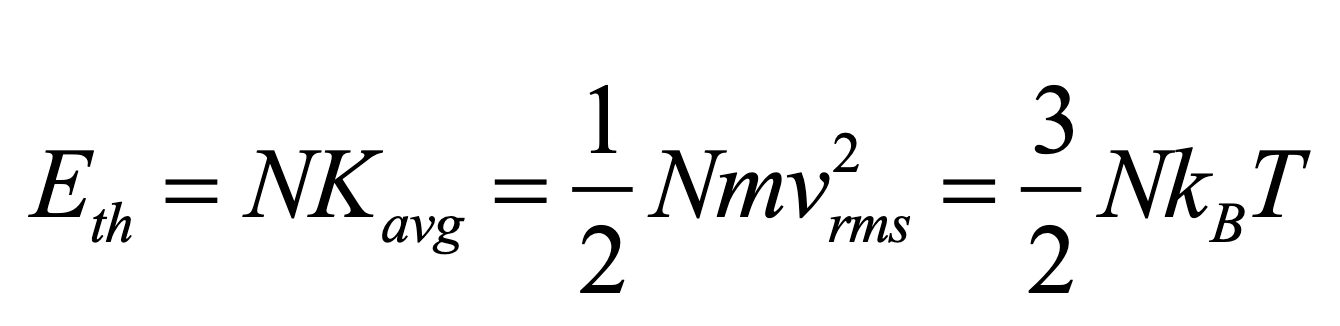Physics Unit 5 Content (FINAL)
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What does dmfp (mean free path distance) mean?
The average distance traveled between collisions.
What is N in terms of random walks?
The number of collisions.
How would you find the total distance covered when given N and dmfp ?
You would multiply N (number of collisions) by the dmfp (average distance between collisions).
What is the root mean squared distance (xrms) and why do we have it? What is the formula for it?
xrms is the root mean squared distance found in order to quantify a distance traveled in random motion.
In 1-D random motion, the probability that a step will be to the left is equal to the probability a step will be to the right, so average distance will always be 0. In order to stop this you square the distances, find the average, then find the square root of that to get the xrms root mean squared.
Formula is…xrms = sqrt(N) * d
N = # of steps
d = step length
What is the equation for Wnet?
Wnet = ∆K + ∆U
What is the relation between ∆Eth and friction?
∆Eth = fk∆x
When an object experiences a displacement ∆x as it slides across a surface that exerts a frictional force (fk ), there is a change in thermal energy given by that equation.
When is kinetic energy at a maximum in terms of potential energy?
Kinetic energy is at a maximum when potential energy is at a minimum.
What is the formula for Froude number in terms of kinetic energy and potential energy? What is it in terms of simplified velocity?
Fr = K/U
K/U = ½ mv2 / mgy → v2/gy
y is the leg length or the distance to the center of mass.
What are the SI units of froude number?
No units for froude number.
What is the approximate froude number for anyone walking at their maximum speed? Why is this important?
0.5
This is important because based on the 0.5 assumption, if you know someones max velocity walking you can approximate their height.
IMPORTANT 19 Question
What’s the approximate maximum walking speed of an adult whose height is 2m and whose legs are 1m long.
Fr = v2/gy
Fr is assumed to be 0.5 for everyone
0.5 = v2/(9.8)(1)
4.9 = v2
v = 2.21 m/s
Need to remember the approximation of Fr number for everyone at their max walking velocity.
Need to know the formula for Fr.
What is the formula for ∆Etherm ?
Just the magnitude of the work of friction.
Only do this if you are doing a 0 net energy equation realistically you should just plug it in as the Wnet exterior and set it equal to ∆K + ∆U like this…
uk N * d = ∆K + ∆U
What is the formula for resilience?
Resilience = Energy put OUT / Energy put IN
Out/In
8J put in and 6 returned would be 6/8.
What is the max and min resilience? What do each of these mean in terms of the conservation of energy?
Resilience = E Out / E in
Max = 1
Min = 0
Max = 1 means that every ounce of energy put in is given back so a totally conserved force.
Min = 0 means that no energy is returned after putting energy in.
In terms of a spring, what forces would you plug into the resilience equation? Like pulling/letting go…
Pulling the spring is force put into the system so that is E in.
Letting go is the spring force acting based on what you put in so that is energy out.
Resilience = E relaxing / E stretching or compressing
A ___ resilience means that less elastic (spring) potential energy is converted into thermal energy when the material relaxes.
Large
A large resilience means that almost all of the energy put in is given back, so less would be lost as thermal energy when it relaxes.
What would the area under a force vs ∆L graph mean for calculating resilience if you have two lines that correspond to the force in vs the force out?
The area under a force vs distance graph corresponds to the work done by that force and resilience is measured in Energy out vs Energy in (which means work out vs work in)
This is because work and energy are measured in joules.
