cardio quiz 1
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
myofibril
thread-like structure found in muscle cells, composed of repeating units called sarcomeres
perfusion of tissues at capillaries over narrow range of hydrostatic pressures
funciton of cardiovascular system
vena cava
blood vessel with the lowest pressure
vein
A
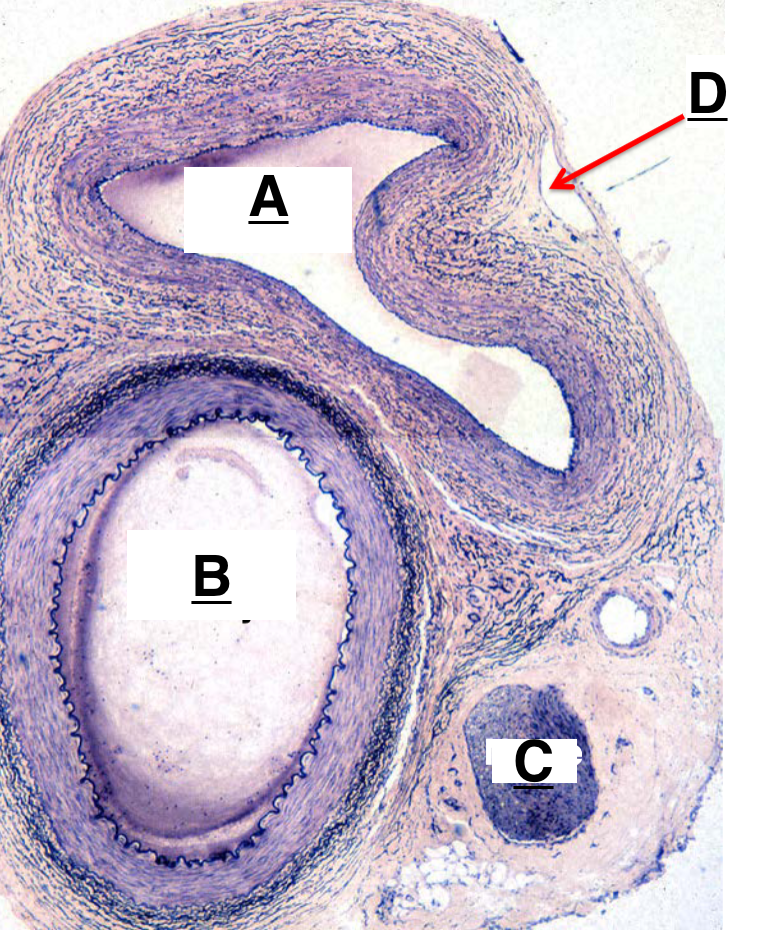
artery
B
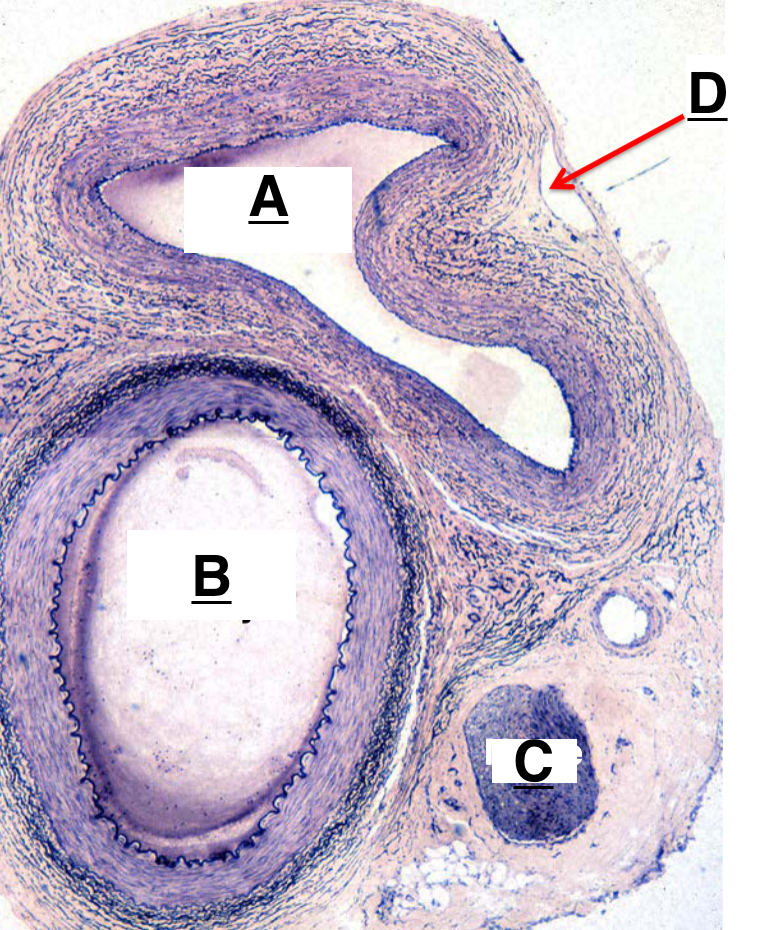
nerve
C
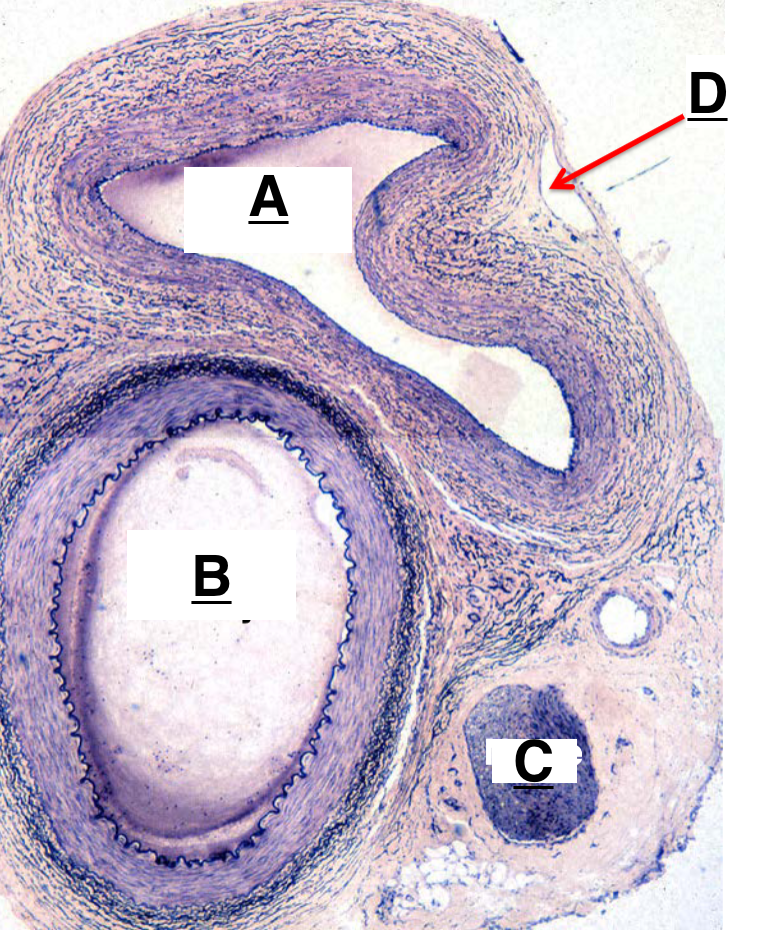
lymphatic vessel
D
