Biochemistry and Cell Signaling: Glycolysis, Enzymes, and G-Protein Pathways
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
The phosphorylation of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is the
committed step in glycolysis because
fructose 1,6-bisphosphate can undergo no other reactions than those of
glycolysis.
Activation of a G protein in response to hormone binding involves dissociation of the
____ subunit from the _________________ subunits.
Alpha, Beta and Gamma
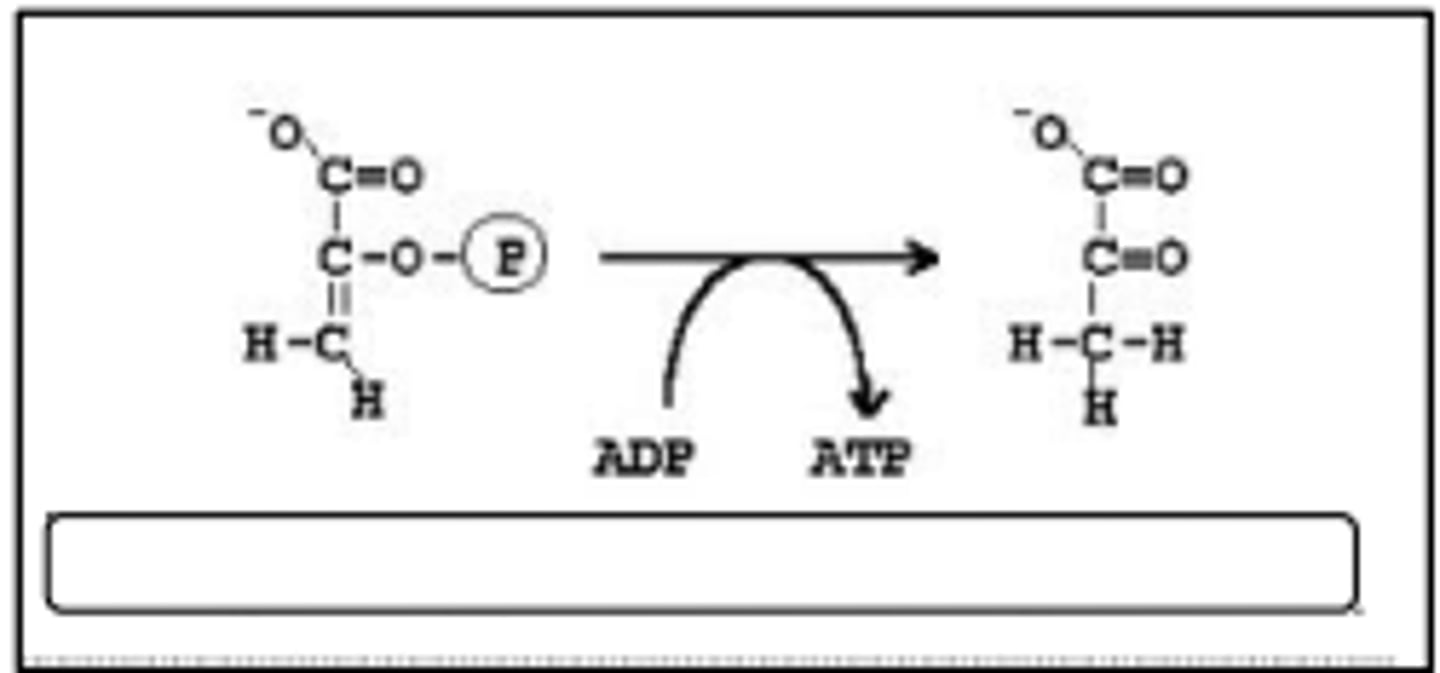
Which enzyme catalyzes the reaction shown?
pyruvate kinase
When insulin signaling is present, the bifunctional enzyme is dephosphorylated, which
leads to an increase in glycolytic activity.
True
Which of the following are positive effectors of isocitrate dehydrogenase? Select all that
apply
ADP
Lipases are responsible for breaking down:
lipids
Which property of the potassium transporter allows the potassium to overcome the
ion-dipole interactions it has with water?
