Week 19b: Skeletal System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/177
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture - Skeletal System 22-23
Last updated 7:36 PM on 3/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
178 Terms
1
New cards
What is the composition of most bones?
Most bones have both compact and spongy tissue. This is especially true of long bones.
2
New cards
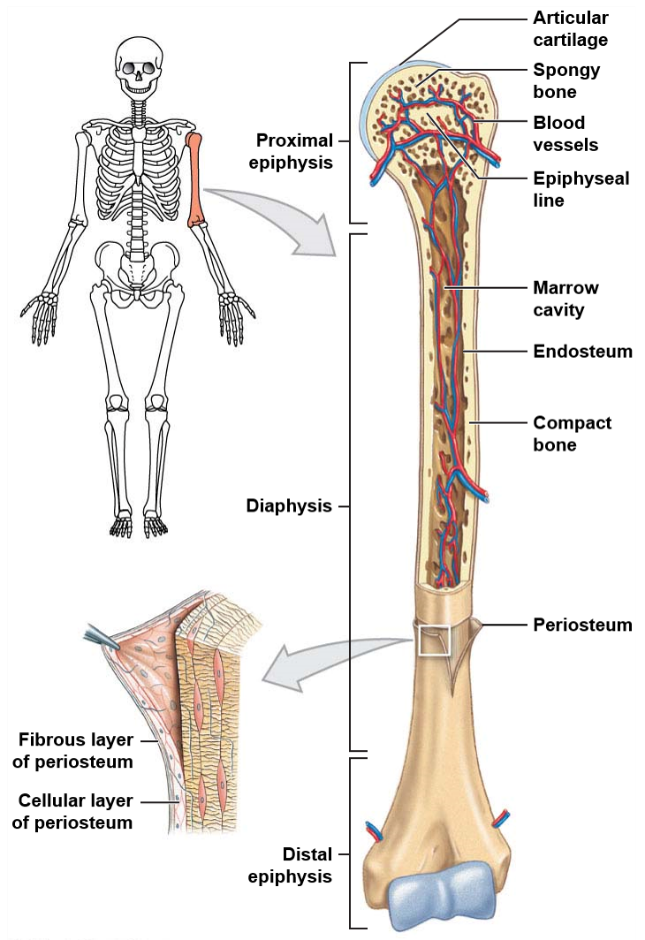
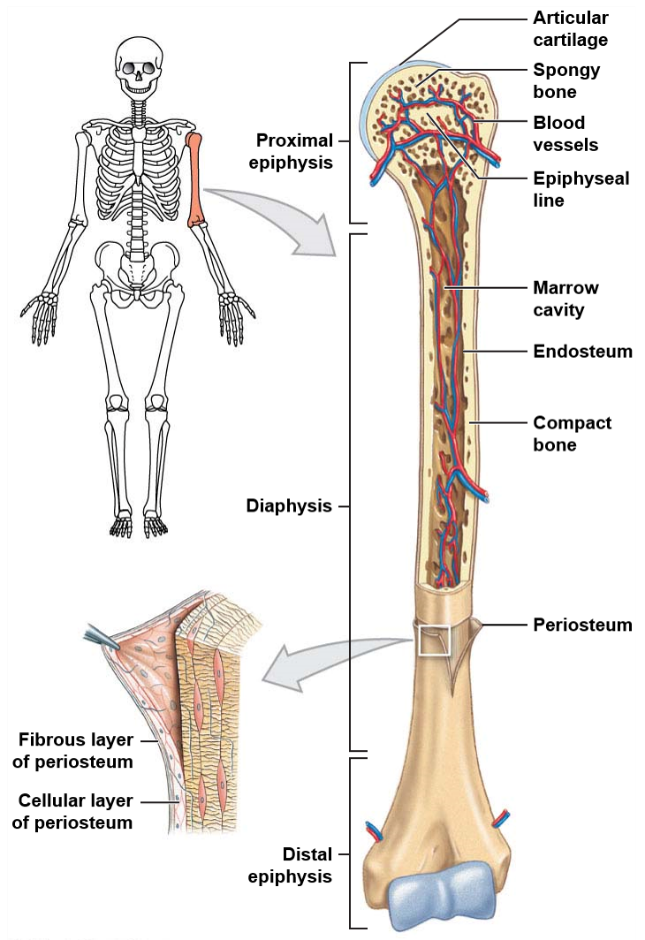
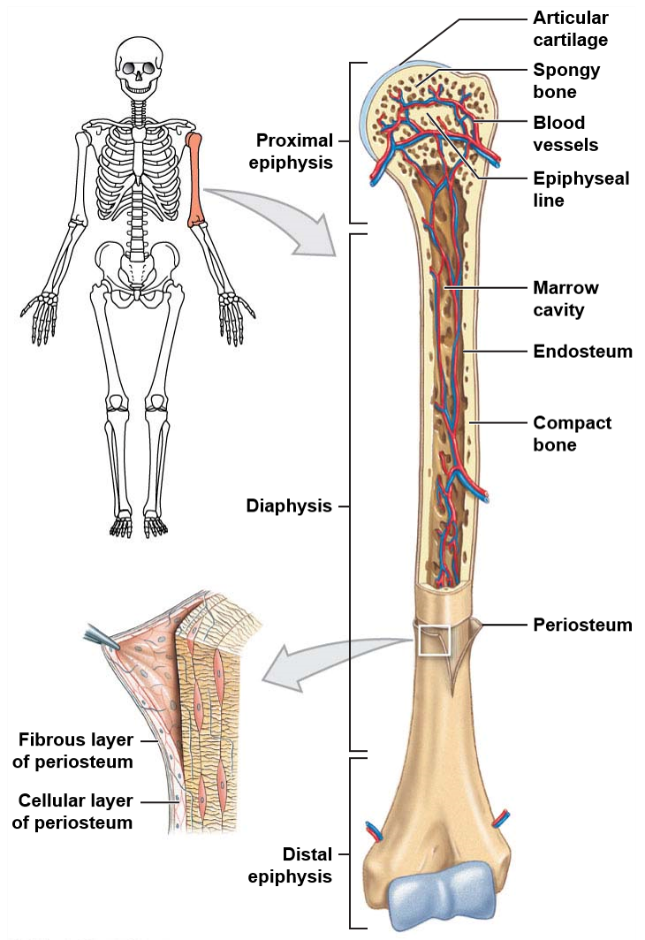
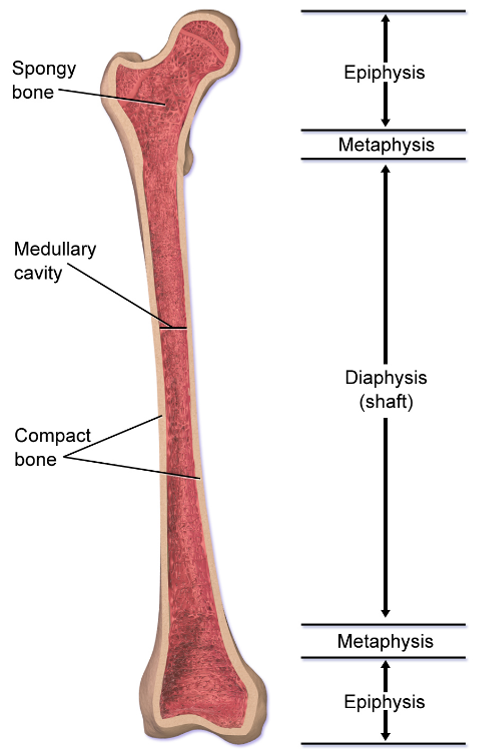
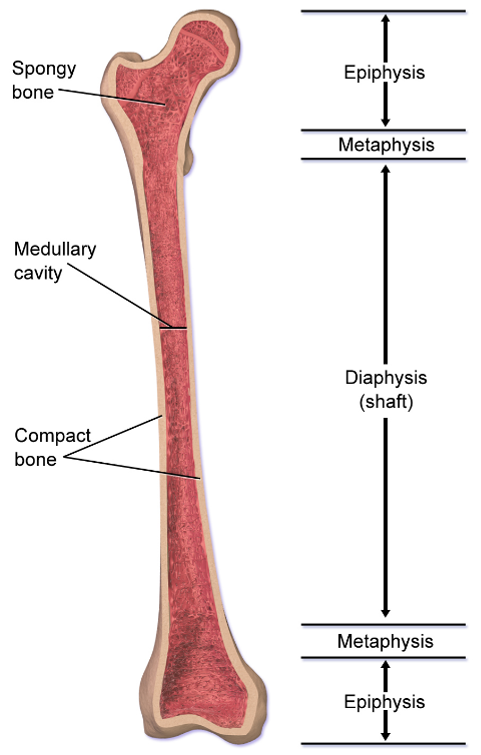
What is the long central shaft of a bone made of?
The long central shaft of a bone, known as the diaphysis, is made of compact bone.
3
New cards
What is the composition of the expanded ends of a bone?
The expanded ends of a bone, known as epiphysis, are made of spongy bone.
4
New cards
What is the function of periosteum in the bone?
The periosteum covers the entire structure of a bone and isolates it from other surrounding tissues.
5
New cards
What are the distinct features of long bones?
Long bones have several distinct features including being longer than they are wide, having an epiphysis at both ends, having a surface of compact bone and a marrow containing interior of spongy bone, and both ends being covered with hyaline cartilage.
6
New cards
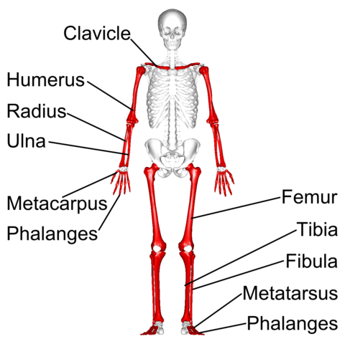
Which skeleton do most long bones belong to, and can you provide examples?
Most long bones belong to the appendicular skeleton, which includes the bones of the arms and legs. Examples include the humerus, ulna, and radius in the arm, the femur, tibia, and fibula in the leg, and the metacarpals, metatarsals, and phalanges in the hands and feet.
7
New cards
Can you give some examples of long bones and their position within the appendicular skeleton?
8
New cards
What are the distinct features of short bones?
Short bones have several distinct features including their length and width being roughly equal, providing strength and support, having a thin layer of compact bone on the surface, and being mostly spongy bone with lots of marrow.
