Endocrine Lab Quiz
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
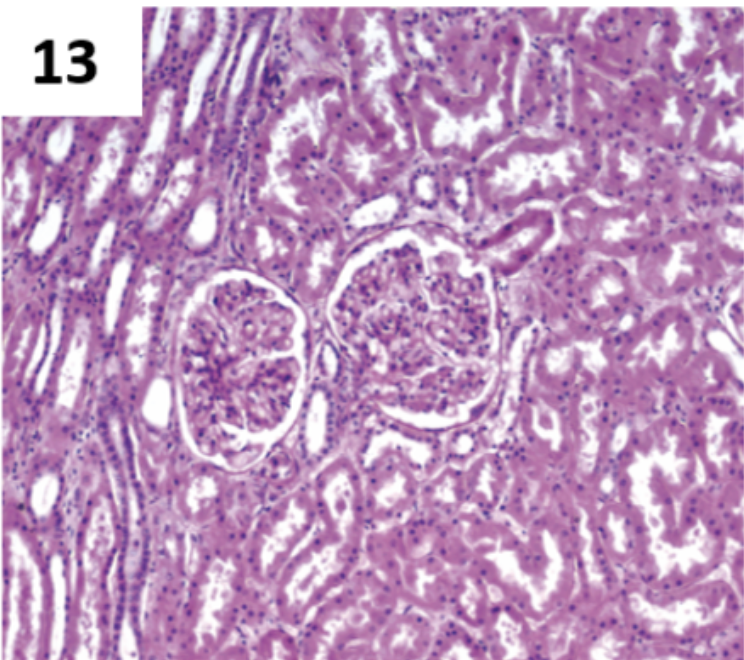
What gland is this?
Kidney
(tubules, nephron)
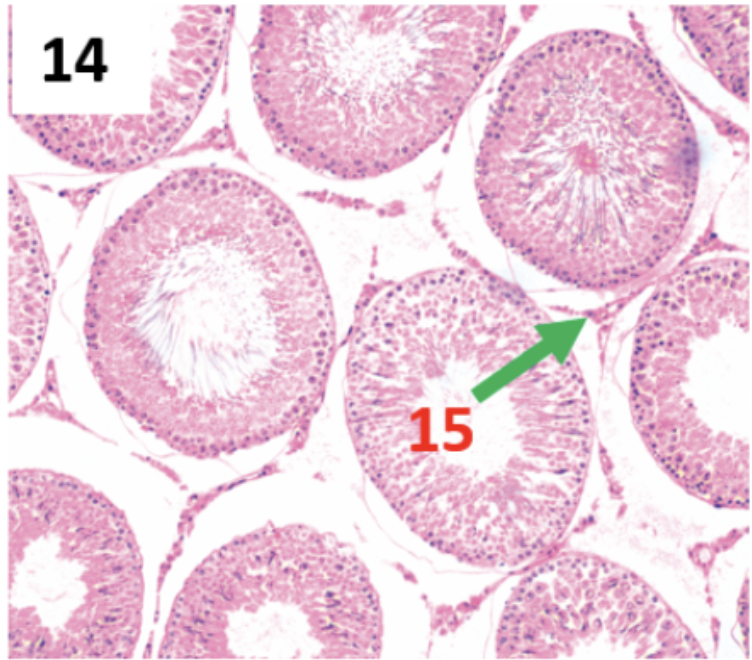
What gland is this?
Testes
Interstial Cells (LEYDIG cells)
What gland is this?
Adrenal Cortex
Adrenal Medulla
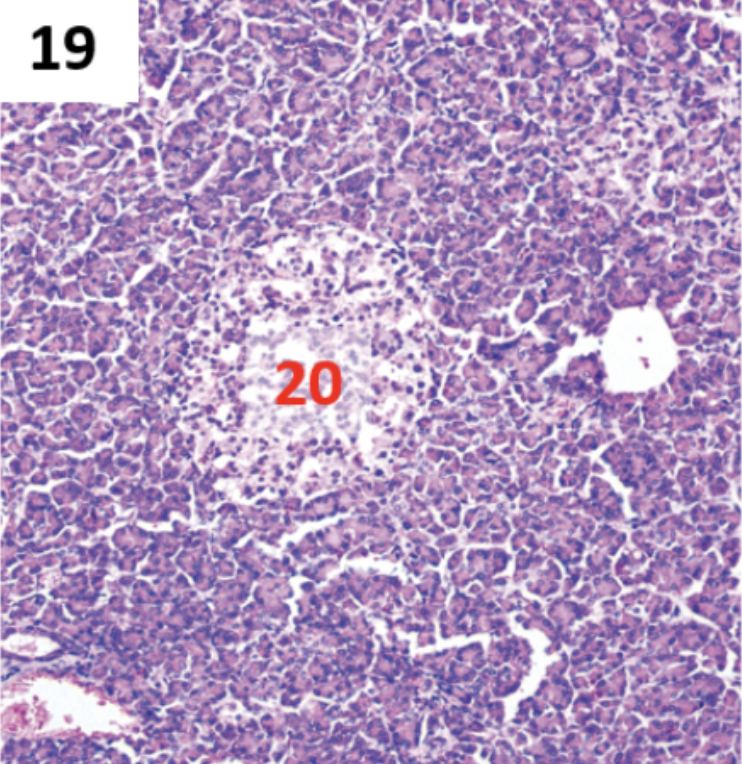
What gland is this?
Thymic Lubules (each lobes)
Thymus Cortex (outside)
Thymus Medulla (inside — white circle)
What gland is this?