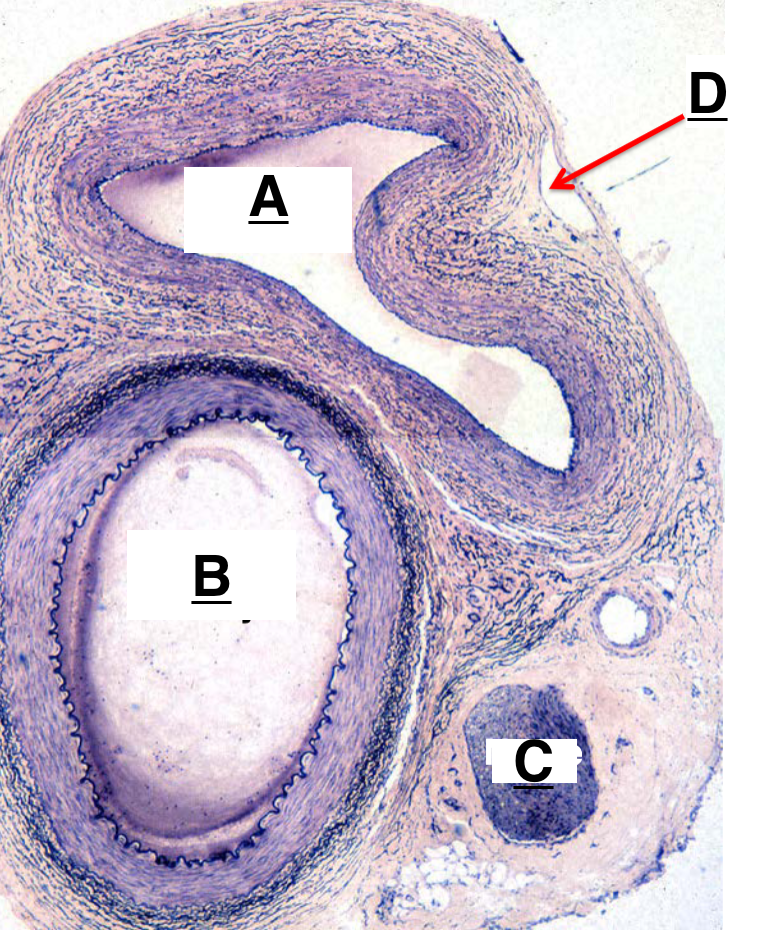
H and E biopsy and DIF biopsy
differential diagnosis for oral lesions
pemphigus vulgaris
immune system attacks desmosomes
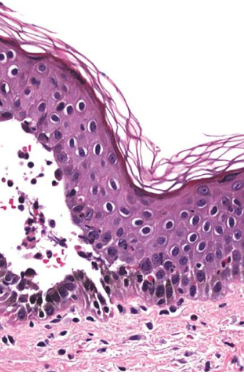
mucous membrane pemphigoid
immune system attacks hemi-desmosomes
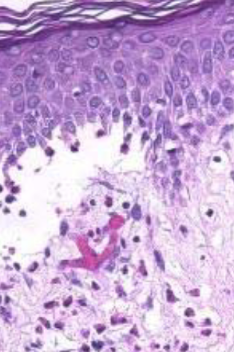
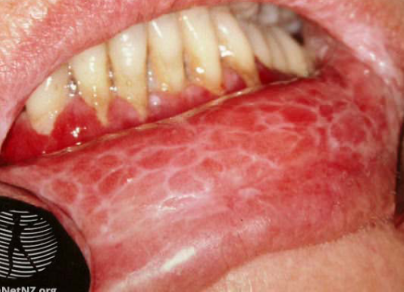
oral lichen planus
a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the mucous membranes, characterized by white patches and lesions.
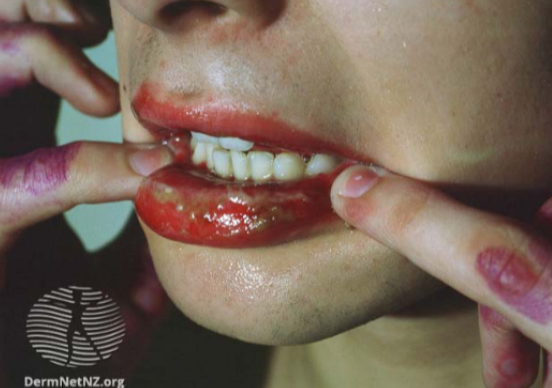
erythema multiform
caused by apoptosis, characterized by distinctive TARGET LESIONS on palms
separation between keratinocytes, separation from basement membrane, dead keratinocytes, heavy inflammation
causes of blister formation
mucous membrane pemphigoid
with which disease is an OCULAR REFERRAL necessary
HSV
most common trigger of erythema multiform
stevens johnson syndrome
a severe skin reaction often triggered by medications, leading to blistering and detachment of the epidermis.
