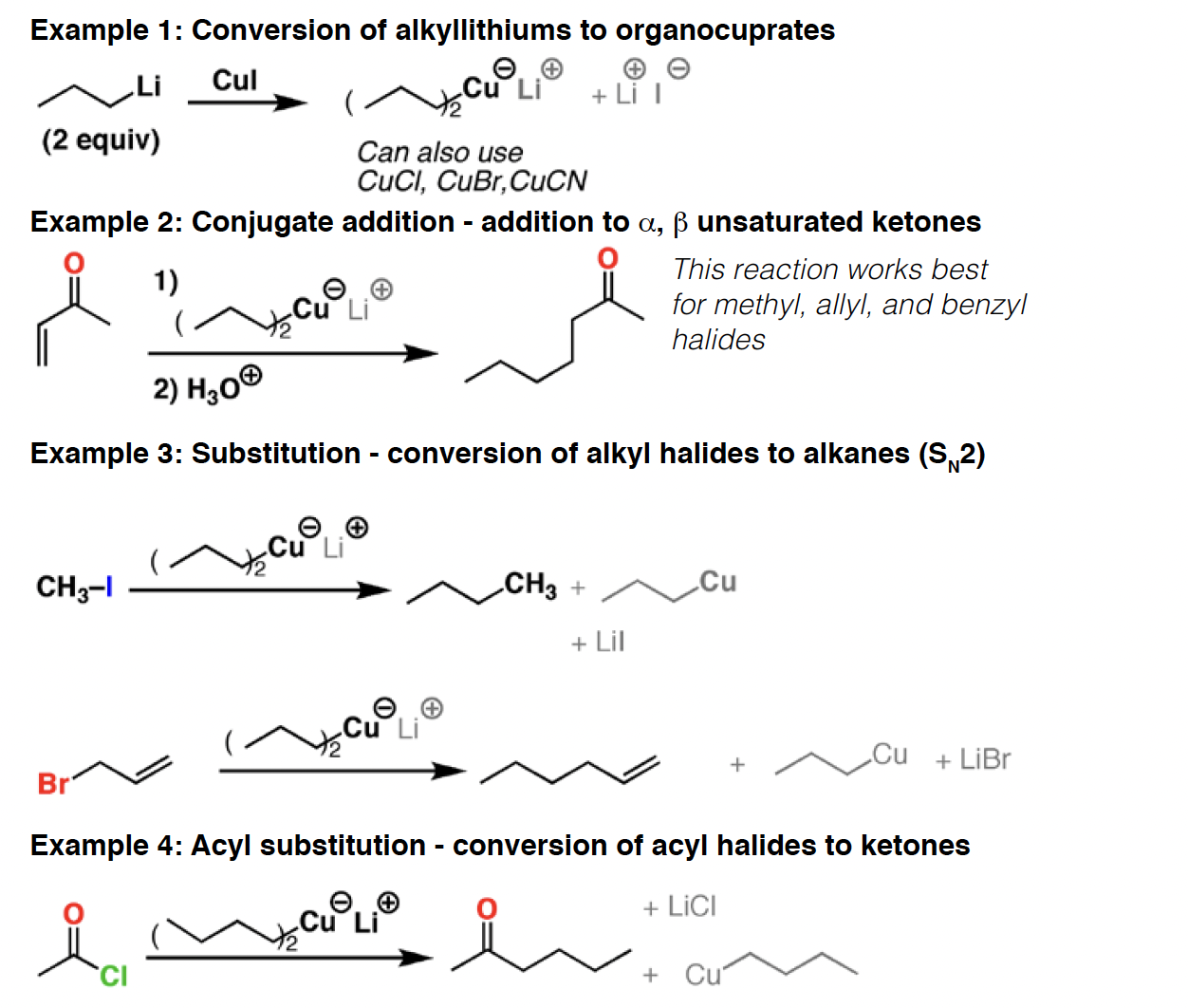
R2CuLi - Gilman are carbon nucleophiles.They will perform [1,4] additions (“conjugate additions”) to a,b unsaturatedketones, as well as SN2 reactions with certain types of alkyl halides. They can also add to acyl halides to give ketones.
