Genetics assignments for exam 1
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
The ________ consists of a linear series of three adjacent nucleotides present in mRNA molecules.
genetic code
What are some of the impacts of biotechnology on crop plants in the United States? Select All that Apply
the development of pest-resistant crops
quicker identification of hazardous organisms in food
the development of transgenic crops
the spread of transgenes from genetically modified crops to wild plants
the development of nutritionally-enhanced crops
the development of herbicide-resistant crops
Which of the following is TRUE about alleles?
An allele is a variant form of a gene.
Which of the following is an example of heredity?
Dalmation dogs all have spots.
In many species, there are two representatives of each chromosome. In such species, the characteristic number of chromosomes is calledthe ________ number. It is usually symbolized as ________.
diploid; 2n
What would happen if, during meiosis, the chromosome number was not halved before egg and sperm formation?
in each successive generation, the offspring would double their chromosome number
Genetics is the study of ________.
inheritance and variation
Organisms that are well understood from a scientific standpoint and are often used in basic biological research are often called ________.
model organisms
Recombinant DNA technology is dependent on a particular class of enzymes, known as ________ that cuts DNA at specific nucleotidesequences.
restriction enzymes
The haploid number of a species is _______.
n
Name the bases in DNA and their pairing specificities.
adenine:thymine
guanine:cytosine
Once a protein is made, its biochemical or structural properties play a role in producing ________.
Phenotype
A ________ is an organism produced by biotechnology that involves the transfer of hereditary traits across species.
transgenic organism
Contrast chromosomes and genes.
Genes take part in the production of proteins through the processes of transcription and translation. They are the functional units of heredity. Chromosomes carry genes and take part in cell division during mitosis and meiosis.
What is the central dogma of genetics?
DNA → RNA → protein
Which of the following is the function of DNA?
DNA is responsible for the storage and replication of genetic information.
What is a gene mutation?
the source of all genetic variation
The functional unit of heredity is a _______.
gene
What is the term given to the theory which states that the fertilized egg contains a complete miniature adult?
preformation
In the 1600s, William Harvey studied reproduction and development. What is the term given to the theory which states that an organismdevelops from the fertilized egg by a succession of developmental events that lead to an adult?
epigenesis
Describe Mendel's conclusions about how traits are passed from generation to generation.
Mendel hypothesized that traits in peas are controlled by specific unit factors. He suggested that unit factors occur in pairs and that unit factors separate from each other during gamete formation.
If you wrote a brief essay discussing the impact of recombinant DNA technology on genetics as we perceive the discipline today, whatapplications of recombinant DNA technology should be included? Select the six correct applications.
Medical Advances and forensics
understanding gene function
plant and animal husbandry
drug development
plant and animal production
What is a homunculus?
a sperm or egg containing a miniature adult, perfect in size and proportion
What term is used to describe the fact that different genes in an organism often provide differences in observable features?
Phenotype
What are the basic subunits of DNA and RNA?
nucleotides
When mutation alters a gene, it may modify or even eliminate the encoded protein's usual ________ and cause an altered ________.
function; phenotype
How has the use of model organisms advanced our knowledge of the genes that control human diseases? Select the two correct statements.
What is learned in one organism can usually be applied to all organisms.
Most model organisms have peculiarities (ease of growth, genetic understanding, abundant offspring).
Which of the following is an example of natural selection?
a bird's beak is able to effectively crack the seeds it encounters
________ is a discipline involved in the development of both hardware and software for processing, storing, and retrieving nucleotide andprotein data.
Bioinformatics
The Age of Genetics was created by remarkable advances in the use of biotechnology to manipulate plant and animal genomes. Giventhat the world population reached 7.5 billion people in 2017 and is expected to reach 9.7 billion in 2050, some scientists have proposedthat only the worldwide introduction of genetically modified (GM) foods will increase crop yields enough to meet future nutritional demands. Pest resistance, herbicide, cold, drought, and salinity tolerance, along with increased nutrition, are seen as positive attributes of GM foods. However, others caution that unintended harm to other organisms, reduced effectiveness to pesticides, gene transfer to nontarget species, allergenicity, and as yet unknown effects on human health are potential concerns regarding GM foods.
environmental impact
likelihood of cross-pollination
allergenicity
A protein's shape and chemical behavior are determined by ________.
its linear sequence of amino acids
Explain why the distribution of protein and nucleic acid in a eukaryotic cell favors nucleic acid as the genetic material.