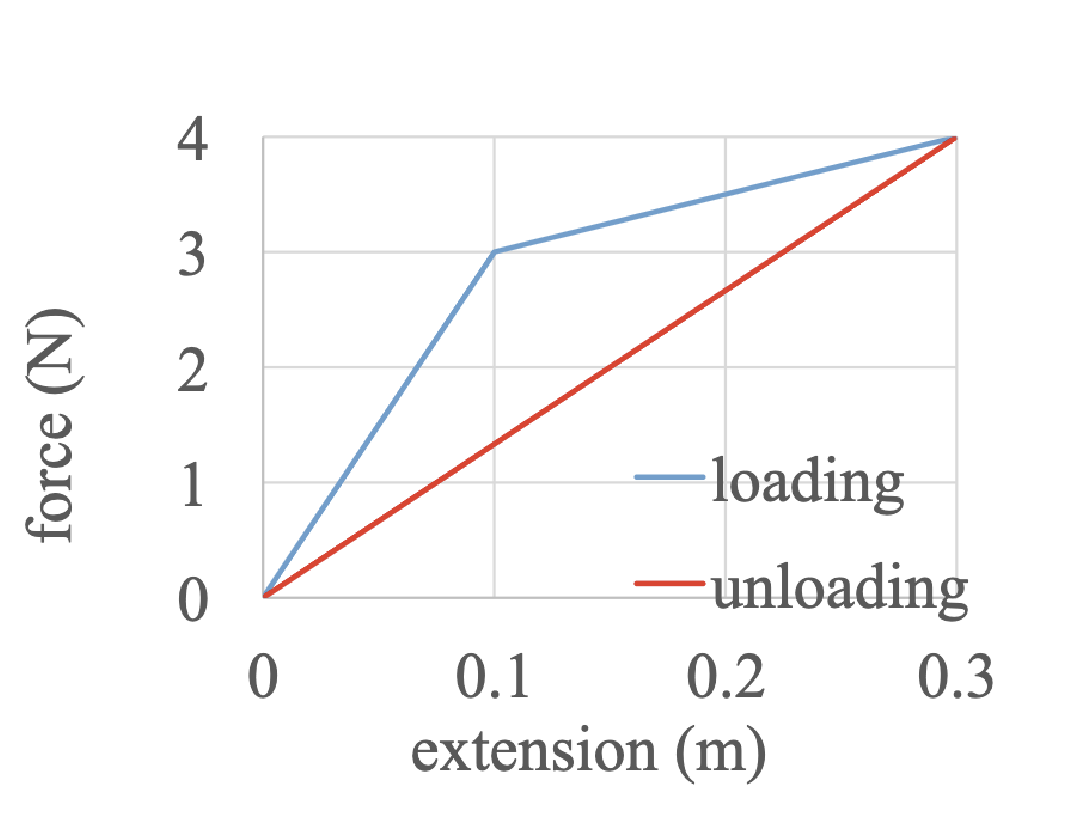
Don’t bother with the specifics but how would you construct a formula to calculate the resilience of this graph…
Find the area under the force out curve (work out)
Find the area under the force in curve (work in)
Divide work out by work in…

Ignore the extra text, but how would you find the resilience?
Find out the initial kinetic energy vs the kinetic energy put out…
Once you have the kinetic energy of the block initially (mgsin(30) 0.6) = 5.88 you can then derive the kinetic energy put out based on the final velocity (1.5) = 2.25
2.25/5.88 = 0.38
(Read this and make sure you understand) Keep in mind that it is important that it is the work in vs the work out, the work in is technically not the gravity it is the spring compressing the 5.88J of kinetic energy into potential energy so that is the spring compressing then the velocity is the potential energy coming out.
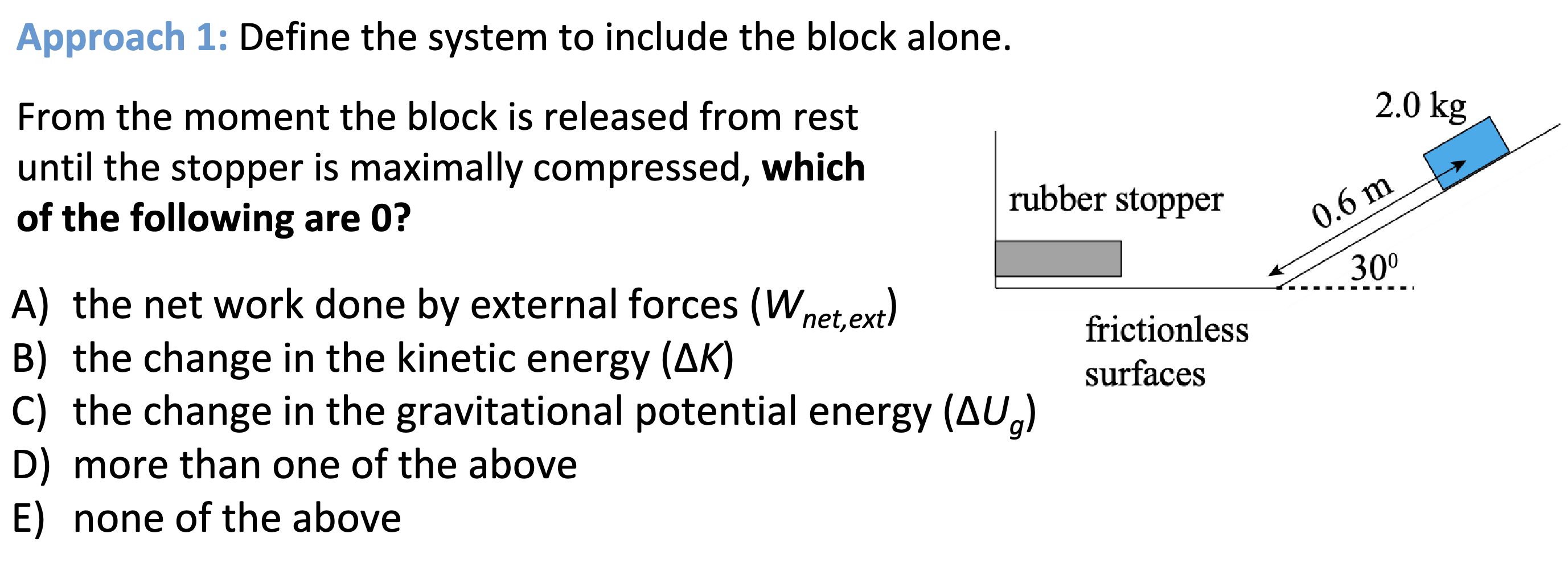
All of the above…
Wnet by external forces is 0 because from when it is released to when it is compressed the kinetic energy remains at 0 and there is no potential energy so Wnet = ∆K + ∆U which is 0.
