BSC1010 EXAM 2 STUDY GUIDE - PITZER
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
___ is when chemical reactions expend energy to make new chemical bonds. (build up)
anabolism
___ is when chemical reactions harvest energy when bonds are broken (break down).
catabolism
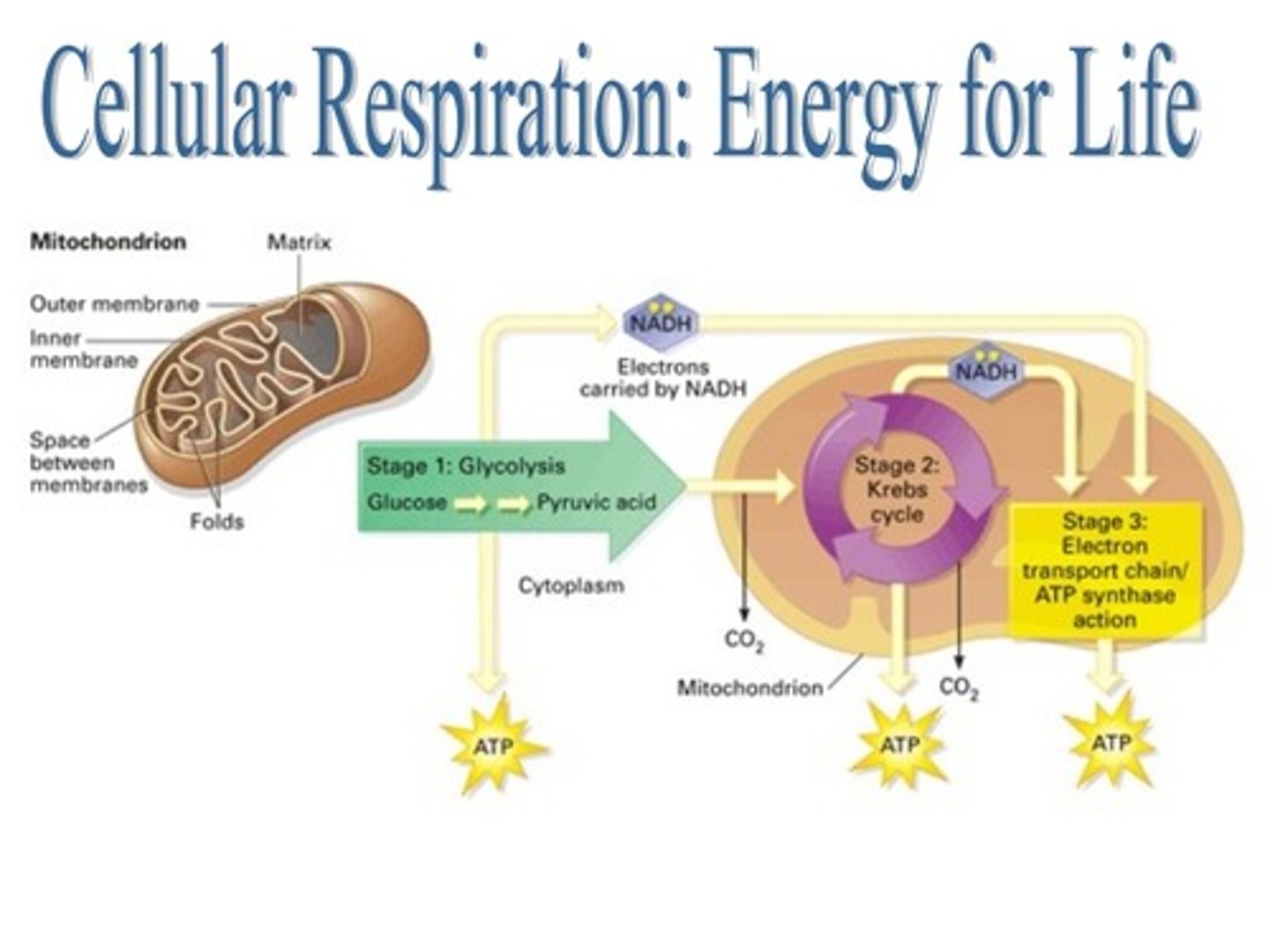
First stage of Cellular respiration is called ___ and it is anaerobic. Meaning, it takes place in the ___.
glycolysis ; cytoplasm
Second stage of Cellular Respiration is the ___. It is a series of reactions that occur in the ___. (Also called the Citric Acid Cycle)
Kreb's cycle ; mitochondria
Third stage requires oxygen: making it aerobic, producing a majority of ATP. It takes place in the __. The ___ involves a series of enzymes called the ETC.
mitocondria ; Electron Transport Chain
Bacteria use outer membranes to do ___ respiration.
aerobic
What is the overall reaction for cellular respiration? What is the formula?
