Cell Bio Exam 3
1/174
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Endocytosis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
175 Terms
Default Pathway Transport
Proteins from the ER move along this vesicular transport route (rough ER to Golgi to PM)
Default Pathway Departure
requires specific protein signals; retention and diversion
Critical role of the Golgi Body
biosynthesis, sorting, dispatching, and recycling to various parts of the cell
Golgi function
remove and add sugars to glycoproteins through the action of resident glycosidases and glycosyltransferases
cis-Golgi network
passes proteins to the stack or returns them back to ER
trans-Golgi network
passes proteins to the plasma membrane, lysosomes, or secretory vesicles
Rate limiting step in protein transport and secretion
ER to golgi
Quality control step: Protein correctly assembled
then protein is exported to the cis-Golgi network by the default pathway
Quality control step: Protein not correctly folded
Denatured or unfolded protein is degraded (can be detrimental like CFTR degradation)
Quality control step: Protein not correctly assembled with other subunits
If still bound to BiP or other chaperones and is actively still undergoing folding, then protein remains in the ER
ER proteins that are retained
BiP and PDI
ER and cis-Golgi receptors
recycle KDEL containing proteins in the cis-Golgi by ferrying them back to ER via transport vesicles
ER KDEL retention sequence removal
results in protein transport to the cell surface via the default pathway
KDEL sequence fusion
to non-ER proteins will retain them in the ER
KDEL sequence makeup
short-stretch of aa sequence (Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu)
ER proteins are either
resident or en route to other destinations
ER proteins before leaving RER must be
folded, modified, and assembled correctly for proper function
RER protein chaperones are
BiP (hsp70 member), calnexin, calreticulin
RER protein chaperones function
prevent aggregation of hydrophobic domains, facilitates folding in ATP-dependent manner, and helps retain partially folded proteins in the ER avoiding premature transit to the Golgi
RER isomerases
protein disulfide isomerase (PDI)
Glycoproteins
All proteins that are exposed to the ER lumen and post-translationally glycosylated
Glycosylation: additions to protein
prefabricated oligosaccharide complex is added en bloc to specific sites on protein chain
Oligosaccharide contains sugars
14= 2GlcNac, 9 Man, 3 Glu
Glycosylation sequence
Asn-X-Ser/Thr, oligosaccharide attached by N-glycosidic bond to Asn side-chain (N-linked or Asn-linked)
Oligosaccharide assembly via transfer reactions
Assembled from nucleotide-and lipid-phosphate linked monosaccharides in the cytosol and ER through a sequential series of transfer reactions
Oligosaccharide assembly carrier lipid
dolichol-PO4 aka polyisoprenoid
Oligosaccharide assembly sugar donors
UDP-GlcNAc, GDP-Man, Dol-P-Man, and DOL-P-Glc
Oligosaccharide assembly modifications
following partial assembly of (GlcNAc)2(Man)5 on the cytosolic side, lipid-sugar precursor flips to lumenal side of the ER for final modifications
Protein Glycosylation Reaction catalyst
oligosaccharyl transferase
Oligosacchryl Transferase function
mediates the transfer of oligosaccharide from lipid carrier to the Asn resiude on the protein
Protein Glycosylation Reaction: Association
Oligosaccharyl transferase is closely associated with the SEC61 complex so protein modifications occur relatively quickly following translocation into the lumen
Glycan Trimming ER
