bio fall semester exam review.
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/182
Last updated 5:49 AM on 12/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
183 Terms
1
New cards
what was produced from the miller urey experiment?
organic compounds such as amino acids
2
New cards
what are the organic compounds
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
3
New cards
what are lipids
\-made up of glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acids.
\-LONG TERM ENERGY SOURCES
\-major part of cell membrane
\-LONG TERM ENERGY SOURCES
\-major part of cell membrane
4
New cards
what is a nucleic acid?
\-dna and rna
\-responsible for transmitting genetic info
\-CHONP
\-responsible for transmitting genetic info
\-CHONP
5
New cards
what are carbohydrates?
\-QUICK ENERGY SOURCES
\-include sugar and starches
\-include sugar and starches
6
New cards
what are proteins?
\-made up of amino acids
\-major component of skin, hair, nails and transportation
\-used as enzymes
\-CHON
\-major component of skin, hair, nails and transportation
\-used as enzymes
\-CHON
7
New cards
what is a catalyst?
anything that can speed up a reaction by lowering activation energy.
8
New cards
what is an enzyme?
proteins that help speed up metabolism or chemical reactions in the body.
9
New cards
Enzymes are…
organic catalysts
10
New cards
Are all enzymes catalysts?
True
11
New cards
Are all catalysts enzymes?
false
12
New cards
at what temp does the enzyme function best?
40 degrees celsius/ 104 degrees Fahrenheit
13
New cards
what chemicals did miller and urey use in the experiment to stimulate earth’s early atmosphere?
mixture of hydrogen, ammonia, methane, & water
14
New cards
molecular organization
cell, compound, molecule, element, atom
15
New cards
what is the carbohydrate monomer?
monosaccharide
16
New cards
what is the carbohydrate polymer?
disaccharide, and polysaccharide
17
New cards
monosaccharides (starchy)
glucose, frcutose, galactose (“ose” indicates sugar)
18
New cards
disaccharides (starchy)
2 monosaccharides bonded together
19
New cards
dehydration synthesis
removal of water to join 2 molecules together - same thing as formation of disaccharides
20
New cards
hydrolosis
breaking down carbs into disaccharides or monosaccharides
21
New cards
animals store excess sugars as the starch
glycogen
22
New cards
plants store excess sugars as the starch
cellulose
23
New cards
whats a monomer of a protein?
amino acids
24
New cards
whats a polymer of a protein?
polypeptide
25
New cards
what help make proteins?
nucleic acids
26
New cards
whats a monomer of a nucleic acid
nucleotide
27
New cards
what does a nucleotide include?
phosphate group, deoxyribose or ribose, and a nitrogen base
28
New cards
what is needed to start a reaction?
activation energy
29
New cards
enzymes can be affected by…
temperature, pH, and concentration
30
New cards
whats a cell?
basic unit of structure and organization of all living organisms.