exergonic ; O2 + C6H12O6 = H2O + CO2 + ENERGY (in the form of ATP)
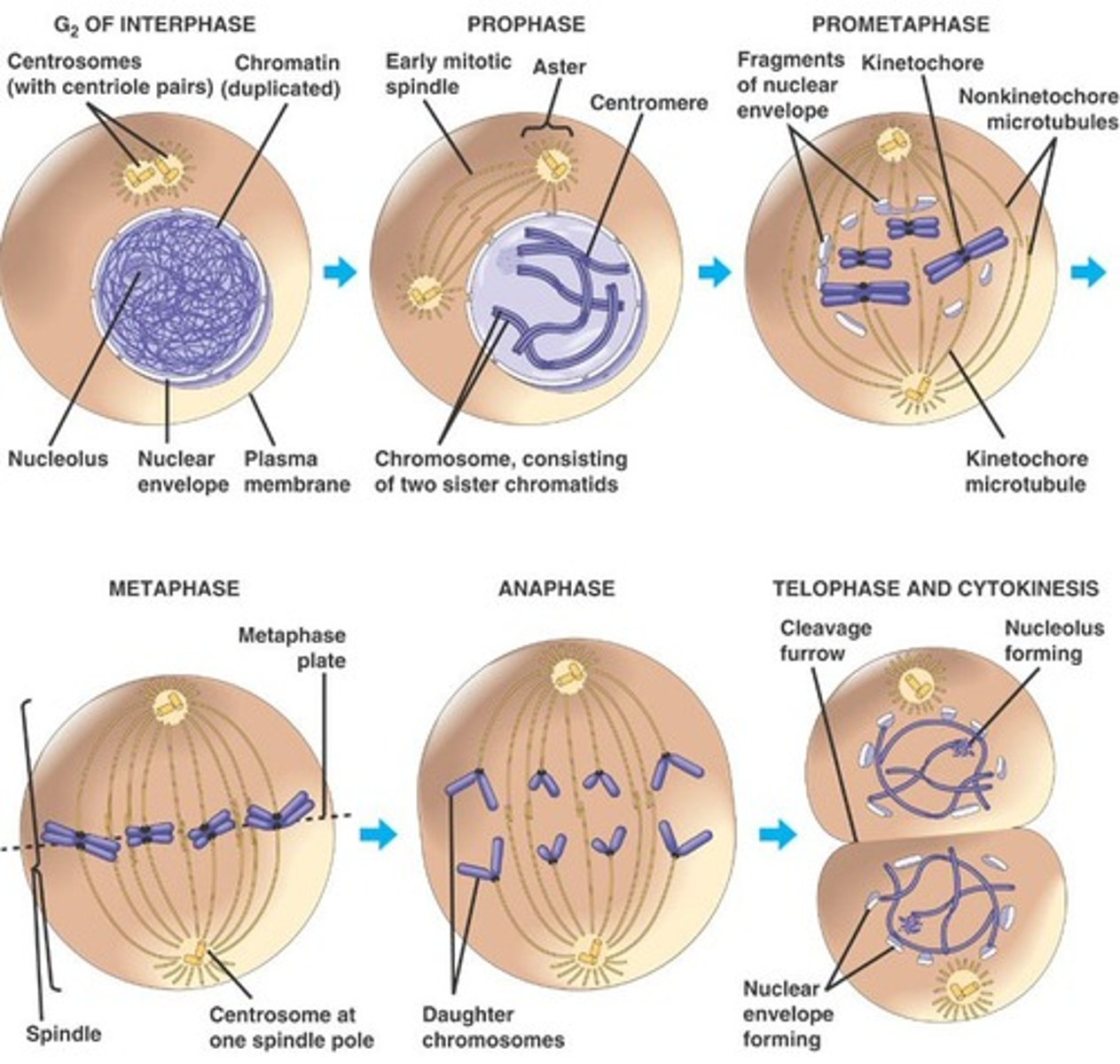
Mitosis phases:
G2 of Interphase, Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
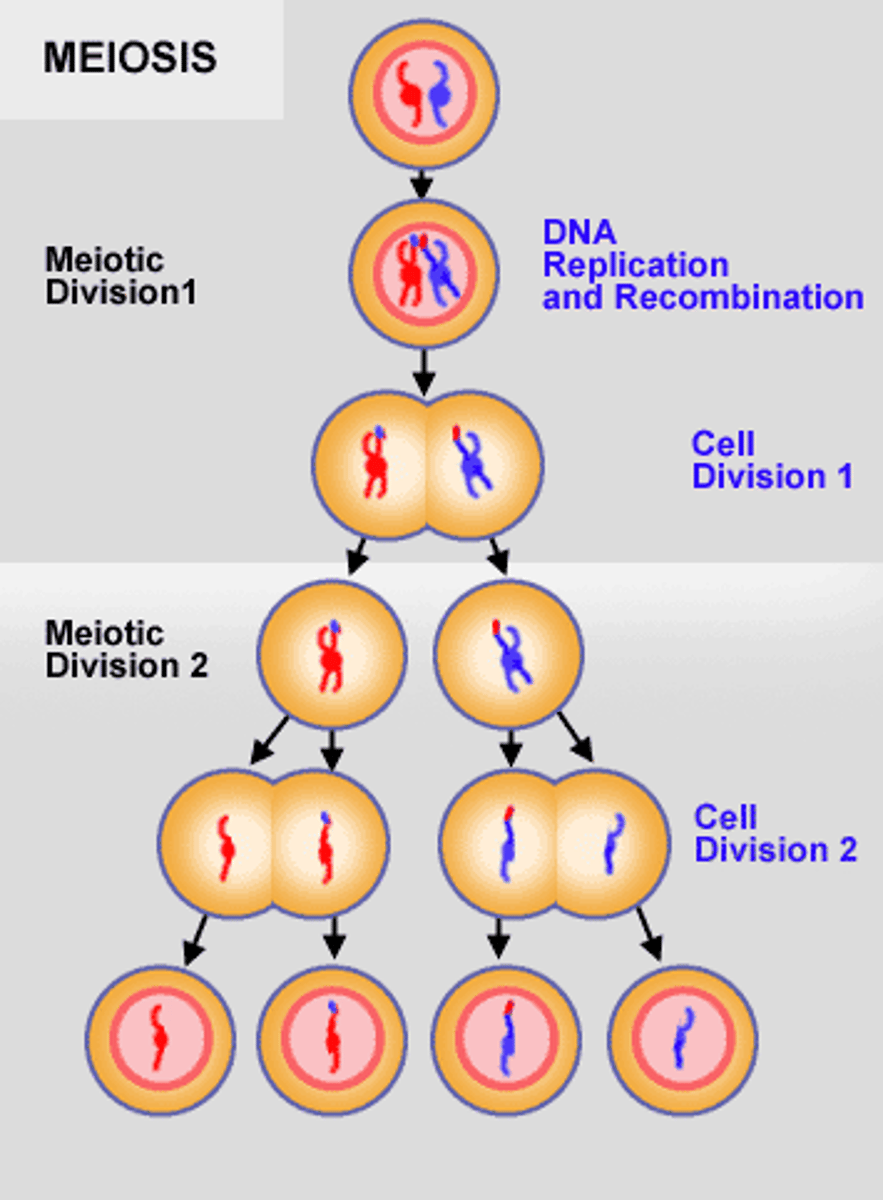
Meiosis phases:
___ states that energy cannot be created nor destroyed. It can only be converted from one form to another.
E.g. sunlight energy --> photosynthesis --> chemical energy
First Law of Thermodynamics
___ states that disorder is more likely than order and that entropy is always increasing.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
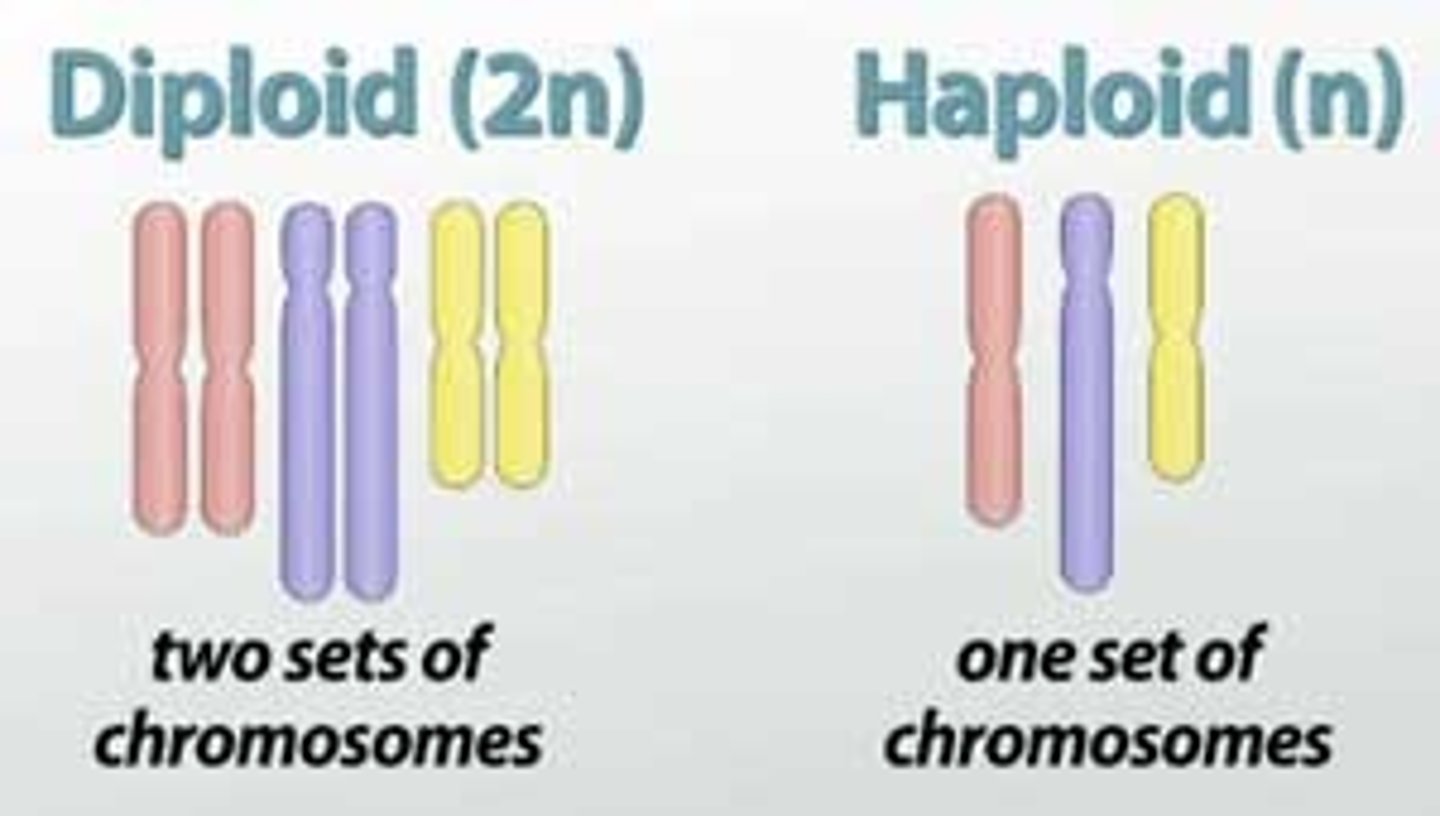
Haploid vs Diploid
Feedback loops are used in order to maintain an internal stable environment (homeostasis). ___ is the stabilization (e.g. temperature regulation)
negative feedback
___ is the amplification to reach stabilization. (e.g. Fruit ripening)
positive feedback
Allosteric ___ increase enzyme activity.
