Structure of DNA and RNA
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
what is DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
what is RNA
Ribonucleic acid
DNA function
holds genetic information
RNA function
transfers genetic information
what forms ribosomes?
RNA and proteins
What do RNA and proteins form?
Ribosomes
Formation of nucleotides:
pentose sugar
nitrogen containing organic base
phosphate group
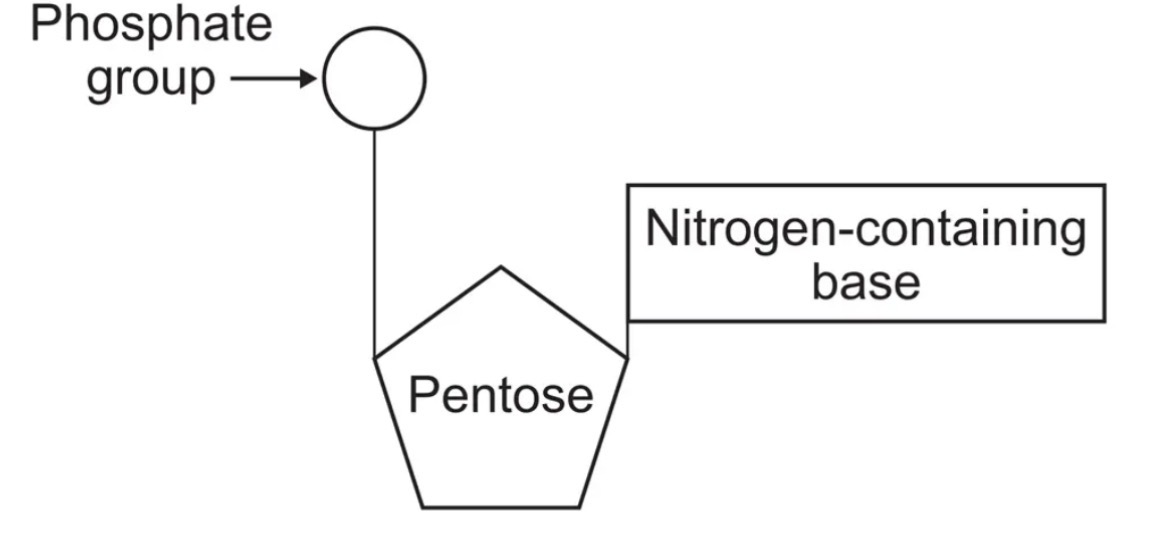
nucleotide
DNA nucleotide
pentose: deoxyribose
base: adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine
phosphate group
RNA nucleotide
pentose: ribose
base: adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil
phosphate group
how are polynucleotides formed?
condensation reaction between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the pentose sugar of another, forming a phosphodiester bond.
how is a phosphodiester bond formed?
condensation reaction between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the pentose sugar of another.
A strong covalent bond to ensure the genetic code is not broken down.
Formation of a DNA molecule:
2 polynucleotide chains
form a double helix
held together by hydrogen bonds between complimentary base pairs
Formation of RNA:
single stranded short polynucleotide chains
Which complementary base pairs can hydrogen bonds form between?
addnine and thymine (2 hydrogen bonds)
cytosine and guanine (3 hydrogen bonds)
how structure relates to the function:
Stable structure due to phosphodiester bonds and the double helix.
Double-stranded so replication can occur using both strands as a template.
Weak hydrogen bonds for easy unzipping of the two strands in a double helix during replication
A large molecule to carry lots of information.
Complementary base pairing allows identical copies to be made.