9
New cards
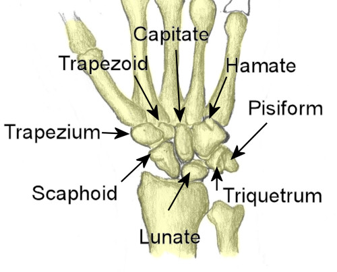
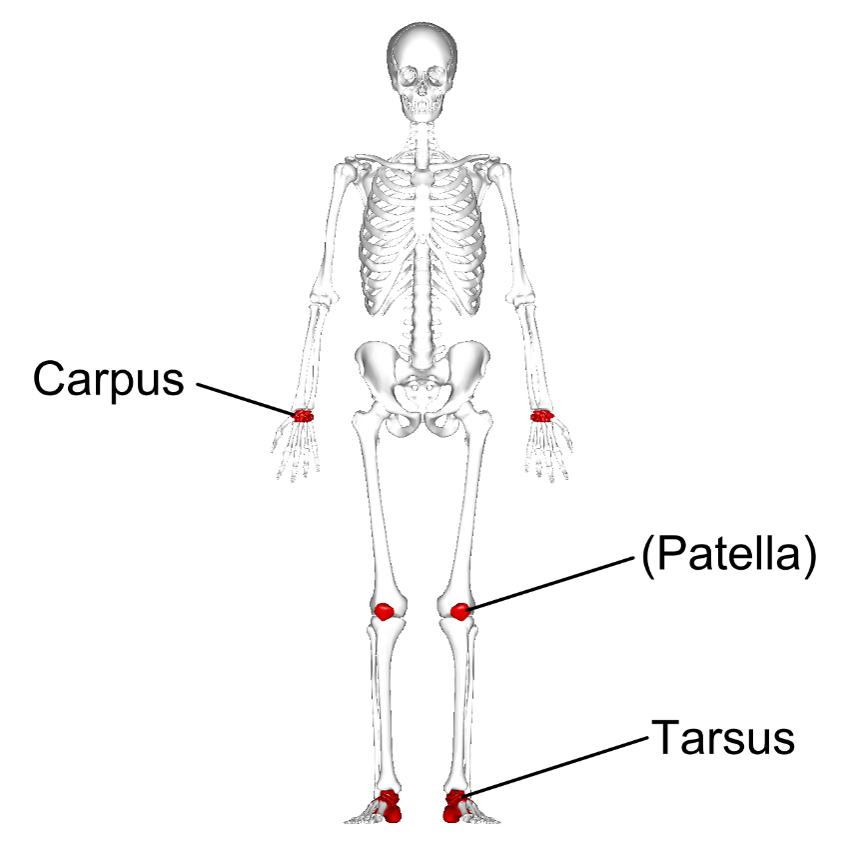
Which skeleton do short bones belong to, and can you provide examples?
Short bones belong to the appendicular skeleton, which includes the bones of the arms and legs. Examples include the carpals in the hand, the tarsals in the foot, and the patella (kneecap).
10
New cards
Can you give some examples of short bones and their position within the appendicular skeleton?
11
New cards
What is the structure of flat bones?
Flat bones are thin and broad.
12
New cards
What is the composition of the anterior and posterior surfaces of flat bones?
The anterior and posterior surfaces of flat bones are composed of compact bone, which protects the spongy bone interior.
13
New cards
In adults, which type of bones produce the highest volume of red blood cells?
In adults, flat bones produce the highest volume of red blood cells.
14
New cards
What are the two main functions of flat bones?
The two main functions of flat bones are the protection of vital organs and providing a base for muscle attachment.
15
New cards
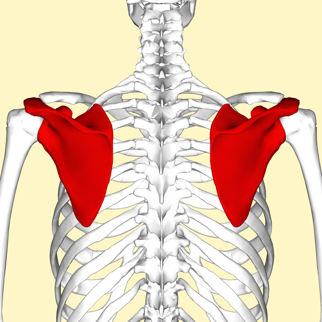
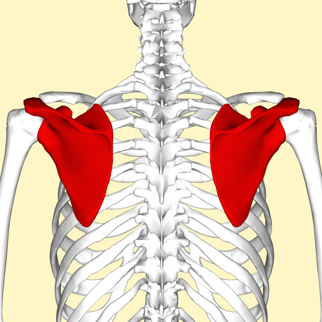
Can you provide examples of flat bones?
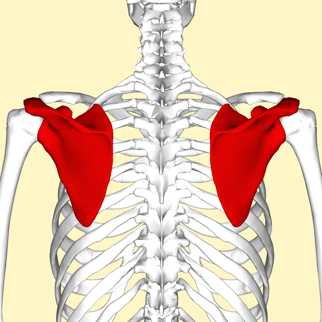
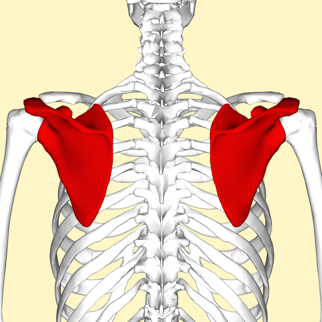
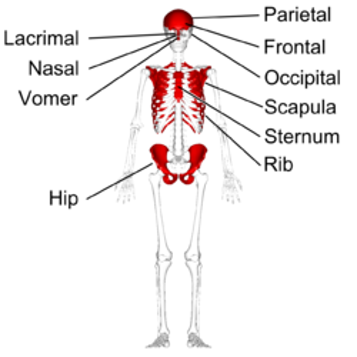
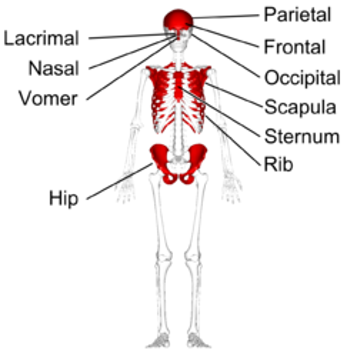
Examples of flat bones include the skull, ribs, sternum, scapula, and pelvis.
16
New cards
Can you give some examples of flat bones and their position within the appendicular skeleton?
17
New cards
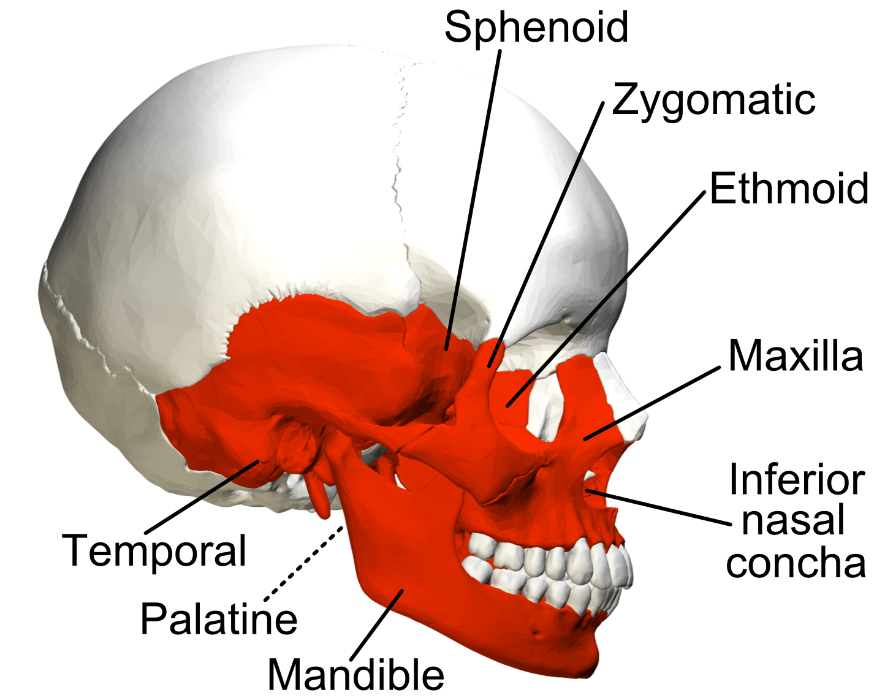
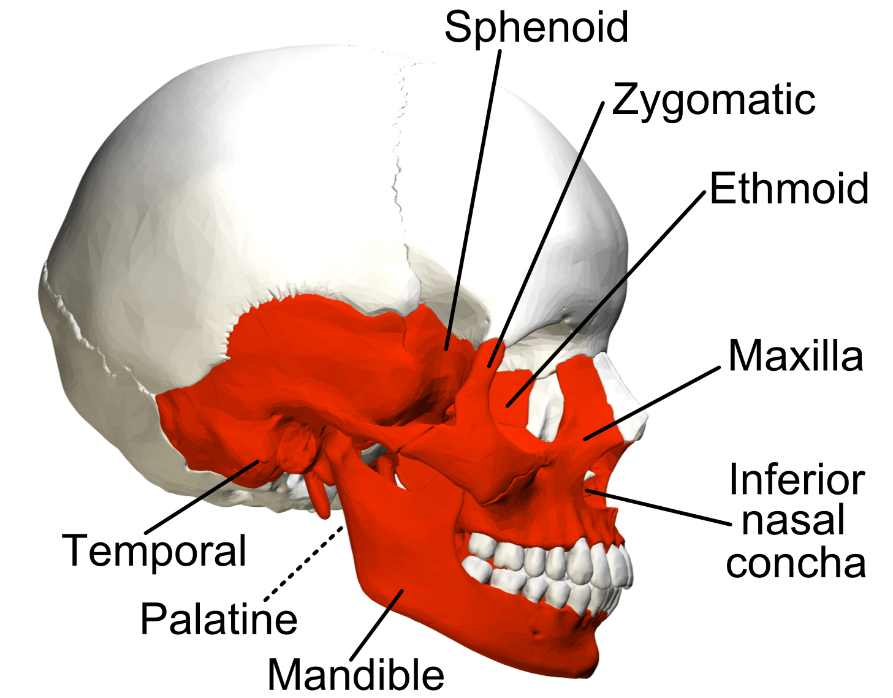
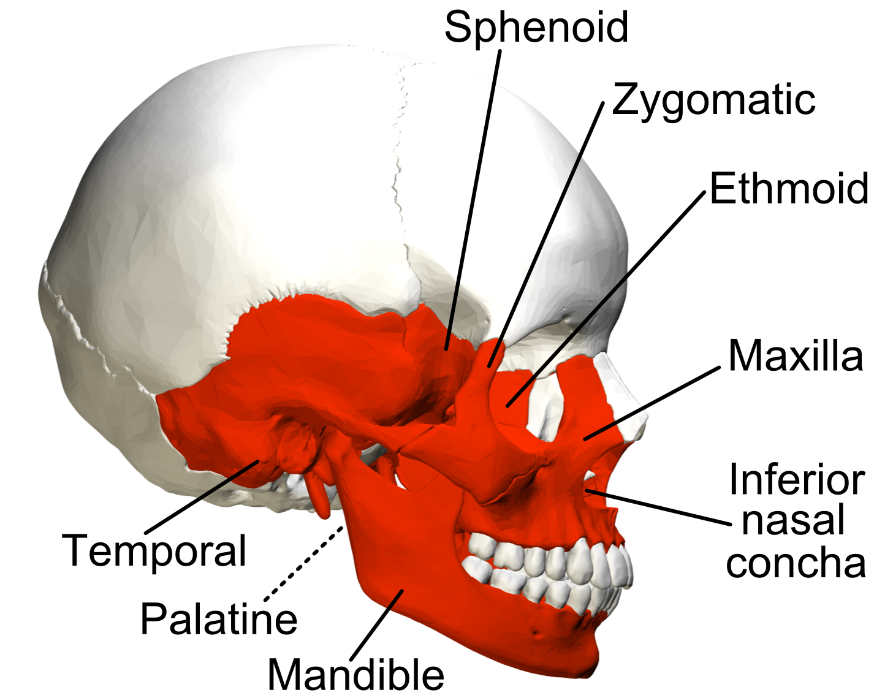
What is the defining characteristic of irregular bones?
The defining characteristic of irregular bones is their non-uniform shapes.
