First/Zero Order & Volume of Distribution, Renal Clearance
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
In zero order, the rate of change is _____ with respect to time. This means the amount eliminated is _______ of drug concentration.The percentage lost _______ as time goes on.
constant
independent
increases
Which order forms a straight line?
zero order
In first order, what does it do to half-life?
half life is constant
In first order, the amount of drug eliminated is ______ on how much drug is present in the body. A constant _______ of drug is eliminated per unit time.
dependent
percentage
What is the formula for Cl?
Cl = K x Vd
what is the formula for Vd?
Vd = dose/Co
What are the 5 factors that governs a drug’s distribution throughout the body?
Log P of the drug: the higher the LogP, the more lipophilic
Molecular Weight: larger MW drugs can’t leave the plasma
Ionization: ionized cells can only leave paracellularly but unionized cells can more transcellularly & paracellularly
Binding to Plasma Proteins: the higher the plasma protein binding, the less likely to leave the plasma
Binding to tissue proteins
When a drug is administered, where does it go first?
goes to the plasma then to the tissues
What can you assume about one compartment model & what happens in this model?
instantaneously & uniform (equal distribution)
elimination of drug occur in this compartment
How does drug flow in the body?
plasma to interstitial fluid
Ionized drug: goes paracellularly only
Unionized drug: goes paracellularly & transcellularly
Interstitial fluid to Intracellular fluid
only unionized drug goes transcellularly into interacellular fluid (cell)
What happens in two compartment models?
Central: dose administered & rapidly distributed (elimination occurs)
Peripheral: drug accumulates & distributes more slowly
drugs that have a very high ________ has a large _______ and small __________.
tissue binding
Vd
Co
No Vd______ than the patient’s _______ volume.
less; plasma
True or false. The more you weigh, the larger your plasma volume is going to be & the larger the intestinal volume.
true
characteristics of a low Vd (3-5) drug
drug is confined to the plasma
either high MW or high protein binding
hydrophilic
characteristics of Moderate Vd (10-20) drug
mostly in the extracellular water (plasma+intestinal fluid)
small MW
hydrophilic
Characteristics of High Vd (>30) drug
evenly distributed throughout the body
lipophilic
small MW
low protein binding
Drug Characteristics of Albumin:
acidic (ionized)
lipophilic
Characteristics of Alpha 1 Acid Glycoproteins drugs
basic
lipophilic
4 Things that alter (decrease) plasma albumin levels:
Liver disease
kidney disease
malnutrition
burn/trauma
5 things that alter (increase) plasma alpha1-AGP
trauma
burns
surgery
inflammatory disease
cancer
What happens in drug interactions involving plasma protein binding displacement, when taking two drugs that have high binding to albumin?
Increased fraction unbound & the patient can experience toxicity due to more free drug
If you have lower affinity to the plasma, your Vd is increased & decreased Concentration
If you have higher affinity to plasma, your Vd is decreased
What is the relation between fraction unbound and hepatic clearance ?
As fraction unbound increases, clearance increases
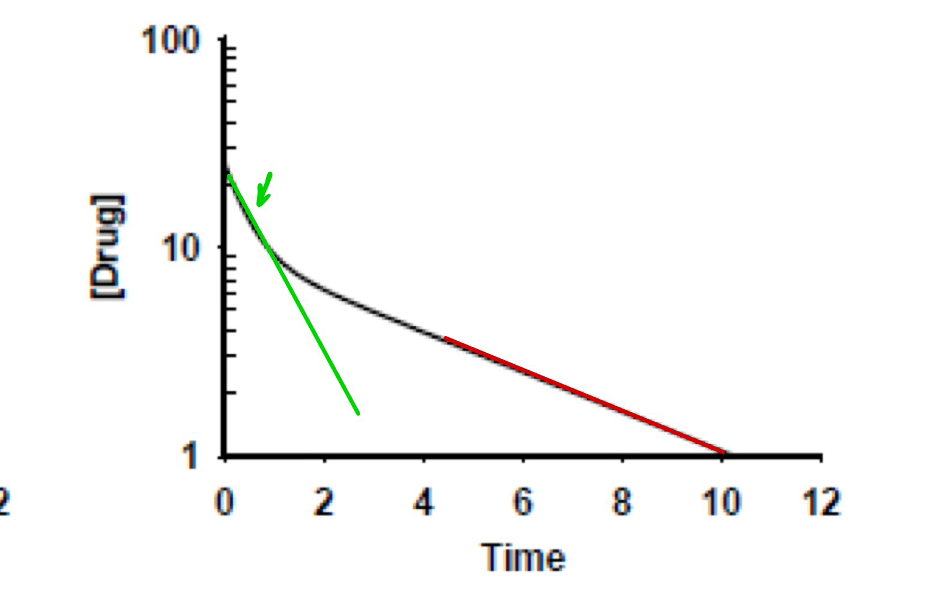
What does the red & green lines represent?
green: distribution phase (alpha)
read: elimination phase (beta)
two compartment model
What goes on in a two compartment model?
drug is administered into the central compartment
drug leaves the central compartment via elimination & moves to the peripheral compartment
Unbound drug reaches distributional equilibrium between the two compartments
As drug is eliminated from the central compartment, unbound drug shifts from peripheral to central compartment to maintain equilibrium