Chest pain
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Y'all better know how treat a heart attack or we're going to have a problem
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
located in the internal organs, blood vessels, and visceral pleura; enters CNS at multiple levels, difficult to locate, described as ache, pressure, tightness, heaviness, discomfort
Tell me about Visceral Pain Fibers
located in dermis/parietal pleura, enters CNS at specific levels and maps to specific areas in parietal cortex, dermal distribution, sharp-type pain that is precisely located
Tell me about Somatic Pain fibers
ACS, PE, Boerhaave syndrome, Aortic dissection, tension pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade/effusion
6 causes of chest pain to always consider in EM
vital w/ pulse oximetry and defib pads; O2 supplementation, IV access, serial EKGs, ASA/nitro (depends on EKG result)
Shotgun orders for Chest Pain
Cardiac, Pulmonary, Neuro, Abdomen, +pertinent systems
Physical exam for cardiac emergencies
aortic aneurysm until r/o (get a CT angio)
Chest pain with a neuro deficit is a…
CBC, Coags (INR, PT, PTT), CMP, Trop, maybe CK, CKMB, lipase, Hcg, U/A, urine tox screen, MAYBE ABG/VBG, D-dimer, stool guaiac, blood/urine culture
Labs for Chest pain homies
CXR (2 view if we can), chest CT, chest CT with PE protocol (CT lung angiogram), CT aortogram (dissection), V/Q scan, DVT U/S
Imaging for Chest pain homies
Young, healthy, no comorbidities (D/C with close follow up)
Which chest pain patients get discharge?
STEMI, NSTEMI, Unstable Angina (at rest), Stable Angina (with exerbation)
Types of Acute Coronary Syndrome encompasses…
Activate the Cath lab/thrombolytic checklist, 324 mg ASA, nitro (up to 3x doses), Oxygen (if under 92%), Morphine (if the nitro didn’t work), CXR (r/o dissection)
Gameplan for a STEMI in the ER (same thing for a suspected NSTEMI)