activator
Allosteric ___ decrease enzyme activity.
inhibitor
Explain the process of Cellular respiration: (Glycolysis, Pyruvate oxidation, Kreb's, and Electron Transport Chain)
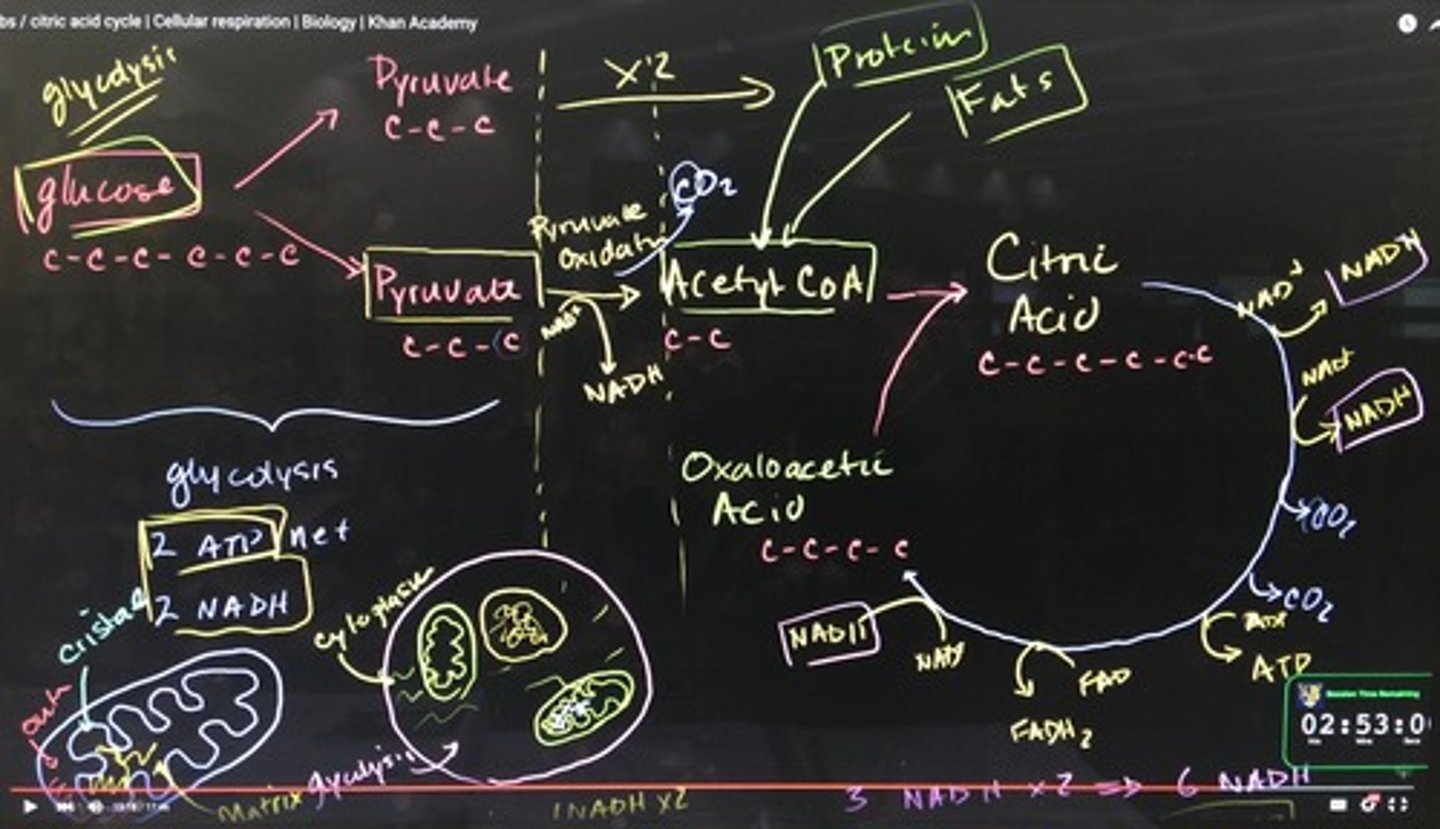
The complete oxidation of glucose proceeds in these four stages:
1) glycolysis
2) pyruvate oxidation
3) Krebs cycle
4) electron transport chain and chemiosmosis
Step 1 of Mitosis:
-chromosomes continue to condense
-centrioles move to each pole of the cell
-spindle apparatus is assembled
-nuclear envelope dissolves
Prophase

Step two of Mitosis:-
-chromosome becomes attached to the spindle apparatus by their kinetochores