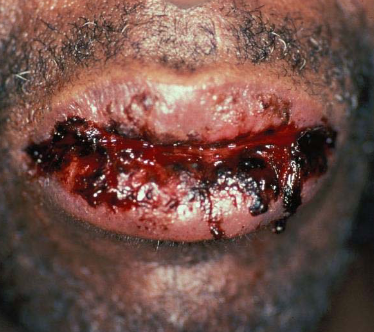
high risk for reactivation (with rituximab)
why should you test for hep B when starting immunosuppressants
associated with lichen planus
why should you test for hep C when starting immunosuppressants
arteriole
A small blood vessel that branches from an artery and leads to capillaries, determinant of SYSTEMIC BLOOD PRESSURE
capillary
gas/nutrient exchange vessel
oral hygiene, topical steroids, systemic steroids, immunosuppressants
general treatment of oral erosive disease
myosin heads crawl along actin filaments, pulling them closer together
what happens to actin and myosin during muscle contraction
provides energy for myosin heads to detach from actin and reattach
role of ATP in muscle contraction
Acetylcholine
neurotransmitter that triggers muscle contraction
binds to troponin, tropomyosin moves and exposes binding sites on actin
role of calcium in muscle contraction
Calcium ions
what is stored in sarcoplasmic reticulum
myofibril bundles
muscle fiber composition
mediastinum
The central compartment of the thoracic cavity, containing the heart, great vessels, trachea, esophagus, and other structures.
middle
part of mediastinum containing heart and pericardium
phrenic nerve
which nerve innervates the fibrous pericardium
epicardium
outer most layer of connective tissue that covers the heart
myocardium
middle layer of heart and bulk, composed of heart muscles
endocardium
innermost layer of heart, lines chambers and valves
cardiac plexus
network of nervees that surround the heart
vagus and sympathetic trunk
nerves that contribute to cardiac plexus
ascending aorta
origin of right and left coronary arteries
coronary sinus
what vessel lies in coronary sulcus
left anterior descending artery
what vessel lies in anterior interventricular sulcus
coronary artery dominance
refers to which coronary artery supplies the majority of the heart's blood supply, typically either right or left
right
most common coronary artery dominance
drain deoxygenated blood from heart to right atrium
function of cardiac veins
thymus, brachiocephalic veins, aortic arch, trachea, esophagus
order of structures in superior mediastinum from anterior to posterior
Umbilical vein
oxygenated blood from placenta to fetus towards liver
Ductus venosus
shunt through which blood bypasses liver to inferior vena cava
Foramen ovale
shunt from right atria to left atria allows bypass of lungs
Ductus arteriosus
shunts blood that enters the pulmonary trunk to descending aorta to bypass lungs
Umbilical arteries
deoxygenated blood from fetus back to placenta for reoxygenated
closure of formaen ovale, ductus arteriosus and ductus venosus
changes that occur after baby takes its first breath
ligamentum teres of liver
the remnant of the umbilical vein that carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus.
medial umbilical ligaments
the remnants of the umbilical arteries that become fibrous cords in the adult
systole
Av valvees close, ventricles contract to pump blood out of the heart, semilunar valves forced open
diastole
AV valves open, blood flows from atria to ventricles, semilunar valves close
SA node
The heart's natural pacemaker, generating electrical impulses that initiate each heartbeat and regulate heart rhythm
wall of right atrium near SVC
where is the SA node
Av node
located at the junction of the atria and ventricles, transmits electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles
Av bundle
A bundle of heart muscle fibers that carry electrical impulses from the atrioventricular node to the ventricles
purkinje fibeers
Specialized fibers that conduct electrical impulses throughout the ventricles, ensuring coordinated contraction
osteoclast
A type of bone cell responsible for bone resorption and remodeling by breaking down bone tissue.
osteocyte
A mature bone cell that maintains bone tissue and regulates mineral content.