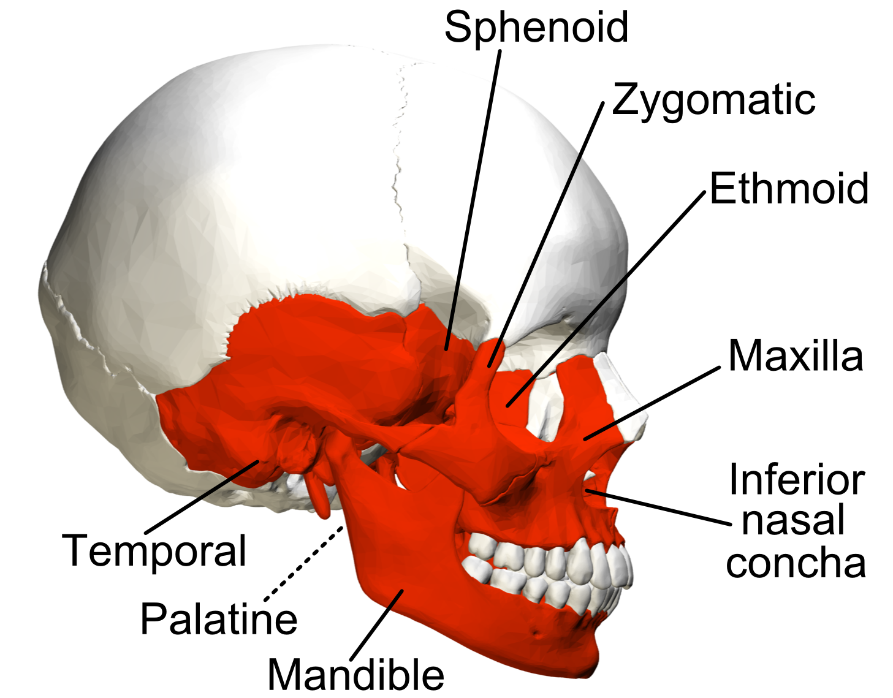
18
New cards
How does the structure of irregular bones reflect their function?
The structure of irregular bones reflects their function. For example, vertebrae provide support while protecting the spinal cord.
19
New cards
What is the common function of irregular bones?
Irregular bones often provide anchor points for the attachment of skeletal muscle. For example, the sacrum.
20
New cards
What is the composition of irregular bones?
Irregular bones are mostly composed of spongy bone, but have a thin layer of compact bone.
21
New cards
What are some examples of irregular bones?
Examples of irregular bones include vertebrae, the sacrum, and facial bones including the mandible.
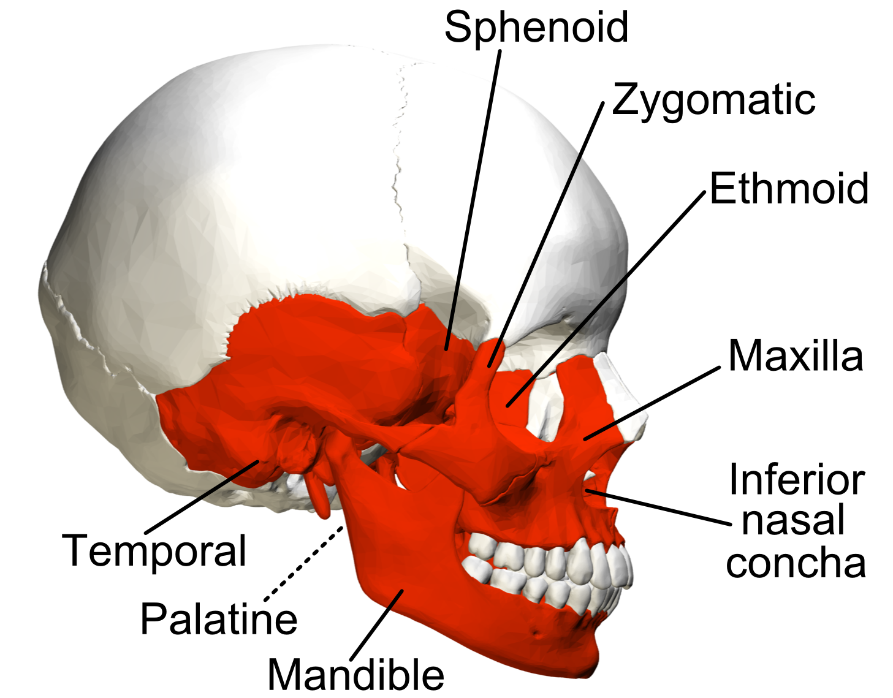
22
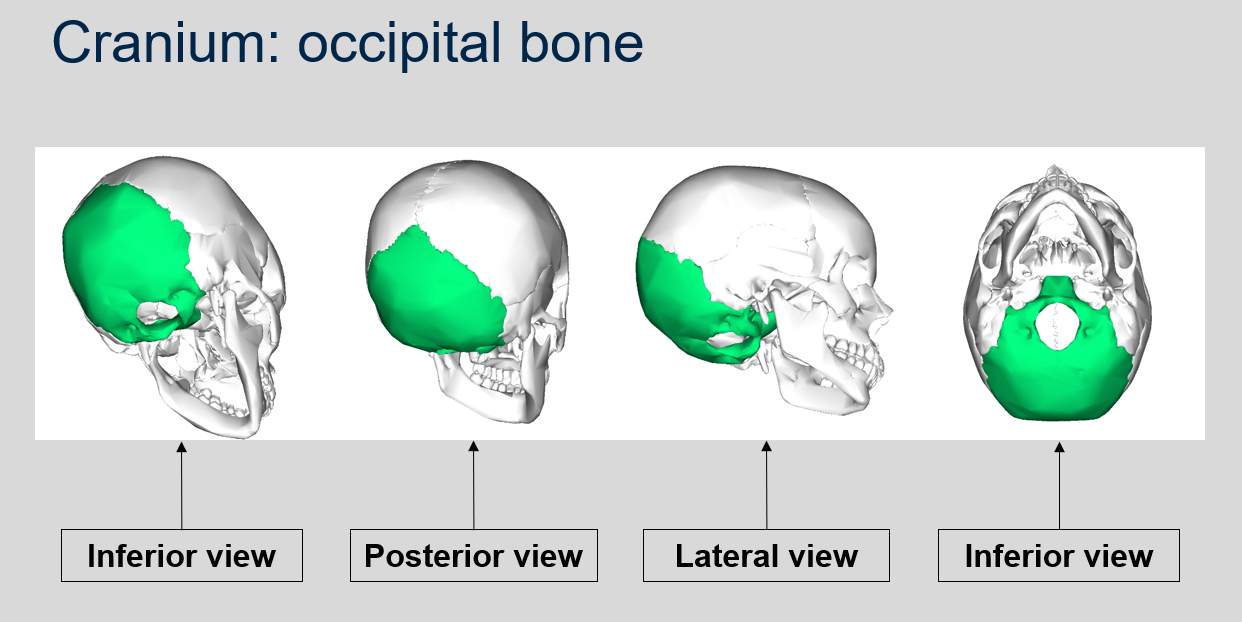
New cards
Can you give some examples of irregular bones and their position within the appendicular skeleton?
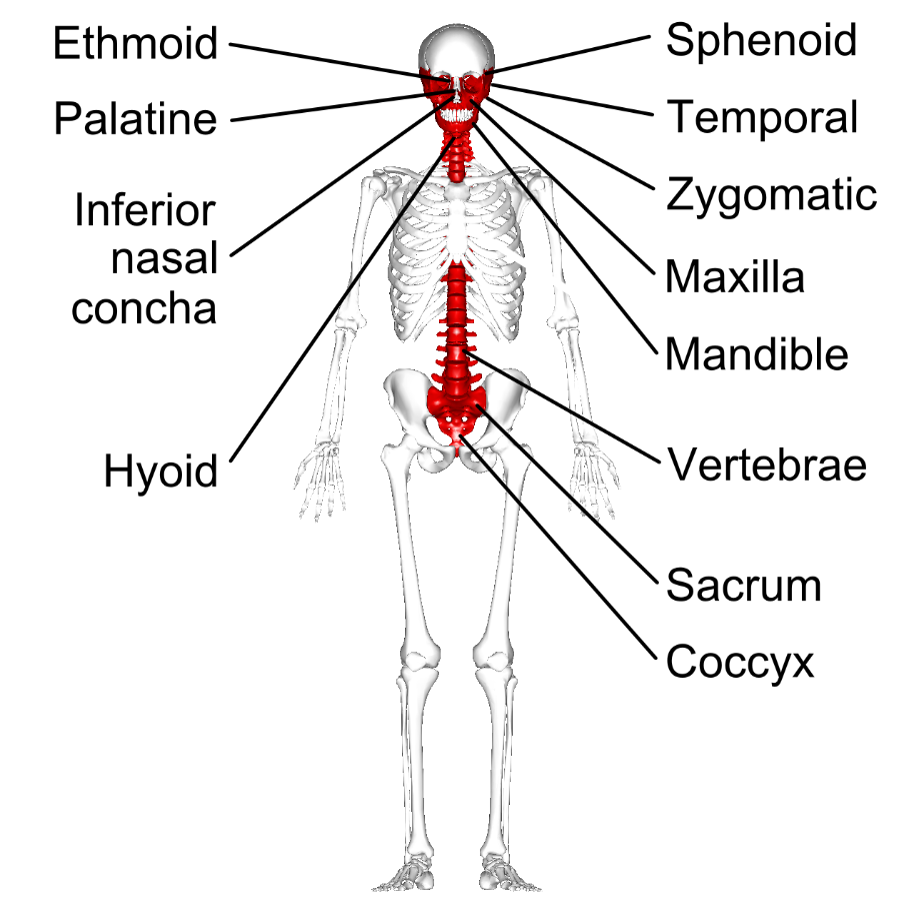
23
New cards
What are Sesamoid bones and where are they found?
Sesamoid bones are short or irregular bones that are embedded within a tendon. They are named after the Latin word for sesame seed.
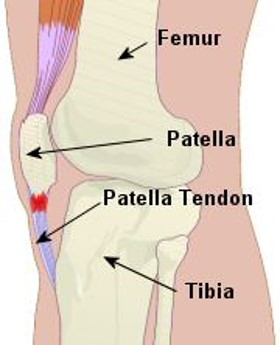
24
New cards
What are sesamoid bones, and where do they occur?
Sesamoid bones are short or irregular bones embedded within a tendon. They occur in tendons that pass over joints to offer more protection.
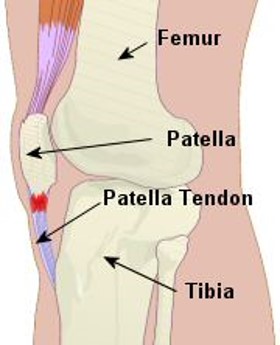
25
New cards
What is the reason for the variation in numbers of sesamoid bones?
Sesamoid bones vary in number as they develop in response to skeletal stress.
26
New cards
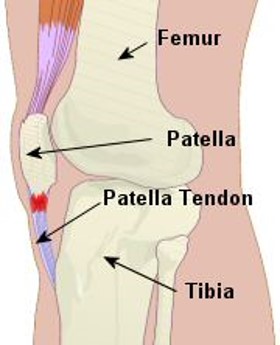
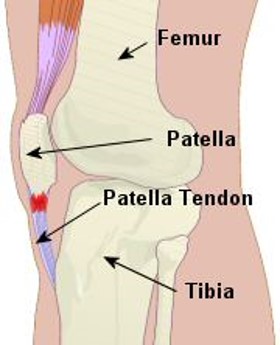
What are some common examples of sesamoid bones?