Pancreas
Eyelets of Langerhans
Langerhans
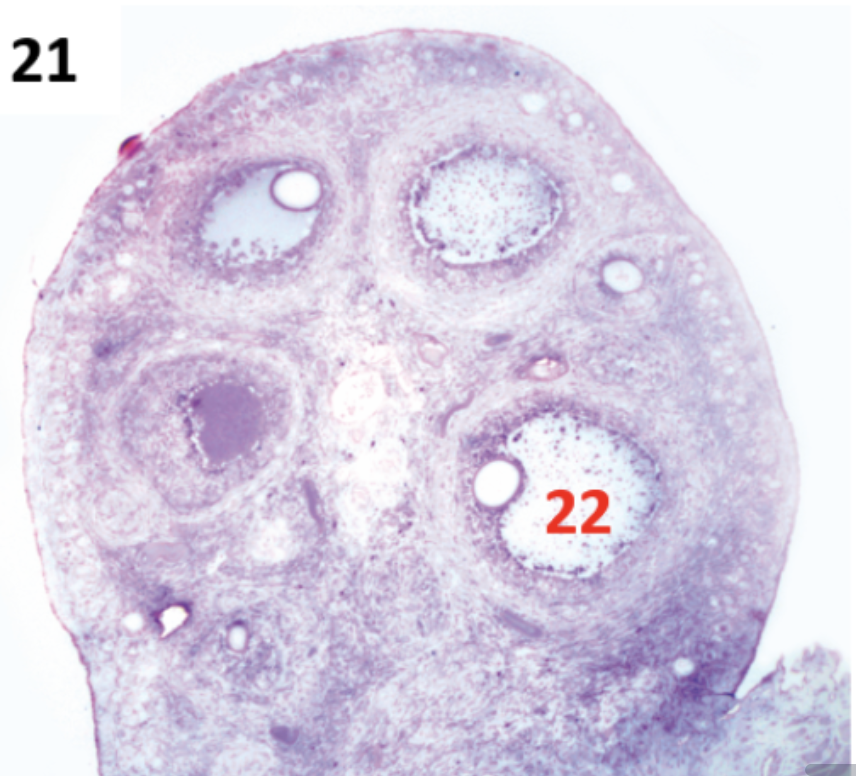
Ovary
Ovarian follicle
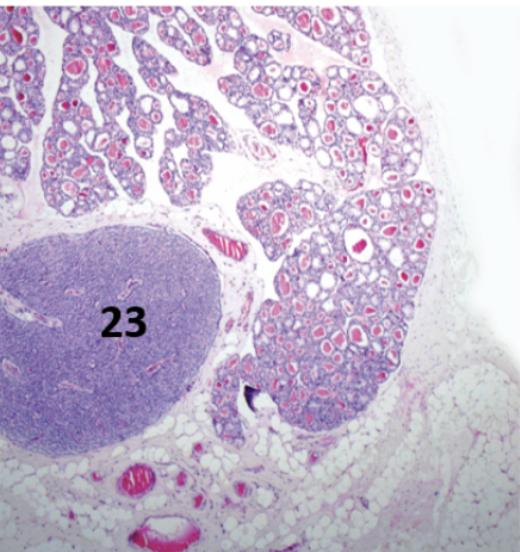
Top. Thyroid
Parathyroid
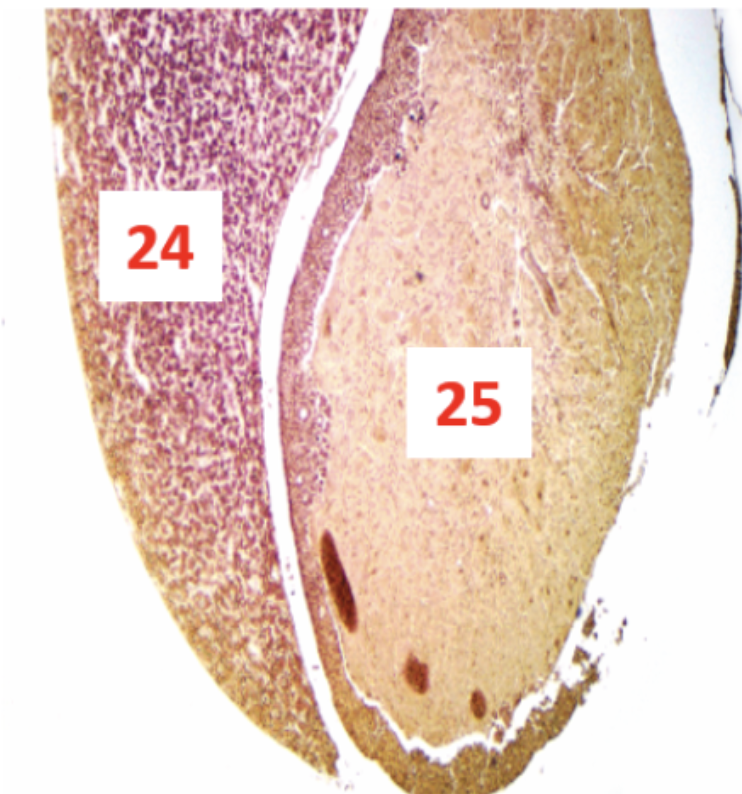
What gland is this?
Anterior Pituitary Gland (Pars Distalis)
Posterior Pituitary Gland (Pars Nervosa)
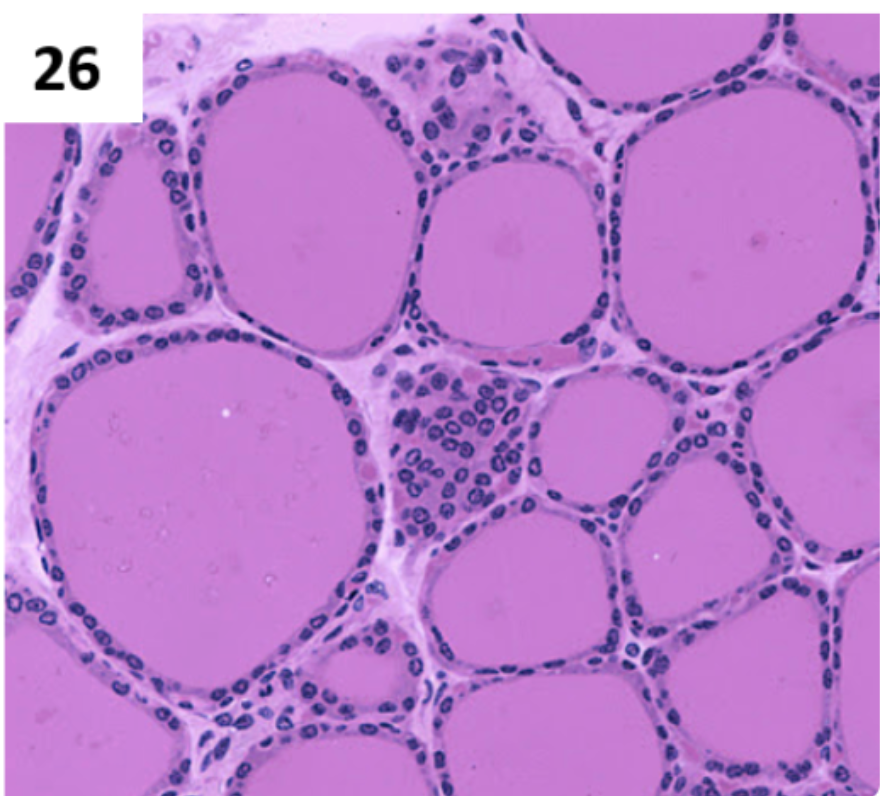
What gland is this?
Thyroid Follicle (big circle) — releases thyroglobulin
Follicular Cells (small purple circles around big circle)
Parafollicular Cells (big clump of tiny purple circles)
What picture is this?
Melatonin
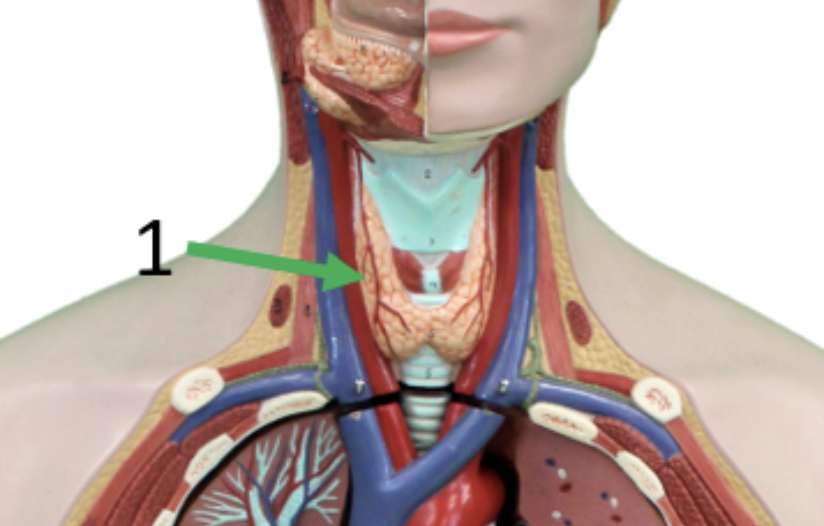
Gland?
Hormone?