RANkL and OPG
secreted by osteocyte and regulate osteoclast activity
osteeoblast
A type of bone cell responsible for bone formation by synthesizing and mineralizing bone matrix
RANKL
a protein involved in bone remodeling that stimulates osteoclast differentiation
OPG
protein that suppresses osteoclast differentiation
reversal phase
phase of bone remodeling marked by reduction of osteoclasts and recruitment of osteoblast precursors
type I collagen
type of collagen produced by osteoblast during formation phase
sclerostin
osteoblast inhibitor expressed as osteoblasts become osteocytes
sclerosteosis
genetic disorder characterized by BONE OVERGROWTH caused by loss of sclerostin
promotes osteoclast differentiation and bone loss
how does periodontitis progress
tunica interna, tunica media, tunica externa
layers of blood vessels
tunica media
largest layer in arteries
tunica externa
largest layer in veins
vaso vasorum
small blood vessels that supply the walls of larger blood vessels
large veins
blood vessels with more vasa vasorum
veins
largere, thinner, vessels with collapsed walls
venule
small blood vessels that collect blood from capillaries and drain into veins, increased permeability during inflammation
arteries
thicker walls, narrower and rounder lumen
continuous capillary
most common type of capillary
fenestrated capillaries
capillaries with small pores that allow for increased permeability, found in organs like the kidneys and intestines.
discontinuous capillaries
capillaries with larger openings that facilitate the passage of larger molecules and cells, typically found in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow
arteriovenous shunt
a direct connection between an artery and a vein that bypasses capillary beds, allowing for rapid blood flow to facilitate heat loss in hot conditions
fibrous skeleton
structure of heart that provides support and electrical insulation between the atria and ventricles