Backbone carbonyl oxygens have strong interactions with the potassium
The reaction that converts 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to 3-phosphoglycerate produces 1
molecule of ATP.
True
An active G-protein will result in increased cellular concentrations of which molecule?
cAMP
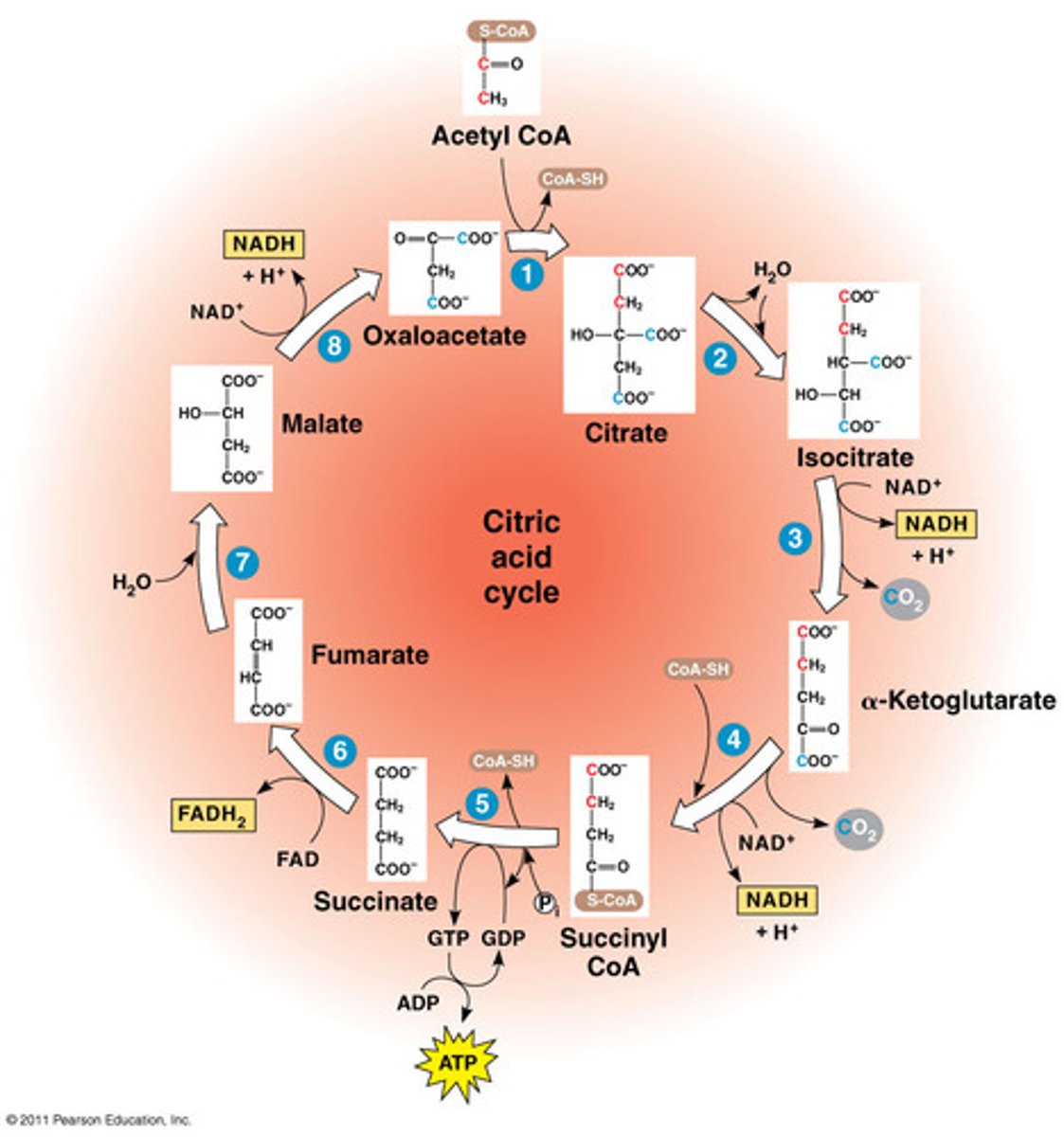
The following are all intermediates of the citric acid cycle: Which of the following will undergo a redox reaction that generates NADH?
