Classification of Elements
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Question mode: Flashcards only. Answer mode: Answer with Definition. Suitable for JEE probably. Catered towards NCERT and IAT. Good luck.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
What led Henry Moseley to realizing that the atomic number of elements is a much more fundamental property than their atomic mass?
He observed regularity in the elements’ characteristic x-ray spectra and plotted a graph of \sqrt{f} (f is the frequency of emitted x-rays) against their atomic numbers, and found it to be a straight line, which was not the case for the graph of \sqrt{f} against atomic mass.
How many elements does the first period contain?
2
How many elements does the second period contain?
8
How many elements does the third period contain?
8
How many elements does the fourth period contain?
18
How many elements does the fifth period contain?
18
How many elements does the sixth period contain?
32
How many elements does the seventh period contain?
32
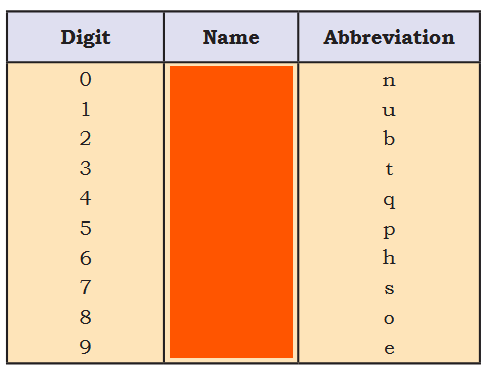
Notation for IUPAC Nomenclature of Elements

Which blocks are included in the “Representative Elements” or “Main Group Elements”?
s and p block
What is the outer shell configuration of noble gases?
ns²np^6
Which group is halogens?
group 17
Which group is chalcogens?
group 16
Which group has the most negative electron gain enthalpies?
halogens (group 17)
how does metallic character vary across a period?
metallic character decreases across a period
How does metallic character vary down a group?
metallic character increases down a group
Most metals have high melting points. What are the three notable exceptions?
mercury (liquid)
gallium (303 K melting point)
caesium (302 K melting point)
Most non-metals have low melting and boiling points. Which two elements are an exception to this?
boron
carbon
What are the 5 metalloids?
silicon
germanium
arsenic
antimony
tellurium
Does reactivity of metals increase or decrease down a group?
increase
Does reactivity of non-metals increase or decrease down a group?
decrease
How is the atomic radius of nonmetals measured?
By using Covalent Radius; half the distance between two nonmetal atoms bonded together by a single covalent bond
How is the atomic radius of metals measured?
By using Metallic Radius; half the distance between two cores in a metal crystal.
How does atomic size vary across a period?
atomic size decreases (generally) across a period
How does atomic size vary down a group?
it increases down the group
Why are the atomic sizes of noble gases not considered in periodic trends?
Because being monoatomic, their atomic radii are very large and cannot be measured by covalent radius or metallic radius. They should be compared only to the van der waal’s radii of other elements
How can ionic radii be measured?
It can be estimated by measuring the distance between cations and anions in ionic crystals
Is a cation bigger or smaller than its parent atom?
smaller
Is an anion bigger or smaller than its parent atom?
bigger
What are isoelectronic species?
atoms and ions with the same number of valence electrons and electronic structure
do isoelectronic species have the same atomic radii? why?
they do not. because nuclear charges can still be different
What is ionisation enthalpy?
It is the energy required to remove an electron from an isolated gaseous atom in its ground state.
What is the SI unit of ionisation enthalpy?
kJ mol-1 or kilo joules per mole
Do you know the difference between first and second ionisation enthalpy?
if not go look at it again because i can’t be bothered to make flashcards for this and honestly it should be obvious enough
Why are ionisation enthalpies always positive?
energy is always required to remove an electron from an atom
Why are second ionisation enthalpies higher than first ionisation enthalpies? (and so on)
because it takes more energy to remove an electron from a net positive atom than a neutral atom due to electrostatic reasons i’m assuming
What is the general trend of ionisation enthalpies across a period?
it usually increases
What is the general trend of ionisation enthalpies down a group?
it usually decreases down a group
Why is the effective nuclear charge experienced by a valence electron less than the actual charge on the nucleus?
due to shielding (repulsion) from other core electrons (in inner subshells)
Why is the first ionisation enthalpy of boron slightly less than the first ionisation enthalpy of berrylium?
Because the electron that gets removed from beryllium is from 2s subshell and the electrong that gets removed from boron is from 2p subshell. 2s electrons are much more closely held by the nucleus than a 2p electron, so 2p electrons are easier to remove and require less energy
Why is the general trend that ionisation enthalpies increase along a group?
because effective nuclear charge increases
Why is the general trend that ionisation enthalpies decrease down a period?
because effective nuclear charge decreases
Why is the first ionisation enthalpy of oxygen slightly less than the first ionisation enthalpy of nitrogen?
Because in nitrogen, each 2p electron occupies a different orbital, but in oxygen, two of the 2p electrons occupy the same orbital, so there’s a lot of electron-electron repulsion which makes it easier to remove that electron. And for half-filled nitrogen’s 2p, that’s far more stable so changing that is bad
What is electron gain enthalpy?