31
New cards
8 characteristics of life
1. made of cells
2. universal genetic code
3. maintain homeostasis
4. respond to environment
5. obtain + use materials + energy
6. grow and develop
7. reproduce
8. change over time
32
New cards
Cell Theory
1. living things are made of cells
2. cells are the basic unit of life
3. cells come from existing cells
33
New cards
all cells have:
cell membrane, DNA, cytoplasm, ribosomes
34
New cards
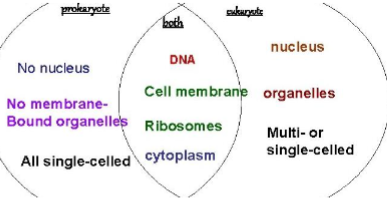
prokaryotes characteristics
\-no nucleus/organelles
\-oldest cells
\-simple/single celled
\-kingdoms: bacteria, archaea
\-oldest cells
\-simple/single celled
\-kingdoms: bacteria, archaea
35
New cards
eukaryotes characteristics
\-nucleus/organelles
\-younger
\-complex/multi-celled
\-kingdoms: protista, fungi, plantae, animalia
\-younger
\-complex/multi-celled
\-kingdoms: protista, fungi, plantae, animalia
36
New cards
prokaryotes and eukaryotes (both) characteristics
\-cell membrane
\-DNA
\-ribosomes
\-cytoplasm
\-DNA
\-ribosomes
\-cytoplasm
37
New cards
Body System level of organization
cells → tissues → organs →organ systems → organism
38
New cards
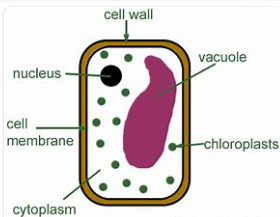
plant cells characteristics
cell wall, large vacuole, chloroplasts, flagella only in gametes
39
New cards
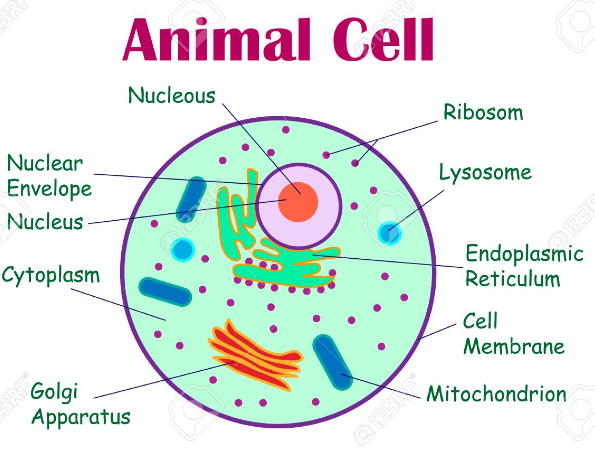
animal cell characteristics
no cell wall, small or no vacuole, no chloroplasts, flagella
40
New cards
plant and animal cell characteristics
mitochondrion, golgi apparatus, rough/smooth endoplasmic rectilum, nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosomes
41
New cards
Nucleus:
holds DNA. found in eukaryotic cells.
42
New cards
Cell Membrane:
outside lipid barrier of cell. controls what enters and leaves cell to maintain homeostasis
43
New cards
Mitochondria:
powerhouse of cell; convert glucose into energy
44
New cards
Ribosome:
makes proteins
45
New cards
vacuole
sac-like structure stores water, salts, food, etc.
46
New cards
cell wall
extra barrier ON TOP of cell membrane for extra support. found in plant cells.
47
New cards
chloroplast:
where photosynthesis occurs, found only in plant cells
48
New cards
lysosome
digests lipids, carbs, and proteins into small molecules; involved in breaking down of cells.
49
New cards
golgi apparatus
modifies, sorts, and packages proteins from the endoplasmic recticulum for storage in cell or secretion outside of cell.
50
New cards
endoplasmic reticulum
where lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled with proteins/other materials that are exported from the cell.
51
New cards
whats the endosymbiotic theory
states that mitochondria and chlorplasts in eukaryotic cells were aerobic bacteria (prokaryotes). theory explains origin of eukaryotic cells.
52
New cards
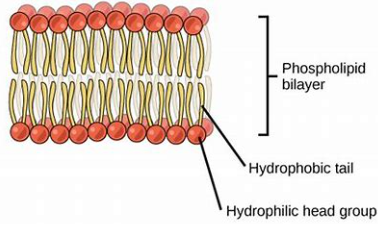
phopholipid bliayer
double layer of phospholipids that make the membrane
53
New cards
phospholipid
the monomer of a cell membrane
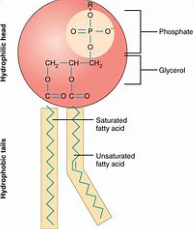
54
New cards
receptor protein
sends and receives messages; usually in from of hormones
55
New cards
channel protein
works like a tunnel → allow things in & out of membrane
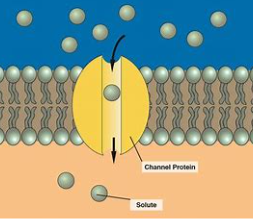
56
New cards
marker protein
often have carb chains. identify cell, every cell has marker proteins.(act as name tag)
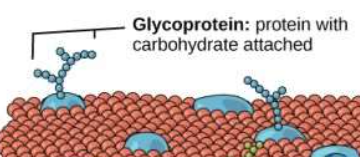
57
New cards
passive transportation characteristics
1. requires NO energy
2. high to low concentration
3. molecules move WITH gradient. Go with the flow!