Isocitrate, alpha-ketoglutarate, malate only
Which of the following is true about the sodium potassium pump?
The conformation of the pump is determined by what molecule is bound to its Asp
residue
Based on the phosphoryl transfer potential table, which of these compounds will most
readily give up its phosphate group?
Lowest # = most readily. Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)
15. Binding of a ligand to a receptor tyrosine kinase causes
___ of the receptor, which then ___ the next protein in the signaling
pathway.
phosphorylation, phosphorylates
In gluconeogenesis, which of the following is considered the major regulatory enzyme?
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
Dephosphorylation of pyruvate dehydrogenase
activates the enzyme through covalent modification
Which of the following is a positive effector of the enzyme pyruvate carboxylase?
Acetyl-CoA
Which of the following is not a characteristic of most naturally occurring fatty acids?
Presence of trans double bonds
For a cell with [Na+]out = 150 mM and [Na+]in = 15 mM at 37°C, which of the following would make the transport of ion into the cell more spontaneous if the potential across the membrane that has an absolute value of 60 mV with the inside of the cell more negative?
Decreasing the ratio of [Na+]in to [Na+]out
The cholera toxin causes severe dehydration due to an excess of ions leaving intestinal
cells and entering the intestinal tract, which leads to excessive water expulsion in the
form of waste. The ion channels in intestinal cells are controlled by a signaling pathway
that utilizes a G-protein; when this signal is active, ion channels are open to allow
movement of ions out of the cell. What is a possible way the cholera toxin affects this
signaling pathway?
It binds to the G-protein and causes it to irreversibly bind GTP while also
inhibiting GTPase activity.
Which of these statements are true?
I. Some, but not all, of the enzymes used in glycolysis are used in gluconeogenesis, just
running in reverse.
II. Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate is an important effector in both glycolysis and
gluconeogenesis
III. The gluconeogenesis pathway has one more step than the glycolysis pathway
I, II, and III
In the reaction
1,3-BPG + ADP -> 3-phosphoglycerate + ATP ΔG° = -18.8 kJ/mol
Calculate ΔG when [1,3-BPG] = 15mM, [3-phosphoglycerate] = 2mM, [ADP] = 12mM, and [ATP]
= 13mM at 25°C. R = 8.314 J mol-1K-1
-23.6 kJ/mol
When insulin signaling is present, the bifunctional enzyme is dephosphorylated, which leads to an increase in glycolytic activity.
True
During glycolysis, the steps between glucose and the formation of the triose phosphates
None of the other answers is correct.
In the reaction
Fructose-6-phosphate + ATP -> Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + ADP ΔG° = -14.2 kJ/mol
Calculate ΔG when [Fructose-6-phosphate] = 5mM, [Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate] = 20mM, [ADP] = 5mM, and [ATP] = 10mM at 25°C. R = 8.314 J mol-1K-1
-12.5 kJ/mol
Given the following reaction:
3-phosphoglycerate + ATP <-> 1,3-BPG + ADP ΔG°' = +18.9 kJ/mol
Which one of these compounds will most readily donate a phosphate group?
Lowest value in the table = most readily. 1,3-BPG
Which of the following are negative effectors of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase? Choose the best answer.
I: ATP
II: acetyl-COA
III: NADH
IV: Pyruvate
V: succinyl-CoA
I, III, and V only
Of the following pairs of metabolites and enzymes, which would be an example of product inhibition within a metabolic pathway?
Glucose-6-phosphate and hexokinase
EGF/Ras is a signaling pathway that is necessary for cell growth. The pathway has been extensively studied due to its involvement in several types of cancer, which is characterized by uncontrolled cell growth. Given your knowledge of the Ras pathway, which mutation is one that could lead to uncontrolled cell growth?
a mutation that eliminates the intrinsic GTPase activity of the Ras protein.
