C2-C6 IGCSE Combined Science
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
Electrolysis
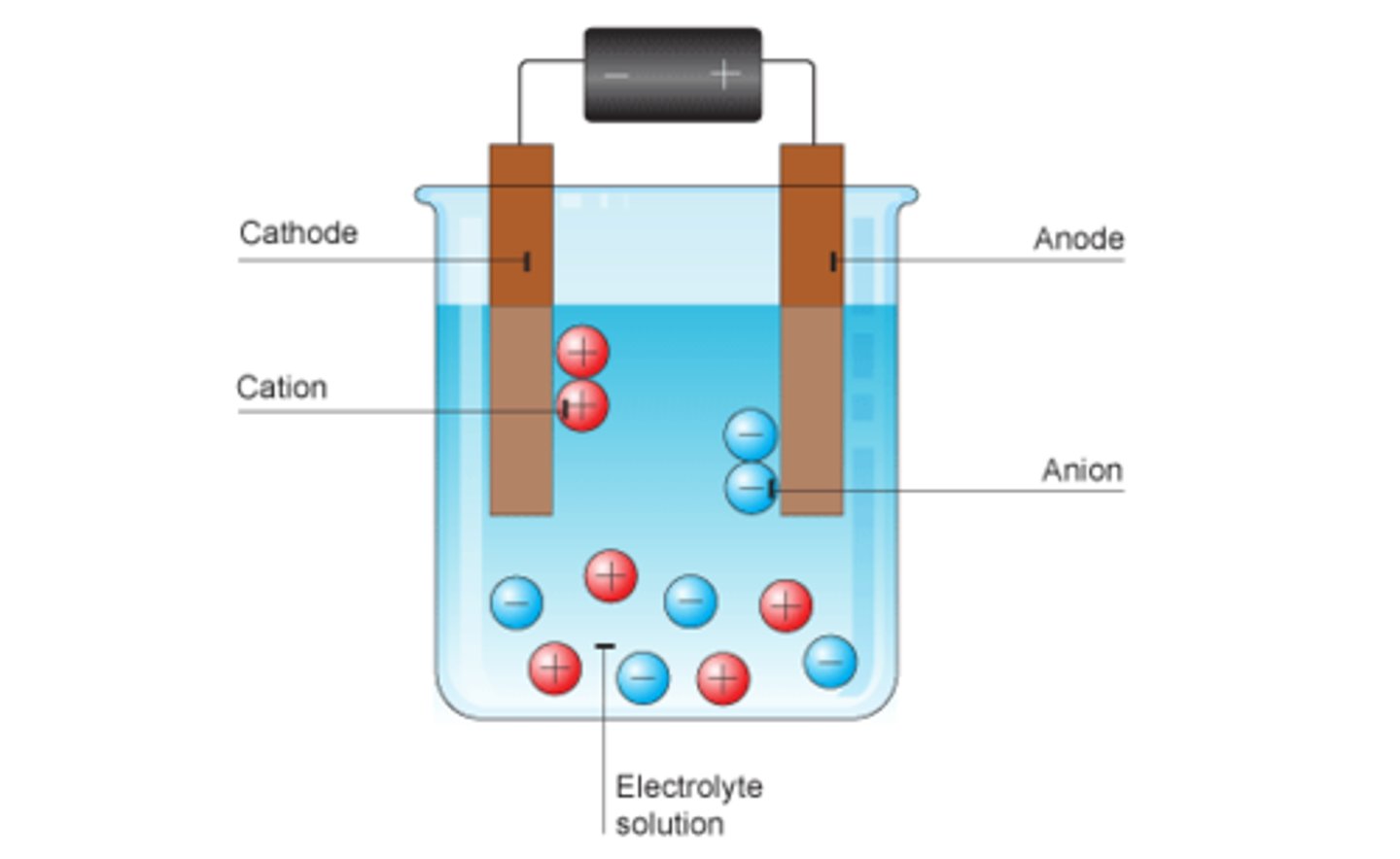
A process by which an electric current breaks chemical bonds in ionic compounds in molten state or aqueous solutions.
Electrolyte
A substance that dissolves in water to give a solution that conducts electric current
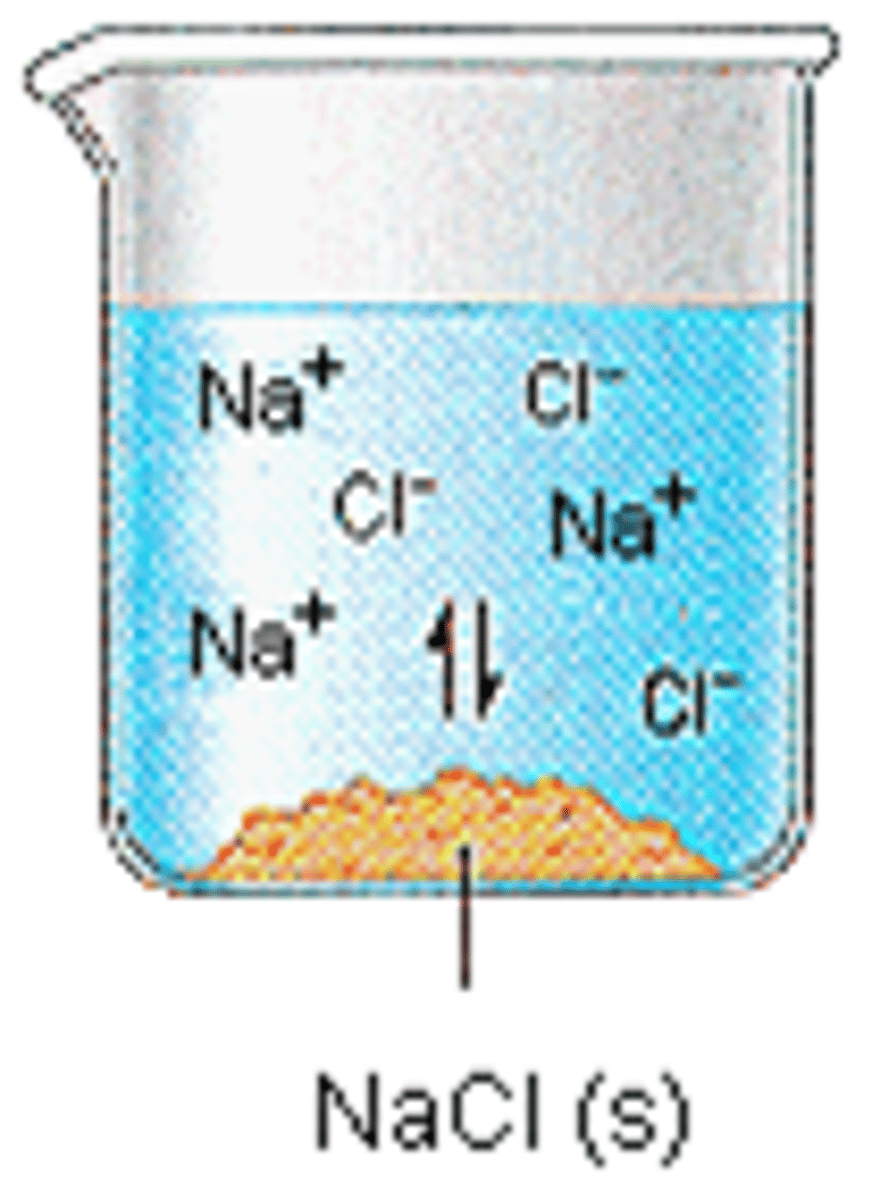
Non-electrolyte
A substance that dissolves in water to give a solution that does not conduct an electric current
Electrical cell
Produces an electric current using the chemical or physical properties of different materials.
Decomposition
A chemical reaction that breaks down compounds into simpler products.