-a second set of microtubules is formed from the poles to each kinetochore
-microtubules begin to pull each chromosomes toward the center of the cell
Prometaphase
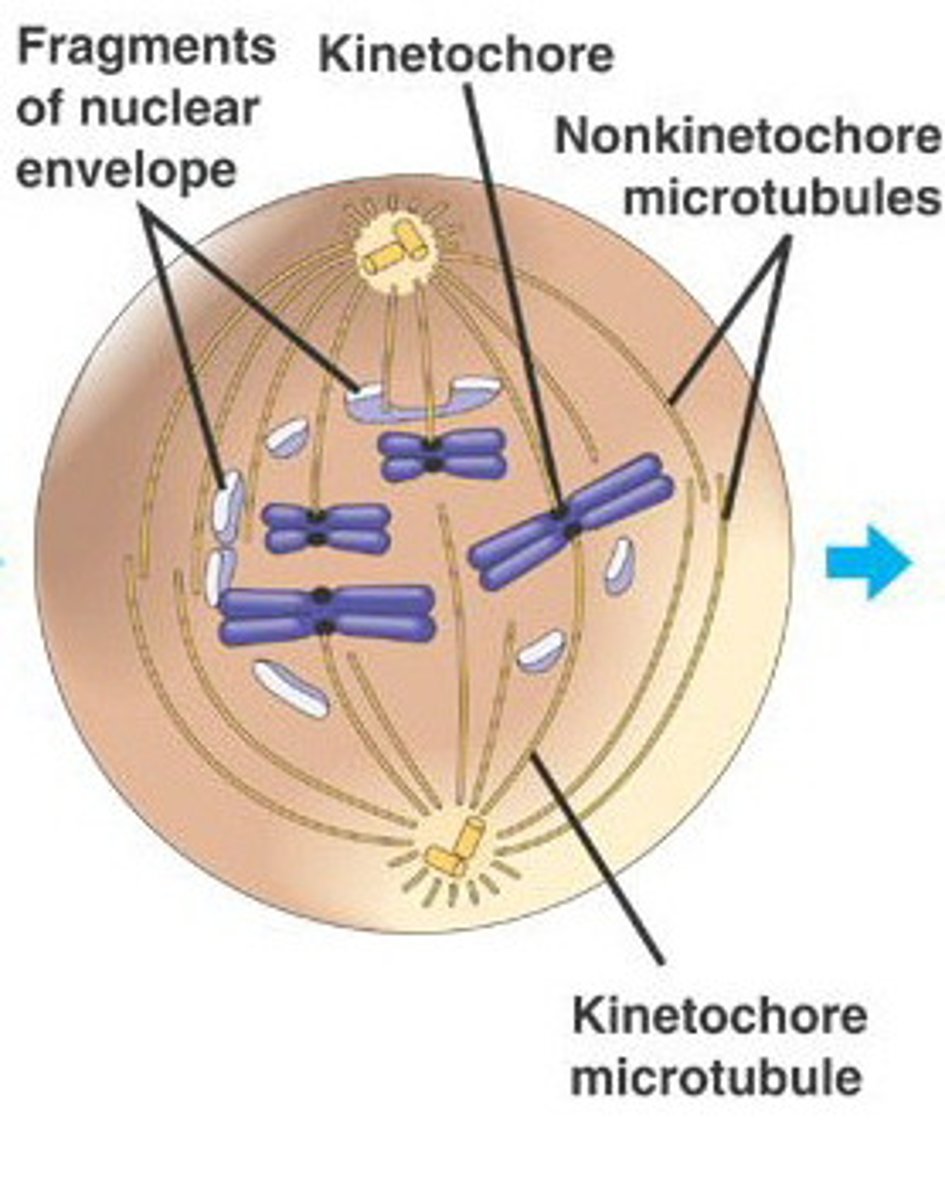
Step three of Mitosis:
-microtubules pull the chromosomes to align them at the center of the cell
-metaphase plate: the imaginary plane through the center of the cell where the chromosomes align
Metaphase
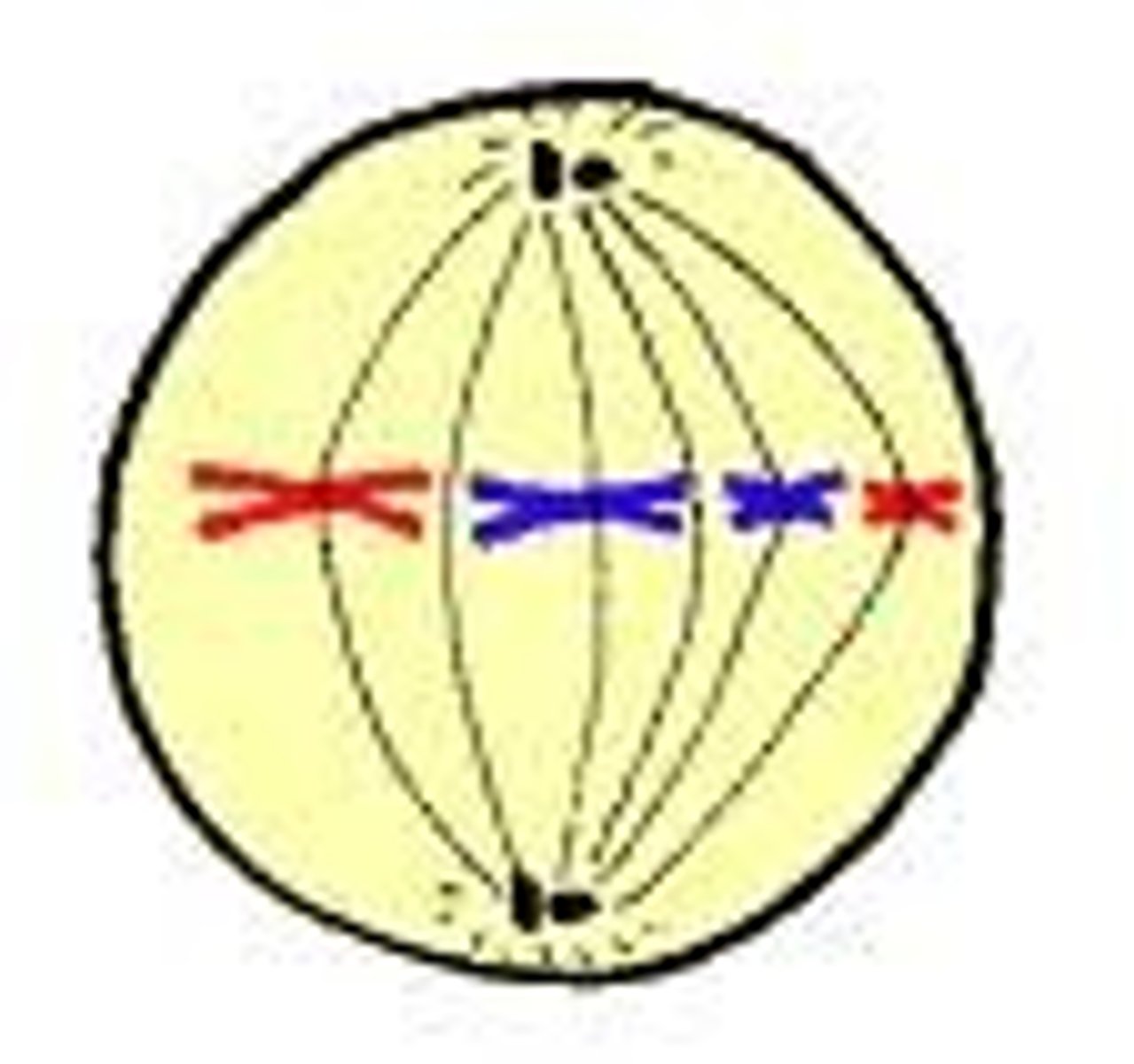
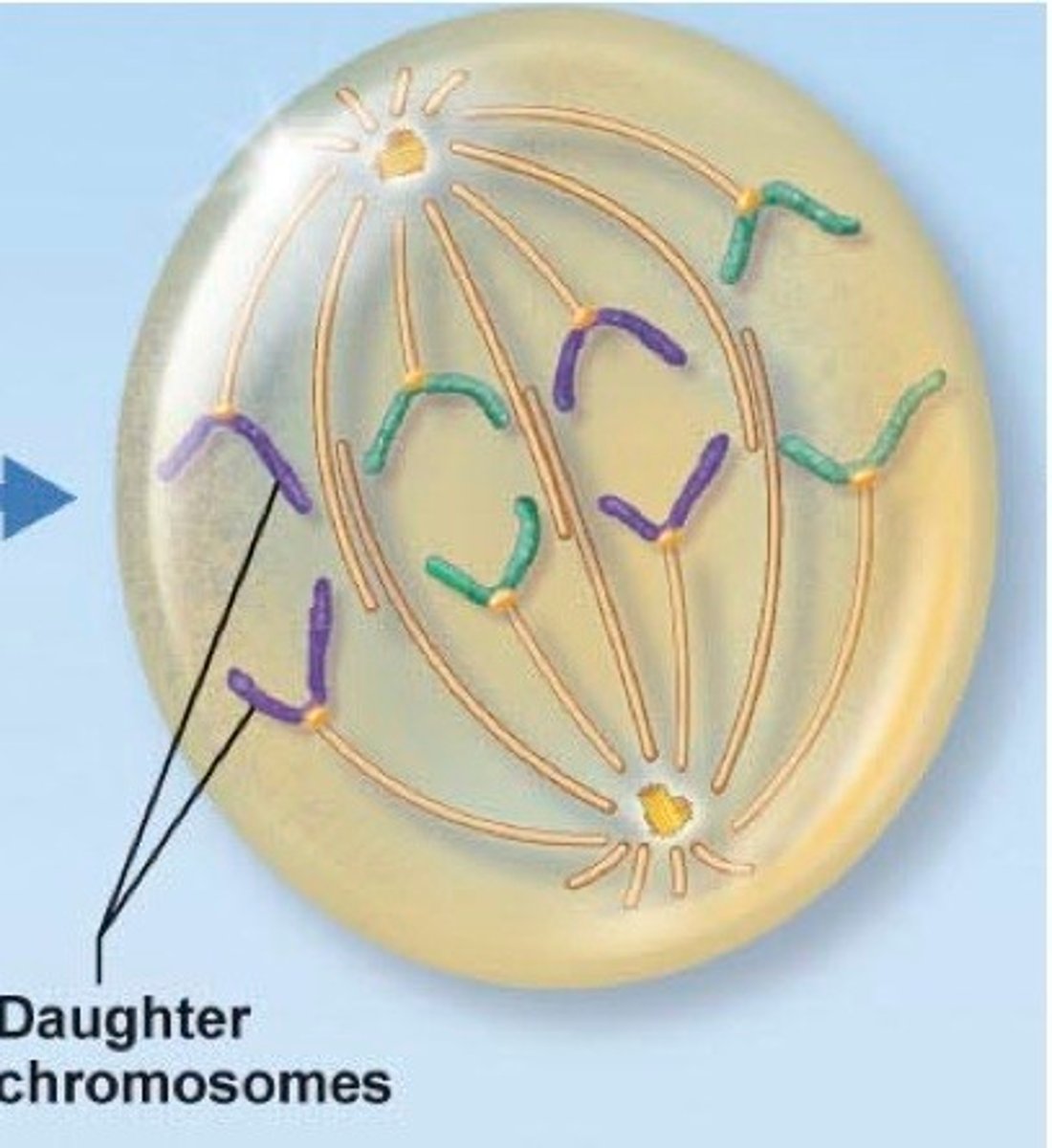
Step four of Mitosis:
-removal of cohesin proteins causes the centromeres to separate
-microtubules pull sister chromatids toward the poles
-in anaphase A the kinetochores are pulled apart
-in anaphase B the poles move apart
