Biology Mitosis and Meiosis 🤑😋
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Metastasis
the spread of cancer cells from the place where they first formed to another part of the body
Oncogenesis
the formation of a cancer
Viruses
can cause mutations of proto-oncogenes & tumor suppressor genes leading to cancer
Cell Theory
all living things are made of cells
cells are the basic unit of life
all cells come from other cells
Stages of Mitosis
prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase
Interphase
Cell grows and carries out normal cell processes
DNA replicates
Chromosome Replication
occurs in S phase and the amount of chromosomes is duplicated
Prophase
the first phase of mitosis and longest: chromatin condenses, nuclear membrane breaks down, nucleolus disintegrates, spindle fibers begin to form
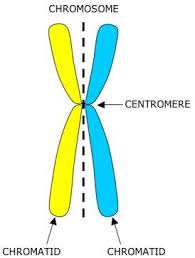
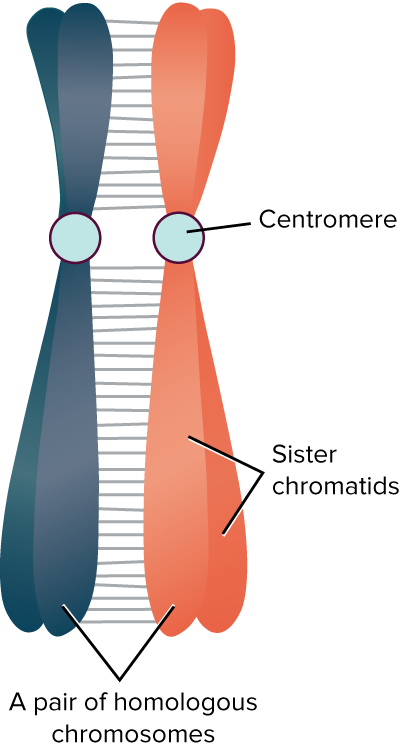
Centromere
structure at center of chromosome where the sister chromatids are attached
Why chromatin condenses
chromatin condenses to make them easier to separate into the two daughter cells
Metaphase
Chromosomes align at the equator
Chromosomes attach to spindle apparatus at the centromere
Anaphase
Microtubules shorten to move chromosomes to the opposite poles
Telophase
Chromosomes reach the poles
Nuclear envelope reforms and nucleolus reappears
chromosomes decondense
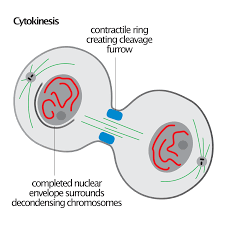
Cytokinesis
the cytoplasmic division of a cell at the end of mitosis or meiosis, bringing about the separation into two daughter cells.
Cytokinesis in Plant Cells (has cell wall)
the cell plate forms dividing daughter cells
Cytokinesis in animal cells (no cell wall)
cleave furrow forms at equator of cell and pinches inward to divide the cell in two
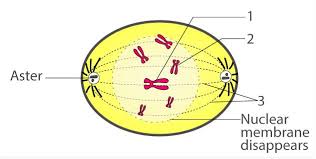
Aster
star-shaped structure made up of microtubules that forms around each centriole pair at the poles of a dividing cell
Mitosis in multi-cellular organisms
cells divide for growth, development, and tissue repair (not to create a new individual)
Mitosis in uni-cellular organisms (Mitotic cell division)
the method of asexual reproduction (ex., binary fission, budding)
Apoptosis
programmed cell death (eliminating unwanted or damaged cells which prevents uncontrolled cell growth and is essential for proper development, tissue homeostasis, and preventing diseases like cancer)
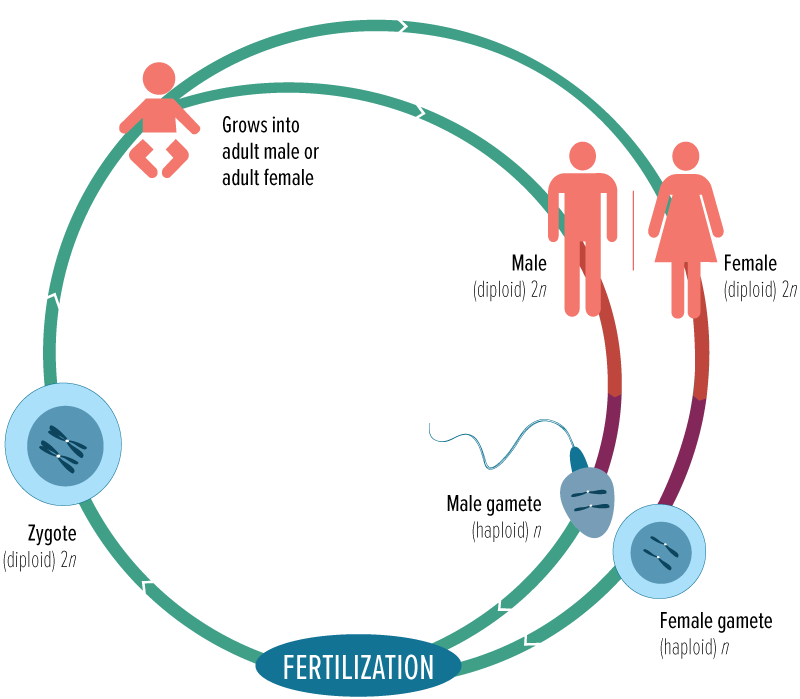
Meiosis
cell division happens to create egg and sperm cells which unite to form a new individual (sexual reproduction)
Prophase vs Prophase I
homologous chromosomes are present in Prophase I where they form pairs during synapsis
Metaphase vs Metaphase I
homologous chromosomes line up instead of individual chromosomes
Anaphase vs Anaphase I
in Anaphase I, homologous chromosomes separate (2n →n) rather than sister chromatids splitting
Meiosis II
