LDH kinetics - Ebiolabs Qs
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Suppose you need to obtain a working (final) pyruvate concentration of 160 µM and a total volume of 3000 µL. How many µL of your 2 mM stock solution of pyruvate do you need?
240
To measure the rate of an LDH-catalyzed reaction you need which of the following?
1. Buffer
2. Lactate
3. Pyruvate
4. NAD+
5. NADH
6. LDH
Buffer, Pyruvate, NADH, LDH
1, 3, 5, 6
Looking at the trace from one experimental run, you note that your absorbance change is linear during the first ten seconds. At 0 seconds, A = 0.792. At 10 seconds, A = 0.568. What is the initial absorbance change per minute for this run?
1.344
If in this experiment you obtain an initial change in absorbance of 0.62 per minute, what is the change in the concentration of NADH in µM per minute? The absorbance coefficient of NADH is 6220 L·mol-1·cm-1 at 340 nm.
99.68
Suppose your cuvette contained 3040 µL and the change in [NADH] was calculated to be 80 µM per minute. How many µmoles of lactate have been formed in that minute?
0.243
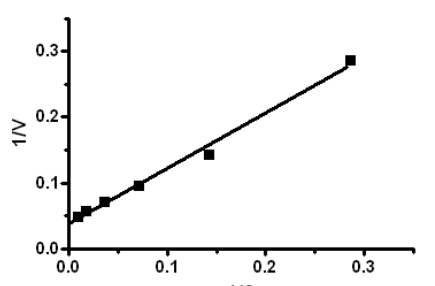
A student collected steady state data and plotted the velocity and substrate concentration as the Lineweaver-Burk plot shown below. Estimate the Vmax.
25
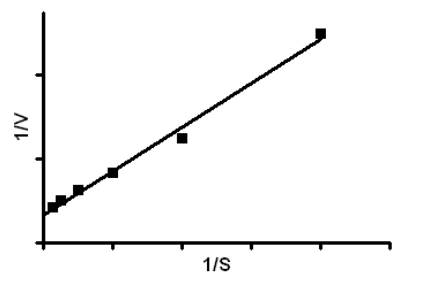
From the Lineweaver-Burk plot shown below a student calculated that the data fitted to a straight line with the equation Y = 0.618X + 0.098. What is the KM?
6.306