PHA618 LAB - Nervous System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:11 PM on 3/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
1
New cards
Central Nervous System Parts
Brain and Spinal Cord
2
New cards
The CNS is the
neural control centre
3
New cards
The PNS consists of
nerves and sensory receptors
4
New cards
What are the functional divisions of the PNS
Sensory (afferent) and Motor (efferent)
5
New cards
What functional division carries impulses from sensory receptors to the CNS
Sensory (afferent)
6
New cards
What functional division carries impulses from the CNS to effectors
Motor (efferent)
7
New cards
What are the divisions of the motor division
Autonomic and somatic
8
New cards
Which motor division involves the voluntary control of skeletal muscle
Somatic
9
New cards
Which motor division involves the involuntary
control of cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands
control of cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands
Autonomic
10
New cards
What part of the neuron receives information
Dendrites
11
New cards
Which part of the neuron transmits electrical impulses
Axon
12
New cards
What type of neuron is found both in the CNS and PNS
Multipolar
13
New cards
What type of message does multipolar neurons send
Motor
14
New cards
What direction do messages from multipolar neurons take
Efferent if they are motor
15
New cards
What types of neurons can be found in the nasal cavity, retina, and inner ear
Bipolar
16
New cards
What type of message do bipolar neurons send
Sensory
17
New cards
What direction do messages from bipolar neurons take
Afferent
18
New cards
What types of neurons can be found in the skin, organ, etc.
Unipolar
19
New cards
What type of message do unipolar neurons send
Sensory
20
New cards
What direction do messages from unipolar neurons take
Afferent
21
New cards
What are the 4 types of neuroglial cells found in the CNS
Oligodendrocytes, Astrocytes, Ependymal Cells, Microglia
22
New cards
What type of neuroglial cells make up the myelin sheath
Oligodendrocytes
23
New cards
What type of neuroglial cells make up the blood-brain barrier
Astrocytes
24
New cards
What type of neuroglial cells produce CSF
Ependymal Cells
25
New cards
What type of neuroglial cells seek out and fight pathogens in the CNS
Microglia
26
New cards
What are the two types of neuroglial cells found in the PNS
Schwann, Satellite
27
New cards
Which neuroglial cells form the myelin sheath in the PNS
Schwann cells
28
New cards
Which neuroglial cells control the environment for ganglia in the PNS
Satellite cells
29
New cards
The brain and spinal cord are covered by three membranes called
Meninges
30
New cards
The meninges has 3 fibrous membranes namely
Dura, Arachnoid, Pia
31
New cards
The tough, outermost membrane connected to the skull that forms a protective tube in vertebral canal called the epidural space
Dura
32
New cards
The middle layer that is thin, avascular, and weblike which does not penetrate smaller depressions
Arachnoid
33
New cards
The space containing CSF
Subarachnoid
34
New cards
The thin, innermost layer directly attached to the brain and contains blood vessels to nourish brain and spinal cord
Pia
35
New cards
CSF is produced by which structure in the brain
choroid plexuses
36
New cards
The two lateral ventricles of the brain are located
within the cerebral hemispheres
37
New cards
The third ventricle of the brain is located
at the midline of the diencephalon
38
New cards
The fourth ventricle of the brain is located _______ and is continuous with the
in the midline of the brain stem, central canal of the spinal cord
39
New cards
Flow of the cerebrospinal fluid
lateral-third-fourth-central/subarachnoid-up around the brain/down the posterior of the spinal cord-up the anterior
40
New cards
The CSF is reabsorbed in the
dural sinus within the dura mater
41
New cards
Functions of CSF
buoyancy, protection, nutrients, chemical stability
42
New cards
The cerebrum is characterized by
gyri (folds) and sulci (shallow grooves)
43
New cards
The left and right cerebral hemispheres are separated by
longitudinal fissure
44
New cards
The left and right cerebral hemispheres are connected by
corpus callosum
45
New cards
The outer surface of the cerebral cortex is made up of
grey matter (neuronal cell bodies and unmyelinated fibers)
46
New cards
The inner surface of the cerebral cortex is made up of
white matter
47
New cards
The myelinated fibers in white matter transmit impulses between
hemispheres, cerebral cortex and lower brain areas
48
New cards
What are the 4 lobes in the cerebral hemisphere?
Frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal, insula
49
New cards
What are the functions of the cerebrum
interpret sensory impulses, control voluntary motor impulses, intellectual processes, will, and personality traits
50
New cards
Lobes responsible for sensation have both a
general sensory and association area
51
New cards
The motor areas of the frontal lobe are
primary motor, pre-motor, Broca’s area
52
New cards
General sensory areas of the parietal lobe
primary sensory area, higher level reasoning
53
New cards
Temporal lobe
Hearing, Wernicke’s area (language)
54
New cards
Occipital lobe
Vision
55
New cards
Complex of deep nuclei in cerebrum, associated with the thalamus
limbic system
56
New cards
Limbic system is involved in
memory (hippocampus), emotions (amygdala), emotional behaviours
57
New cards
Acts as a switching station for incoming sensory messages
Thalamus
58
New cards
Monitors the internal environment and helps regulate homeostasis
Hypothalamus
59
New cards
Directs the sensory messages to the appropriate lobe of the cerebrum
Thalamus
60
New cards
The thalamus serves as a switching station for incoming sensory messages except those for
smell
61
New cards
The brainstem is composed of the
* medulla oblongata
* pons
* midbrain
* reticular formation
* pons
* midbrain
* reticular formation
62
New cards
All ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) information passes through
Medulla oblongata
63
New cards
Most inferior section of the brainstem
Medulla oblongata
64
New cards
Contains centers to regulate heart rate, respiratory rate, and blood vessel diameter
Medulla oblongata
65
New cards
Emetic centre
Medulla oblongata
66
New cards
Large bulge on the anterior surface of the brainstem between the medulla oblongata and the midbrain
Pons
67
New cards
Serves as a bridge for motor tracts to the cerebellum
Pons
68
New cards
The midbrain has four bulges called ---- on its ------ surface
colliculi, posterior
69
New cards
The two superior colliculi are important
visual reflexes
70
New cards
The two inferior colliculi are important
auditory reflexes
71
New cards
Groups of cell bodies (called nuclei in the CNS, ganglia inthe PNS) are scattered throughout the brainstem
Reticular formation
72
New cards
Important for arousal
Reticular formation
73
New cards
responsible for sleep-wake cycles
Reticular formation
74
New cards
Second largest brain region
Cerebellum
75
New cards
The cerebellum is inferior to the _ and - lobes
occipital, temporal
76
New cards
The cerebellum is posterior to _ and -
pons, medulla oblongata
77
New cards
The two hemispheres of the cerebellum is connected by
the vermis
78
New cards
The outer layer of gray matter surrounding inner white matter in the cerebellum is called
arbor vitae
79
New cards
Controls and coordinates the interaction of skeletal muscles
Cerebellum
80
New cards
Controls posture, balance, and muscle coordination
Cerebellum
81
New cards
Damage results in loss of equilibrium, muscle coordination, and muscle tone
Cerebellum
82
New cards
Responsible for reflexive memory
Cerebellum
83
New cards
The spinal cord is a solid structure from the
foramen magnum to L1
84
New cards
extends from the inferior end of the spinal cord
cauda equina
85
New cards
Descends from medulla oblongata through foramen magnum
Spinal cord
86
New cards
Passes through vertebral canal to level of 2nd lumbar vertebra
Spinal cord
87
New cards
Functions of spinal cord
Transmits impulses to and from brain
88
New cards
Cranial Nerve I (------) is a ------ nerve for -----
olfactory, sensory, smell
89
New cards
Cranial Nerve II (------) is a ----- nerve for -----
optic, sensory, vision
90
New cards
Cranial Nerve III (-------) is a ----- nerve for -------
oculomotor, motor, eye movement
91
New cards
Cranial Nerve IV (-----) is a ------ nerve for -------
trochlear, motor, eye movement
92
New cards
Cranial Nerve V (-------) is a ----- for ------.
trigeminal, mixed, sensory - pain, touch, and temperature for the\]eye and lower and upper jaws, motor - chewing
93
New cards
Cranial Nerve VI (----) is a ----- nerve for -----
abducens, motor, eye movement
94
New cards
Cranial Nerve VII (----) is a ----- nerve for -----.It is sensory for taste and motor for facial expression.
facial, mixed, sensory - taste, motor - facial expression
95
New cards
Cranial Nerve VIII (-------) is a ----- nerve for ----.
vestibulocochlear, sensory, hearing and balance
96
New cards
Cranial Nerve IX (-----) is a ------- nerve for -----. It is sensory for taste and motor for swallowing.
Glossopharyngeal, mixed, sensory - taste, motor - swallowing
97
New cards
Cranial Nerve X (----) is a ----- nerve for ----.
vagus, mixed, sensory and motor for organs in thoracic and abdominal cavities
98
New cards
Cranial Nerve XI (------) is a ----- nerve for------.
accessory, motor, trapezius, sternocleidomastoid, and muscles of the larynx.
99
New cards
Cranial Nerve XII (------) is a ----- nerve for-----
hypoglossal, motor, tongue
100
New cards
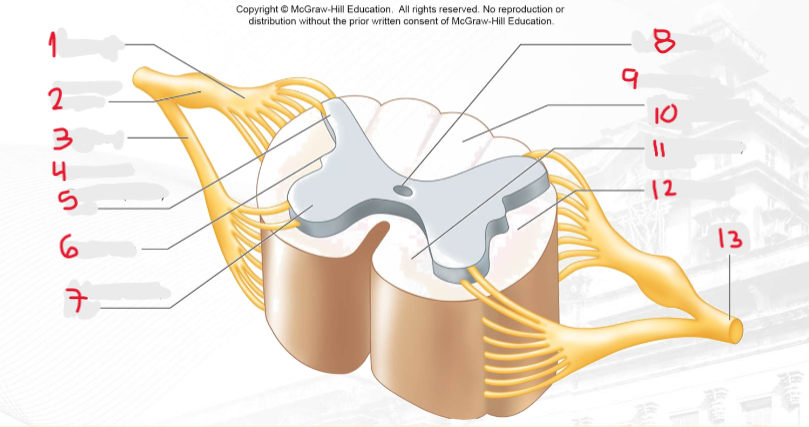
1
dorsal root