APES Unit 4: Earth Systems and Resources
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
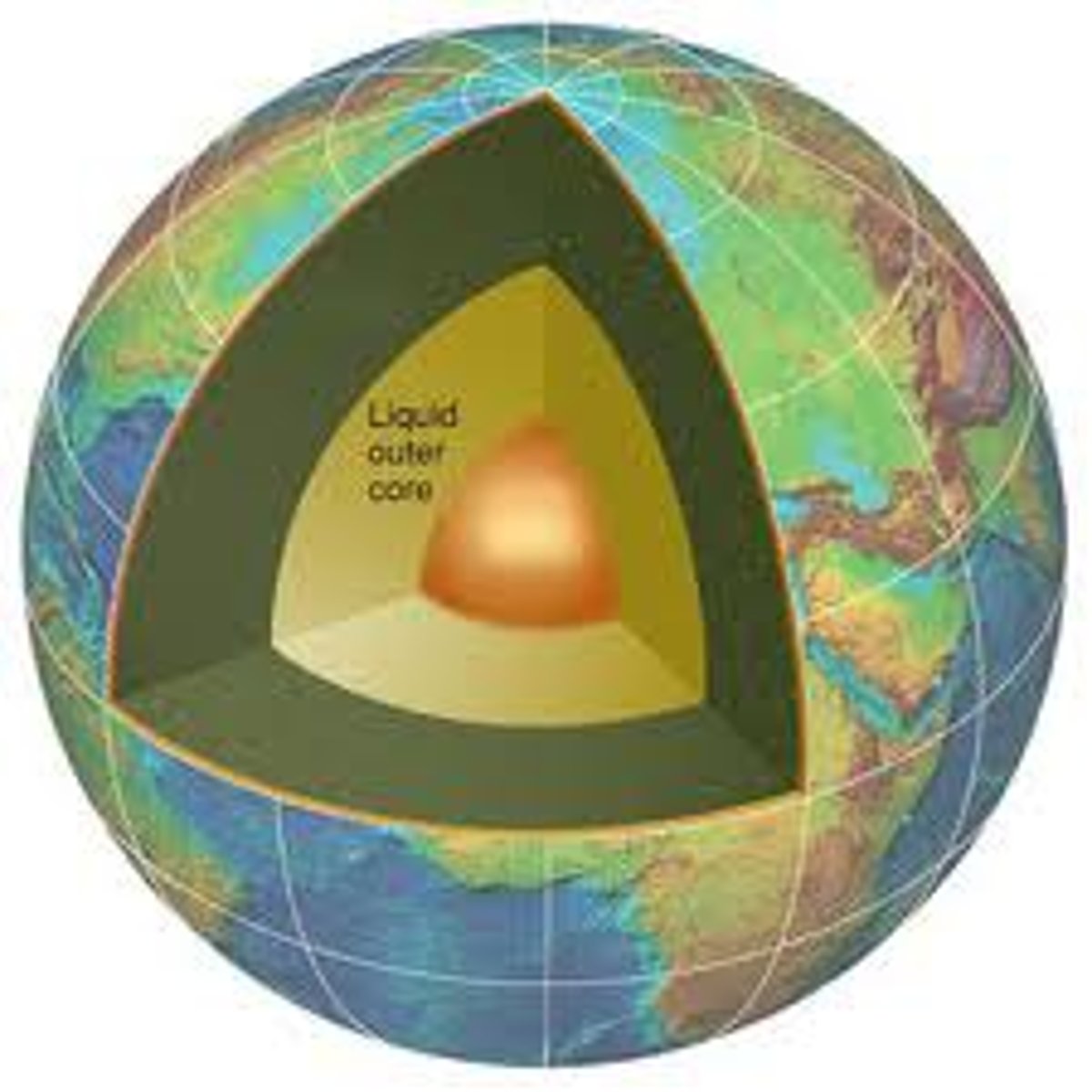
Earth's core
The extremely hot and dense center of the earth, which is believed to be composed of iron and nickel
Earth's mantle
the part of the earth between the core and the the crust, about 2,900 km thick and makes up nearly 80 percent of the Earth's total volume.The mantle is made up of magma and rock.
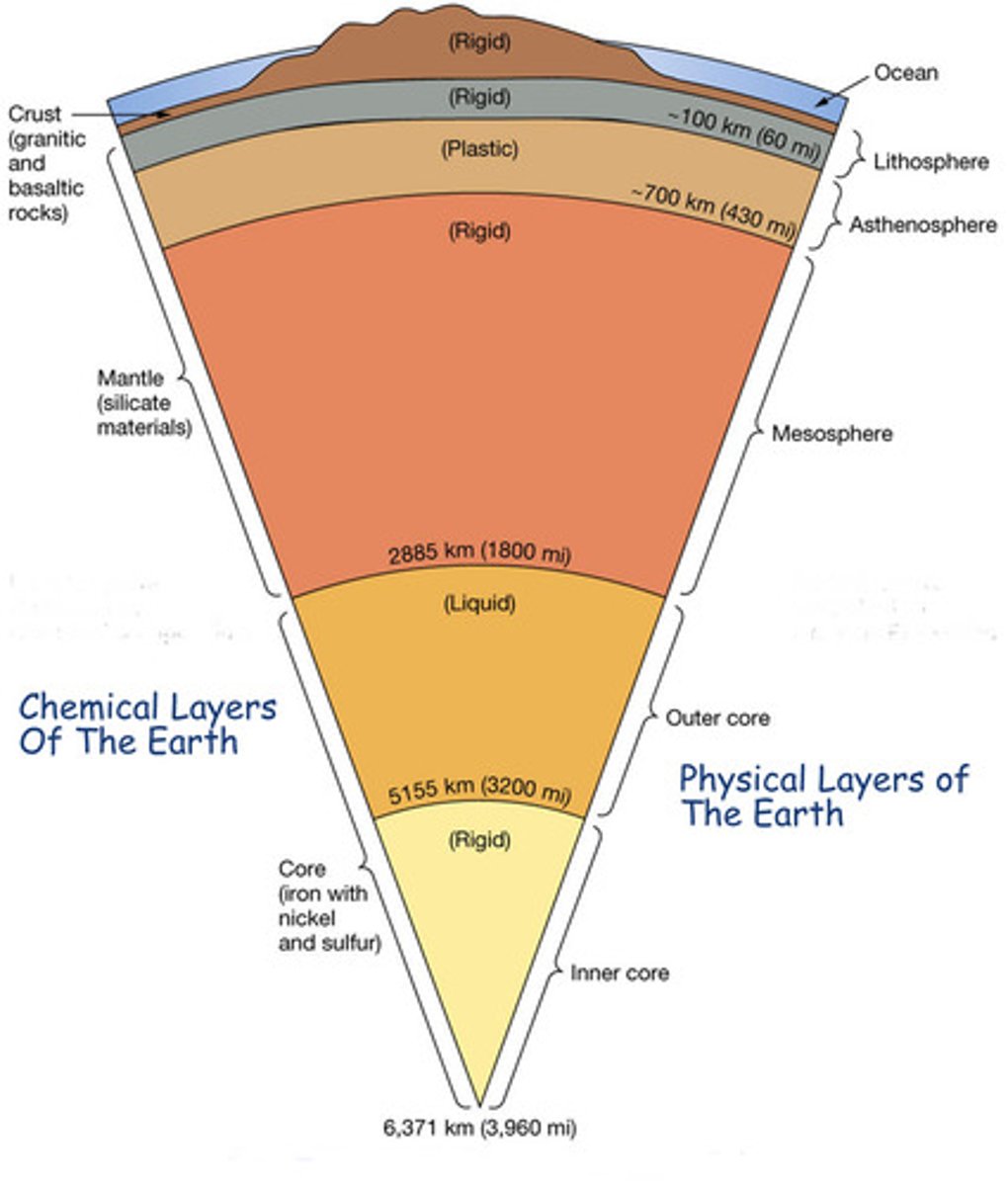
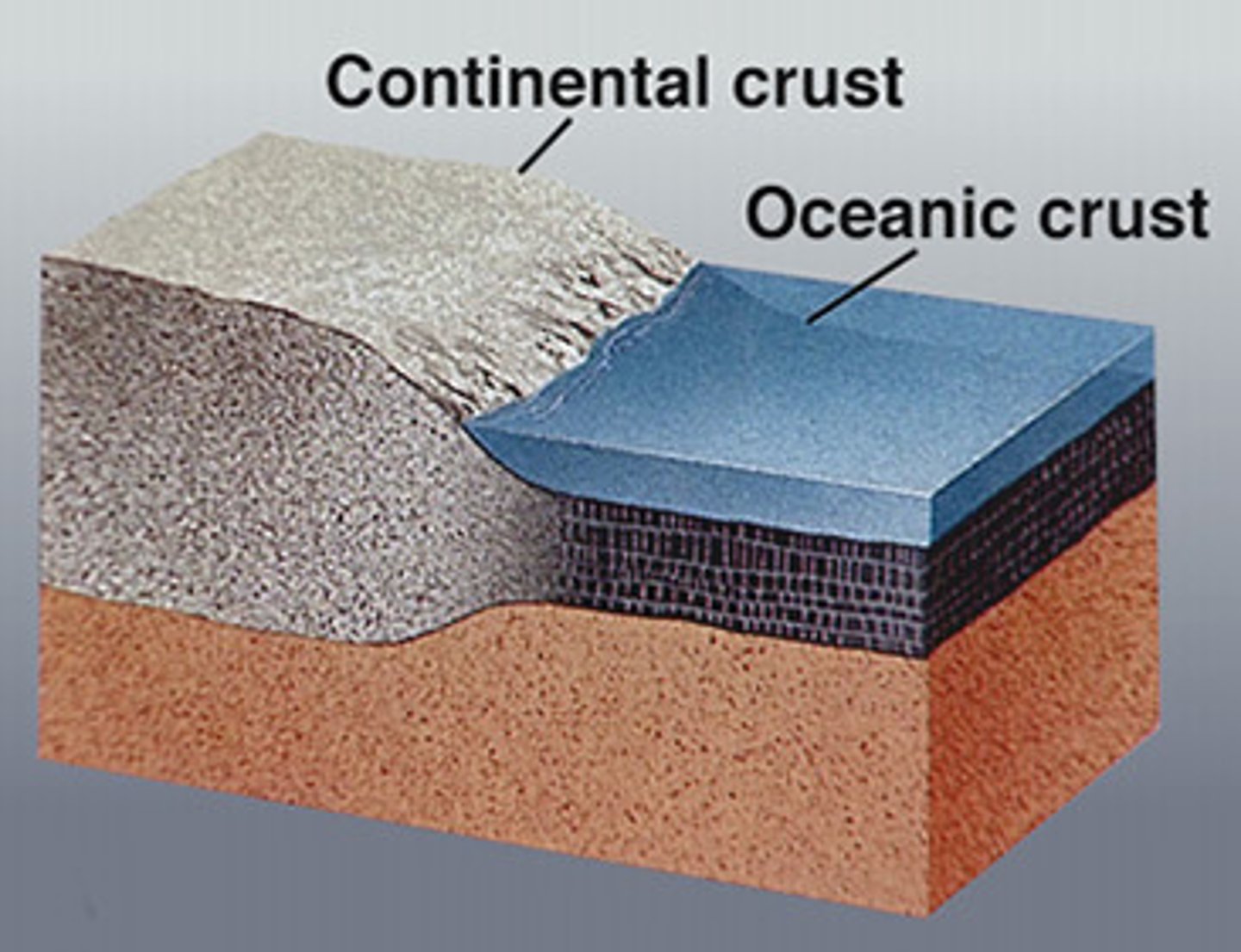
Earth's crust
earth's outermost layer of rock made up of both dry land and ocean floor
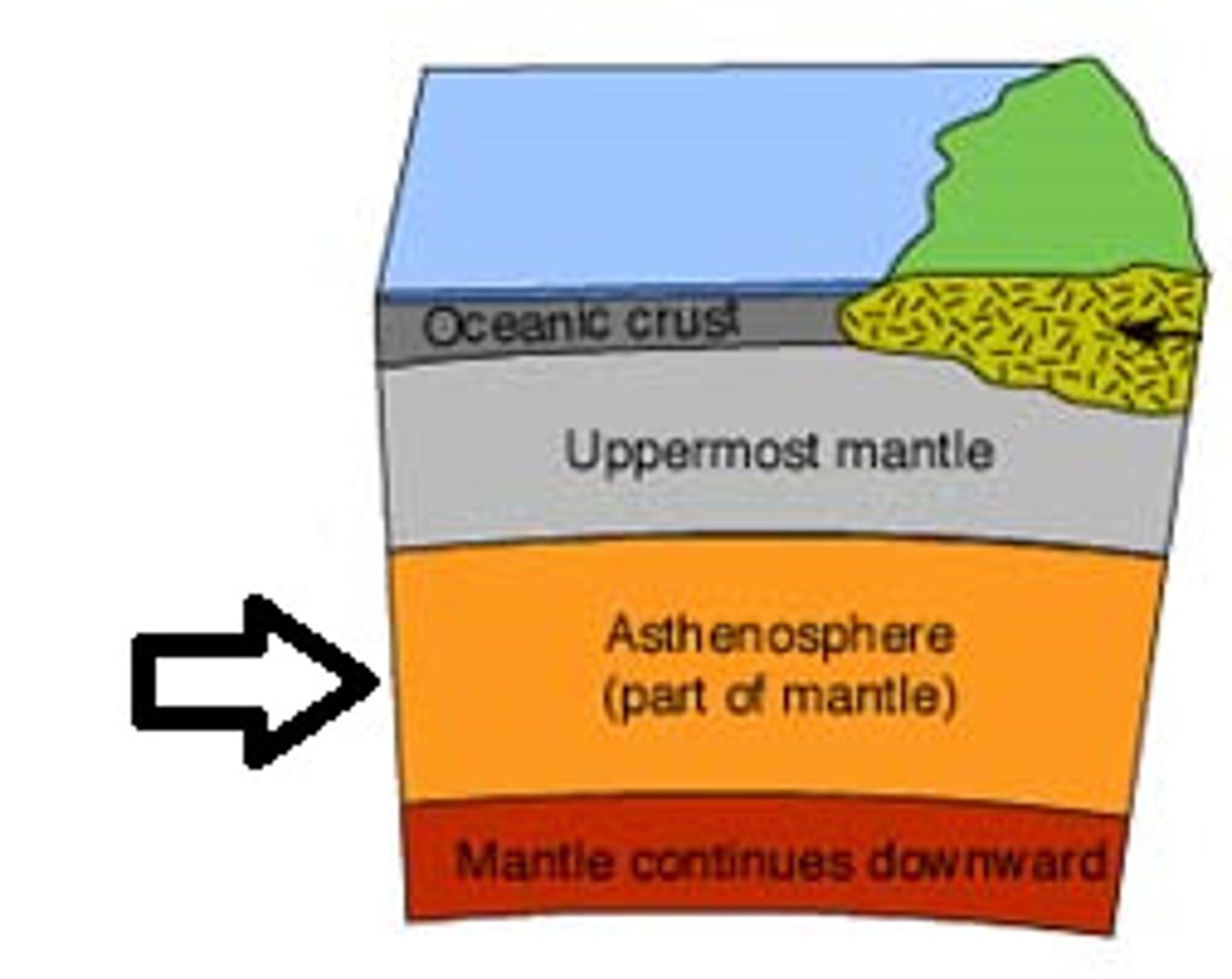
Lithosphere
A rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust.
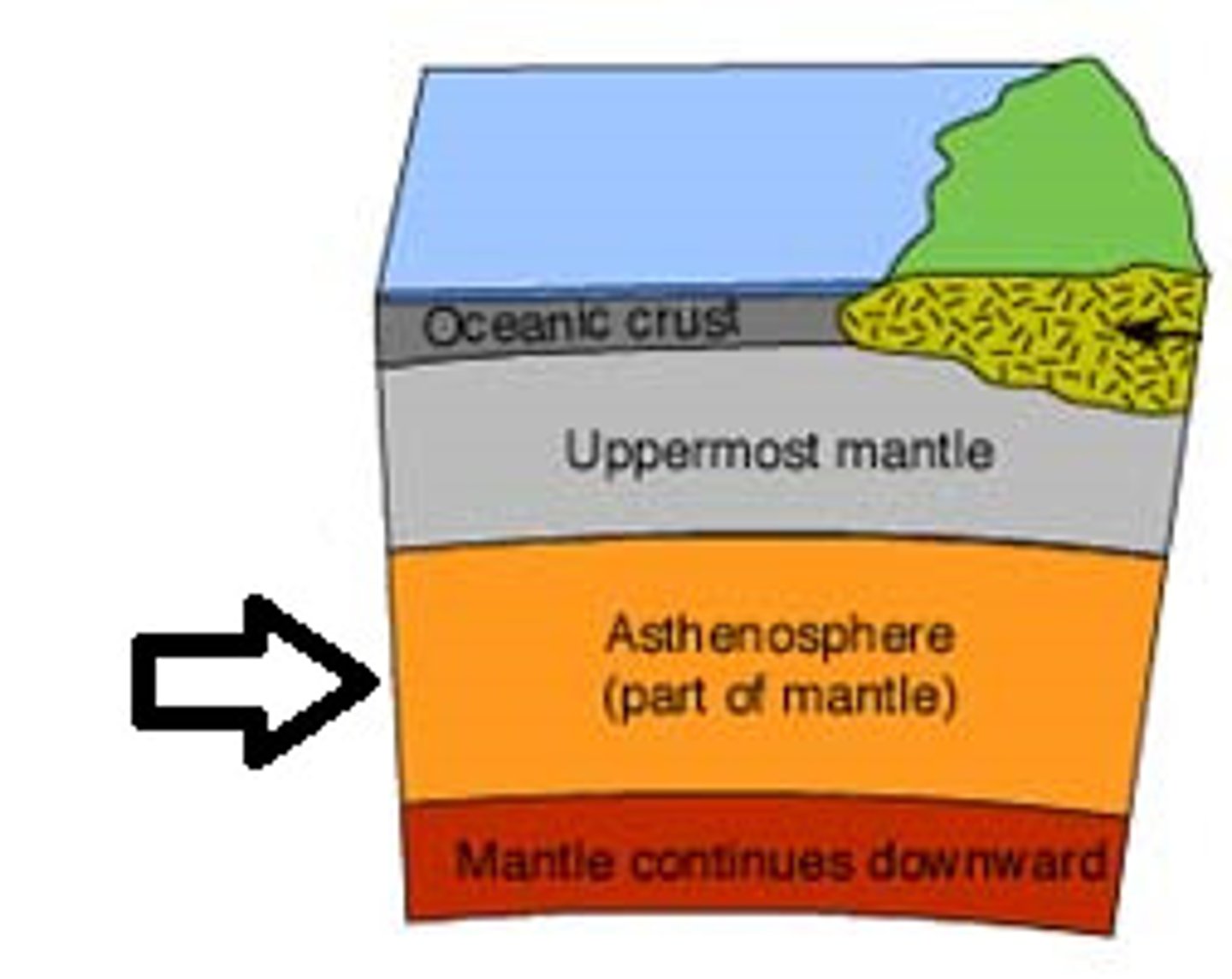
Asthenosphere
The soft layer of the mantle on which the lithosphere floats.
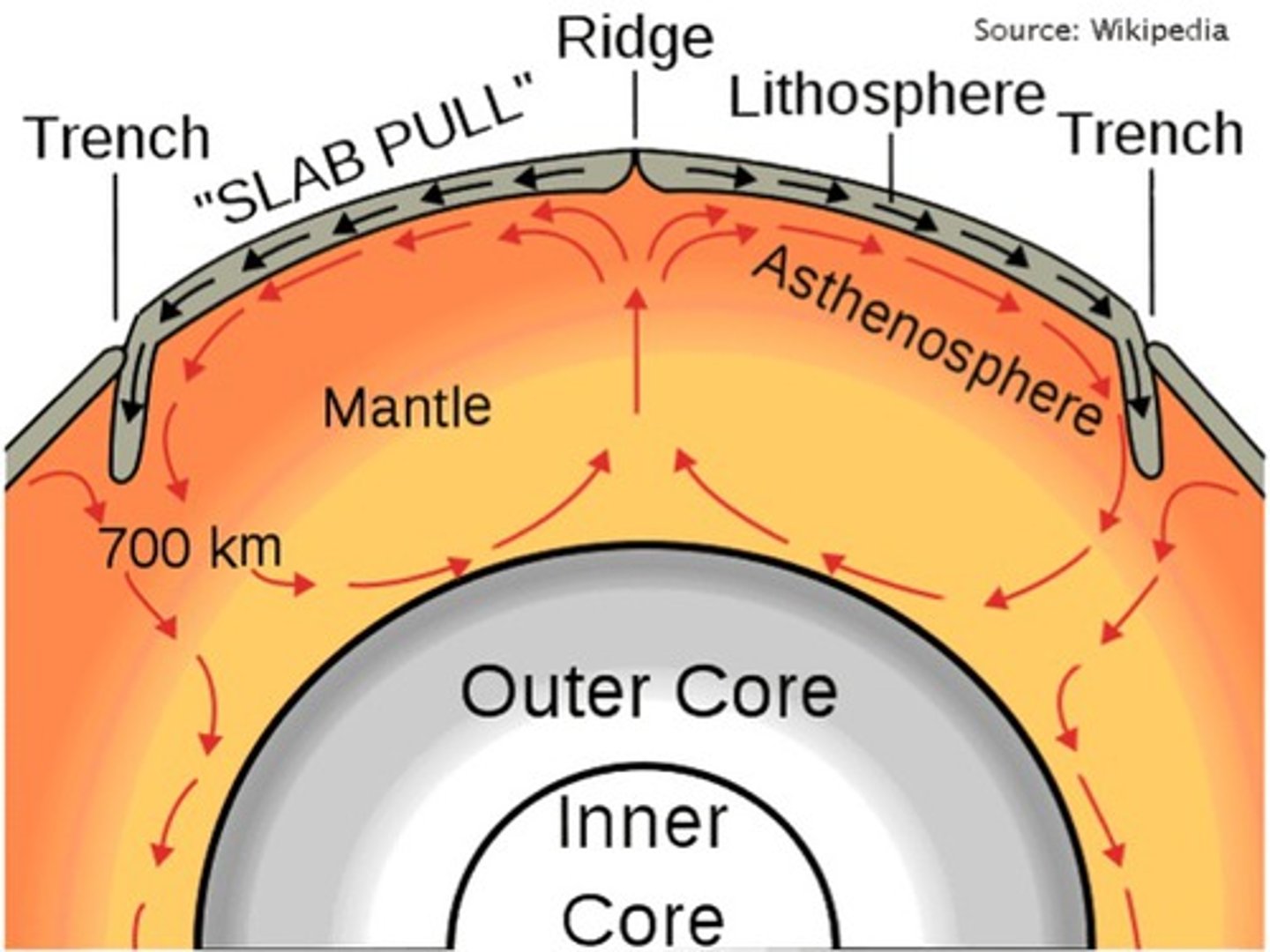
convection currents
a current caused by the rising of heated fluid and sinking of cooled fluid
Magma
A molten mixture of rock-forming substances, gases, and water from the mantle
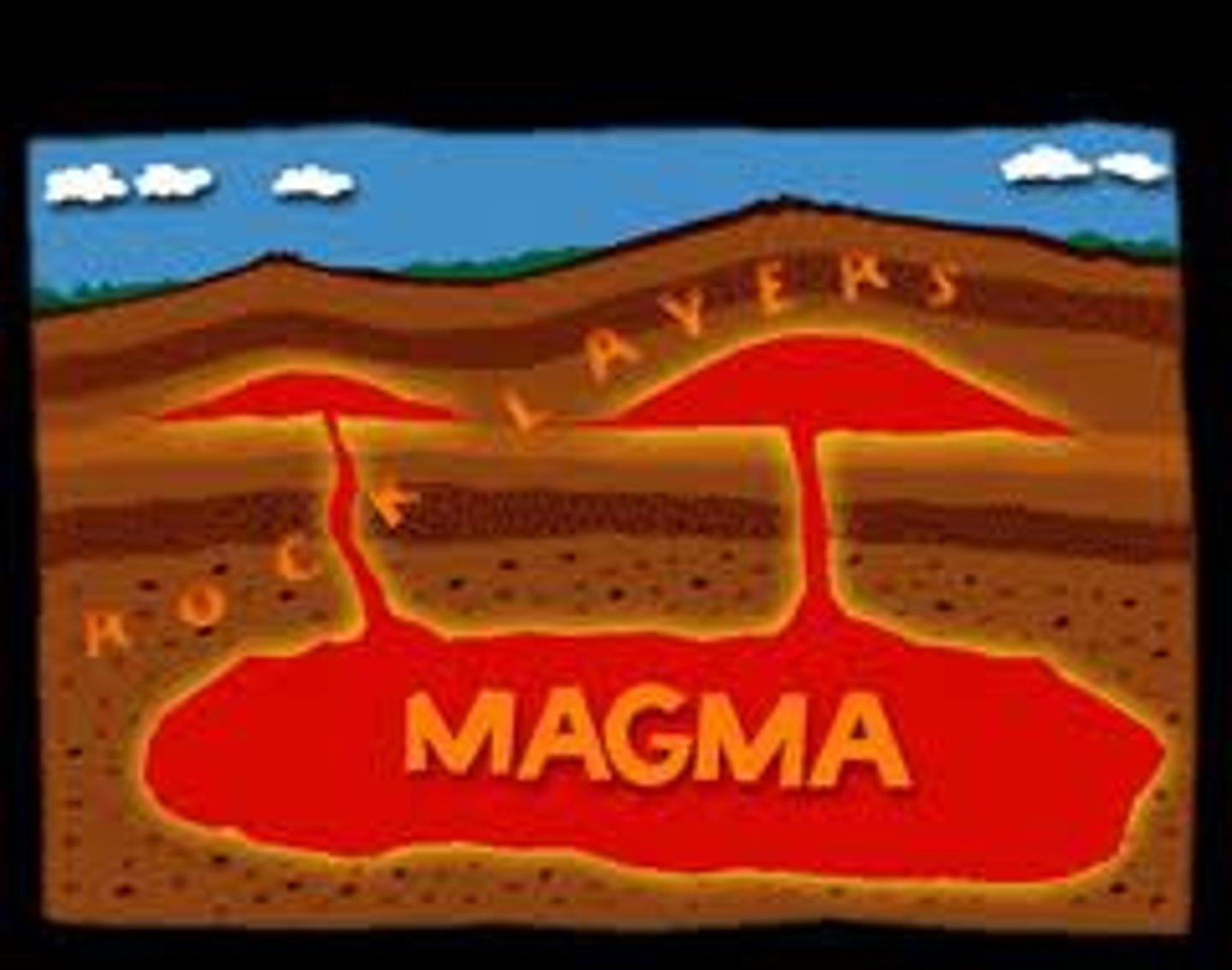
Lava
Liquid magma that reaches the surface; also the rock formed when liquid lava hardens.