bundle of His
a group of heart muscle fibers that transmits electrical impulses from the atrioventricular node to the ventricles, COORDINATING CONTRACTION
macule
flat lesion less than 1 cm
papule
raised lesion less than 1 cm
patch
flat lesion greater than 1 cm
plaque
raised lesion greater than 1 cm
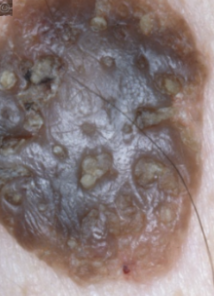
Seborrheic keratosis
benign epidermal growth, “stuck on” appearance
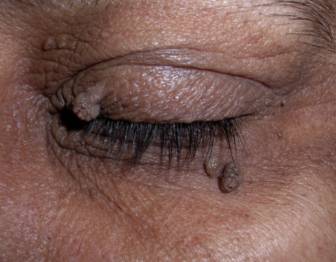
skin tags
benign epidermal growth, increased prevalence with pregnancy age, diabetes, and obesity
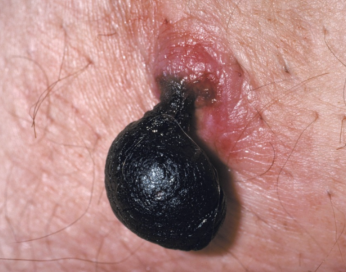
thrombosed skin tag
a skin tag that has formed a blood clot, leading to a painful and discolored lesion
Acanthosis nigricans
benign velvety darkened skin, increased prevalence with obesity and insulin resistance
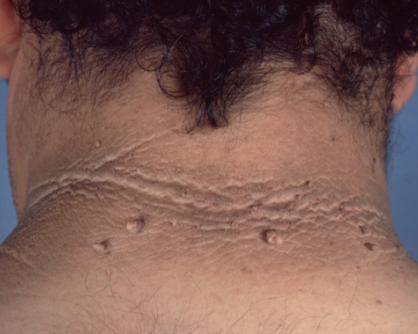
Cherry angioma
benign vascular proliferation, increased prevalence with pregnancy
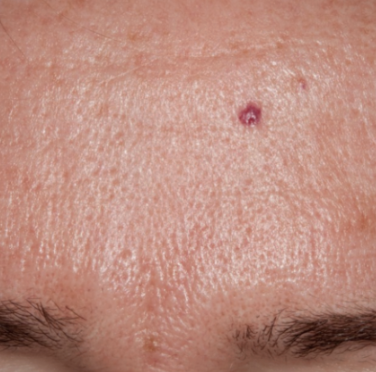
bite fibroma
benign fibroma caused by trauma, painless asymptomatic
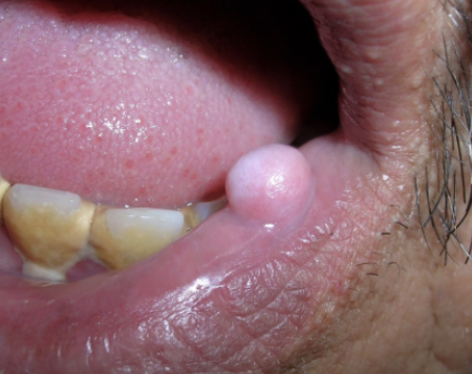
Fordyce spots
ectopic sebaceous glands, asymptomatic, no treatment needed
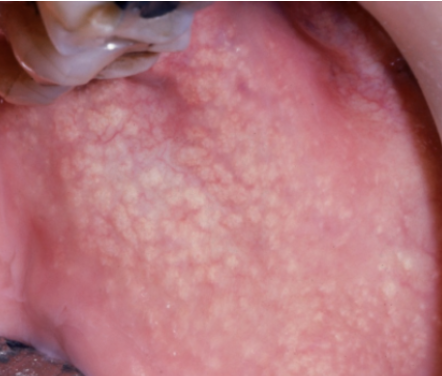
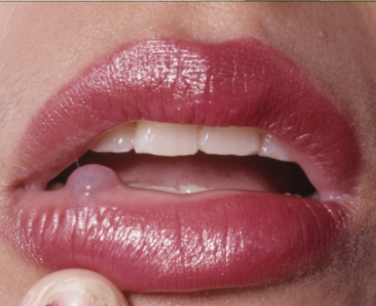
Mucocele
rupture of minor salivary gland, swells and pops repeatedly
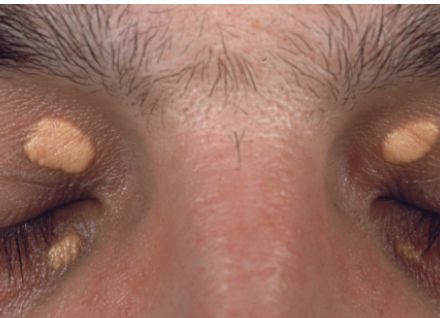
Xanthelasma
yellow, raised deposit of cholesterol that typically appears on the eyelids
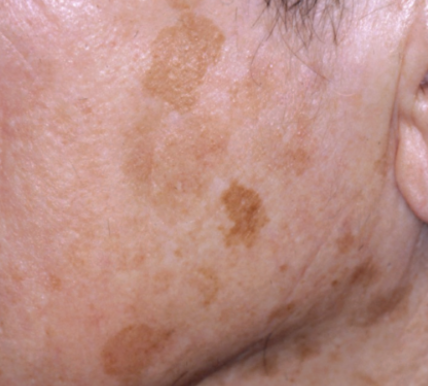
Solar lentigo
benign brown patches associated with sun exposure
nevi
common benign skin growths, often called moles, that can vary in color and size.
changes in size, shape, color, itching, bleeding
when to worry about nevi
how long has it been there, has it changed
key questions that may suggest a more serious lesion
rapid growth, symptomatic (pain, bleeding, itching, burning)
qualities of serious skin lesions