transition metals
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Why are d-block transition elements magnetic?
They have unpaired electrons
Properties of d-block transition elements?
Hard, ductile, malleable
What is a transition metal complex?
A central metal atom/ion surrounded by ligands that bind to the metal through electron donation
What is a coordination complex?
None of the ligands bind through a carbon atom
What is an organometallic complex?
At least one ligand binds through a C atom
How are electrons assigned to atomic orbitals?
Aufbau principle
Hund’s rule
Pauli Exclusion principle
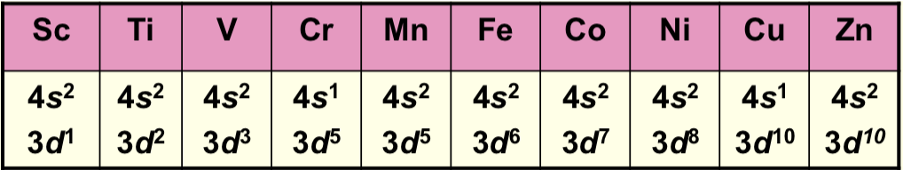
Why are Cr and Cu exceptions?
Extra stability is gained from half or fully filled subshells
What happens when a metal is in a compound (electron configuration)?
The filling order reverts to 3d before 4s
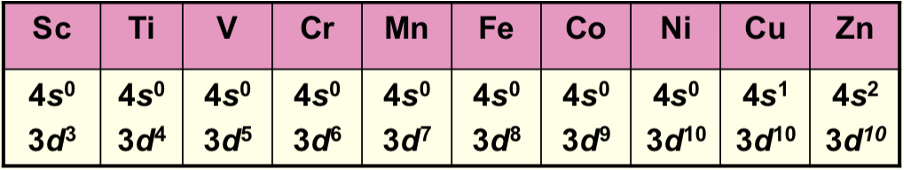
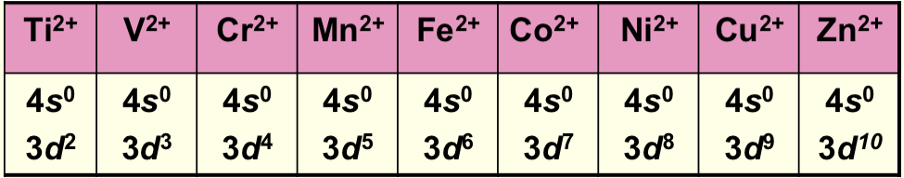
How are electrons removed from orbitals on ionisation?
s electrons are removed before d electrons
Why does ionisation energy increase across the periodic table?
Increasing effective nuclear charge
What is the coordination number?
The number of ligands around a metal
Is the metal a Lewis acid or base?
Is the ligand a Lewis acid or base?
Metal is a Lewis acid as it accepts electrons
Ligand is a Lewis base as it donates electrons
Why are transition metals able to readily form complexes?
They have energetically available empty d orbitals
Why are good bases generally good ligands?
They have an available electron pair
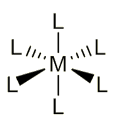
What is the shape of coordination number 6?
Angles?
Octahedral
90º adjacent angles, 180º opposite angles
What are the two shapes for coordination number 4?
Angles?
Tetrahedral, 109.5º
Square planar, adjacent 90º; opposite 180º
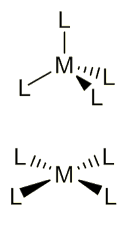
What are ligands?
Electron pair donors
What are monodentate ligands?
Coordinate to a metal through one donor atom
What are polydentate ligands?
Coordinate to a metal through more than one atom
What is a chelate ring?
Two or more donor atoms coordinate to a single metal
What are constitutional/linkage isomers?
Same formula, different atom to atom connectivity
What are stereoisomers?
Same formula, same atom to atom connectivity, different arrangements in space
What are the two types of stereoisomers?
Geometrical isomerism
Optical isomerism
Do tetrahedral complexes form geometric isomers?
No
Do square planar complexes form geometric isomers?
When two ligands are the same

What is the difference between cis and trans isomers?
Cis = identical ligands adjacent to each other, 90º
Trans = identical ligands opposite, 180º

Do octahedral complexes form geometric isomers?