plate tectonics/ contiental drift
The theory that pieces of Earth's lithosphere are in constant motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle.
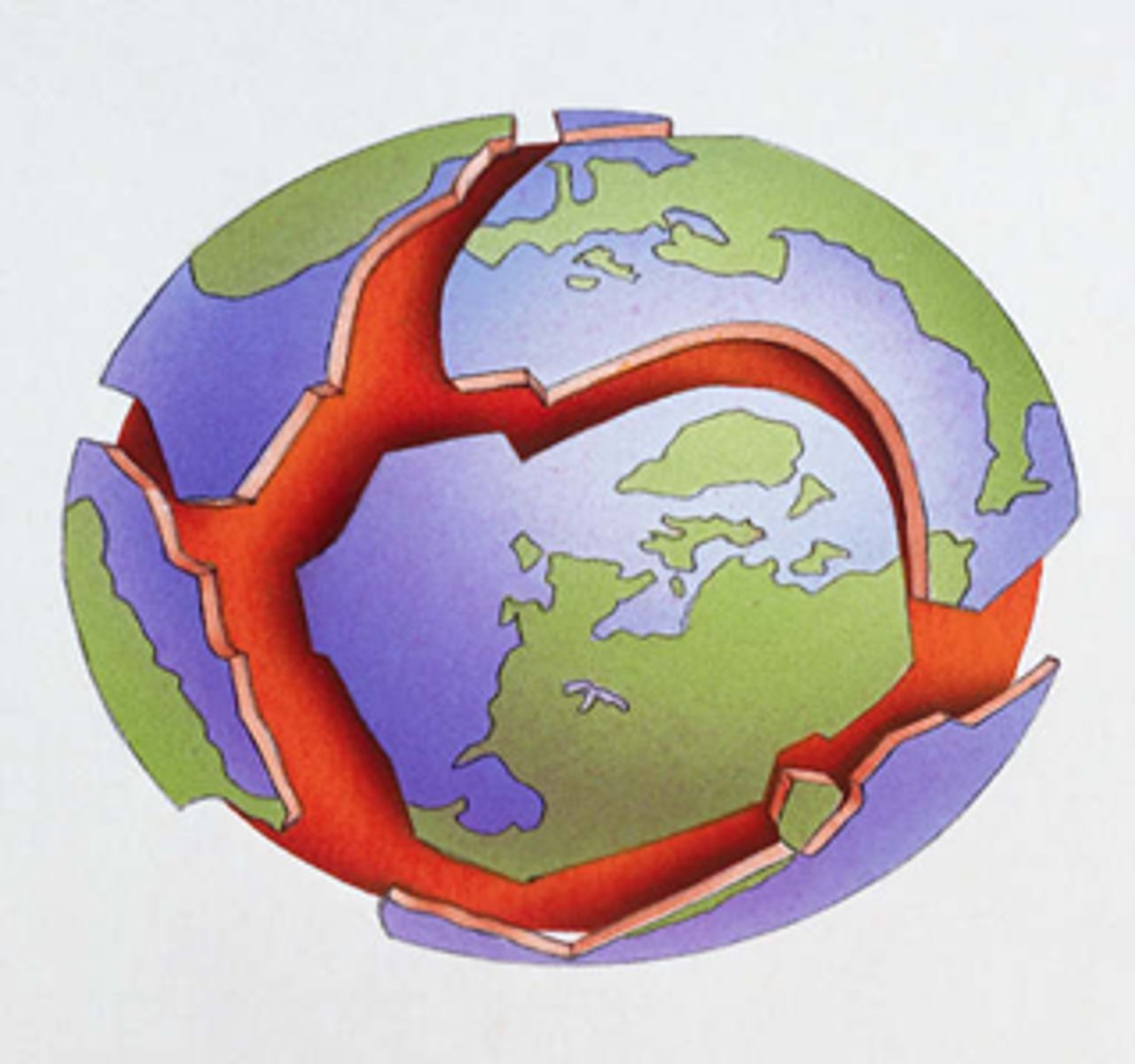

plate boundaries
At plate boundaries, Earth's crust is broken (fault) and rocks slip past each other in one of 3 types of plate boundaries.
convergent boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move toward each other.
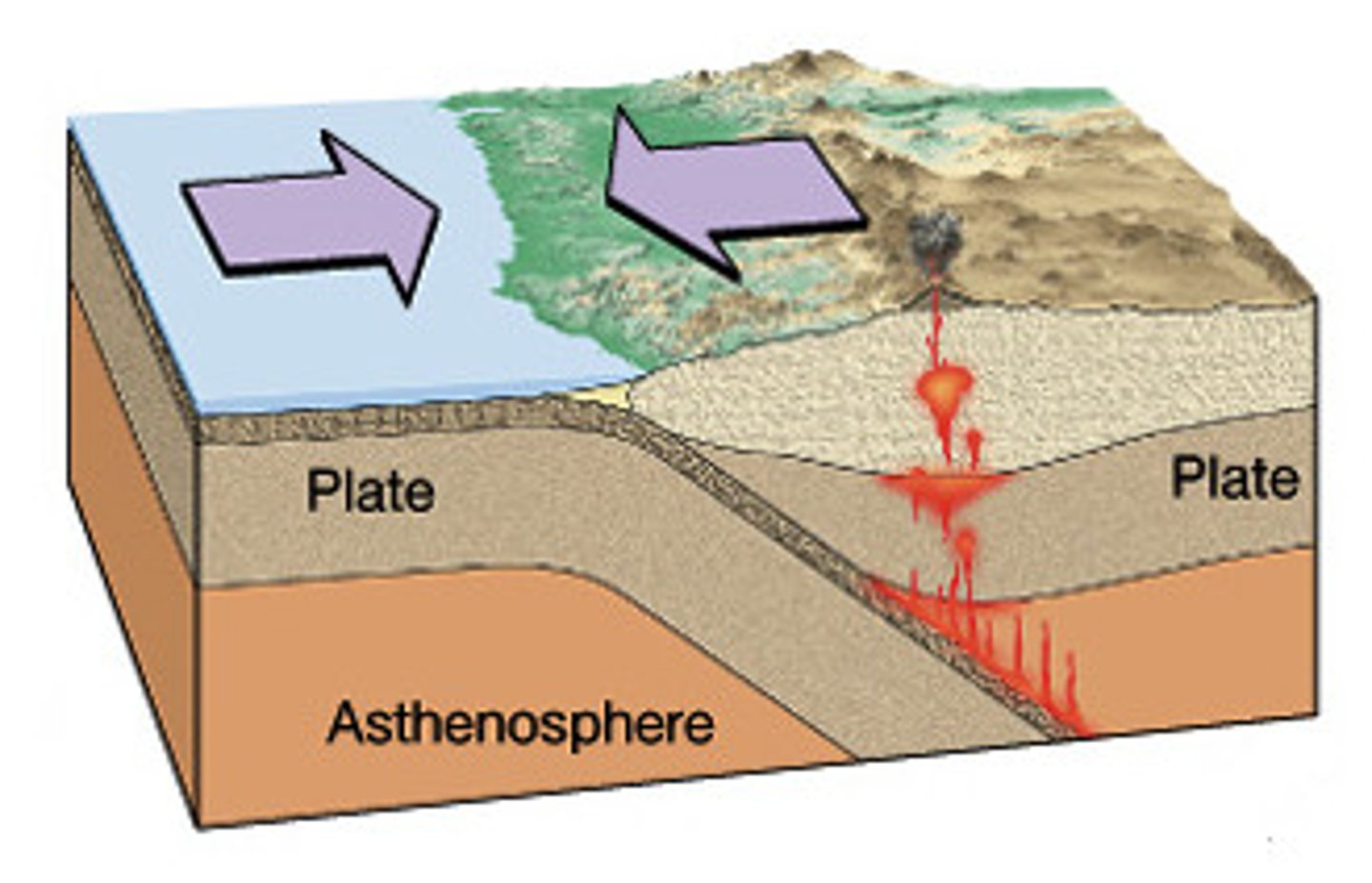
subduction zone
in tectonic plates, the site at which an oceanic plate is sliding under a continental or oceanic plate.
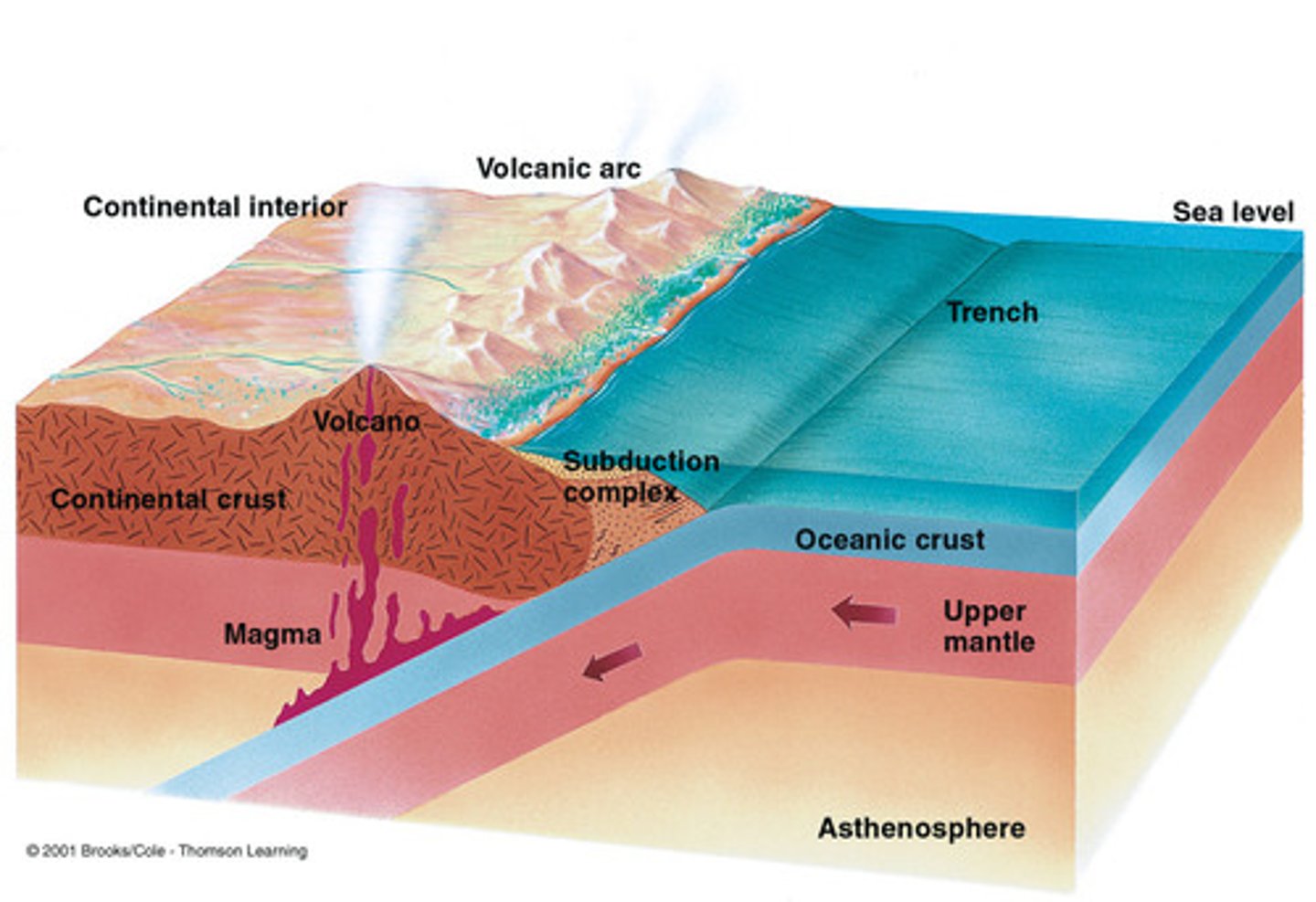
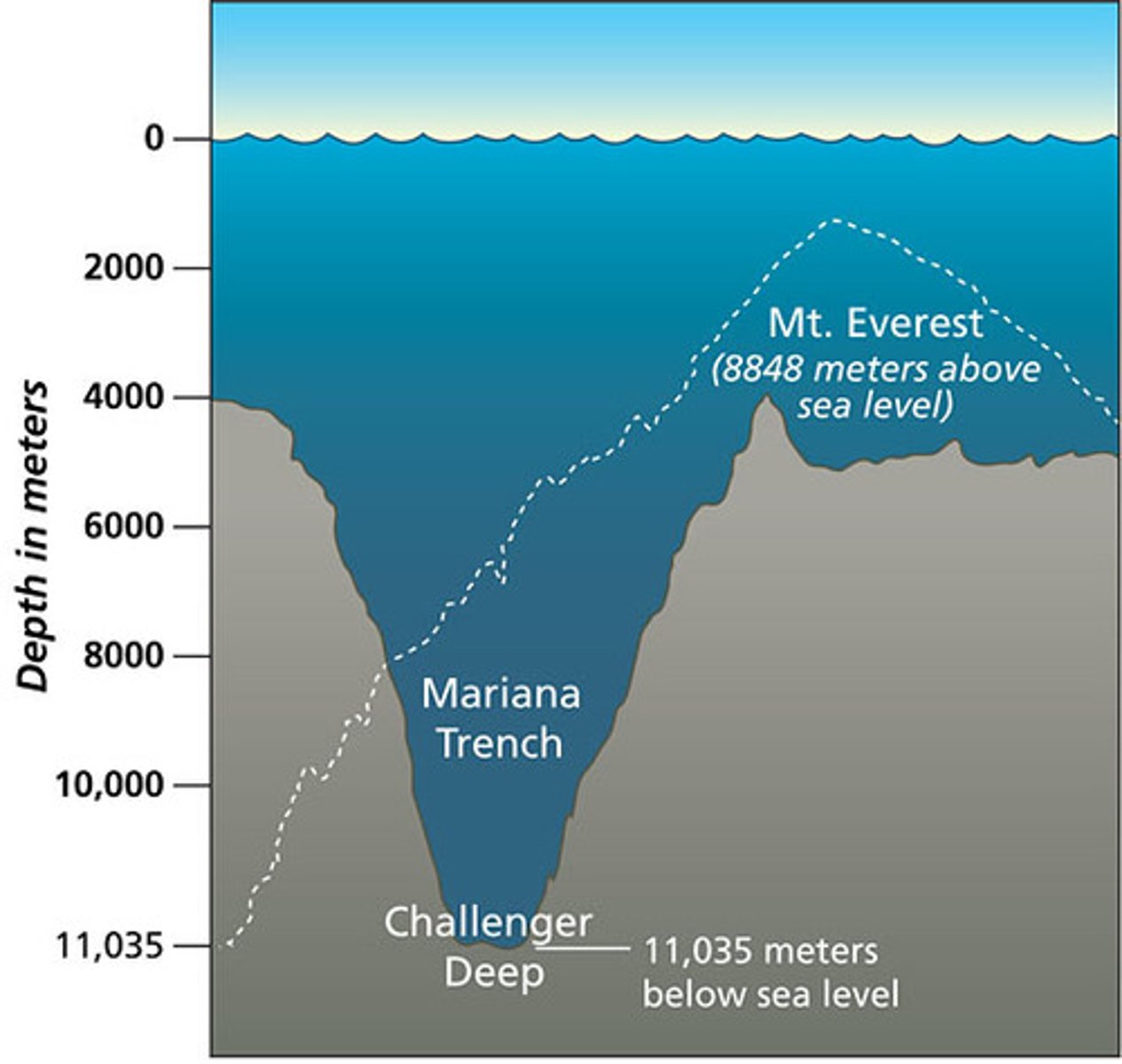
Mariana Trench
The location of the deepest trench on earth made from two oceanic crusts converging.
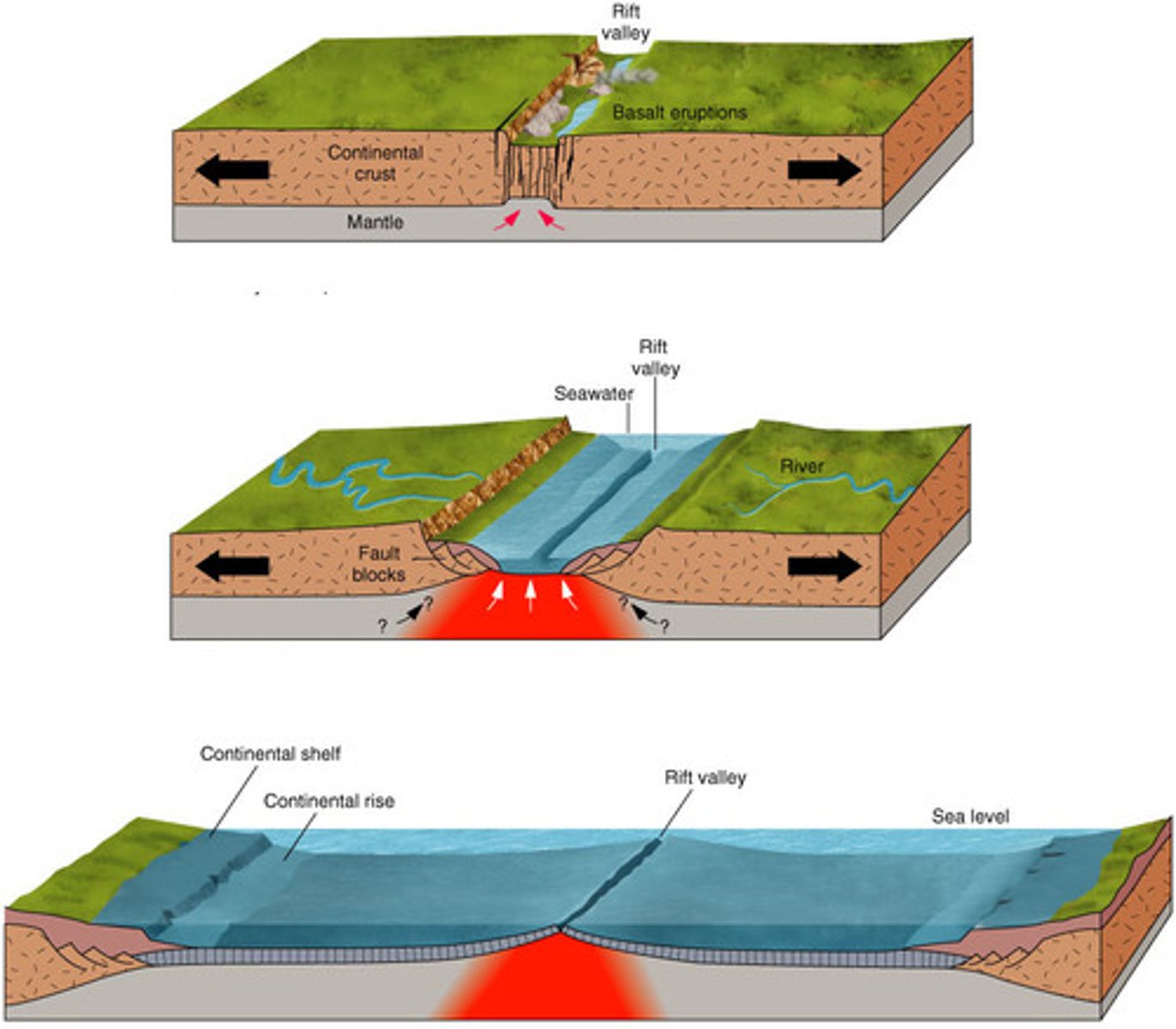
divergent boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move away from each other.
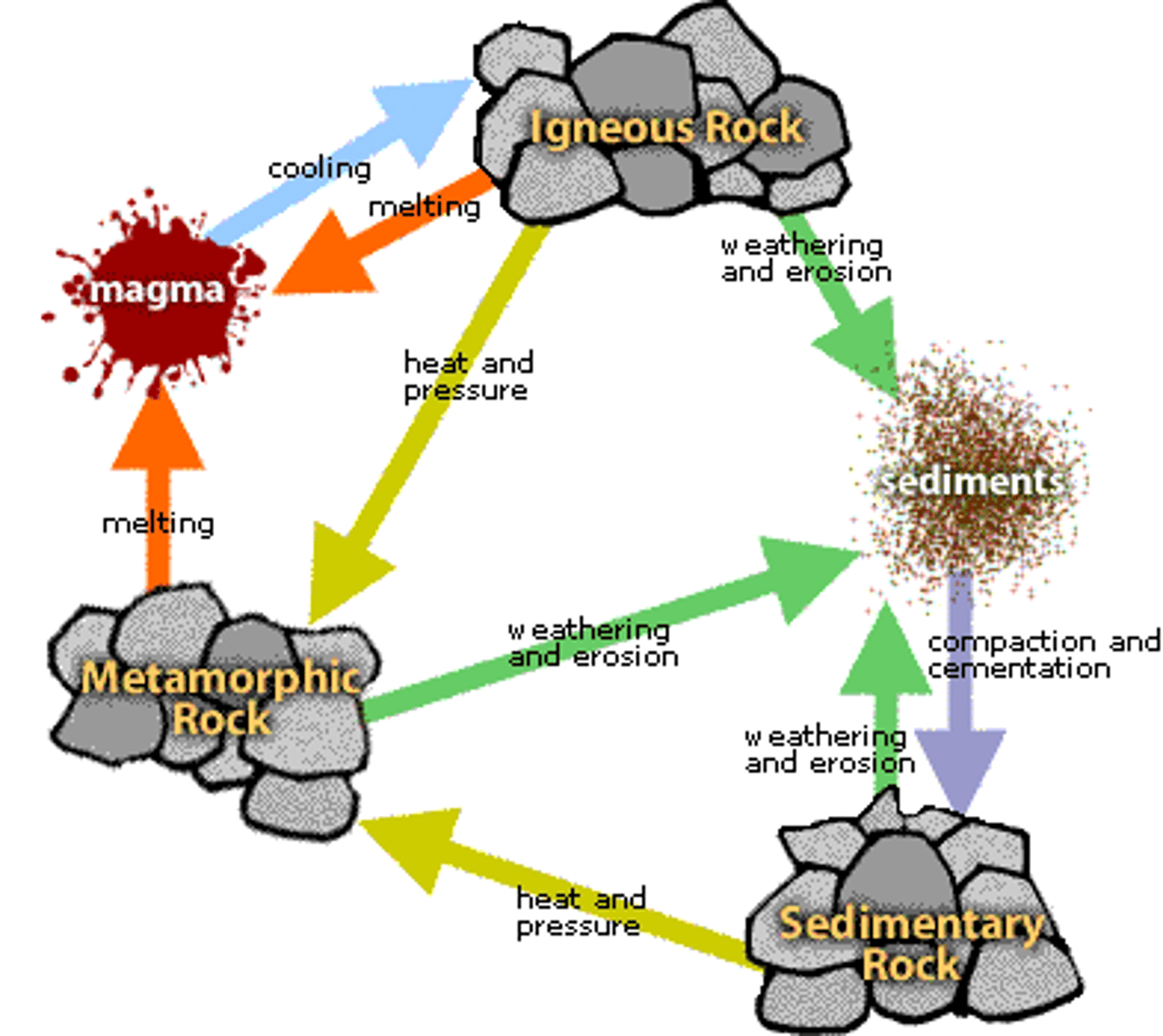
rock cycle
A series of processes on the surface and inside Earth that slowly changes rocks from one kind to another
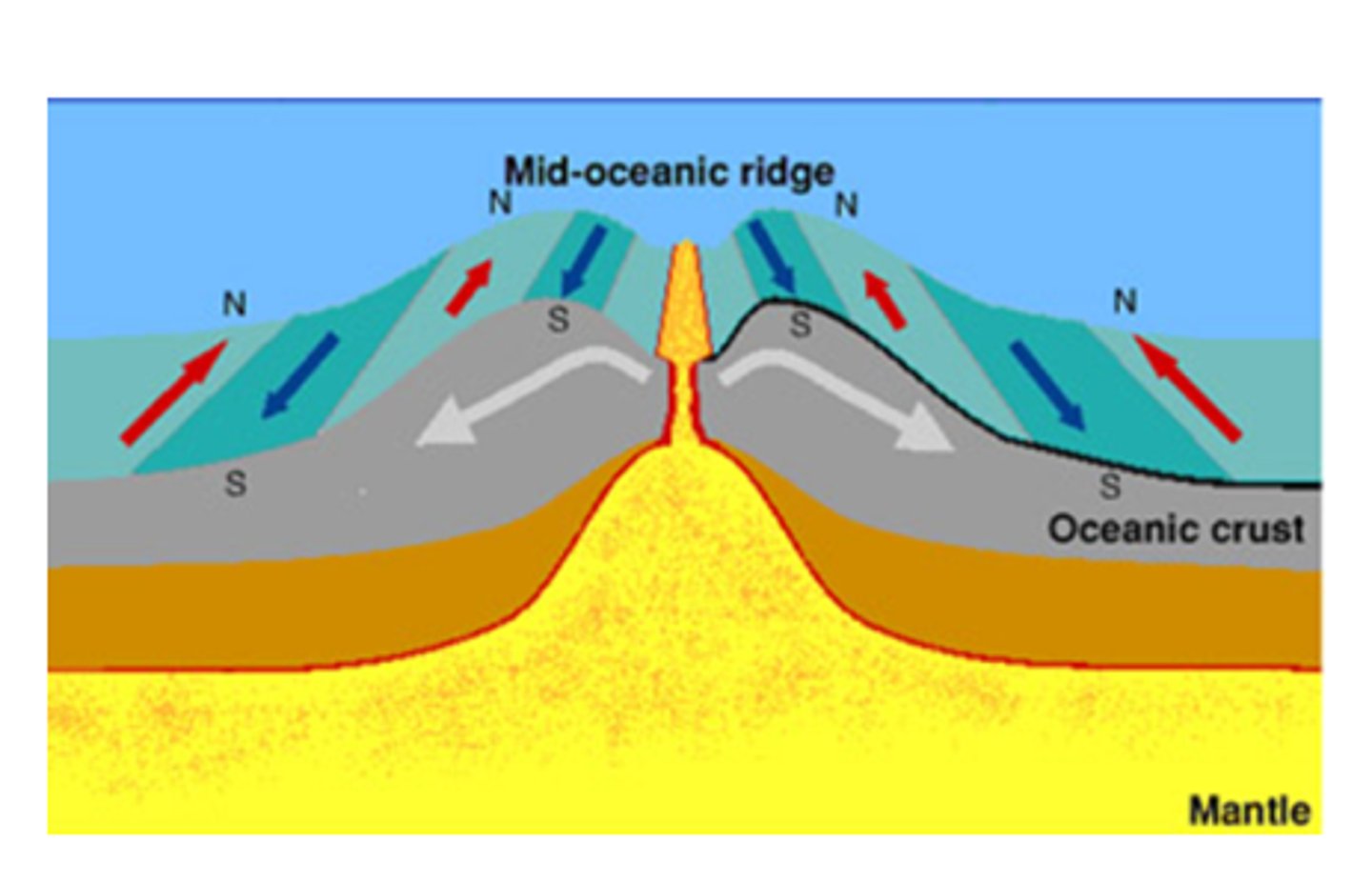
sea-floor spreading
The process by which molten material adds new oceanic crust to the ocean floor
igneous rock
a type of rock that forms from the cooling of molten rock at or below the surface