The enthalpy change accompanying the process in which an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom to convert it into a negative ion
Which group has the most negative value of electron gain enthalpy?
group 17
Which group has the most positive value of electron gain enthalpy?
group 18
What is the general trend of electron gain enthalpy across a period?
The value of electron gain enthalpy gets more and more negative across a period
What is the general trend of electron gain enthalpy down a group?
The value of electron gain enthalpy gets more and more positive down a group.
Why is the electron gain enthalpy of oxygen less negative than that of the element below it in the periodic table (Sulphur)?
Because when an electron is added to oxygen it is added to a smaller subshell (n=2) and faces more repulsion from the electrons in that subshell, but when an electron is added to sulphur it is added to a larger subshell (n=3) and has more space to occupy so faces less repulsion, so yeah
Why is the electron gain enthalpy of fluorine less negative than that of the element below it in the periodic table (chlorine)?
Because when an electron is added to fluorine it is added to a smaller subshell (n=2) and faces more repulsion from the electrons in that subshell, but when an electron is added to chlorine it is added to a larger subshell (n=3) and has more space to occupy so faces less repulsion, so yeah
Can the second electron gain enthalpy be negative?
NAH
Can the third electron gain enthalpy be negative?
NAH
Is there a relationship between the magnitude of the first electron gain enthalpy and the second electron gain enthalpy?
YAH
-|\Delta H_{eg\ 1}|<|\Delta H_{eg\ 2}
in other words
\Delta H_{eg\ 1} + \Delta H_{eg\ 2} >0 always
What is the formula that relates electron gain enthalpy to electron affinity?
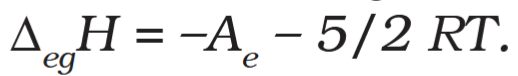
What is the unit of electron gain enthalpy?
kJ / mol
or kilo joule per mole
What is the electronegativity of fluorine according to the Pauling Scale?
4.0
What is the trend for electronegativity across a period?
it increases
What is the trend for electronegativity down a group?
it decreases
What is the electronegativity of chlorine according to Pauling Scale?
3.0
What are the electronegativities of the elements from the second period? How can you remember that?
it starts at 1.0 Lithium, increases in increments of 0.5, then ends at 4.0 Fluorine

Why do some elements from the second and third period exhibit diagonal relationship?
They have similar charge/size ratio, which means that they have the same ionic potential, therefore they have similar polarizing power and form compounds of similar covalent and ionic character.
Why is the chemical behaviour of elements from the first period so different from the chemical behaviour of elements from the second period in the same group?
small size / large size
large charge/radius ratio
high electronegativity
first period has only 4 orbitals and second period has 9 orbitals so a lot more possible oxidation states
What is the chemical nature of oxides formed from the left side of the periodic table?
basic
What is the chemical nature of oxides formed from the middle of the periodic table?
amphoteric or neutral
What is the chemical nature of oxides formed from the right side of the periodic table?
acidic
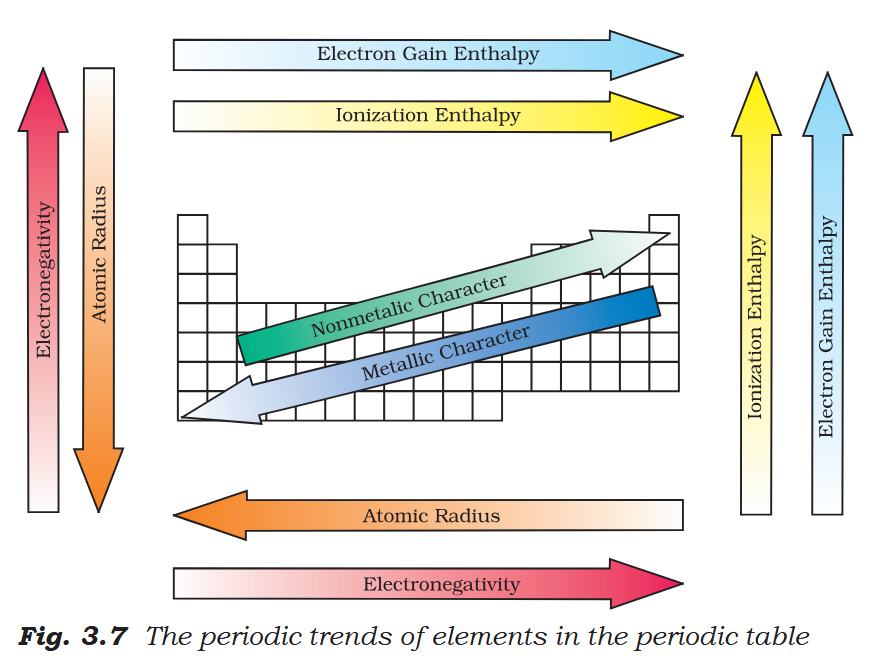
cool stuff huh
yea