intro the the kidney
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
week 4 ctb
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
functions of the kidney
endocrine and homeostatic organs
homeostasis
filters plasma
regulates excretion of metabolic waste and toxins in urine
rebasorption of of essential nutrients
endocrine:
production and release of:
erythropoietin
active form of vit D
renin- regulation of BP
homeostatic kidney
contributes to homeostasis by removing substances from plasma
selectively retains certain substances and excreting others
reabsorption of essential nutrients/ions
excretion of metabolic waste/toxins
regulation of body fluid composition
regulation of total body fluid volume (regulation of BP)
key processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion to eventually form urine
macro and micro structures reflect their functions
uniferous tubules
made uo of numerous uniferous tubulues and associated blood vessels in cortex and medulla
uniferous tubule = nephron + collecting duct
plasma is filtered in nephron and solutes are reabsorbed/secreted
filtrate to be excreted is collected in collecting duct to be excreted as urine
uniferous tubule diagram
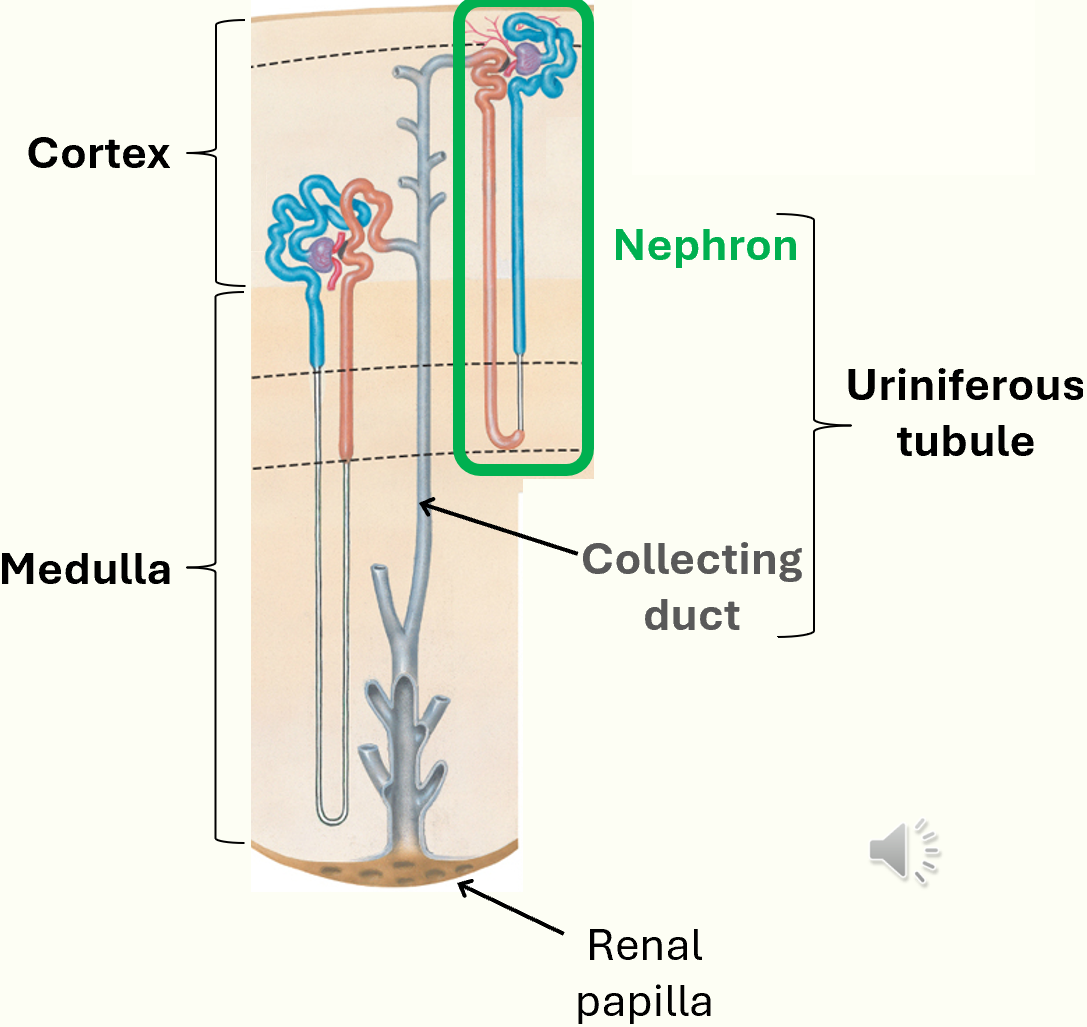
nephron
functional unit of kidney
1 million per kidney
tubular structure made of epithelial cells
parts of a nephron
renal corpuscle (glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule)
proximal covoluted tubule (PCT)
loop of Henle
distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
collecting duct
microvasculature
nephrons have 2 arterioles and 2 capillary networks
blood enters glomerulus via afferent arteriole and leaves via efferent arteriole
high pressure glomerular capillaries:
filtration
low pressure peritubular capillaries:
reabsorption/secretion
renal corpuscle
made up of glomerulus (glomerular capillaries) and Bowman’s capsule
filters blood to form an initial filtrate
Bowman’s capsule appearance is like a double walled cup that surrounds glomerular capillaries
outer layer = parietal layer
simple squamous (structural)
inner layer = visceral layer
modified simple squamous (podocytes → filtration)
mesangiel cells provide support between glomerular capillary loops
arteriole at either end of glomerular capillary bed facilitates high pressure in glomerulus for filtration
filtration barrier
podocytes wrap around glomerular capillaries and their interlinked foot processes form filtration slits
filtration barrier formed by:
glomerular capillary endothelium: fenestrated
basement membrane: negatively charged
epithelial cells (podocytes): interdigitating foot processes and filtration slits
limits passage of substances from blood based on size, charge and shape
epithelia of nephron
after glomerular filtration, filtrate passes into Bowman’s capsule
flows along nephron tubule segments
tubule made up up of epithelial cells
epithelial layers adapted for functional role in different parts of nephrons
proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
tubule segment
unmodified filtrate leaves Bowman’s space and enters PCT
simple cuboidal cells with microvilli forming brush border to increase SA
approx 70% of water, sodium, chloride, AAs, glucose reabsorption
secretion of some drugs/waste molecules