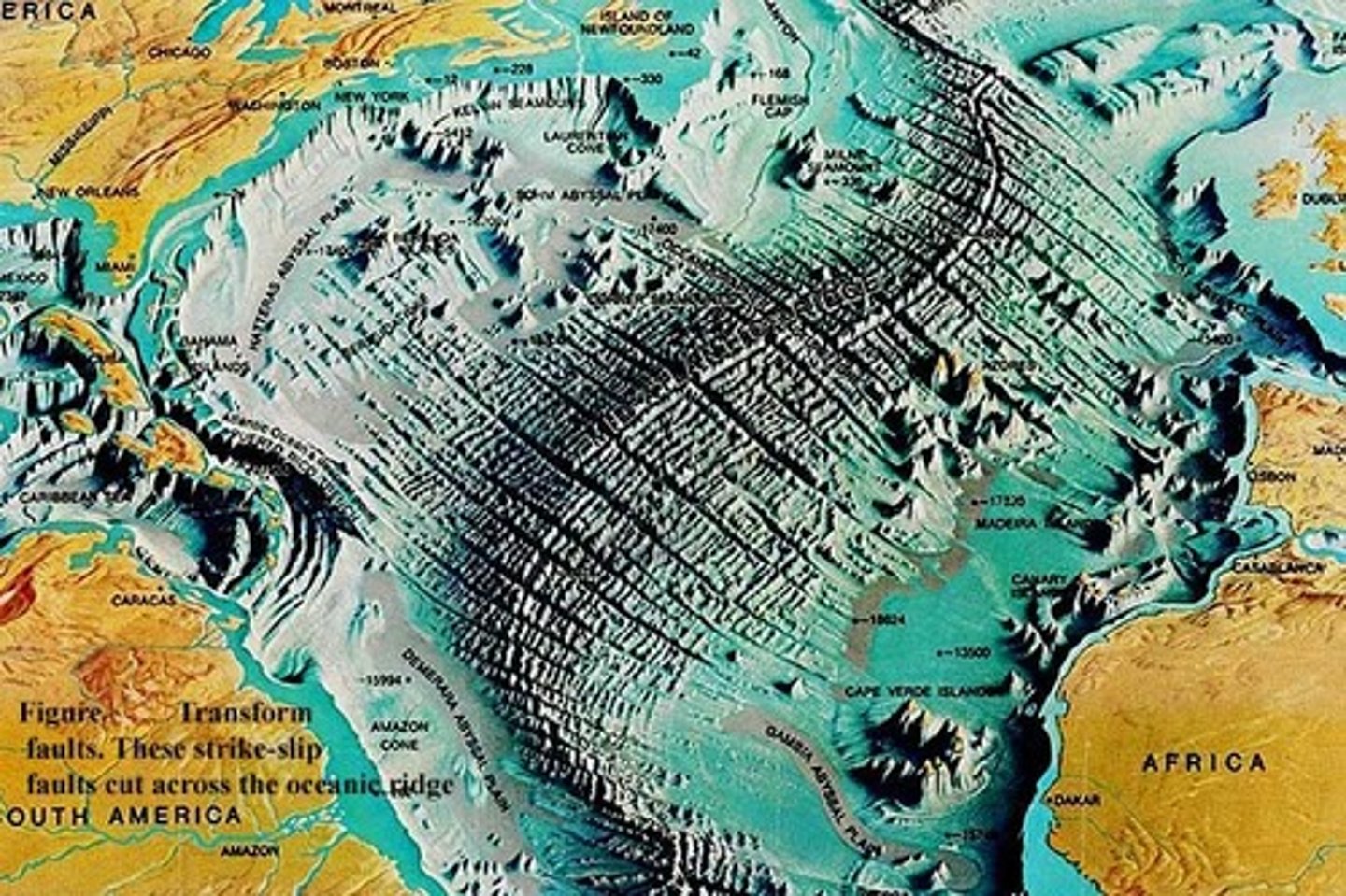
Mid-Atlantic Ridge
divergent boundary in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean
sedimentary rock
A type of rock that forms when particles from other rocks or the remains of plants and animals are pressed and cemented together

East Pacific Rise
This is an example of sea floor spreading at a divergent boundary.
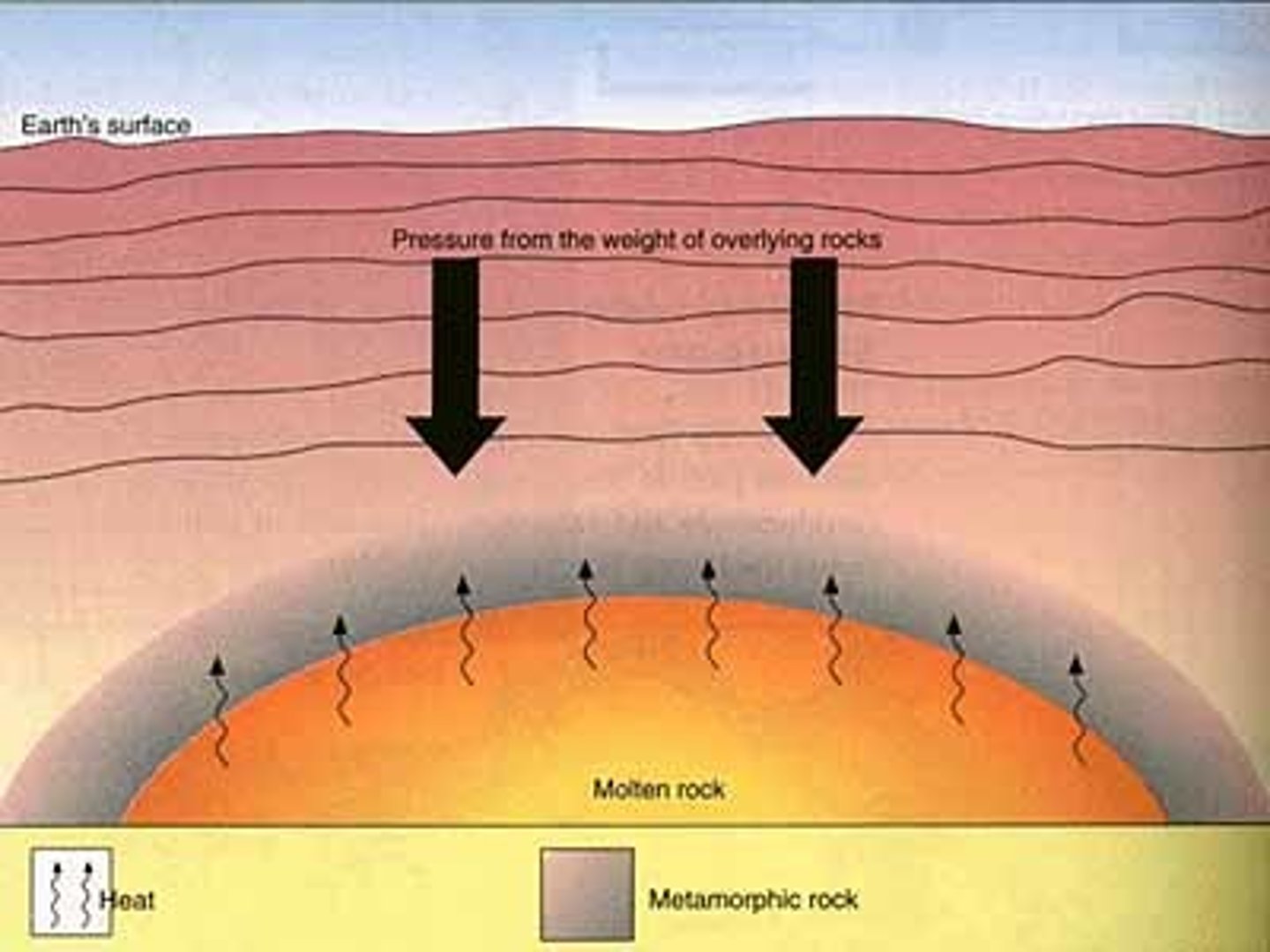
metamorphic rock
A type of rock that forms from an existing rock that is changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions.
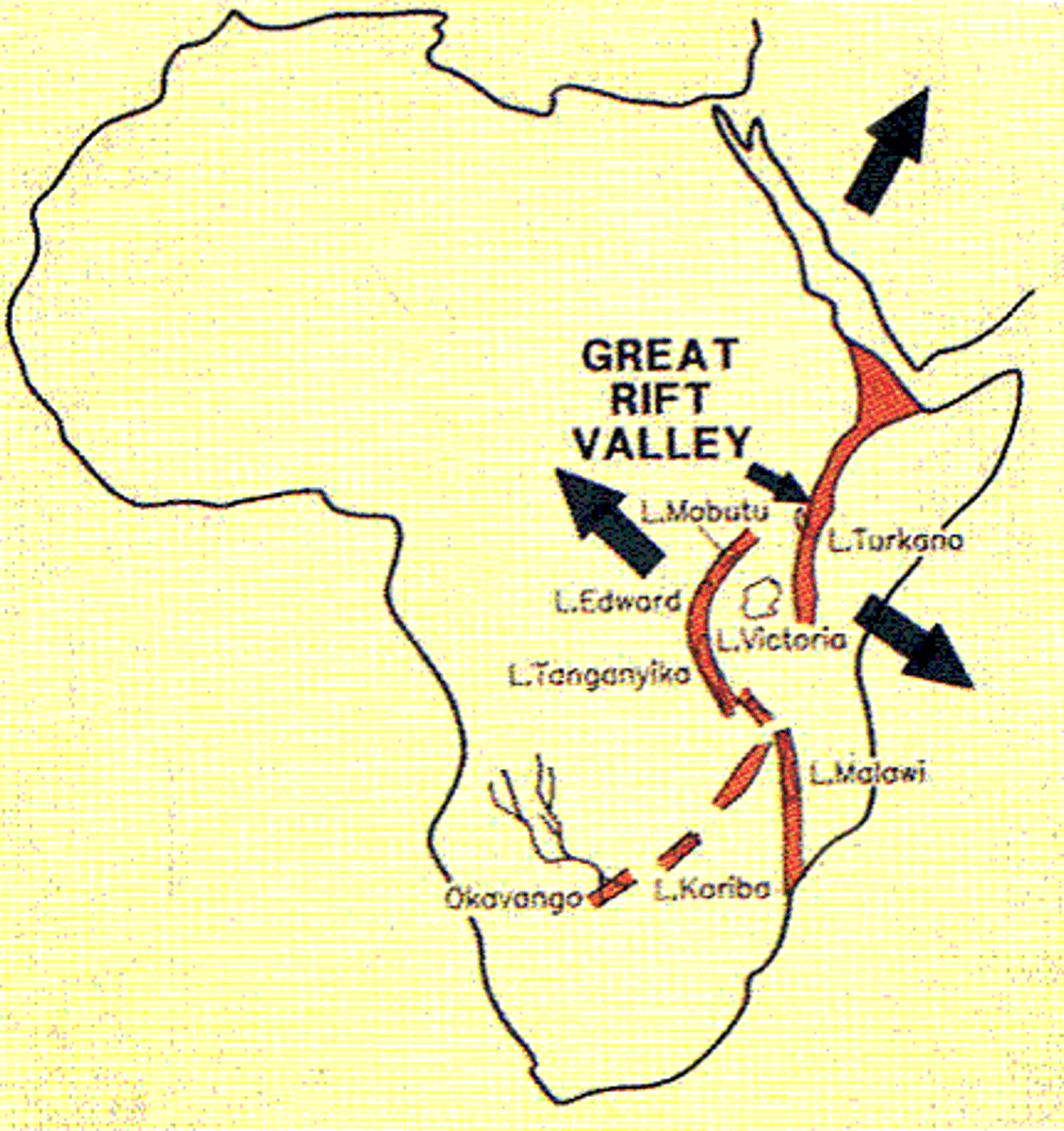
Great Rift Valley
the largest rift in the earth's surface
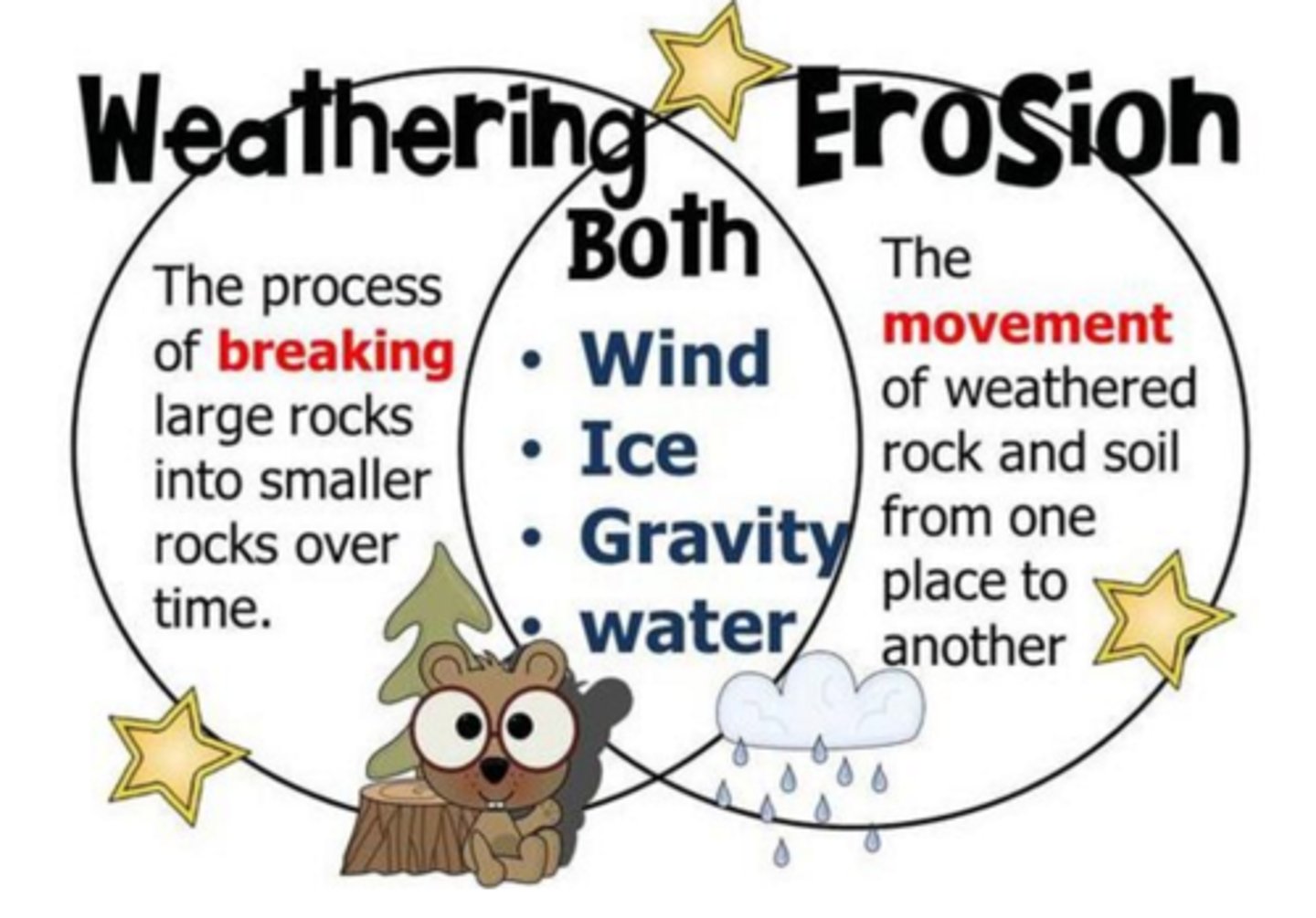
weathering and erosion
rocks breaking down by wind and water
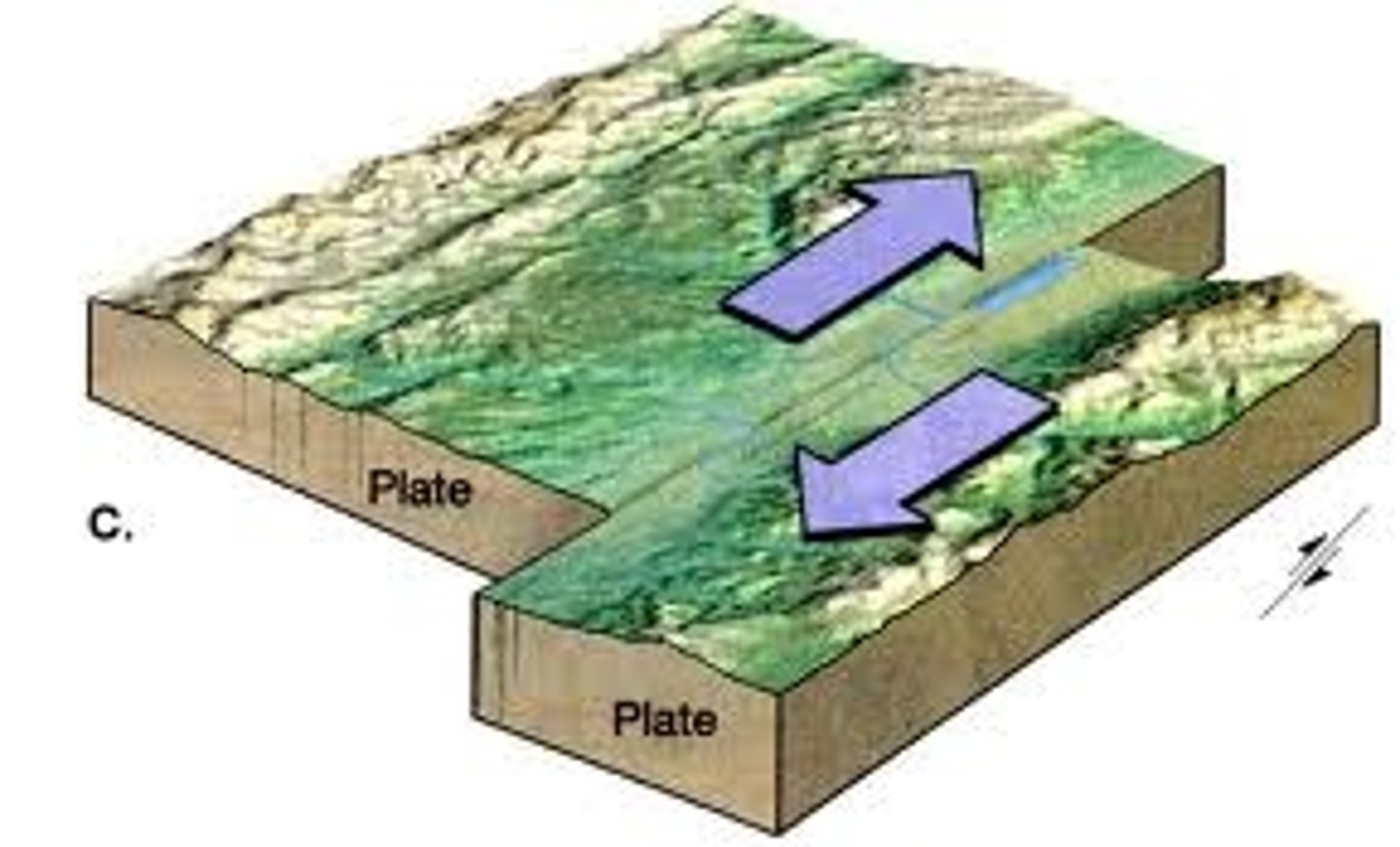
transform boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions
Sediment Deposition
Solid bits of weathered rock are eroded, then deposited by wind, water, ice, and gravity