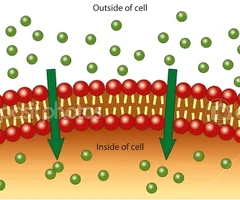
58
New cards
active transport characteristics
1. requires energy
2. low to high concentration
3. molecules move AGAINST gradient
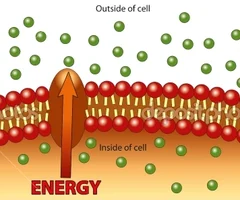
59
New cards
diffusion
molecules naturally move from high to low concentration until equilibrium is reached.
requires NO ENERGY.
requires NO ENERGY.
60
New cards
facilitated diffusion
movement of larger molecules from high to low concentrations through channel proteins until equilibrium is reached and requires no energy.
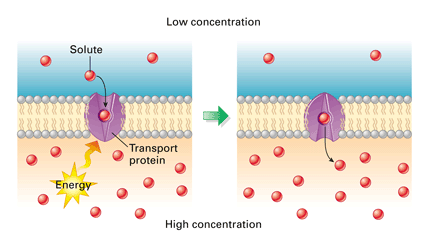
61
New cards
osmosis
diffusion of water from high to low concentration until equilibrium is reached.
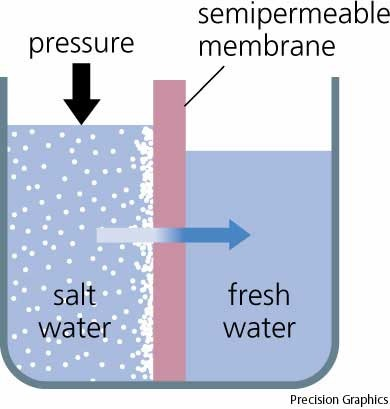
62
New cards
ATP:
energy storage molecule
63
New cards
“Hypo”
lesser, lower
64
New cards
“hyper”
more, higher
65
New cards
“iso”
equal”
66
New cards
“tonic”
solute concentration
67
New cards
Solute
anything but water
68
New cards
Solvent
H20 (water)
69
New cards
Hypotonic Solution
* solution w/ LOWER solute concentration OUTSIDE cell
* water moves INTO cell
* cell will burst
* water moves INTO cell
* cell will burst
70
New cards
Isotonic Solution
* solution w/ = solvent & solute concentration
* cell is in equilibrium
* water moves in/out @ equal rate
* cell is in equilibrium
* water moves in/out @ equal rate
71
New cards
Hypertonic Solution
* solution w/ HIGHER solute concentration OUTSIDE of cell
* water will move OUT of cell
* cell will shrink
* water will move OUT of cell
* cell will shrink
72
New cards
Hypotonic Solution effect on cells
Animal Cell: swells, may burst (cytolosis)
Plant Cell: normal, vacuole is full, turgor pressure
Plant Cell: normal, vacuole is full, turgor pressure
73
New cards
Isotonic Solution effect of cells
Animal Cell: normal
Plant Cell: wilts, no pressure on cell wall, vacuole is not as full
Plant Cell: wilts, no pressure on cell wall, vacuole is not as full
74
New cards
Hypertonic Solution effect on cells
Animal Cell: shrivels up and dies
Plant Cell: membrane shrinks & breaks from cell wall (plasmolysis)
Plant Cell: membrane shrinks & breaks from cell wall (plasmolysis)
75
New cards
Endocytosis
taking in of large particles
76
New cards
Exocytosis (exo=exterminate)
removal of large particles
77
New cards
osmoregulation
control of water balance.
if you drink a lot of water, water levels in blood will be higher than normal. hypothalamus will send a message to the pituitary gland, will send hormones through circulatory system to increase kidney filtration, will cause you to pee, brings water levels back to normal and the feedback loop shuts off.
if you drink a lot of water, water levels in blood will be higher than normal. hypothalamus will send a message to the pituitary gland, will send hormones through circulatory system to increase kidney filtration, will cause you to pee, brings water levels back to normal and the feedback loop shuts off.