∆K is 0 as well because it goes from v=0 when released to v = 0 when fully compressed (all energy stored as potential).
∆Ug is 0 because there is no gravitational potential energy anyway because the system doesn’t include the earth.
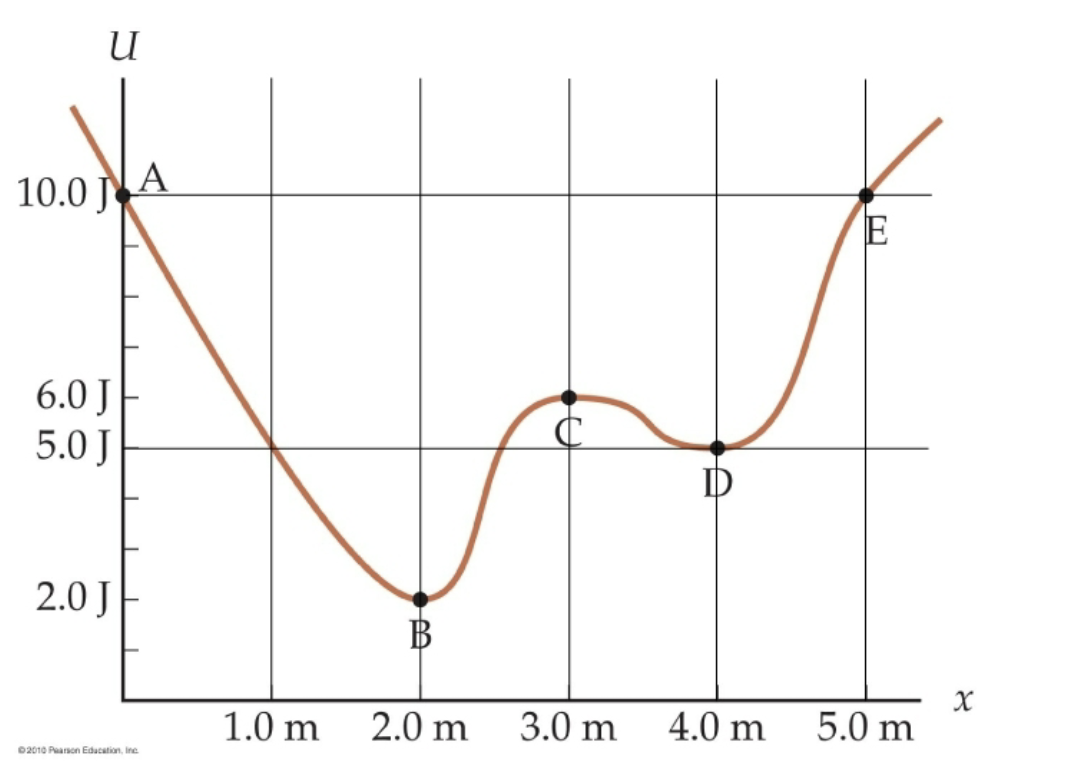
With this image explain what a potential energy well or a bound state is…
A potential energy well or bound state is when an object is bound to a certain area where it cannot escape because its total energy is less than the total energy required to overcome a hump.
For example if the ball was released below point c it would never be able to overcome point c.
Based on a graph of potential energy vs interatomic spacing, what would the bond length correspond to?
The average value between the maximum and minimum possible separations between the two atoms given a total energy.
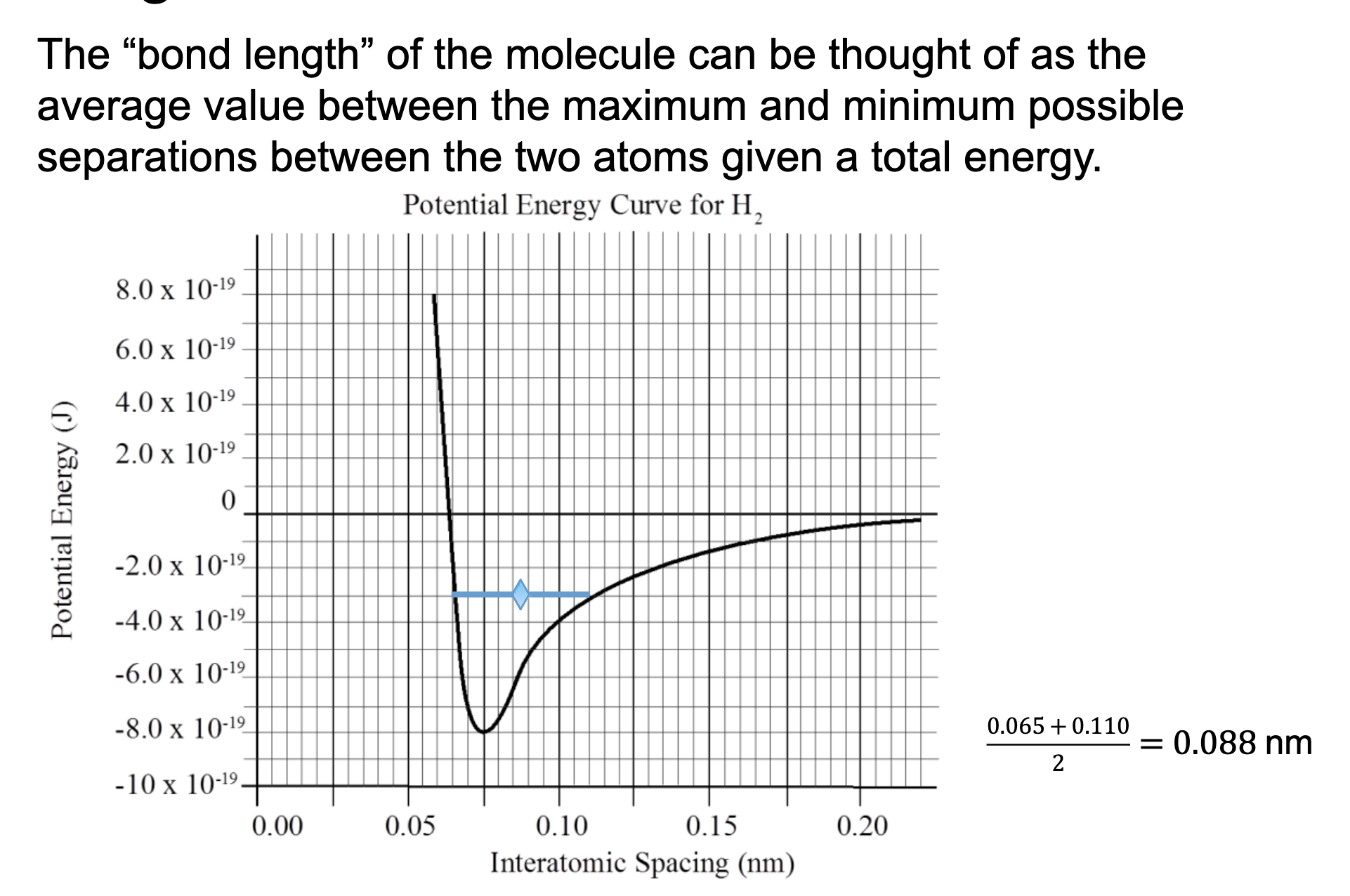
If the total energy of the system of two bound hydrogen atoms is -3×10^-19 J then what is the minimum amount of energy that needs to be added in order to BREAK the bond?
3×10^-19