Anaphase
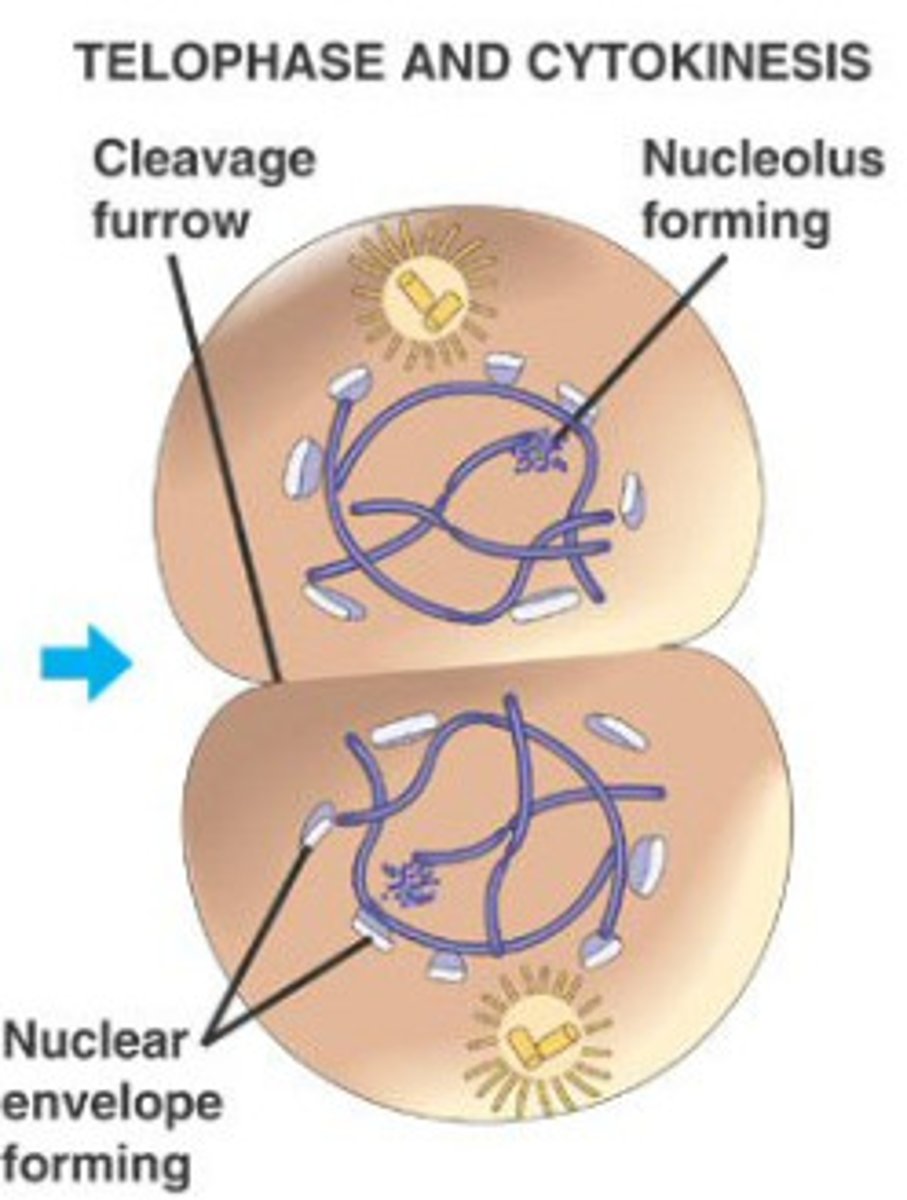
Final phase of Mitosis:
-spindle apparatus disassembles
-nuclear envelope forms around each set of sister chromatids
-chromosomes begin to uncoil
-nucleolus reappears in each new nucleus
Telophase
How do the microtubules push/pull the chromosomes around?
motor proteins
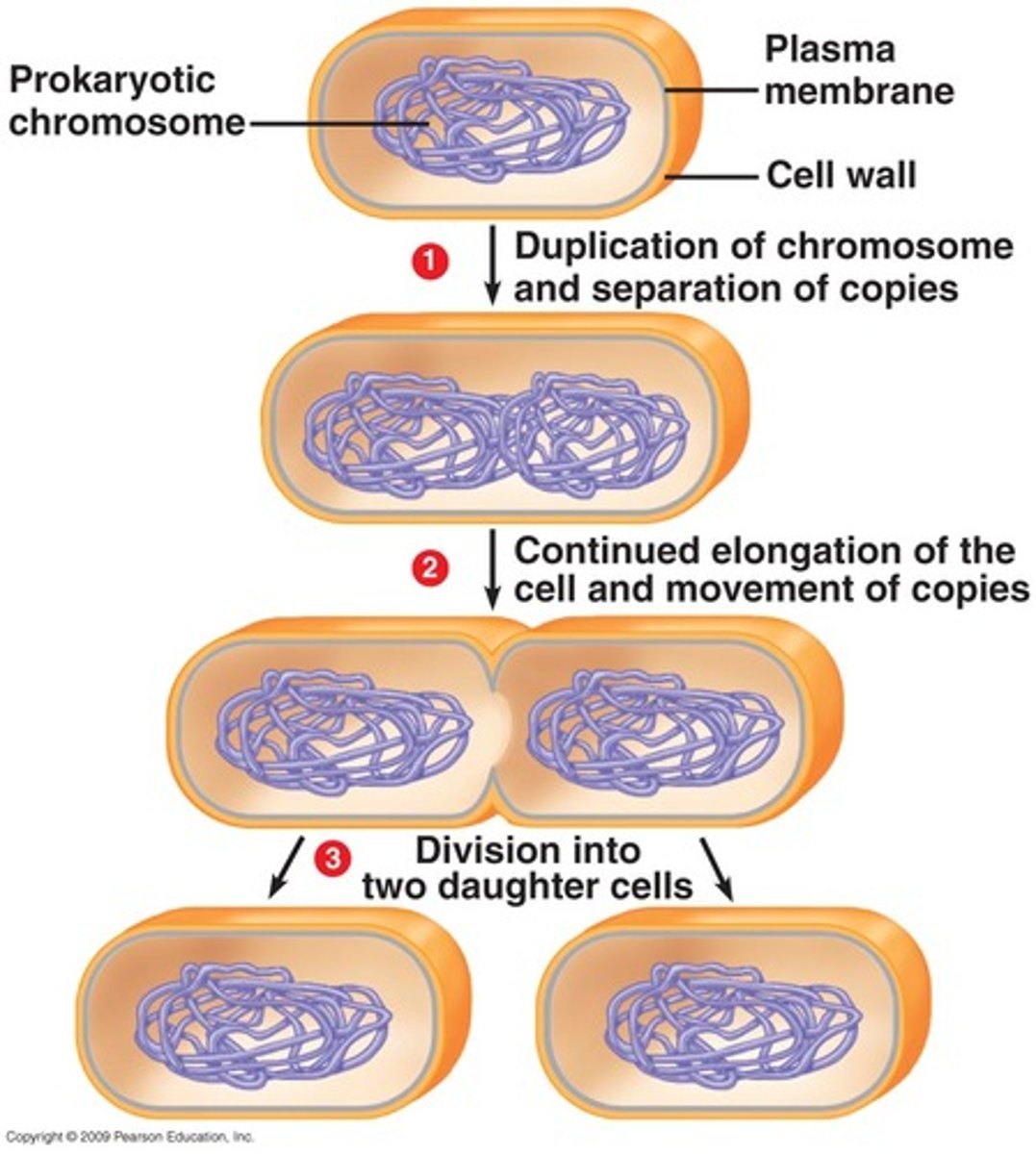
What is binary fission?
the process in which bacteria, the single, circular chromosome, is replicated. Replication begins at the origin of replication and proceeds biodirectionally. New chromosomes are partitioned to opposite ends of the cell. A septum then forms to divide the cell into two.