Function
Target TIssue
Thyroid
Thyroxine (T3,T4), Calcitonin
Regulate Basal Metabolic Rate, inhibits osteoclast
All cells in the body, bones
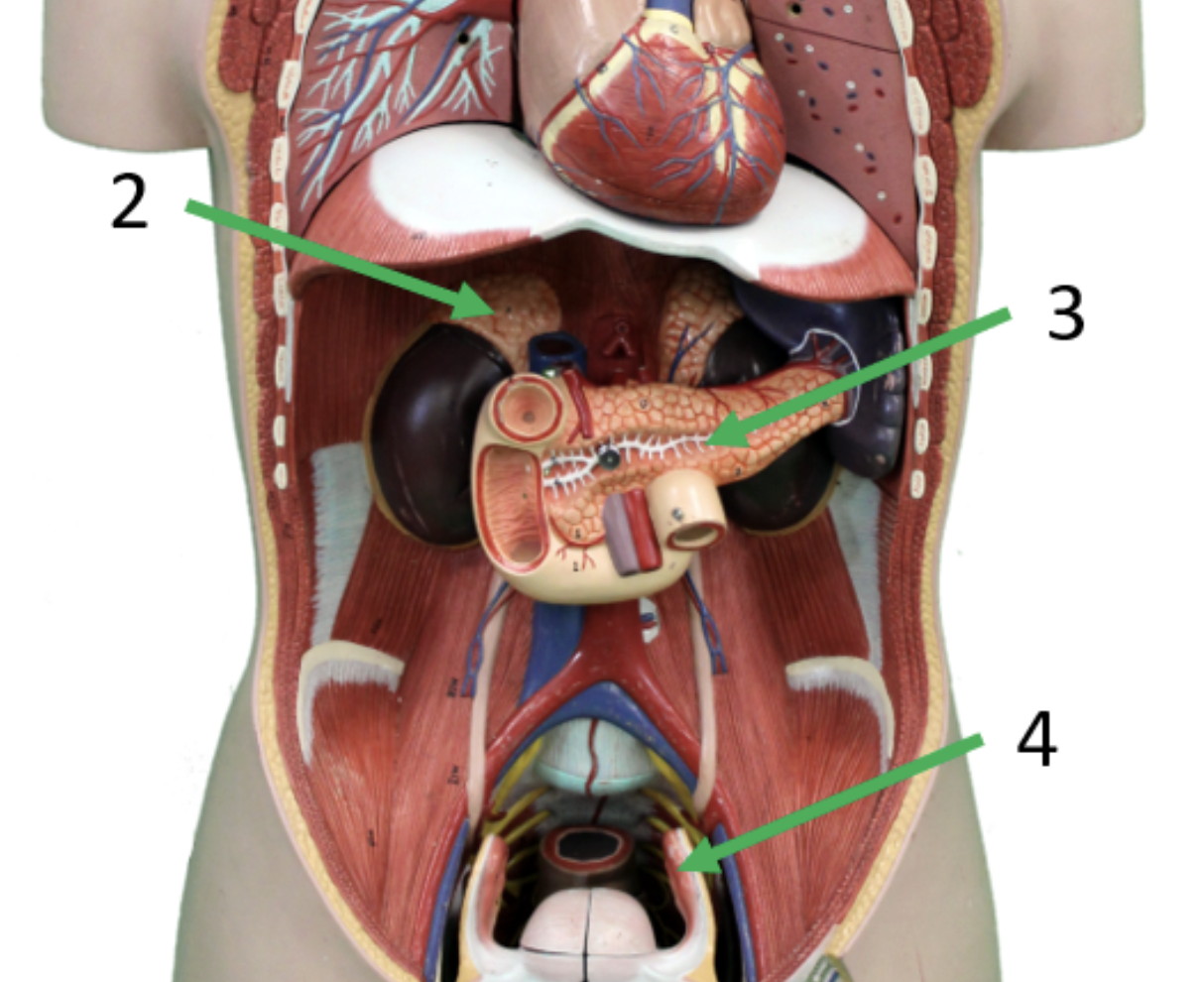
Describe gland #2
Gland
Hormone
Function
Target Tissue
Adrenal Gland
Adrenal Cortex: Aldosterone Cortisol, Androgens —— Adrenal Medulla: Epinephrine, Norepinephrine
Stimulate body’s fight or flight response, surppress inflammation
liver, muscle, fat, kidneys, heart, blood vessels, liver, adipose tissue
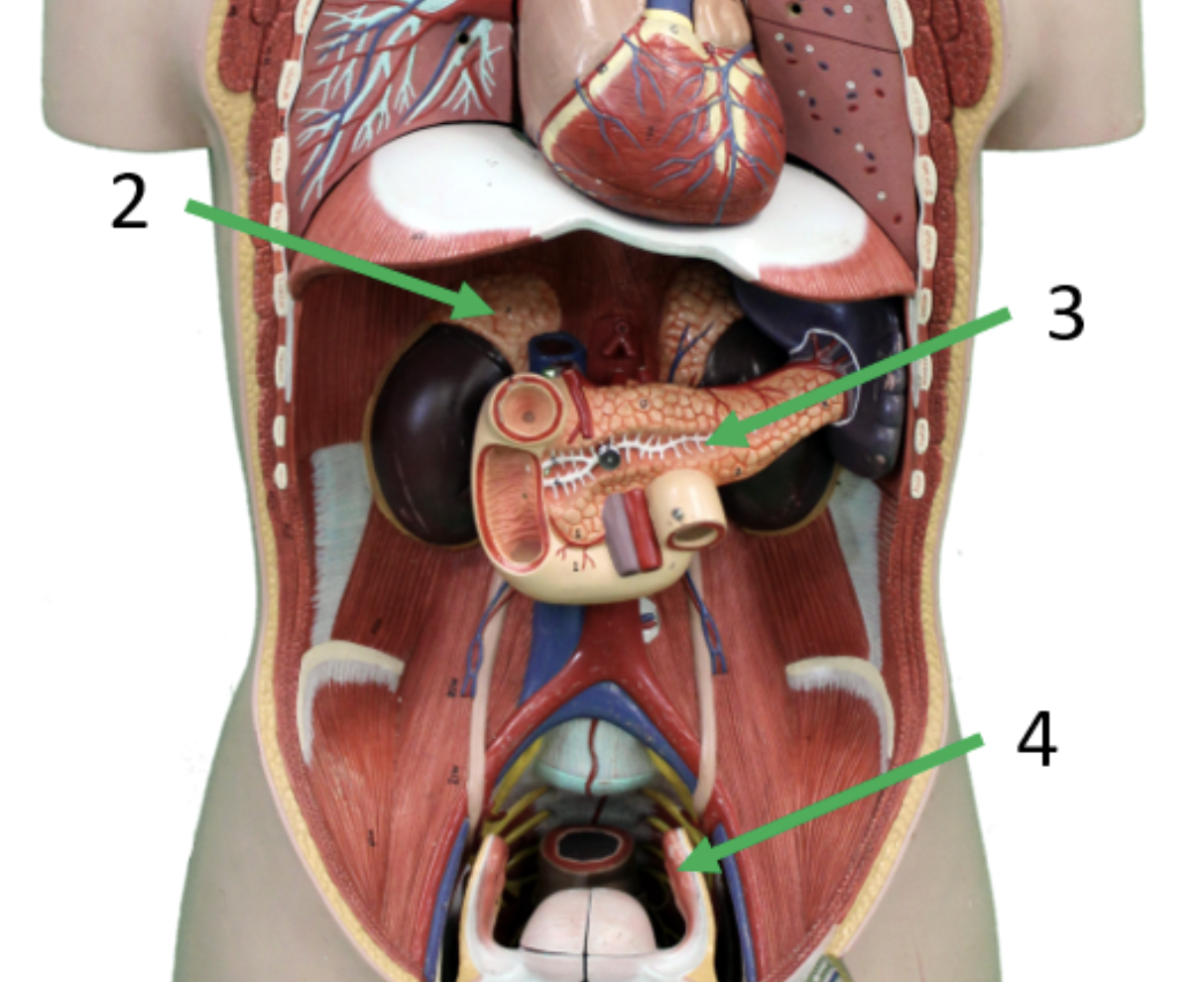
Describe gland #3
Gland
Hormone
Function
Target Tissue
Pancreas
Insulin, Glucagon
Regulates glucose levels in the blood
Insulin lowers blood sugar levels— Glucagon raises blood sugar levels
Liver, muscle, adipose tissue,
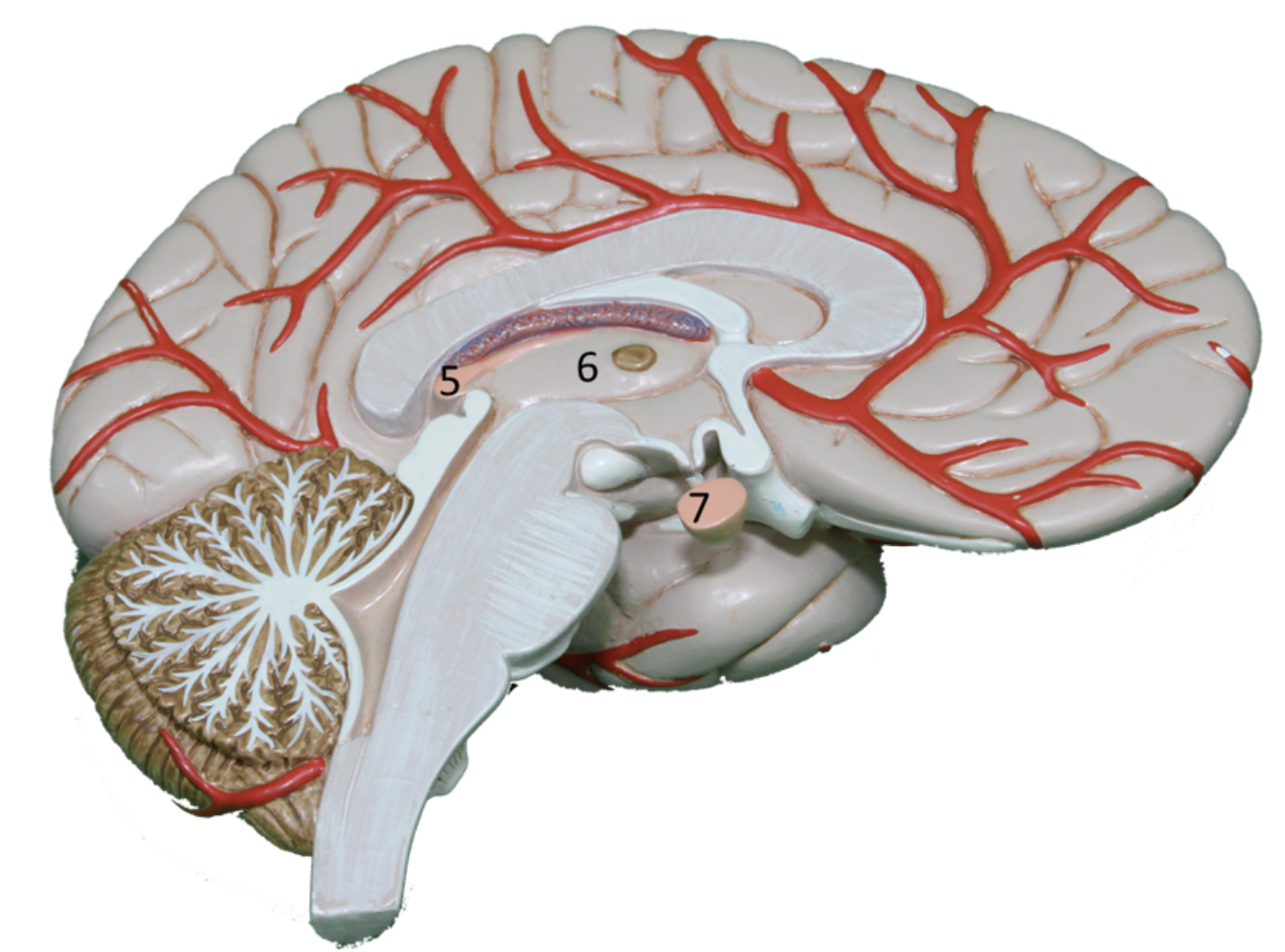
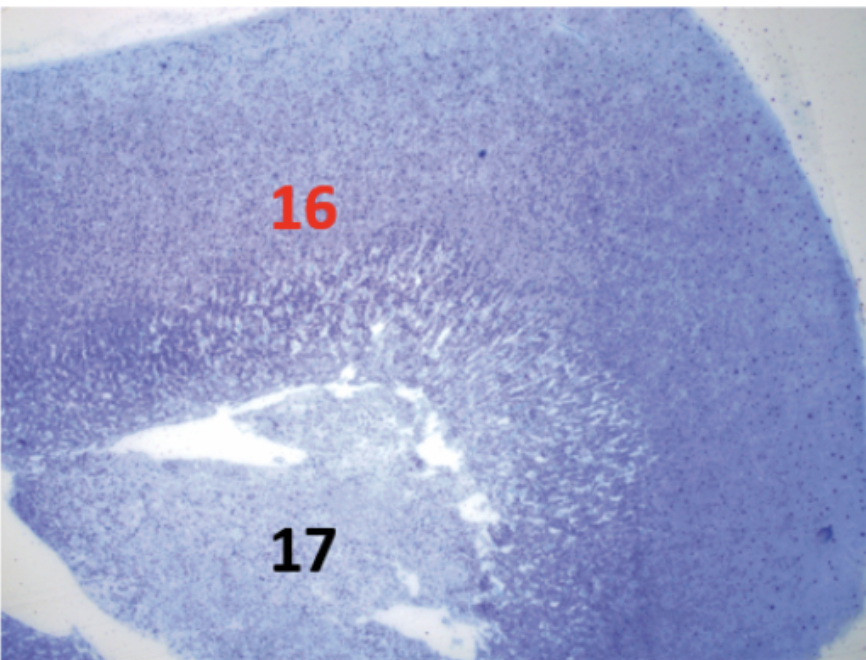