Getting a bonds total potential energy to 0 means that the bond is broken.
U = 0 → atoms are infinitely far apart, no interaction.
E_total = 0 → atoms have just enough energy to break the bond and escape to infinity.
When E = 0, the atoms can still feel forces until they're far apart — but they're no longer trapped.
The bond breaks when the total energy reaches zero or higher.
What is the slope of a potential energy vs distance curve? What does the sign of the slope correspond to in terms of force?
The force.
Potential energy is like 1/2kx² which would be like the force * distance, so if you divide by distance then you just get force. You’d divide because that gets slope.
The sign of the slope is the opposite of the direction of the force, so a negative slope corresponds to a positive direction of force.
This is because ∆U = -Wnet so Work is the opposite sign of potential energy.
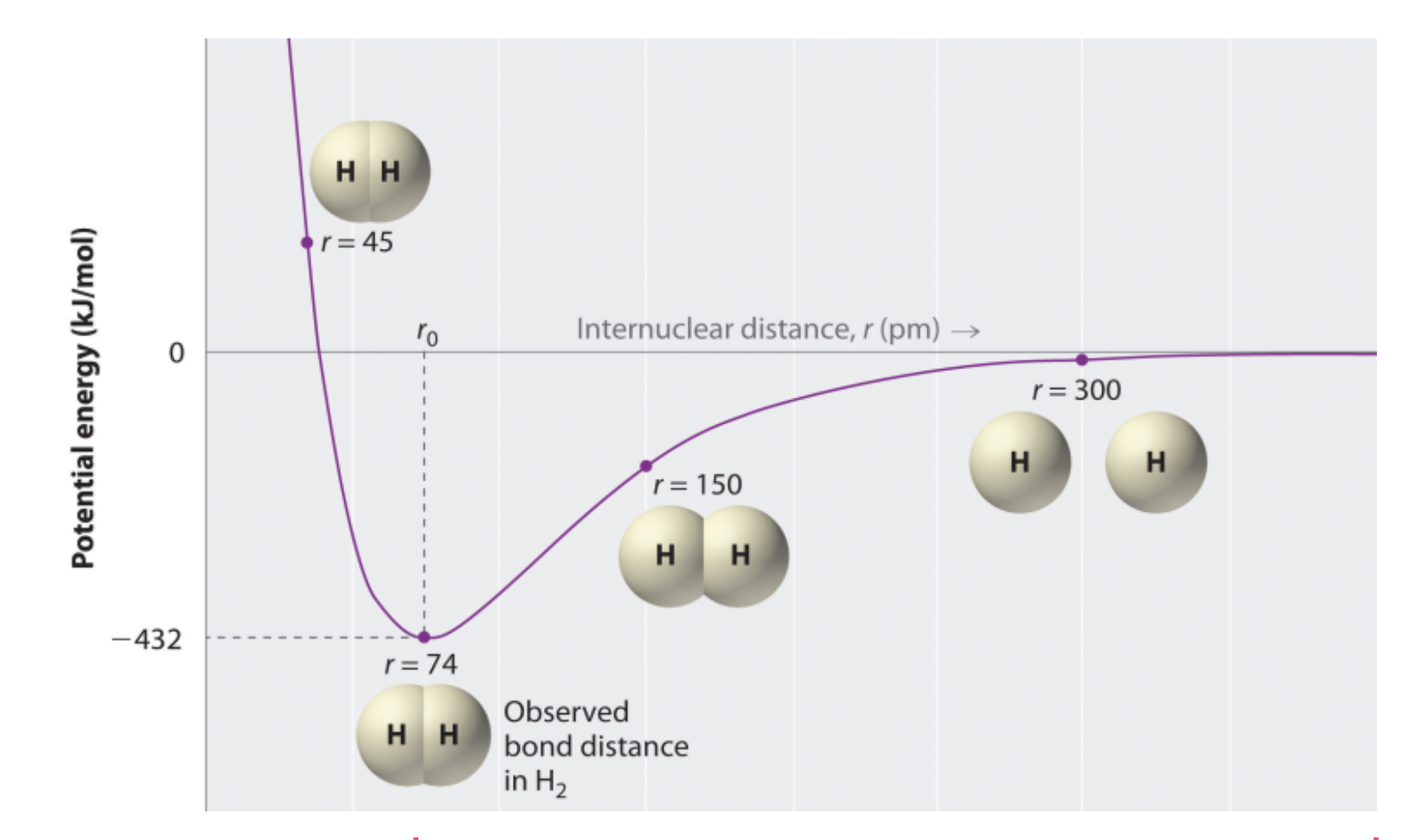
As atoms get closer and approach a minimum potential energy what type of forces dominate? As the spread apart and rise in potential energy what forces dominate?