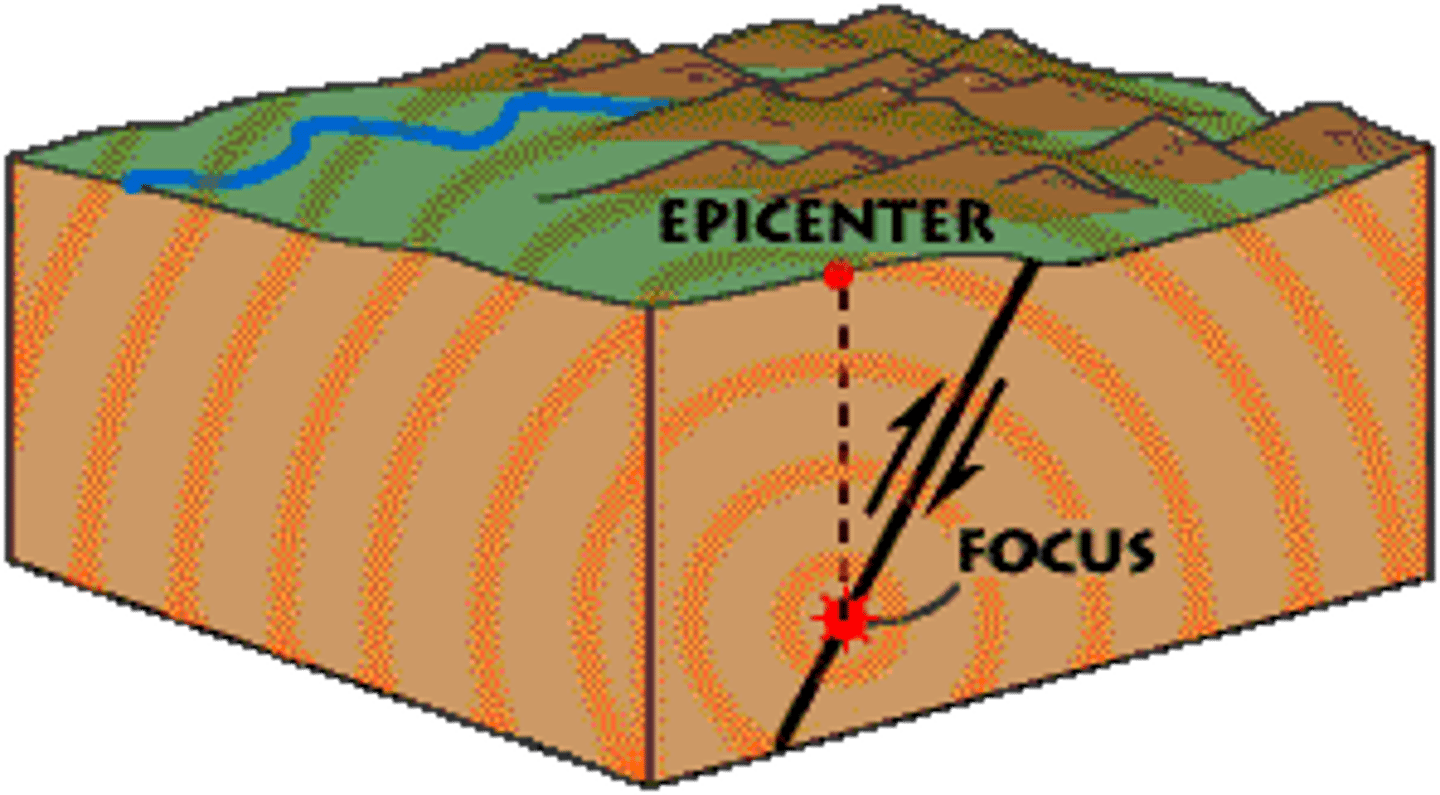
earthquake
The shaking that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth's surface.
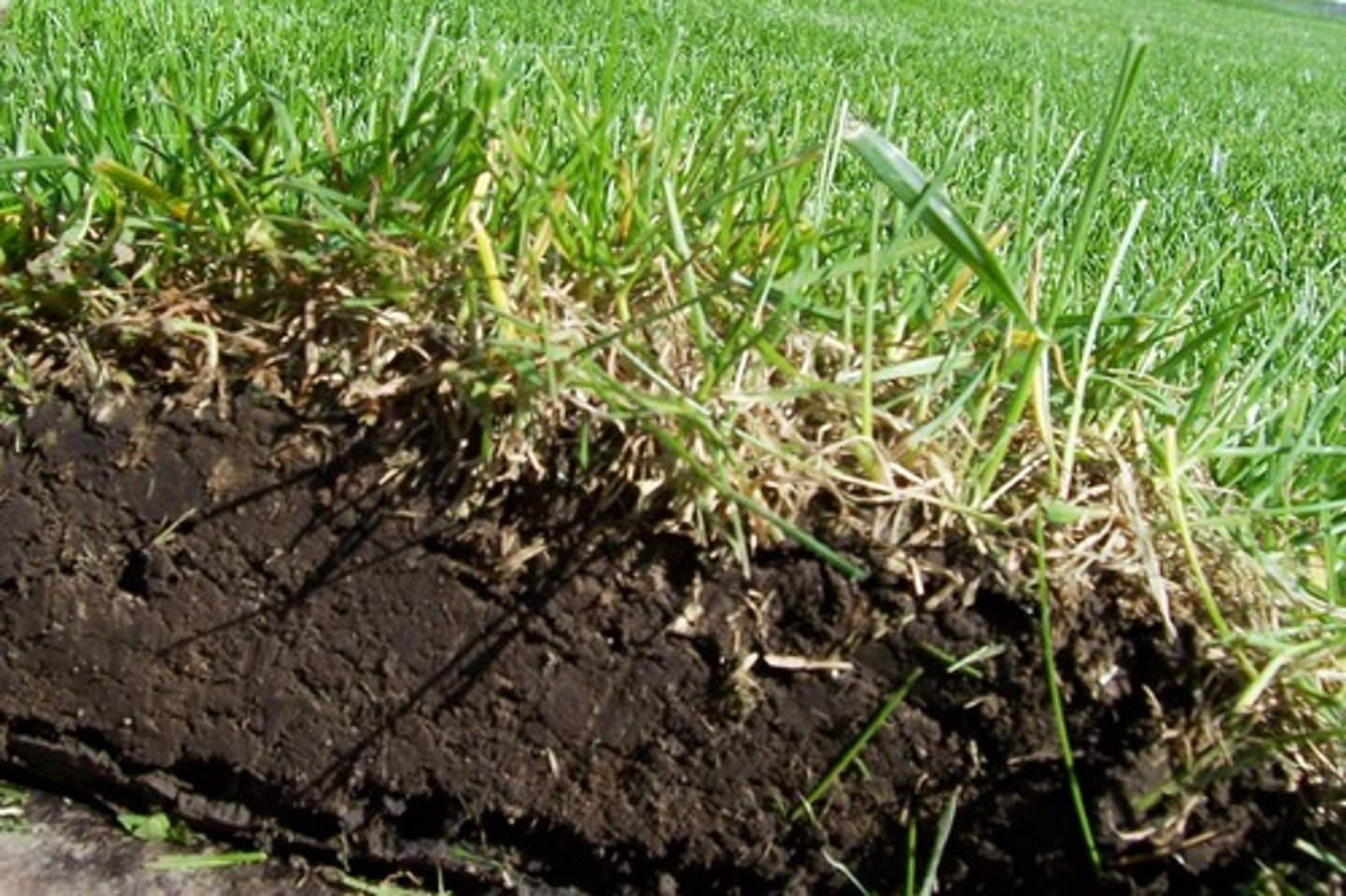
soil
The loose, weathered material on Earth's surface in which plants can grow.

seismic activity
the frequency and intensity of earthquakes experienced over time
parent material
the rock material from which the inorganic components of a soil are derived
Epicenter
Point on Earth's surface directly above an earthquake's focus
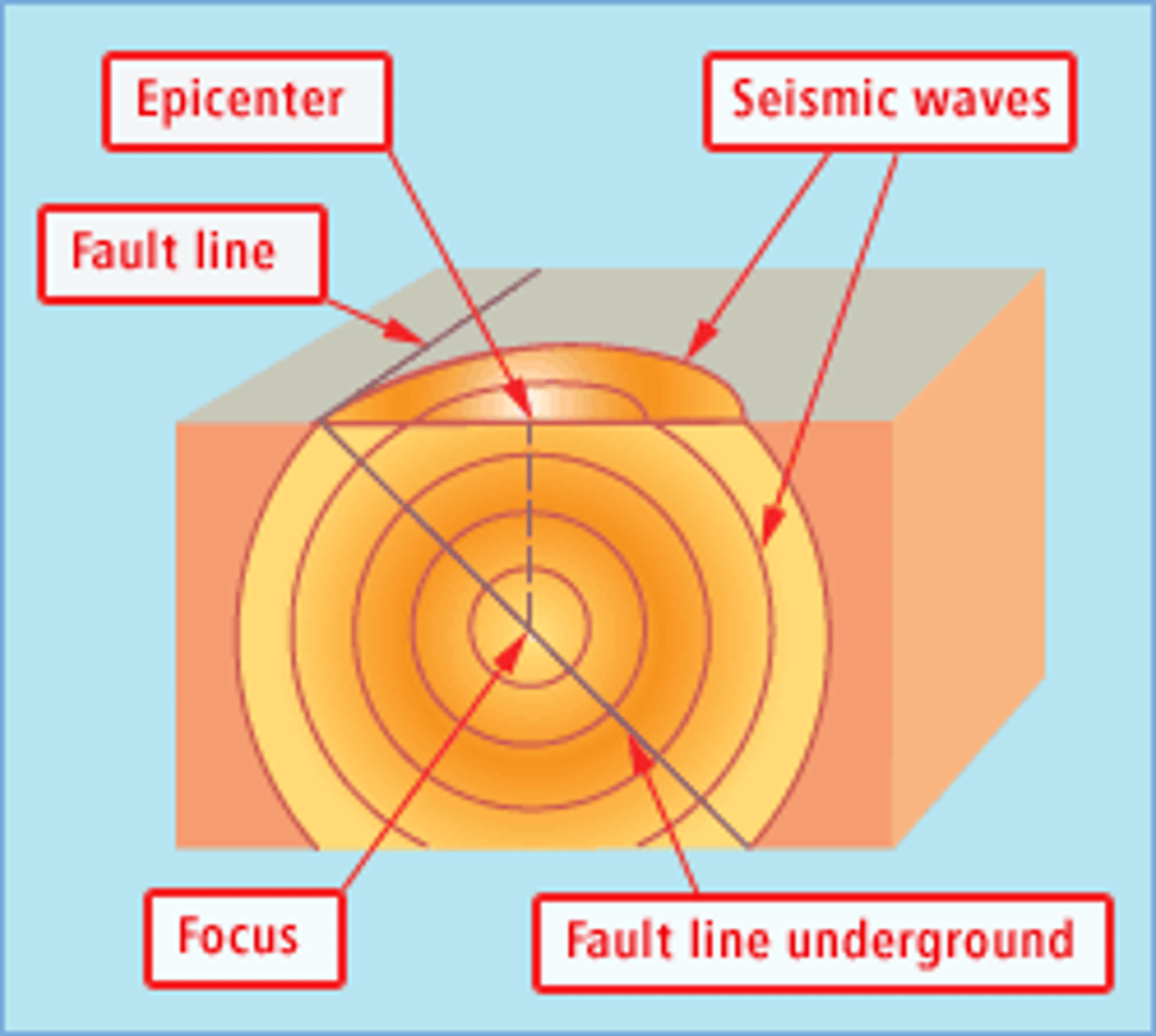
Soil horizons in order
O, A, E, B, C, R
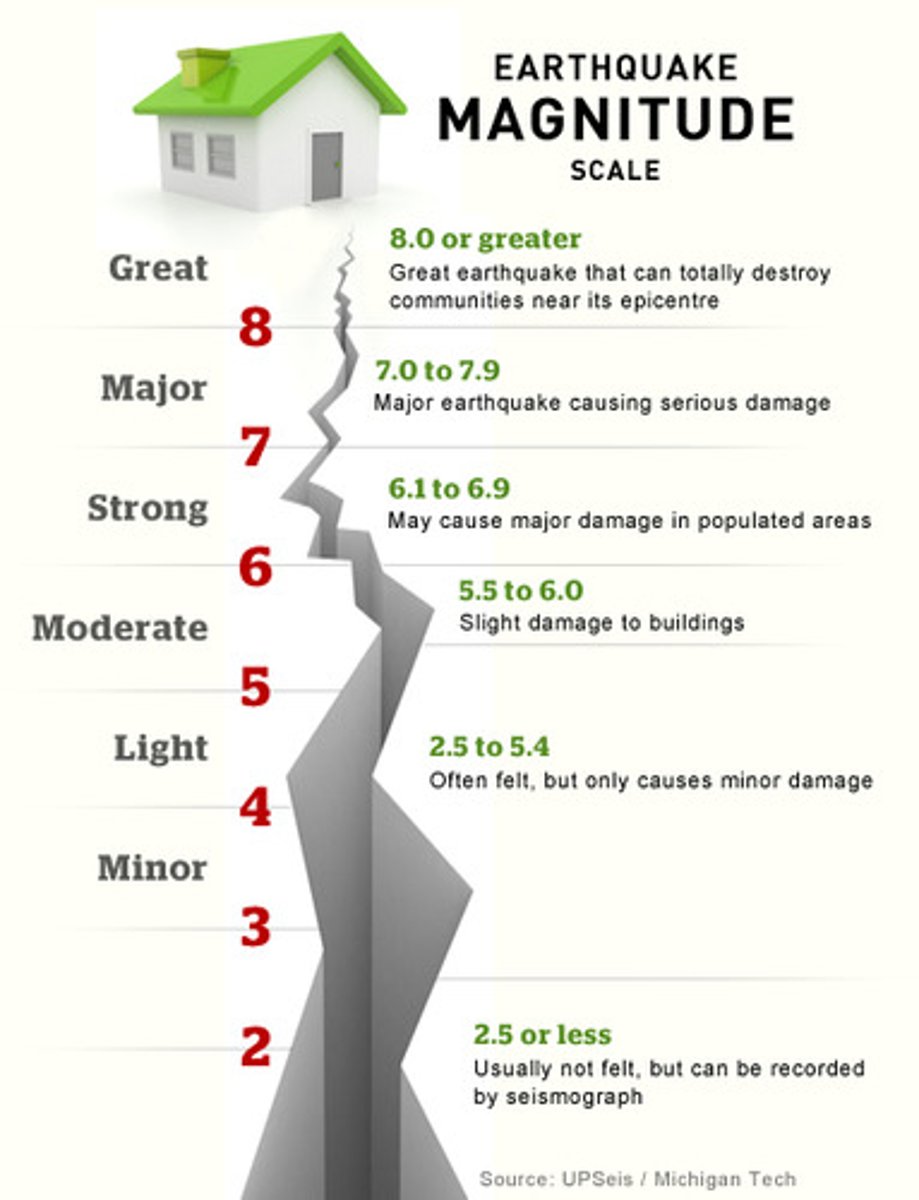
Richter scale
a logarithmic scale of 1 to 10 used to express the energy released by an earthquake
Organic Layer (O-horizon)
The uppermost layer; it is rich in organic material.

Volcanoes
an opening in the Earth's crust through which molten lava, ash, and gases are ejected.

humus layer
incomplete decomposition on top of the soil, layer of dark brown or black material formed

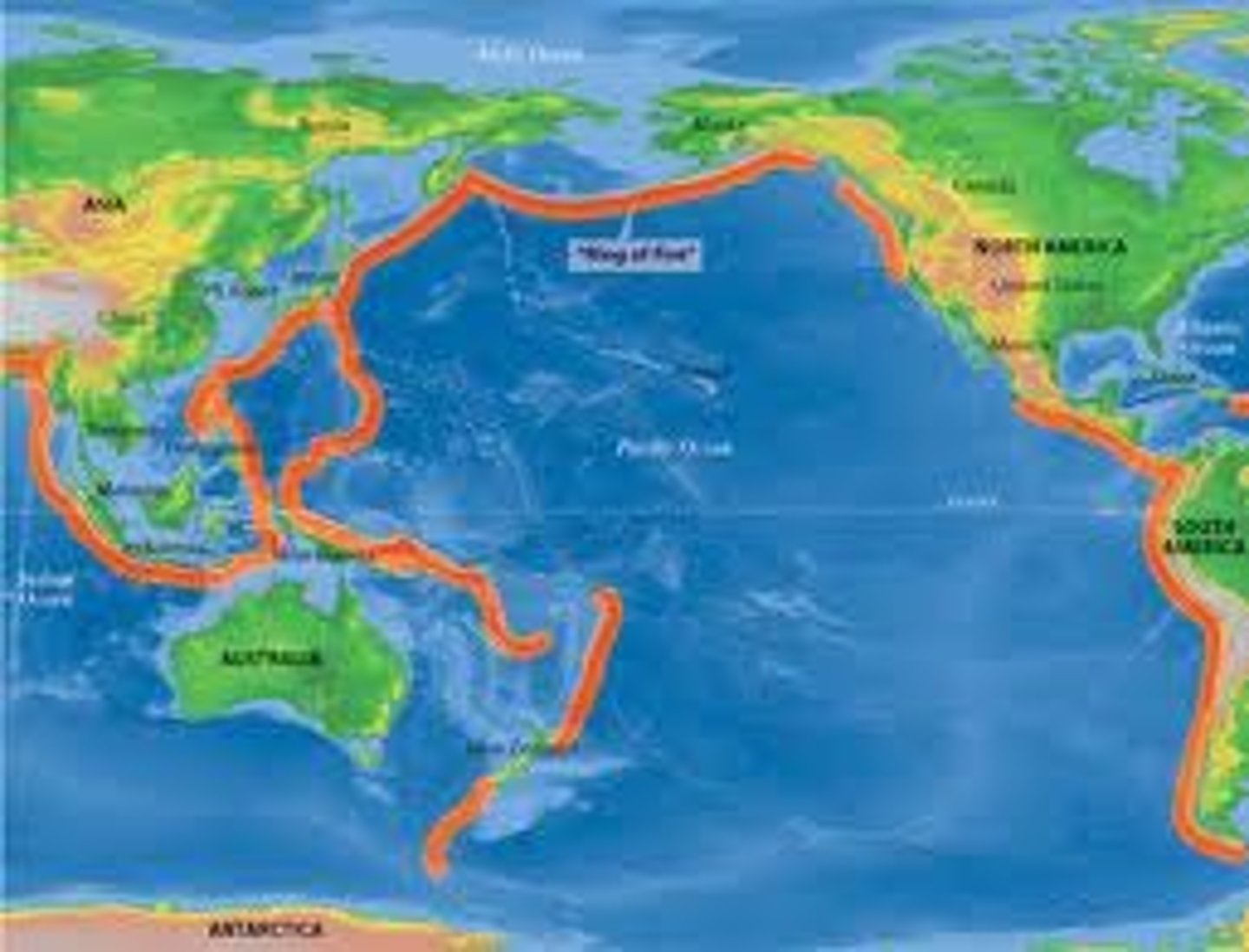
Pacific Ring of Fire
Ocean-girdling zone of crustal instability, volcanism, and earthquakes resulting from the tectonic activity along plate boundaries in the region.
top soil
Mixture of humus, clay, and other minerals that forms the crumbly, topmost layer of soil.

