8 - Gas Laws and the Mole
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
To be accompanied with exam questions - CALCULATIONS ARE KEY FOR THIS TOPIC!!!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
State Charles’s law
At constant pressure, the volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature measured on the Kelvin scale.
{V/T = constant}
Explain why Charles’s law is consistent with pV = nRT, the equation of state of an ideal gas
pV = nRT → V/T = nR/P = constant /
n and R constant for a fixed mass of gas and p also constant
Under what conditions of temperature and pressure does the equation pV = nRT most accurately describe real gas behaviour?
High temperature //
low pressure
Give two reasons why ammonia deviates from ideal gas behaviour
Strong H bonding (intermolecular forces) between its molecules / polar molecule //
particles occupy volume //
collisions not elastic
A racing car tyre contained 294g of nitrogen gas occupying a volume of 0.168m3 at a temperature of 293K. Calculate the pressure of the gas inside the tyre in Pa.

What is meant by the term ideal gas?
One that obeys all the assumptions of the kinetic theory of gases under all conditions of temperature and pressure
Which one of the noble gases would you expect to behave most like an ideal gas? Justify your answer
Helium (He)
Atoms have smallest volume / weakest intermolecular forces / fewest electrons / lowest boiling point
State Avogadro’s law
Equal volumes of gases contain equal numbers of molecules, under the same conditions of temperature and pressure
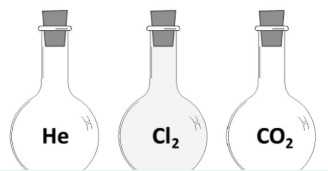
The diagram shows three containers, each filled with a different gas. Each container holds the same volume of gas at the same temperature and pressure.
Which contains the largest number of atoms? Explain
CO2 //
equal numbers of molecules (moles) / according to Avogadro’s law / CO2 molecule has more atoms than H2 or Cl2
Give two reasons why real gases deviate from ideal behaviour at high pressures and low temperatures
Molecules not point masses / molecules have volume / molecules occupy space //
molecules attract (repel) one another / intermolecular forces between molecules
Gay-Lussac’s Law of Combining Volumes
In a reaction between gases, the volumes of the reactants and the products are in a small whole number ratio, provided the volumes are measured at the same temperature and pressure.
What is meant by a mole of a substance?
The amount of a substance that may contain as many particles as there are in twelve grams of carbon twelve
State Boyles’ law
At constant temperature, the volume of a fixed mass of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure
Give two assumptions of the kinetic theory of gases
Made up of particles that move in a rapid straight-line motion //
volume of particles is negligible //
no forces of attraction or repulsion between molecules //
collisions between molecules perfectly elastic //
average kinetic energy of molecules proportional to kelvin temperature
How many moles of gas are present in a sample containing 1.8 × 1024 atoms of chlorine at s.t.p.?
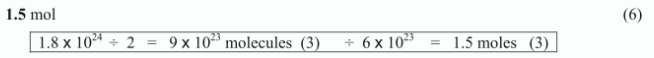
Give one reason why carbon dioxide is more easily liquified than helium
Stronger intermolecular forces / higher mass / bigger molecules / polarity of C to O bond / has more electrons