Anode
Positive electrode

Anions
Negatively charged ions
Cathode
Negative electrode
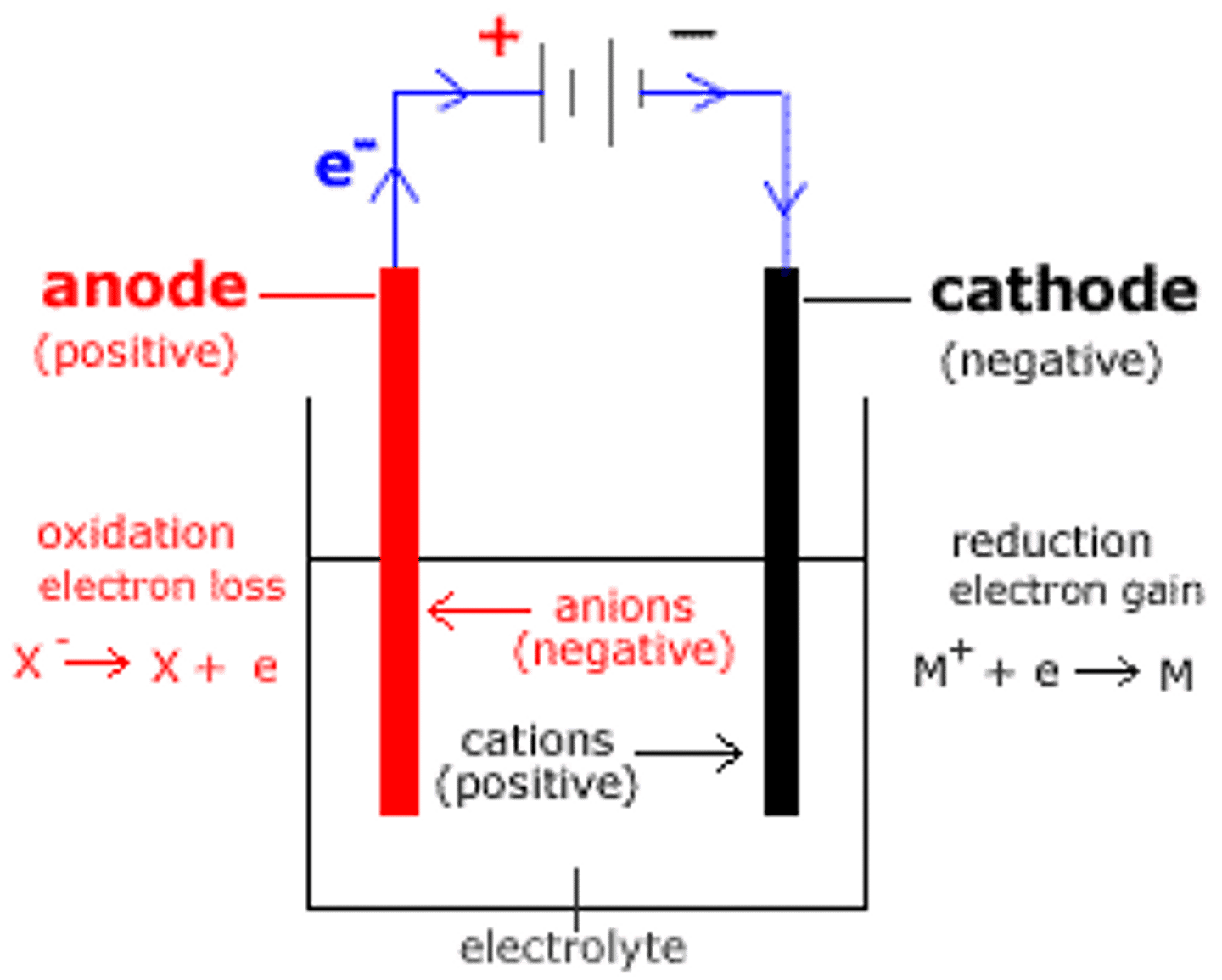
Cations
Positively charged ions

Inert electrode
An electrode that does not react with the other parts of the cell. Example carbon or graphite electrodes
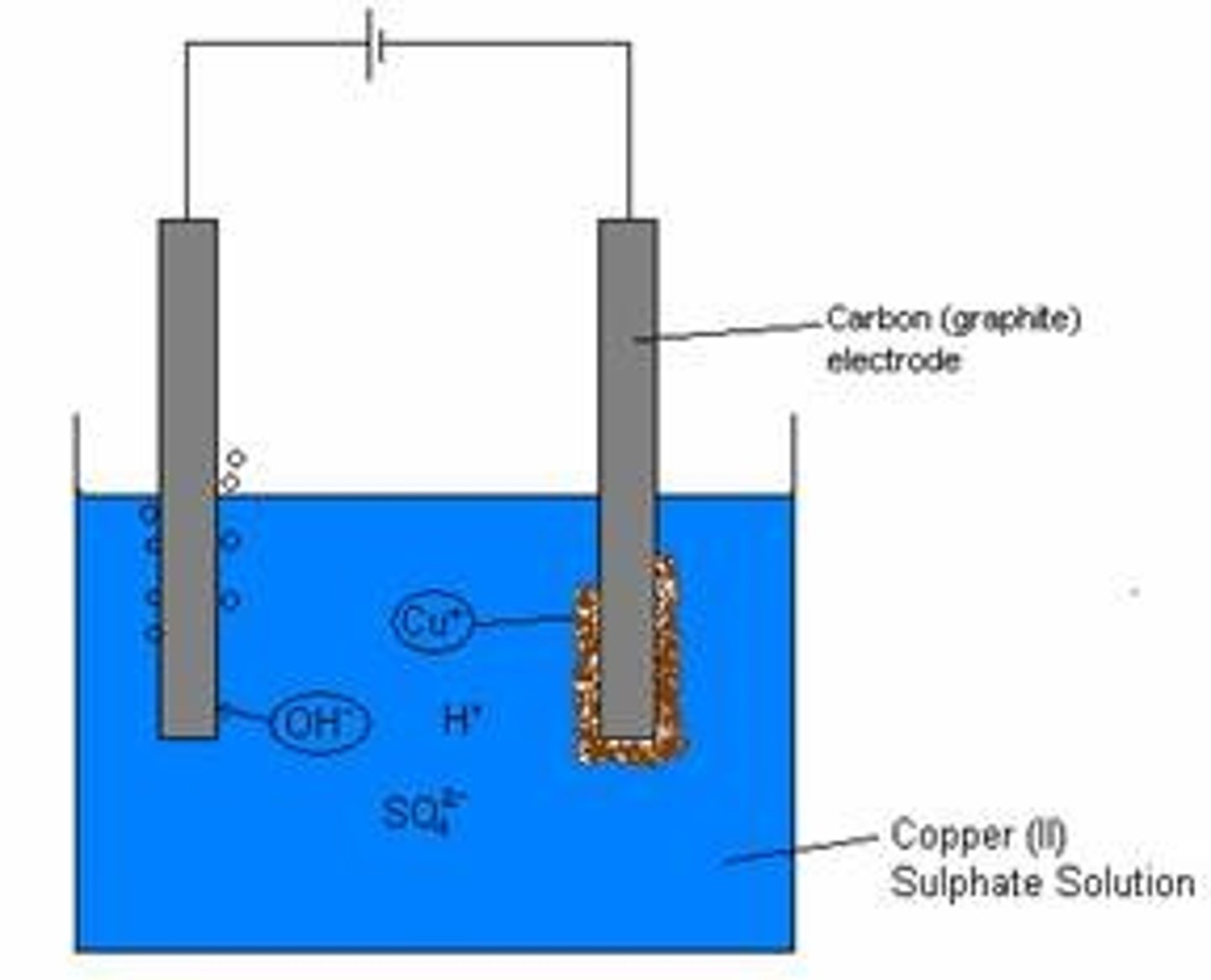
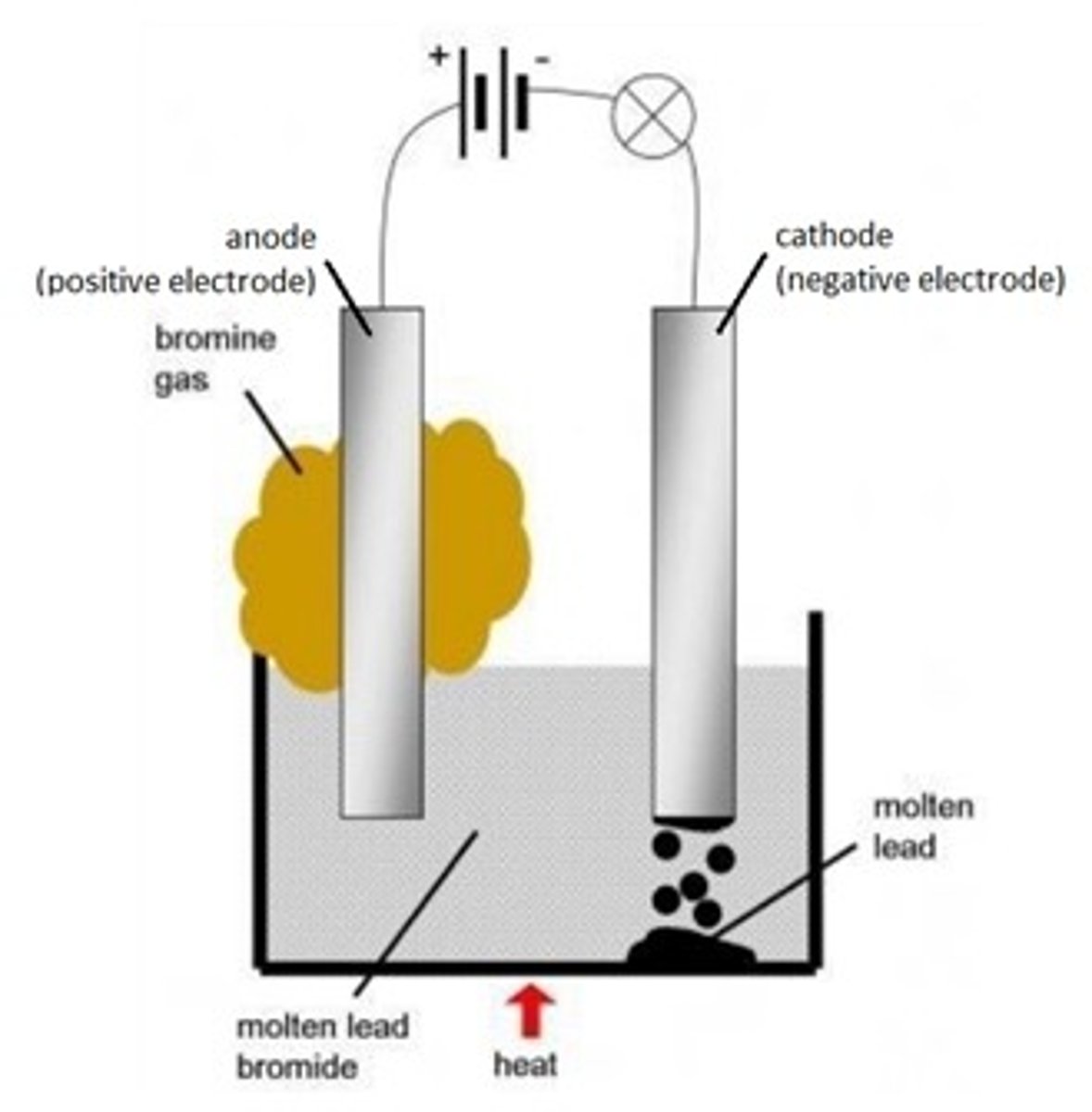
Electrolysis of molten lead bromide
PbBr₂ (l) ⎯→ Pb(s) + Br₂ (l)
Brown fumes of bromine gas is formed at the anode. Silvery lead is deposited at the cathode.