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors w/in 24 hrs, SBP < 90, bradycardia, RV infarct (elevation in inferior leads with reciprocal changes in V5-V6)
C/I to nitro
contact cardio, anticoag with enoxaparin/heparin, admit the patient
Once we confirm an NSTEMI (confirmed with elevated troponins or those trending upward), what is the game plan?
Follow up (can the patient be seen in 3 days by cardio), stress testing, cardiac CT (CAC scores)
Disposition for suspected angina depends on
History, EKG, Age, Risk Factors, Troponin (if positive they aint leaving)
HEART Score risk stratification (0-3 discharge with follow/up or stress; 4-6 admit; 7+ interventional candidiate)
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Chest pain w/ or w/o SOB (maybe just SOB) is a characteristic of
Wells (start here), PERC (if wells less than 4)
PE diagnostic algorithms
Clinical signs/symptoms of a DVT, PE is the most likely, Tachycardia, immobilization at least 3 days or surgery in the last 4 weeks, previously diagnosed DVT/PE, hemoptysis, malignancy w/ treatment within 6 months or palliative
Tell me the Wells Criteria
50 y/o+, tachycardia, less than 95% on RA, unilateral leg swellings, hemoptysis, recent surgery/trauma, prior PE/DVT, female hormone use
Tell me the PERC criteria (any positive means we are ordering a D-Dimer)
CT pulmonary angio (🏆), V/Q scan (preg/allergies), Venous U/S (DVT - if you find a DVT and they have chest pain, treat the PE girl)
Imaging for PEs
Anticoags (enoxaparin 1 mg/kg BID), admit/discharge based on HESTIA/PESI
Gameplan for a confirmed PE
Aortic Dissection
What occurs after a violation of the intima that allows blood to enter the media and dissect between the intimal and adventitial layers - associated with Marfans
sudden onset of ripping/tearing chest pain that radiates through the upper back
Presentation of a Aortic Dissection
unilateral pulse deficit, neurological deficits, blood pressure discrepancy (low sensitivity)