Some common examples include the patella and the pisiform.
27
New cards
What are the five major functions of the skeleton?
1. Support – both for the entire body and individual tissues/muscles/organs
2. Storage of minerals – bones store ions that are essential for many physiological processes
3. Blood cell production – red blood cells for gas exchange; white blood cells for immunity
4. Protection – skeletal structure surround soft tissues, e.g. ribs protect the heart and lungs
5. Leverage – long bones function as levers to change the size and direction of forces
28
New cards
How many bones are in the human skeleton and what are the subdivisions?
There are 206 bones in the human skeleton, which are subdivided into the axial skeleton containing 80 bones including the skull, thoracic cage and spine, and the appendicular skeleton containing 126 bones including upper and lower limbs, along with their attachment points.
29
New cards
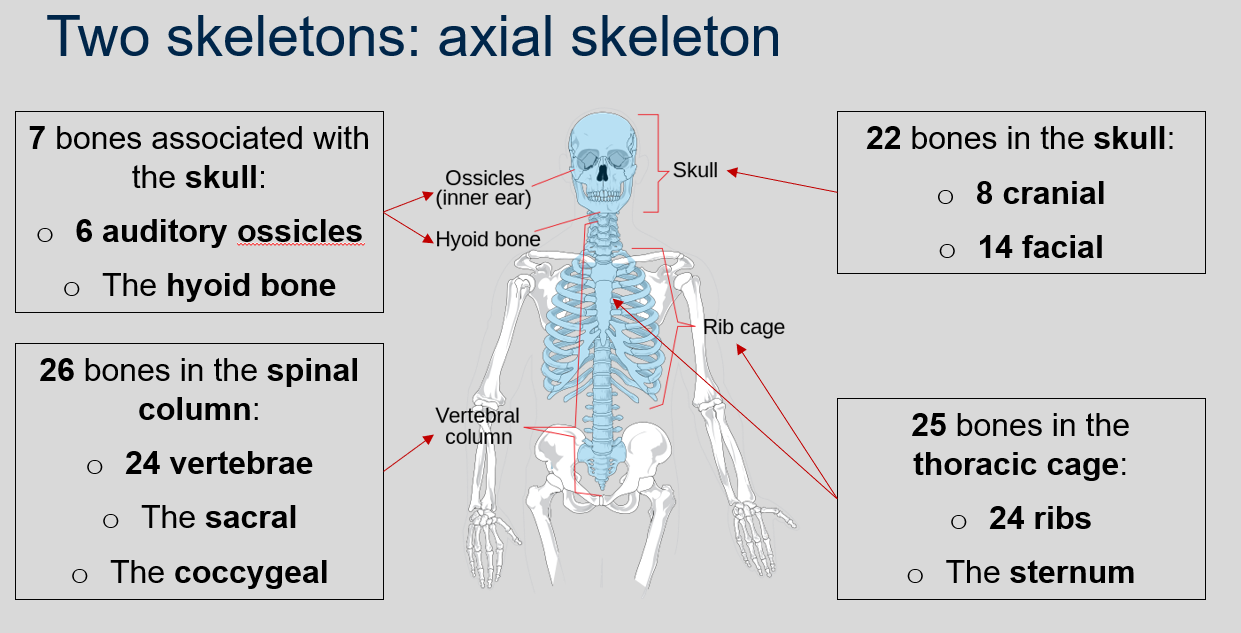
What is the axial skeleton?
The axial skeleton is a part of the human skeleton that includes 80 bones, including 22 bones in the skull (8 cranial and 14 facial), 7 bones associated with the skull (6 auditory ossicles and the hyoid bone), 25 bones in the thoracic cage (24 ribs and the sternum), and 26 bones in the spinal column (24 vertebrae, the sacral, and the coccygeal).
30
New cards
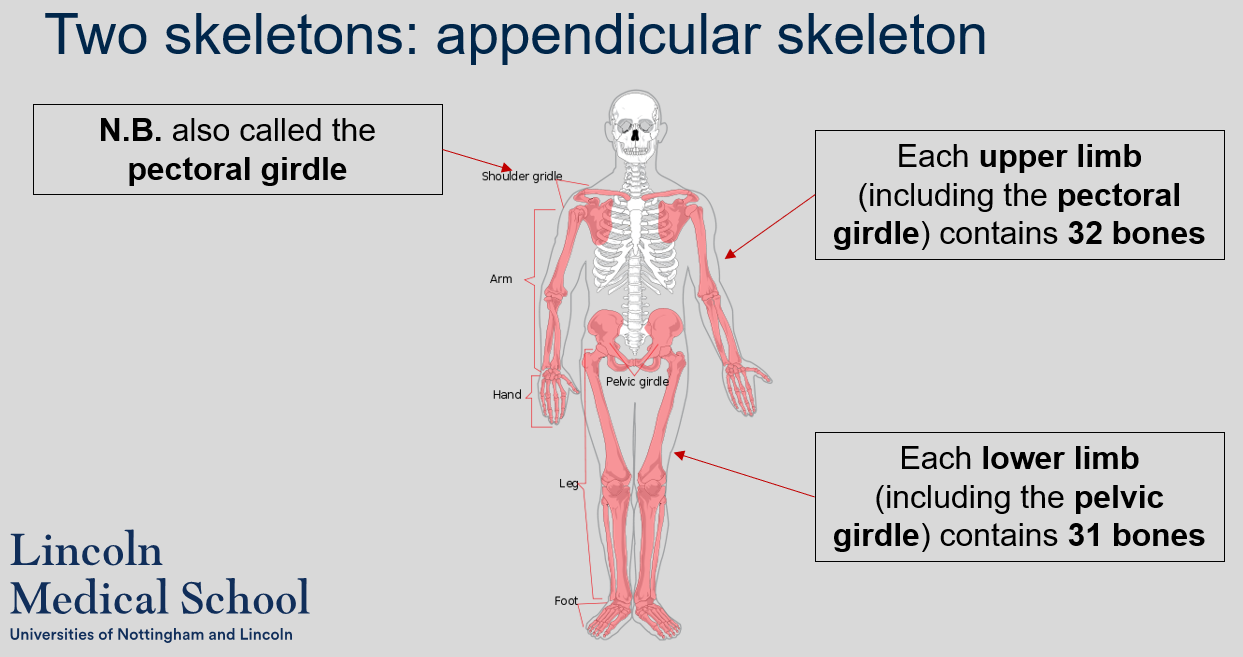
How many bones are there in each upper limb (including the pectoral girdle) and each lower limb (including the pelvic girdle) of the appendicular skeleton?
Each upper limb (including the pectoral girdle) contains 32 bones and each lower limb (including the pelvic girdle) contains 31 bones.
31
New cards
What is another name for the shoulder girdle?
The shoulder girdle is also called the pectoral girdle.
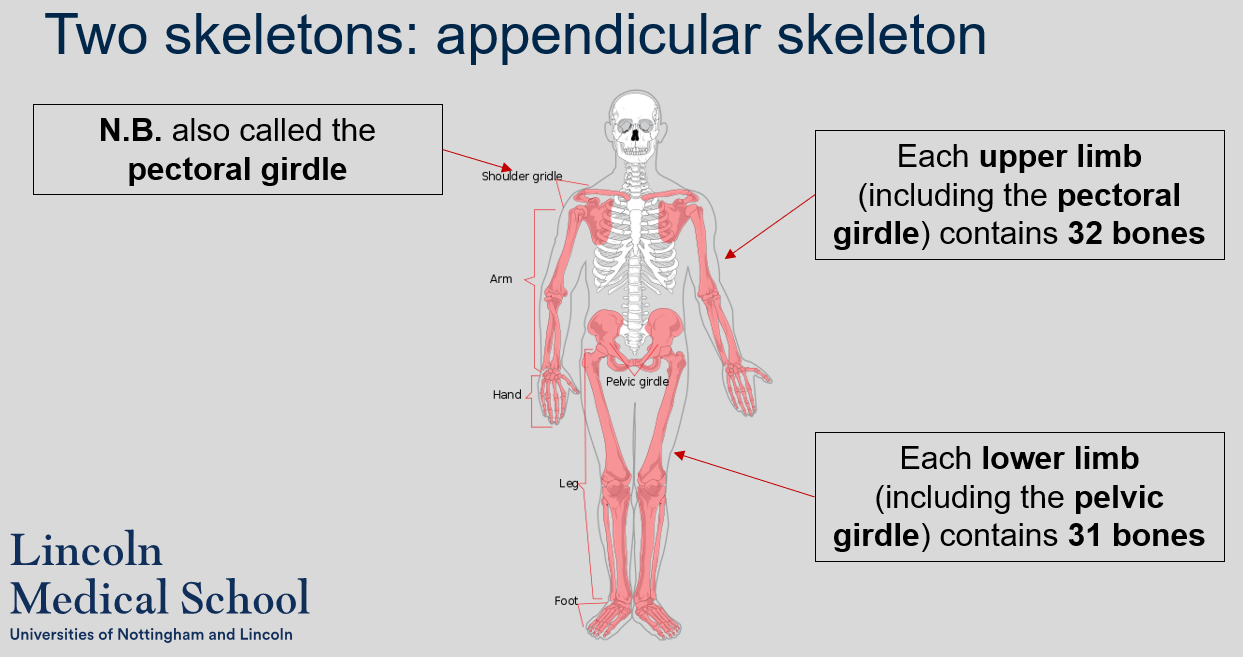
32
New cards
What is the name and position of the principle bones that compose the skeleton?
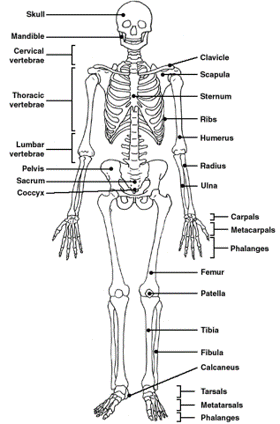
33
New cards
What are the functions of the vertebral column?
The functions of the vertebral column include:
* Support of head, neck and trunk
* Facilitation of the transmission of weight and forces throughout the body
* Protection of the spinal cord
* Maintenance of posture when sitting and standing.
* Support of head, neck and trunk
* Facilitation of the transmission of weight and forces throughout the body
* Protection of the spinal cord
* Maintenance of posture when sitting and standing.