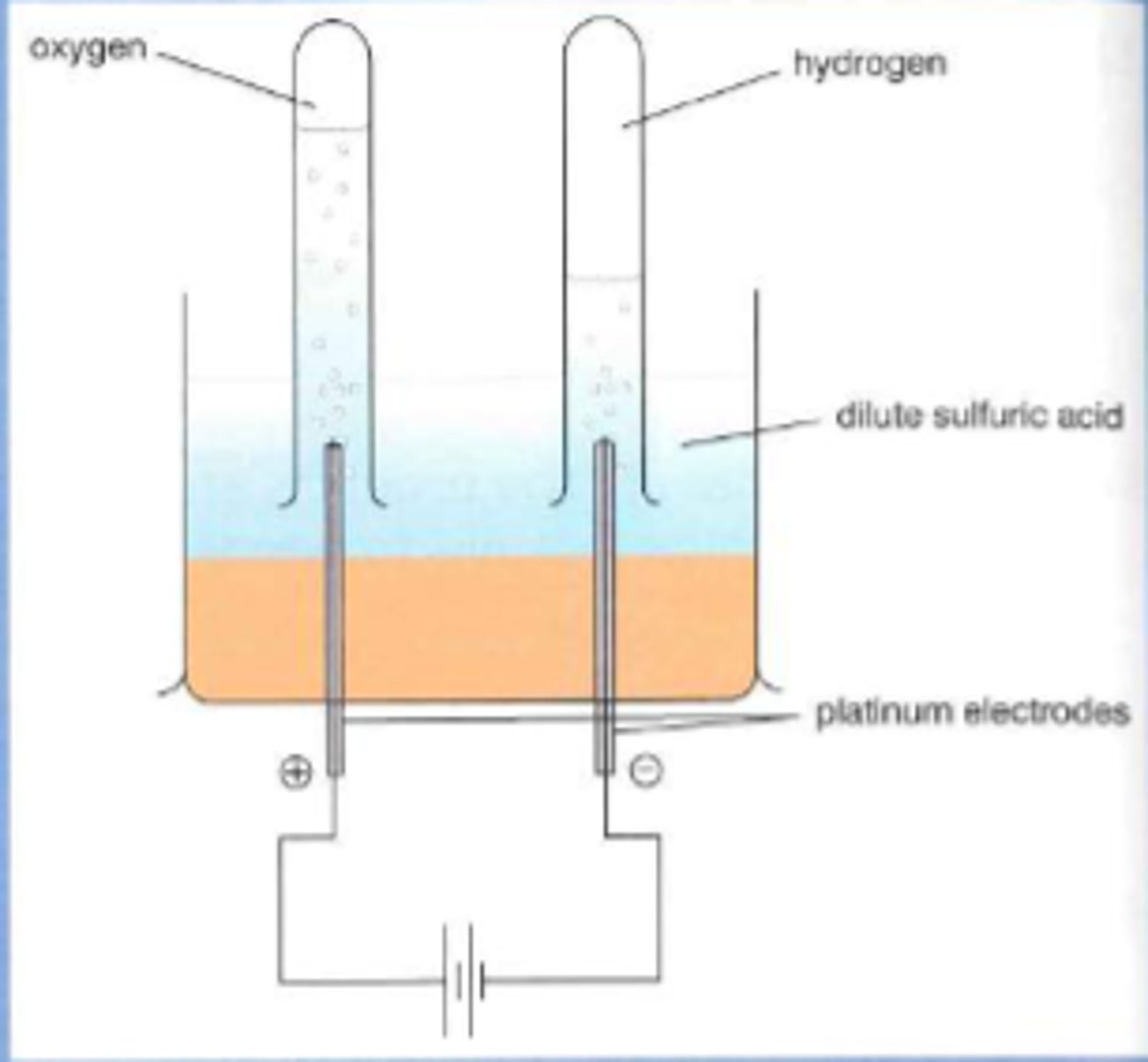
Electrolysis of dilute sulfuric acid
Hydrogen gas is produced at the cathode and oxygen gas is produced at the anode.
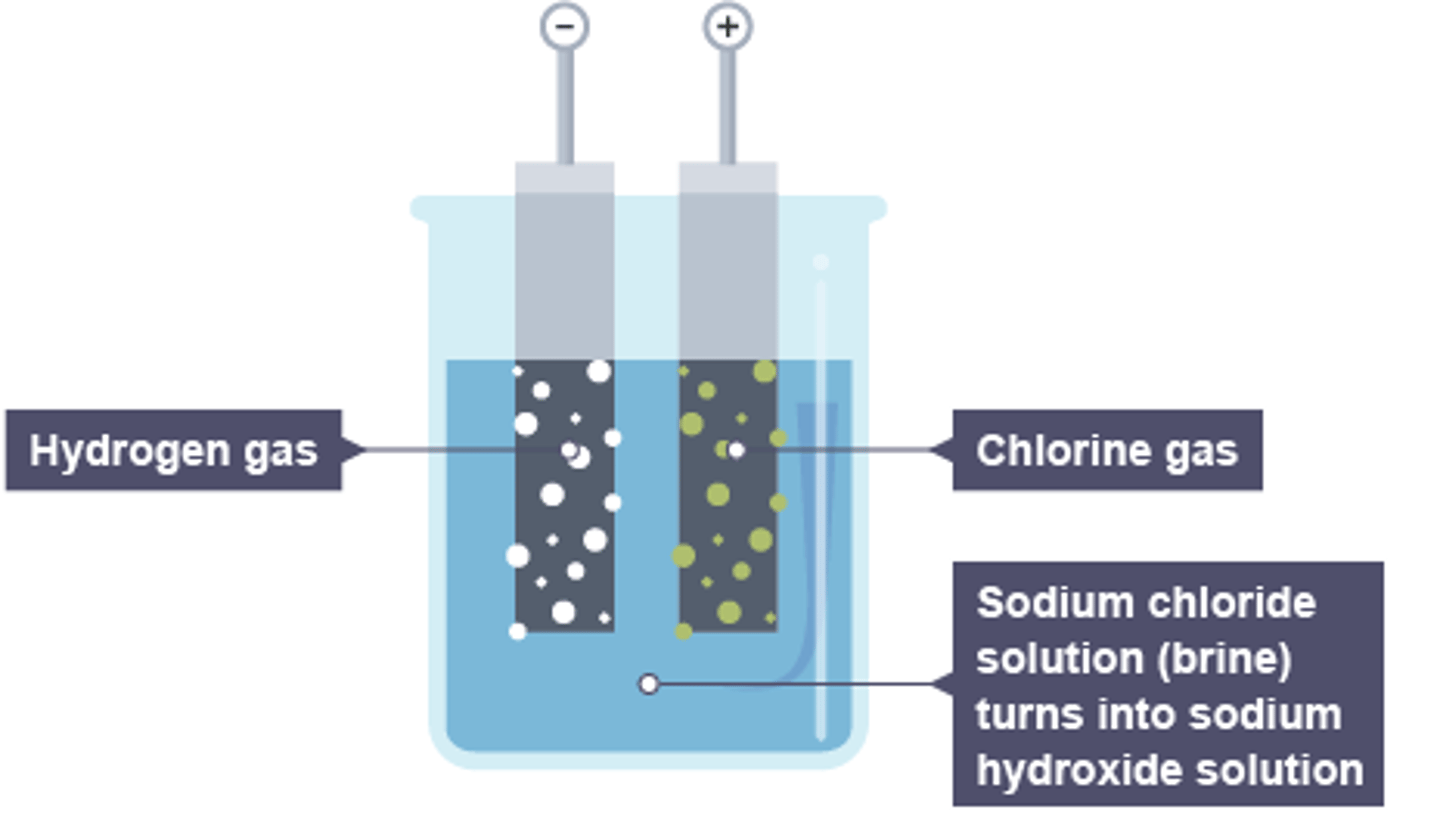
Electrolysis of sodium chloride solution
Hydrogen is produced ta the cathode and chlorine gas is produced at the anode.
Physical change
A change that does not produce a new substance and is usually easy to reverse
Chemical change
A change that produces a new substance with different properties and is usually difficult to reverse
Signs of chemical change
Indicators such as colour change, temperature change, or effervescence (fizzing)
Rate of reaction
The speed at which reactants are converted into products
Effect of concentration on rate
Increasing concentration increases rate because more particles are present leading to more collisions
Effect of pressure on rate
Increasing pressure increases rate because particles are closer together leading to more collisions
Effect of surface area on rate
Increasing surface area increases rate because more particles are exposed for collisions
Effect of temperature on rate
Increasing temperature increases rate because particles have more kinetic energy and collide more frequently with greater energy
Catalyst
A substance that increases the rate of reaction and is unchanged at the end of the reaction
Effect of catalyst on activation energy
A catalyst lowers the activation energy of a reaction
Collision theory
A theory stating that reactions occur when particles collide with sufficient energy and correct orientation
Successful collision
A collision between particles with energy greater than the activation energy resulting in a reaction
Activation energy
The minimum energy that particles must have to react
Redox reaction
A reaction in which oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously
Oxidation (electron definition)
The loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation number
Reduction (electron definition)
The gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation number
Roman numerals in ion names
Indicate the oxidation number of a transition metal ion such as iron(II) or iron(III).
What is an exothermic energy transfer?
Energy transfer to the surroundings
What happens to the temperature in an exothermic reaction?
It increases
What is an endothermic energy transfer?
Energy transfer from the surroundings
What happens to the temperature in an endothermic reaction?
It decreases
how do you calculate enthalpy change
energy of products-energy of reactants
Give five examples of exothermic chemical reactions
Neutralization, respiration Self-heating cans, hand warmers & combustion
Give four examples of endothermic chemical reactions
Thermal decomposition, sports injury pack, electrolysis & photosynthesis
What is a reaction pathway?
Diagram showing how the energy changes in a reaction
what direction do exothermic reaction go in reaction pathways
downwards
what direction do endothermic reaction go in reaction pathways
upwards
What is activation energy?
