121: need to memorize!
1/122
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ch 1-10, updated periodically
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
antimony
Sb (metalloid)
aluminum
Al
argon
Ar
Arsenic
As (metalloid)
Barium
Ba
Beryllium
Be
Bismuth
Bi
Boron
B (metalloid)
Bromine
Br (diatomic!)
Cadmium
Cd
Calcium
Ca
Carbon
C
Cesium
Cs
Chlorine
Cl (diatomic!)
Chromium
Cr
Colbat
Co
Copper
Cu
Fluorine
F (diatomic!)
Gallium
Ga
Germanium
Ge (metalloid)
Gold
Au
Helium
He
Hydrogen
H (diatomic!)
Iodine
I (diatomic!)
Iron
Fe
Lead
Pb
Lithium
Li
Magnesium
Mg
Manganese
Mn
Mercury
Hg
Neon
Ne
Nickel
Ni
Nitrogen
N (diatomic!)
Oxygen
O (diatomic!)
Phosphorus
P
Platinum
Pt
Potassium
K
Radium
Ra
Rubidium
Rb
Silicon
Si (metalloid)
Silver
Ag
Sodium
Na
Strontium
Sr
Sulfur
S
Tin
Sn
Titanium
Ti
Uranium
U
Zinc
Zn
what does 1 ml equal?
1 cubic cm
density
mass/volume
c to f
1.8(C)+32=F
C to K (vice versa)
K=C+273.15
Tellurium is a…
metalloid!
average mass=?
(mass isotope #1 * % abundance/100)+(mass isotope #2 * % abundance/100)…(and so on)
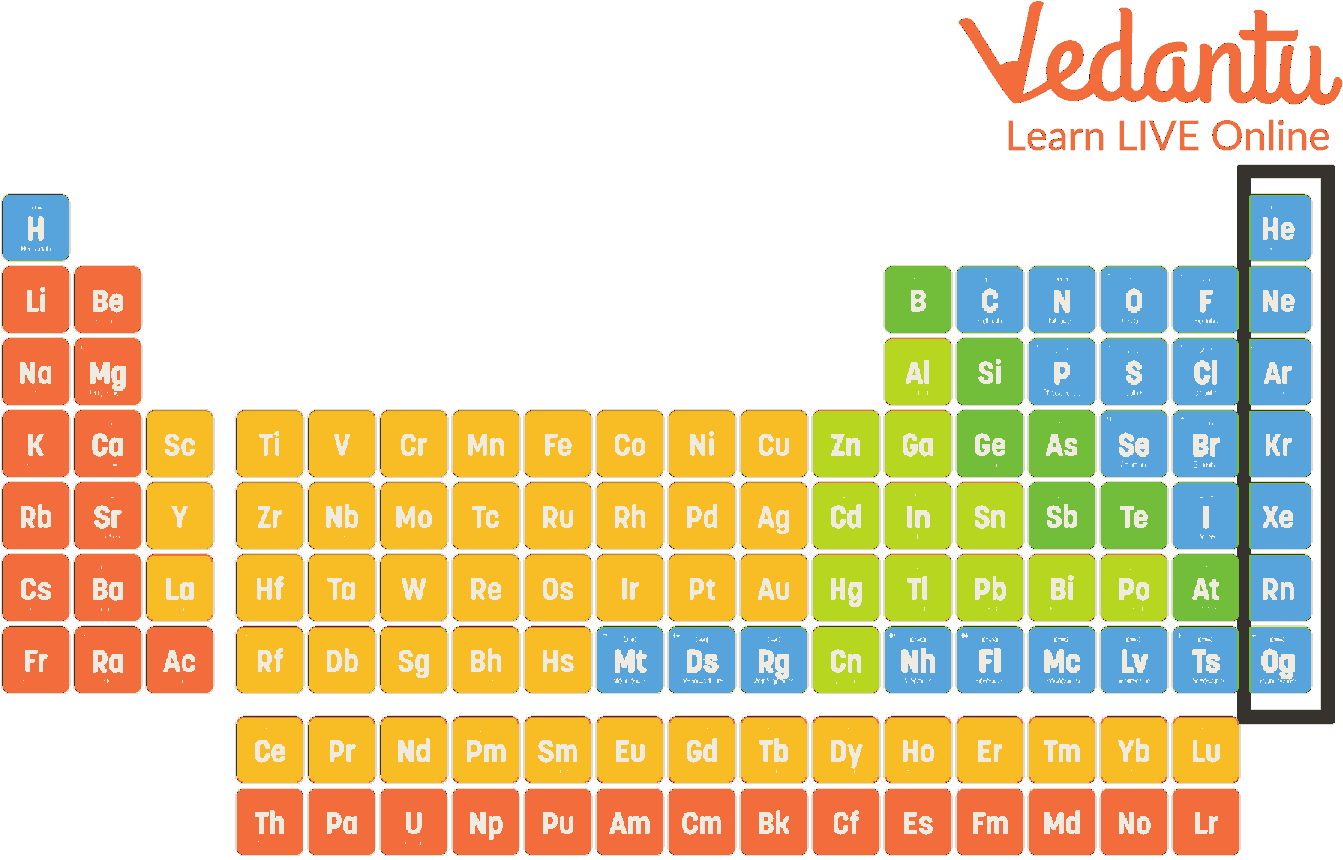
alkali metals

