Unit 4: Magnetic Fields
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics
AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism
Unit 4: Magnetic Fields
Solenoids
Ampère's Law
Biot-Savart Law
Magnetic Fields
Magnetic Field Produced by a Current-Carrying Wire
Force Between Two Parallel Current-Carrying Wires
Forces on a Wire in an External Magnetic Field
Magnetic & Electric Field Interactions
Right Hand Rule
Right Hand Rule
12th
Last updated 6:29 AM on 4/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
1
New cards
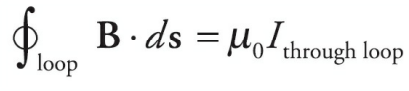
Ampere’s Law
States that the magnetic field around a closed loop is proportional to the current flowing through the loop. It is a fundamental law in electromagnetism and is used to calculate the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying wire or a solenoid.
2
New cards
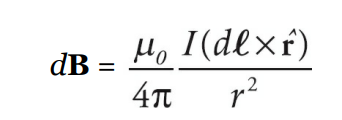
Biot–Savart law
This law describes the magnetic field generated by a steady electric current. It states that the magnetic field at any point is directly proportional to the current and the length of the conductor. It also depends on the distance between the point and the conductor. The direction of the magnetic field is perpendicular to both the current and the distance vector.
3
New cards
Magnetic fields
These are created by moving electric charges.
4
New cards
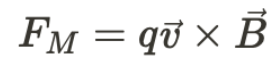
force from a magnetic field
5
New cards
F \= q(v x B)
Lorentz force (When a charged particle moves through a magnetic field, it experiences a force perpendicular to both the direction of motion and the magnetic field. )
6
New cards
F \= qE
When both magnetic and electric fields are present, the particle experiences a combined force that is the vector sum of the two individual forces.
7
New cards
F \= I L x B
When a wire carrying current is placed in an external magnetic field, it experiences a force.
8
New cards
B_perp \= B sin(theta)
If the wire is not perpendicular to the magnetic field, then only the component of the magnetic field perpendicular to the wire will cause a force.
9
New cards
T \= F * r * sin(theta)
When a wire is twisted, a torque is applied to it.
10
New cards
k \= T / theta
torsional stiffness
11
New cards
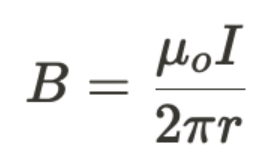
internal magnetic field created by a very long current-carrying wire
12
New cards
F \= μ₀I₁I₂L / 2πd
force between the wires
13
New cards
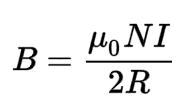
Biot-Savart Law
it states that the magnetic field at a point is proportional to the current density and the distance from the point to the current element.
14
New cards
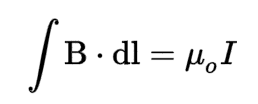
Ampère's Law
The law states that the line integral of the magnetic field around a closed loop is equal to the current passing through the loop multiplied by a constant known as the permeability of free space.
15
New cards
Solenoid
Its function is to generate a strong magnetic field as a current flows through the wire.