sand
the coarsest soil, with particles 0.05,2.0 mm in diameter.
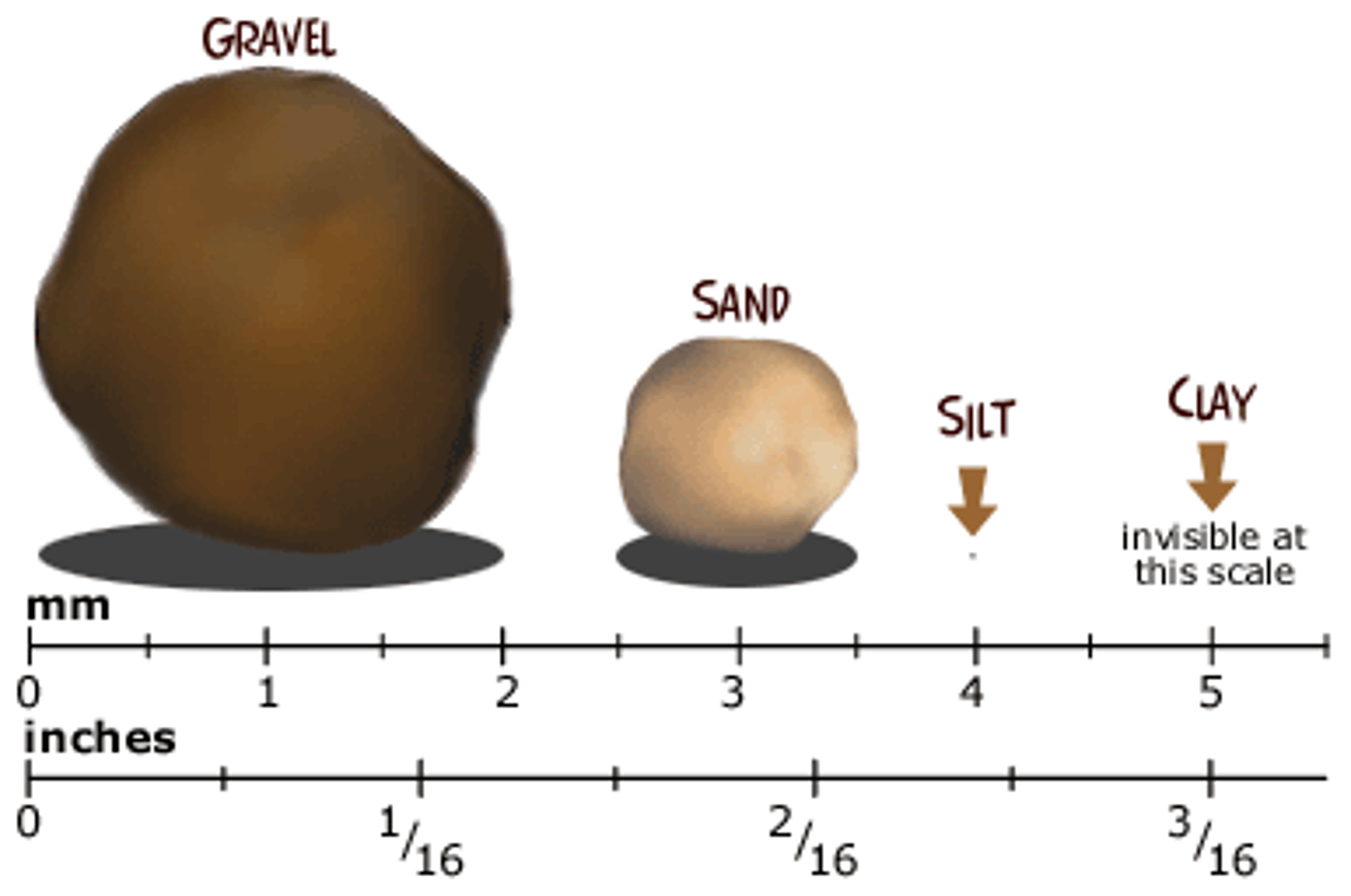
silt
fine particles of fertile soil
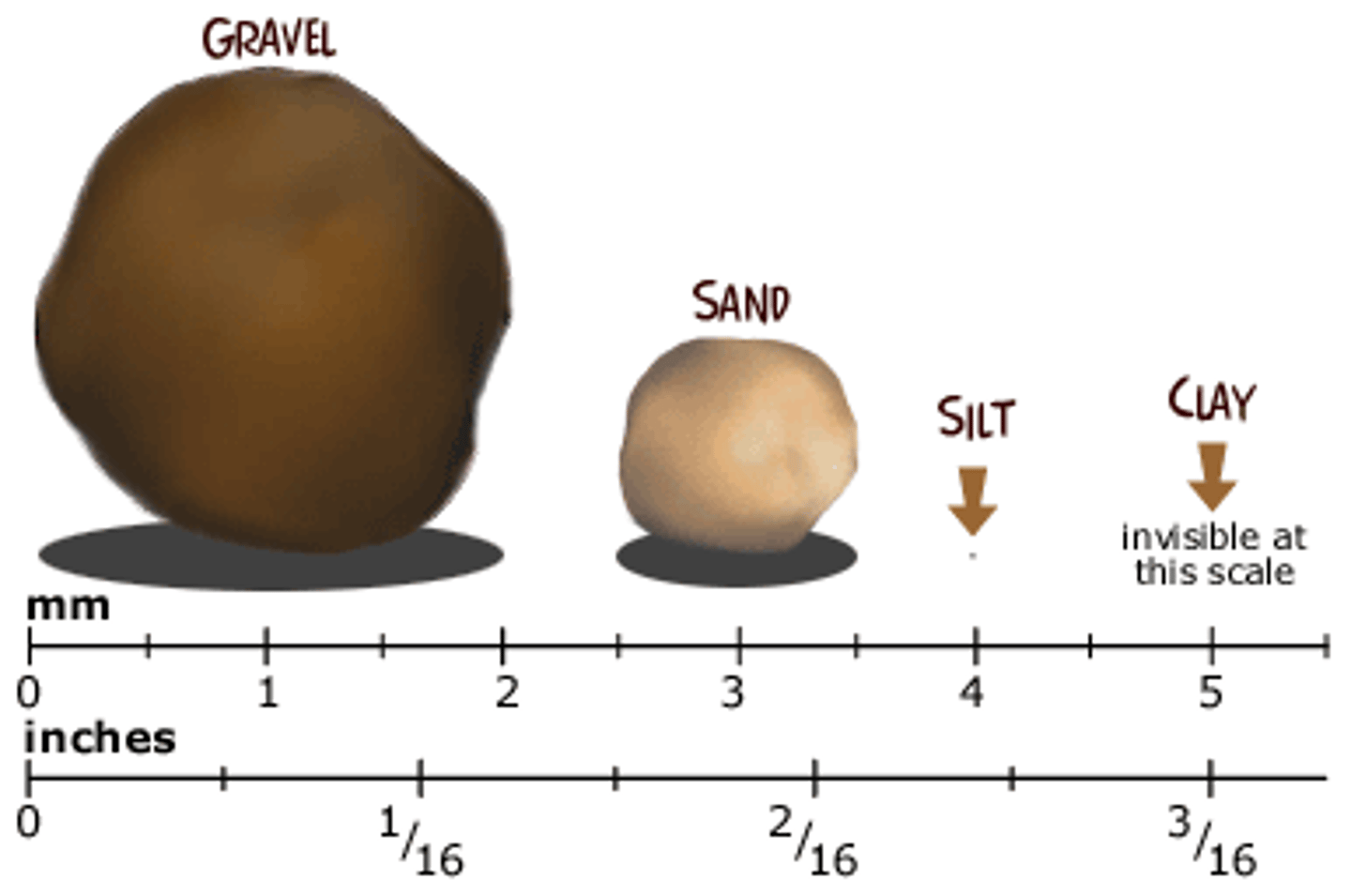
clay
A natural, earthly material that retains its shape and hardens when fired
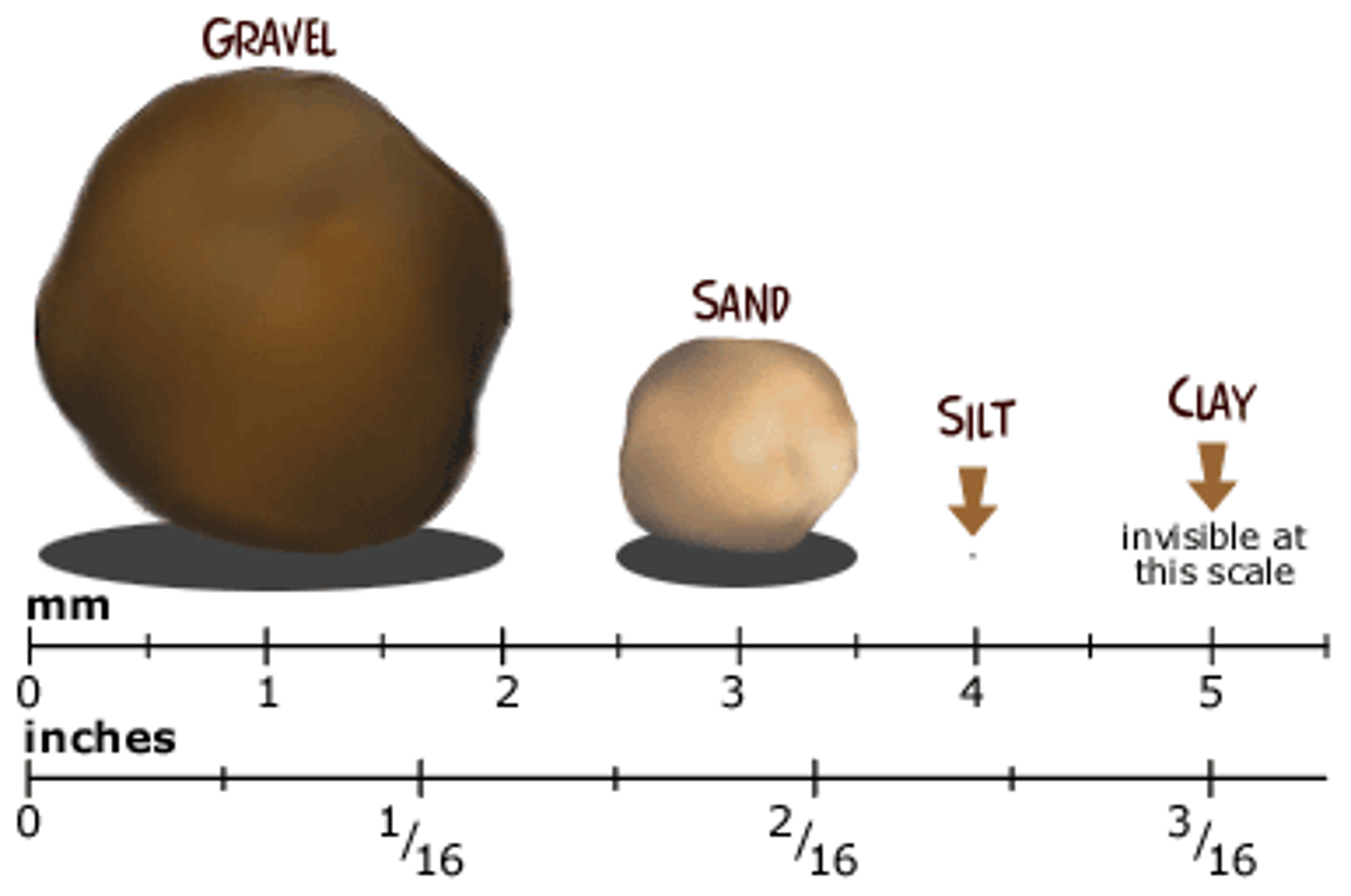
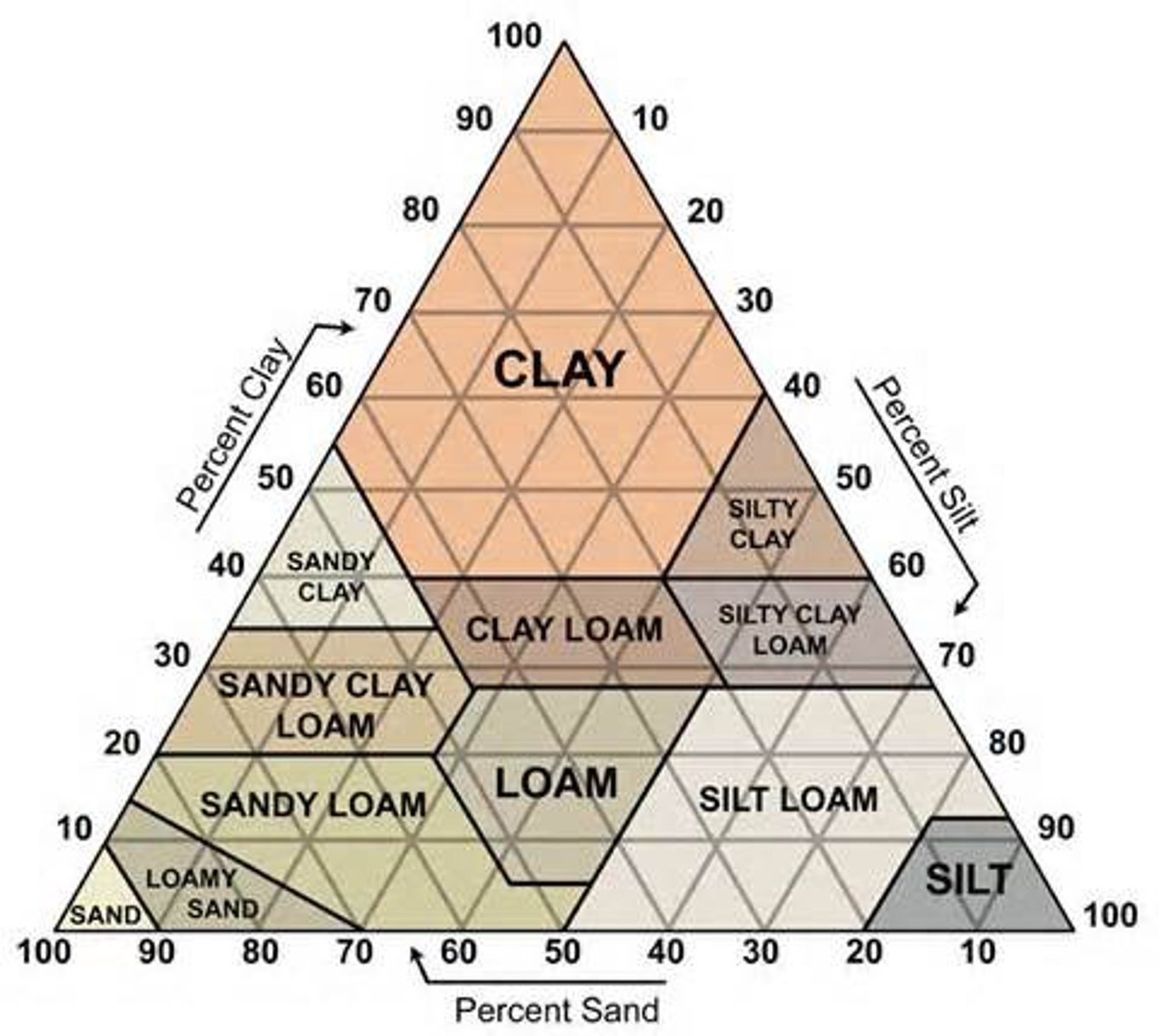
soil triangle
a graphic explanation of the proportions of sand, silt, and clay in soil
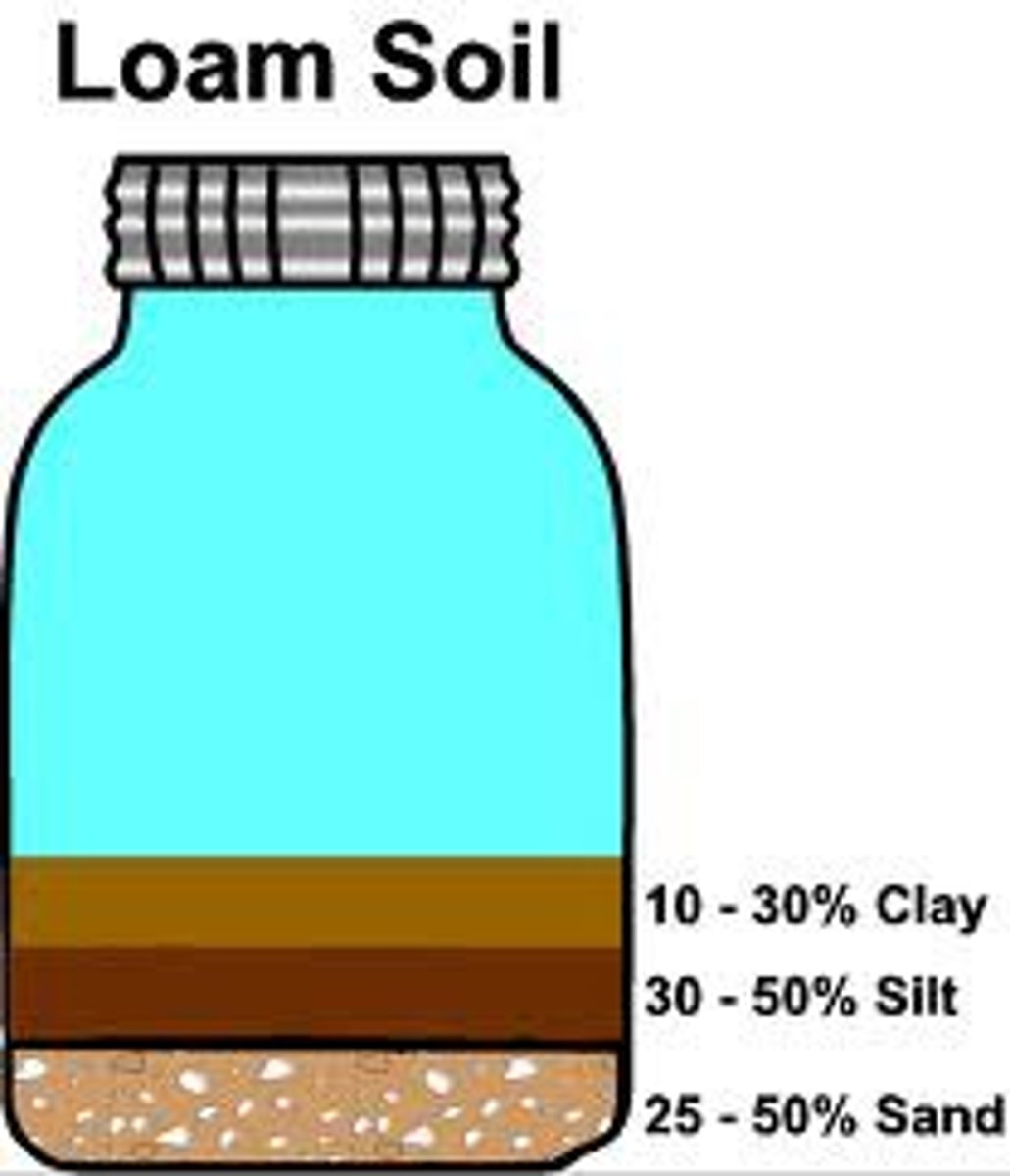
Loam
Rich, fertile soil that is made up of about equal parts of clay, sand, and silt.
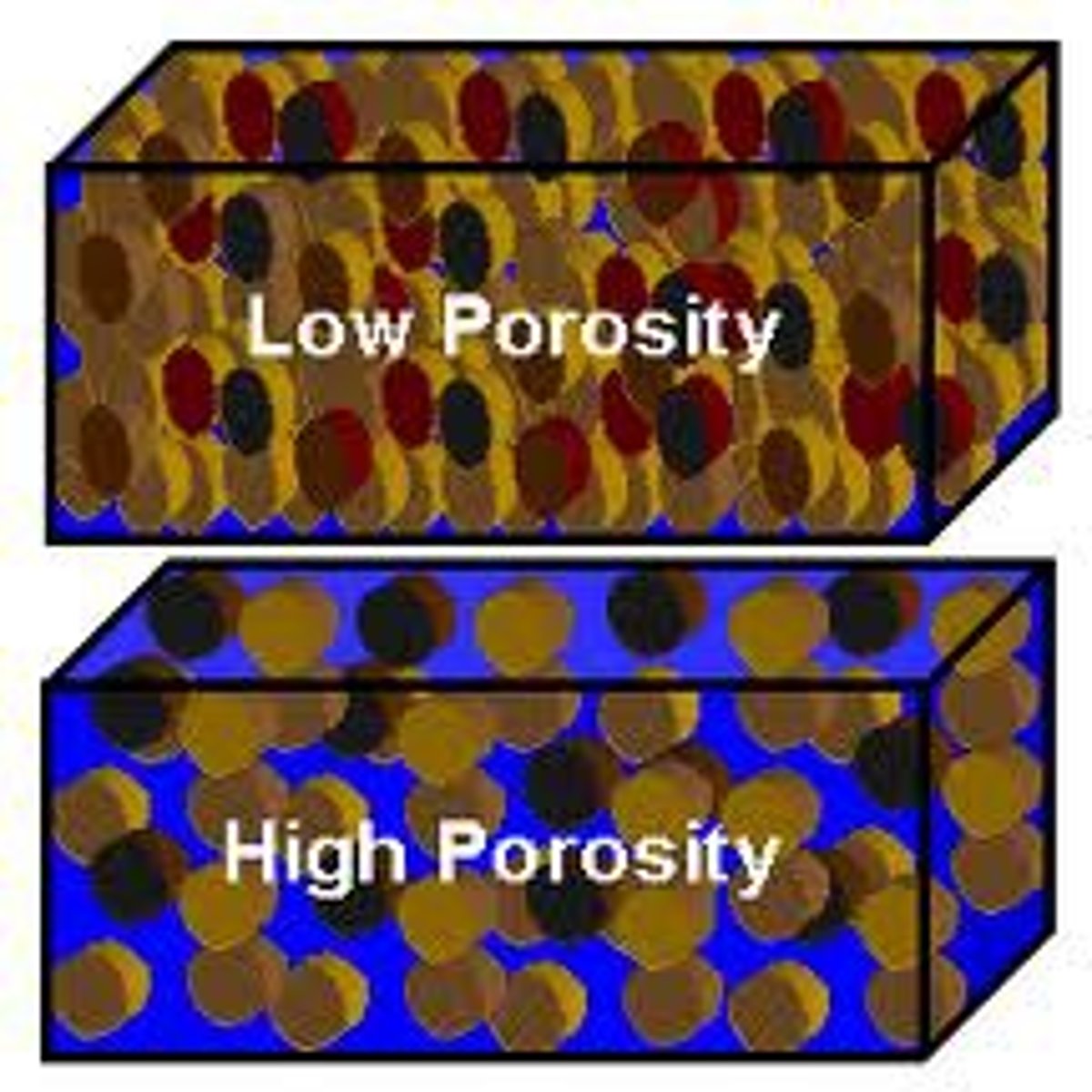
Porosity
the volume of open spaces in rock or soil
Permability
The ability of rock or sediment to let fluids pass through its open spaces or pores.
climate
Overall weather in an area over a long period of time

weather
The condition of Earth's atmosphere at a particular time and place.

Tropsphere
starts at the earths surface, where all weather occurs, temp falls
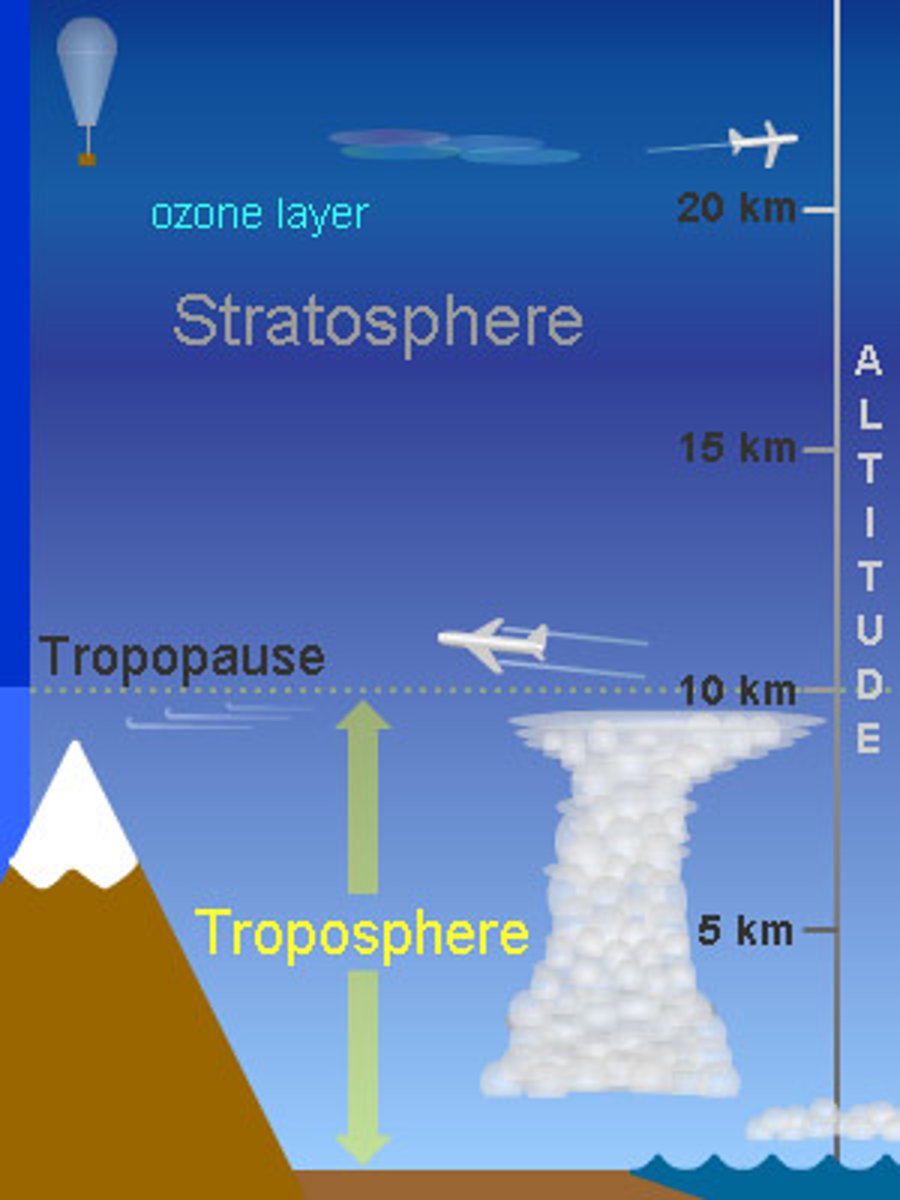
Stratosphere
second layer of the atmosphere, 12 to 50 km, Ozone held here, absorbs UV radiation

Mesosphere
The layer of Earth's atmosphere immediately above the stratosphere
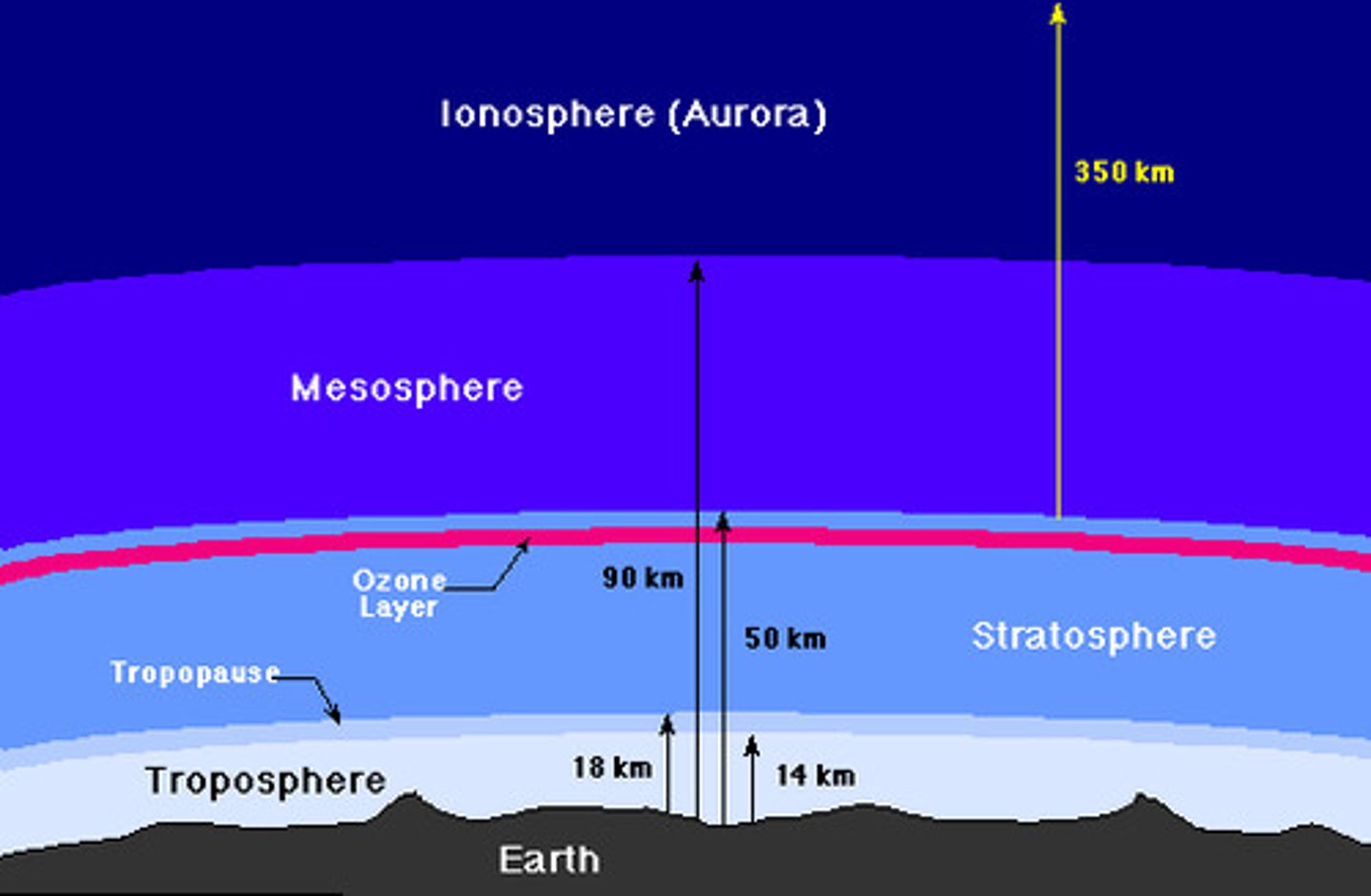
Thermosphere
The uppermost layer of the atmosphere, in which temperature increases as altitude increases

