PHYL 142 EXAM 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/374
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:13 AM on 3/29/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
375 Terms
1
New cards
Where is the heart positioned in the thoracic cavity?
Heart is located slightly to the left
There’s a concavity in the left lung to accommodate the heart
There’s a concavity in the left lung to accommodate the heart
2
New cards
What is the heart’s own blood supply?
Coronary arteries
3
New cards
The right coronary artery is also known as
posterior descending artery (PDA)
4
New cards
The left coronary artery is also known as
left anterior descending (LAD) circumflex artery
5
New cards
What are the coronary veins draining from the posterior surface of the heart?
* great cardiac vein
* small cardiac vein
* posterior cardiac vein
* middle cardiac vein
* small cardiac vein
* posterior cardiac vein
* middle cardiac vein
6
New cards
What are the coronary veins draining from the anterior surface of the heart?
* great cardiac vein
* small cardiac vein
* anterior cardiac vein
* small cardiac vein
* anterior cardiac vein
7
New cards
Where do coronary veins go?
All drain into the coronary sinus
8
New cards
What is the function and location of epicardial fat?
Location:
* between the heart wall and pericardial sac
Function:
* insulate and cushion heart and coronary vessels
* provide energy to myocardium
* between the heart wall and pericardial sac
Function:
* insulate and cushion heart and coronary vessels
* provide energy to myocardium
9
New cards
What is excess epicardial fat associated with?
* heart disease
* obesity
* obesity
10
New cards
How is fat distributed?
Visceral - apple shaped = more epicardial fat
Subcutaneous - pear shape = less epicardial fat
Subcutaneous - pear shape = less epicardial fat
11
New cards
What is ischemia?
* INADEQUATE BLOOD SUPPLY TO AN ORGAN
* decreased blood flow to tissue
* decreased oxygen and nutrient to tissue
* builds up metabolic waste
* leads to cell death
* decreased blood flow to tissue
* decreased oxygen and nutrient to tissue
* builds up metabolic waste
* leads to cell death
12
New cards
What is myocardial infarction?
* a heart attack = cardiac ischemia
* cardiac muscle and cells die from lack of oxygen and nutrients
* cardiac muscle and cells die from lack of oxygen and nutrients
13
New cards
What is known as the widow-maker?
* left anterior descending artery blockage
* deadliest coronary occlusion
* caused by left anterior descending artery blockage
* deadliest coronary occlusion
* caused by left anterior descending artery blockage
14
New cards
What does the left anterior descending artery of the heart supply?
Most of the left ventricle and interventricular septum
15
New cards
What is the blood flow of deoxygenated blood?
right ventricle → pulmonary arteries → lungs
16
New cards
What is the blood flow of oxygenated blood?
left ventricle → aorta → rest of the body
17
New cards
How does a myocardial infarction affect heart function?
Scar tissue develops
18
New cards
What is the most leading cause of death in the US?
heart disease
19
New cards
What is ventricular remodeling?
* loss of cardiomyocytes (heart muscle cells)
* remaining cardiomyocytes thicken
* fibroblast secrete collagen (fibrosis) that can’t contract
* remaining cardiomyocytes thicken
* fibroblast secrete collagen (fibrosis) that can’t contract
20
New cards
myocardial infarction symptoms
* chest pain
* dizziness, nausea, vomiting
* jaw/neck/back pain
* arm/shoulders pain
* shortness of breath
* dizziness, nausea, vomiting
* jaw/neck/back pain
* arm/shoulders pain
* shortness of breath
21
New cards
What is referred pain?
pain at a site different from where it is actually happening
common in myocardial infarctions
common in myocardial infarctions
22
New cards
Which sex has a higher risk of getting a MI?
Males have higher lifetime risks and develop earlier
23
New cards
What are the myocardial infarction disparities?
* females die more often from MIs
* males are more likely to develop MIs at 65/yo
* females develop at 75 y/o
\
* males are more likely to develop MIs at 65/yo
* females develop at 75 y/o
\
24
New cards
Different MI symptoms between male and female
females are more likely to experience shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, and jaw/back pain
25
New cards
How can a MI be diagnosed?
MIs can be diagnosed using tests like electrocardiograms or echocardiograms
26
New cards
What are treatments for MI?