78
New cards
thermoregulation
process of maintaining internal temp. within tolerable range.
\
you go out jogging in summer, hypothalamus sends a message to Pituitary Gland to bring your body temperature down, sends hormonal messages through the circulatory system to the sweat glands, will secret to the surface of your body in order to cool your body back until your body is back to its normal levels and the feedback loop will shut off
\
you go out jogging in summer, hypothalamus sends a message to Pituitary Gland to bring your body temperature down, sends hormonal messages through the circulatory system to the sweat glands, will secret to the surface of your body in order to cool your body back until your body is back to its normal levels and the feedback loop will shut off
79
New cards
glucose regulation
process of maintaining optimal blood glucose levels
If you eat alot of food, hypothalamus will recognize that your blood sugar levels are starting to peak, will send a message through your circulatory system to your pancreas that will secrete hormone insulin, will cause your cells to allow more sugar in and will combine these sugars to make a starch called glycogen, will get stored away in your liver, which will help get sugar out of your blood and bring your blood sugar back to normal which will end the feedback loop
If you eat alot of food, hypothalamus will recognize that your blood sugar levels are starting to peak, will send a message through your circulatory system to your pancreas that will secrete hormone insulin, will cause your cells to allow more sugar in and will combine these sugars to make a starch called glycogen, will get stored away in your liver, which will help get sugar out of your blood and bring your blood sugar back to normal which will end the feedback loop
80
New cards
positive feedback loop
keeps the stimulus in the same direction and presumably speeds up the action.
81
New cards
negative feedback loops
process in which the body senses a change, and activates mechanisms to reverse that change.
example: thermoregulation and glucose regulation
example: thermoregulation and glucose regulation
82
New cards
Hypothamulus
recognize pH in blood, b/p, body temp, respiratory levels
83
New cards
Pituitary gland
master gland of endocrine system
84
New cards
Circulatory System
network connected to the heart that deliver molecules through the body.
85
New cards
respiratory system
responsible for taking in oxygen and removing carbon dioxide from lungs
86
New cards
nervous system
transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body, including internal organs
87
New cards
muscular system
enables movement of body parts
88
New cards
skeletal system
give structure and make blood cells
89
New cards
endocrine system
sends chemical signals to the other body systems to turn them on or off. Hormones are produced in this system.
90
New cards
lymphatic (immune) system
responsible for making white blood cells to fight infections.
91
New cards
James Watson and Francis Crick
discovered structural model of DNA
92
New cards
how many chromosomes does the body have?
46(2n or diploid)
93
New cards
DNA characteristics
* contains deoxyribose sugar
* double stranded
* A-T & C-G
* never leaves nucleus
* double stranded
* A-T & C-G
* never leaves nucleus

94
New cards
RNA characteristics
* contains ribose sugar
* single stranded
* A-U & C-G
* can leave nucleus
* located in cytoplasm
* helps make protein
* single stranded
* A-U & C-G
* can leave nucleus
* located in cytoplasm
* helps make protein
95
New cards
DNA & RNA characteristics (both)
* located in nucleus
* function in protein synthesis
* composed of nucleotides
* function in protein synthesis
* composed of nucleotides
96
New cards
mRNA, messenger RNA
copies/carries DNA code
97
New cards
tRNA, transfer RNA
carries amino acids
98
New cards
rRNA, ribosomal RNA
guides process in the ribosome
99
New cards
what term describes DNA to mRNA?
transcription
100
New cards
what term describes mRNA to Protein
translation