Describe gland #5
Gland
Hormone
Function
Target Tissue
Pineal
Melatonin
Regulates circadian rhythm or sleep-wake cycle)
Brain region; Hypothalamus, Pituitary, Liver, Gonads, Pancreas
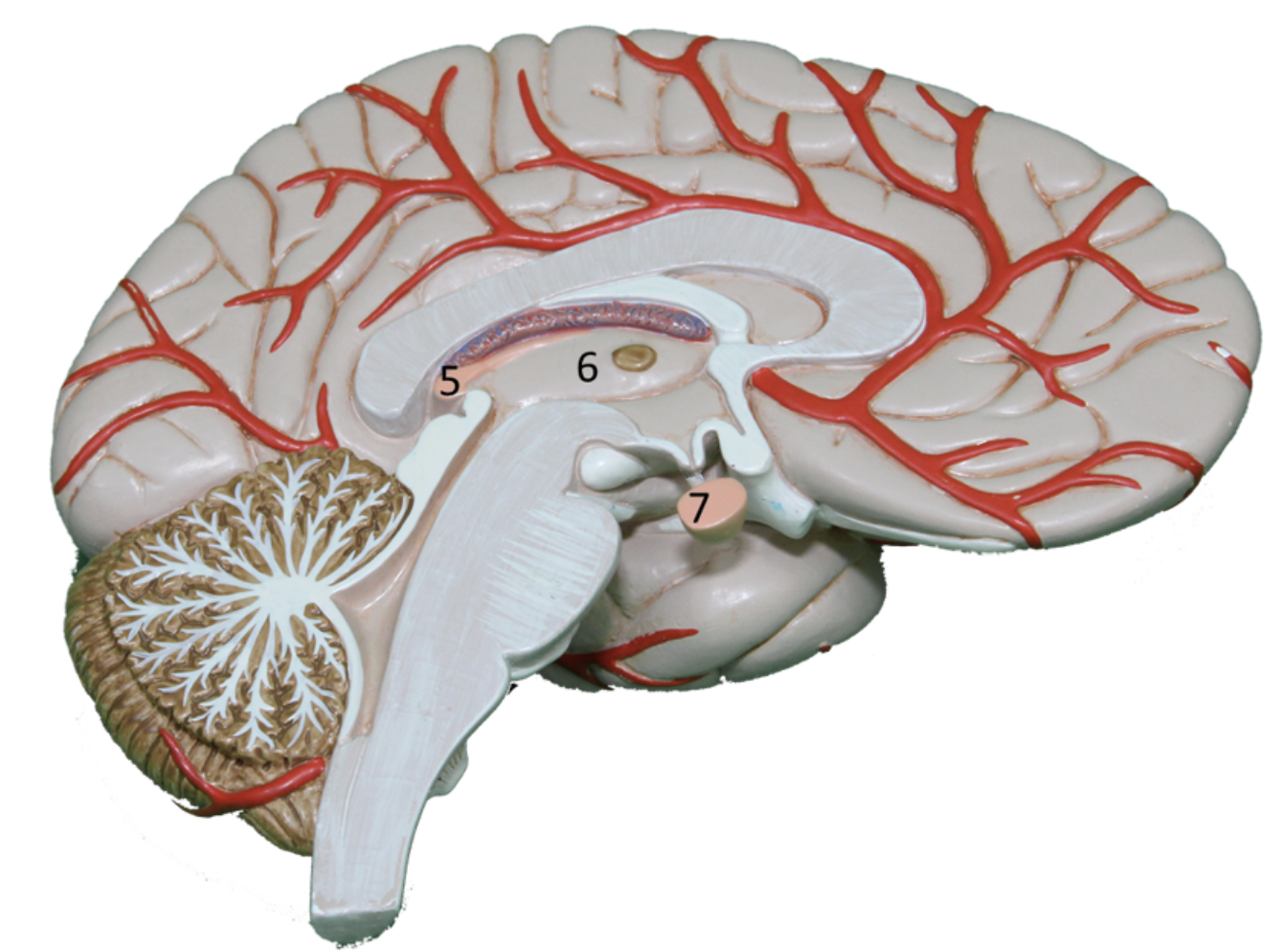
Describe gland #6
Gland
Hormone and Function
Target Tissue
Hypothalamus
Secretes releasing hormones to control Anterior Pituitary gland and to generate nerve impulses to control Posterior Pituitary gland.
Anterior Pituitary, Posterior Pituitary (storage)
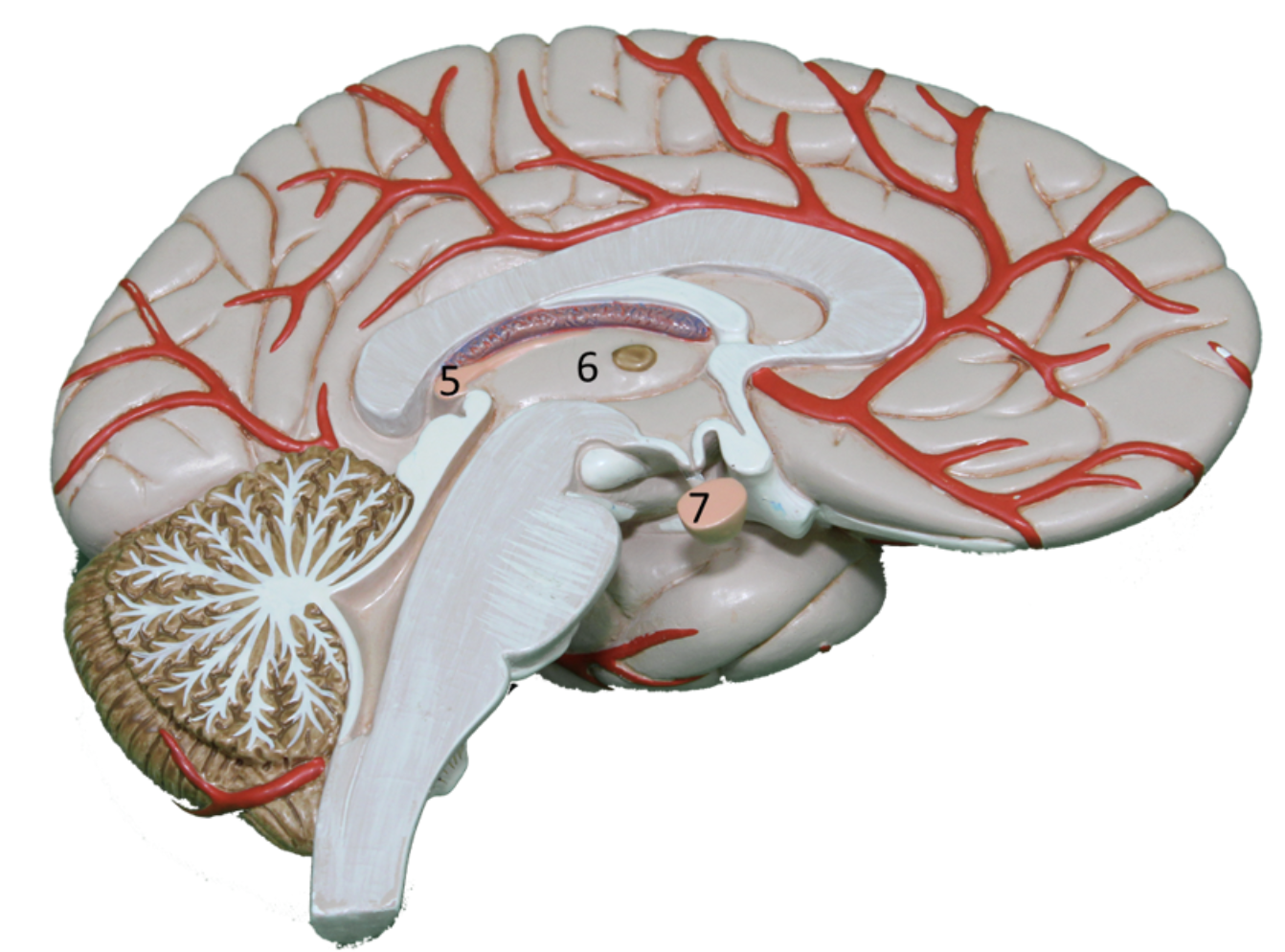
Describe gland #7
Gland
Hormone
Function
Target Tissue
1. Pituitary Gland
2. Anterior Pituitary Gland: (FLAT PEG)
Follicle (FSH)
Luteinizing (LH)
Adrenocorticotropin (ACTH)
Thyroid (TSH)
Prolactin
Melanocyte (MSH)
Growth Hormone (hGH):
Posterior Pituitary Gland:
Anti Diuretic Hormone (ADH)/ Vasopressin
Oxytocin
“MASTER GLAND”; producing hormones that control vital functions like growth, metabolism, reproduction, and stress response
Thyroid, Adrenals, Gonads, Kidneys, Liver, Adipose tissue
Anterior Pituitary Gland Hormones
Anterior Pituitary Gland: (FLAT PEG)
Follicle (FSH): Pubertal development; females=stimulates growth of ovarian follicle (egg production) ; males=stimulate sperm production (spermatogenesis)
Luteinizing (LH): work with FSH to regulate reproductive function; females; triggers ovulation, form corpus luteum producing progesterone; males=stimulates leydig cells in the testes to produce testosterone
Adrenocorticotropin (ACTH): “stress hormone” stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce and release cortisol; regulates metabolism, BP, and immune response to stress.