Exosphere
The outer layer of the thermosphere, extending outward into space.

solar radiation
Transmission of energy from the sun in the form of electromagnetic waves.
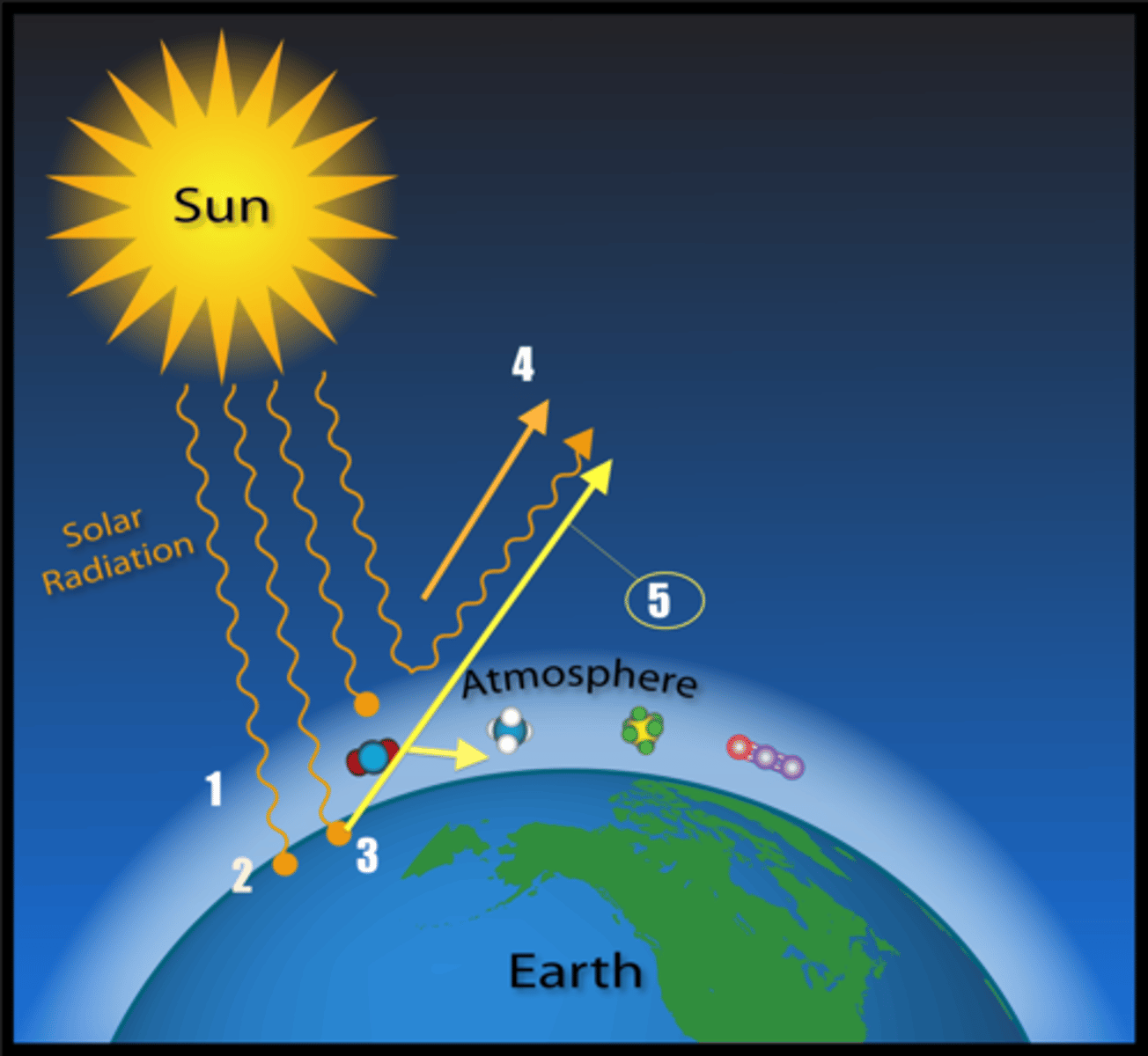
Insolation
incoming solar radiation
infrared radiation
-Radiation felt as heat.
-Absorbed by earth's surface, gases, and particles
-Heats our atmosphere.
-Long, less dangerous wavelength
Water holding capacity
how well soil can retain water (sand is low, clay is high)