DNA is found where primary genetic functions occur; protein is found everywhere.
Consider the following two statements about DNA melting temperature:1) The melting temperature of a sample of DNA is the temperature at which 50% of the double helices in the sample have completely denatured.2) A molecule with 53% GC base pairs would have a higher melting temperature than a molecule of equivalent length with 53% AT base pairs.
Statement 1) is false; statement 2) is true.
T/F: Guanine and adenine are purines found in DNA.
True
Which of the following statements about DNA structure is true?
The nucleic acid strands in a DNA molecule are oriented antiparallel to each other, meaning they run in opposite directions.
The form of DNA that is observed to adopt a left-handed helix is ________.
Z-DNA
What is the hyperchromic effect?
A hyperchromic effect is the increased absorption of UV light as double-stranded DNA is converted to single-stranded DNA.
What does Tm imply?
The temperature at which half of the sample is denatured.
The form of DNA that is believed to be most biologically significant is ________.
B-DNA
Any two nucleic acid fragments will spontaneously hybridize if they encounter each other as long as they are
complementary and antiparallel
Why would D-DNA and E-DNA be unlikely to be found in the genomes of living organisms?
They only occur in helices lacking guanine, and it is exceptionally unlikely to find an organism that has no guanine.
In an analysis of the nucleotide composition of double-stranded DNA to see which bases are equivalent in concentration, which of the following would be true?
A + C = G + T
Watson and Crick used information from several individuals to construct their model of DNA. Whose X-ray diffraction studies were critical to their work?
Rosalind Franklin
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of the genetic material?
It is composed of protein.
DNA has______as the sugar in its nucleotides. The pyrimidines found in DNA are
Deoxyribose
thymine and cytosine
RNA has______as the sugar in its nucleotides. The pyrimidines found in DNA are
Ribose
uracil and cytosine
The purines found in both nucleic acids are
adenine and guanine
Considering the structure of double-stranded DNA, which kind(s) of bonds hold one complementary strand to the other?
hydrogen
Which technique can be used to identify the location of genes on a chromosome?
FISH
What is the physical state of DNA after it is heated and denatured?
single-stranded
If 15% of the nitrogenous bases in a sample of DNA from a particular organism are thymine, what percentage should be cytosine?
35%
A particular ________ carry the information for making a particular protein, but ________ can be used to make any protein.
gene and mRNA; a ribosome and a tRNA
storage
expression
variation
replication
stable maintenance and passage of information
production of a phenotype
potential for alteration
duplication of genetic material
Reverse transcriptase is an enzyme found in association with retroviral activity. It has the property of ________.
synthesis of DNA from an RNA template
Genetic functions in a eukaryote can be observed in ________.
chloroplasts, mitochondria, and the nucleus
Arrange the principal forms of RNA in order of abundance from least abundant to most abundant.
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
A primitive eukaryote was discovered that displayed a unique nucleic acid as its genetic material. Analysis provided the following information:
1. The general X-ray diffraction pattern is similar to that of but with somewhat different dimensions and more irregularity.2. A major hyperchromic shift is evident upon heating and monitoring UV absorption at 260 3. About 75 percent of the sugars are deoxyribose, while 25 percent are ribose.4. Base-composition analysis reveals four bases in the following proportions
purine-purine base pairing
more flexibility than DNA; possible kinking or folding
helical structure
hydrogen bonding between base pairs
possibly more strands than in DNA
Which enzyme makes DNA from an RNA template?
Reverse transcriptase
If protein were the genetic principle and not nucleic acid, significant mutagenic effects would be detected at ________.
280 nm
Regarding the structure of DNA, the covalently arranged combination of a deoxyribose and a nitrogenous base would be called a(n) ____________.
nucleoside
The Central Dogma specifies that the information in ________.
DNA is copied into an RNA molecule during transcription, and the information in that RNA molecule is used to make a protein during translation
What does it mean for a double helix of DNA to be antiparallel and complementary?