* drugs and medications
* anticoagulants (beta blockers)
* agioplasty and stent
* coronary bypass
* anticoagulants (beta blockers)
* agioplasty and stent
* coronary bypass
27
New cards
What is percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)?
used to unfold wire/metal meshes (stent) to hold vessels open
28
New cards
What is angioplasty?
Inflatable balloons that are used to widen blocked areas for blood to flow
29
New cards
What are risk factors for MI?
* age
* genetic and family history
* male (2x the risk)
* lifestyle factors: tobacco, hypertension, inactivity, obesity
\
* genetic and family history
* male (2x the risk)
* lifestyle factors: tobacco, hypertension, inactivity, obesity
\
30
New cards
What are symptoms of a stroke?
* drooping face
* asymmetry or weakness in arm
* slurred speech
* trouble seeing/walking/understanding
* asymmetry or weakness in arm
* slurred speech
* trouble seeing/walking/understanding
31
New cards
What is a coronary artery bypass graft? (CABG)
* uses blood vessels from elsewhere to deliver around blockages
* routes oxygenated blood from aorta or major arteries
* delivers blood downstream of blockage
* routes oxygenated blood from aorta or major arteries
* delivers blood downstream of blockage
32
New cards
What are types of strokes?
* brain attack
* cerebrovascular accident (CVA)
* ischemia
* blockage of arteries causing ischemia
* cerebrovascular accident (CVA)
* ischemia
* blockage of arteries causing ischemia
33
New cards
What is systole?
* squeeze
* contract
* ejecting blood
* contract
* ejecting blood
34
New cards
What is diastole?
* dilate
* relaxation
* fills with blood
* relaxation
* fills with blood
35
New cards
What happens during systole?
contraction → relaxation → fills with blood
36
New cards
What happens during diastole?
relaxation → pressure decreasing → filling
37
New cards
What are the phases of the cardiac cycle?
1. atrial systole
2. isovolumetric ventricle contraction
3. ventricle ejection
4. isovolumetric ventricle relaxation
5. ventricle filling
38
New cards
What happens during atrial systole?
* atria: systole (squeeze) blood is forced into the ventricles
* ventricle: diastole
* tricuspid and mitral valve: open
* pulmonary and aortic valve: close
* BLOOD FLOWS FROM HIGH TO LOW
* ventricle: diastole
* tricuspid and mitral valve: open
* pulmonary and aortic valve: close
* BLOOD FLOWS FROM HIGH TO LOW
39
New cards
What happens during isovolumetric ventricular contraction?
* first heart sound is beat
* ALL VALVES SHUT
* atria: diastole
* ventricle: systole
* tricuspid and mitral valve: close
* pulmonary and aortic valve: close
* ALL VALVES SHUT
* atria: diastole
* ventricle: systole
* tricuspid and mitral valve: close
* pulmonary and aortic valve: close
40
New cards
What happens during ventricular ejection?
* PRESSURE BUILDS UP IN VENTRICLES
* atria: diastole
* ventricle: systole
* tricuspid and mitral valve: close
* pulmonary and aortic valve: open
* atria: diastole
* ventricle: systole
* tricuspid and mitral valve: close
* pulmonary and aortic valve: open
41
New cards
What happens during isovolumetric ventricular relaxation?
* VENTRICLES ARE RELAXING AND ALL VALVES ARE SHUT
* CAUSE SECOND HEART SOUND
* atria: diastole
* ventricle: diastole
* tricuspid and mitral valve: open
* pulmonary and aortic valve: close
* CAUSE SECOND HEART SOUND
* atria: diastole
* ventricle: diastole
* tricuspid and mitral valve: open
* pulmonary and aortic valve: close
42
New cards
What happens during ventricular filling?
* pressure in ventricles drop
* ATRIA HAS GREATER PRESSURE
* BLOOD FLOWS INTO ATRIA THEN VENTRICLES
* mitral & tricuspid valves: open
* atria & ventricles: diastole
* ATRIA HAS GREATER PRESSURE
* BLOOD FLOWS INTO ATRIA THEN VENTRICLES
* mitral & tricuspid valves: open
* atria & ventricles: diastole
43
New cards
What is the blood flow through the heart?
