Bio 1201 exam 3
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
LSU
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
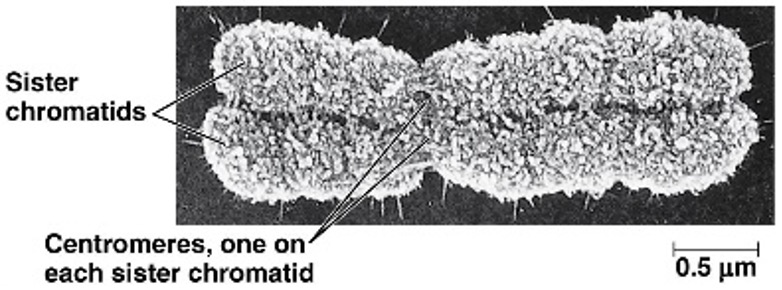
At what part of the cell cycle would you see a chromosome that looks like this?
M
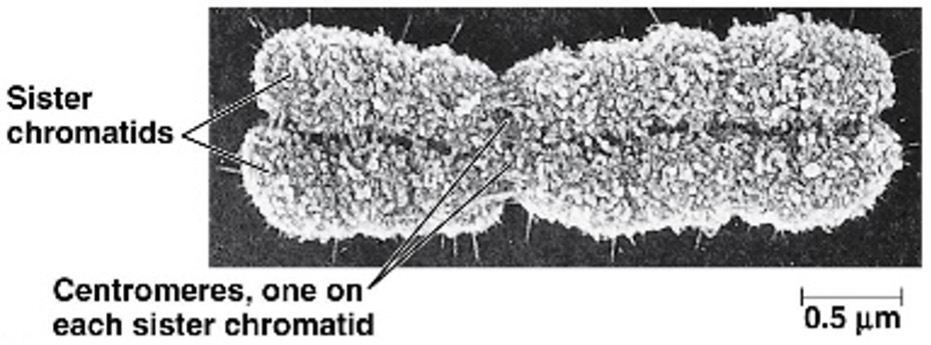
The chromosome begins M phase looking as shown. When does it split?
Anaphase
Which best describes the kinetochore?
a structure composed of several proteins that associate with the centromere region of a chromosome and that can bind to spindle microtubules
From prophase through metaphase of mitosis, each chromosome has _____ DNA molecules, while from anaphase through telophase of mitosis, each chromosome has _____ DNA molecule(s).
two; one
If you were given a slide and told that the cells on it were performing cytokinesis, how would you tell if you had plant cells or animal cells?
Look for a cell plate or a cleavage furrow
Which comes immediately after S phase in the cell cycle?
G2
If a cell that had two copies of each chromosome, but problems with the spindle caused the sister chromatids to remain attached to each other and to only one spindle pole, what cells would result?
cells with 4 copies of each chromosome and 0 copies of each chromosome
You are observing a line of rat cells and see that they repeatedly make mistakes in the cell cycle by going through the G2 checkpoint too early. This could be due to a…
problem with expression of a cyclin
The decline of MPF activity at the end of mitosis is due to…
the degradation of cyclin
If a cell does not receive a go-ahead signal at G1 checkpoint during cell cycle, name the phase it enters as a nondividing state
G0
Binary fission is more like animal cell division than plant cell division because
bacteria and animals both pinch in to separate the cytoplasm into two pieces
Privet shrubs and humans each have a diploid number of 46 chromosomes per cell. Why are the two species so dissimilar?
the two species has appreciably different genes
Why is it more practical to prepare karyotypes by viewing somatic diploid cells rather than haploid gametes?
both sets of chromosomes, which are present in somatic diploid cells, need to be examined
Why does sexual reproduction (via meiosis) have an advantage over asexual reproduction (via mitosis)?
Meiosis increases genetic variation among offspring
The mosquito Aedes aegypti has a karyotype of 2n = 6. Through independent assortment alone, how many chromosomal combinations can be made during meiosis?
3
A human cell containing 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome is…
A sperm
If the DNA content of a diploid cell in the G1 phase of the cell cycle is x, then the DNA content of the same cell at metaphase of meiosis I will be
2x
Which of the following is not a reason that peas were well suited for Mendel’s breeding experiments?