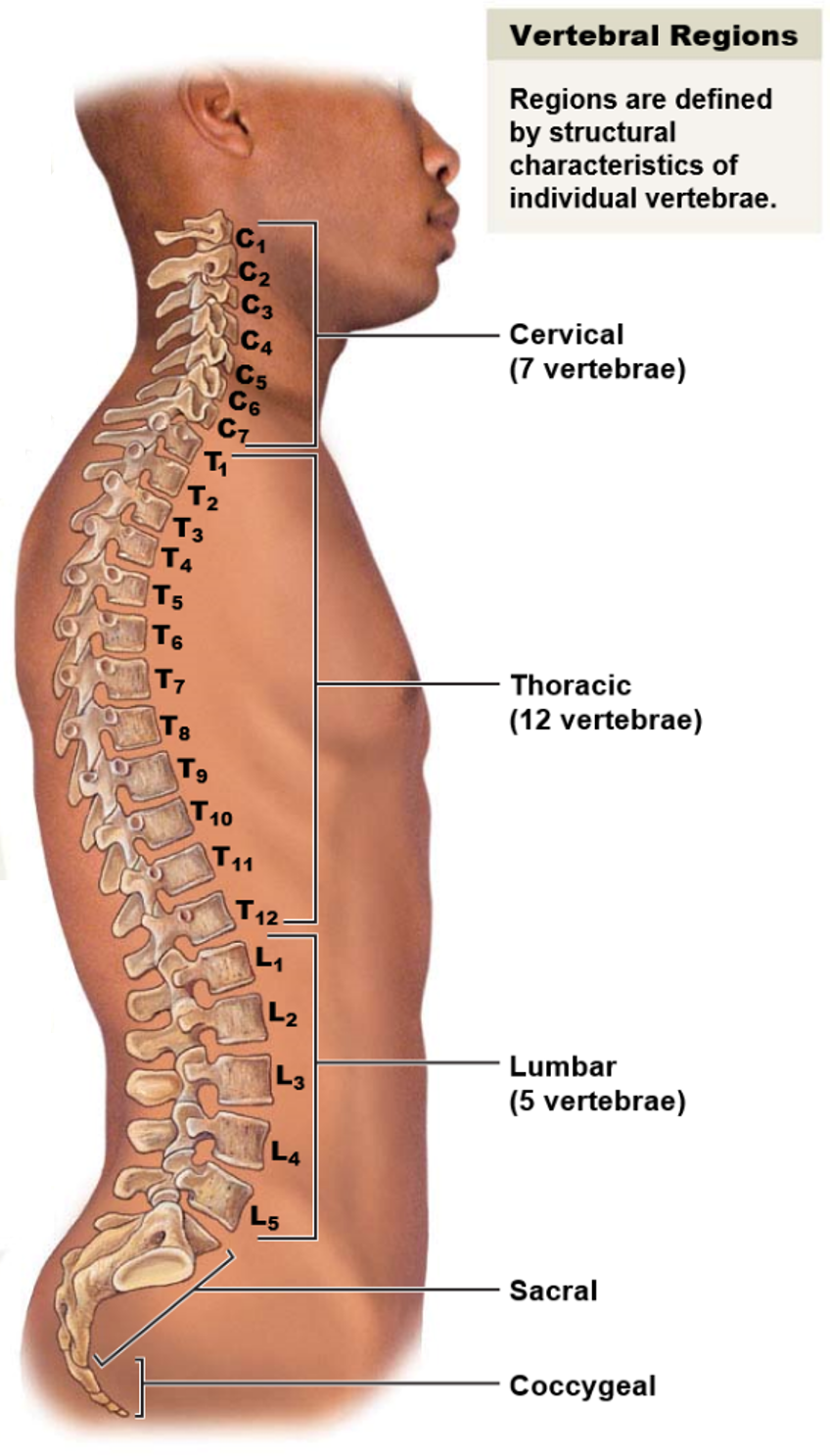
34
New cards
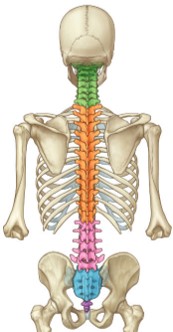
What are the five vertebral regions and how many bones are in each region?
The five vertebral regions and the number of bones in each region are:
* Cervical region: 7 vertebrae
* Thoracic region: 12 vertebrae
* Lumbar region: 5 vertebrae
* Sacrum: 1 bone
* Coccyx: 1 bone
In total, there are 26 bones in the vertebral column.
* Cervical region: 7 vertebrae
* Thoracic region: 12 vertebrae
* Lumbar region: 5 vertebrae
* Sacrum: 1 bone
* Coccyx: 1 bone
In total, there are 26 bones in the vertebral column.
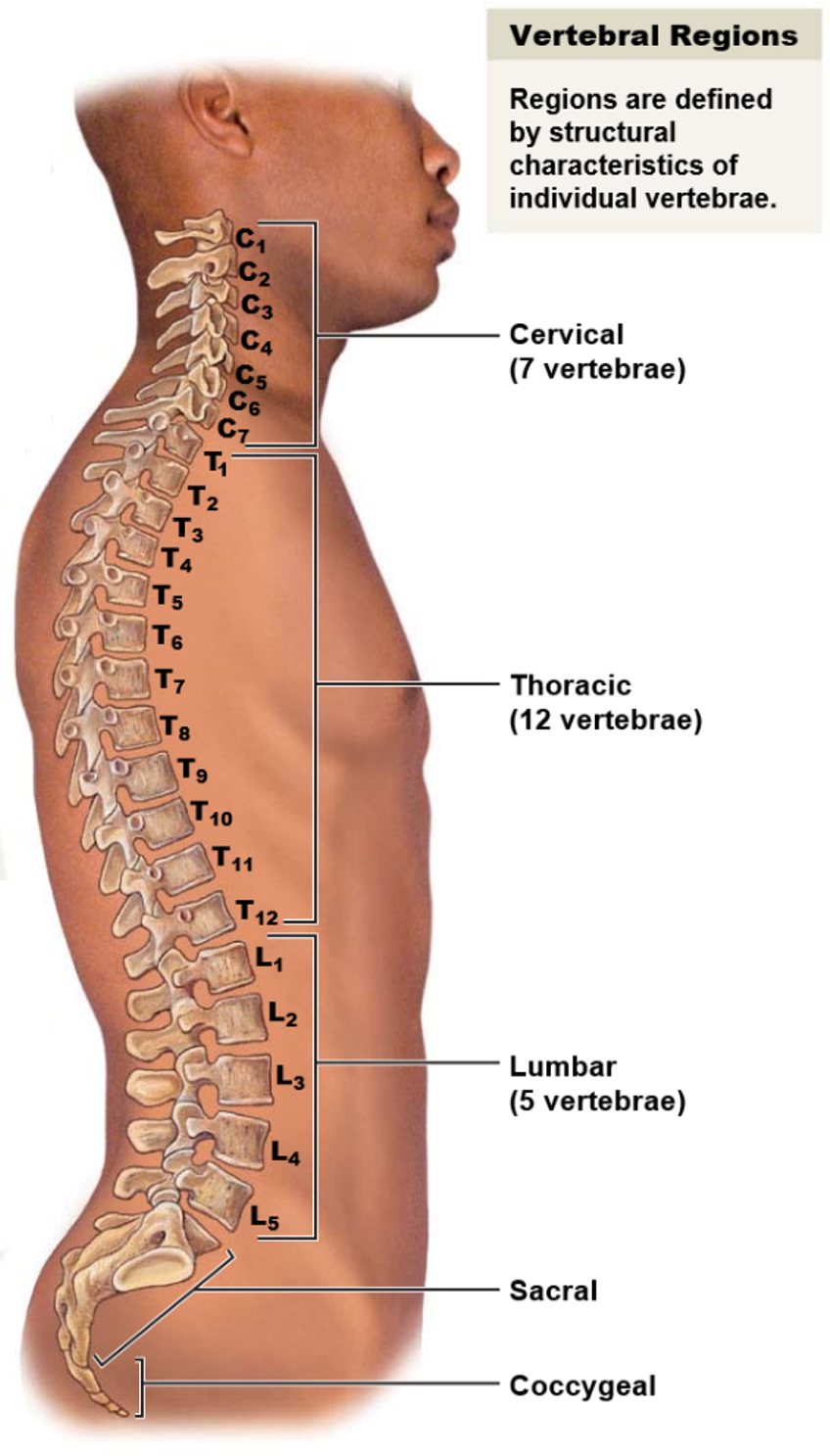
35
New cards
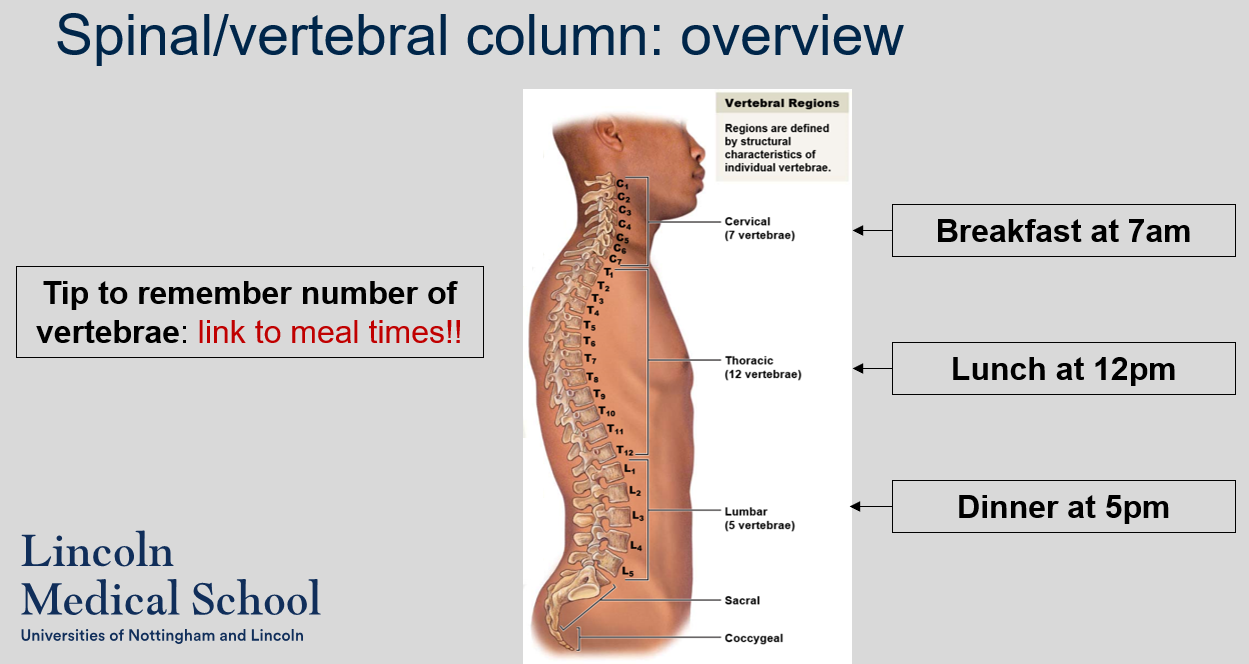
What is a tip to remember the number of vertebrae in each region of the vertebral column?
A helpful tip to remember the number of vertebrae in each region of the vertebral column is to link it to meal times:
* Breakfast at 7am: There are 7 cervical vertebrae
* Lunch at 12pm: There are 12 thoracic vertebrae
* Dinner at 5pm: There are 5 lumbar vertebrae.
* Breakfast at 7am: There are 7 cervical vertebrae
* Lunch at 12pm: There are 12 thoracic vertebrae
* Dinner at 5pm: There are 5 lumbar vertebrae.
