General Microbiology Lecture 5A - Viruses Part 1
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is the general structure of viruses?
Acellular microbes, not free living because they need a host, causes infections to all groups of organisms
What is the specific structure of viruses?
Made up of virions
What are virions?
Virtual particles
What are the common components of virions?
nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), can be single stranded (ss) or double stranded (ds), protein coat (capsid), enveloped or naked
What is an example of a naked virus?
Atadenovirus
What is an example of an enveloped virus?
HIV, influenza, hepatitis C, measles
What are the three shapes of virions?
Helical, icosahedral, complex
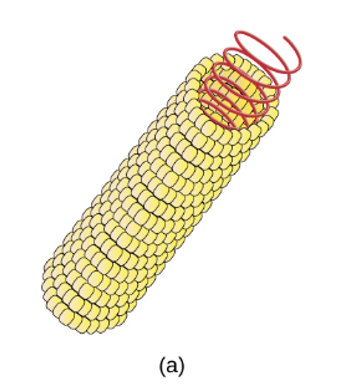
What shape of virion is?
helical
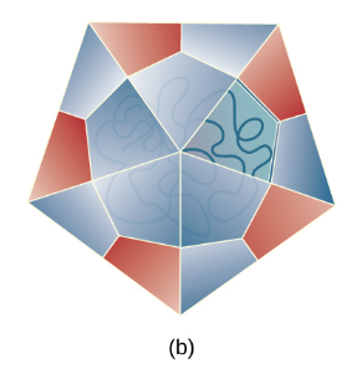
What shape of virion is?
icosahedral

What shape of virion is?
complex
Describe a helical shape virion.
Capsid arranged in a tube, up to 20 nm wide and 500 nm long
Describe an icosahedral virion.
Capsid made of equilateral triangles arranged in a spherical shape
Describe a complex virion.
Has a complex structure, outer wall and capsid
What is an example of a virus with a helical shaped virion?
Tobacco mosaic virus
What is an example of a virus with an icosahedral virion?
Polio virus, adenovirus, rhinovirus
What is an example of a virus with a complex virion?
Bacteriophage, variola virus
What shape of virion can an enveloped virus have?
Can be either icosahedral or helical
What system is used to classify viruses taxonomically?
The Baltimore system which is based on the structure of the viral genome, DNA or RNA, ss or ds, sense (+) or sense (-)
What is the family of viruses?
End in -viridae
What is the genera/genus of viruses?
End in -virus
What is the species of viruses?
Disease caused by virus
What are bacteriophages?
Bacteria virus that is found everywhere bacteria is
What is the difference between lytic and temperate phages?
Lytic phages directly replicate and lyse (destroy) their host cells while temperate phages can either replicate and lyse the host or integrate their DNA into the host’s genome becoming a prophage and replicating with the host.
What is CRISPR?
immune system in bacteria that is used to defend against bacteriophages
What are the main components of CRISPR?
Nuclease, Cas9, Guide RNA
What is nuclease?
enzyme that can cut DNA
What is Cas9?
Nuclease that cuts DNA
What is Guide RNA?
Targets where Cas9 cuts DNA
What are the steps for CRISPR?
1. Cas proteins bind viral DNA and cuts it into small pieces
2. Cut pieces are integrated into CRISPR array
3. crRNAs are used as template by Cas protein to recognize and destroy viral DNA
What does it mean when a virus is enveloped?
virus has a phospholipid bilayer
What is a filamentous phage?
single stranded, productive infections, do not kill host