Thyroid (TSH): stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones regulate the body's metabolic rate, heart function, muscle control, and brain development.
Prolactin: primarily acts on the mammary glands to stimulate milk production (lactation) after childbirth. It also plays a role in regulating reproductive functions and immune system function.
Melatonin: regulates the sleep-wake cycle (circadian rhythm); its production increases in the evening to promote sleep.
Growth Hormone (hGH): critical for stimulating growth, cell reproduction, and regeneration in children. In adults, it plays a key role in metabolism, body composition, and tissue repair.
Posterior Pituitary Hormones
Anti Diuretic Hormone (ADH)/ Vasopressin: regulate water balance, blood pressure, and sodium levels
Oxytocin: essential for social bonding, reproduction, childbirth, and lactation
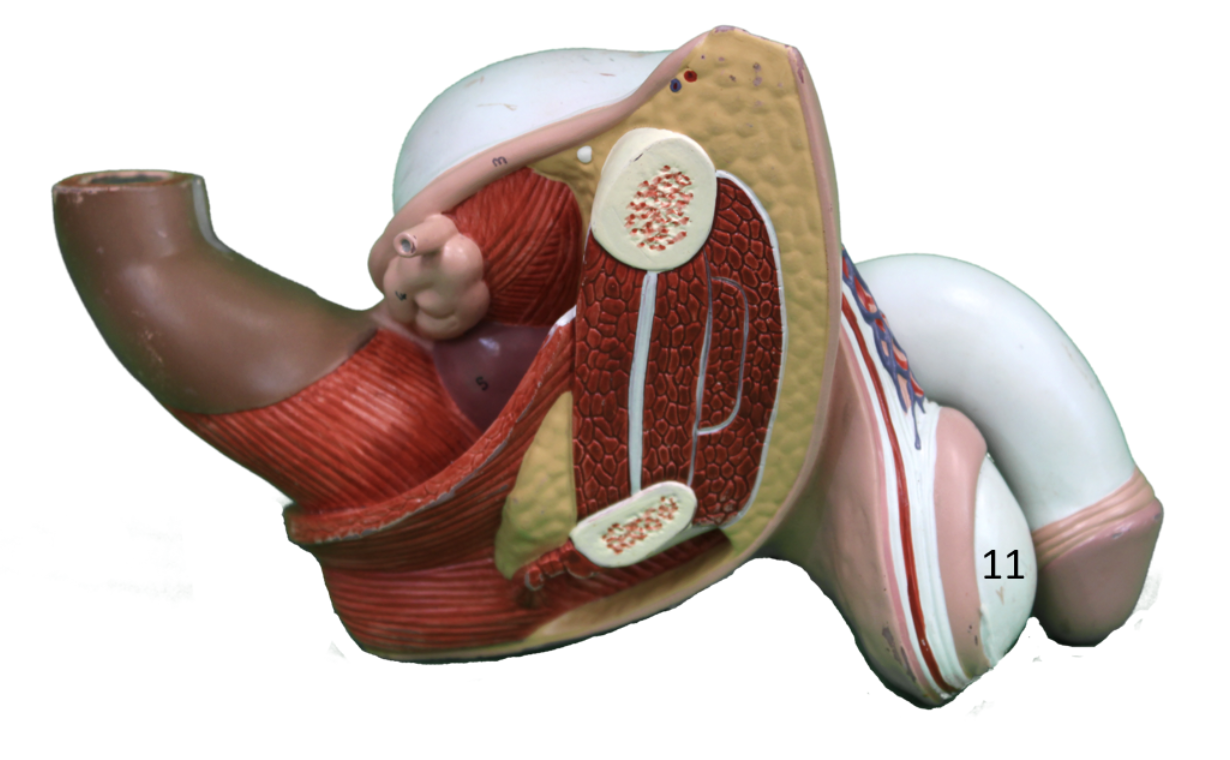
Describe gland #11
Gland
Hormone
Function
Target Tissue
Testes
Testosterone
sperm production; drives male characteristics (voice, muscle, hair)
Prostate gland, seminal vesicles, epididymis, and scrotum.
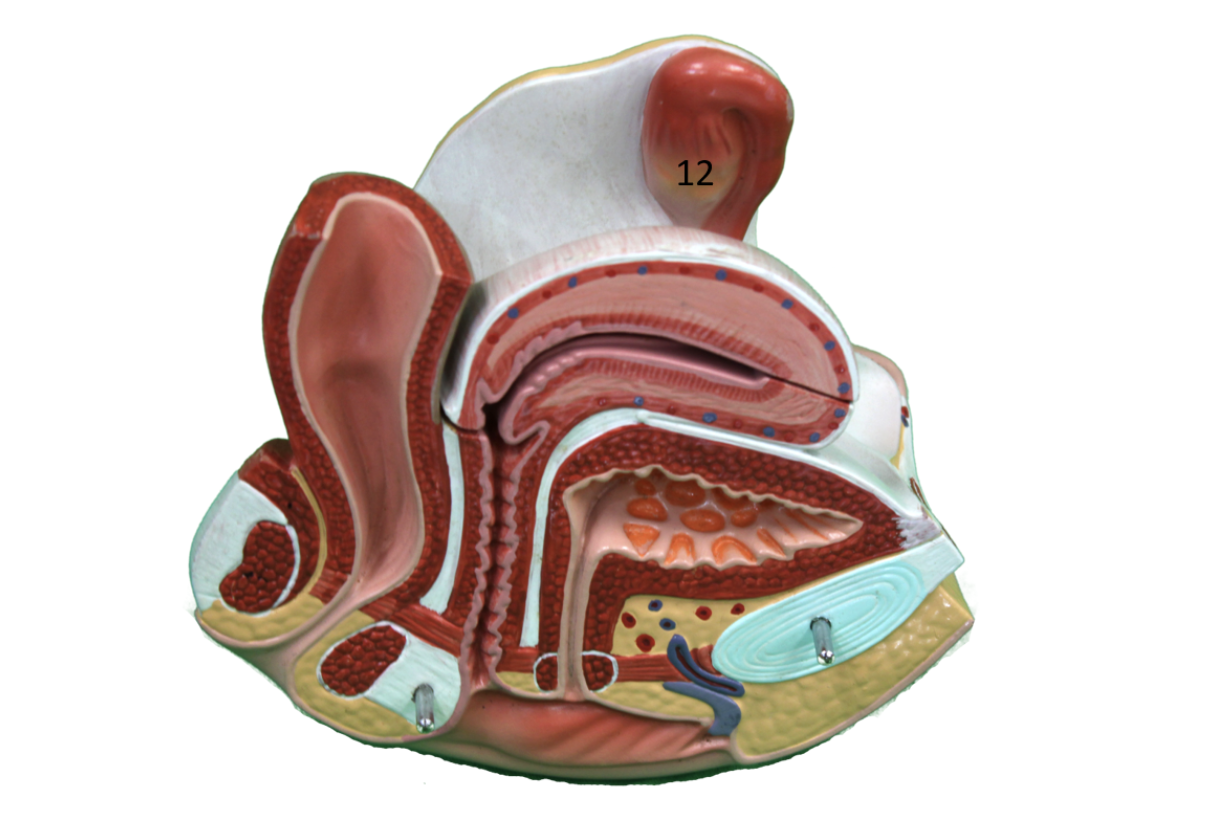
Describe gland #12
Gland
Hormone
Function
Function
Target Tissue
Ovary
Progesterone, Estrogen
Progesterone: Peaks after ovulation (luteal phase) to thicken the uterine lining, making it rich in nutrients for implantation.