When the two strands in double-stranded DNA associate with each other, one strand runs 5' to 3' in one direction, the other strand runs in the same plane, but with a 3' to 5' orientation (antiparallel). Hydrogen bonding between strands occurs between adenines and thymines, and between cytosines and guanines, which are in turn called complementary base pairs.
The basic structure of a nucleotide includes ________.
base, sugar, and phosphate
Explain the technique of electrophoretic separation of DNA fragments
A mixture of different sized DNA molecules are subjected to an electric field, and migrate through a semisolid matrix such that smaller fragments travel further in the matrix.
Rank the following base pairs according to their stability.
Most stable:Guanine-Cytosine
Least stable: Adenine-Thymine
Spleen diesterase is an enzyme that breaks the covalent bond that connects the phosphate to the 5' carbon. If the dinucleotide is digested with spleen diesterase, to which base and to which carbon on the sugar is the phosphate now attached?
A; 3'
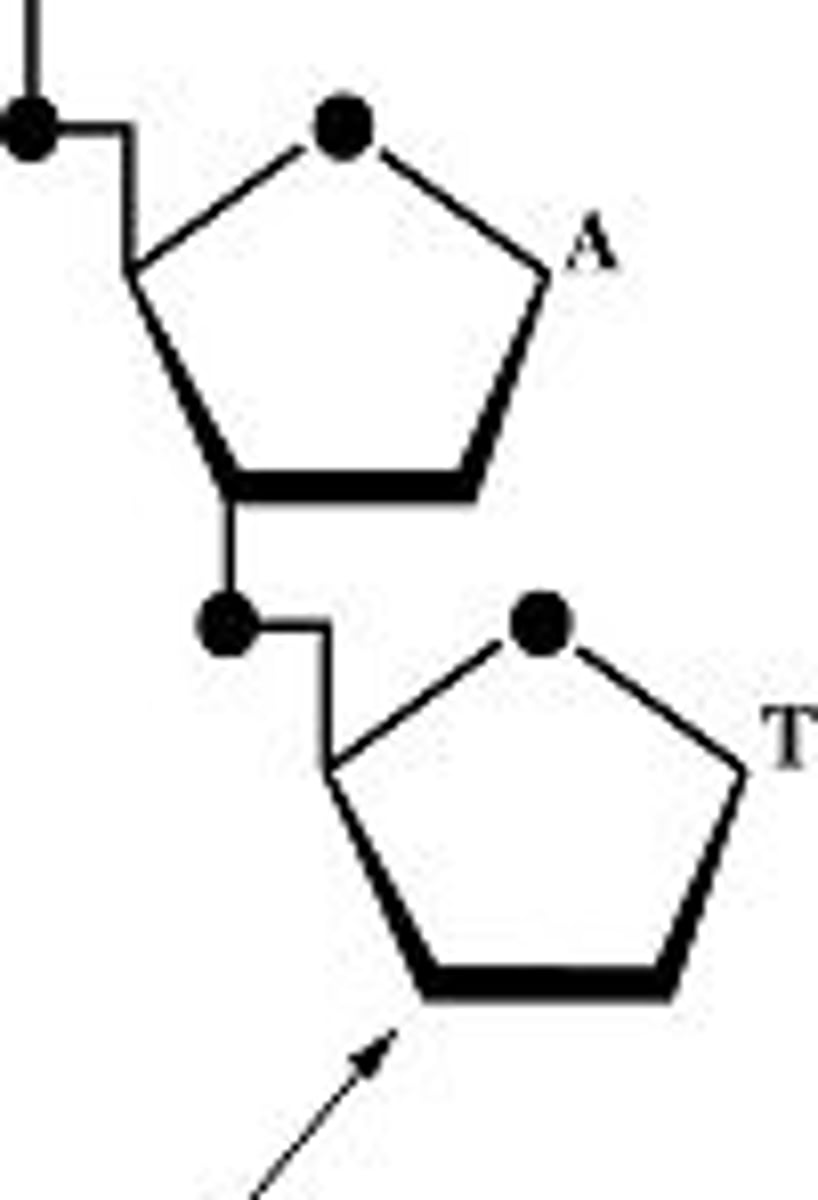
If you were told that this molecule could be found in either DNA or RNA, depending on the identity of the chemical groups labeled (X) and (Y), the nitrogen-containing ring structure would have to be ________.