Which subunit of the heterotrimeric G proteins binds GDP and GTP?
alpha
You drop phospholipid molecules into a nonpolar solvent. You would expect these to self-organize into _______________ with __________________ pointing outward toward the solvent.
Bilayers; the nonpolar tails
How many steps of the Citric Acid Cycle involve the cleavage of a high-energy thioester bond?
2
Which of these statements are true?
All of the enzymes used in glycolysis are used in gluconeogenesis, just running in reverse.
Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate is an important effector in both glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
The gluconeogenesis pathway has one more step than the glycolysis pathway
II and III only
Which of these are true about the sodium potassium pump?
I. It transports sodium ions out of the cell
II. It transports potassium ions into the cell
III. It is open to the inside of the cell when ATP is bound to the ATPase protein.
I, II, and III
The secondary messenger cAMP is produced by the enzyme ______.
Adenylate cyclase
The gross (total) yield of ATP from the metabolism of one glucose to two molecules of pyruvate is four molecules of ATP. However, the NET yield is only two molecules of ATP. Why are the gross and net values different?
Because the energy investment phase uses two molecules of ATP, while the energy generation phase produces 4 ATP.
For the following sugar, which carbon will become the anomeric carbon upon cyclization?
the carbon that was the carbonyl carbon (C=O) in the sugar's open-chain form
EGF/Ras is a signaling pathway that has been extensively studied due to its involvement in several types of cancer, which is characterized by uncontrolled cell growth. Given your knowledge of the Ras pathway, which mutation is one that could lead to uncontrolled cell growth?
Permanent dimerization of the receptor.
Permanent dimerization of the receptor.
What molecule is produced in each of the regulatory steps of the citric acid cycle?
NADH
Which form of the heterotrimeric G protein complex is the inactive form?
G alpha beta gamma
A muscle cell is exposed to conditions where ATP levels are high, but glycolysis continues at an increased rate. Which of these might cause glycolysis to remain active despite high ATP levels?
There are loss-of-function mutations on the allosteric sites of PFK and pyruvate kinase.
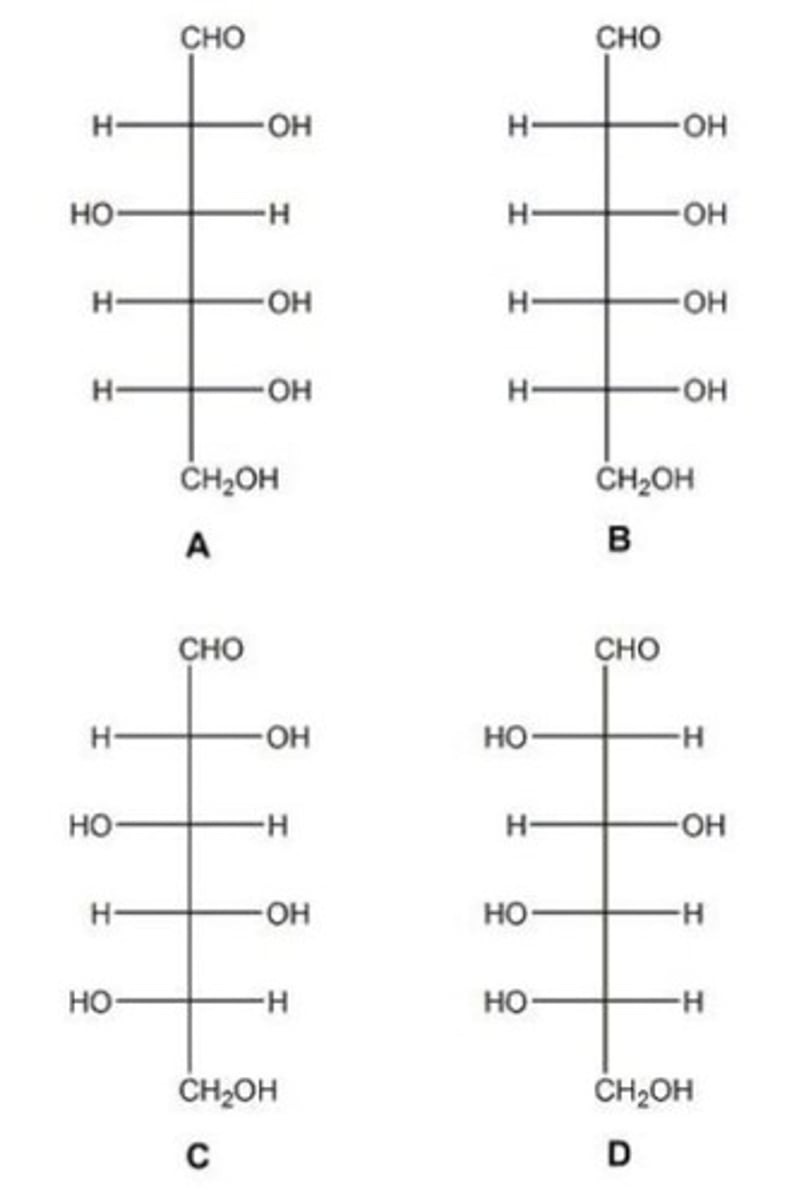
Which of the sugars shown in the figure are L sugars?
