Flow rates and Pulmonary Function Tests
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
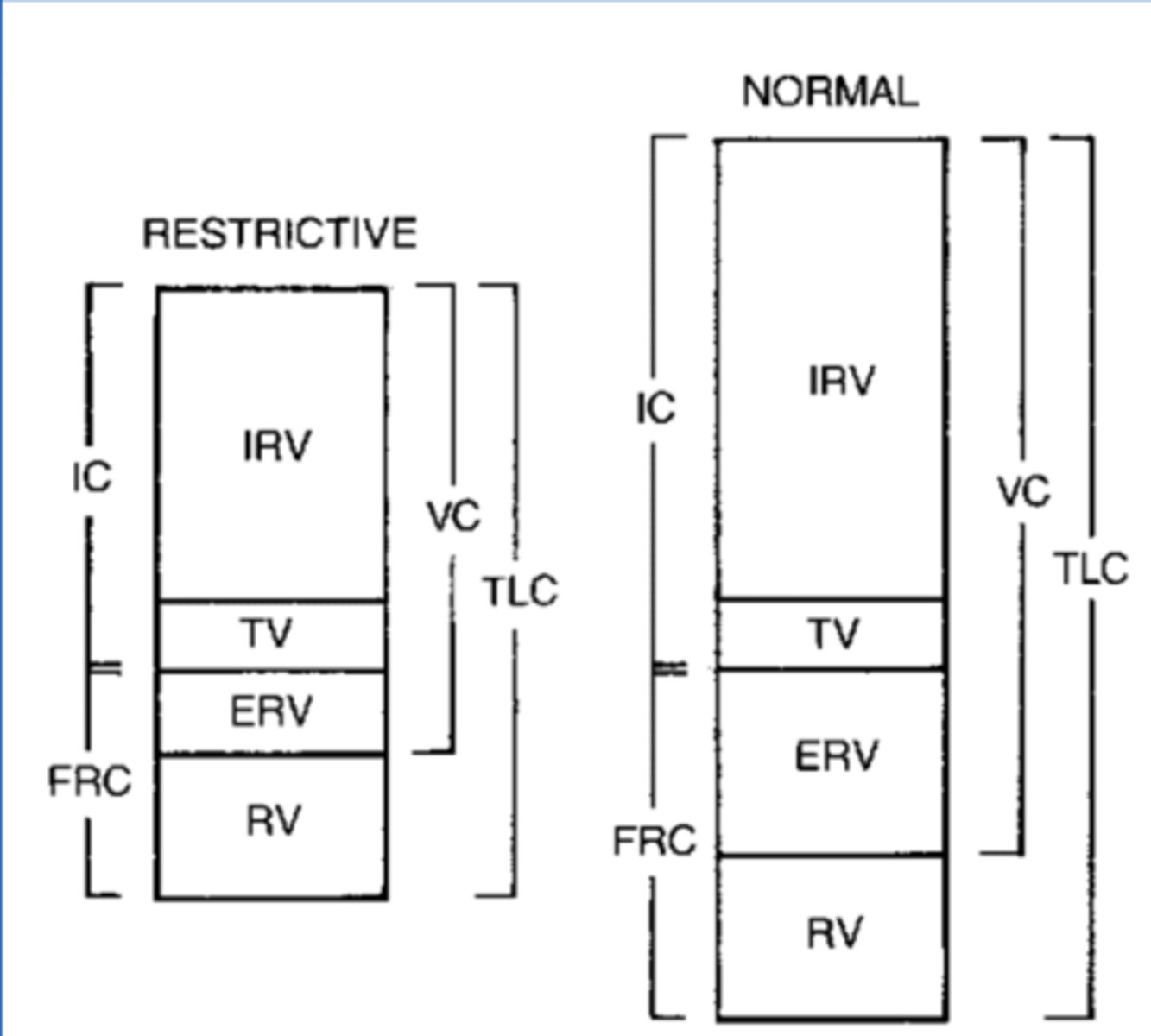
Restrictive Disorders
Can't expand lungs, smaller sonic cup, harder to inhale
Extrinsic disorders (outside of lungs)
-Scoliosis, Diaphragm paralysis & Obesity
Intrinsic disorders (inside the lungs)
-Pulmonary edema & fibrosis
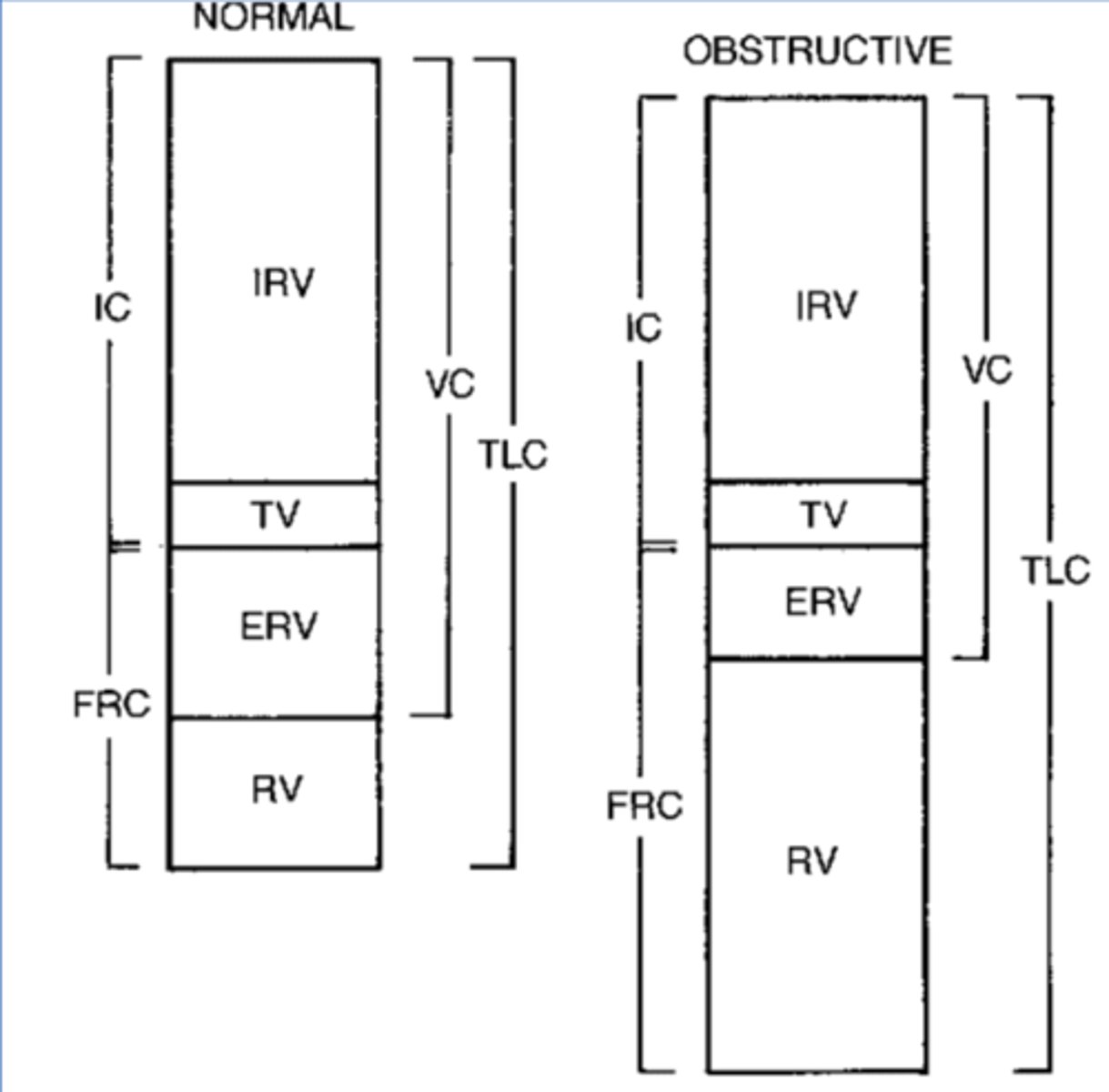
Obstructive Disorders
Airway disorder, smaller straw, takes forever to exhale
Asthma
COPD
Cystic Fibrosis
FEV1 tests for this
Forced vital capacity (FVC) test
Amount of air that can be forcibly & rapidly exhaled after a full inspiration
Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 second (FEV1)
How much can u blow out in 1 sec.
Measures small airways
Measure of flow rate: tests Obstructive disorders
Diffusion carbon dioxide (DLCO)
Used to determine cross sectional surface area
Gas exchange from lungs to blood
DLCO = Surface Area over alveoli Thickness
DLCO low = less surface area or hypoventilation
If surface area increases what happens to DLCO?
Diffusion rate increases
If thickness increases what happens to DLCO?
Diffusion rate decreases
Extrinsic DLCO
Hypoventilation, Scoliosis, & Obesity
>80% DLCO/VA
Intrinsic DLCO
Low surface area or increased thickness. Emphysema, Pulmonary fibrosis, & Pulmonary hypertension
<80% DLCO/VA
PImax
Maximum Inspiratory Pressure. Max pressure during inspiration. Measures strength of muscles of inspiration