Repulsive then Attractive
Repulsive because they are too close at the left side so they need to push apart, then attractive because after the minimum they went to far away and want to come back together until the attractive force is too weak and the bond breaks.
Most stable at that potential energy minimum though.
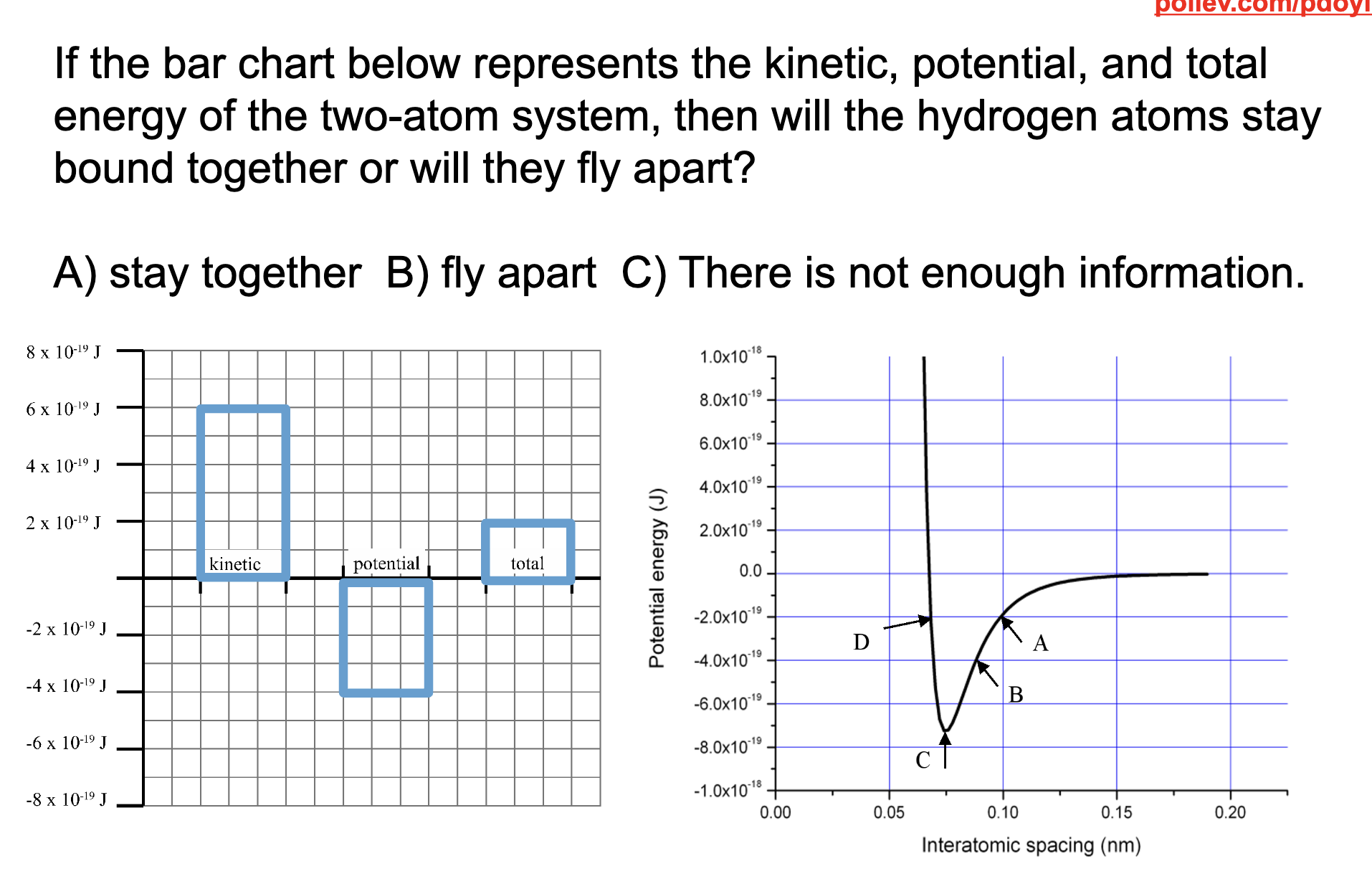
Fly apart, this is because the total potential energy is like -4 and the kinetic is 6 meaning the total energy of the bond will end up being above 0 which means that the molecules are unbound and the bond is broken.