RLi - Organolithium reagents are extremely strong bases and good nucleophiles. they react with carbonyl compounds (aldehydes, ketones, esters, etc.) and epoxides. Being strong bases, they will also react with groups containing acidic hydrogens.
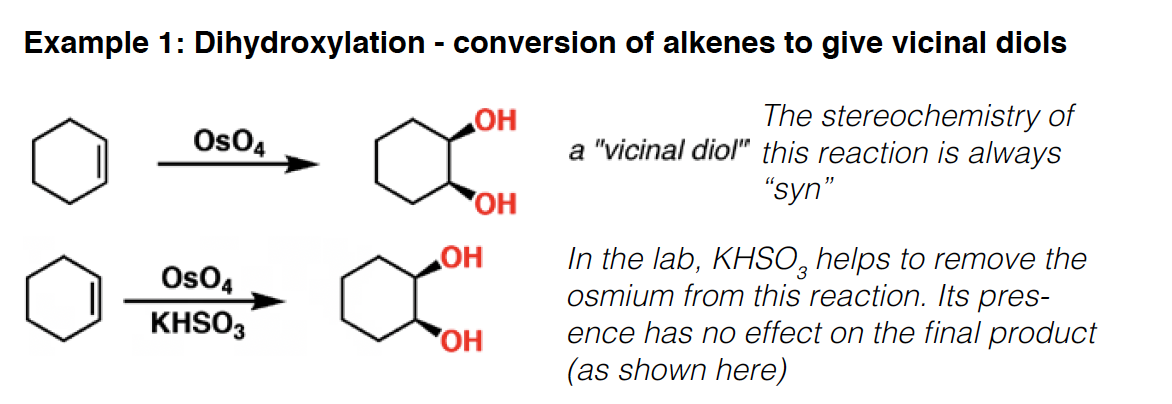
OsO4 - Osmium tetroxide is a reagent for the formation of 1,2-diols (vicinal diols) from alkenes. The selectivity for this reaction is always syn
PBr3 - Phosphorus tribromide is a reagent for converting alcohols to alkyl bromides. It will also convert carboxylic acids to acid bromides (acyl
bromides
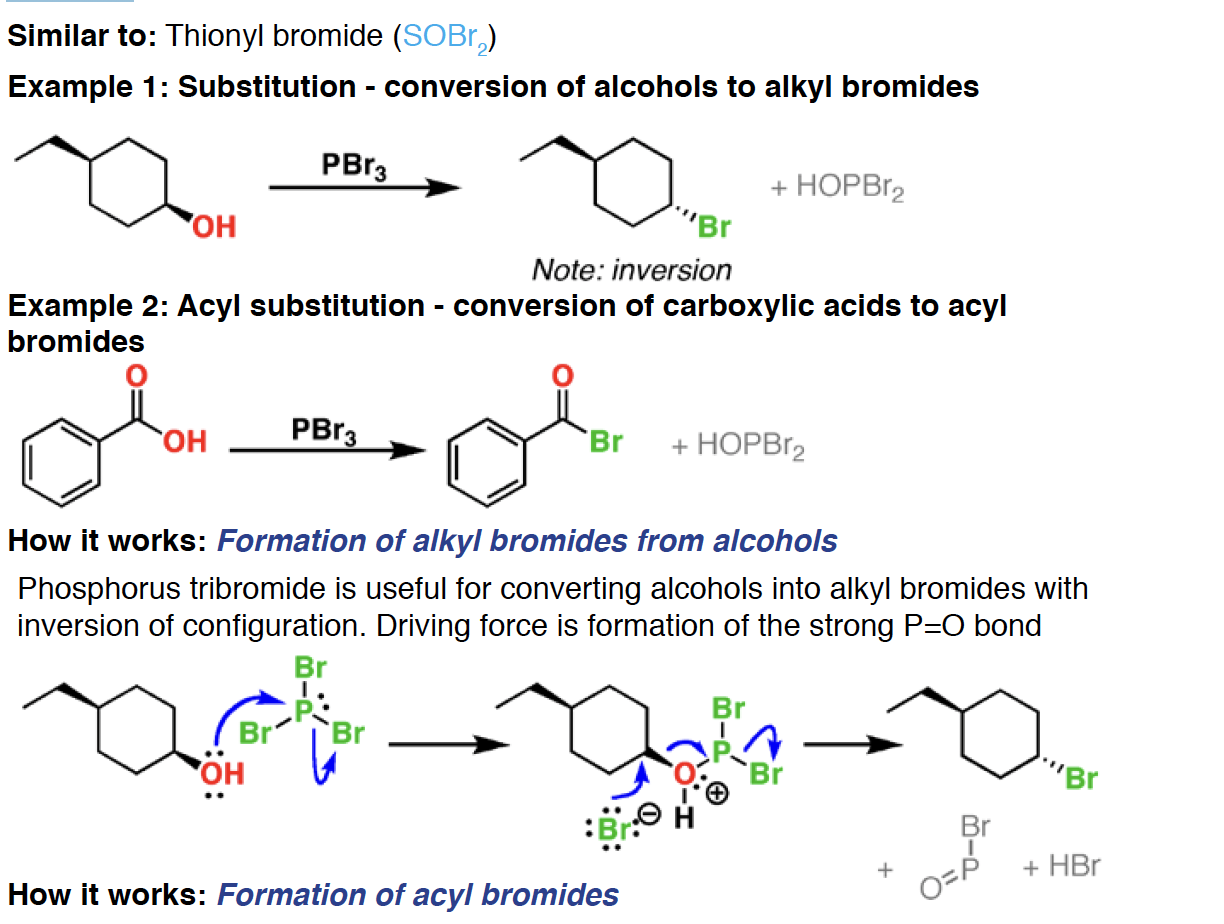
Pd/C - Palladium adsorbed on charcoal (carbon) [Pd/C] is a heterogeneous catalyst. In the presence of hydrogen gas (H2) it will convert alkenes and alkynes to alkanes, with syn addition of hydrogen