When two or three ligands are the same
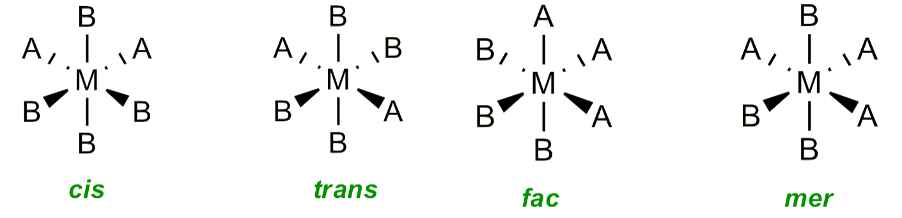
What are the differences between fac and mer isomers?
Three identical ligands form a face = facial, 90º
Three identical ligands in plane = meridional, 90º and 180º
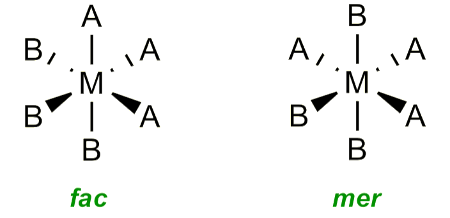
How to use triangles to determine fac and mer isomers?
If the triangle goes through the middle, then it is mer
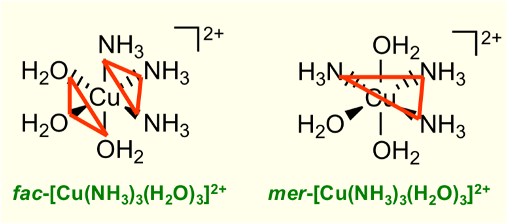
What is optical isomerism?
When an object cannot be superimposed onto its mirror image
What are the optical isomers called?
Enantiomers
Do tetrahedral complexes form optical isomers?
Only if all 4 ligands are different
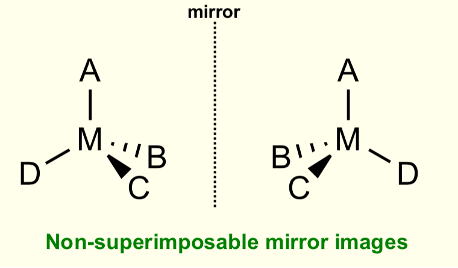
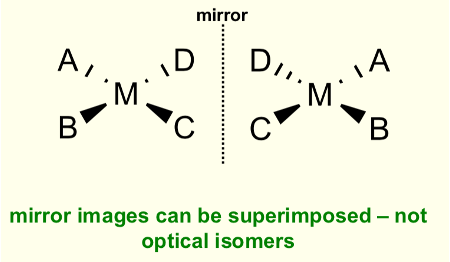
Do square planar complexes form optical isomers?
No
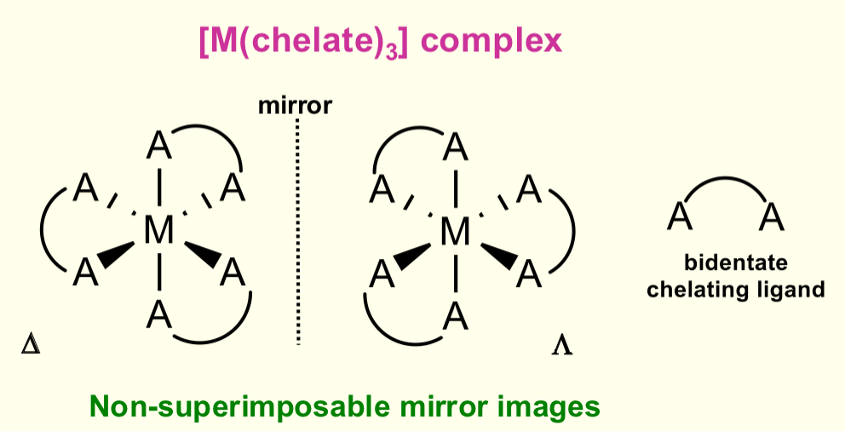
Do octahedral complexes form optical isomers?
Does not occur with mono dentate
Occurs when there are 2 or 3 bidentate chelating ligands
![<p>In an octahedral [MA<sub>2</sub>(chelate)<sub>2</sub>] complex, which is chiral?</p><p>therefore how many isomers does it have?</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/007d7202-a13d-4adb-81b3-8259d233b319.png)
In an octahedral [MA2(chelate)2] complex, which is chiral?
therefore how many isomers does it have?
The cis isomer is chiral and can form optical isomers
It has three isomers
How to name complexes?
Ligands first (in alphabetical order), then metal
How to name a compound (i.e. complex and counter ions)?
Cation first then anion