SIPmax
Maximal Sustained Inspiratory Pressure. Add resistance to inspirations. Measure of endurance of inspiratory muscles
PEF
Peak Expiratory Flow. Maximum flow of air during forced expiration
VE
Minute Volume Ventilation. Volume of air expired in 1 minute. VE = TV x Respiratory Rate
Normal Lung Sounds
Bronchial
Vesicular
Bronchovesicular
Bronchial
Loud tubular sounds that are hollow and higher pitched. Inspiration less than expiration - 1:3
Vesicular
Rustling and breezy sound that is soft and low pitched. Inspiration longer than expiration - 3:1
Bronchovesicular
Combo of bronchial & vesicular. Inspiration & Expiration are equal - 1:1
Adventitious (Abnormal Lung Sounds)
Continuous
-Pleural Friction Rub
-Rhonchi
-Stridor
-Wheeze
Discontinuous
-Crackles
Pleural Friction Rub
dry, crackling sound heard during both inspiration and expiration
Rhonchi
Low pitched sounds similar to snoring or gurgling
Stridor
High pitched wheeze
Wheeze
Musical or whistling sound
Crackles
High pitched popping during inspiration.
-Early: Bronchitis
-Late: Pneumonia, CHF, atelectasis
S1 (heart sounds)
AV valves close. LUB
S2
Aortic and pulmonary valves close. DUB
S3
early diastole. "Ventricular gallop". Due to distended ventricle wall during passive draining of blood from atrium. CHF
S4
late diastole. "Atrial gallop". Vibration heard during atrial contraction. Myocardial Infarction or Hypertension