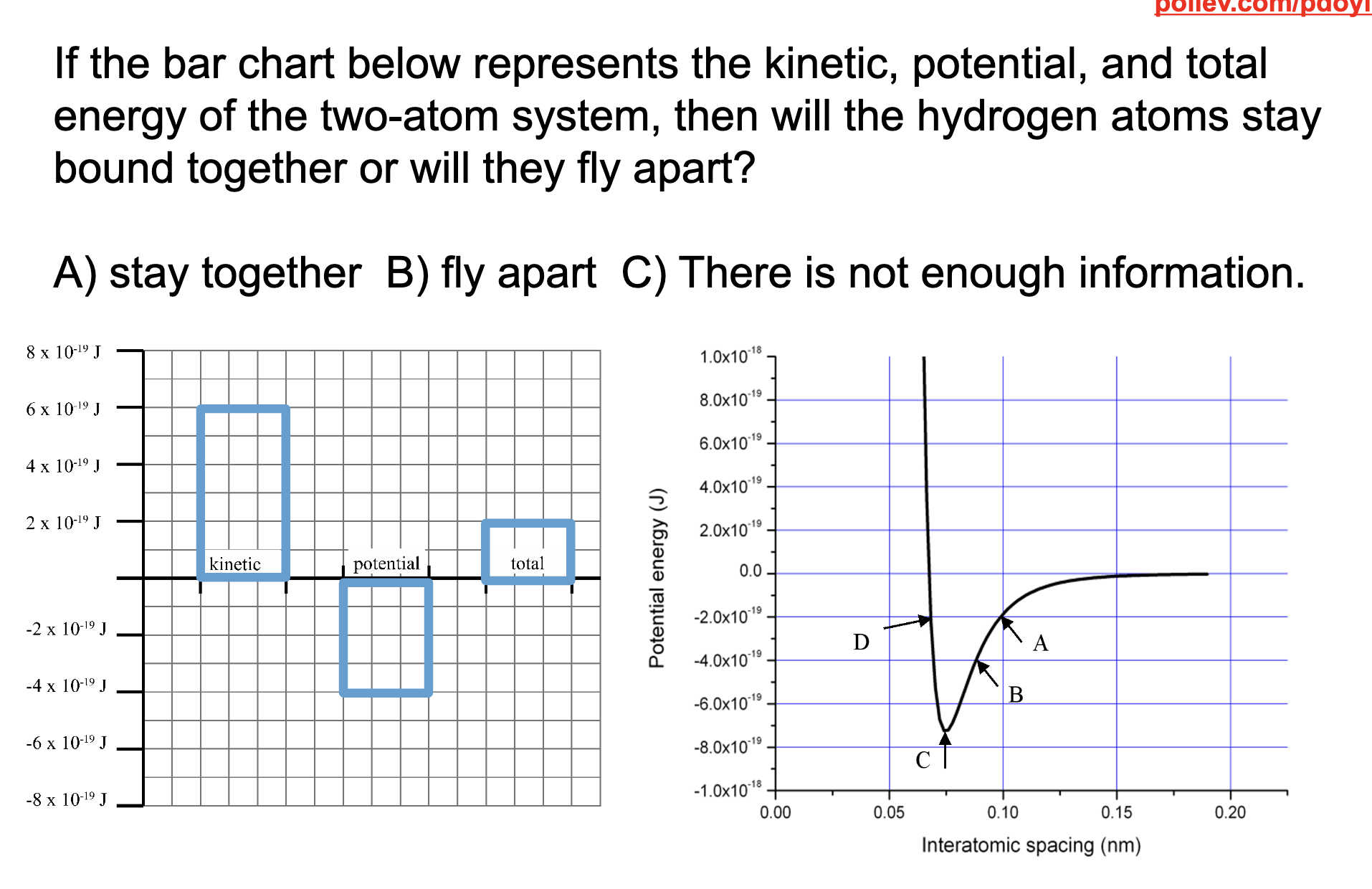
What is the most stable bond location in terms of potential energy on a potential energy vs interatomic spacing graph? What does this point correspond to in terms of attractive and repulsive forces?
The potential energy minimum is where the bond is most stable and this is because this is also the conformation where the attractive and repulsive forces are balanced.
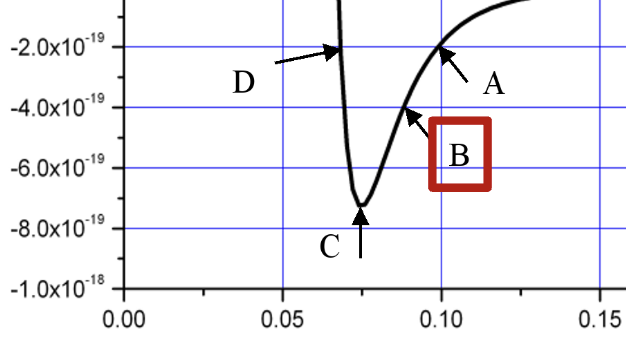
At point B if the potential energy is -4J and the total energy of the system is -2J what is the kinetic energy of the bond at this bond distance?
+2J
U + K = Total Energy
You’re potential energy must add to the total energy of the system so if the total energy is more positive than the current potential energy, the kinetic energy has to be positive in order to make potential energy and kinetic add to the total energy of the system.
In a two-atom system, what does the total energy need to be in order for the atoms to fly apart.
Total energy needs to be 0, meaning there is no attractive or repulsive forces.