Estrogen: Rises in the first half (follicular phase) to rebuild the uterine lining (endometrium) after menstruation and trigger ovulation.
Uterus, Mammary gland, brain
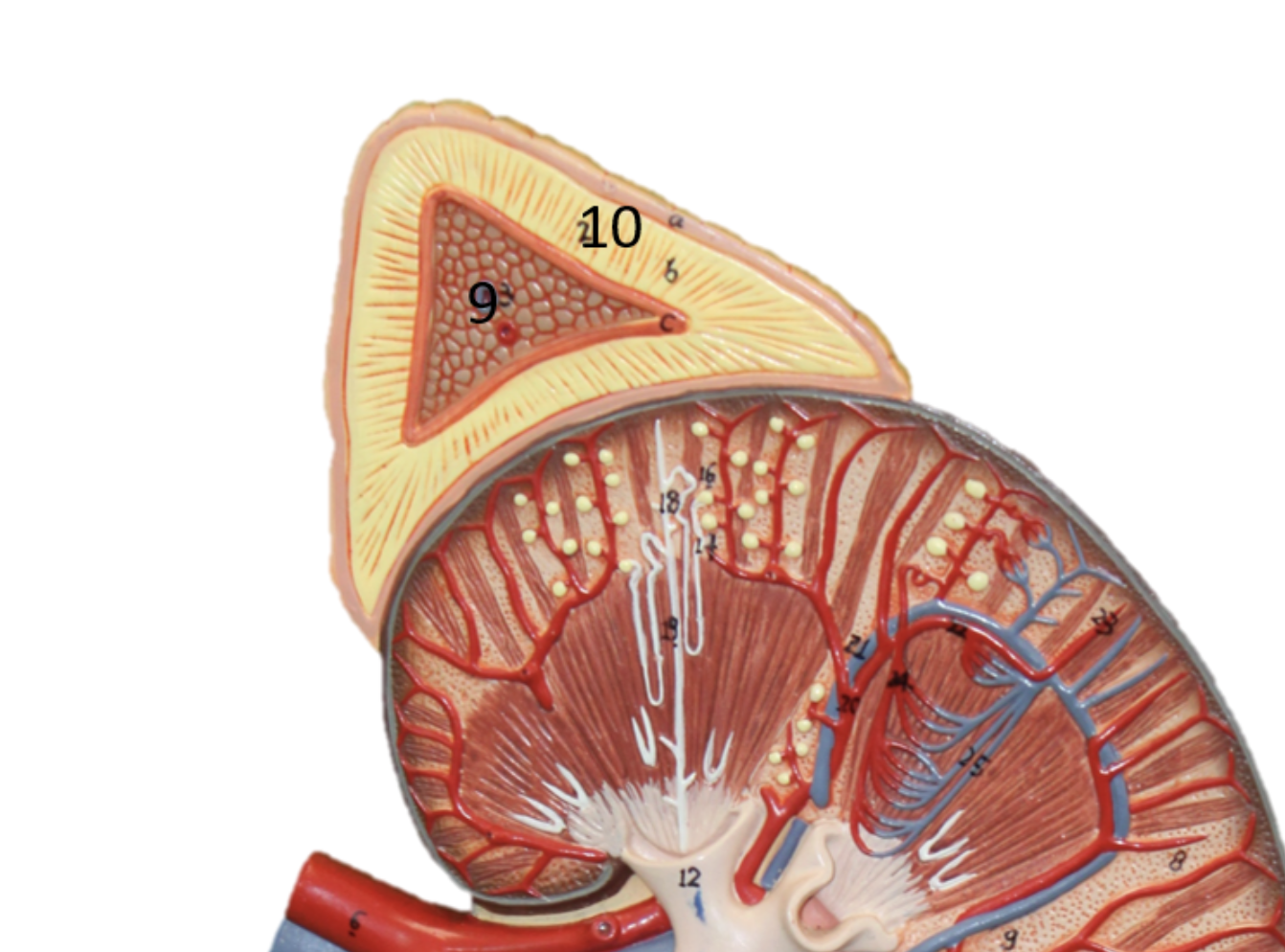
Describe gland #10
Gland
Hormone
Function
Target Tissue
Adrenal Cortex
Aldosterone, Cortisol, Androgen
Regulates salt and water balance, suppress inflammation and depress function of immune system, stimulate sex characteristics of both females and males)
Kidney, muscles, liver, WBC, fat tissue, reproductive organs
3 layers of Adrenal Cortex
Zona Glomerulosa: Aldosterone
Zona Fasciculata: Cortisol, Cortisone
Zona Reticularis: Androgen (Testosterone, estrogen)