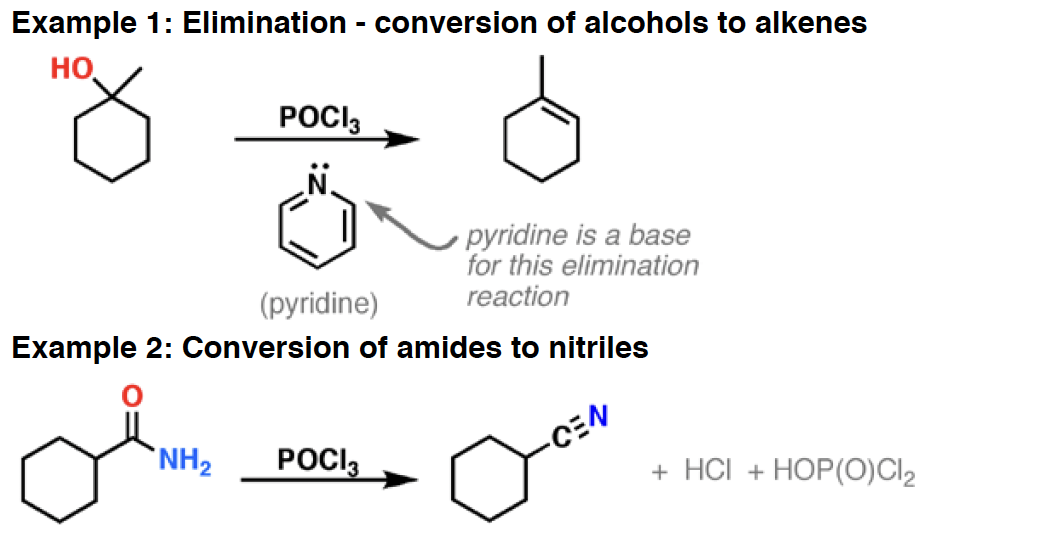
POCl3 - Phosphorus oxychloride (POCl3) is used for the dehydration of alcohols to alkenes. Essentially it converts alcohols to a good leaving group, which is then removed by added base (often pyridine). It can also be used to convert amides to nitriles
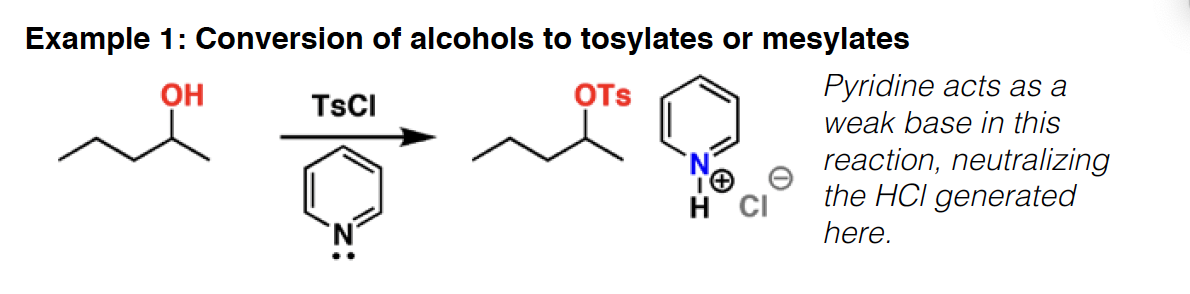
Pyridin - Pyridine is a mild base. Since it bears no charge it is especially soluble in organic solvents. It is often used in reactions that generate HCl and other strong acids - it acts much like a “sponge” for strong acid
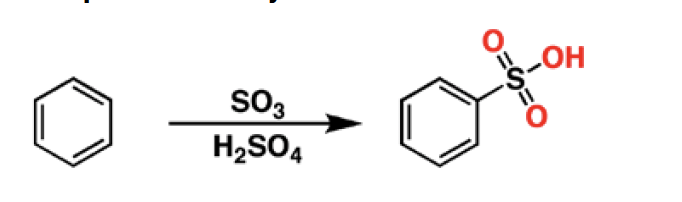
SO3 - Sulfur trioxide is a reagent for the sulfonylation of aromatic groups. In the presence of acid, it will lead to the formation of sulfonic acids