What is first repulsive or attractive when moving to the left to right (getting atoms further apart).
Repulsive then Attractive
If Etotal = K + U < 0 what sort of state is the molecule in?
A bound state, the molecules are bound together with a bond length equal to the average length from the furthest distance to the closest distance of the atoms.
The steep rise in potential energy as you make atoms closer together is caused by what?
Pauli exclusion principle.
Bonds breaking ____ energy and bonds forming ____ energy.
Bonds breaking requires (puts in) energy and bonds forming releases (puts out) energy.
This means that if it takes 600J of energy to break a bond (putting in that 600J of energy) then the bond must have had a potential energy of -600J
(remember in order to break a bond you have to get total energy to 0 meaning you have to add energy).
If the bond energy of C-H is 413J what is the potential energy of this bond?
-413J
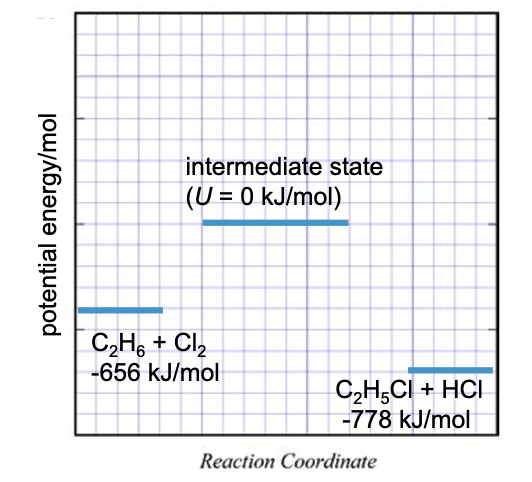
Explain each line on this graph…
The total potential energy of all the bonds that need to break is -656
In order to break them you must add 656 J of energy to break it.
Now the bonds form and release energy from forming a C-Cl bond and an H-Cl bond which creates a lower potential energy.
This means the system released more energy than it absorbed to break the bond so it is exothermic (releases more energy).
Energy must be added to this system for the reaction to occur.
Reactants have more potential energy than the products.
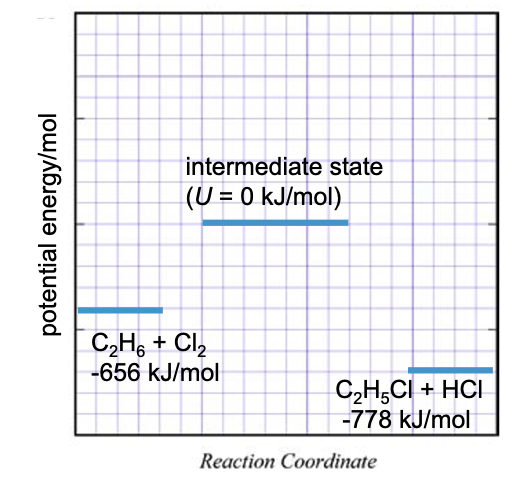
Which will have more kinetic energy?
The products because the potential energy is smaller.
What is the formula for Eth?
Eth = 3/2 N Kb T
N is the number of gas molecules in the system.
T is the temperature
Kb is the boltsman constant.
So as you increase the number of particles at the same temperature you would have higher thermal energy.
As you increase the temperature you get a higher thermal energy for the same number of particles.
For two water cups of the same volume, if one has a higher temperature, which has a higher thermal energy…why?
The one with the higher temperature because
Eth = 3/2 N Kb T
So if you increase T you would increase Eth
For two water cups of different volumes each with the same temperature, which has a higher thermal energy and why?
The one with the larger volume, this is because it would have a larger number of gas particles (N)
Eth = 3/2 N Kb T
What is absolute 0?
The temperature at which all molecular motion has ceased.
Conversion of Celsius to Kelvin…
°C + 273 = K
What is the SI unit for pressure?
Pa or N/m2
What is the ideal gas law…
pV = nRT
If you have the number of particles N how can you convert to moles?
6.022×1023 particles/mol
So divide by 6.022×1023 to get the number of moles to use in the ideal gas law equation.
A pot of water is placed over a fire, the temperature increases, is the work done on the system positive, negative, or zero?
Zero
This is because Wnet + Q = ∆E
So adding heat (Q) increases the total energy but it doesn’t do any work.
Work done on a system is ___ work.
Work done by a system is ___ work.
Work done on a system is positive work.
Work done by a system is negative work.
What is the area under a p/v curve?
The work.
It is path dependent, so depending on the point where it started and ended impacts its sign and depending on the path it takes alters the area underneath the curve.
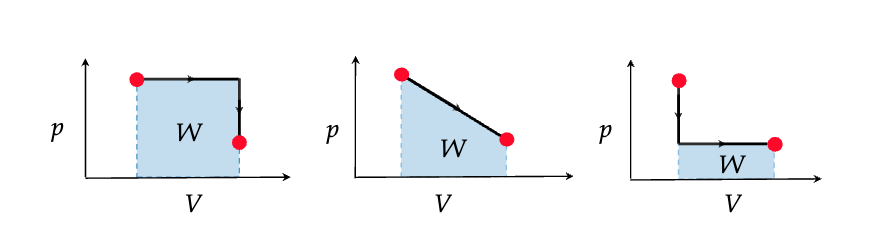
Use this image to explain why work done on the system and heat exchanged by the system is path dependent.
In these 3 cases the initial and final temperature is the same, so the change in thermal energy is the same. However, the work done on the system (Won) and the heat exchanged by the system (Q) are not the same.