Peas have an unusually long generation time
A pea plant is heterozygous at the independent loci for flower color (Pp) and seed color (Yy). What types of gametes can it produce?
four gamete types: pY, py, PY, and Py
A cross between homozygous purple-flowered and homozygous white-flowered pea plants results in offspring with purple flowers. This demonstrates
dominance
The following offspring were observed from many crossings of the same pea plants. What genotypes were the parents?
465 purple axial flowers 152 purple terminal flowers
140 white axial flowers 53 white terminal flowers
The alleles for purple, white, axial and terminal characters are P, p, A, a respectively.
PpAa x PpAa
Suppose that Mendel’s hypothesis that inheritance is “particulate” rather than due to blending were wrong. Which observation would he have not made?
Crossing two-purple flowered heterozygotes produced purple-flowered and white-flowered plants
What do you call an organism containing two different alleles for the same gene?
Heterozygote
If there is an organism with two identical alleles for the same gene, what would the organism be?
a and c
The trait which is not expressed in the F1 generation of monohybrid cross is called
Recessive
genotypes made of the same alleles
homozygous
different forms of genes for a single trait
alleles
gene that is always expressed
dominant
gene that is expressed only in the homozygous state
recessive
genotypes made of two different alleles
heterozygous
What is the phenotypic ratio of Mendel’s dihybrid crosses in the F2 generation?
9:3:3:1
How many characters are involved in a dihybrid cross of a particular organism?
2
Imagine a locus with four different alleles for fur color in an animal, Da, Db, Dc, and Dd. If you crossed two heterozygotes, DaDb and DcDd, what genotype proportions would you expect in the offspring?
25% DaDc, 25% DaDd, 25% DbDc, 25% DbDd
The agouti gene in mice plays a role in determining coat color. At this locus, the genotype AA produces an “agouti coat,” and the heterozygote Aa produces a yellow coat. The aa homozygotes, however, die very early in development. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of live mice resulting from a cross of two Aa mice?
2:1 yellow:agouti
In man normal pigmentation is due to a dominant gene (C), albinism to its recessive allele (c). If a phenotypically unaffected couple produces an albino child, what is the probability that their next child is an albino?
25%
In dragons, wings are a dominant trait, but some dragons are born wingless.
i. If a wingless dragon is crossed with one that is heterozygous, how many of its offspring will also be wingless?
50%
In dragons, wings are a dominant trait, but some dragons are born wingless.
ii. What are the chances that two heterozygous dragons have a whelp that is wingless?
25%
In pea plants, yellow seed color is dominant to green seed color. If a heterozygous pea plant is crossed with a plant that is homozygous recessive for seed color, what is the probability that the offspring will have green seeds?
50%
Red eyes (R) in fruit flies are dominant over white eyes (r). Using Punnett squares, find the possible eye colors of the F1 generation for each of the following crosses.
i. Rr X rr
50% red, 50% white
Red eyes (R) in fruit flies are dominant over white eyes (r). Using Punnett squares, find the possible eye colors of the F1 generation for each of the following crosses.
ii. rr X RR
100% red
Red eyes (R) in fruit flies are dominant over white eyes (r). Using Punnett squares, find the possible eye colors of the F1 generation for each of the following crosses.
iii. Rr X Rr
75% red, 25% white
Genes which tend to be inherited together are called
Linked genes
Who conducted the X-ray diffraction studies that were key to the discovery of the structure of DNA?
Franklin
What enzyme compensates for replication-associated shortening of linear chromosomes?
telomerase
Which of the following results from Griffith’s experiment is an example of transformation?
Mouse dies after being injected with a mixture of heat-killed S and living R cells.
Suppose a double-stranded DNA molecule was shown to have 22% guanine bases. What would be the expected percentage of adenine bases in that molecule?