Physical Exam findings of Aortic Dissection
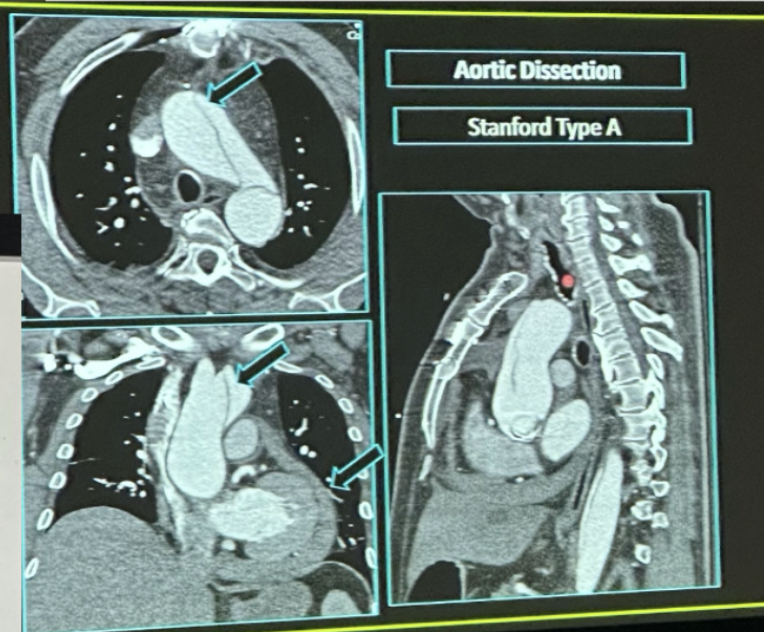
involves ascending aorta (type A - emergency), limited to descending aorta (type B)
Stanford classification of Aortic Dissection
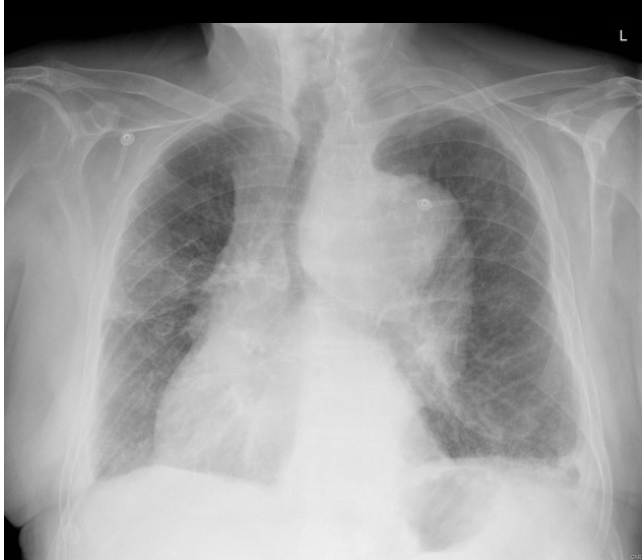
Widened mediastinum, abnormal aortic contour, pleural effusion
CXR findings of a Aortic Dissection
CT Angio
Imaging of choice for aortic dissection
Call a surgeon, Antihypertensives (esmolol - for a quick on/off)
Treatment plan for Aortic Dissection
Boerhaave syndrome
A full thickness perforation of the esophagus after a sudden rise in intra-esophageal pressure - usually due to a sudden, forceful emesis (most common), coughing, straining, seizures, childbirth
Hx of sudden onset, sharp, substernal chest pain after vomiting, tachycardia, fever, dyspneic, diaphoresis, maybe crepitus in the neck or chest
Findings in Boerhaave Syndrome
CT with oral water soluble contrast
Imaging for Boerhaave Syndrome
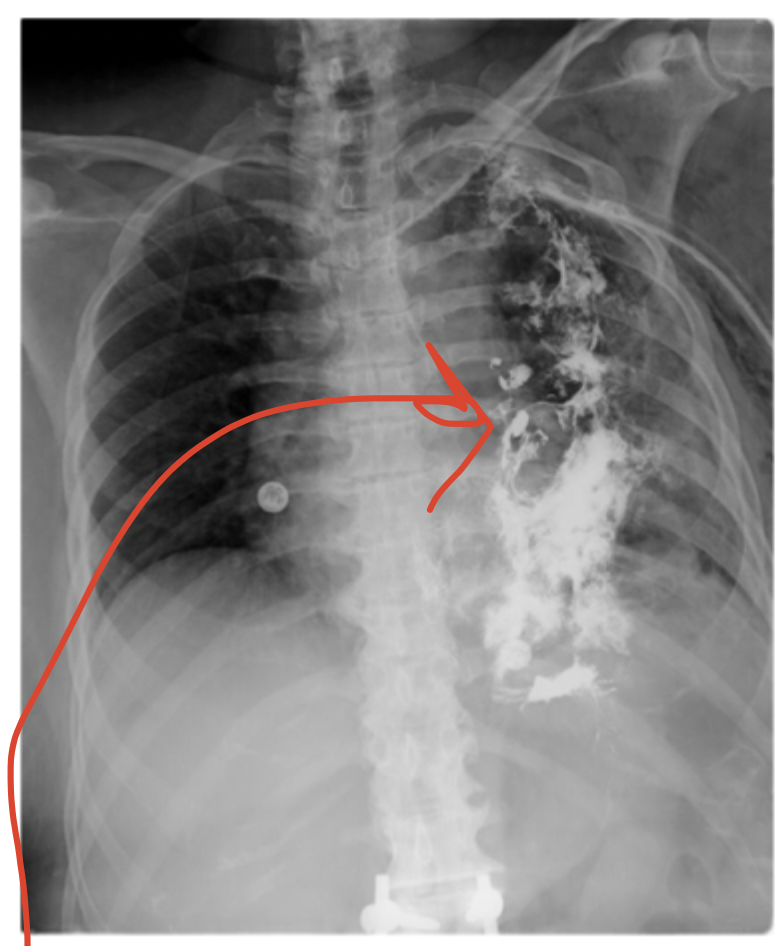
Call a surgeon, prepare to treat a tension pneumo
Game plan for Boerhaave Syndrome
Pneumothorax
Air accumulation in the pleural space that is more common in tall, slender males

Smoking, chronic lung diseases
Risk factors of a pneumothorax
decreased breath sounds, hyperresonance to percussion on the ipsilateral side
Findings in a pneumothorax
observation, oxygen development, (chest tube in the big ones)
Gameplan for a small (under 3 cm) stable, spontaneous pneumo (1-3% will convert to a tension pneumo)
Tension Pneumo
If air continues to accumulate in the pleural space causing a mediastinal shift, what do we have on our hands?
Hemodynamic instability, tachypnea, hypotension, decreased oxygen sat, JVD, tracheal deviation
Findings in a tension pneumo
emergency needle thoracostomy chest decompression followed by a chest tube
Gameplan for tension pneumo
CLINICAL (if you see it on x-ray you missed it)
Diagnostics for tension pneumo?