loop of Henle: thin limbs
3 main parts with different characteristics:
thin descencing limbs
thin ascending limbs
thick ascending limbs
loop of Henle: thin descending limb
low permeability to ions
no active reabsorptiom or secretion of solutes
high permeable to water
simple squamous epithelium
loop of Henle: thin ascending limb
permeable to ions but essentially no active reabsorption or secretion of solutes (passive only)
completely impermeable to water
simple squamous epithelium with tight junctions
loop of Henle: thick ascending limb
highly permeable to ions: active reabsorption of sodium/other solutes
impermeable to water
simple cuboidal cells
the 3 sections of LOH function to generate hyperosmolar interstitial fluid in medulla (relative to plasma)
important in urine conc
distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
divided into early and late parts
simple cuboidal cells
highly permeable to ions/solutes: active reabsorption of sodium and other solutes
secretion of K+ and H+
variable water permeability depending on precise part of distal tubule and presence of ADH
early distal tubule passes back to vascular pole of its own renal corpuscle to form: juxtaglomerular apparatus
juxtaglomerular apparatus: JGA
3 components to JGA:
macula densa: specialised cells within part of early distal tubule that passes next to vascular pole of its own renal corpuscle
granular or juxtaglomerular cells in afferent arteriole
extraglomerular mesanglial cells (Lasic cells)
involved in tubuloglomerular feedback and control of BP
collecting duct
final site for urine processing
simple columnar cells
water permeability of medullary collecting duct under hormonal control by ADH
surrounded by a medullary interstitial fluid with a high conc of solutes
key role in regulating degree of urine concentration by controlling water reabsorption
body fluid homeostasis
maintaining a constant volume and stable composition of body fluids essential for homeostasis
including electrolute balance and BP regulation
requires precise matching of intake and output
some poorly regulated, insensible water losses
most water output is via kidneys (urine)
kidneys play major role in body fluid volume and composition regulation
ICF
male total body water: 42 litres (60% body weight)
varies with age, sex, body fat
ICF= 28 litres
distributed in different compartments separated by semi permeable cell membranes
composition of fluids varies between compartments (cells) as cell membrane is permeable to water but not to most electrolytes
ECF
14 litres
further divided into 2 main compartments
interstitial fluid (1.1 litres): surrounds cells
plasma (3 litres): non cellular component of blood
composition of plasma and ECF is similar due to equilibration across capillary membrane
capillary membrane highly permeable to water and electrolytes but not to most plasma proteins
body fluid composition
ECF:
sodium is main cation (+ve)
chloride is main anion (-ve)
ICF:
potassium is main cation
phosphate and organic anions are main anion
potassium is main osmotically active electrolyte
different compartments have different compositions but are in osmotic equilibrium
sodium is main osmotically active electrolyte
by regulating Na+, kidneys can directly regulate body fluid volume