AP Psych Unit One Test (module 1-8)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:05 PM on 9/29/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
1
New cards
1. Socrates Plato
- mind/body seperate
- mind continue after death
- knowledge is innate (born within)
2. Aristotle
- knowledge comes from observation
- knowledge isn't innate
- you need data
- mind/body seperate
- mind continue after death
- knowledge is innate (born within)
2. Aristotle
- knowledge comes from observation
- knowledge isn't innate
- you need data
Early Philosopher (Greeks)
2
New cards
1. Renee Decartes
- proved that fluid in brain flows from nerve to muscle, causing movement
- dissected animals
- proved that fluid in brain flows from nerve to muscle, causing movement
- dissected animals
Early Philosophers (French)
3
New cards
1. John Locke
- mind is blank slate at birth (TABULA RASA)
2. Francis Bacon
- founder of modern science
- founded empiricism
- mind is blank slate at birth (TABULA RASA)
2. Francis Bacon
- founder of modern science
- founded empiricism
Early Philosophers (British)
4
New cards
knowledge comes from experience
*francis bacon
*francis bacon
Empiricism
5
New cards
- father of psychology
- created first psych lab (set apart psych for philosophy)
- experiment: 2 dif trials, subjects told to press the key when hearing sound of ball drop
- created first psych lab (set apart psych for philosophy)
- experiment: 2 dif trials, subjects told to press the key when hearing sound of ball drop
William Wundt
6
New cards
- Wundt's student
- STRUCTURALISM
- INTROSPECTION
- STRUCTURALISM
- INTROSPECTION
Edward Titchener
7
New cards
studying elements of mind
Structuralism
8
New cards
A method of self-observation in which participants report their thoughts and feelings
- what you think abt your own mental processes
- unreliable
- what you think abt your own mental processes
- unreliable
Introspection
9
New cards
- NATURAL SELECTION (traits that give advantage are selected natural for next generations)
- influenced william james
- influenced william james
Charles Darwin
10
New cards
- FUNCTIONALISM
- introduced principles of psych
- introduced principles of psych
William James
11
New cards
structures of consciousness must have a function
- everything has purpose
- nose smells, but why?
- everything has purpose
- nose smells, but why?
Functionalism
12
New cards
- memory researcher
- denied psych PhD bc #sexism
- first female president of APA
- denied psych PhD bc #sexism
- first female president of APA
Mary Whiton Calkins
13
New cards
- first female to get phD in psych
- book: Animal Mind
- book: Animal Mind
Maragaret Floy Washburn
14
New cards
- psych should be objective science
- only study what u can see, not unseen mental processes
- only study what u can see, not unseen mental processes
Behaviorism
15
New cards
1. B.F Skinner
- worked w animals
- organisms repeat positive outcomes
- #BFFR, BFB (bffr, B.F Behaviorist)
2. John B. Watson
- little Albert study
- psych only deals with observable events (rejected introspection)
- worked w animals
- organisms repeat positive outcomes
- #BFFR, BFB (bffr, B.F Behaviorist)
2. John B. Watson
- little Albert study
- psych only deals with observable events (rejected introspection)
Behaviorists
16
New cards
*Unconscious effects behavior
- developed PSYCHOANALYSIS
- developed PSYCHOANALYSIS
Sigmund Freud
17
New cards
- unconscious/childhood experiences affect behavior and mental processes
- opposing behavioralism
- opposing behavioralism
Psychoanalysis/Freudian Psychology
18
New cards
- humans strive to reach full potential
- personal growth
- "third force" in psych
- personal growth
- "third force" in psych
Humanistic Psychology
19
New cards
Controversy about if genes or experiences make psychological traits (twin studies)
1. Nature
- behaviors/mental processes happen bc innate, bc you're born with it
- socrates plato, rene decartes, charles darwin
2. Nurture
- behaviors/mental processes happen bc experience and environment
- aristotle, john locke
1. Nature
- behaviors/mental processes happen bc innate, bc you're born with it
- socrates plato, rene decartes, charles darwin
2. Nurture
- behaviors/mental processes happen bc experience and environment
- aristotle, john locke
Nature vs Nurture
20
New cards
emotions, dreams, disorders, age of first step, remembering
Gender Differences
21
New cards
- study of human thriving (#thrivingnvibing)
- goal: find out human strengths & strengthen ppl
- goal: find out human strengths & strengthen ppl
Postivie Psychology
22
New cards
*understanding behavior/mental processes from 3 main keypoints:
1. Behavioral Perspective
- how observed behaviors impact mental processes
2. Biological Perspective
- how biological/physiological processes impact mental processes
- genes, hormones, hand sweating
3. Cognitive Perspective
- how interpretations of situations impact mental processes
- thoughts, memories, problem solving
1. Behavioral Perspective
- how observed behaviors impact mental processes
2. Biological Perspective
- how biological/physiological processes impact mental processes
- genes, hormones, hand sweating
3. Cognitive Perspective
- how interpretations of situations impact mental processes
- thoughts, memories, problem solving
Biopsychosocial Approach
23
New cards
study of mental processes (thinking, learning, remembering)
