The New Deal
1/207
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
208 Terms
Franklin Delano Roosevelt
32nd President of the United States, inaugurated in 1933.

New Deal
Roosevelt's plan to combat the Great Depression.

Great Depression
Severe economic downturn beginning in 1929.

First Hundred Days
Initial period of Roosevelt's presidency with significant reforms.

Wall Street Crash
1929 market crash leading to the Great Depression.
Unemployment Rate
1 in 4 Americans unemployed during the Great Depression.
Hoovervilles
Shantytowns named after President Hoover, symbolizing poverty.
Emergency Relief Construction Act
Legislation creating public works jobs for unemployed.
Economic Crisis
The worst economic situation since the Civil War.
Bank Failures
Over 1,450 banks closed in 1932, losing customers' savings.
Social Safety Net
Absence of welfare and unemployment insurance pre-New Deal.
Herbert Hoover
President blamed for the Great Depression's severity.
Inaugural Speech
Famous speech by Roosevelt during his 1932 inauguration.
Financial Sector Reform
New laws aimed at stabilizing the banking system.
Job Creation
Programs designed to reduce unemployment during the Depression.
Natural Resource Development
Government initiatives to manage and utilize natural resources.
Agricultural Reform
Policies aimed at improving farming conditions and prices.
Industrial Recovery
Efforts to revitalize American industry post-Depression.
Economic Indicators
Metrics used to assess the health of the economy.
Public Works
Government-funded projects to create jobs and infrastructure.
Charity Reliance
Dependence on charity before government assistance existed.
Political Unpopularity
Hoover's declining popularity due to economic failures.
Historic Government Action
Significant legislative measures taken during Roosevelt's first days.
Reconstruction Finance Corporation
Loaned federal money to businesses for relief.
Hoover's Tax Policies
Raised taxes and tariffs, worsening the Depression.
Franklin Roosevelt Inauguration
Became president in 1933 during the Great Depression.
Great Depression Unemployment Rate
Nationwide unemployment reached about 25%.
Failed Banks Definition
Banks that completely went out of business.
Social Safety Net
Did not exist at the start of the Depression.
New Deal
FDR's programs to create a social safety net.
FDR's Background
Came from privilege, attended Harvard College.