Occurs after Meiosis I and is very similar to mitosis except for that the number of chromosomes has been halved — produces 4 total haploid cells
Chromatin
long fibers made of DNA and protein molecules
Chromosome
condensed chromatin
Sister chromatids
two identical copies of a chromosome formed after DNA replication, joined at the centromere, and separated during cell division

Homologous chromosome
one of a matching pair of chromosomes, one inherited from each parent
Body cell
a non-sex cell (somatic cell)
Gamete
a sex cell (egg/sperm) (haploid)
Zygote
a fertilized egg
Diploid cell (2N)
a cell containing two homologous sets of chromosomes, one from each parent (46)
Haploid cell (N)
a sex cell containing a single set of chromosomes (23)
steps of interphase
G1 (first gap), S (Synthesis), G2 (second gap)
How meiosis allows for genetic variation
Different possible alignments of chromosomes, (crossing over) the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes, random fertilization of egg by sperm
Outcome of meiosis
a diploid (2N) cell becomes 4 genetically different, haploid (N) cells
Outcome of mitosis
produces 2 genetically identical diploid (2N) cells)
Synapsis
paring of homologous chromosomes
Tetrad
4 sister chromatids of paired homologous chromosomes
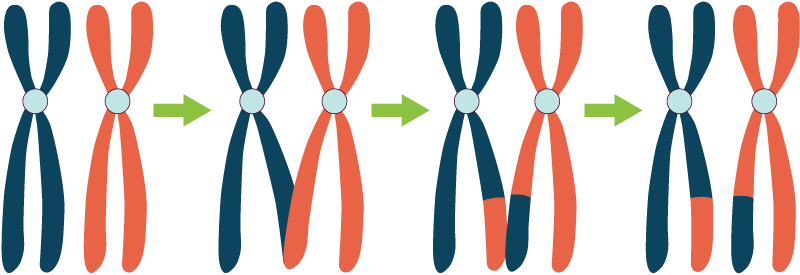
Result of crossing over
genetic variety in gametes
Amount of Nuclear Divisions in Mitosis
1 Nuclear Division
Amount of Nuclear Divisions in Meiosis
2 Nuclear Divisions
Difference between Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis:
1 diploid → 2 daughter diploids
1 nuclear divisions
genetically identical
reproduce (uni-cellular)
growth, maintainance, repair (multi-cellular)
Meiosis
1 diploid → 4 haploids sex cells
2 nuclear divisions
genetically different
makes sex cells (sperm/egg/gamete)
How to remember steps of mitosis
PMAT (Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase)
Shortest Stage of mitosis
anaphase
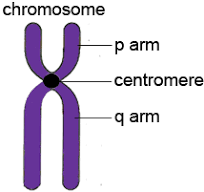
P vs Q arm
P arm is shorter and Q and is longer
they are separated by the centromere
Karyotype
the general appearance of the complete set of chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism
Edward’s Syndrome
Trisomy in chromosome 18 (3 copies instead of 2)
Down syndrome
Trisomy in chromosome 21 (3 copies instead of 2)
Sex Chromosome
Chromosome 23:
XX → Female
XY → Male
Non-sex Chromosomes
The other 22 pairs of chromosomes are autosomes
Genetic errors in Chromosome 23
in female: XX → X_ (Turner’s Syndrome)
in male: XY → XXY (Klinefelter’s Syndrome)
Nondisjunction
the failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division.
Importance of genetic variation
crucial for a species' ability to adapt to changing environments (allows for a range of traits within a population)
Telomeres
a region of repetitive DNA sequences at the end of a chromosome which protect the ends of chromosomes and become slightly shorter with each division