7.2 Smoking
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Smoking is the main cause of premature death and preventable illness in the UK
Responsible for approximately 122,000 deaths per year,
People who smoke have a 50% change of dying prematurely
on average 10 years earlier due to smoking
After the age of 35 years, a person loses 3 months of life expectancy
for every year of continued smoking
In 2019, 15% of all deaths in adults aged 35
over in England were attributed to smoking
For every death caused by smoking, approximately 20 smokers will be suffering from a smoking-related disease,
with the cost to the NHS in England per annum estimated at £2.5billion per annum
Smoking during pregnancy
can have many negative effects for both mother and foetus.
benefits of smocking cessation

There are various pharmacological treatments to help patients stop smoking:
nicotine replacement therapy NRT
varenicline
bupropion
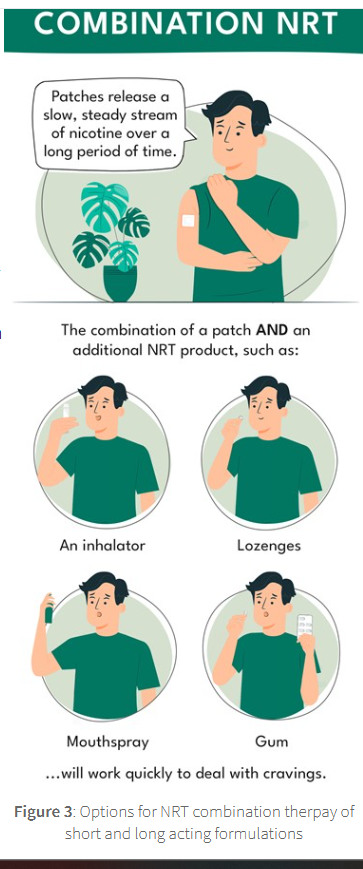
nicotine replacement therapy
there are many formulations which provide short term/ long term effects and their combination provides the most effective therapy
there is no evidence that any particular product formulation is more effective an another
products are tailored to the patients need
short acting products should be used to manage cravings
gum
inhalator
long acting products last for either 16-24 hours with different strengths availiable
patches
patient who had 10 or more cigarettes per day
start 25mg patch and reduce
patients who had less than 10 cigarettes a day
start 15mg patch and reduce → 10mg
monotherapy can be preferred
can be used in pregnant/breastfeeding women as benefits > risk
varenicline (Champix)
selective nicotine-receptor partial agonist
varenicline produces agonist activity at α4β2 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
(like nicotine does but varenicline is significantly less potent
varenicline has a higher affinity for this receptor than nicotine does
meaning that in the presence of nicotine varenicline will compete for the receptor thus nicotine cannot bind which in turn will help reduce the reward reinforcement associated with smoking.
varenicline dose regimen
Days 1–3: 500 micrograms once a day then increase,
Days 4–7: 500 micrograms twice a day then increase,
Day 8 onwards: 1 mg twice a day
varenicline To be started 1-2 weeks before target stop date
12 week course but varenicline can be repeated for a further 12 weeks in abstinent individuals to stop relapse
varenicline Cautioned in psychiatric illness and those with a history of seizures
Avoid varenicline in pregnancy
Bupropion
Initially was used to treat depression
Mechanism of action is unclear, but thought to inhibit the neural pathways of addiction and withdrawal
Bupropion Dosed 150mg daily for 6 days, then 150mg twice daily to give a total course length of 7-9 weeks
Lower doses of Bupropion in the elderly and those with factors for seizures
Discontinue Bupropion if abstinence not achieved at 7 weeks
Bupropion Contraindicated in pregnant/breastfeeding women and those with a history of seizures