cytosine
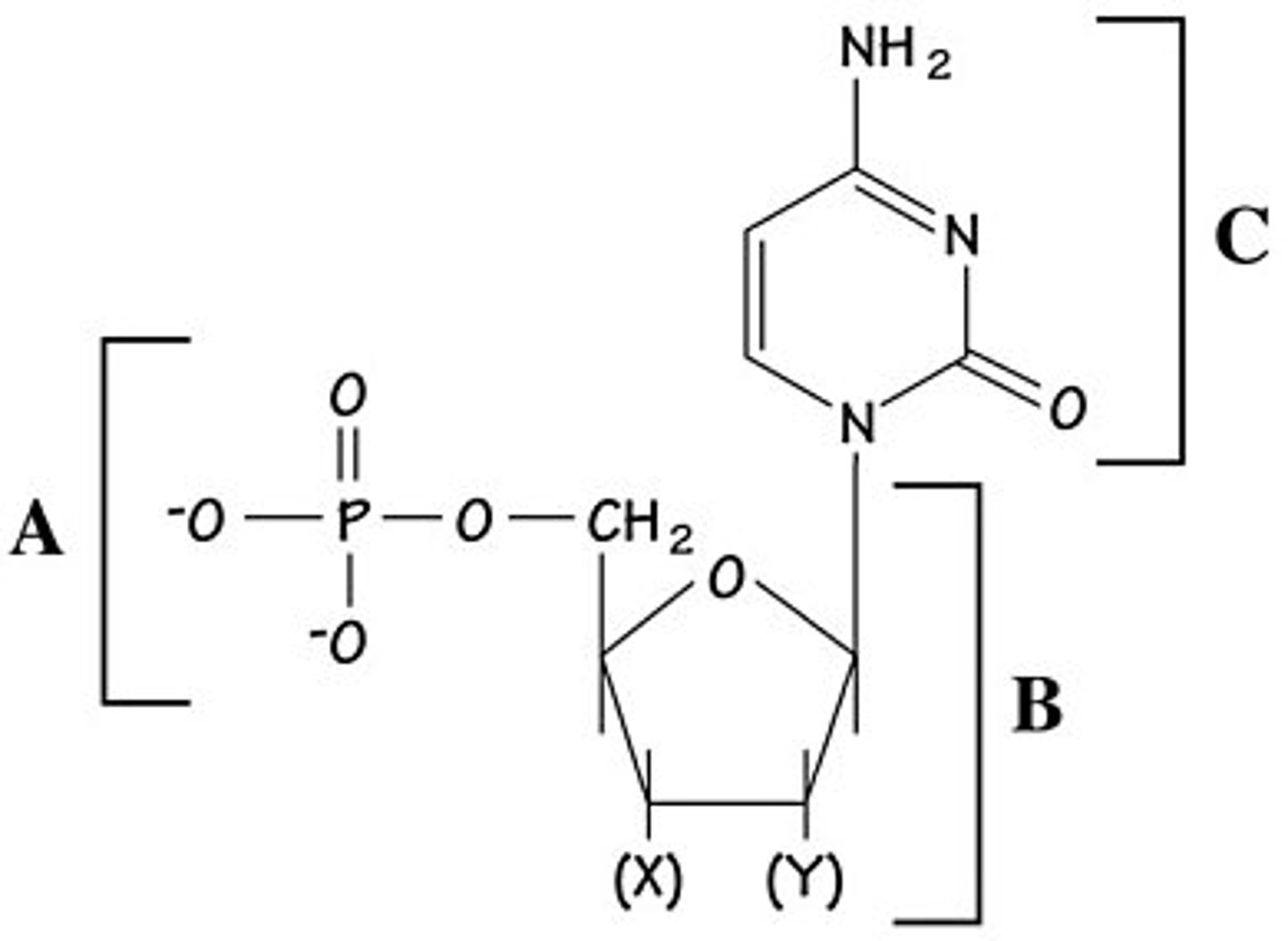
If this molecule were found in a DNA chain, the chemical group labeled (X) would be ________ and the chemical group labeled (Y) would be ________.
