4.3 - Monopolistic competition, TP uncertainty & Brexit
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Are certain TP realistic
Firms may not know what tariffs in place in future but have to make trade decisions today
Under functioning international systems it can be realistic - WTO pre Trump
Under WTO rules nations cant raise tariffs above bound rate
Some uncertainty within bounds but mitigates a bit
MFN tariffs dont move much in reality
PTAs more certain than general WTO MFN
Classic trade models
Ricardian model
argues trade takes place due to CA
CA caused by different productivities between sectors & nations
HO model
Different factor abundance between nations + goods with different factor intensity drive trade
New trade model - Krugman 1979
Explain trade between similar countries (similar in productivity & factor endowment) - NOT EXPLAINED BY CLASSICAL MODELS
Increasing RtS {Larger market size
Consumer love for variety. {
Monopolistic competition - each firm monopolist of residual D for its variety
Monopolistic comp with heterogenous firms - Assumptions
Basic model assumes homogenous firms - in reality no true
Exporters more productive on avg BUT even among Exporters there is heterogeneity
More productive firms will charge lower p - to increase market share
Under heterogeneity, firms have to pay a sunk/fixed cost to enter a market - source of RtS
Sunk/fixed - if paid before/after learning market conditions to enter
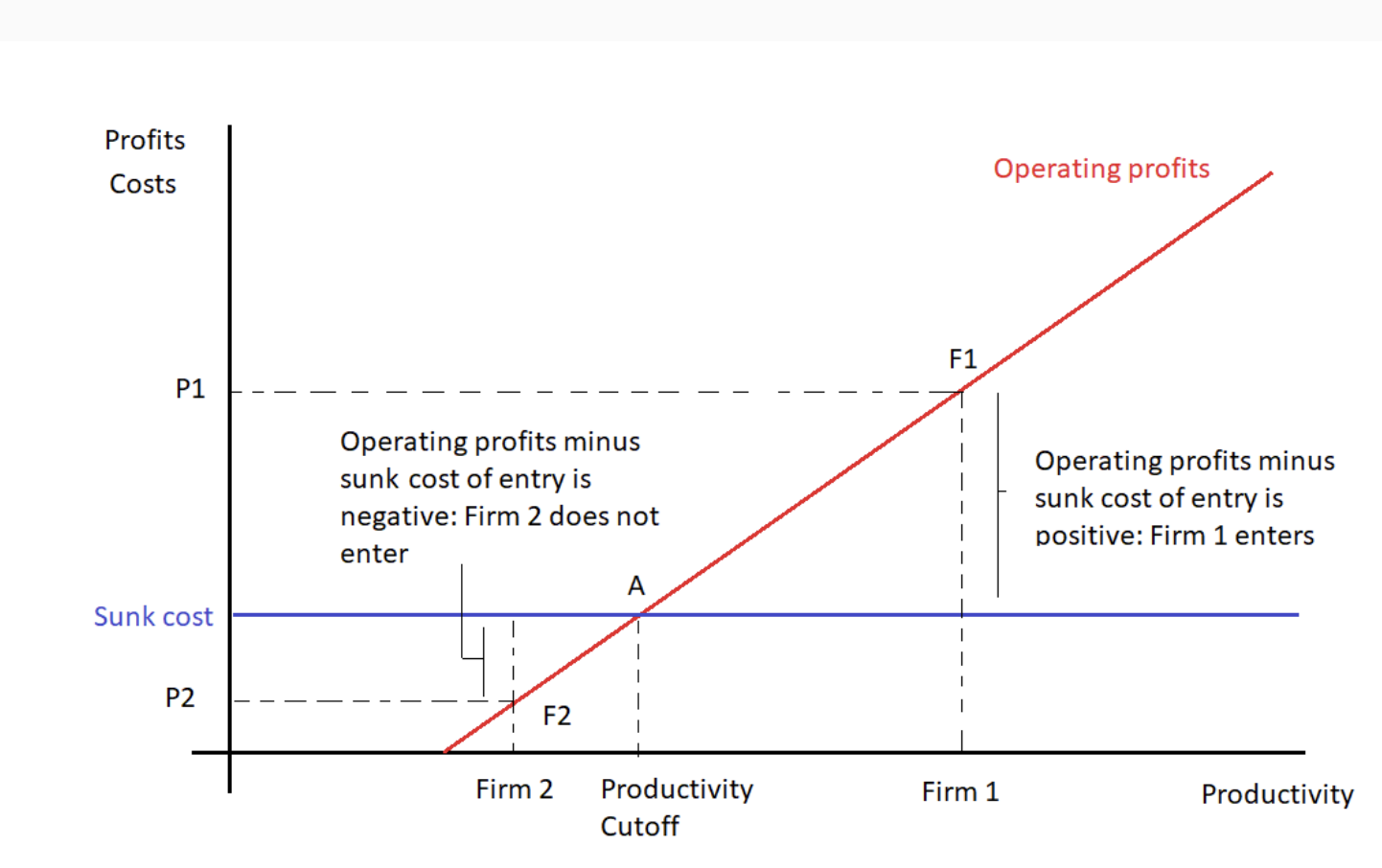
LR equilibrium of heterogenous firms model
Firms enter market until marginal firm equates Expected profits to sunk entry cost
E(pi) = sunk cost
Mono comp with heterogenous firms - graph
Firms have an idea of future profits
Firms only join the market if E(pi) > sunk cost
Only most productive join (productivity UP = pi UP)
2 doesnt enter but 1 does
Mono comp with heterogenous firms - with FT effects
Similar result to case with homogenous firms
Less productive dom firms exit
More productive F firms join & start exporting to H
Access to variety UP → Welfare UP
Productivity increases as least productive leave → P falls
Mono comp with heterogenous firms - graph
Assume no dom firms
H charges tariff on M - t a % of sales → profits fall
Some F exporters wont enter market (pi < sunk)
Consumer access to variety falls → CS down
Firms only enter if productivity > B
Firms with productivity A-B leave market
firms reevaluate if they want to invest in X capital

TP uncertainty theory
Firms have to make investment decisions when entering a market - often under uncertainty
They decide based on Pi given information available today