The minimum energy with which particles must collide in order to react
What is bond energy?
The energy required to break a bond or the energy released when a bond is formed
What are the units for bond energy?
kJ/mol
In terms of energy transfer, bond breaking is
Endothermic
In terms of energy transfer, bond making is
Exothermic
Draw and label a reaction pathways for an exothermic reaction
heat given out to surroundings = enthalpy change
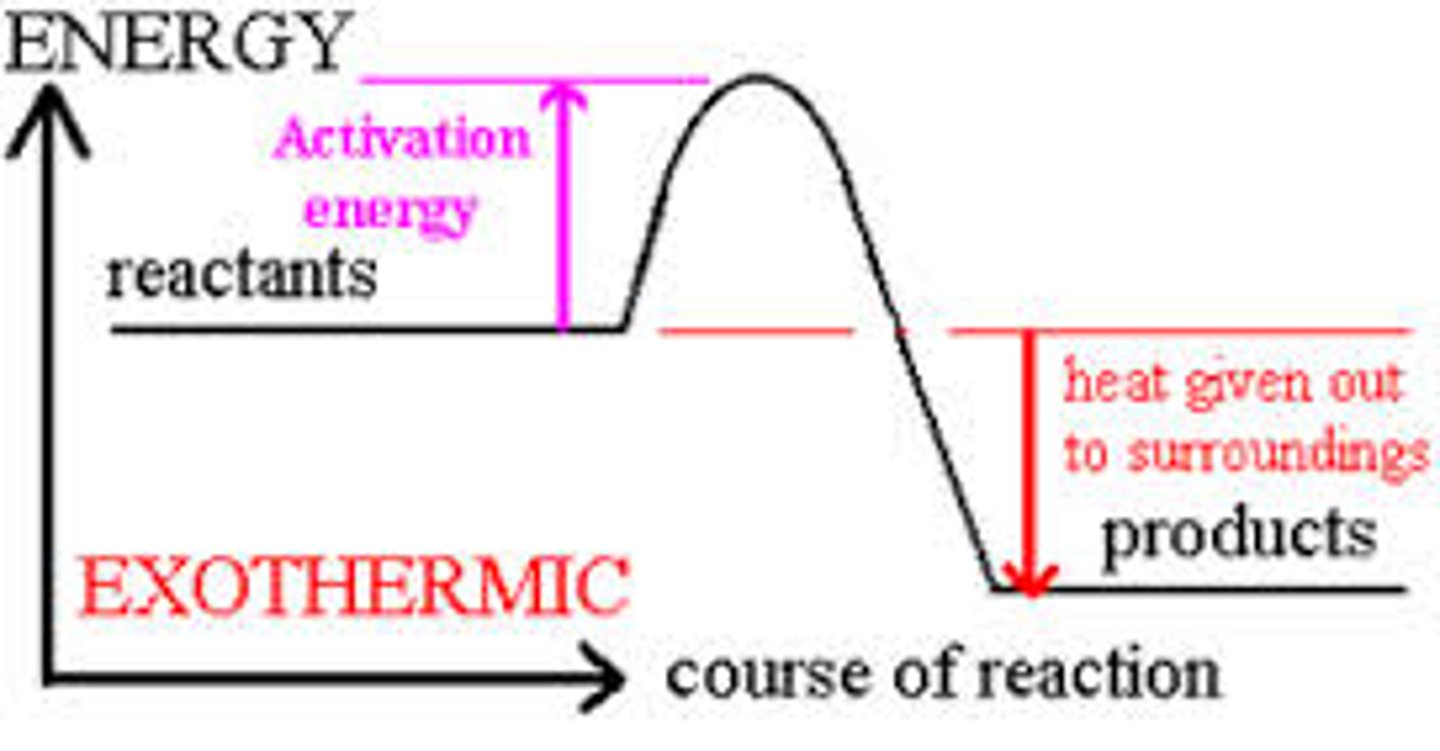
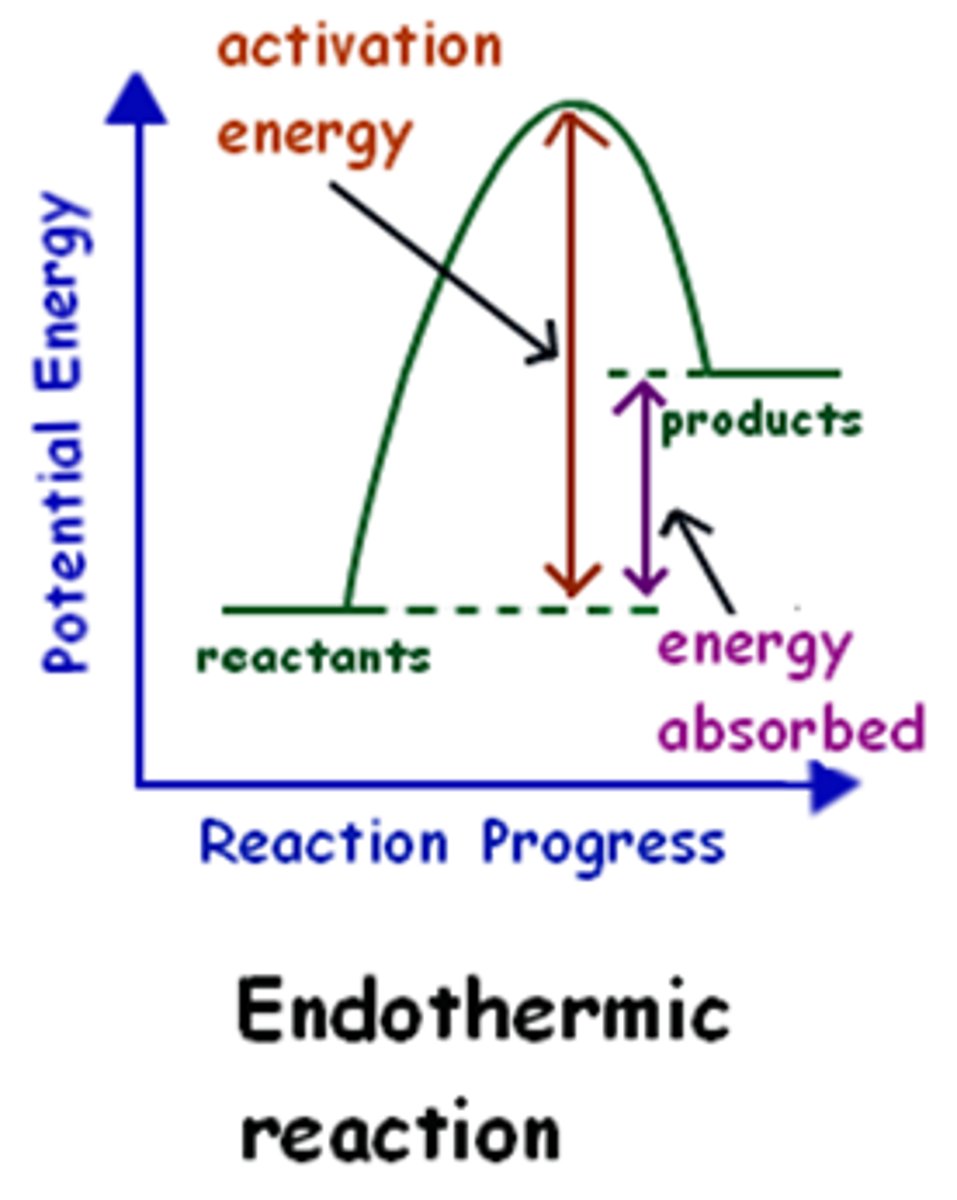
Draw and label a reaction pathways for an endothermic reaction
heat absorbed = enthalpy change
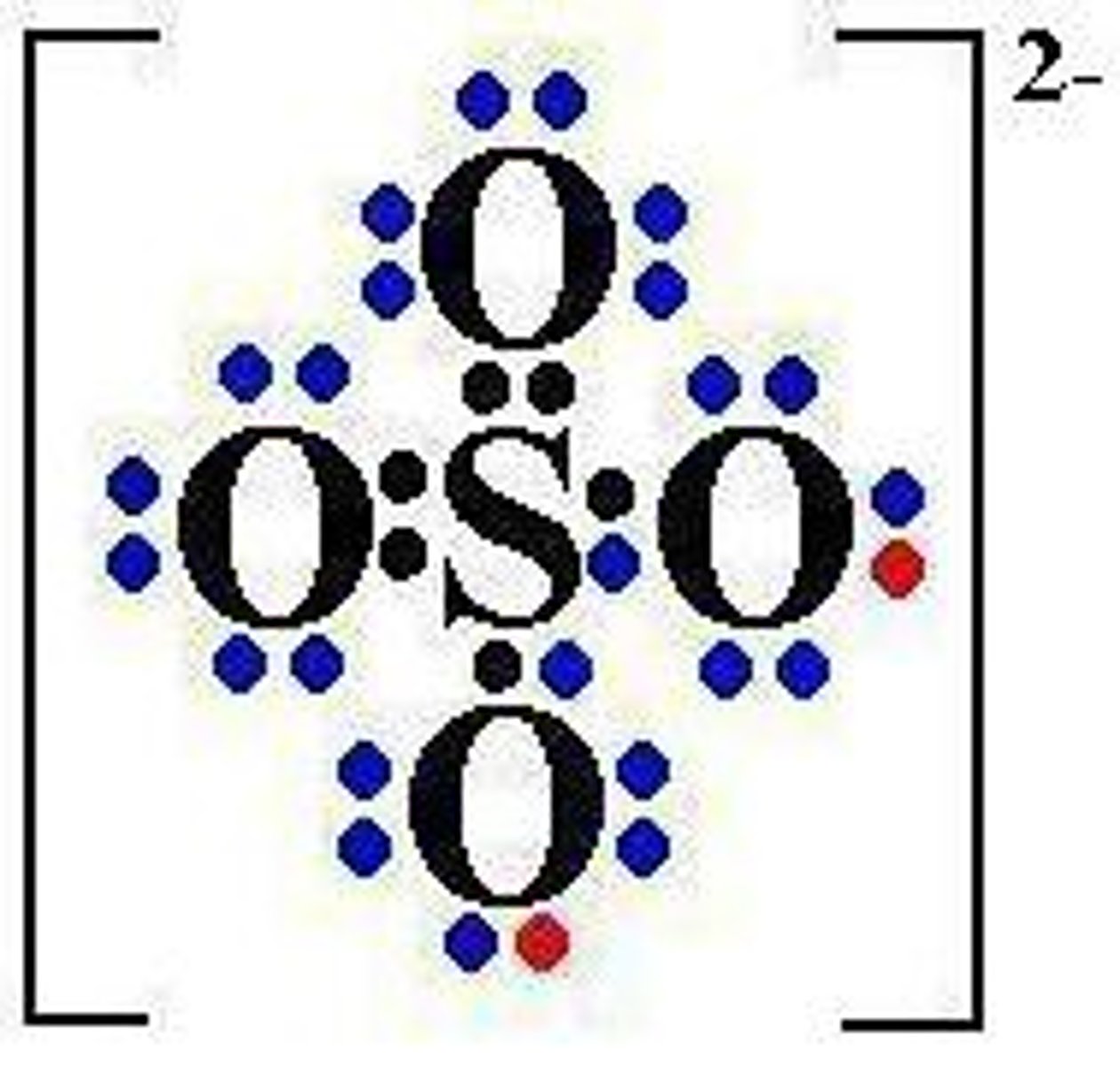
chemical symbol
a letter or group of letters representing an element in a chemical formula

compound ion
an ion made up of several different atoms covalently bonded together and with an overall charge
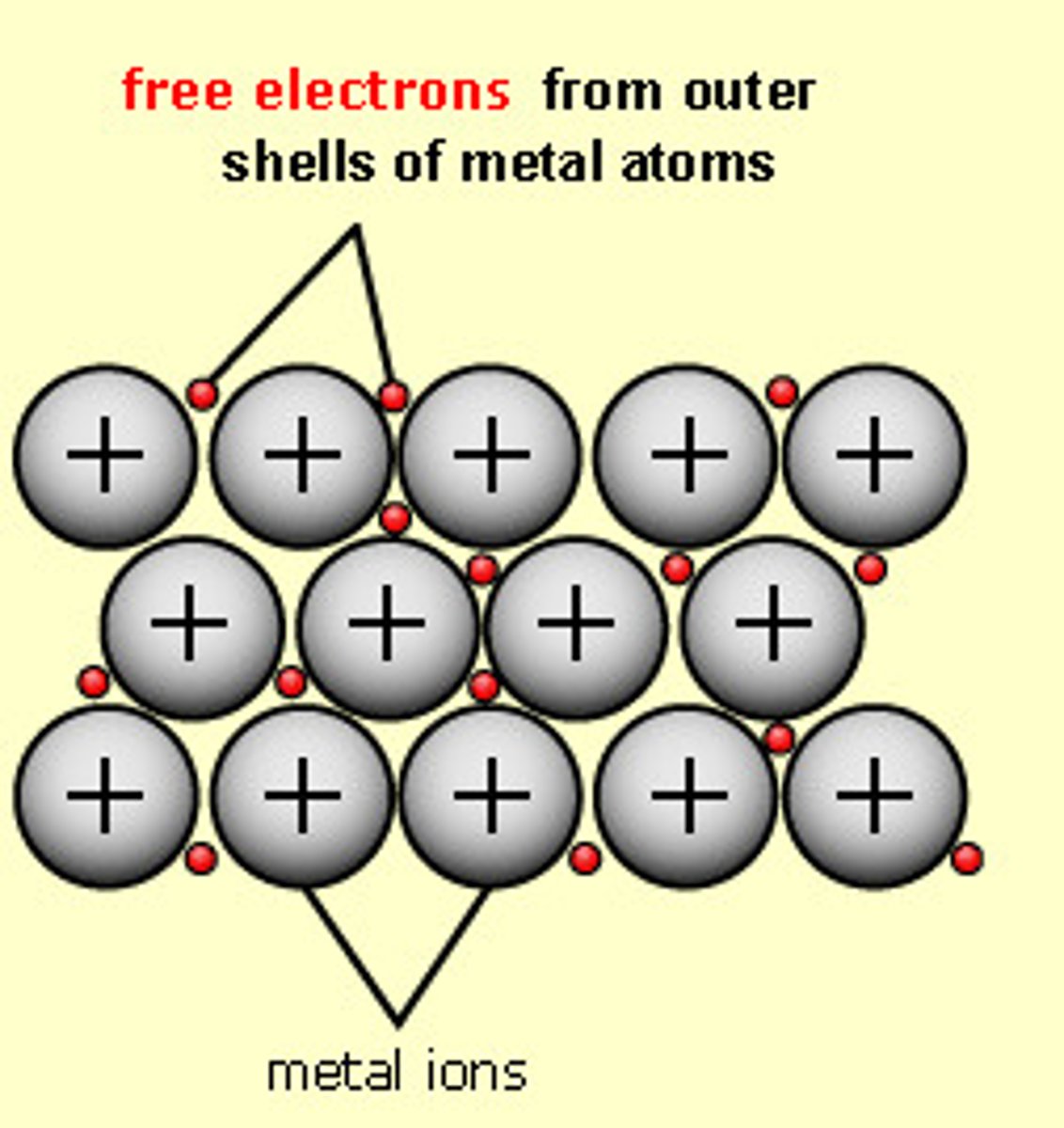
giant metallic lattice
a three-dimensional structure of positive ions and delocalised electrons, bonded together by strong metallic bonds; elements that are metals will be structured this way