OH; H
Approximately 21% of the human genome is comprised of nucleotides containing C. Given this information, calculate the percentage of the human genome that is comprised of nucleotides containing G, T, and A.
21 % of the human genome is comprised of G.
21% % of the human genome is comprised of T.
29% of the human genome is comprised of A.
An alien species was discovered that has DNA comprised of 6 different bases: G binds to C; A binds to T: and X binds to Y. Approximately 16% of this alien genome is comprised of nucleotides containing C, and 22% is comprised of nucleotides containing Y. Given this information, calculate the percentage of the alien genome that is comprised of nucleotides containing G, T, A, and X.
16 % of the alien genome is comprised of G
12% of the alien genome is comprised of T
12% of the alien genome is comprised of A
22% of the alien genome is comprised of X
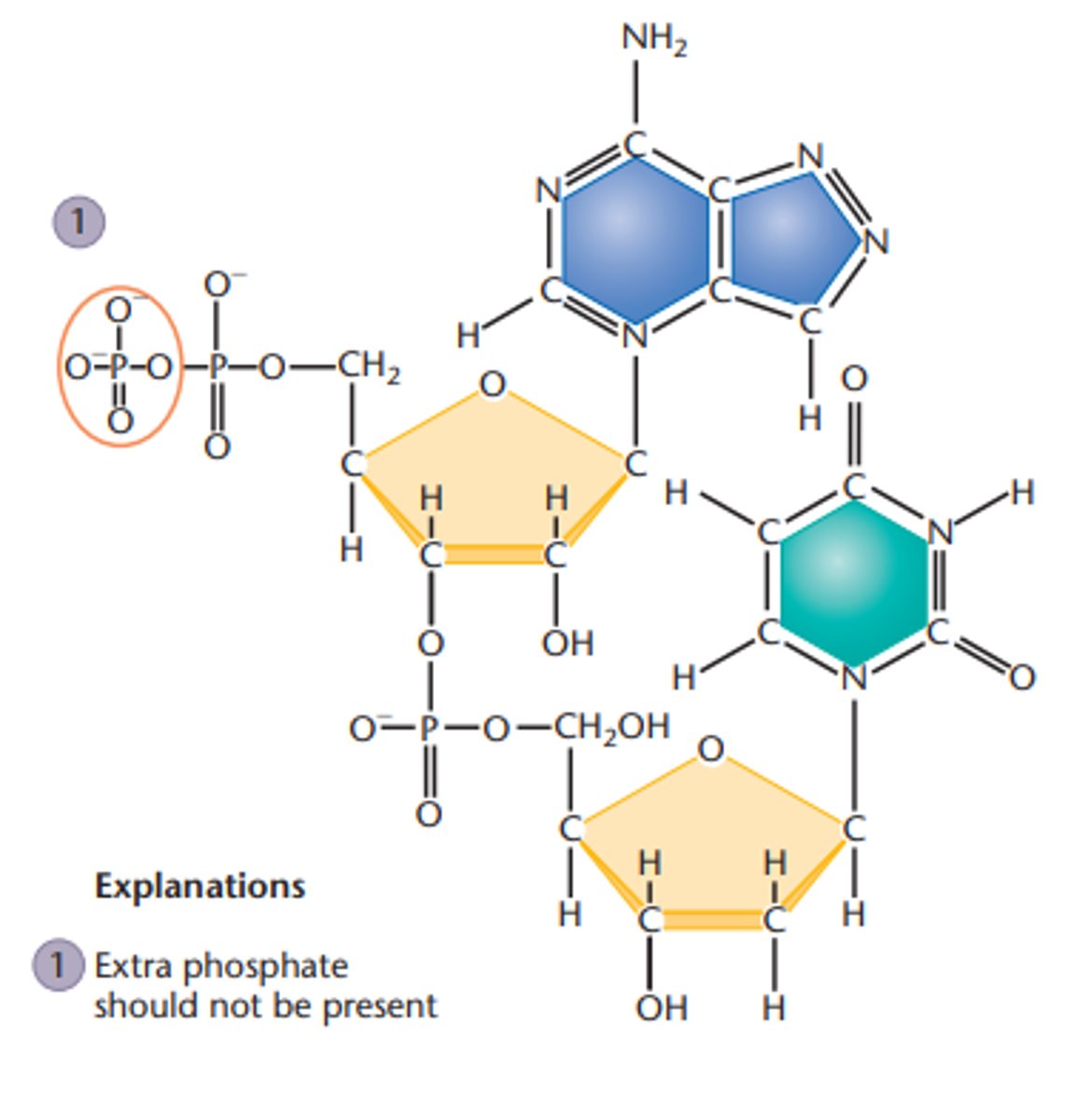
A genetics student was asked to draw the chemical structure of an adenine- and thymine-containing dinucleotide derived from DNA.