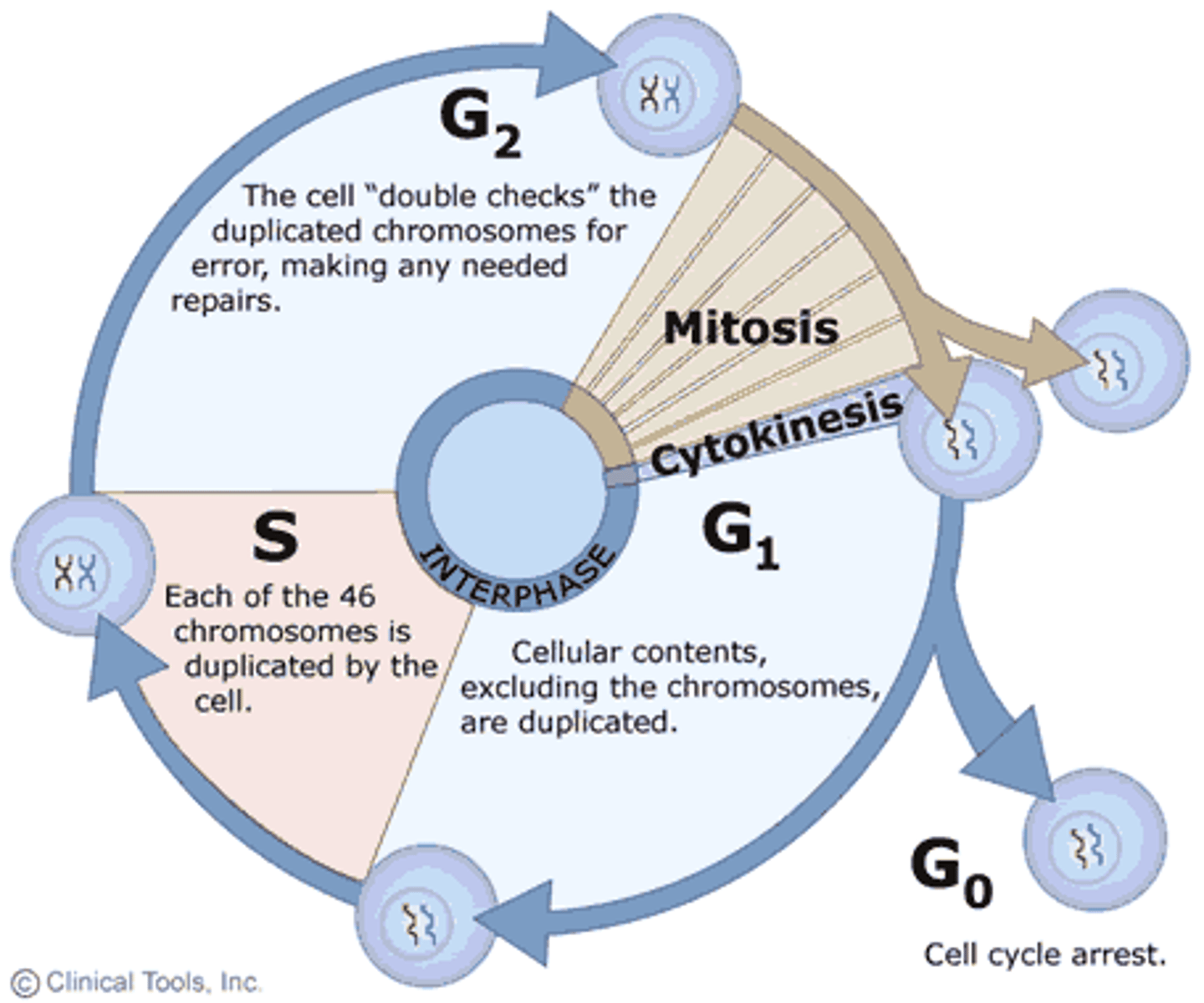
What are the stages of the cell cycle?
1) G1 (growth phase 1)
2) S (synthesizes a replica of the genome)
3) G2 (growth phase 2) Mitochondria and other organelles replicate
4) M (mitosis)
5) C (cytokinesis)
During ___, electrons are shuttled through electron carriers to a final electron acceptor. The goal is to produce ATP.
cellular respiration
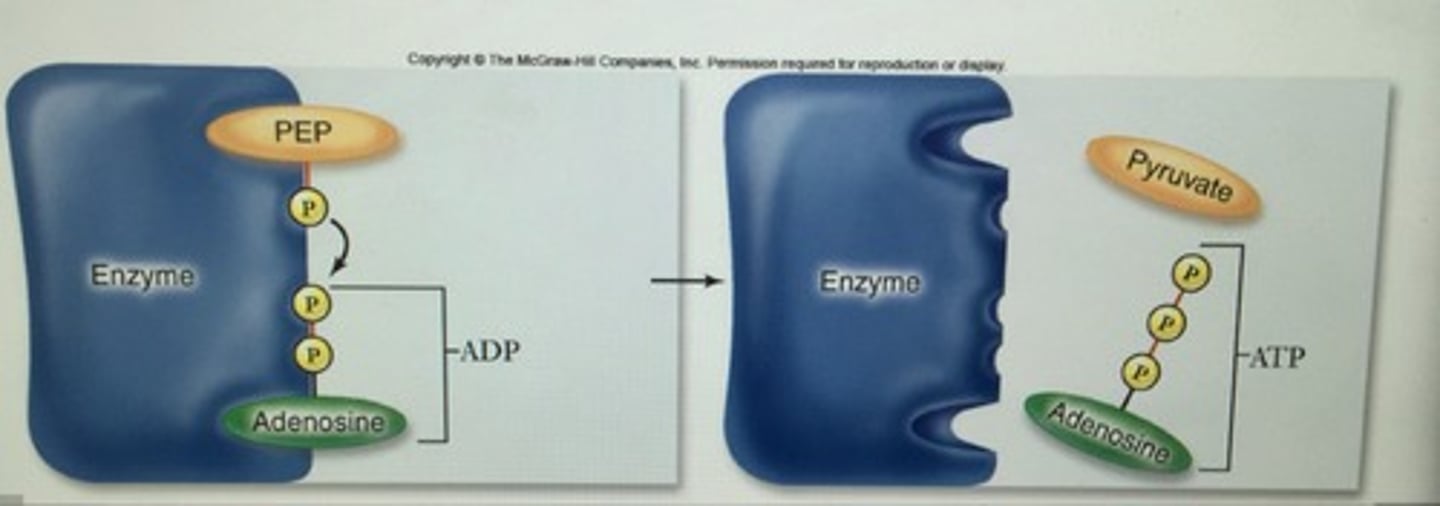
Cells are able to make ATP via;
1) __; transferring a phosphate direcly to ADP from another molecule
2) ___; use of ATP synthase and energy derived from a proton (H+) gradient to make ATP
substrate-level phosporylation , oxidative phosphorylation
Which came first: DNA, RNA, or Protein? Why?
The issue isn't entirely solved yet. RNA has four different nucleotides, and so far scientists have only produced two of them. However, scientists are "closing in" on the other two. If they succeed, it will show that the spontaneous formation of an RNA replicator is not so improbable after all, and that the first replicator was most likely made of RNA.