giant covalent structure
a large lattice of covalently bonded atoms, can be found in covalent compounds and some non-metallic elements
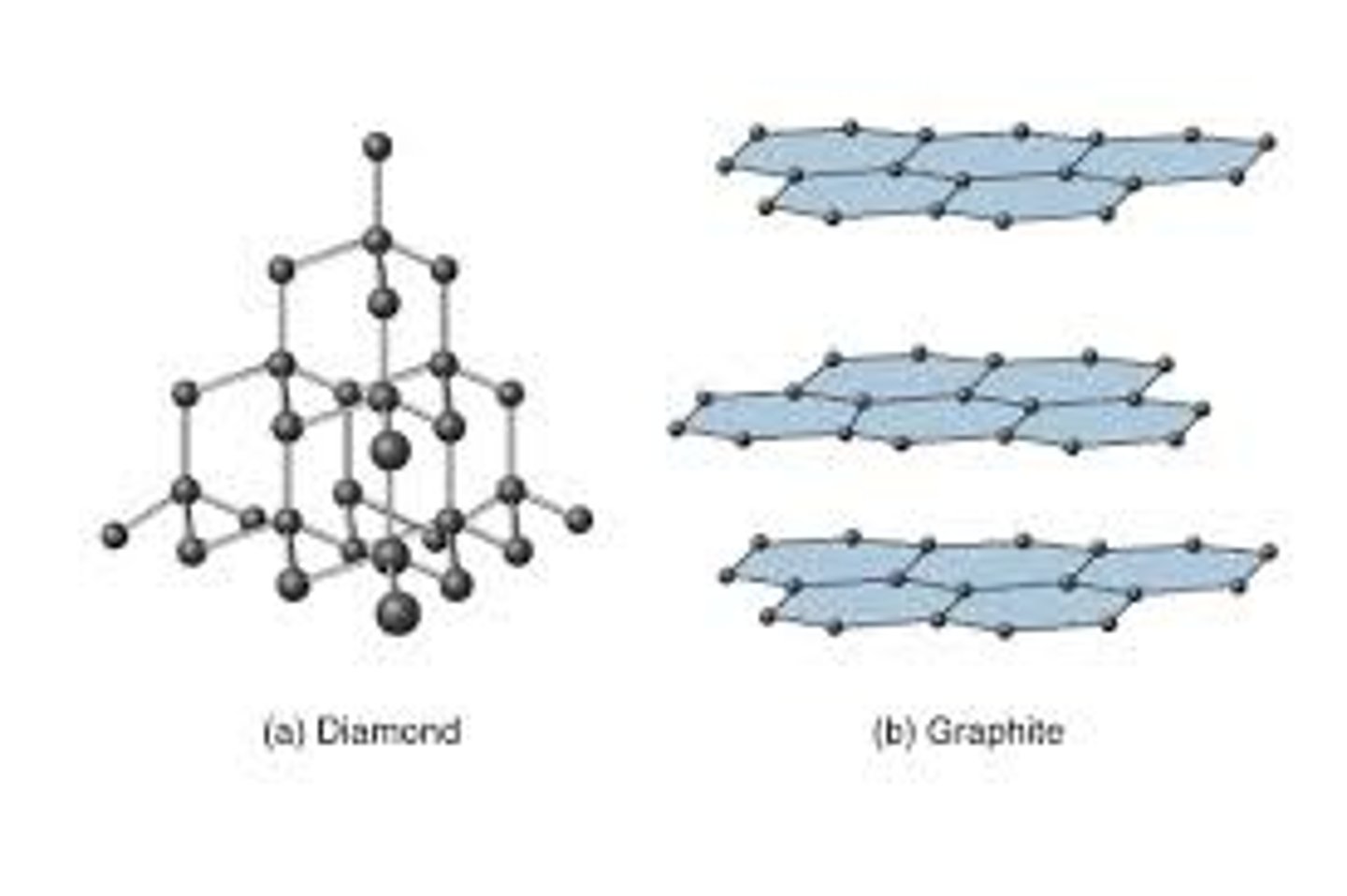
simple molecules (elements)
elements found in nature covalently bonded to at least one other atom of the same type

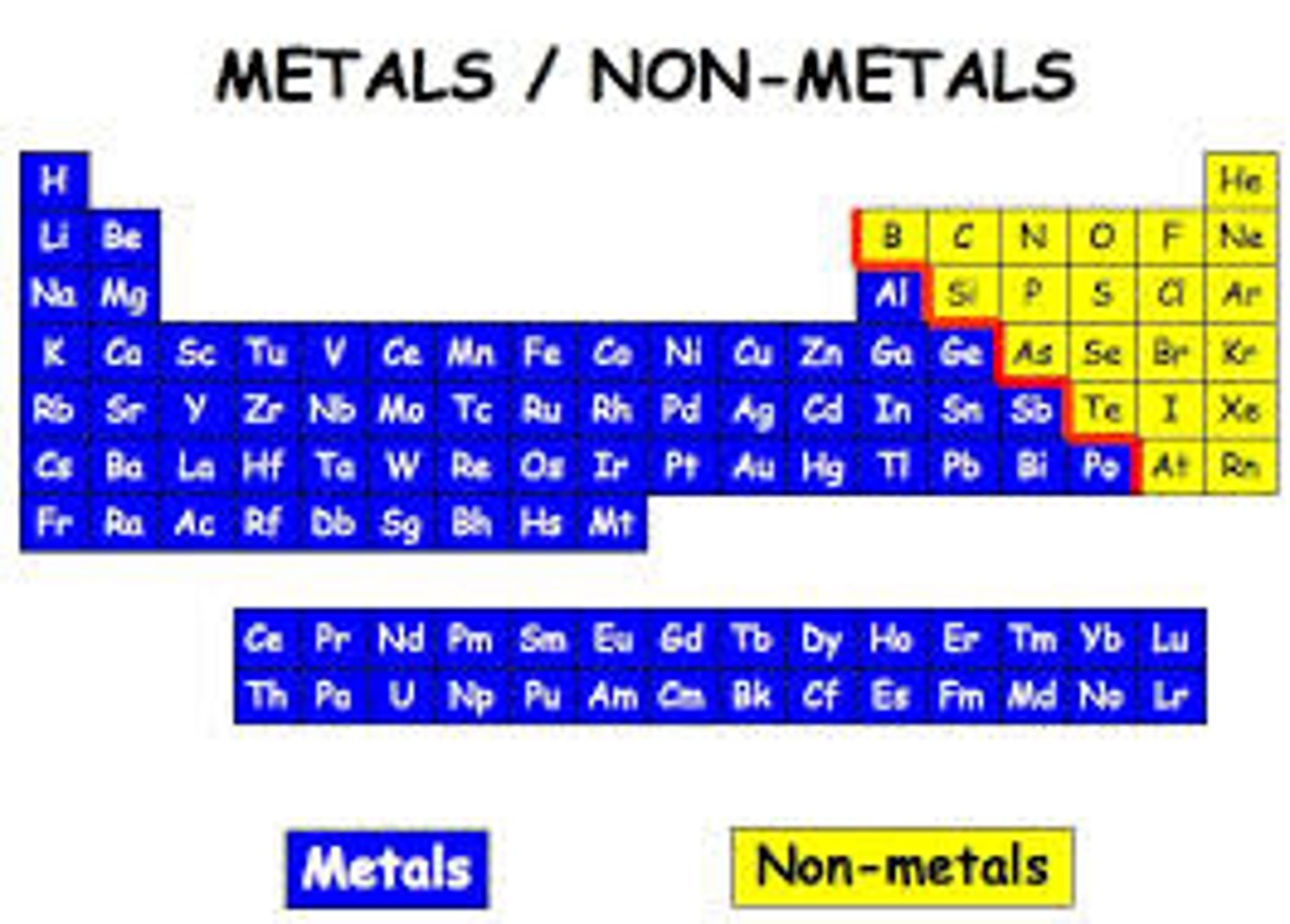
side of the periodic table that has metals
left
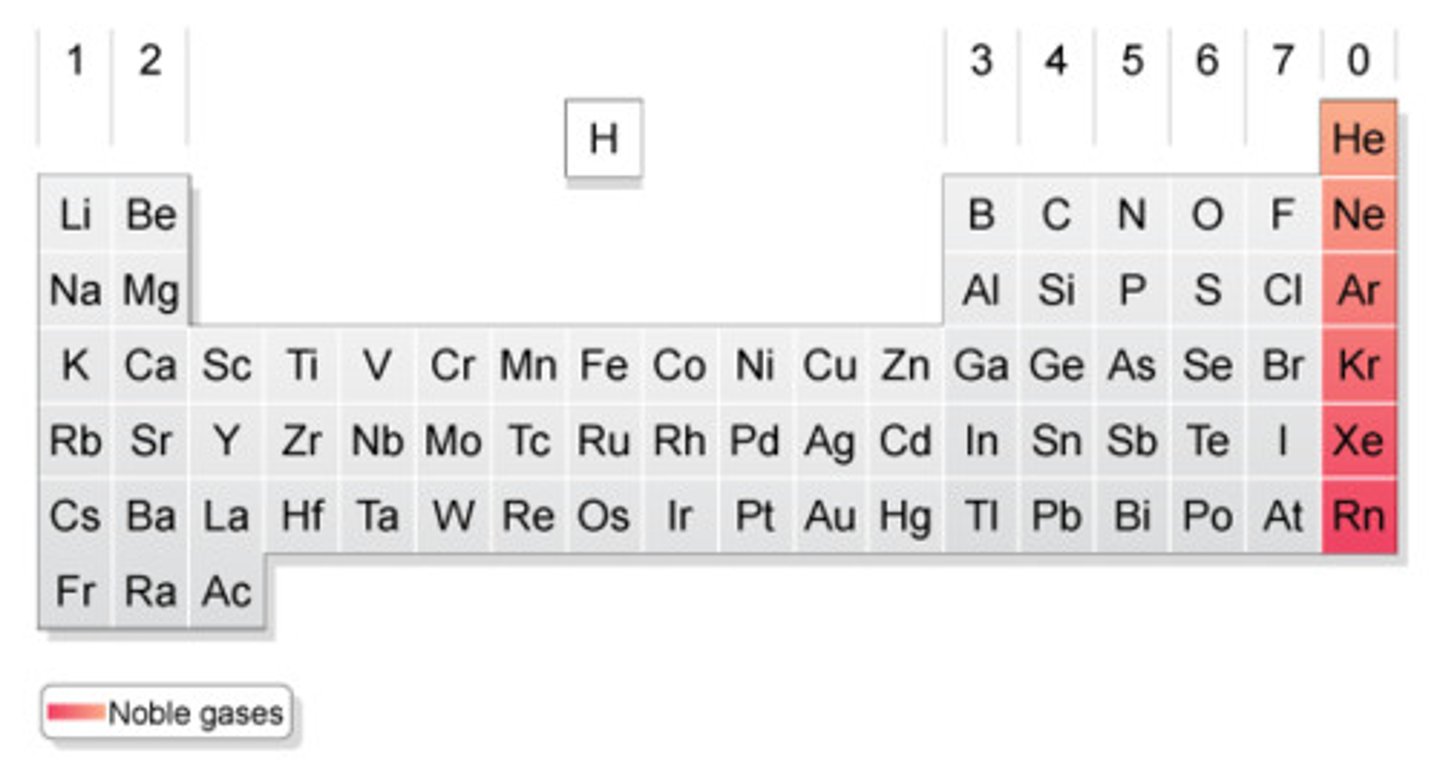
noble gases
found in nature as single atoms and in group 8 of the periodic table
carbonate
CO3 2-
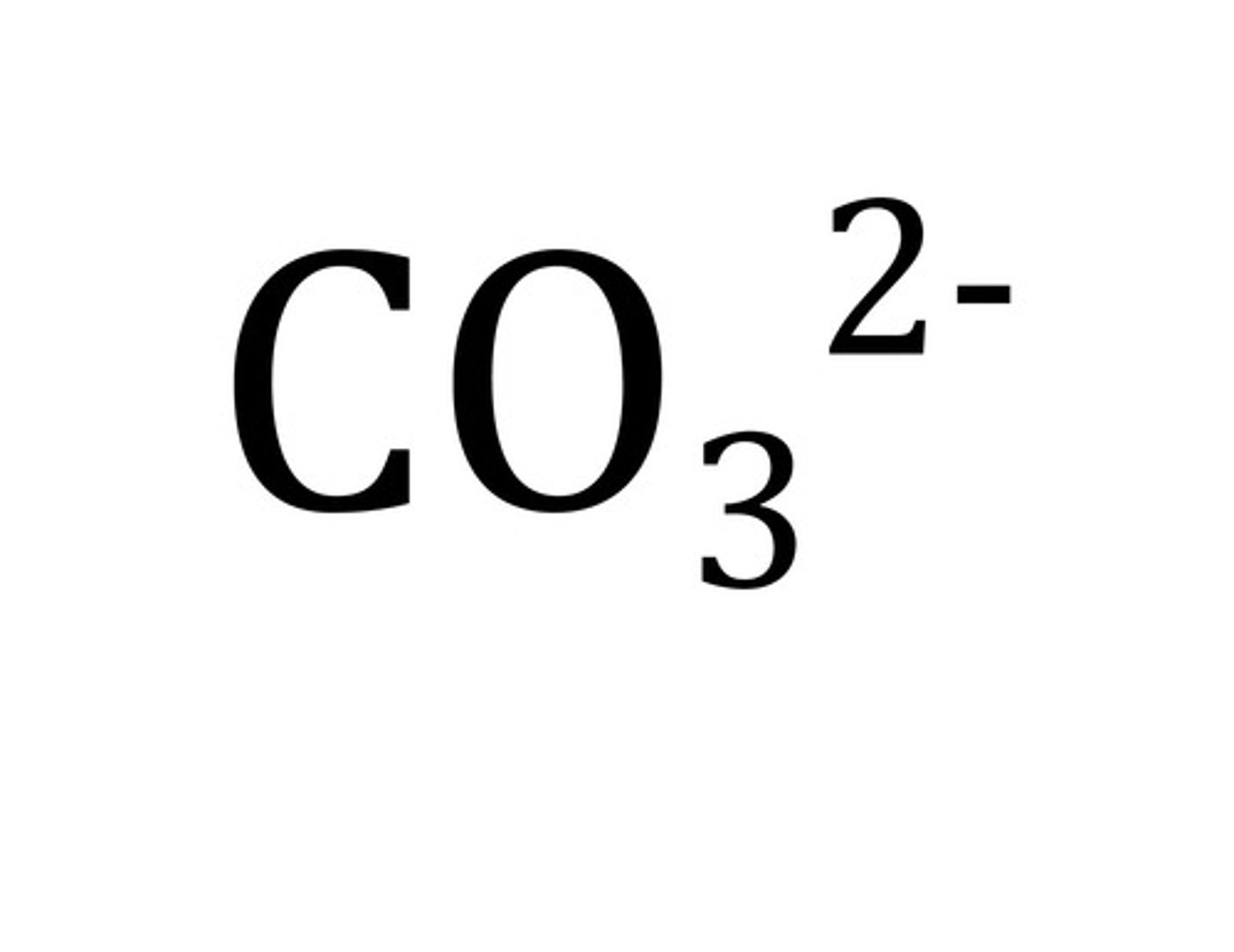
nitrate
NO3-
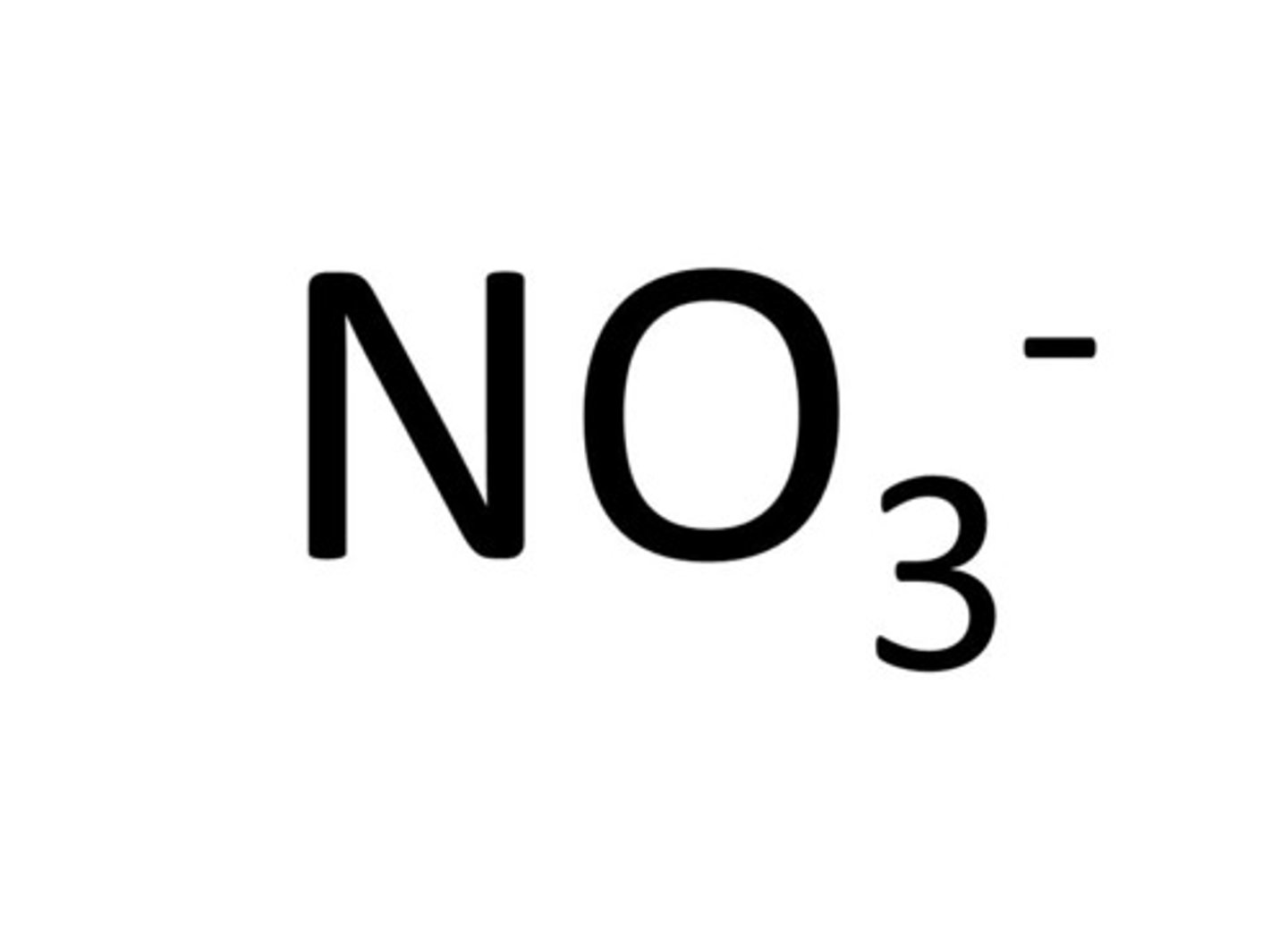
sulfate
SO4 2-
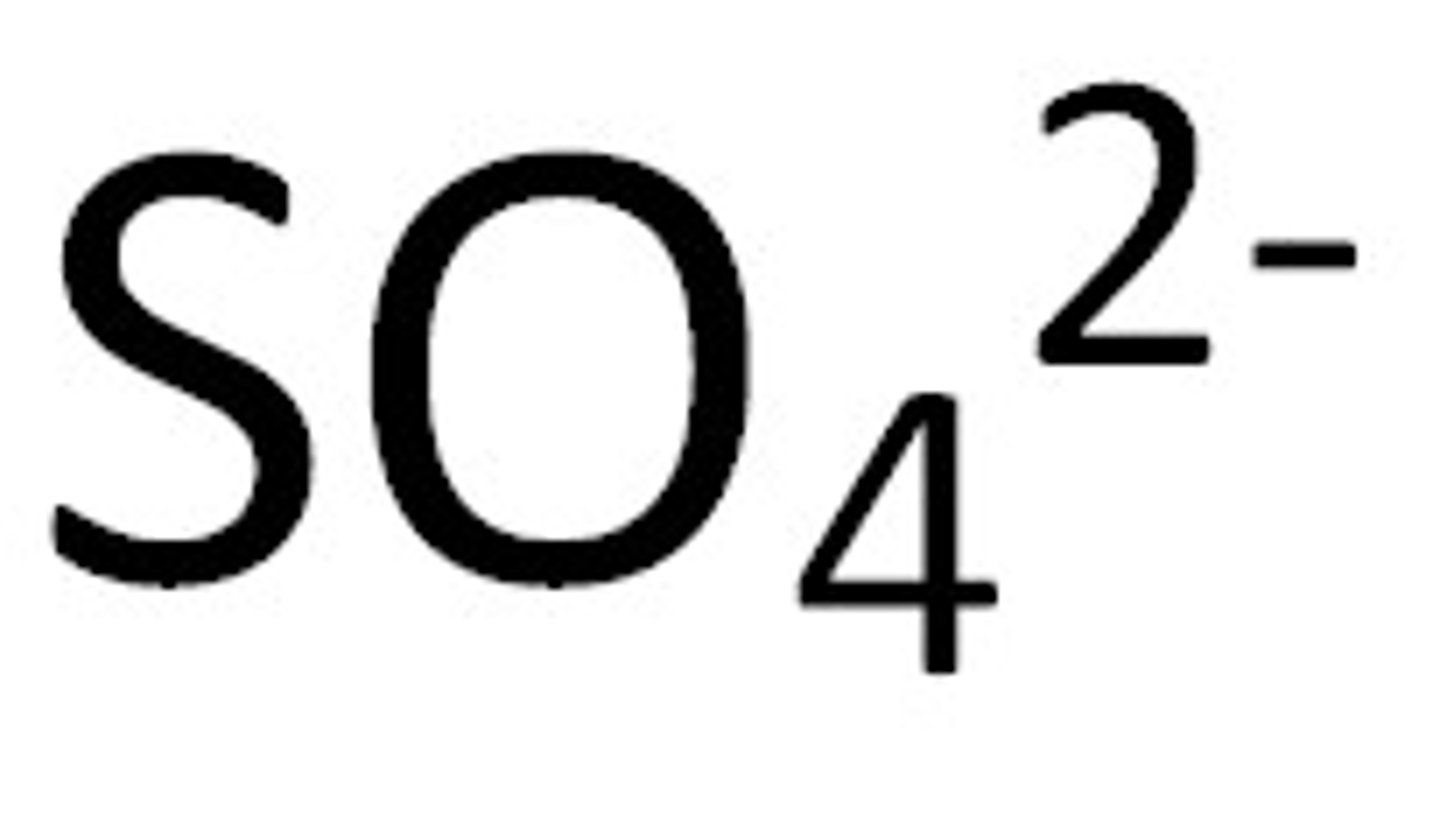
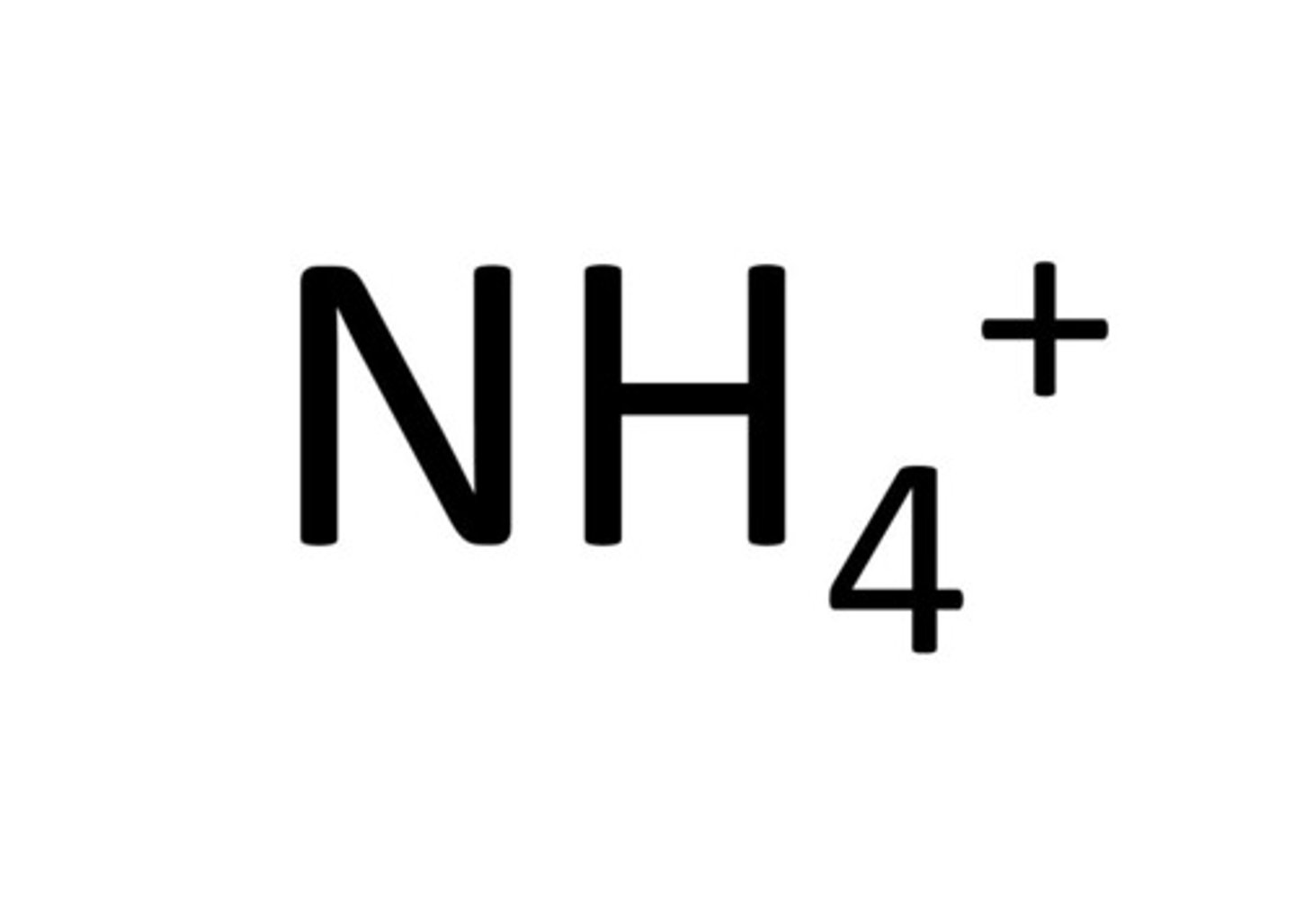
ammonium
NH4+
stoichiometry
the relationship between the relative quantities of substances taking part in a reaction or forming a compound
valency
the number of bonds an atom can form
how to determine valency of elements in groups 1-4
it equals the group number
how to detemine the valency of elements in groups 5-7