The student made more than six major errors. One of them is circled, numbered 1, and explained below the diagram.
-The C-1´ of the sugar is bonded to the wrong nitrogen in adenine.
-In the adenine ring, a nitrogen is at position 8 rather than position 9.
-There are too few bonds between C-5 and C -6 of thymine
-There are too many bonds between the N-3 and C-2 of thymine
-There is a hydroxyl group at C-2´ on the top sugar (attached to adenine) instead of hydrogen
-The C-5' on the bottom sugar has an extra hydroxyl group.
-There is a methyl group missing from the C-5 position of thymine.
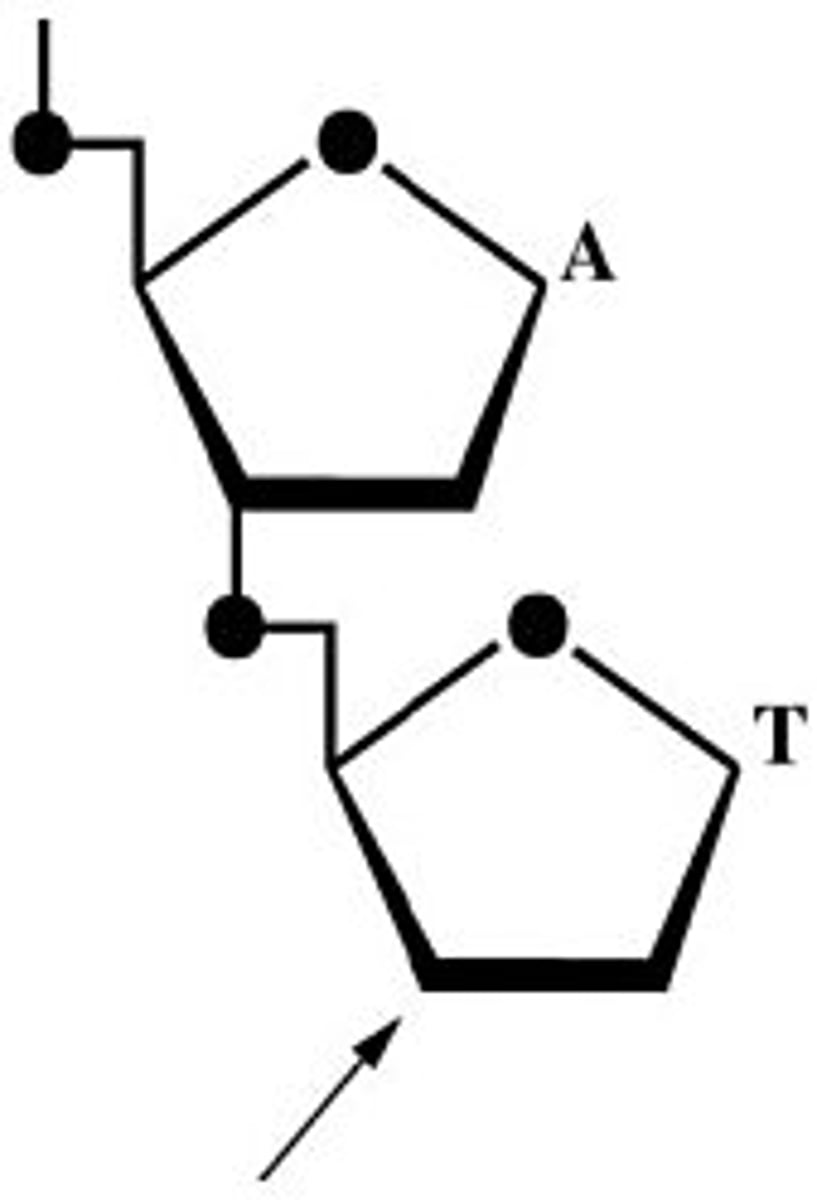
The figure below shows a representative dinucleotide:
This figure represents ________, and the arrow is closest to the ________ end.