Cognitive Psychology
24
New cards
study of brain activity linked with mental processes
- how mind processes/retains info
- how mind processes/retains info
Cognitive Neuroscience
25
New cards
how natural selection helps survival of genes
Evolutionary Perspective
26
New cards
how drive for personal growth impacts behavior/mental processes
Humanistic Perspective
27
New cards
how unconscious drives/conflicts behavior and mental processes
Psychodynamic Perspective
28
New cards
how behavior/thinking vary across situations and cultures
Social-Cultural Perspective
29
New cards
Survey, Question, Read, Retrieve, Review
- testing effect: better memory after retrieving, instead of just re-reading
- testing effect: better memory after retrieving, instead of just re-reading
SQ3R Method
30
New cards
Basic
- aims to increase psychology's knowledge
Applied
- uses psych to solve real world problems
- aims to increase psychology's knowledge
Applied
- uses psych to solve real world problems
Basic vs. Applied Psychology
31
New cards
Clinical
- treats disorders
- PhD
- therapy and conseling
Psychiatrist
- MD
- prescribes drugs
- treats disorders
- PhD
- therapy and conseling
Psychiatrist
- MD
- prescribes drugs
Clinical Psychologists vs Psychiatrists
32
New cards
believing you would've known, after finding out the outcome
Hindsight Bias
33
New cards
thinking we know more than we do #gaslightingmyself
Overconfidence
34
New cards
thinking you see a pattern just to make sense of it
Perceiving patterns in random events
35
New cards
1. Curiosity (wanna find truth)
2. Skepticism (keeping us from accepting ideas w/o proof)
3. Humility (admitting when wrong when proven by facts)
2. Skepticism (keeping us from accepting ideas w/o proof)
3. Humility (admitting when wrong when proven by facts)
3 Elements of Scientific Attitude
36
New cards
theory, hypothesis, testing, interpreting results
Scientific Method
37
New cards
idea that organizes observation
Theory
38
New cards
testable prediction that's implied by theory
Hypothesis
39
New cards
exact procedures in study (important to REPLICATE)
Operational Definition
40
New cards
doing procedures again (replication = confirmation)
Replication
41
New cards
1. case studies
2. naturalistic observations
3. survey
2. naturalistic observations
3. survey
Descriptive Methods
42
New cards
individual/group studied in depth to find out something new
PROS
- lots of quantitive data
- gives direction for further study
CONS
- can't always be generalized
PROS
- lots of quantitive data
- gives direction for further study
CONS
- can't always be generalized
Case Study
43
New cards
observing behavior in natural setting
(watching animals in jungle)
PROS
- subjects more "normal" outside lab
- data collecting doesn't disturb subjects
CONS
- independent variable not isolated
- observations from researcher are subjective
(watching animals in jungle)
PROS
- subjects more "normal" outside lab
- data collecting doesn't disturb subjects
CONS
- independent variable not isolated
- observations from researcher are subjective
Naturalistic Observation
44
New cards
self reported behaviors
PROS
- glance at people's observations
CONS
- opinions not always true, can scew outcome
PROS
- glance at people's observations
CONS
- opinions not always true, can scew outcome
Survey
45
New cards
flaw in sampling that makes it not representable
Sampling Bias
46
New cards
sample that represents population because subjects have equal chance of inclusion (aka RANDOM)
Representative Sample
47
New cards
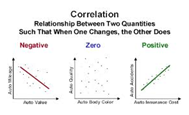
A relationship between two things
*NOT CAUSATION*
*NOT CAUSATION*
Correlation
48
New cards
two variables increase/decrease together
(people who eat more food for breakfast (rise), have more energy (rise))
(people who eat more food for breakfast (rise), have more energy (rise))
Positive Correlation
49
New cards
two variables where one increases, other decreases
(as we get older (rise), we sleep less (fall))
(as we get older (rise), we sleep less (fall))
Negative Correlation
50
New cards
statical index of relationship between variables
(shows how strongly they correlate)
r = correlation
- the closer r is to -1 or +1, the stronger the correlation
- (-) and (+) just mean if it's a negative or positive correlation: -0.70 is a stronger correlation than +0.28
(shows how strongly they correlate)
r = correlation
- the closer r is to -1 or +1, the stronger the correlation
- (-) and (+) just mean if it's a negative or positive correlation: -0.70 is a stronger correlation than +0.28
Correlation Coefficient

51
New cards
represents values of two variables
- slope shows that positive or negative correlation
- the closer the "scatter"/dots are to the line, the stronger the correltion
- slope shows that positive or negative correlation
- the closer the "scatter"/dots are to the line, the stronger the correltion
Scatterplot
52
New cards
thinking there's a correlation, when there really isn't/isn't proof there is
(wearing "lucky" jersey means team wins)
(wearing "lucky" jersey means team wins)
Illusory Correlation
53
New cards
when the first measurement is extreme (super high or super low), and the second measurement is closer to the mean (goes back down to the average)
Ex: doing horrible first apush test, then slowly getting to class average