36
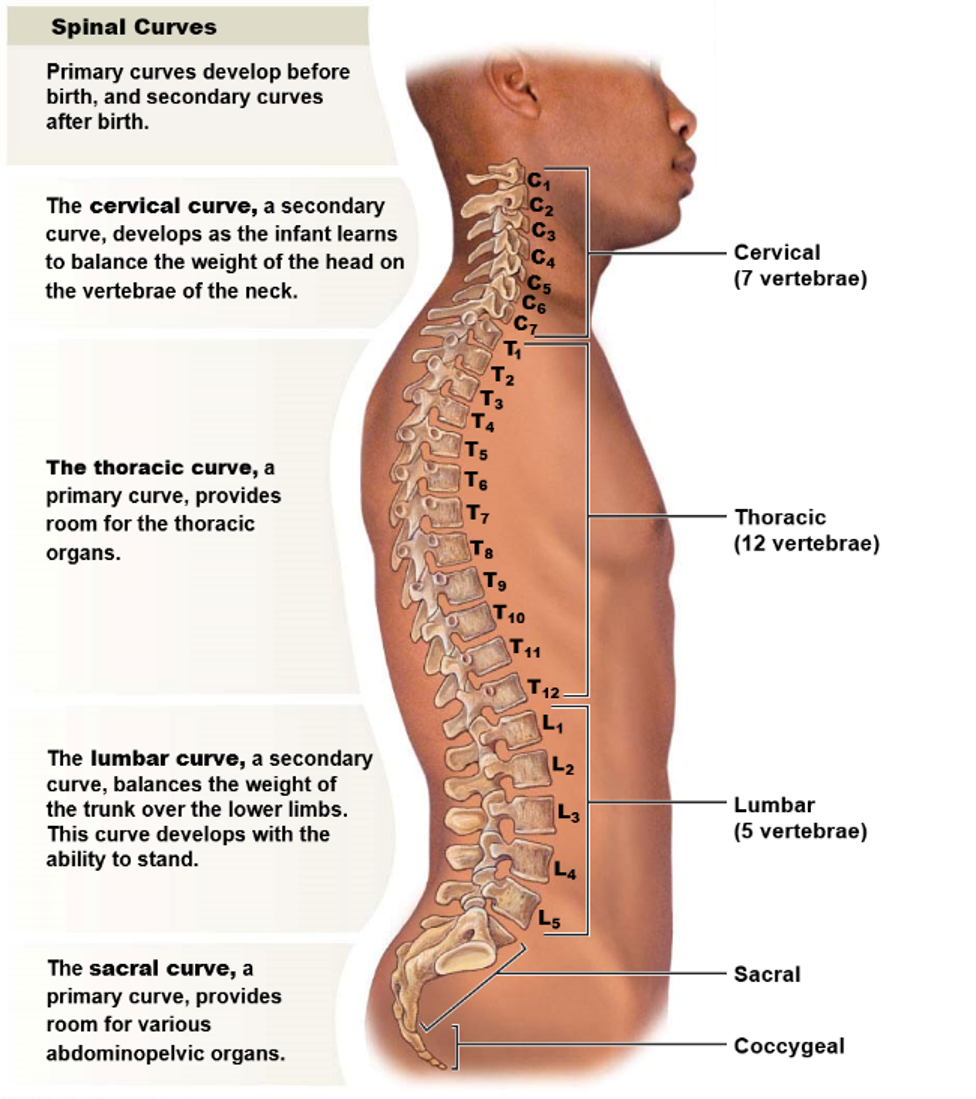
New cards
What is the purpose of curvature in the vertebral column?
The purpose of curvature in the vertebral column is to ensure that the center of gravity sits on the midline and balances the body's weight.
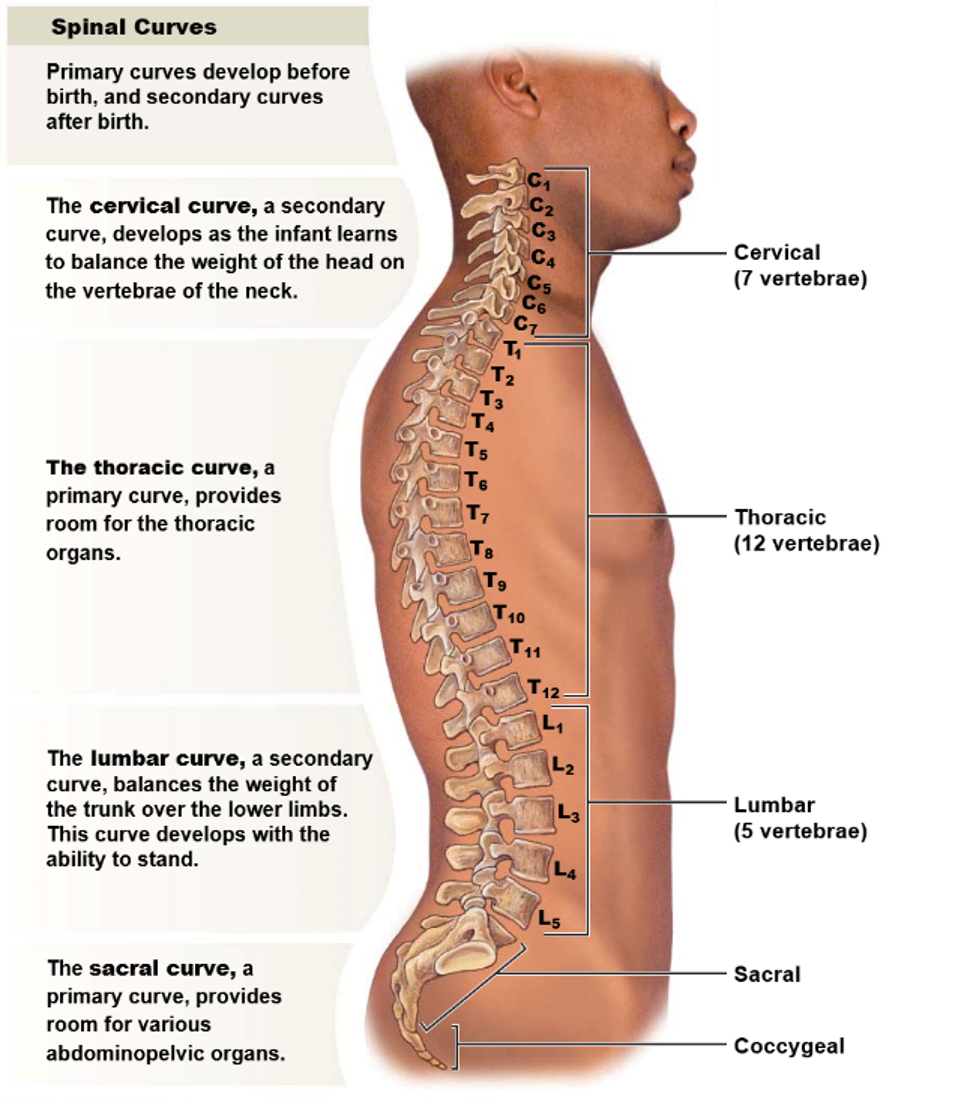
37
New cards
How many curvatures are there in the vertebral column and what are their names?
From a lateral view, there are four curvatures in the vertebral column:
* Two primary curvatures present from birth: the thoracic curvature and the sacral curvature
* Two secondary curvatures that develop later: the cervical curvature and the lumbar curvature.
* Two primary curvatures present from birth: the thoracic curvature and the sacral curvature
* Two secondary curvatures that develop later: the cervical curvature and the lumbar curvature.
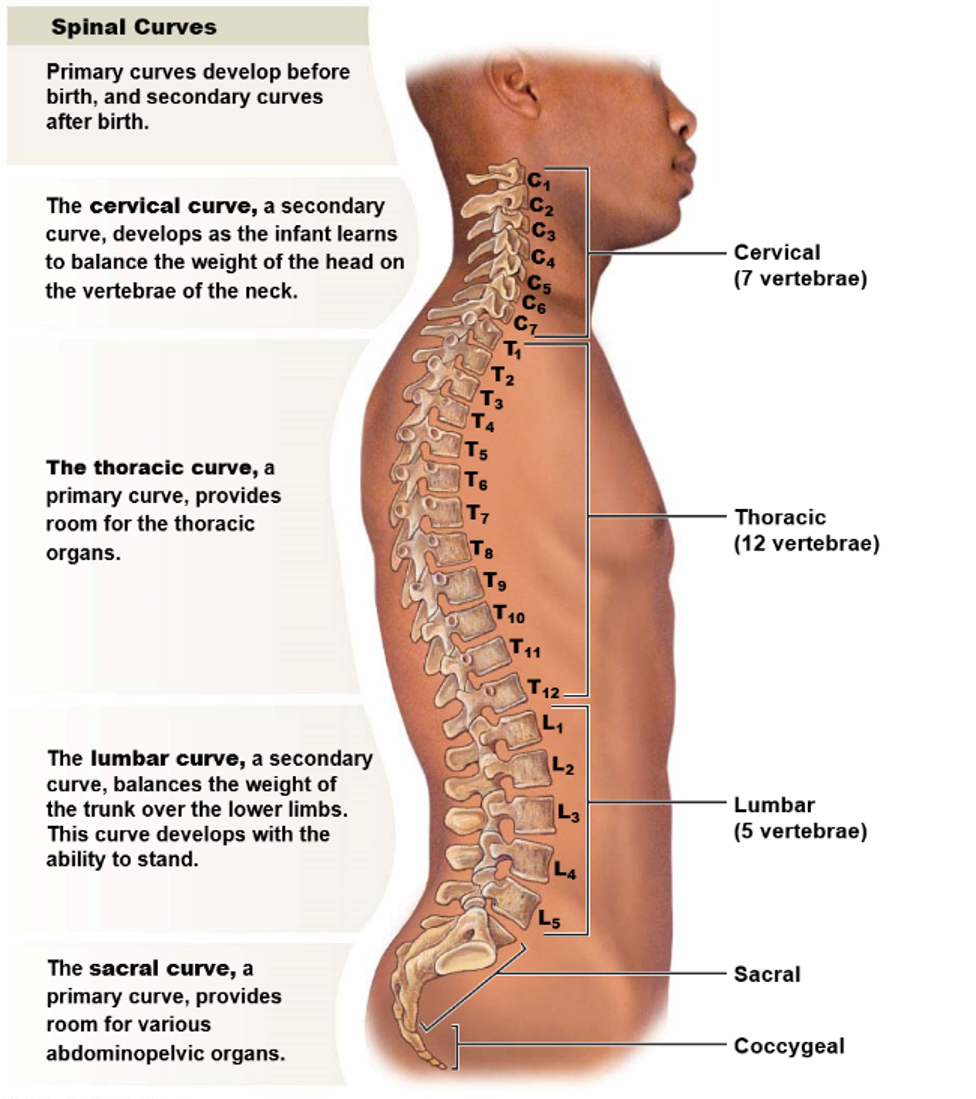
38
New cards
What is the function of each curve in the vertebral column?
39
New cards
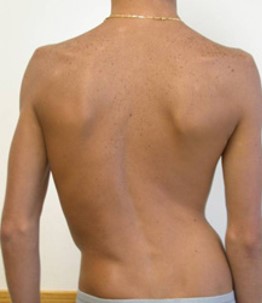
Is scoliosis a congenital condition?
Yes, scoliosis is a congenital condition.