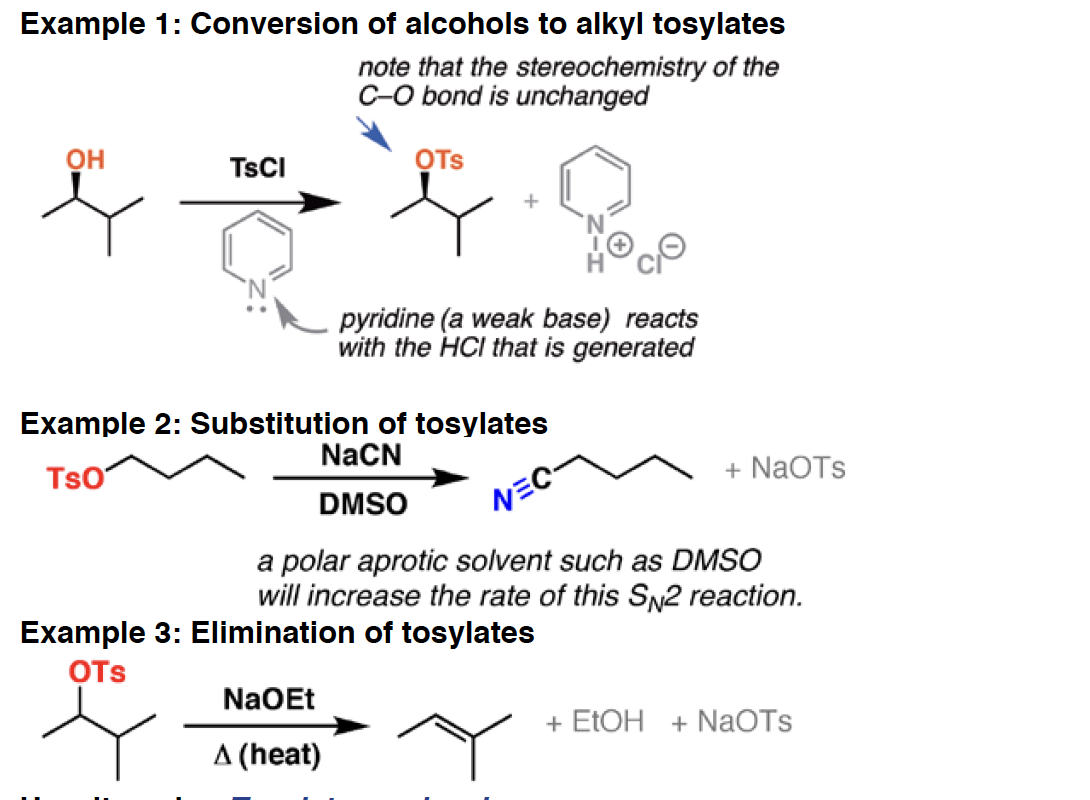
TsCl - Tosyl chloride (TsCl) will convert alcohols to sulfonates, which are excellent leaving groups in elimination and substitution reactions. TsO– is the conjugate base of the strong acid TsOH.
Gilman reagenser laver ?…
Gilman reagenser laver 1,4 addition
Aminer laver …
Aminer laver 1,4 additioner
Grignard og Alkyl lithium laver
1,2 addition
Hvad er AcOH
Eddikesyre pka: 5
Hvad er Grignard?
Grignard er stærke basser og gode nukleofiler
Nukleofil: OH⁻, Cl⁻, NH₃, H₂O, CN⁻, alkaner med π-bindinger (som alken og alkyner).
donerer et elektronpar: Nukleofiler er elektrontætte og har ofte en negativ ladning eller frie elektronpar, som gør dem reaktive over for positive eller delvist positive områder.