Original high-mannose glycan complex is further processed and terminal 3-Glc and 1-Man is removed before exiting the ER
Glycan Trimming Golgi
further removal and addition of sugars occurs, glycosidases remove and glycosyltransferases add
Sugar processing in the golgi involves
complex oligosaccharides and high manose oligosaccharides
cis Golgi network sorting
involves phosphorylation of oligosaccharides on lysosomal proteins
cis cisterna of Golgi stack function
removal of Man
medial cisterna of Golgi stack function
removal of Man and addition of GlcNAc
trans cisterna of Golgi stack function
addition of Gal and NANA
trans Golgi network sulfation
of tyrosines and carbohydrates, then sorting occurs
Golgi vesicular transport model
Golgi is static and transport vesicles ferry cargo between stacks
Cisternal Maturation Model
Golgi cisternae mature as they move forward through the stack. At each stage Golgi resident proteins carried forward are moved backward via vesicle transport
Lysosome acid hydrolases
nucleases, proteases, glycosidases, lipases, phosphatases, sulfatases, phospholipases
the lysosomes is the site where
several distinct vesicular pathways converge
Lysosomal pathways
biosynthetic (ER-Golgi), endocytic, autophagic, and phagocytic pathway (macrophages and neutrophils)
Lysosomal hydrolase synthesis
hydrolases and membrane proteins are synthesized and sorted by Golgi and then delivered via transport vesicles that traffic through late endosomes
Lysosome signal patch
read by glycosyltransferases in cis-Golgi that add mannose 6-phosphate (Man-6-P) tag to proenzymes which is read by receptors present in the trans-Golgi network
Man-6-P receptor functions
binds and segregates hydrolases from other other protein traffic exiting the Golgi
Vesicle forward transport
ER phosphate addition to M6P receptor binding to Receptor-dependent transport
Vesicle recycling transport
Receptor dependent transport to lysosomal phosphate removal to acidic pH disassociation to recycling to Golgi
Lysome-associated membrane proteins
LAMPs follow default secretory pathway to the plasma membrane
Lysosome Membrane Protein Pathway
default pathway to plasma membrane also followed by small percent of hydrolases and Man-6P-R. Scavenger pathway elucidated by certain lysosomal storage diseases
Hurler Disease basis
lysosomal enzyme required for the breakdown of glycosaminoglycans (ECM proteins) is missing; large accumulation of undigested material
Hurler Disease rescue
diseased culture cells are co-cultured with normal cells, which rescues mutant cells and is capable of breaking down GAGs
Hurler Cell scavenging
normal cells produce missing hydrolase and some escape via default pathway. Hurler cells can scavenge WT hydrolases in media using normal Man-6-P receptors at PM
I-Cell disease
hydrolases are missing due to defect in GlcNAc phosphotransferase so there is no Man-6-P tag, receptor fail to sort and target hydrolases
Reasons for endocytosis
uptake of nutrient molecules; clearance of harmful substances, cellular debris, and infectious organisms; maintenance of surface-to-volume ratio
The type of endocytosis is distinguished
by the size of the import vesicle and the material being ingested
Phagocytosis
greater than 250nm; uptake of large, particulate matter
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
between 250-300 nm; uptake of macromolecules via specific cell surface receptors
Pinocytosis (cellular sipping)
less than 150 nm; uptake of fluid and dissolved solutes
Much of the ingested material is delivered to
lysosomes
Protozoa
does phagocytosis, ingestion of food particles
Macrophages and neutrophils