28%
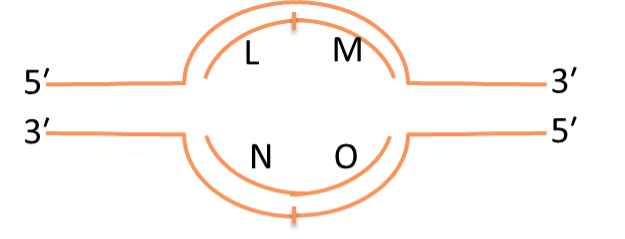
Consider the replication bubble diagrammed at the right. Which letters represent leading strands?
L and O
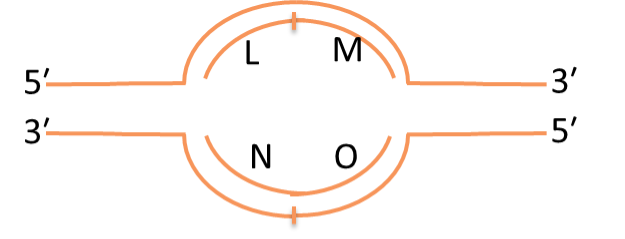
Consider the replication bubble diagrammed at the right. Which letters represent places where one could find Okazaki fragment
M and N
In Meselson and Stahl’s experiment proving semiconservative DNA replication, they started with bacteria grown in a heavy isotope of nitrogen and then switched them to a light isotope. They then observed the DNA density after one and two rounds of replication. What was the result after one round of replication?
all hybrid DNA
Imagine a bacterial replication fork. Synthesis of which new strand(s) would be affected by mutations in the enzyme DNA polymerase III?
both leading and lagging strands
In Meselson and Stahl’s experiment proving semiconservative DNA replication, they started with bacteria grown in a heavy isotope of nitrogen and then switched them to a light isotope. They then observed the DNA density after one and two rounds of replication. What was the result after two rounds of replication?
equal amounts of light and hybrid DNA
Black eyes are dominant to orange eyes, and green skin is dominant to white skin. A male MendAlien with black eyes and green skin, has a parent with orange eyes and white skin. A female MendAlien with orange eyes and white skin. If these male and female MendAliens were to mate, the predicted phenotypic ratio of their offspring would be _____.
1 black eyes, green skin : 1 black eyes, white skin : 1 orange eyes, green skin : 1 orange eyes, white skin
A cross between two individuals that are heterozygous for eye and skin color would be an example of a _____ cross.
dihybrid
A phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1 in the offspring of a cross indicates that _____.
both parents are heterozygous for both genes
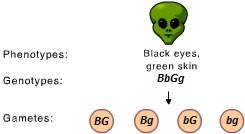
The observed distribution of alleles into gametes is an illustration of _____.
Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment
An individual heterozygous for eye color, skin color, and number of eyes mates with an individual who is homozygous recessive for all three characters; what would be the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? [Hint: B = black eyes, b = orange eyes; G = green skin, g = white skin; C = two eyes, c = one eye]
1 black eyes, green skin, two eyes : 1 black eyes, green skin, one eye : 1 black eyes, white skin, two eyes : 1 black eyes, white skin, one eye : 1 orange eyes, green skin, two eyes : 1 orange eyes, green skin, one eye : 1 orange eyes, white skin, two eyes : 1 orange eyes, white skin, one eye
A BbGg x bbgg cross yields a phenotypic ratio of approximately 5 black eyes, green skin : 5 orange eyes, white skin : 1 black eyes, white skin : 1 orange eyes, green skin. Which of the following best explains these results?
Mendel's law of independent assortment is being violated.
In a situation in which genes assort independently, what is the ratio of the gametes produced by an AaBB individual?
1 AB : 1 aB
If B represents the allele for black eyes (dominant) and b represents the allele for orange eyes (recessive), what would be the genotypic ratio of a cross between a heterozygous black-eyed MendAlien and an orange-eyed MendAlien?
0 homozygous black (BB): 1 heterozygote (black) (Bb): 1 homozygous orange (b
Which of these is a testcross?
A? x A? |
aa x aa |
A? x Aa |
A? x aa |
A? x AA |
A? x aa
What is the difference between heterozygous and homozygous individuals?
All of the gametes from a homozygote carry the same version of the gene while those of a heterozygote will differ.