1. blood enters the body via the posterior and anterior vena cava into the right atrium
2. right atrium contracts, pushing the blood through the right atrial ventricular valve (tricuspid) into ventricle
3. ventricle contracts then pushes blood via the semilunar valve to the pulmonary arteries
4. goes to lungs and picks up oxygen
5. comes back oxygenated via the pulmonary veins to the left atrium
6. left atrium contracts then pushes blood into left ventricle
7. left ventricle contracts then pushes the blood via the aortic valve to the aorta
8. aorta to rest of the body
44
New cards
What does the cardiac conduction system do?
coordinates and drives cardiac muscle contraction
45
New cards
What are conducting cells?
* specialized cardiac muscle cells
* not nerves
* generate electrical action potentials and spread them throughout the heart
* control the cardiac conduction system
* not nerves
* generate electrical action potentials and spread them throughout the heart
* control the cardiac conduction system
46
New cards
What is electrical potential?
* work needed to move a charge in an electric field
* potential energy per unit charge
* potential energy per unit charge
47
New cards
What is membrane potential?
* electrical charge inside a cell based on \[+\] & \[-\] ion concentrations
* difference in electrical potential between cytosol inside a cell and extracellular fluid outside of the cell
* difference in electrical potential between cytosol inside a cell and extracellular fluid outside of the cell
48
New cards
What is autorhythmicity?
pacemaker cells triggering their own action potentials
49
New cards
What makes up the cardiac conduction system?
specialized cardiomyocytes
50
New cards
What are different anti-arrhythmic medications?
class 1: Na+ channel block
class 2: Beta blocker
class 3: K+ channel blocker
class 4: Beta blocker
class 2: Beta blocker
class 3: K+ channel blocker
class 4: Beta blocker
51
New cards
What are different types of class 1 Na+ channel blocks?
weak: lidocaine & phenytoin
moderate: quinine & procainamide
strong: flecainide & propaferone
moderate: quinine & procainamide
strong: flecainide & propaferone
52
New cards
What are examples of class 2 Beta blockers?
* proparnolol
* metoprolol
* metoprolol
53
New cards
What are different types of class 4 Ca+ channel blockers?
* verapamil
* diltiazem
* diltiazem
54
New cards
What are different types of class 3 K+ channel blockers?
* amiodaron
* solatol
\
* solatol
\
55
New cards
What makes up the conducting system of the heart and pacemaker potential?
* sinoatrial (SA) node
* atrioventricular (AV) node
* bundle branches
* purkinje fibers (subendocardial branches)
* atrioventricular (AV) node
* bundle branches
* purkinje fibers (subendocardial branches)
56
New cards
What happens when the action potential is at the SA node?
1. slow influx of Na+ pre potential
2. rapid influx of Ca 2+ depolarization
3. outflow of K+ repolarization
4. threshold
57
New cards
What is prepotential?
gradual slow increases in membrane potential toward threshold
58
New cards
What are contractile cell potentials?
* pacemaker cell action potentials (SA and AV node)
* purkinje action potential
* atrial action potentials
* ventricular action potentials
* purkinje action potential
* atrial action potentials
* ventricular action potentials
59
New cards
Intracellular fluid
has more K+ inside
60
New cards
Extracellular fluid
has more Na+, Cl-, and Ca2+
61
New cards
What is polarization?
unequal balance of ions and shared molecules on either side of a membrane
62
New cards
What happens when a resting cell’s membrane potential reaches a certain voltage?
* ion channels open and close
* ions move in and out of the cell
* big change in action potentials occur
* ions move in and out of the cell
* big change in action potentials occur
63
New cards
What is an action potential?
* a set of sequence of ion movement and membrane potential change in excitable cells
* do not occur until a certain voltage is reached
* do not occur until a certain voltage is reached
64
New cards
What is a cardiac action potential?
* different with neuronal action potential
* pacemaker cell
* ventricular
* pacemaker cell
* ventricular
65
New cards
What is a threshold?
* membrane potential voltage needed for a cell to start an action potential
* slightly positive
* slightly positive
66
New cards
What is a prepotential?
* gradual slow increase in membrane potential toward threshold
* can be used by the pacemaker cells to reach their threshold
* can be used by the pacemaker cells to reach their threshold
67
New cards
What are calcium channel blockers?
* block Ca2+ channels
* can be used to treat arrythmias (lower blood pressure)
* verapamil
* can be used to treat arrythmias (lower blood pressure)
* verapamil
68
New cards
What are different types of cardiomyocyte action potentials?