it is equal to 8-the group number
valency of group 8 elements (the noble gases)
0; they don't form bonds
cross over method for working out chemical formulae for simple covalent compounds with a central atom
write down the chemical symbols, write the valencies of each element, "cross over", simplify if needed
molecular formula
a chemical formula that shows the actual number of atoms of each element present in a molecule of the compound
cross over method for working out chemical formulae for ionic compounds
write down the chemical symbols, write the charges of each ion, "cross over" charges to get the number of opposite atoms present
charge of metal ions
positive
charge of hydrogen ion
positive
charge of non-metal ions
negative
how to determine charge of ions from elements in groups 1-4
charge equal to group number
how to determine charge of ions from elements in groups 5-7
8-group number for charge
charge of transition metals
given in brackets with a name, such as copper (I) or Cu (II) so that the charge is equal to the number in the bracket
word equation
an equation in which the reactants and products in a chemical reaction are represented by words
reactants
the substances that take part in and undergo change during a chemical reaction
products
the substance(s) produced by a chemical reaction
balanced chemical equation
statement of a chemical reaction with the number of each type of atom equalized for both the products and reactants
state symbols
solid (s), liquid (l), gas (g), and aqueous (aq)
aqueous
dissolved in water
ionic equation
the simplified equation for a reaction involving ionic substances: only those ions which actually take part in the reaction are shown
Element
a substance that cannot be separated or broken down into simpler substances by chemical means
Compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
mixture
material composed of two or more elements or compounds that are physically mixed together but not chemically combined
Electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge
Proton
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
Nucleus