When constructing a Punnett square, the symbols on the outside of the boxes represent _______, while those inside the boxes represent _______.
gametes, progeny
True or false? The same phenotype can be produced by more than one genotype
true
True or false? In diploid organisms, a dominant phenotype will only be expressed if the individual is homozygous dominant for that trait.
false
If an organism with the genotype AaBb produces gametes, what proportion of the gametes would be Bb?
none
Two mice are heterozygous for albinism (Aa) . The dominant allele (A) codes for normal pigmentation, and the recessive allele (a) codes for no pigmentation. What percentage of their offspring would have an albino phenotype?
25
A tall, purple-flowered pea plant (TtPp) is allowed to self-pollinate. (The recessive alleles code for short plants and white flowers.) The phenotypic ratio of the resulting offspring is 9:3:3:1. What is the genotype of the plant whose phenotype appeared once out of every 16 offspring (the "1" in the 9:3:3:1 ratio)?
ttpp
Which of the following is true about a plant with the genotype AABbcc?
it has recessive alleles at three loci |
it is triploid |
it is heterozygous at two loci |
it will not express the recessive c allele |
it is homozygous at two loci |
it is homozygous at two loci
Consider pea plants with the genotypes GgTt and ggtt. How many types of gametes can be produced by each of these two plants?
four, one
Phenylketonuria is an inherited disease caused by a recessive allele. If a woman and her husband are both carriers, what is the probability that their first child will be a girl without phenylketonuria?
3/8
Meiosis I produces _____ cells, each of which is _____.
two ... haploid
Meiosis II typically produces _____ cells, each of which is _____
four ... haploid
During _____ sister chromatids separate.
anaphase II
At the end of _____ and cytokinesis, haploid cells contain chromosomes that each consist of two sister chromatids.
telophase I
Synapsis occurs during _____.
prophase I
Homologous chromosomes migrate to opposite poles during _____.
anaphase I
During _____ chromosomes align single file along the equator of a haploid cell.
metaphase II
At the end of _____ and cytokinesis there are four haploid cells.
telophase II
During _____ a spindle forms in a haploid cell.
prophase II
Homologous pairs of chromosomes are lined up independently of other such pairs during _____
metaphase I
Crossing over, resulting in an increase in genetic variation, occurs between _____.
nonsister chromatids of homologous chromosomes
In human gamete production there is an average of _____ crossover events per chromosome pair.
2–3
DNA replication produces two identical DNA molecules, called _____ , which separate during mitosis.
sister chromatid(s)
After chromosomes condense, the _____ is the region where the identical DNA molecules are most tightly attached to each other.
centromere(s)
During mitosis, microtubules attach to chromosomes at the _______
During mitosis, microtubules attach to chromosomes at the kinetochore(s).
In dividing cells, most of the cell's growth occurs during ________
interphase
The ______ is a cell structure consisting of microtubules, which forms during early mitosis and plays a role in cell division.
mitotic spindle(s)
During interphase, most of the nucleus is filled with a complex of DNA and protein in a dispersed form called _______
chromatin
In most eukaryotes, division of the nucleus is followed by ________, when the rest of the cell divides.
cytokinesis
The ________ are the organizing centers for microtubules involved in separating chromosomes during mitosis.
centrosome(s)
Nucleoli are present during _____.
interphase
Cytokinesis often, but not always, accompanies _____.
telophase
Chromosomes become visible during _____.
prophase
Centromeres divide and sister chromatids become full-fledged chromosomes during _____.
anaphase
Spindle fibers attach to kinetochores during _____.
prometaphase
If a eukaryotic cell is in the G1 phase of the cell cycle, which statement about the cell’s chromosomes must be correct?
Each chromosome is made of a complex of DNA and associated proteins
During ______, a cell is metabolically active.
interphase
Which pairs of molecules make up an active MPF?
cyclin and a cyclin-dependent kinase
A ____ is an enzyme that attaches phosphate groups to other proteins.
Cdk
Which molecule is maintained at a relatively constant level throughout the cell cycle but requires a cyclin to become catalytically active?
Cdk