40
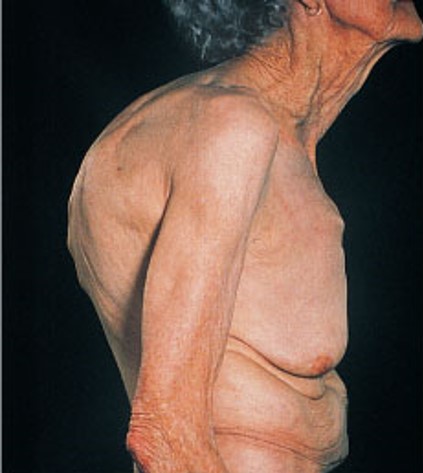
New cards
What is the effect of kyphosis on the thoracic curvature?
Kyphosis exaggerates the thoracic curvature.
41
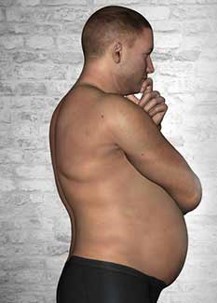
New cards
What is the effect of lordosis on the lumbar curvature?
Lordosis exaggerates the lumbar curvature.
42
New cards
Which vertebrae in the cervical region articulate with other bones?
In the cervical region:
* C1 articulates with the occipital bone
* C7 articulates with T1.
* C1 articulates with the occipital bone
* C7 articulates with T1.
43
New cards
What is the characteristic feature of the thoracic vertebrae?
In the thoracic region, all vertebrae articulate with at least one pair of ribs.
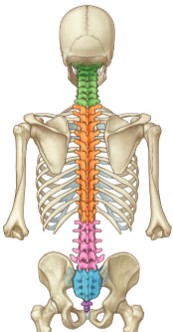
44
New cards
Which vertebra in the lumbar region articulates with the sacrum?
In the lumbar region, L5 articulates with the sacrum.
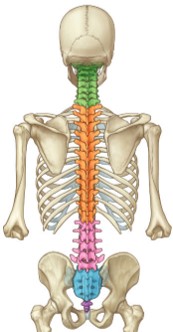
45
New cards
How is the sacrum formed during embryonic development?
The sacrum forms from five fused vertebrae during embryonic development.
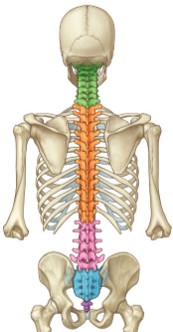
46
New cards
What is the coccygeal bone, and how does it form?
The coccygeal bone is a small, triangular bone located at the base of the vertebral column. It forms from four small bones that used to be the tail during embryonic development.
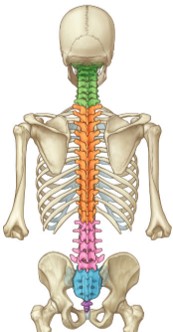
47
New cards
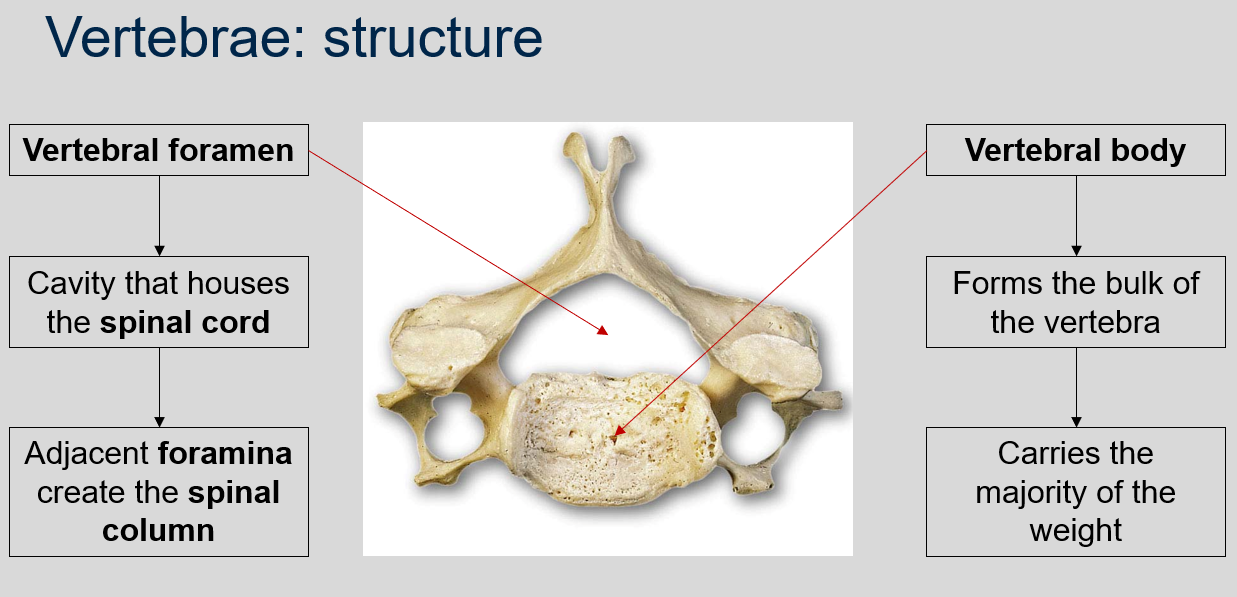
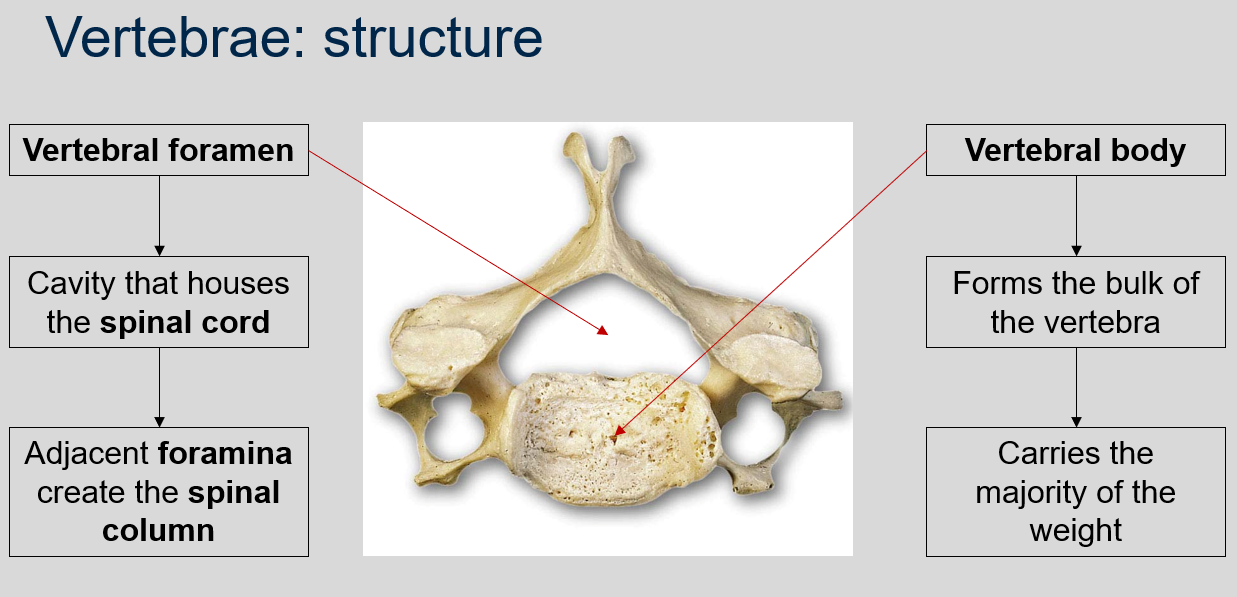
What is the vertebral foramen, and what does it house?
The vertebral foramen is a canal or opening that runs through the center of each vertebra in the vertebral column. It houses the spinal cord and other neural tissues, and the adjacent foramina create the spinal column.
48
New cards
What is the vertebral body, and what is its function?
The vertebral body is the thick, disc-shaped front portion of a vertebra that forms the bulk of the vertebra and carries the majority of the weight.
49
New cards
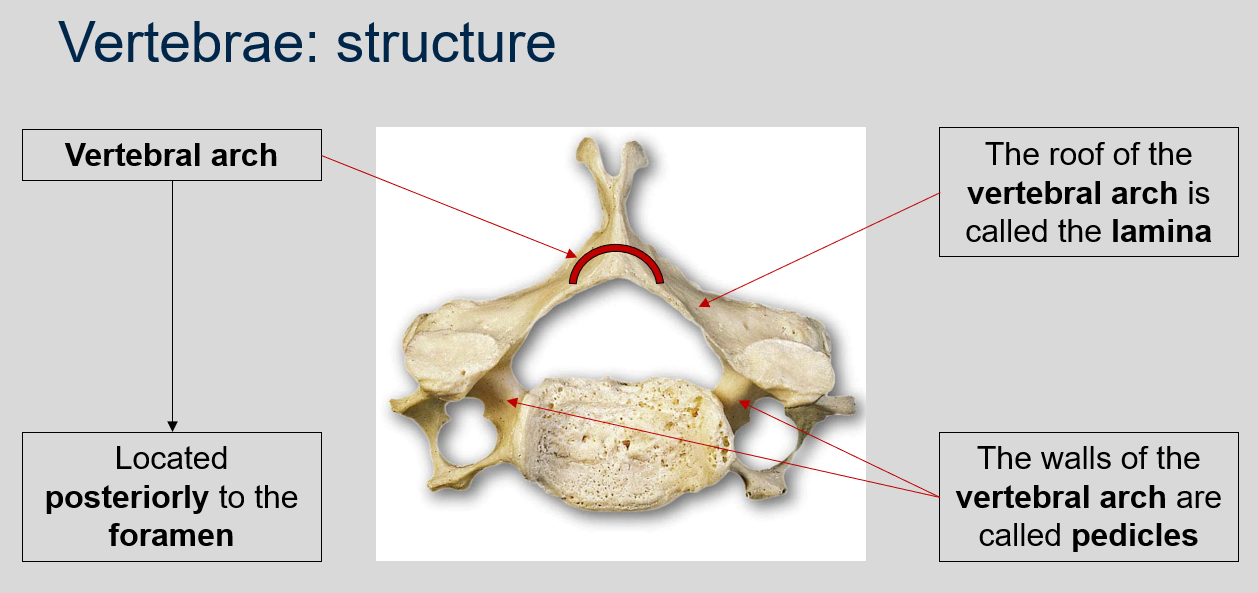
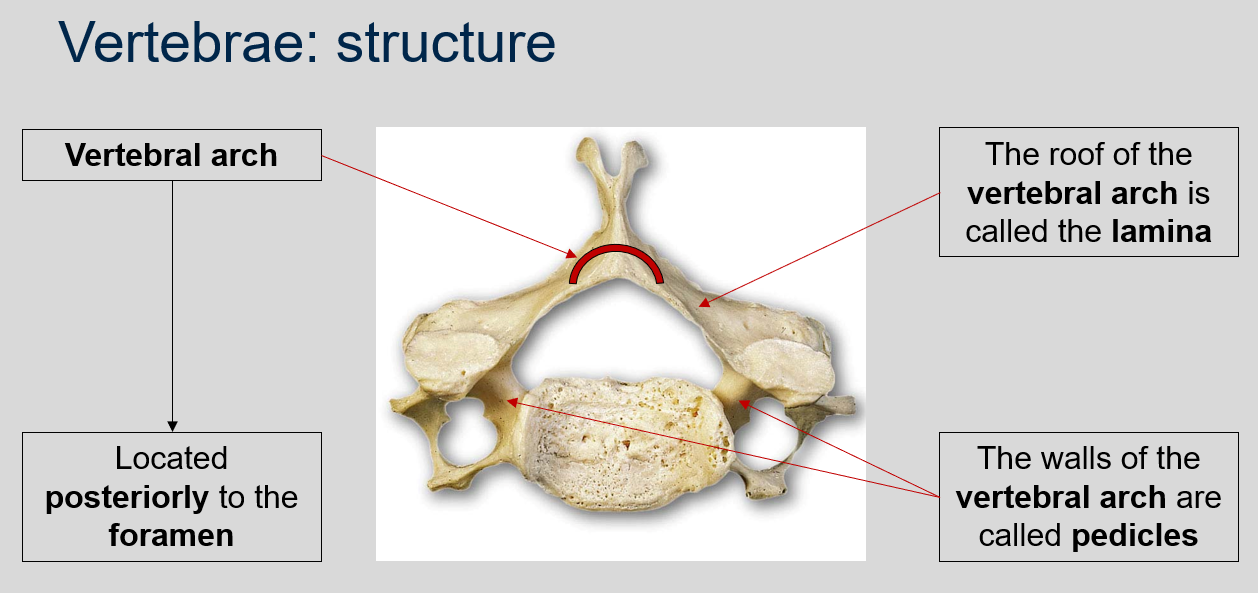
Where is the vertebral arch located?