visible light
Electromagnetic radiation that can be seen with the unaided eye
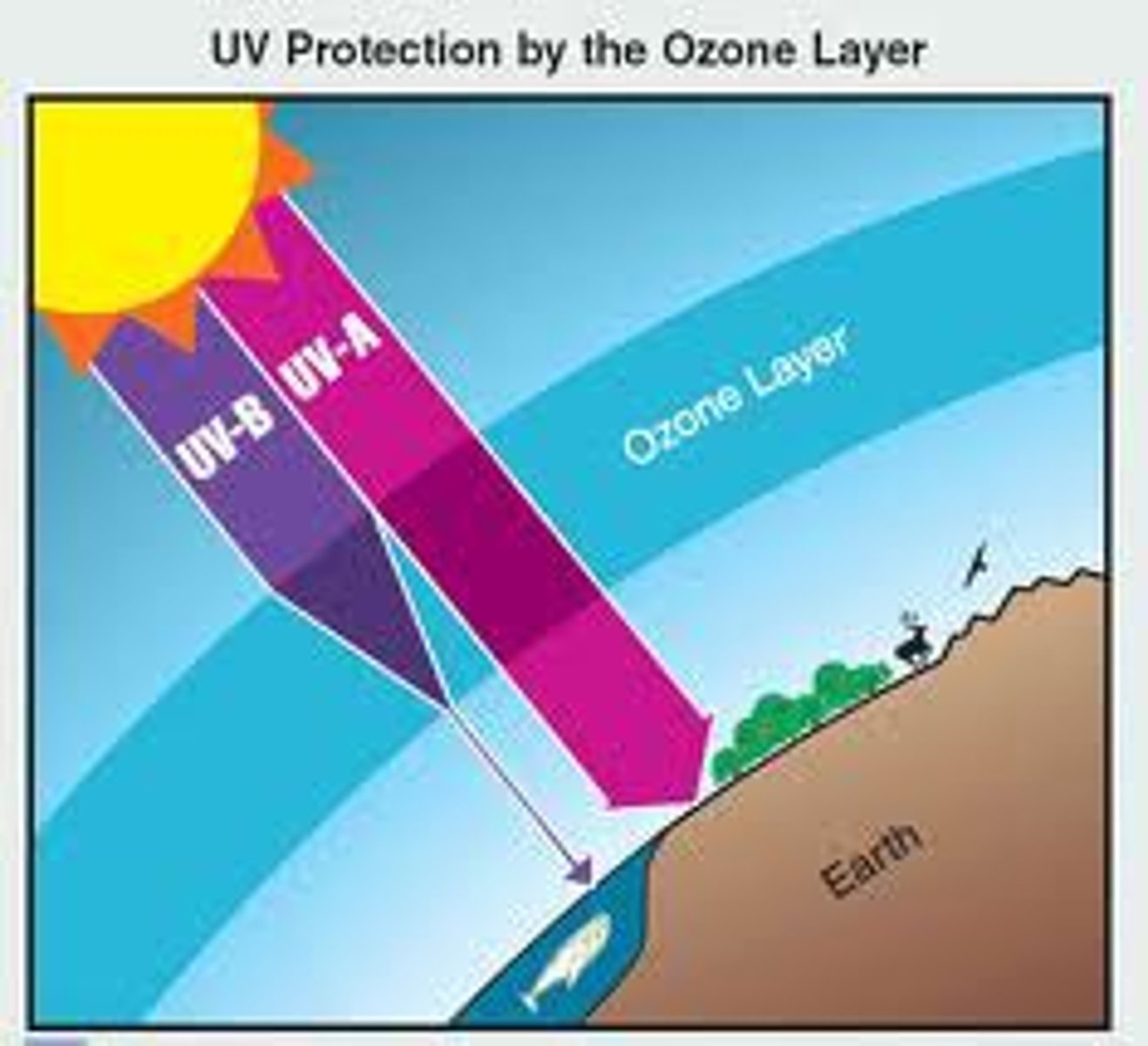
ultraviolet radiation
a type of energy that comes to Earth from the Sun, can damage skin and cause cancer, and is mostly absorbed by the ozone layer
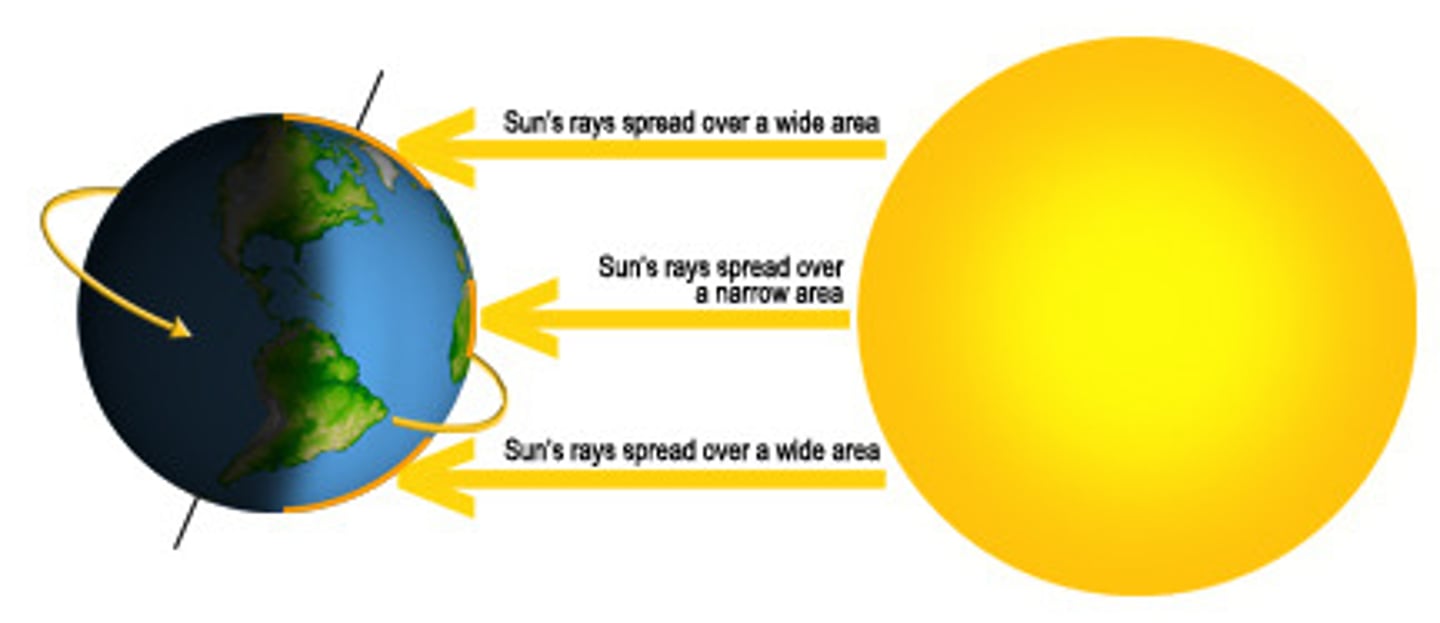
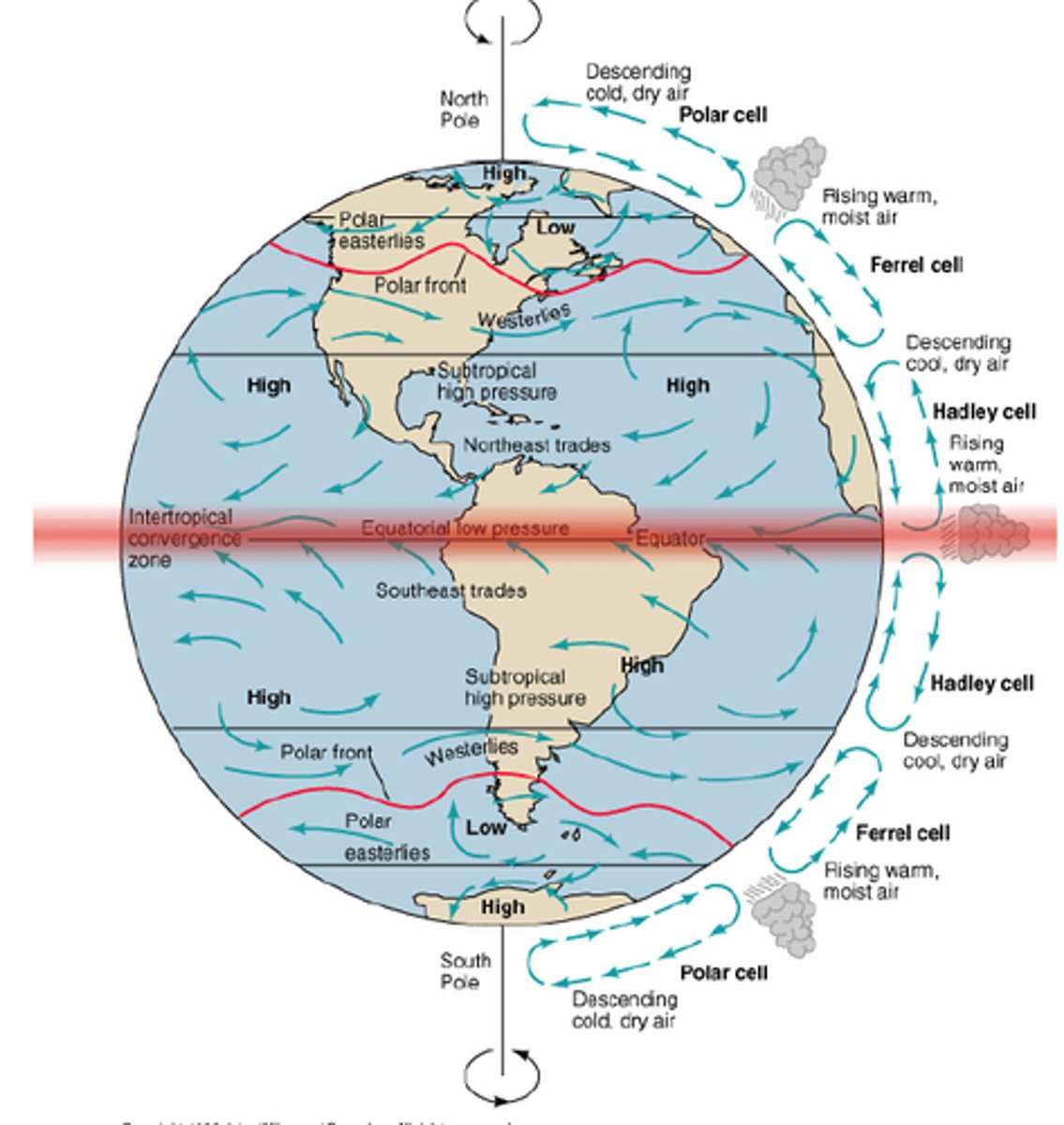
intertropical convergence zone
An area of Earth that receives the most intense sunlight; where the ascending branches of the two Hadley cells converge.
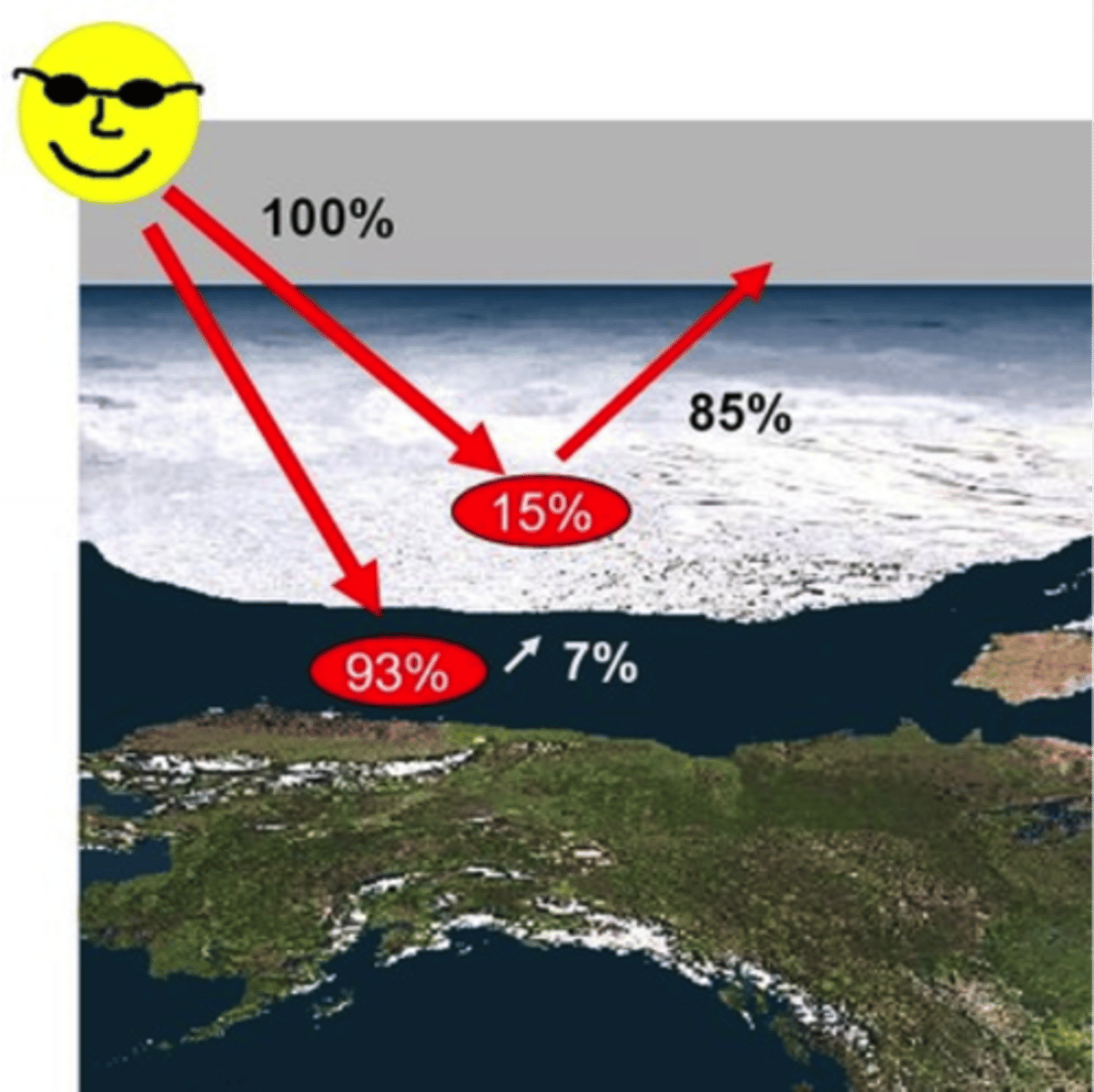
Albedo
Ability of a surface to reflect light
Atmospheric convection current
global patterns of air movement that are initiated by the unequal heating of Earth
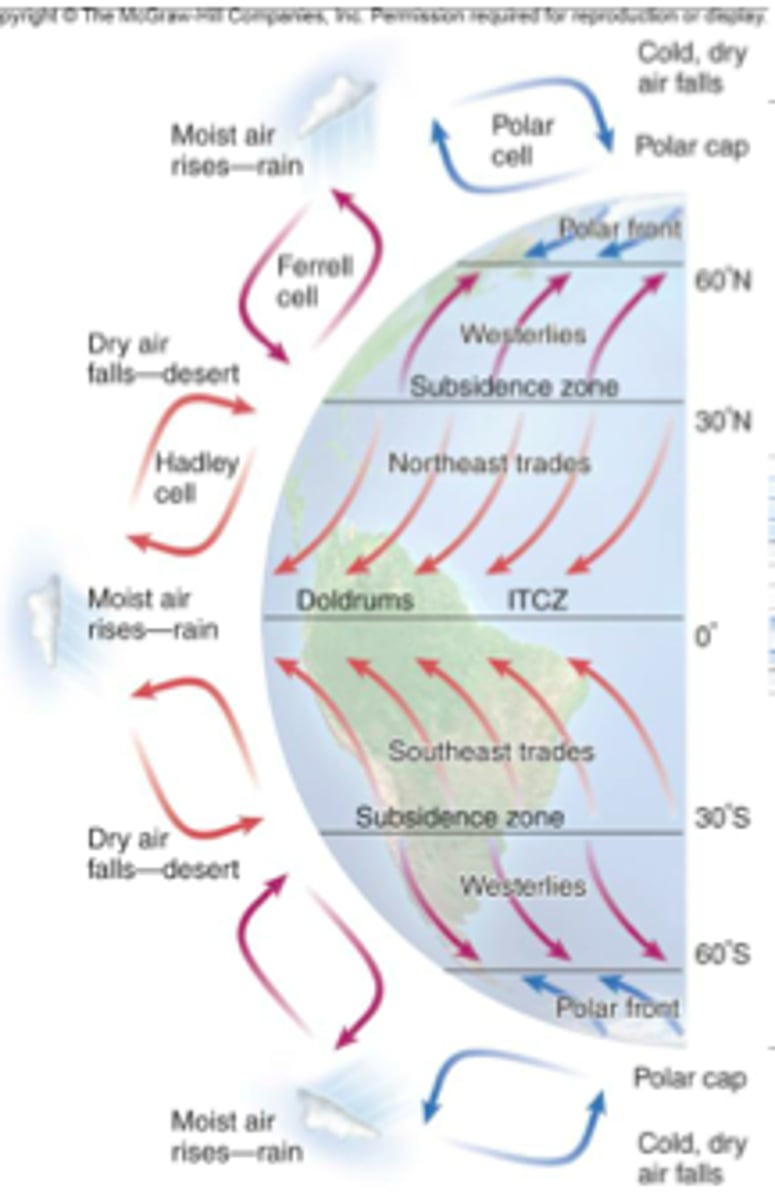
Hadley Cell
a system of vertical and horizontal air circulation predominating in tropical and subtropical regions and creating major weather patterns.
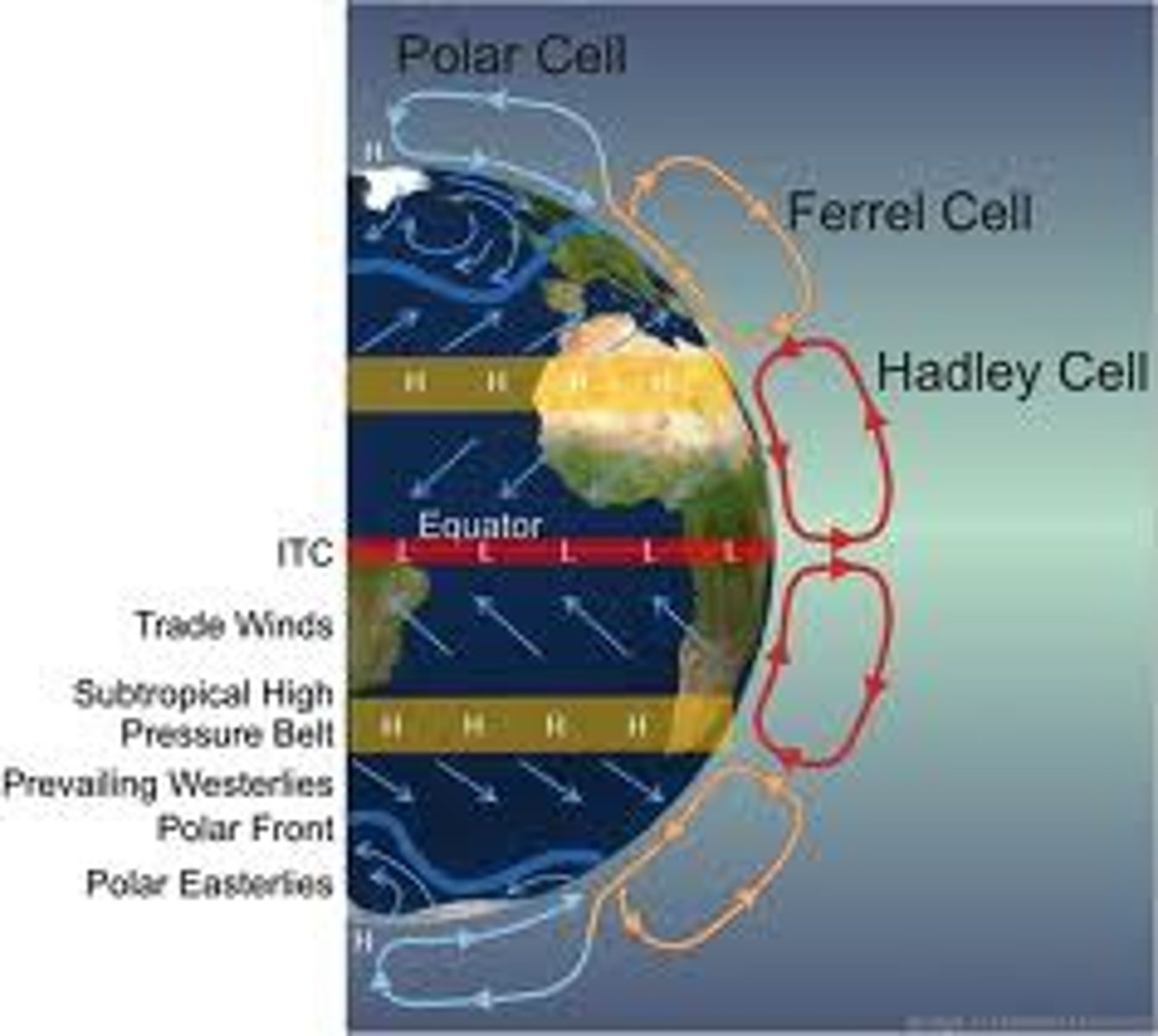
Ferrel Cell
A convection current in the atmosphere that lies between Hadley cells and polar cells
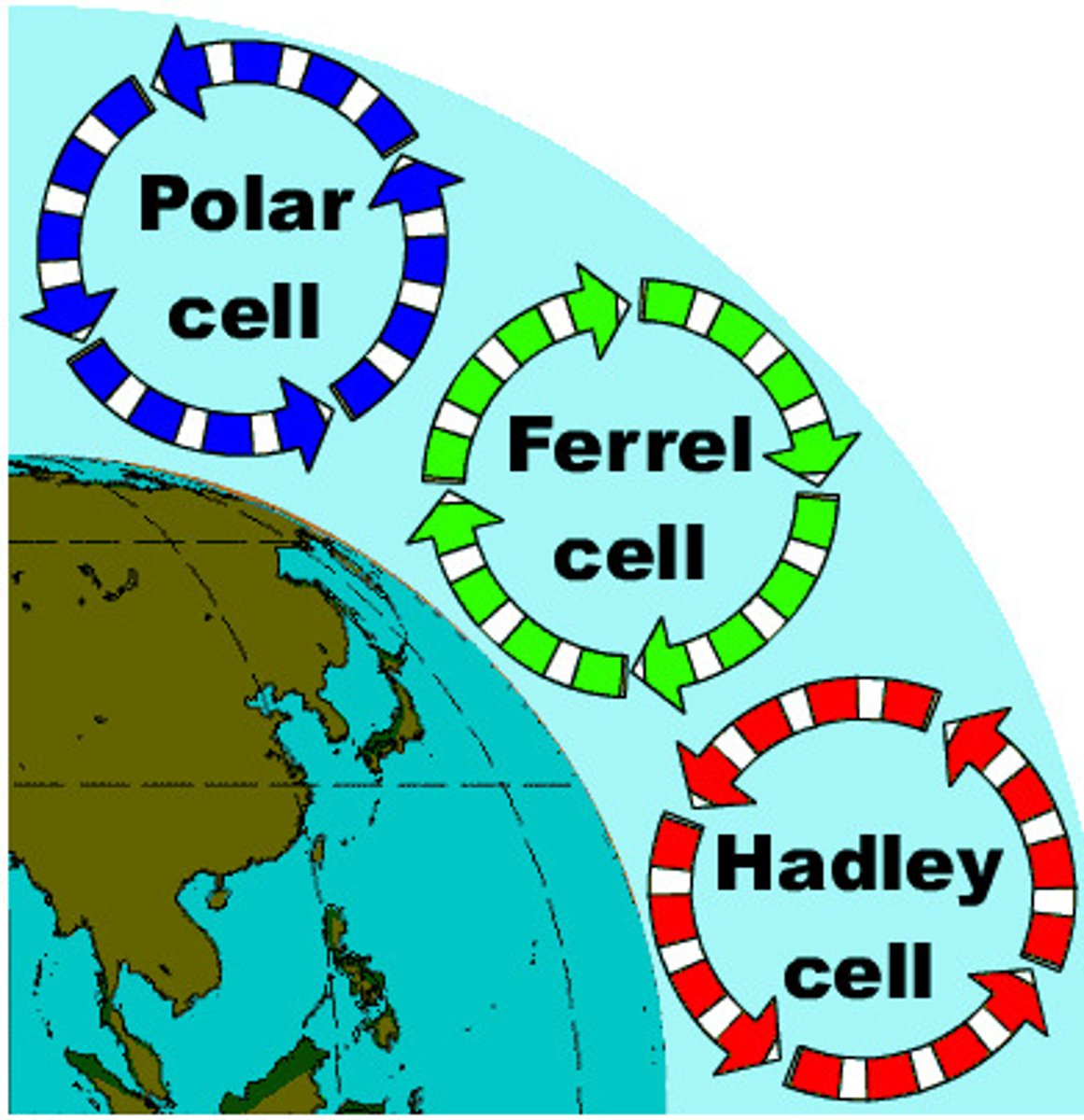
Polar cell
Cells of air circulation occurring between 60 degrees north and south and each pole.
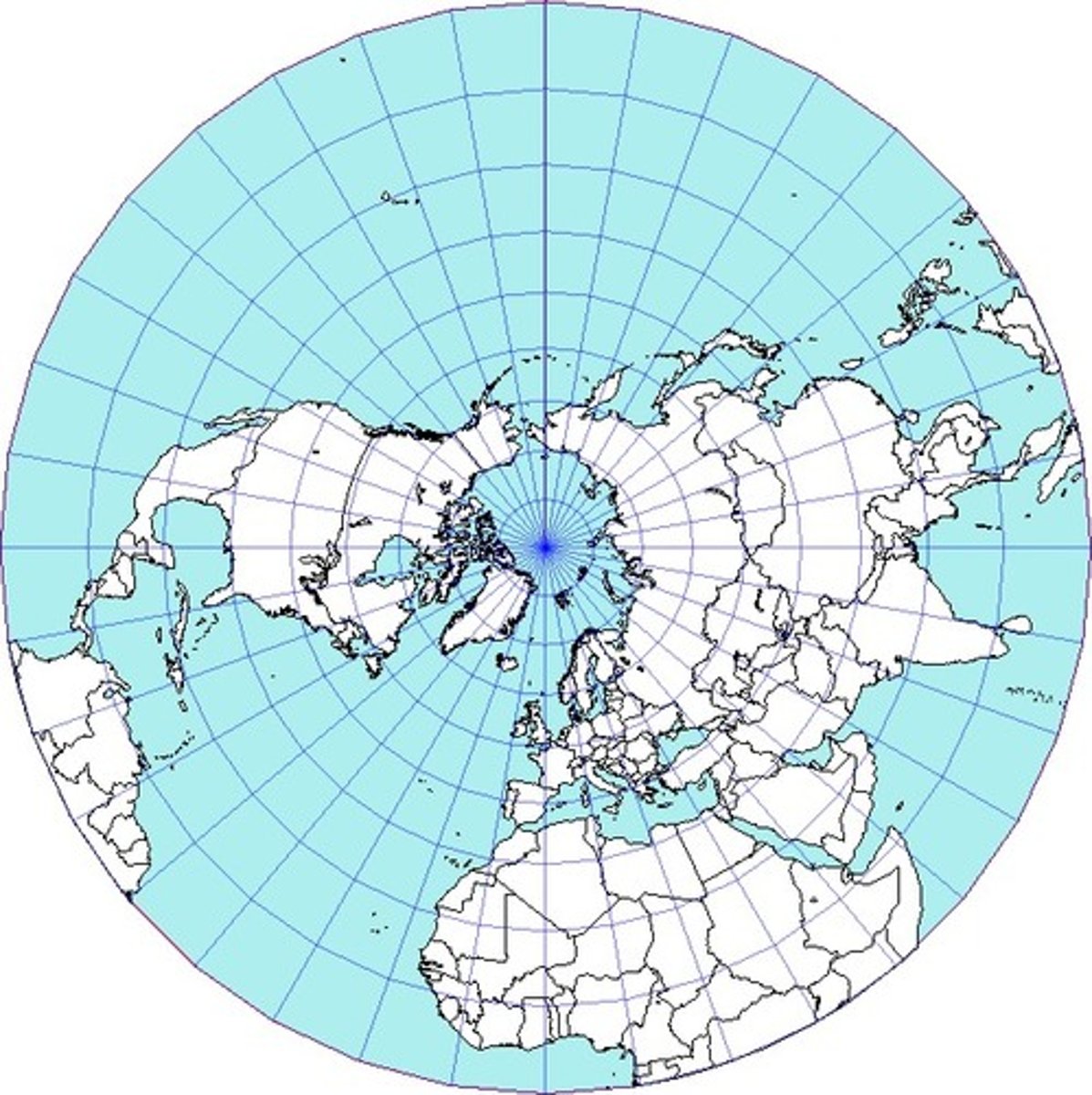
Coriolis effect
Causes moving air and water to turn left in the southern hemisphere and turn right in the northern hemisphere due to Earth's hemisphere.
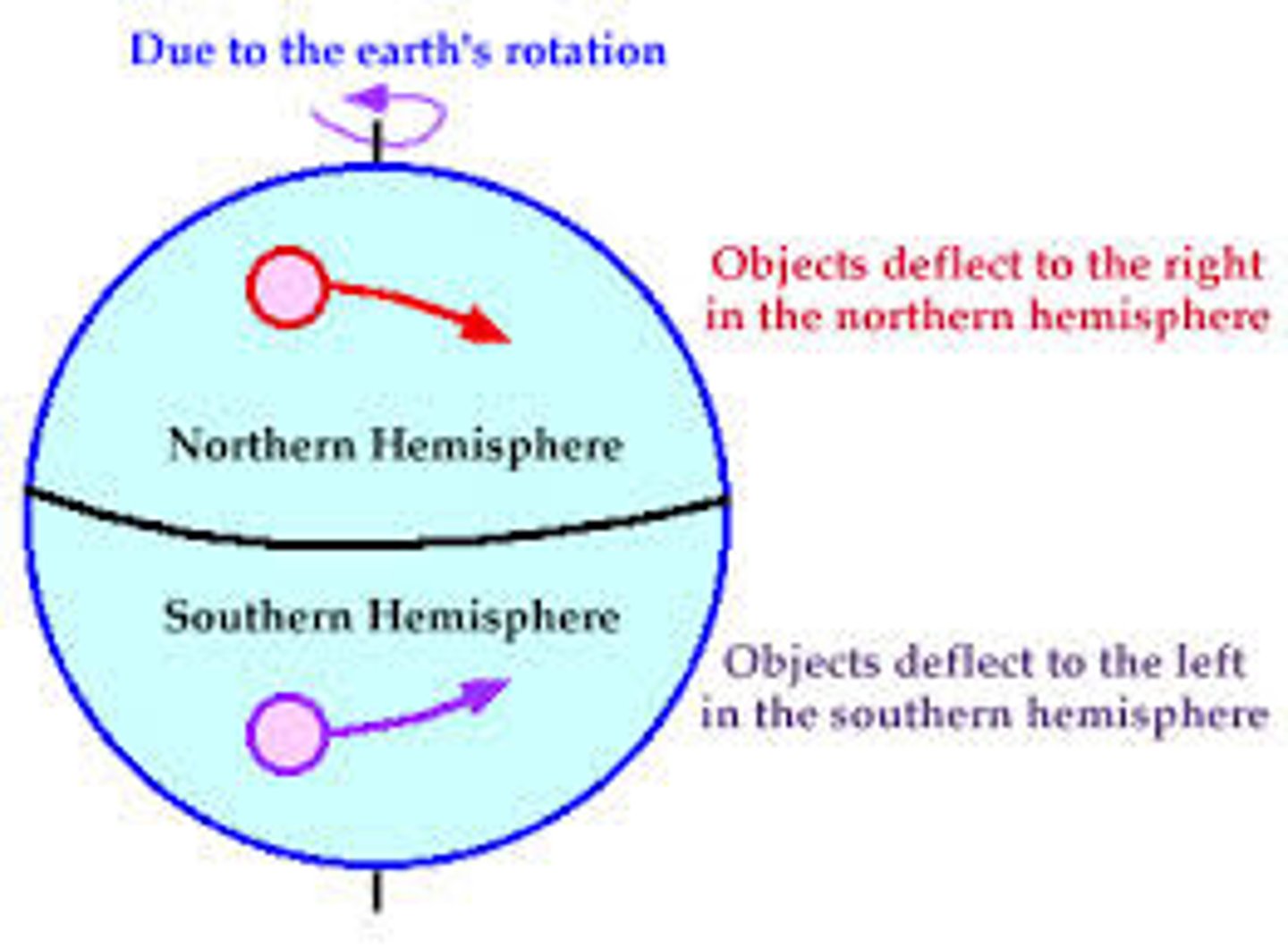
rain shadow effect
Precipitation falls on the windward side of a mountain range, resulting in lush vegetation & a warm, moist climate on one side, but a desert area on the leeward side.
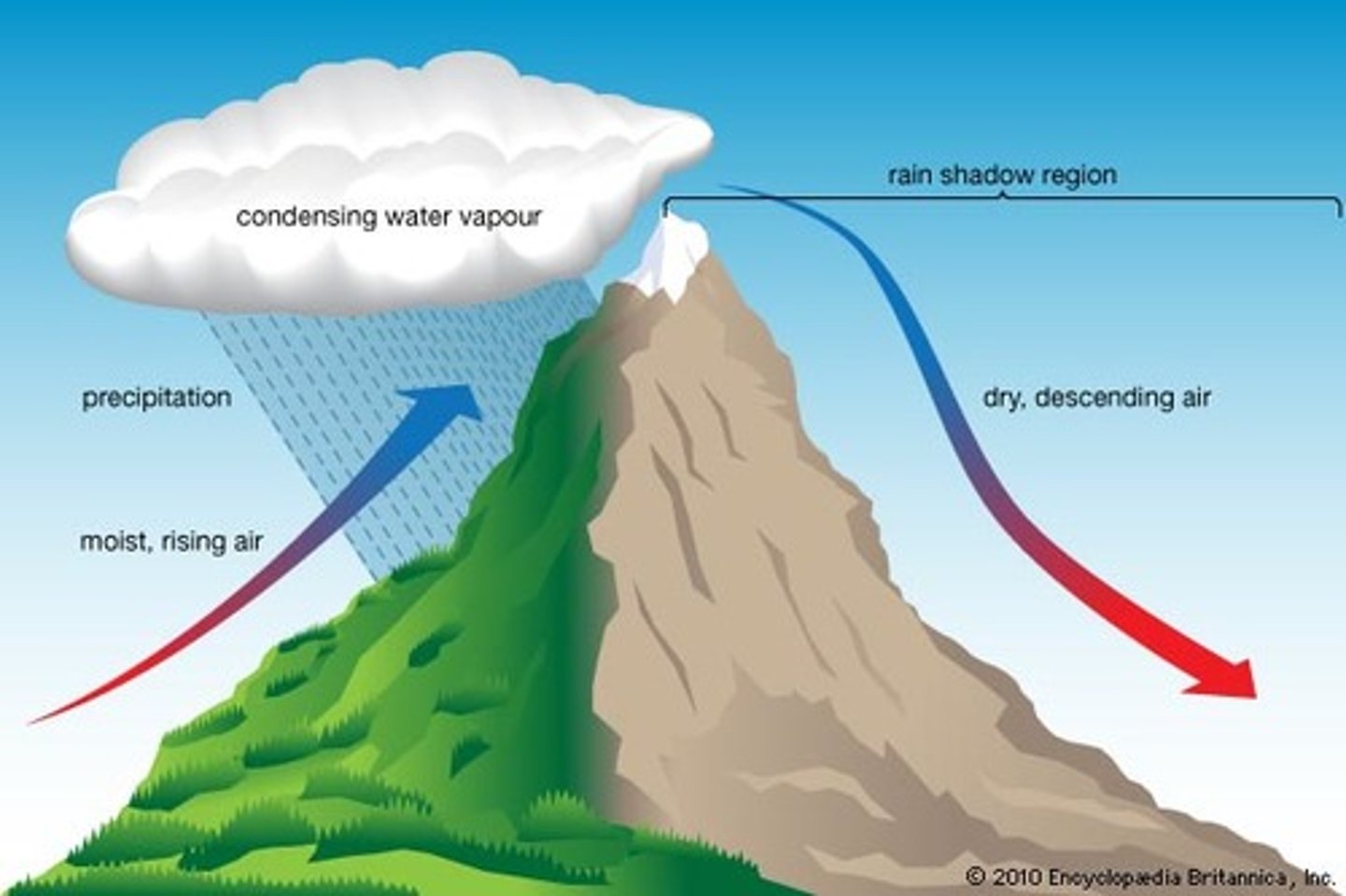