* pacemaker cell action potentials
* SA node potential
* AV node potential
* His-purkinjie action potentials
* contractile cell action potentials
* atrial action potential
* ventricular action potential
* SA node potential
* AV node potential
* His-purkinjie action potentials
* contractile cell action potentials
* atrial action potential
* ventricular action potential
69
New cards
What is the normal adult heart rate?
60 - 100 bpm
70
New cards
Heart rate (HR)
* changes with age and health
* newborns and children have faster heart rate
* max HR decreases with age
* newborns and children have faster heart rate
* max HR decreases with age
71
New cards
What is chronotropy?
refers to heart rate (changes)
72
New cards
What is tachycardia?
heart rate that is greater than 100 bpm
73
New cards
What is bradycardia?
heart rate that is less than 60 bpm
74
New cards
Big box of ECG length
0\.2 sec
75
New cards
Little box of ECG length
0\.04 sec
76
New cards
Fast (L-type) Ca2+ channel
can cause a huge peak in the action potential
77
New cards
What is the sinus rhythm?
normal depolarization of the sinus node (SA) and atria
78
New cards
What is the normal sinus rhythm?
normal human heart rhythm with normal ECG tracings
79
New cards
What is an ECG?
* gives a lot of information on how conduction and heart system is working
* changes in wave shapes or timing could indicate abnormalities or disease
* changes in wave shapes or timing could indicate abnormalities or disease
80
New cards
What is autorhymicity?
the ability of pacemaker cells to trigger their own action potentials
81
New cards
What is cardiac muscle excitation?
Na+ and Ca+ flow from conducting cell to contractile cell through gap junctions
82
New cards
What is the process of action potentials in cardiac contractile cells?
1. sodium channels open with more sodium outside
2. sodium flows in which makes cell more positive
3. depolarization occurs and sodium channels close
4. calcium channels plateau and repolarize
5. K+ channel closes
83
New cards
What happens during skeletal muscle contraction?
calcium binds to myosin and actin
84
New cards
What does ECG stand for?
electrocardiogram
85
New cards
What is superventricular tachycardia (SVT) also known as?
paroxysmal atrial tachycardia
86
New cards
What is superventricular tachycardia?
SVT occurs when the electrical system that controls the heart rhythm is not working properly
87
New cards
What is ventricular fibrillation? (V-Fib)
* ventricle depolarization becomes erratic which usually leads to cardiac arrest
* heart doesn’t pump blood to rest of the body
* heart doesn’t pump blood to rest of the body
88
New cards
What is a cardiac arrest?
sudden stop in heart function that is deadly
89
New cards
What is an automated external defibrillator? (AED)
* delivers about 3000 volt charge
* depolarizes the entire heart
* stops arrhythmia
* allows SA node to restore rhythm
* ineffective on hearts that have stopped beating completely
* depolarizes the entire heart
* stops arrhythmia
* allows SA node to restore rhythm
* ineffective on hearts that have stopped beating completely
90
New cards
What is the cardiac output equation?
CO = HR (heart rate) x SV (stroke volume)
91
New cards
What is cardiac output? (CO)
* amount of blood pumped by each ventricle in one minute
* unit of volume (L or mL/min)
* unit of volume (L or mL/min)
92
New cards
What is stroke volume? (SV)
volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle in one beat
93
New cards
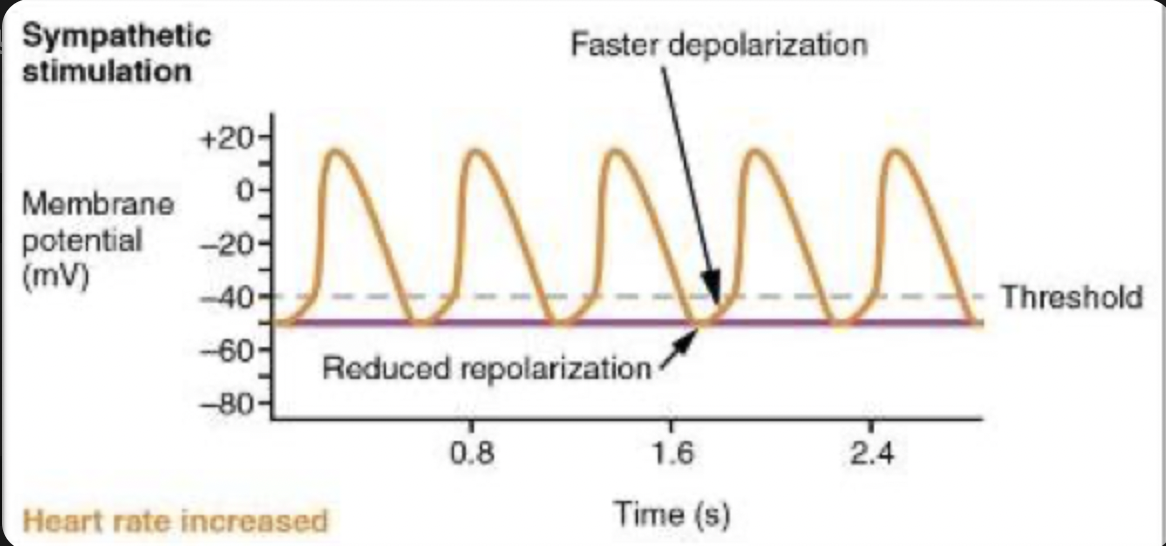
What is the sympathetic effect on heart rate?