___ are molecules that catalyze reactions in living cells. They are catalysts, most (not all) are proteins, their activation energy is required for a reaction, and they are not charged or consumed by the reaction. (Most of the scientific names end is -ase).
enzymes
___ is the energy available to do work. Denoted by the symbol G.
free energy
___ is the process in which all chemical reactions occurring in an organism occur in sequence. It is the product in which one reaction is the substrate for the next. Many of these steps take place in organelles.
metabolism
___ is the reaction requiring INPUT of energy.
(DG = positive)
endergonic reaction
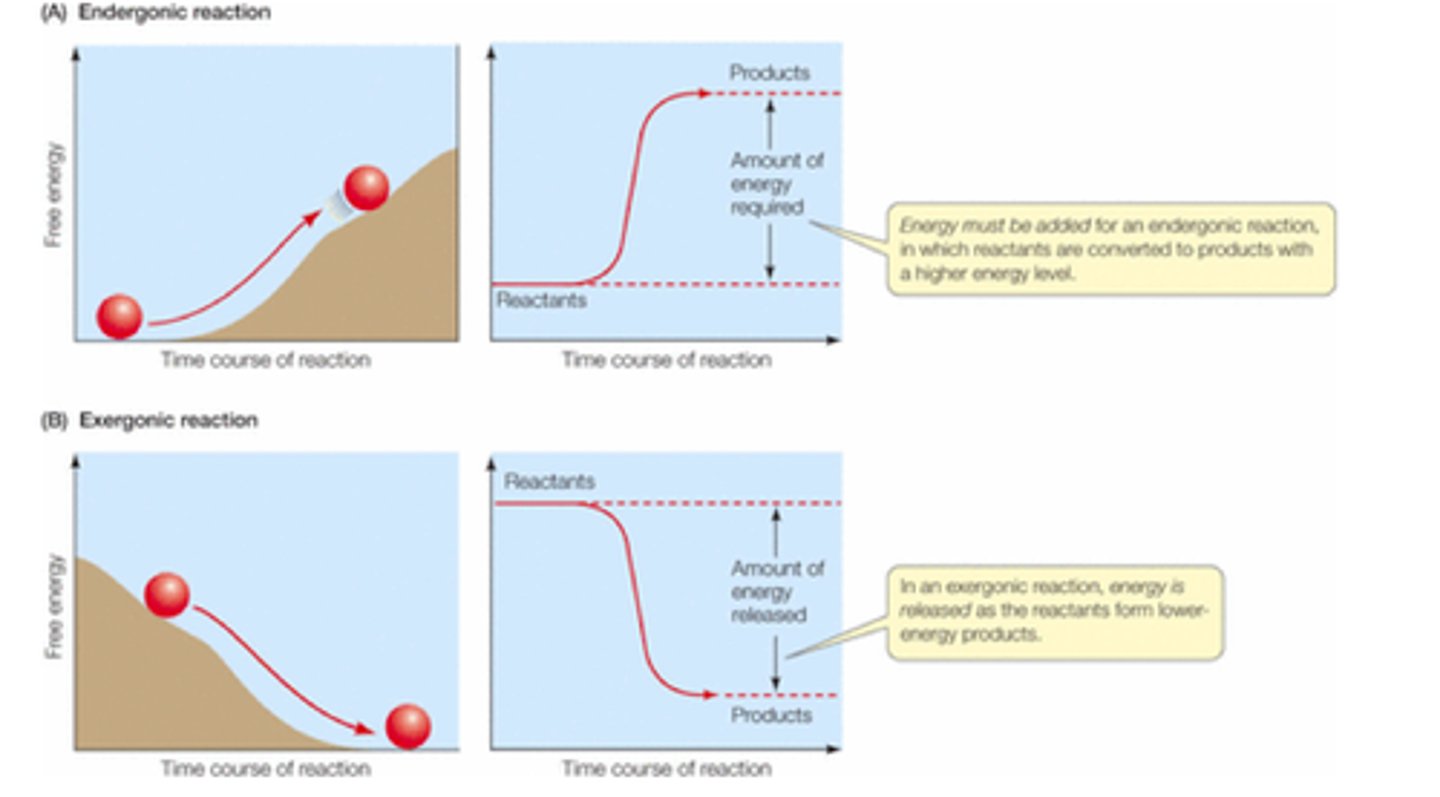
___ comes from potential energy stores in chemical bonds that can be transferred from one molecule to another by way of electrons.
biological energy
What is OIL RIG?
Oxidation Is Losing
Reduction Is Gaining
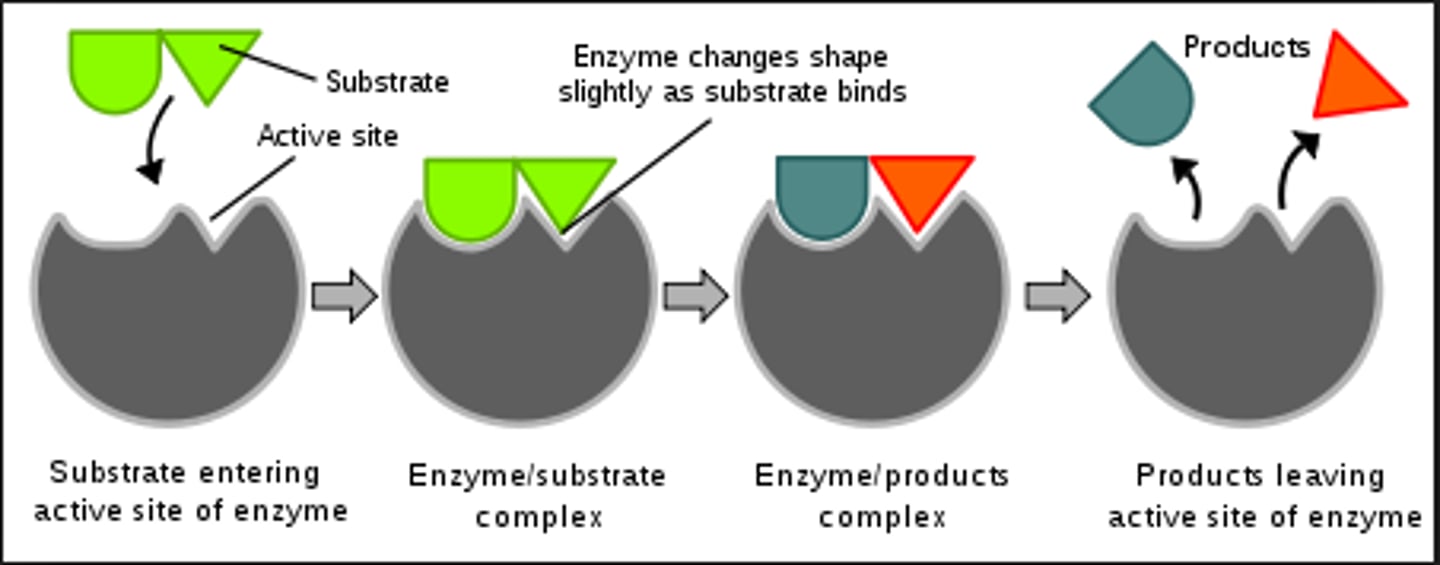
__ is the region of the enzyme that binds to the substrate. Binding an enzyme to a substrate causes the enzyme to change shape, producing a better induced fit between the molecules.
active site
Energy is the capacity to do work, consisting of two types ___ (energy of motion) and ___ (stored energy). E.g. Mechanical, Electric current, Heat, Light
kinetic , potential
___ energy contained in a molecule's chemical bonds
free energy = enthaply - (entropy x temperature)
G = H - TS
enthalpy
A measure of the randomness or disorder of the universe that is no longer able to do work is ___.
entropy
The ___ is the nonprotein organic molecule, e.g. NAD, that is part of an enzyme that is involved in allowing the enzyme perform its function; helps catalyze the reaction often by acting as a donor or acceptor of electrons.
coenzyme
___ is one or more nonprotein components required by enzymes in order to function; many cofactors are metal ions, others are organic coenzymes. E.g. Vitamins and Minerals
cofactor (THIS IS ORGANIC)
___ unwinds DNA's double helix
helicase
___ synthesizes RNA primers
primase
___ stabilizes single stranded regions
single-strand binding proteins (SSB)
___ relieves torque (coils)
gyrase
__ synthesizes DNA
polymerase III
___ erases primer and fills gaps
polymerase I
___ joins the ends of DNA segments, DNA repair
ligase
What did Erwin Chargaff determine about the structure of DNA?
1) amount of adenine = amount of thymine
2) amount of cytosine = amount of guanine
The ___ consists of two sugar-phosphate backbones, nitrogenous bases toward the interior of the molecule, bases to form hydrogen bonds with complementary bases on the opposite sugar-phosphate backbone.
double helix/DNA
DNA only binds on ___ prime carbons.