Gyres
Huge circular moving current systems dominate the surfaces of the oceans.
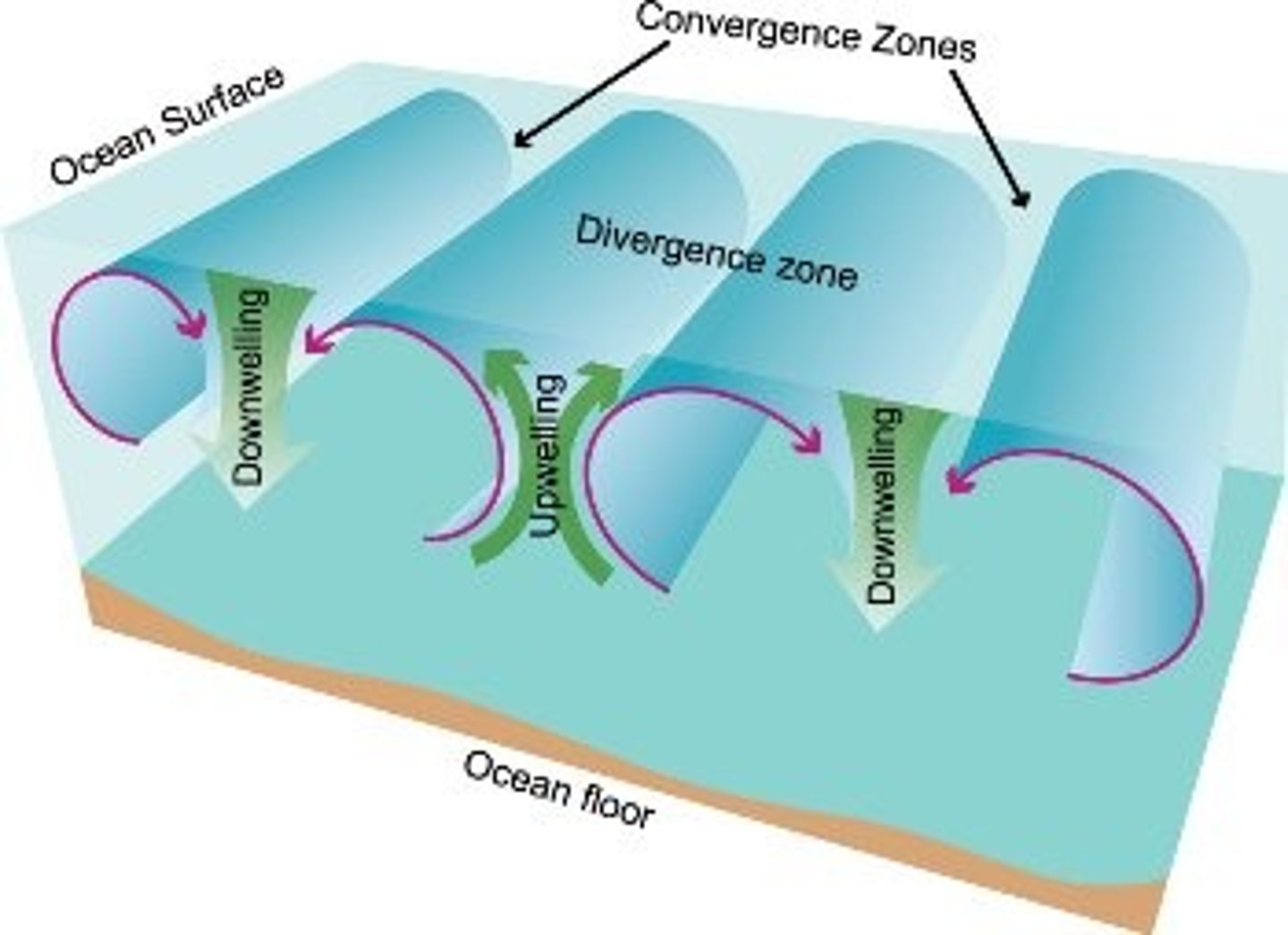
Upwelling
The movement of deep, cold, and nutrient-rich water to the surface
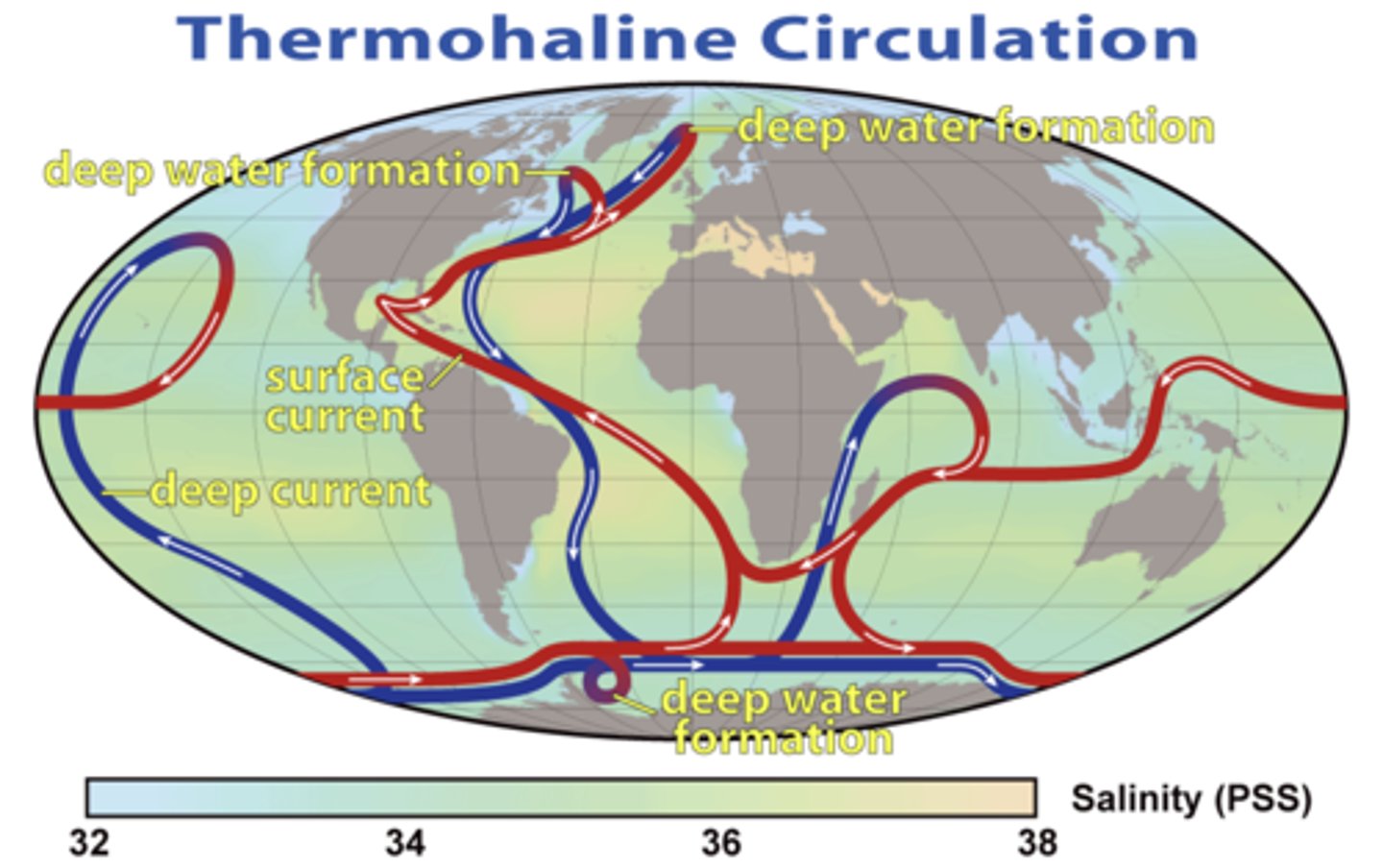
thermohaline circulation
Movement of ocean water caused by density difference brought about by variations in temperature and salinity. As ocean water freezes at the poles it concentrates salt, and the colder, denser water sinks.
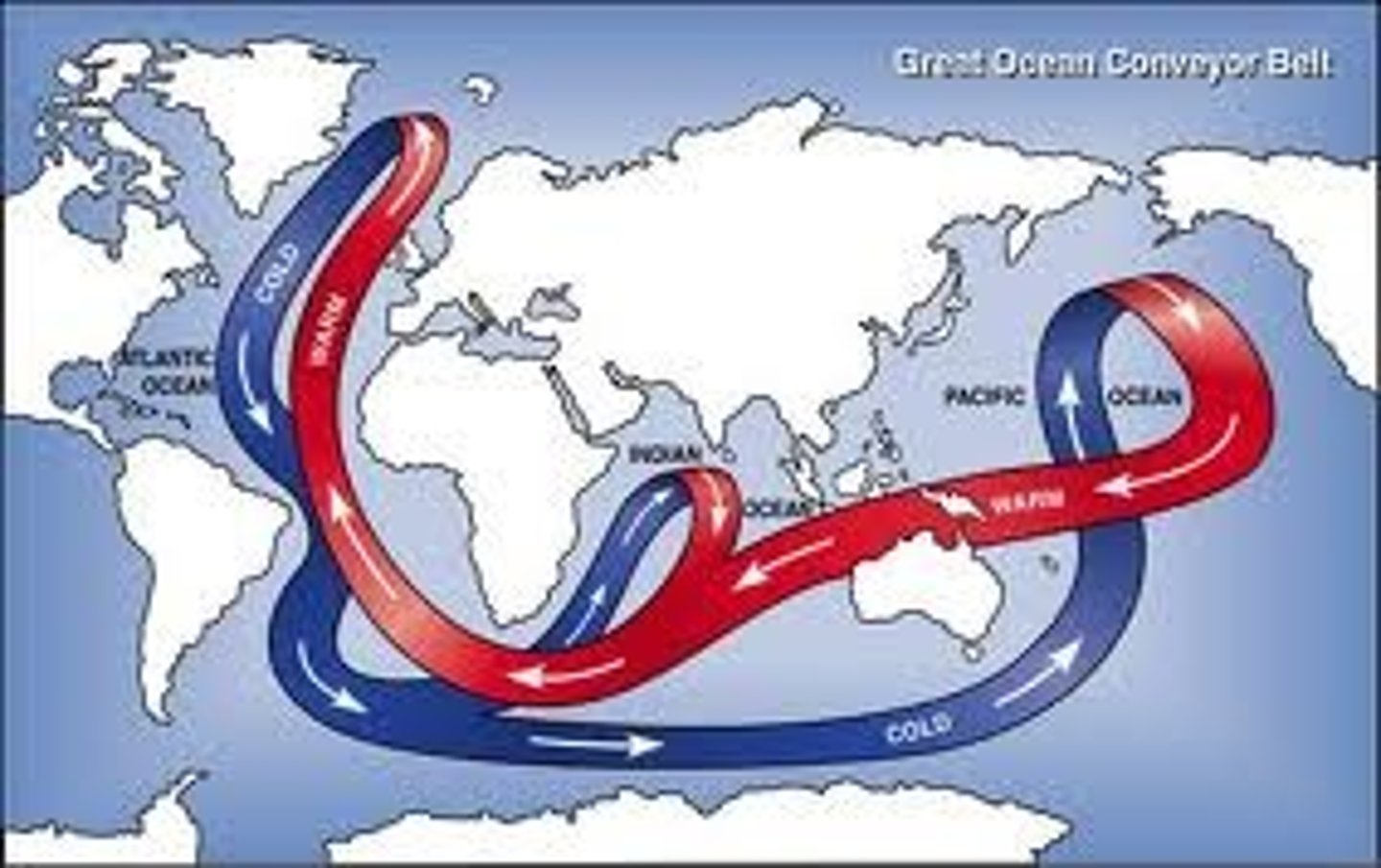
Great Ocean Conveyor Belt
Is a constantly moving system of deep-ocean circulation driven by temperature and salinity. The great ocean conveyor moves water around the globe.
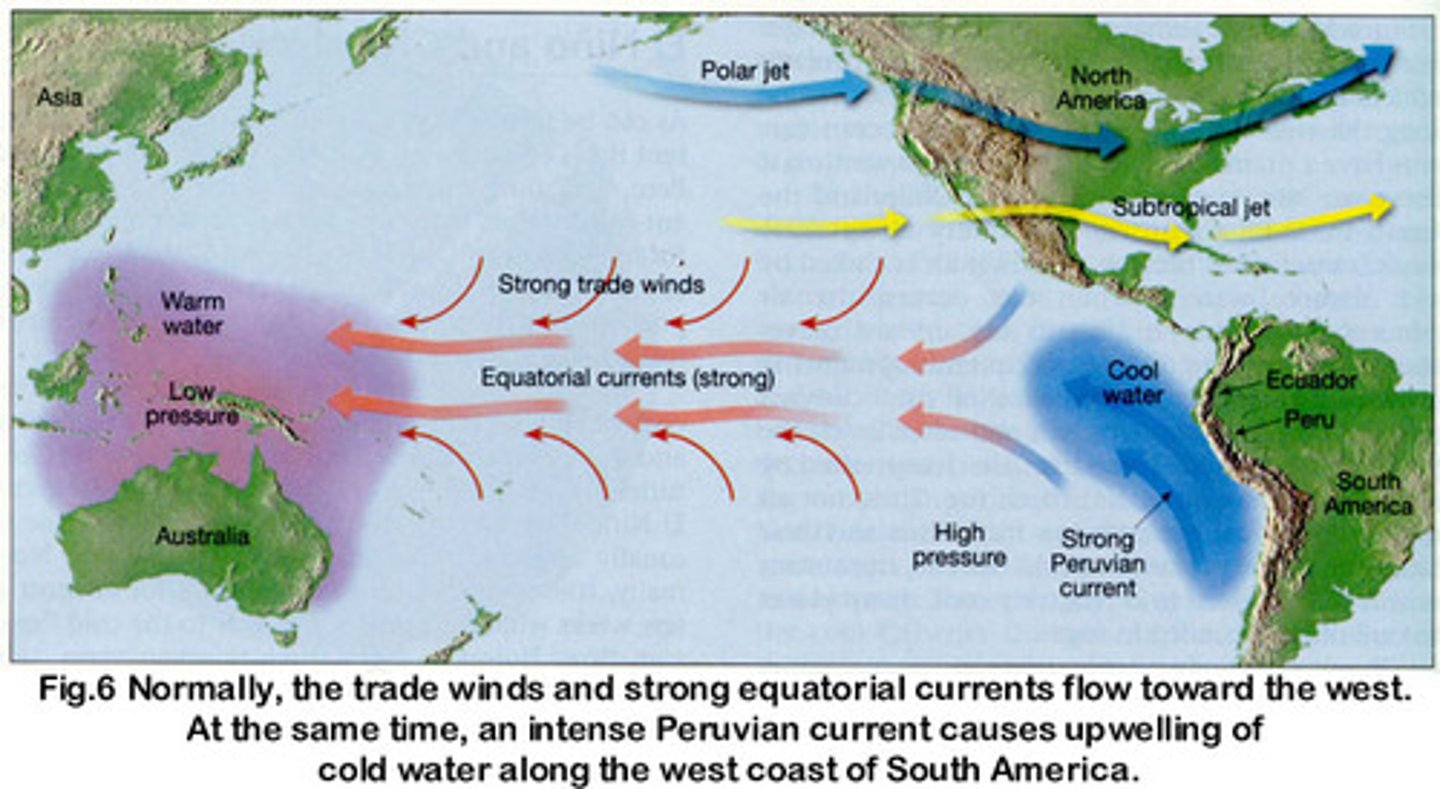
ENSO
El Niño Southern Oscillation, see-sawing of air pressure over the S. Pacific
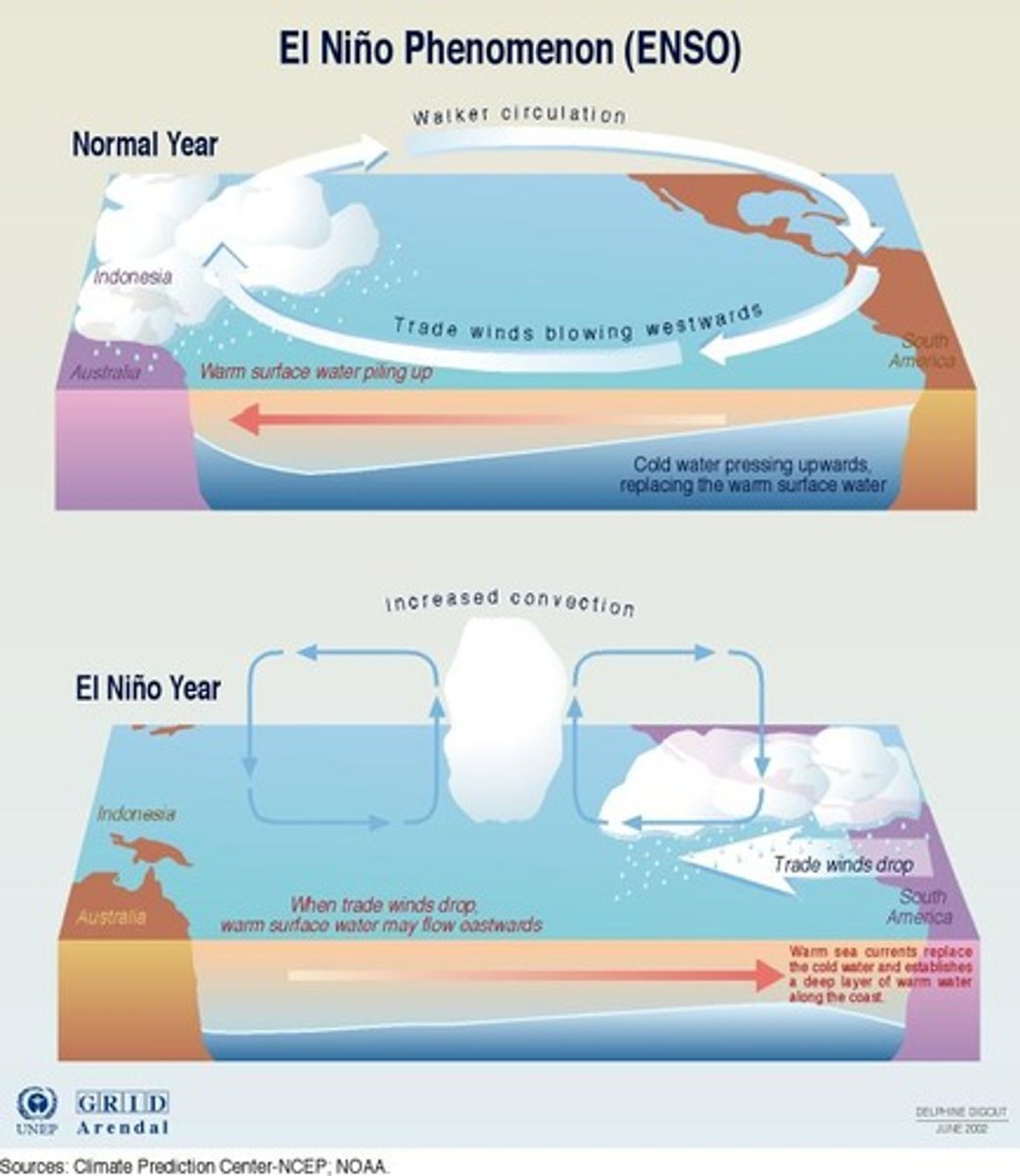
La Nina Effect
a change in the eastern Pacific Ocean in which the surface water temperature becomes unusually cool
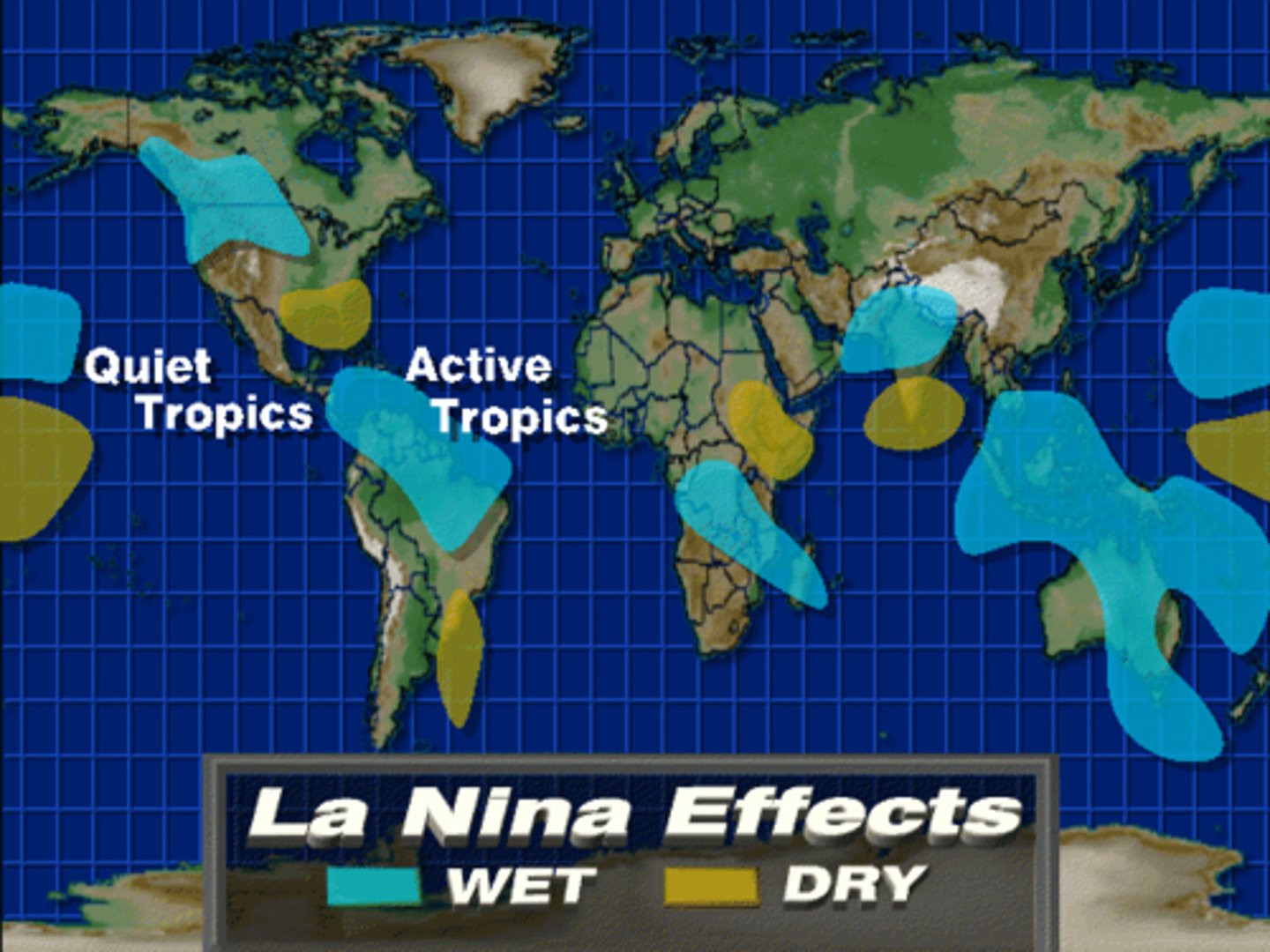
El Nino
an irregularly occurring and complex series of climatic changes affecting the equatorial Pacific region and beyond every few years, characterized by the appearance of unusually warm, nutrient-poor water off northern Peru and Ecuador, typically in late December.
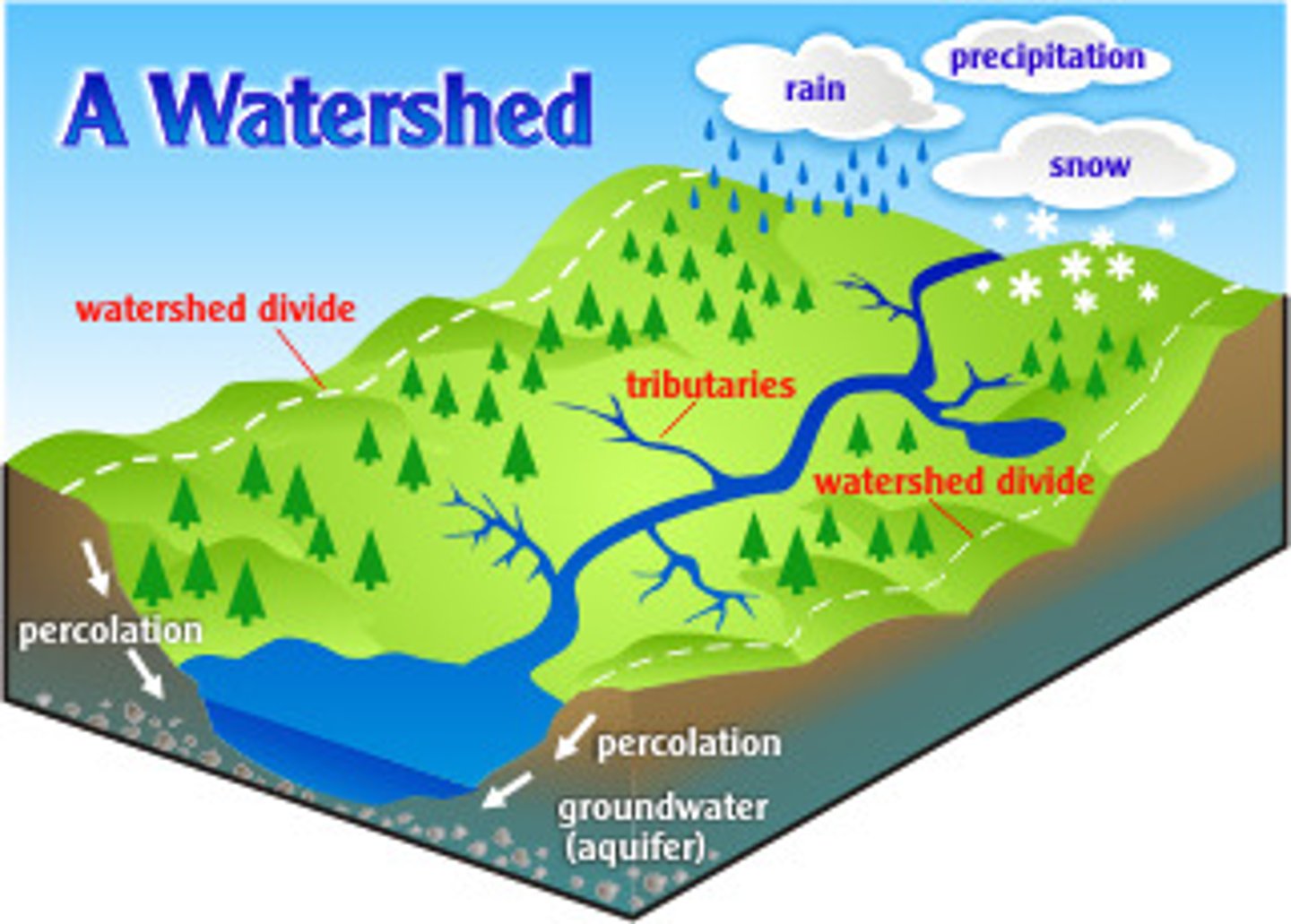
Watershed
An ecosystem where all water runoff drains into a single body of water
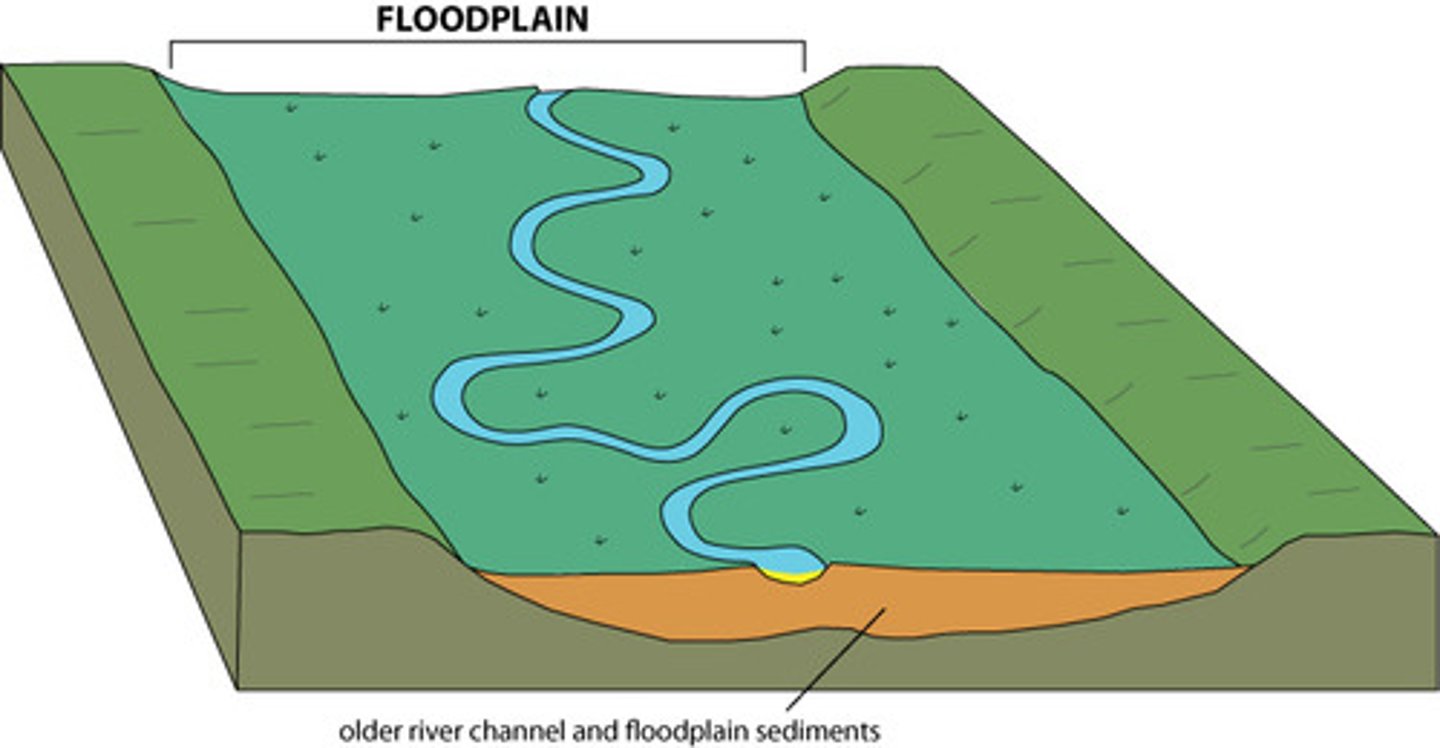
Floodplain
The area subject to flooding during a given number of years according to historical trends.
watershed divide
the line that separates neighboring drainage basins