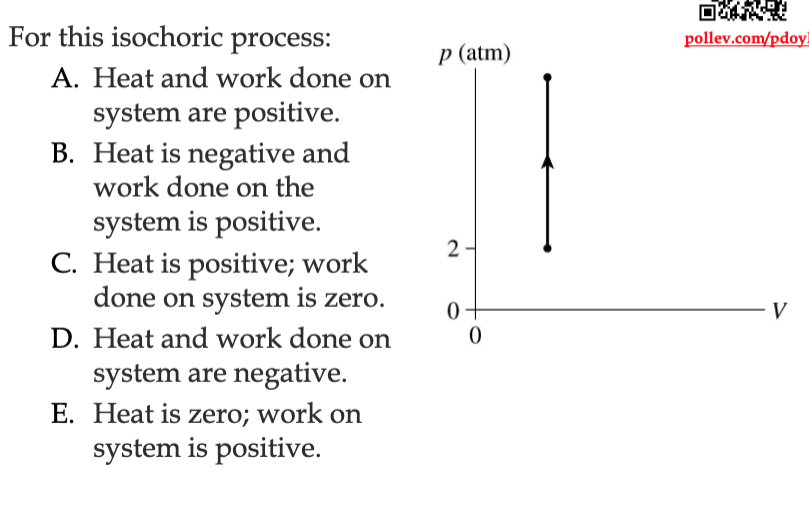
Heat is positive because the temperature increases from lower point to higher point.
Work is 0 because there is no area underneath the curve.
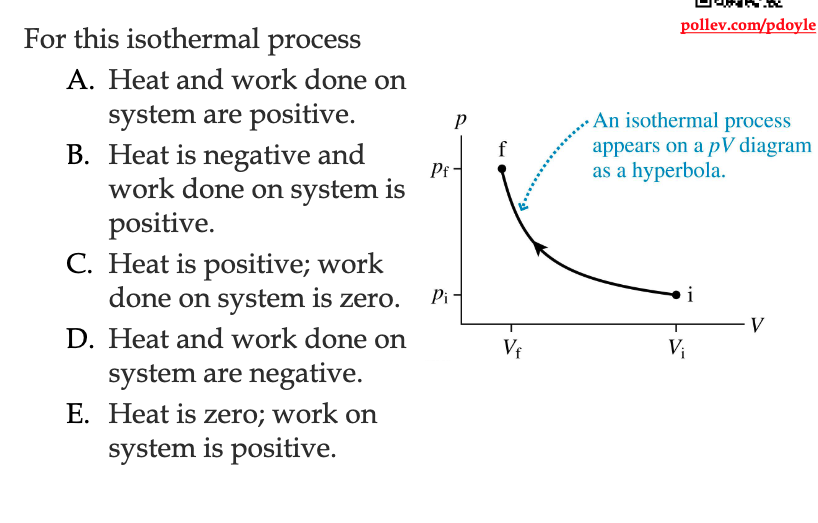
The answer is heat is negative and work done on the system is positive…
1) The velocity decreases and pressure increases, meaning something is smushing down on this system (adding force doing + work).
2) Isothermal means that temperature doesn’t change, so Eth = 3/2 N Kb T and we have a constant N and T so ∆Eth has to be 0.
3) ∆Eth = Won + Q, so if the work on is + and the ∆Eth is 0 then Q must be negative!
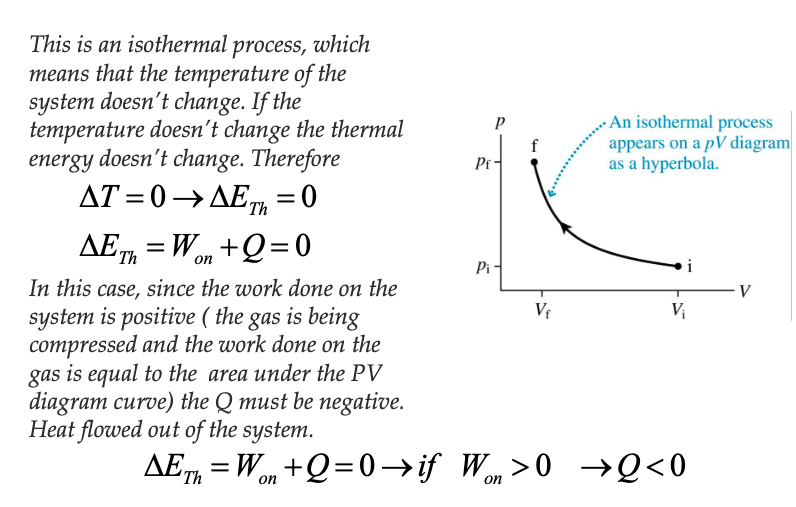
Equation relating W, Q, ∆Eth as well as the equation for ∆Eth
KNOW THESE ONES!
∆Eth = 3/2 N Kb ∆T
∆Eth = Won + Q
If the points on a pv graph are going from right to left (volume is decreasing, pressure increasing) what is the work?
That means the work done is positive because imagine that when volume is decreasing and pressure is increasing something is pushing in on that system.
If the points on a pv graph are going from left to right (volume is increasing and pressure decreasing) what is the work?
This means that the work done is negative because imagine that the system is pushing out to get more volume and to have less pressure. Like you pushing out of a straight jacket you are doing work on the jacket. help.
What is diffusion?
The random motion of a group of particles that causes them to spread out over a time from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
What is root mean squared distance? What’s the formula?
The distance of each particle from x=0 squared, then the average of those squared distances, then the square root of that average.
xrms = sqr(x2) = sqr(N) * dmfp
Relate Eth to N, Kavg kb and T