phagocytes that help with binding, clearance, and destruction of bacteria, damaged cells, and cellular debris
Fibroblasts
phagocyte that helps with connective tissue remodeling
Receptor-mediated event
cells possess surface receptors that recognize specific or generic sites on various particles they then bind particle the progressively extend pseudopodia to engulf particle
Engulfment requires
receptor-ligand interactions around the surface of the particle
Receptor-ligand interactions induce
localized changes in the cortical cytoplasm
Calcium fluxes at cortical cytoplasm
induce formation of gel-like cytoplasm
Pseudopodia receptor-ligand interactions
membrane-coupled pseudopod extension and actin polymerization
When is engulfment at pseudopodia completed
when pseudopodia meet and fuse forming phagosome
Ingested particles initially reside
in phagosomes where oxygen metabolites help kill bacteria
Lysosomes fuse with phagosomes
to form phagolysosomes that have acid hydrolases to digest phagosome contents
Residual bodies
phagolysosomes that contain non-digestible material
Pathogen escape mechanism
Free bacterium enters host cell via zipepr mechanism
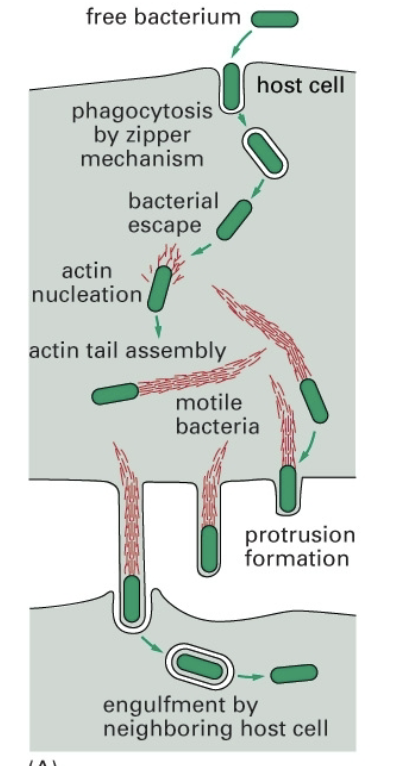
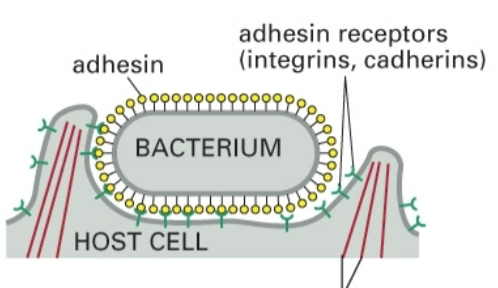
Zipper mechanism
Bacterium’s adhesin attaches to receptors (integrins, cadherins) on host cell
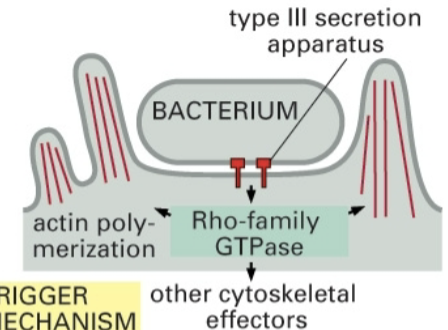
Trigger mechanism
Bacterium attaches to type 3 secretion apparatus
Pathogens can also invade
non-phagocytic cells
Yersinia
invasin-beta1 integrins (zipper)
Listeria
E-cadherin (zipper)
Salmonella
effector injection in host cell (trigger)
Virulence methods used by pathogens
escape
prevent fusion with lysosomes
survive in phagolysosome
Listeria escape mechanism
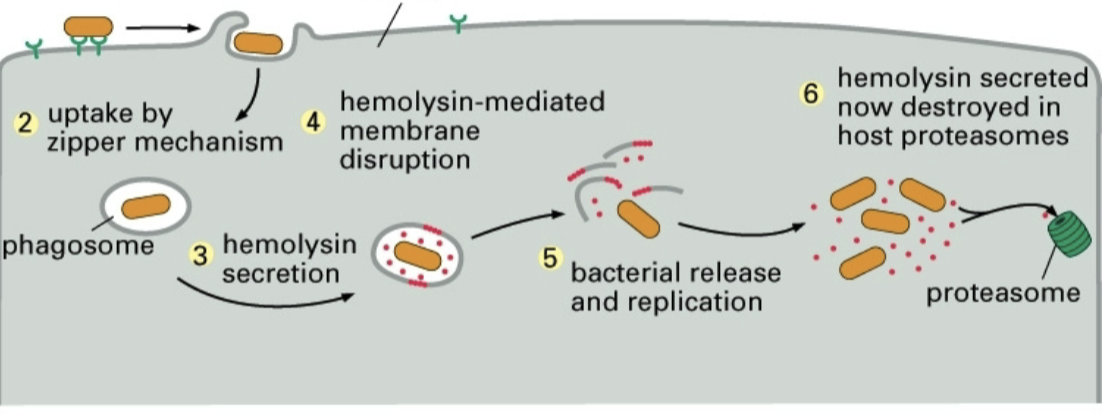
Receptor-mediated nutrient endocytosis
Cholesterol uptake via LDL receptors, delivery to lysosomes (lipoproteins like LDL, HDL and metals like Fe)
Brown and Goldstein won the nobel prize for
Genetic analysis of human disposed to heat attacks due to atheroscloerosis, defective LDL receptors, resulting in increases in blood serum cholesterol levels
Hormones, growth factors, and immunoglobulins are uptaken by
receptor-mediated endocytosis
Receptor mediated endocytosis of harmful substances
modified glycoconjugates and coagulation factors
Receptor mediated endocytosis efficiency
is increased to greater than 1000 fold by specific cell surface receptor mediation that bind ligand with high affinity
Receptor-ligand complexed enter cells
specialized membrane structures like clathrin-coated plaques and pits
Clathrin coated pits
specialized endocytic structures that collect endocytic receptors, excluding other membrane proteins and concentrating endocytic receptors
Defective receptors in clathrin coated pits
reduced binding to cargo LDL and have defective cytoplasmic tails
Clathrin coat proteins
clathrin heavy and light chains along with adaptor complexes that mediate interaction between receptors and clathrin
Clathrin assembly drives
coated pit formation and vesicle budding
Clathrin heavy chains
180 kDa hinged rods
Clathrin light chains
33 kDa accessory proteins
Clathrin protein structures
triskelion, formed of heterohexamer (3 heavy aand 3 light chains)
Triskelia polymer formation is regulated by
clathrin light chains
Triskelia polymerization
the self-assembly of clathrin triskelions into a lattice-like polymer network which is composed of hexagons and pentagons
Triskelia polymerization assembly process acts
to mechanically form the curved, budded membrane
Clathrin adaptors
aka adaptin, complexes that mediate clathrin binding to specific membrane receptors
Clathrin PM adaptor
AP-2