C and D
Which of the following enzymes requires ATP as a substrate?
Phosphofructokinase
The coenzyme ______ is the oxidizing agent in glycolysis.
NAD+
The RAS protein plays a similar role in biosignaling pathways to which of the following molecules?
Heterotrimeric G protein
Chloride shift is a phenomenon observed in red blood cells that assists in maintaining the potential of the cell. When red blood cells release a bicarbonate anion to the outside environment, a chloride anion is simultaneously moved by the transporter to keep the membrane potential the same. What type of transporter would be most appropriate for this process?
Antiporter
Which of these would NOT terminate a signal cascade?
I) Irreversible binding of the primary messenger to the receptor
II) Degradation of the secondary messenger
I only
Which of the following is true about sphingolipids?
They are commonly found in neural tissue as sphingomyelin.
Which is true about the potassium ion channel?
None of the other choices is correct.
Which of the following BEST describes the reaction catalyzed by E2 in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
Attachment of a 2-carbon molecule to coenzyme A.
The regeneration of NAD+ is essential for glucose catabolism via the glycolytic pathway.
True
The futile cycle describes the wasteful process of catabolizing a molecule just to make it again in an opposing anabolic pathway. If glucose gets broken down to two pyruvate molecules that are then funneled into gluconeogenesis to make a glucose molecule, what is the NET change in energy? Assume 1 ATP = 1 GTP
Net loss of 4 ATP
Which of the following is NOT a factor that explains the high phosphoryl transfer potential of ATP?
Reduction in entropy upon ATP hydrolysis
A nonpolar molecule with three cyclohexane rings fused to a cyclopentane ring is best classified as:
A steroid
Consider only the electrochemical gradient of Cl- for a hypothetical cell with a membrane permeable to Cl-. What membrane potential would be necessary to sustain a [Cl-]in of 123 mM and a [Cl-]out of 12 mM? Answer to the nearest mV (whole number). Be sure to include the sign as appropriate with negative indicating a net negative charge inside the cell and vice versa.
Temperature = 37°C
R = 8.314 J/molK
F = 96,485 C/mol
62 mV
If there were to be a mutation that halted the citric acid cycle after the production of alpha-ketoglutarate, what would the net yield of this halted cycle be ?
1 NADH
Match the gluconeogenesis reaction to the enzyme that catalyzes it: Glucose 6-phosphate + H2O → Glucose + Pi
Glucose 6-phosphatase
Match the gluconeogenesis reaction to the enzyme that catalyzes it:
Oxaloacetate + GTP → Phosphoenolpyruvate + GDP
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
Match the gluconeogenesis reaction to the enzyme that catalyzes it:
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + H2O → Fructose 6-phosphate + Pi
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
Match the gluconeogenesis reaction to the enzyme that catalyzes it:
Pyruvate + ATP → Oxaloacetate + ADP
Pyruvate carboxylase