Center of an atom
Neutron
A subatomic particle that has no charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Atomic Mass
Number of protons and neutrons
electron shells
An energy level representing the distance of an electron from the nucleus of an atom.
Electron Configuration
the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom
group number
the number of the vertical column that an element is in on the Periodic Table
period number
A horizontal row of elements in the periodic table
Noble Gases
the elements in Group 8 of the periodic table, very unreactive
ionic bonding
Chemical bonding that results from the electrical attraction between cations and anions
ions
charged particles
Diatomic Molecules
molecules made up of two atoms of the same element
Covalent Bonding
results from the sharing of electron pairs between two atoms
Dot and cross diagram
A diagram to show the electron sharing in a molecule
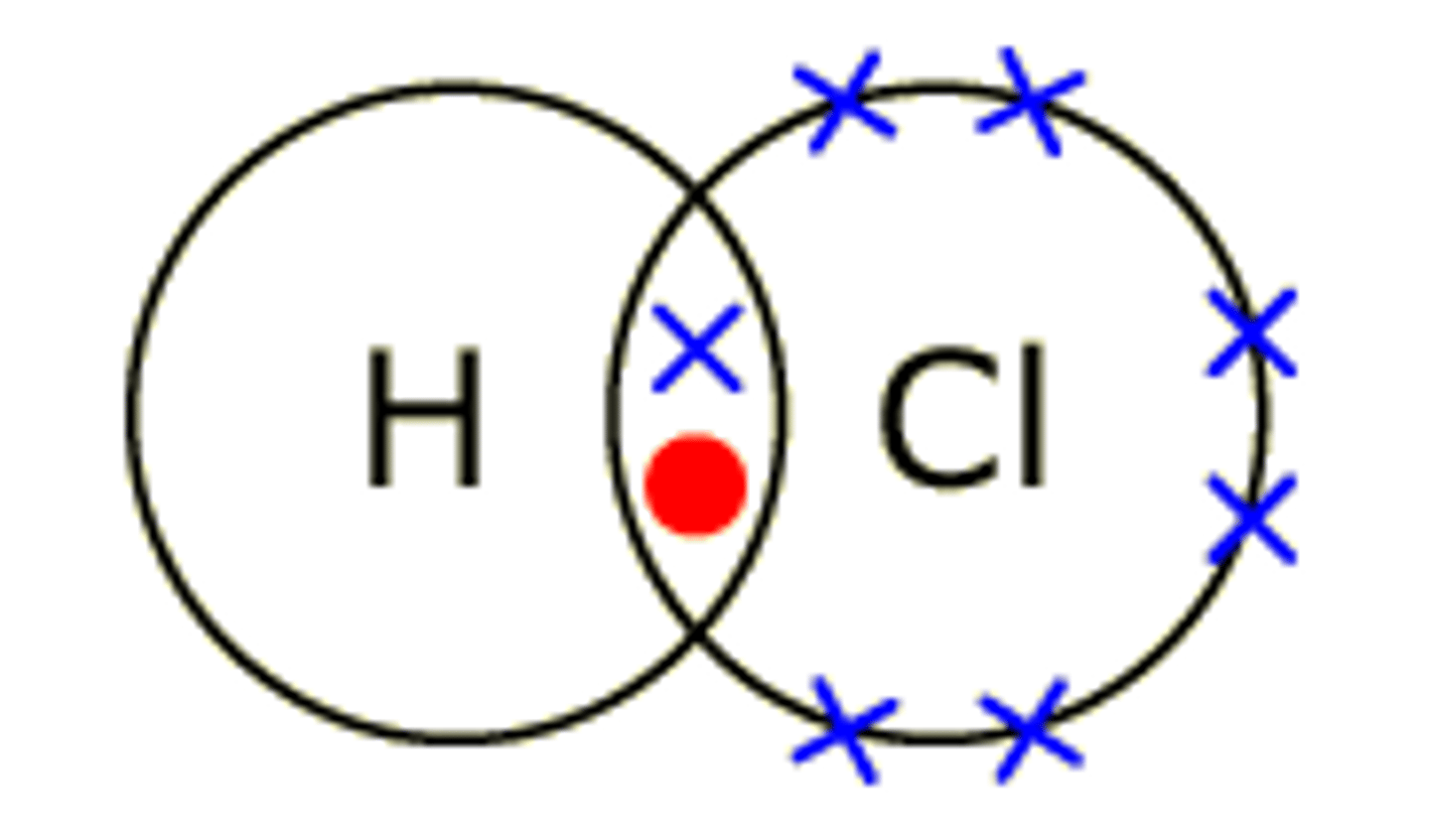
Max Number of electrons first valance shell
2
Max Number of electrons valance shell 2 and higher
8