Entry cost sunk upon joining BUT changing conditions can reduce Pi
may force them to leave market & lose sunk cost
markup p < initial investment
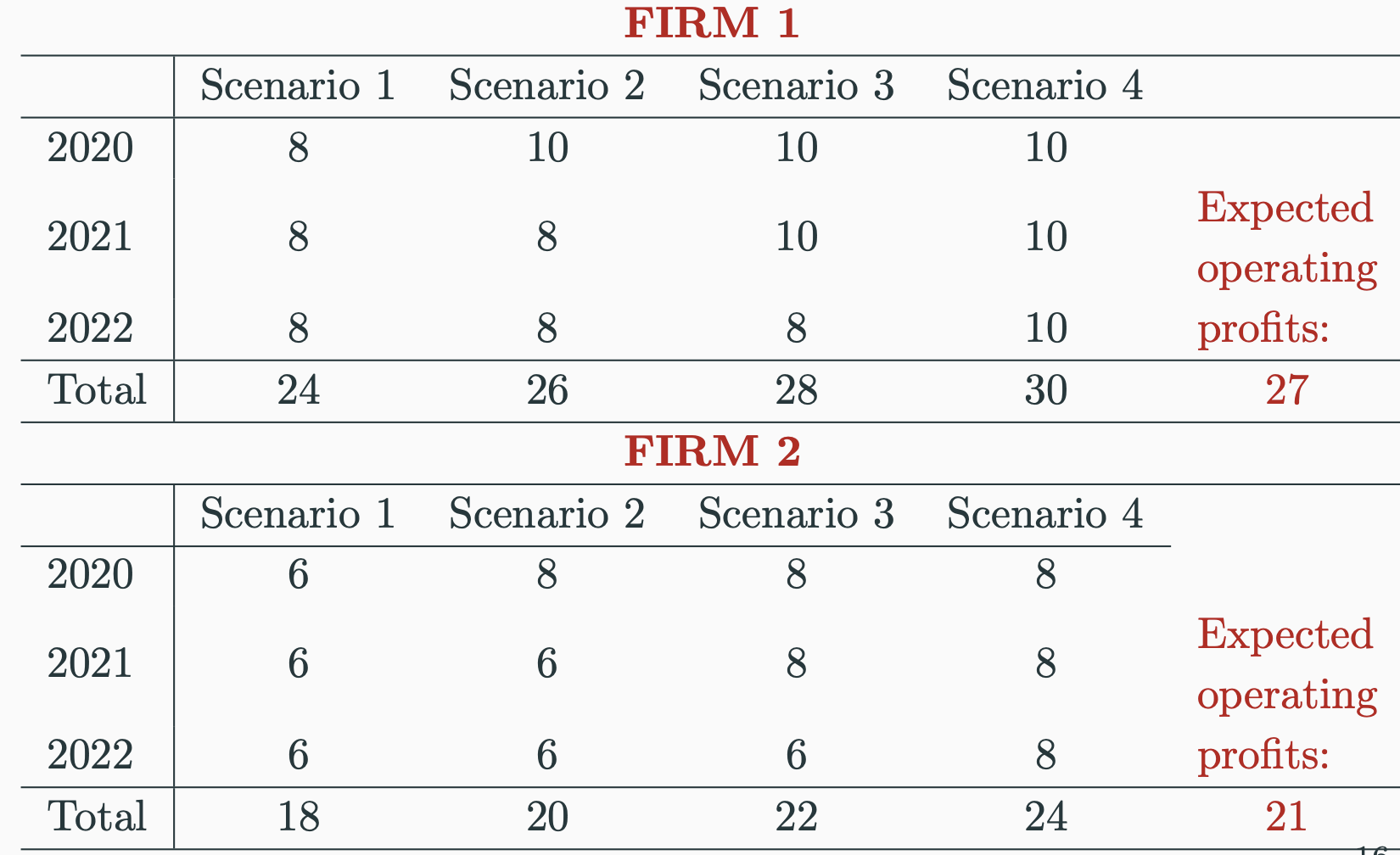
TP uncertainty example OV
Assume an event makes tariff rate uncertain - scenarios equally likely
2 firms - 2 is less productive than firm 1
dont discount future profits
To X to F, each firm has to invest in X capital today
Sunk cost = £23000 in this example
4 scenarios - tariffs rise in 2020,21,22 or never
tariff UP = profits fall
TP uncertainty example RESULTS
If firms certain tariffs wont rise then both X
1: 30-23 > 0. 2: 24-23>0
However there is 75% chance tariffs rise
1: 27-23 > 0. 2: 21-23<0
only 1 X if it decides to enter market
TP uncertainty graph
Firms with productivity B-C leave / dont join market - even though tariffs still t0
uncertainty of rise forces them out
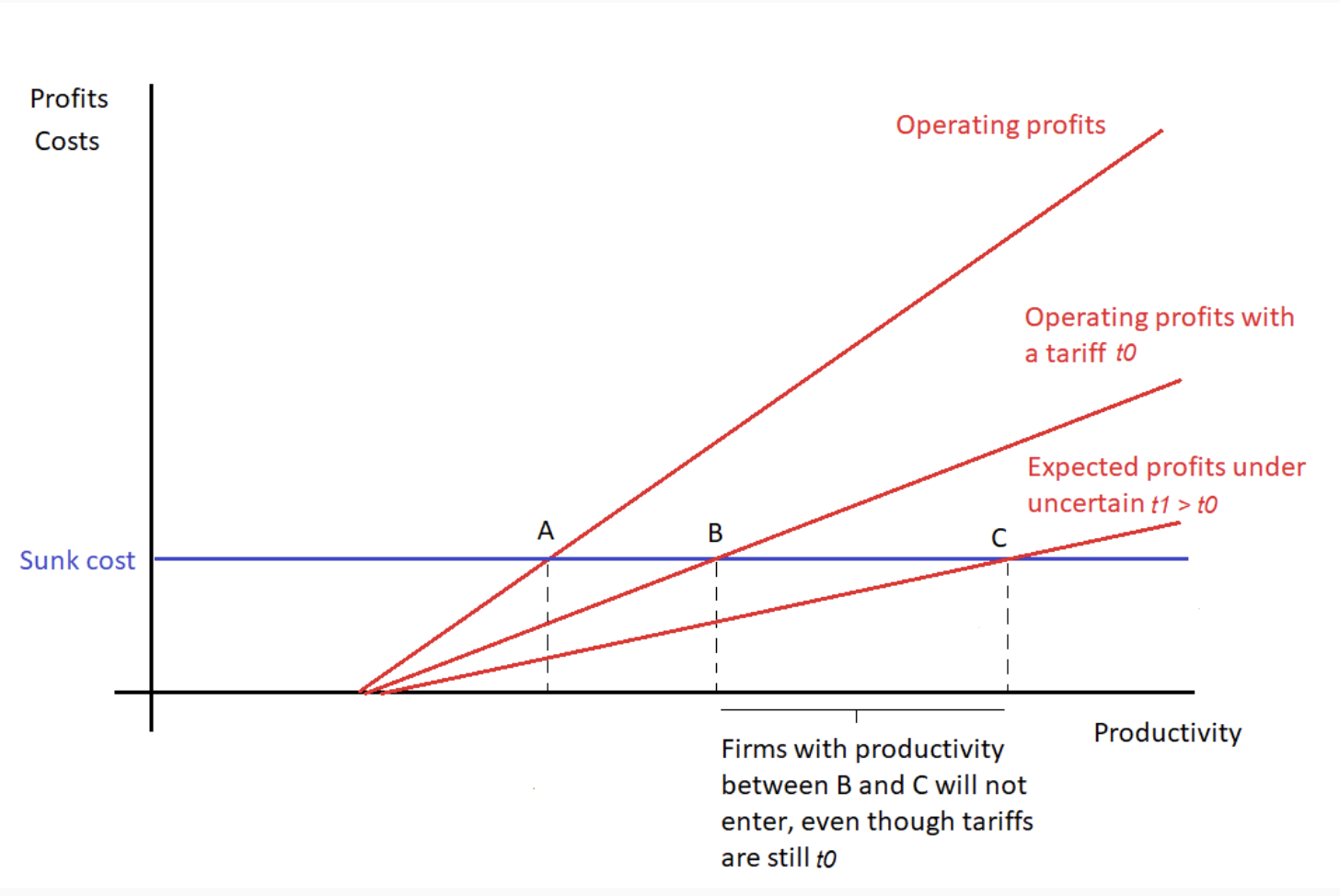
TP uncertainty effects
Fewer firms join market / more leave from the tariff uncertainty
Aggregate F X fall as no. exporters fall
Varieties fall → CS falls
F firms that exit due to TP uncertainty could be replaces by less efficient dom firms
Productivity down → P rise
Therefore TPU works as protection for dom firms
Brexit uncertainty
2015 general election winners promised referendum
created TP uncertainty
Caused EU & UK firms to lower E(pi) due to expected tariff rise
decreased market entry
CS fell Varieties down + M price index UP
Brexit uncertainty measured - Graziano et al (2020) OV
Used betting market probabilities as prob of Brexit + opinion polls
showed uncertainty varied over time
Brexit uncertainty measured - Graziano et al (2020) RESULTS - impact on EU X to UK
Impact on EU X to UK relative to non-EU
X fell sharply when referendum date announced
X fell again when article 50 put in place (but recovered)
Shows extreme uncertainty
Brexit uncertainty measured - Graziano et al (2020) RESULTS - Tariff threat & Trade
Paper estimated avg trade across affected products
-11-20% trade between UK & EU
Bilateral trade down -15% if MFN applied to all products
Brexit uncertainty measured - Graziano et al (2020) RESULTS - Uncertainty & M price
Import price captured changes in CS effectively
M price of EU goods relative to all M tracked closely with Brexit probabilities
strong supportive evidence of model
If only focused on high risk of tariff products (proxy of UK tariff to EU was EU MFN tariffs)
still tracks Brexit prob well
With mean tariff threat - M price index 12% increase
Brexit uncertainty alone increased consumer prices by +0.5-0.7%