Theodore Roosevelt Relation
Fifth cousins, Theodore was a Republican.
FDR's Polio Infection
Paralyzed both legs, limited mobility with braces.
Empathy Development
Disability gave FDR a 'common touch' with citizens.
Governor of New York
Elected in 1928, proved leadership during Depression.
Temporary Emergency Relief Administration
Disbursed $20 million to aid New Yorkers.
Laissez-Faire Economics
Belief that government should not intervene in economy.
Market Correction Philosophy
Depressions are natural; government intervention is wrong.
Hoover's Economic Philosophy
Believed in minimal government intervention during crises.
FDR's Activism
Believed government must protect citizens from hardship.
Political Career Setback
FDR's polio nearly ended his political ambitions.
Class Warfare Concern
Hoover viewed FDR as a dangerous radical.
Common Touch
FDR's ability to relate to less fortunate citizens.
Aid Comparison
No state had provided as much aid as FDR.
Hoover's Stubbornness
Left office bitter, resistant to change.
FDR's Determination
Reentered politics with renewed focus after polio.
FDR
Franklin D. Roosevelt, 32nd U.S. President.
Progressive
Belief in government shaping society.
Great Depression
Severe worldwide economic downturn in the 1930s.
Social Duty
Government aid as a responsibility, not charity.
Bold Experimentation
FDR's philosophy of trying new methods.
Polio
Disease causing FDR's lower-body paralysis.
Wheelchair
Device used by FDR for mobility.
Leg Braces
Supportive devices worn by FDR for standing.
Stage Managed
Carefully controlled public image of FDR.
Democratic Party
Political party FDR represented during presidency.
Herbert Hoover
Unpopular Republican president before FDR.
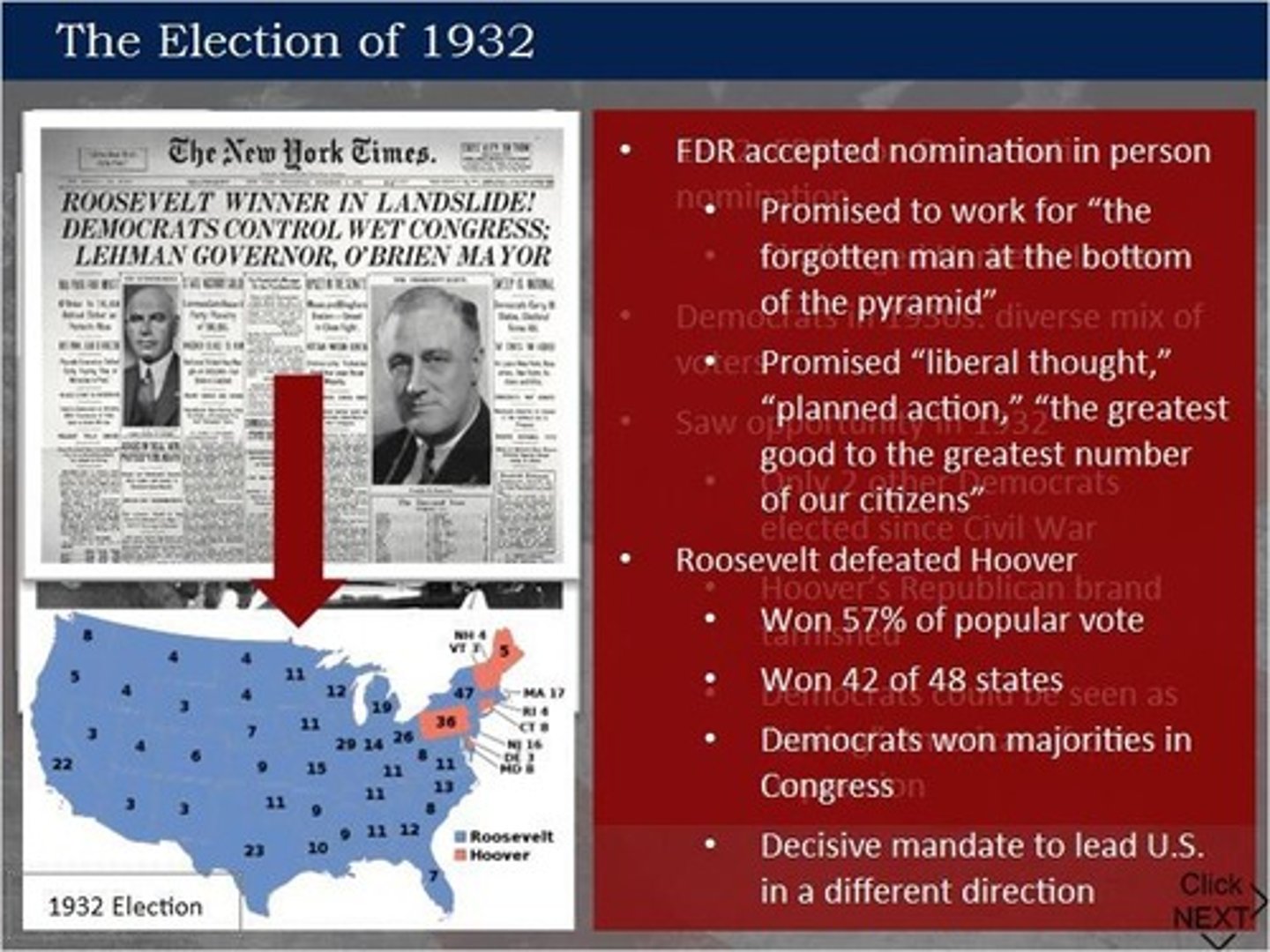
1932 Election
FDR won Democratic nomination against Hoover.
Diverse Voters
Mix of demographics in 1930s Democratic Party.
Southern Conservatives
One faction of 1930s Democratic voters.
Northeastern Liberals
Another faction of 1930s Democratic voters.
Urban Immigrants
Demographic group supporting the Democratic Party.
Union Members
Labor supporters of the Democratic Party.
White Supremacists
Controversial faction within the Democratic Party.
Political Transformation
Democrats aimed to reshape American politics.
Chicago Convention
Event where FDR accepted the nomination.
Republican Brand
Perception of the Republican Party during the Depression.
Tarnished Reputation
Negative view of Republicans due to Hoover.
First Candidate Nomination Acceptance
FDR was the first to accept in person.
Forgotten Man
Term used by FDR for marginalized citizens.
Liberal Thought
Advocacy for progressive social policies.
Planned Action
Organized government response to economic issues.
Greatest Good
Philosophy prioritizing welfare of most citizens.
New Deal
FDR's program for economic recovery.
Electoral Landslide
FDR won 57% of the popular vote.
Decisive Mandate
Authority granted to lead by election results.
New Deal Coalition
Alliance of diverse groups supporting FDR.
Bank Panic
Widespread bank failures due to withdrawals.
80% Bank Closure
Percentage of banks closed by FDR's inauguration.
Dictatorial Powers
Potential emergency powers for crisis management.
Adolf Hitler
Leader of Germany during economic crisis.
Benito Mussolini
Italian dictator during the Great Depression.
Joseph Stalin
Soviet leader who rose during economic turmoil.
March 4, 1933
Date of FDR's presidential inauguration.
Radio Ownership
90% of Americans owned radios in 1933.
Fear Itself
FDR's phrase emphasizing overcoming fear.
National Disaster Diagnosis
FDR's analysis of economic conditions in 1933.
Withered Leaves
Metaphor for failing industrial enterprises.
Unemployment Crisis
High rates of joblessness during the Great Depression.
Economic Recovery
Process of revitalizing the economy post-crisis.
Frankness and Vigor
Qualities of leadership essential for overcoming challenges.
Mob Violence Preparedness
Military readiness in response to economic distress.
The Great Depression
Economic downturn beginning in late 1929.
Hundred Days
First months of FDR's presidency with major reforms.
Brain Trust
Group of advisors and experts for FDR.
Frances Perkins
First female U.S. cabinet member, Secretary of Labor.
20th Amendment
Changed presidential inauguration date to January 20.
Giuseppe Zangara
Assassin who attempted to kill FDR in 1933.
Anton Cermak
Mayor of Chicago, wounded in Zangara's assassination attempt.
Direct recruiting
Government employment strategy during economic crisis.