alkaline earth metals
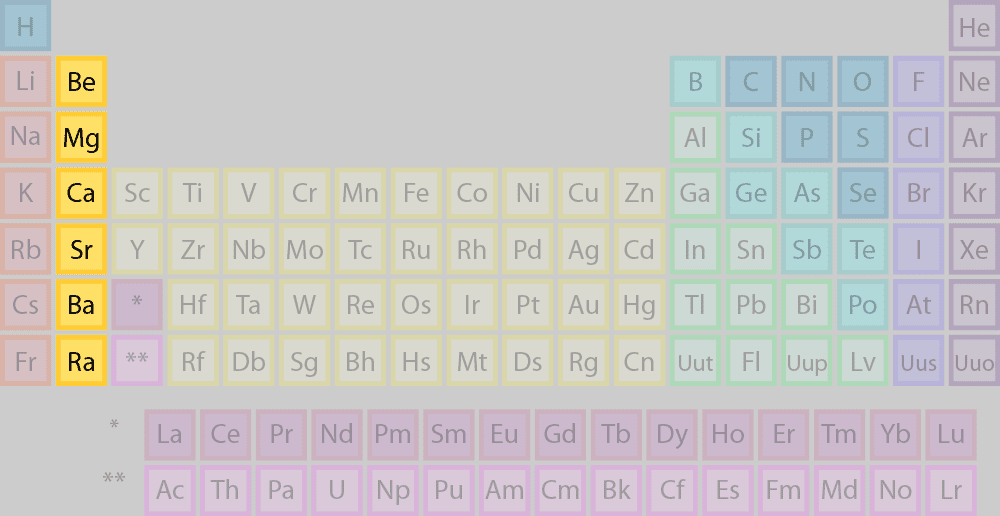
transition metals
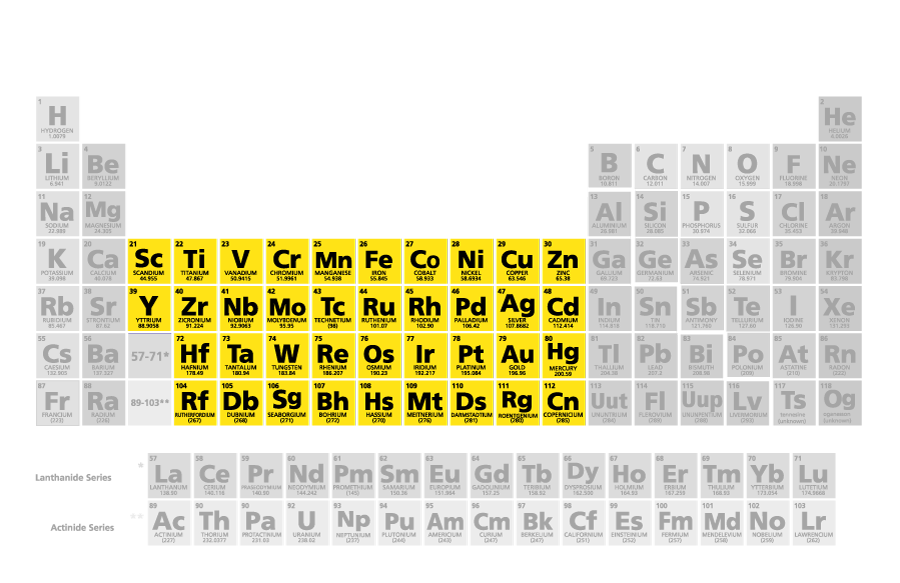
halogens
noble gases
hydroxide

hydronium
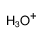
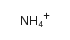
ammonium
nitrate