GFR (Girl be FR)
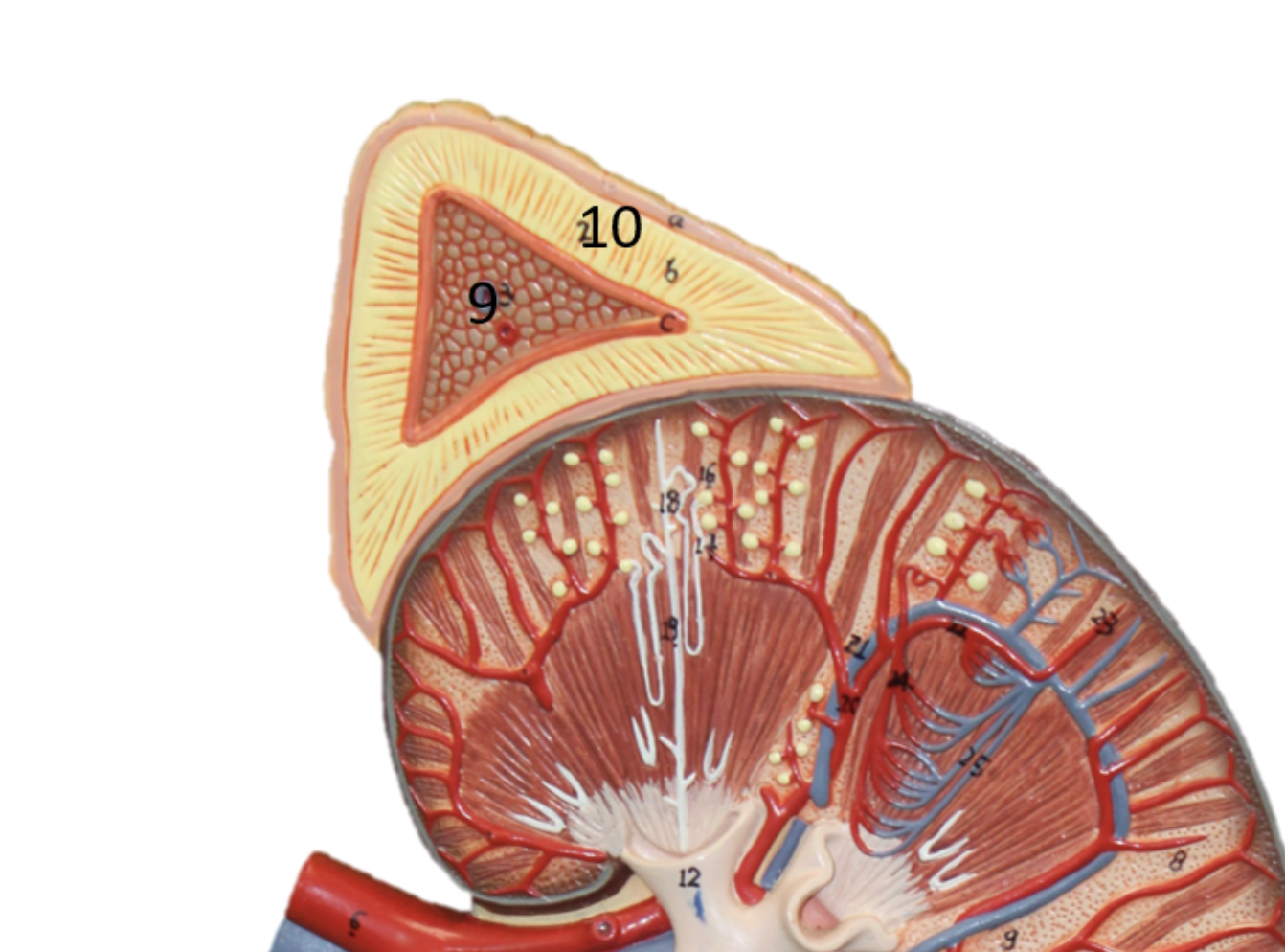
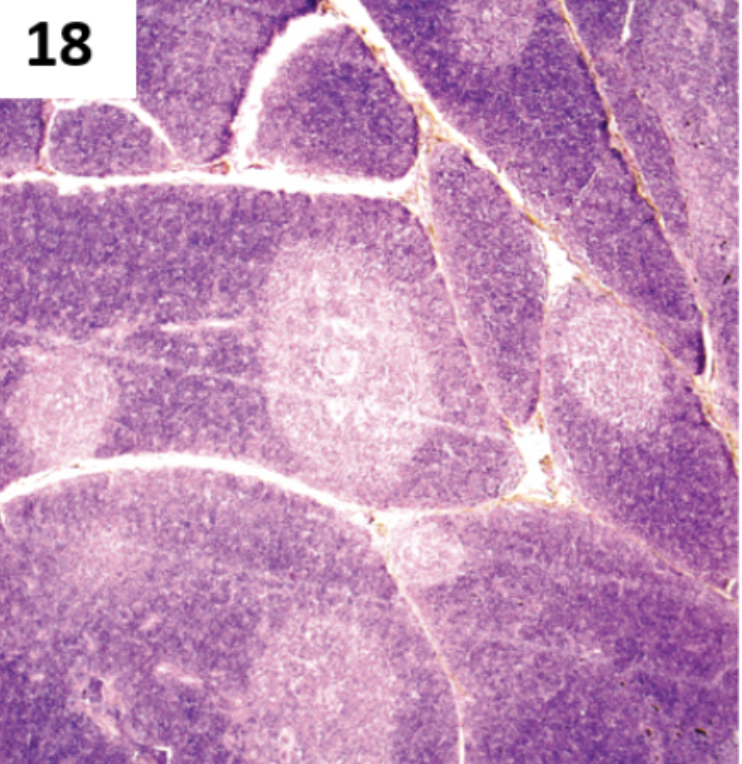
Describe gland #9
Gland
Hormone
Function
Target Tissue
Adrenal Medulla
Epinephrine, Norepinephrine (ADRENALINE)
Stimulates the body’s fight or flight response
heart, blood vessels, lungs, liver, eyes, adipose tissue, digestive and urinary system
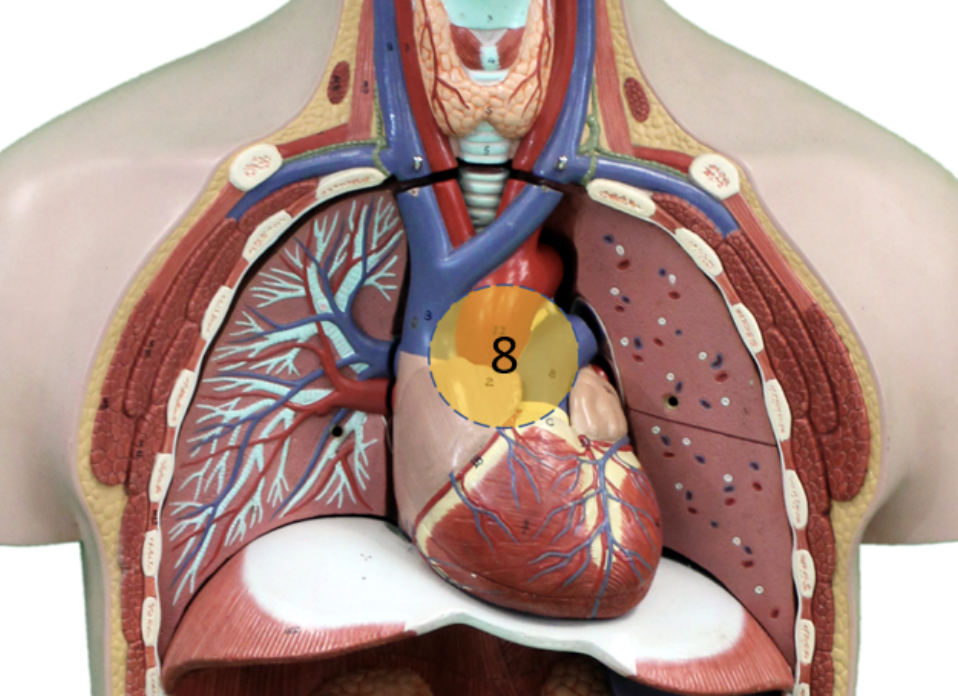
Describe gland #8
Gland
Hormone
Function
Target Tissue
Thymus
Thymosin
Stimulates maturation of white blood cells (WBC), regulate immunocompetence of WBC.
WBC
Kidney
Hormone
Function
Erythropoietin
regulates red blood cell (RBC) production in the bone marrow in response to low oxygen levels (hypoxia)