increases the sympathetic cardiac nerve heart rate
94
New cards
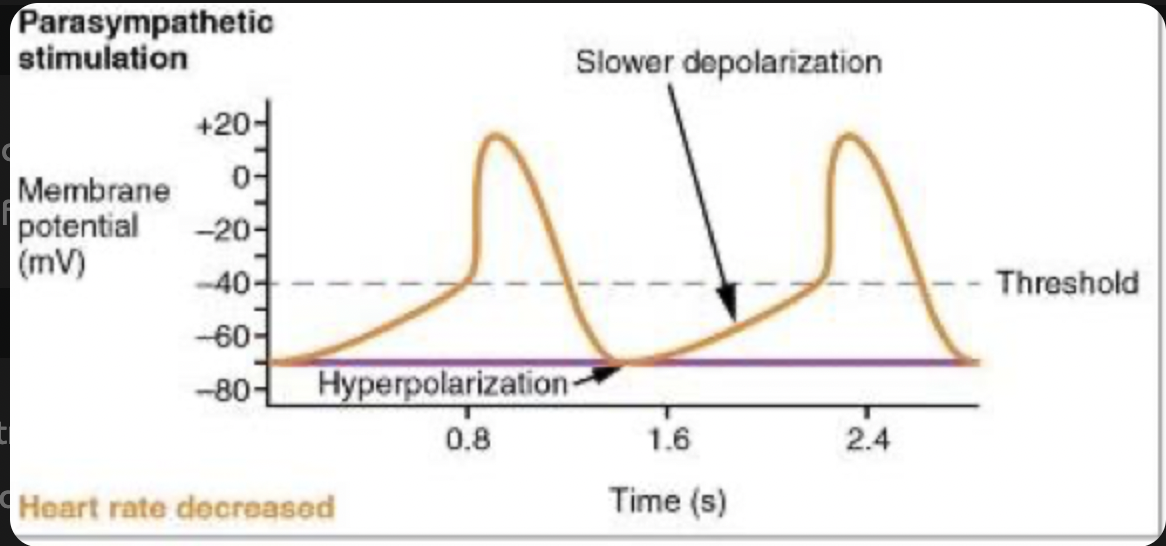
What is the parasympathetic effect on heart rate?
decreases the vagus nerve heart rate
95
New cards
What is the stroke volume equation?
SV = EDV (end-diastolic volume) - ESV (end systolic volume)
96
New cards
What is end-diastolic volume (EDV)?
* amount of blood in ventricles at the end of atrial systole
* “preload”
* volume when fully relaxed
* “preload”
* volume when fully relaxed
97
New cards
What is the ejection fraction equation?
SV (stroke volume) / EDV (end-diastolic volume) x 100
98
New cards
What is cardiac reserve?
difference between maximum and resting CO
measures the residual capacity of the heart to pump blood
measures the residual capacity of the heart to pump blood
99
New cards
What is a venous return?
amount of blood returning from the __**vena cava**__ to the __**right atrium**__
100
New cards
What is a preload?
amount of blood or stretch in the ventricles just before systole