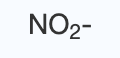
nitrite
perchlorate

chlorate
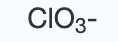
chlorite

hypochlorite

carbonate
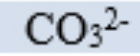
bicarbonate
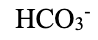
cyanide

sulfate
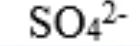
sulfite
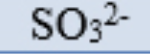
phosphate
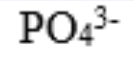
hydrogen phosphate
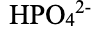
dihydrogen phosphate
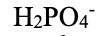
phosphite
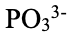
acetate
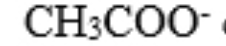
permanganate
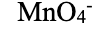
water
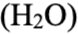
Ammonia
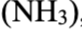
Hydrogen Sulfide
hydrofluoric acid
HF (weak)
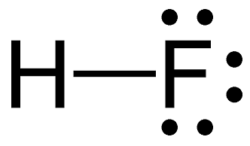
hydrochloric acid
HCI (strong acid)

hydrobromic acid
HBr (strong)
hydroiodic acid
HI
chloric acid
HCIO3 (strong)
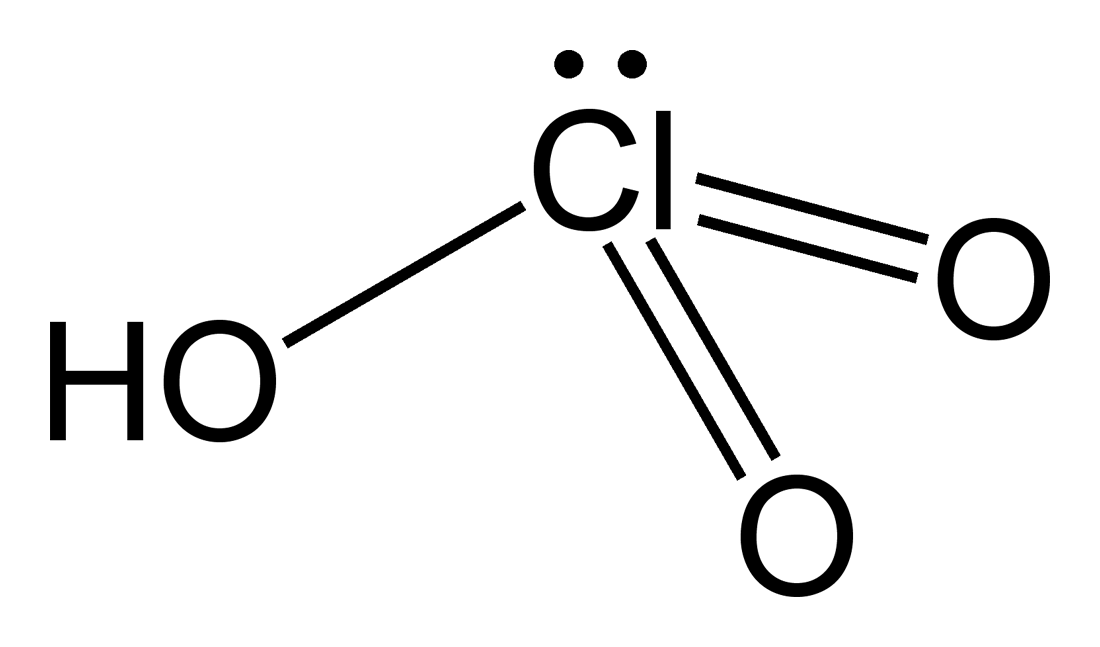
perchloric acid
HCIO4 (strong)
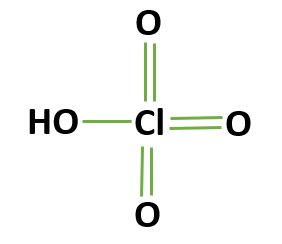
nitric acid
HNO3 (strong)
sulfuric acid
H2SO4 (strong)
acetic acid
CH3COOH or C2H4O2 (weak)
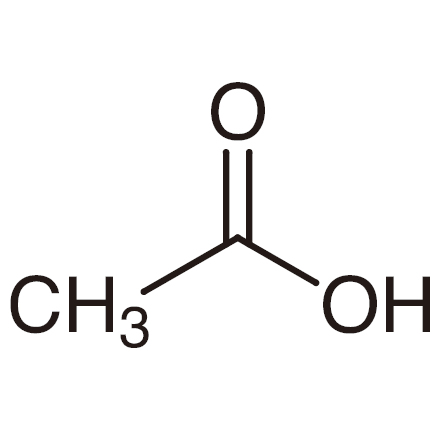
methane
CH4
ethane
C2H6
propane
C3H8
naming alcohols
change ending to -ol
number to specify location (e.g 2-Propanol)
acids: anion ends w/ -ide
add prefix hydro-, change ending with -ic acid
acids: anion ends with -ite
change ending to -ous acid
acids: anion ends with -ate
change ending to -ic acid
(g)
gas
(s)
solid