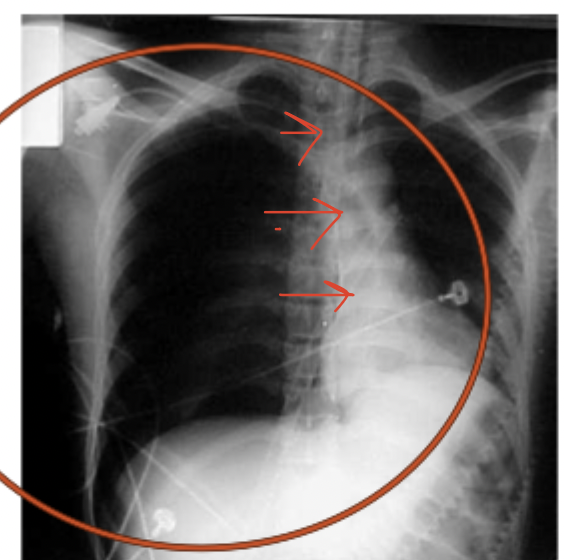
pleural effusion
Accumulation of fluid in the pleural space
dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, infectious signs and symptoms, decreased breath sounds, hypo-resonance
Findings in pleural effusions
Admit, Drain/culture, Therapeutic thoracentesis with drainage of 1.0 to 1.5 L (if dyspnea at rest), empyemas require thoracostomy tubes
Game plan for pleural effusions
Pneumonia
An infectious accumulation in the alveoli
Fever, cough, back pain, pleuritic chest pain, N/V (if irritating the diaphragm)
Findings in Pneumonia
Lobar consolidation on CXR (🏆), CT for complicated cases
Imaging for Pneumonia
CURB-65, PORT score, PSI (pneumonia severity index)
Disposition for pneumonia in the ED depends on
Amoxicillin + Azithro/doxy (healthy), Augmentin + Azithro/doxy (comorbidities or recent Abx), Levofloxacin/Moxifloxacin/Lefamulin (non-beta lactam or structural lung disease); corticosteroids if signs of shock
Abx for pneumonia (community acquired, we’re in the ER not inpatient duh)
Sharp, severe, constant, substernal pain that may radiate to back, neck, or shoulders but is relieved by leaning forward and worsens when lying down, pericardial friction rub, diffuse ST-elevation with PR depression, fever, malaise, tachy
Findings in pericarditis
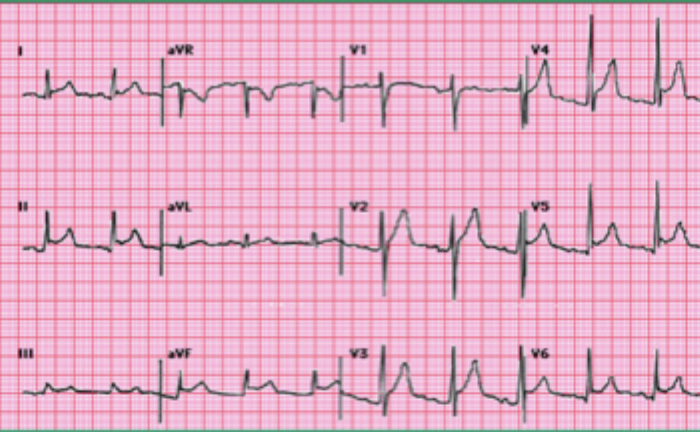
Admit, NSAIDs, ASA (post-MI), Colchicine (prevents recurrence), corticosteroids (if refractory), treat the underlying, no anticoags, pericardiectomy (last resort)
Gameplan for pericarditis
Pericardial effusion
Fluid accumulation in the pericardial sac due to trauma (usually) characterized by sharp, substernal chest pain, dyspnea, orthopnea, dysphagia, and/or hoarseness
muffled/distant cardiac sounds, JVD, pulsus paradoxus, hypotension
Findings in pericardial effusions
post-cardiac cath, renal failure, trauma, malignancy
Risk factors for pericardial effusions
Bedside U/S (sub-xyphoid or parasternal view) 🏆, CXR (enlarge radiopaque sillhouette)
Diagnostics for pericardial effusions
hypotension, muffled heart sounds, JVD
Cardiac tamponade is characterized by Beck’s triad, what is this?
pericardiocentesis (needle place sub-xyphoid) followed by a pericardial window
Game plan for cardiac tamponade
ADMIT
An patient who is not hemodynamically stable…