Ex: doing horrible first apush test, then slowly getting to class average
Regression to the Mean
54
New cards
1. manipulate other factors
2. hold control group (don't emphasize independent variable on them)
2. hold control group (don't emphasize independent variable on them)
Establishing Cause & Effect
55
New cards
assignment participants to groups by chance to minimize preexisting differences between two groups
- helps eliminate confounding variable
- helps eliminate confounding variable
Random Assignment
56
New cards
experiment when participants don't know abt treatment
- controls subject bias
- controls subject bias
Single Blind
57
New cards
experiment when participants and researchers don't know who gets treatment
- controls subject and experimenter bias
- controls subject and experimenter bias
Double Blind
58
New cards
experimental results caused by expectations alone
- subjects think they're getting something, so act like that even though they really aren't
- placebo = inert treatment (pill w/o med in it)
- decaf coffee, fake mood drugs
- subjects think they're getting something, so act like that even though they really aren't
- placebo = inert treatment (pill w/o med in it)
- decaf coffee, fake mood drugs
Placebo Effect
59
New cards
an unstated factor that influences results
(random assignment helps prevent this)
(random assignment helps prevent this)
Confounding Variable
60
New cards
how much an experiment predicts what it's supposed to
Experimental Validity
61
New cards
statistics that summarize the data collected in a study
Descriptive Statistics
62
New cards
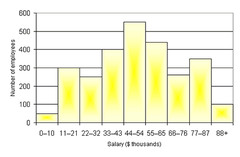
bar graph that shows frequency distribution
- how often something occurs
- how often something occurs
Histogram
63
New cards
where data centrals around (main data points)
1. MEAN
- Average. add #'s, divide by number of #'s
2. MEDIAN
- Middle score. put #'s in order from high to low, then find middle
3. MODE
- Most frequent. find most popular number, can be multiple or none
*MEAN NOT ALWAYS BEST bc super high/low numbers can skew mean higher or lower*
*median better
1. MEAN
- Average. add #'s, divide by number of #'s
2. MEDIAN
- Middle score. put #'s in order from high to low, then find middle
3. MODE
- Most frequent. find most popular number, can be multiple or none
*MEAN NOT ALWAYS BEST bc super high/low numbers can skew mean higher or lower*
*median better
Central Tendency
64
New cards
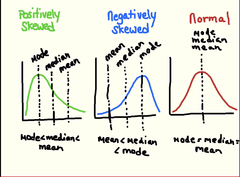
Positively Skewed
- outliers on positive side (pulls mean higher)
Negatively Skewed
- outliers on negative side (pulls mean lower)
- outliers on positive side (pulls mean higher)
Negatively Skewed
- outliers on negative side (pulls mean lower)
Skewed Distribution
65
New cards
different between highest and lowest value
- helps with variation
- helps with variation
Range
66
New cards
how far away from mean/average
- shows if scores packed together or dispersed
- shows if scores packed together or dispersed
Standard Deviation
67
New cards
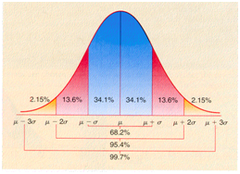
bell shaped curve, most scores near the average, and less near extremes
- 68% of scores, 1 standard deviation from mean
- 95% of scores, 2 standard deviation from mean
- 99% of scores, 3 standard deviation from mean
- 68% of scores, 1 standard deviation from mean
- 95% of scores, 2 standard deviation from mean
- 99% of scores, 3 standard deviation from mean
Normal Curve
68
New cards
data that lets people assume sample data is true for a population
Inferential Statistics
69
New cards
Descriptive
- describe data, measure central tendency
- presenting, organizing, summarizing
Inferential
- relationships between variables
- predicting trends
- describe data, measure central tendency
- presenting, organizing, summarizing
Inferential
- relationships between variables
- predicting trends
Descriptive vs Inferential Statistics
70
New cards
how likely it is that the result occurred by chance
(p-value)
p < 0.5, 95% likely result wasn't bc of chance
(p-value)
p < 0.5, 95% likely result wasn't bc of chance
Statistical Significance
71
New cards
1. descriptive
- observe/record behaviors
2. correlational
- natural occurring relationships
3. Experimental
- exploring cause and effect
- observe/record behaviors
2. correlational
- natural occurring relationships
3. Experimental
- exploring cause and effect
Basic Research Methods
72
New cards
How lab conditions in everyday life
Finding: how good at detecting faint light in dark room
Principal: how good at flying plane at night
Finding: how good at detecting faint light in dark room
Principal: how good at flying plane at night
Specific Finding & Theoretic Principals
73
New cards
- teach us about humans
- have more simple systems
- have more simple systems
Why psychologists study animals
74
New cards
*protect human research participants*
1. Informed consent
2. Protection from harm
3. Right to withdrawal
4. Confidentiality
5. Debriefing (explaining)
- DECEPTION = when true purpose isn't revealed
- debriefing is when you let subjects know about the deception that occured
1. Informed consent
2. Protection from harm
3. Right to withdrawal
4. Confidentiality
5. Debriefing (explaining)
- DECEPTION = when true purpose isn't revealed
- debriefing is when you let subjects know about the deception that occured
Ethical Guidelines