DNA; 3'
Histones contain large amounts of________mino acids such as_________. Thus, they can bind electrostatically to the_________phosphate groups of nucleotides. Nucleosomes are composed of____
positively charged
ysine and arginine
negatively charged
all histones except H1
In E. coli , the genetic material is composed of ________.
circular, double-stranded DNA
Rank the following levels of chromatin compaction in eukaryotes from the least compact to the most compact.
naked DNA, nucleosome, solenoid, loop domains, chromatid, and metaphase chromosome
Which histone helps stabilize the solenoid structure?
H1
Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) are capable of remodeling chromatin by adding acetyl groups to various lysine residues in histones that comprise the nucleosome. Following this modification, the lysine residue no longer has a positive charge. Which statement is true?
Histones in general have a net positive charge that allow them to bind to DNA. Acetylation of histones, decreases their positive charge and weakens the histone-DNA interaction.
Examples of histone modifications are acetylation (by histone acetyltransferase, or HAT), which is often linked to gene activation, and deacetylation (by histone deacetylases, or HDACs), which often leads to gene silencing typical of heterochromatin. Such heterochromatinization is initiated from a nucleation site and spreads bidirectionally until encountering boundaries that delimit the silenced areas.
In the heterozygous state (w + /w ), a variegated eye is produced, with white and red patches. How might one explain position-effect variegation in terms of histone acetylation and/or deacetylation?
The red patches are caused by the acetylation of the histones associated with the DNA of the w + allele.
The white patches are caused by the deacetylation of the histones associated with the DNA of the w + allele.
Chromatin of eukaryotes is organized into repeating interactions with protein octamers called nucleosomes. Nucleosomes are composed of which class of molecules?
histones
Eukaryotic chromosomes contain two general domains that relate to the degree of condensation. These two regions are ________.
called heterochromatin and euchromatin
_______are duplicated copies of genes that have undergone________and ______ the origianl gene
pseudogenes
considerable mutation
share some homology to
In the formation of nucleosomes, one histone class, H1, is not directly involved, yet it does associate with DNA to form higher level chromosomal structures. Where does this histone (H1) associate?
It binds to linker (spacer) DNA between nucleosomes.
As chromosome condensation occurs, a 300- A______or six______coiled together. Such a structure is called a_______These fibers form a________that further condense into the chromatin fiber and are then coiled into chromosome arms making up each________
fiber
nucleosomes
solenoid
series of loops
chromatid
Nucleosomes are composed of________different histone molecules, each of which exists________, thus forming a(n) octamer . Histone H1______and is associated with________
four
twice
octamer
is between nucleosomes
linker DNA
While much remains to be learned about the role of nucleosomes and chromatin structure and function, recent research indicates that in vivo chemical modification of histones is associated with changes in gene activity. One study determined that acetylation of H3 and H4 is associated with 21.1 percent and 13.8 percent increases in yeast gene activity, respectively, and that histones associated with yeast heterochromatin are hypomethylated relative to the genome average [Bernstein et al. (2000)].
Speculate on the significance of these findings in terms of nucleosome - DNA interactions and gene activity.
Hypomethylation decreases gene expression.
Changes in the binding of nucleosomes to DNA due to acetylation enable genes to be more accessible to factors that promote transcription.
What makes up the protein component of a nucleosome core?
Two tetramers of histone proteins
What is the first order of chromatin packing?
Coiling around nucleosomes
True/ False: The second order of chromatin packing occurs when nucleosomes coil together to form a fiber that is 300 nm in diameter.
False