Elektrofil: H⁺, NO₂⁺, BF₃, Br₂, carbonylforbindelse
er en partikel, der accepterer et elektronpar for at danne en kemisk binding. Elektrofiler er elektrontomme og har ofte en positiv ladning eller et delvist positivt område.
Ozonlyse af Alkyn
Danner carboxylsyre
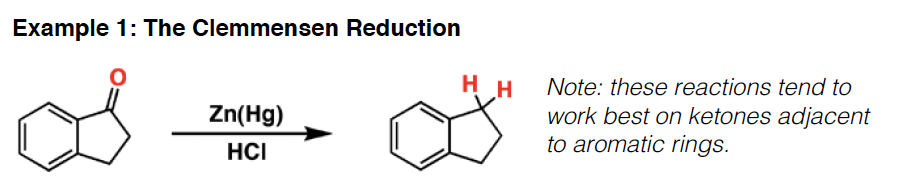
Reduktion af Keton til alkan (syre betinget)
Oxidation af keton med KMnO4 og base
danner dicarboxylsyre
LDA tager
Alfa hydrogener
Persyre
bruges til epoxider
En forbindelse opfylder Hückels regel, hvis antallet af π-elektroner i dens konjugerede system er 4n + 2, hvor n er et ikke-negativt helt tal
Dette betyder, at forbindelser med 2, 6, 10, 14, 18, osv. π-elektroner vil være aromatiske.