3'
Cytokinesis
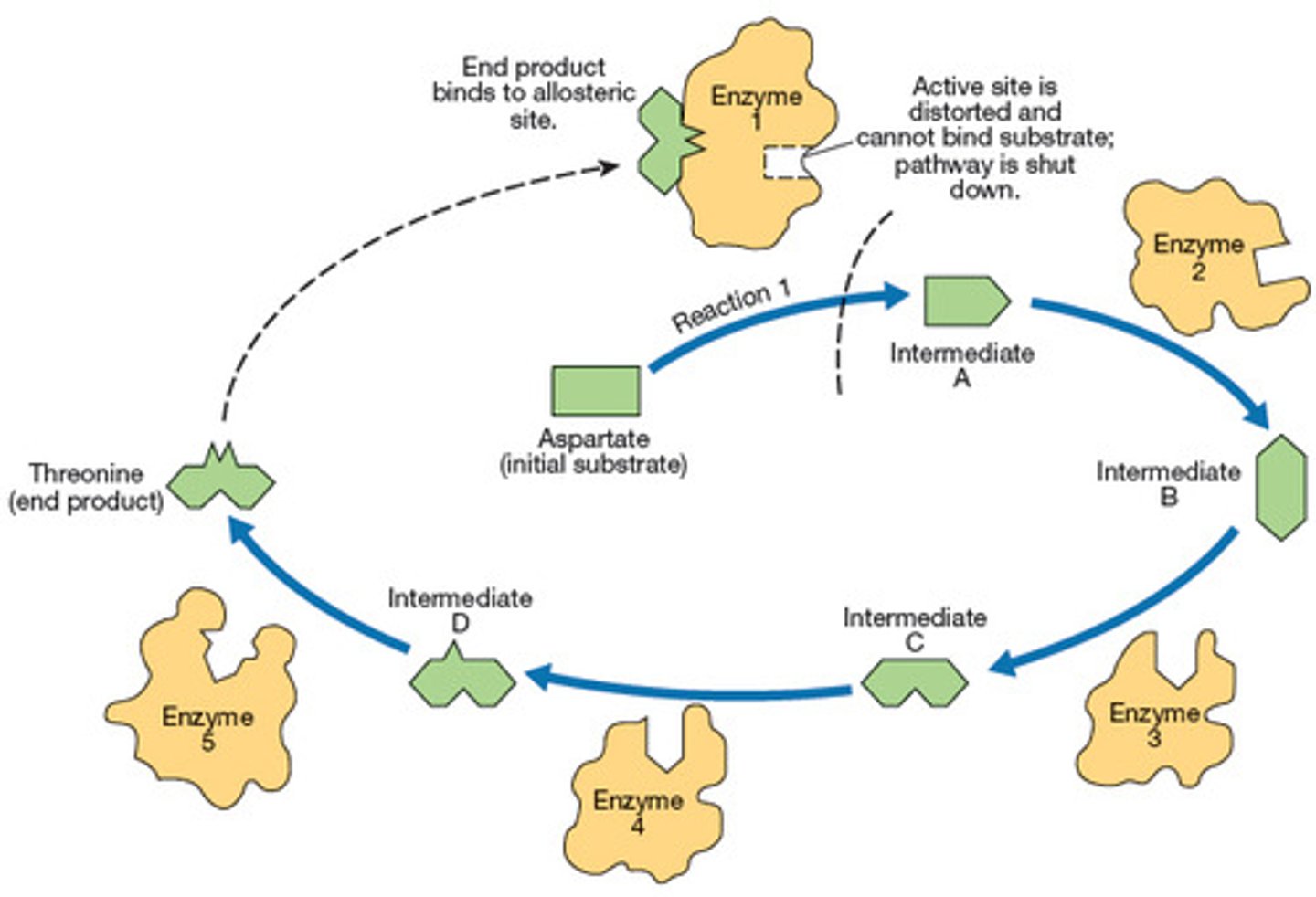
How are metabolic pathways regulated?
Through allosteric inhibition.
A ___ generalizes a body of observations. At the time it is made, no exceptions have been found to a law. These explain things, but they do not describe them.
scientific law
A ___ is an educated guess, based on observation. It's a prediction of cause and effect.
hypothesis
Lack of ___ activity is hypothesized as a big culprit to aging and cancer.
telomerase
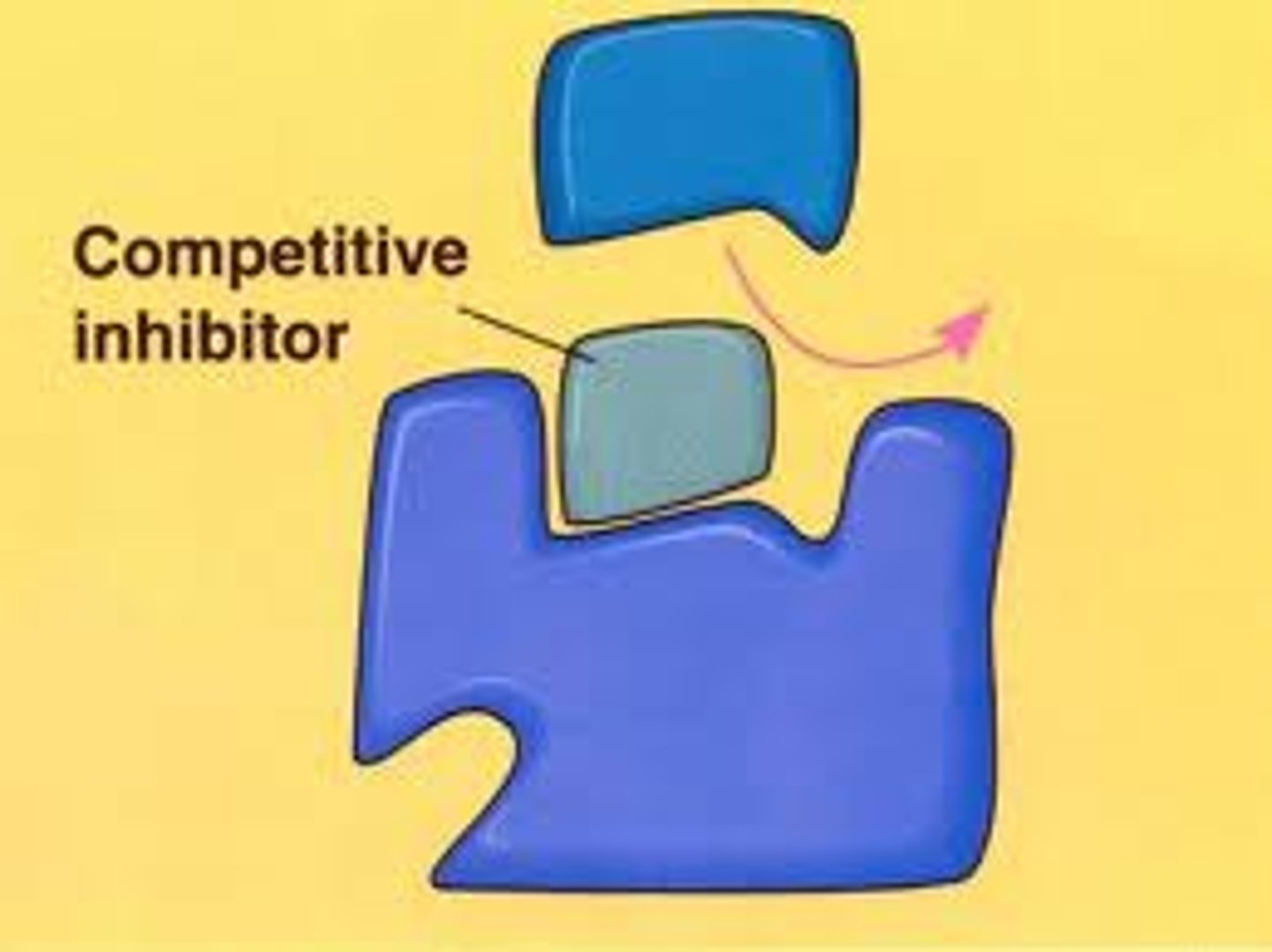
Competitive inhibition:

The process that results in the complete oxidation of glucose using oxygen as the final electron acceptor is ___. Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor for an electron transport chain that produces a proton gradient for the chemiosmotic synthesis of ATP.
aerobic respiration
The use of electron transport to generate a proton gradient for chemiosmotic synthesis of ATP using a final electron acceptor other than oxygen is ___.
anaerobic respiration
___ is the enzyme-catalyzed extraction of energy from organic compounds without the involvement of oxygen.
fermentation
The biosynthetic or constructive part of metabolism; those chemical reactions involved in biosynthesis is ___.
anabolism