The vertebral arch is located posteriorly to the foramen in each vertebra.
50
New cards
What is the name of the roof of the vertebral arch?
The roof of the vertebral arch is called the lamina.
51
New cards
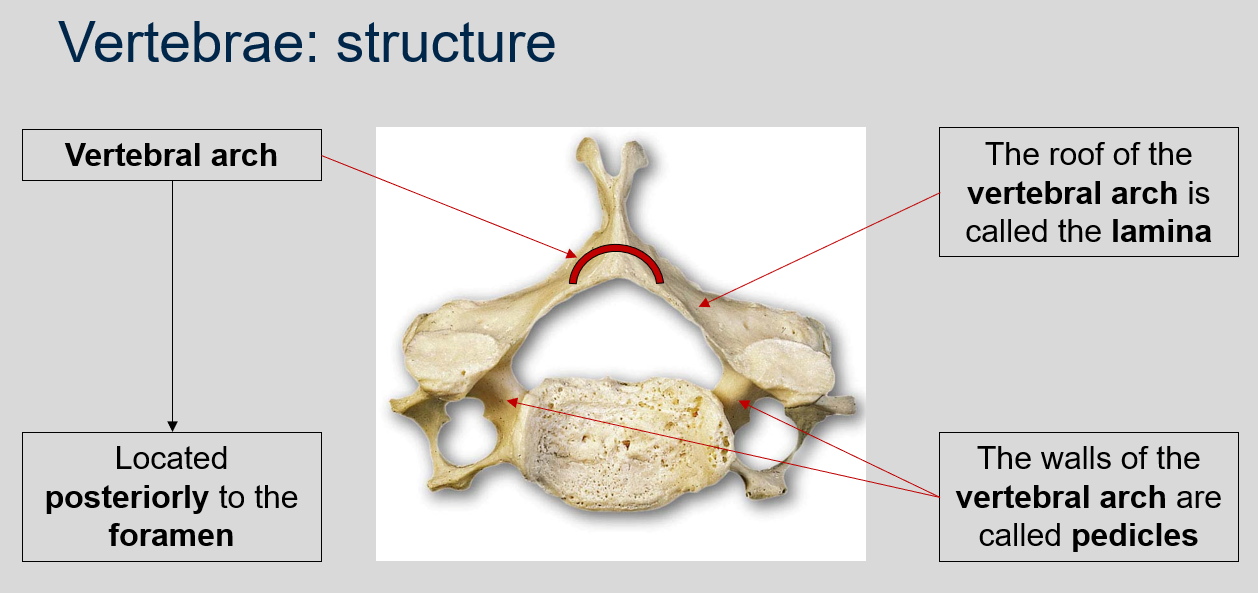
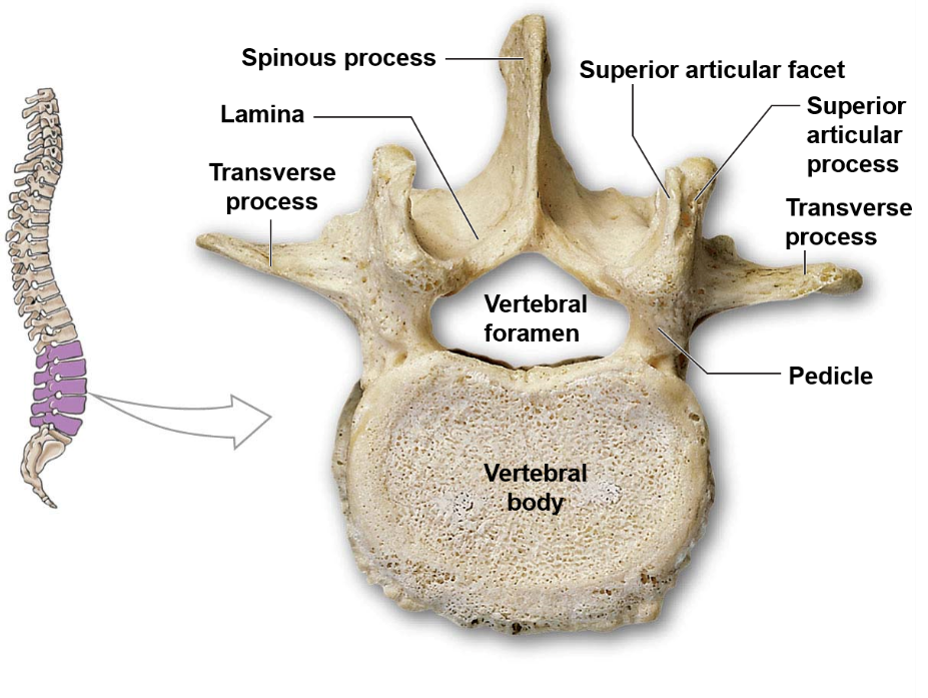
What is the name of the walls of the vertebral arch?
The walls of the vertebral arch are called pedicles.
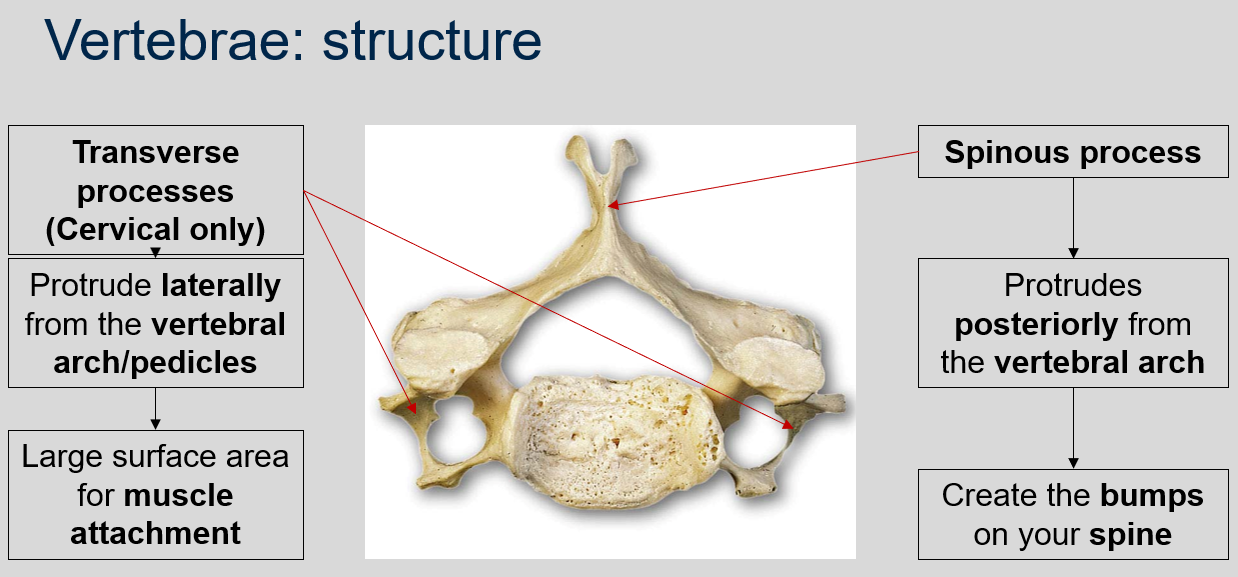
52
New cards
What are transverse processes in the cervical vertebrae, and what is their function?
In the cervical vertebrae, transverse processes protrude laterally from the vertebral arch/pedicles and provide a large surface area for muscle attachment.
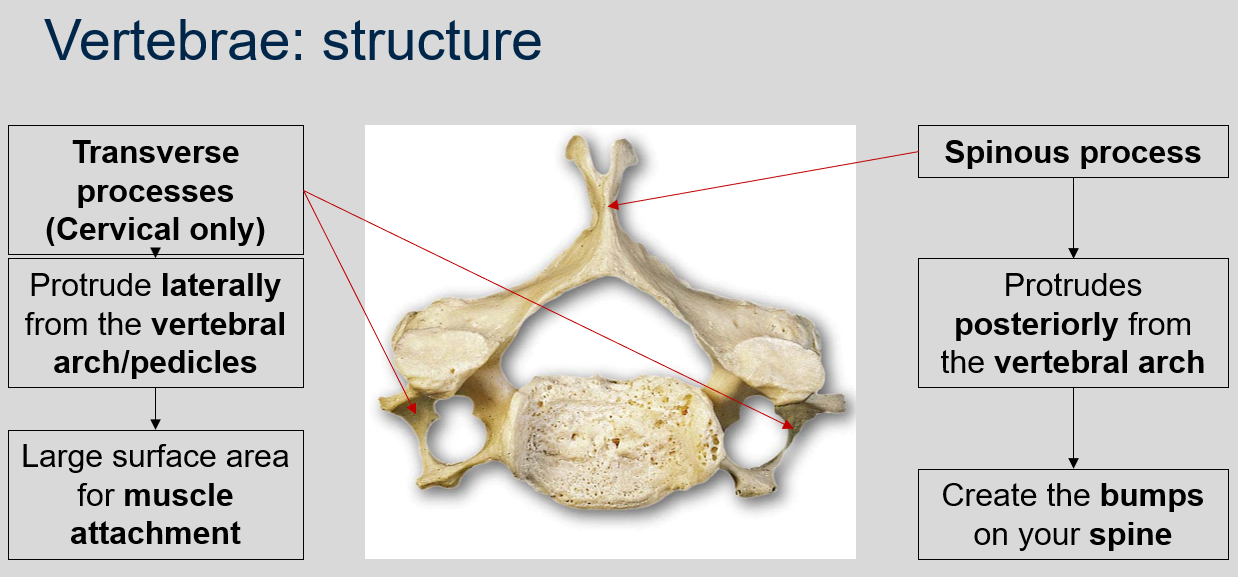
53
New cards
What is a spinous process in a vertebra, and what is its appearance?
A spinous process is a bony projection that protrudes posteriorly from the vertebral arch, creating the bumps on your spine.
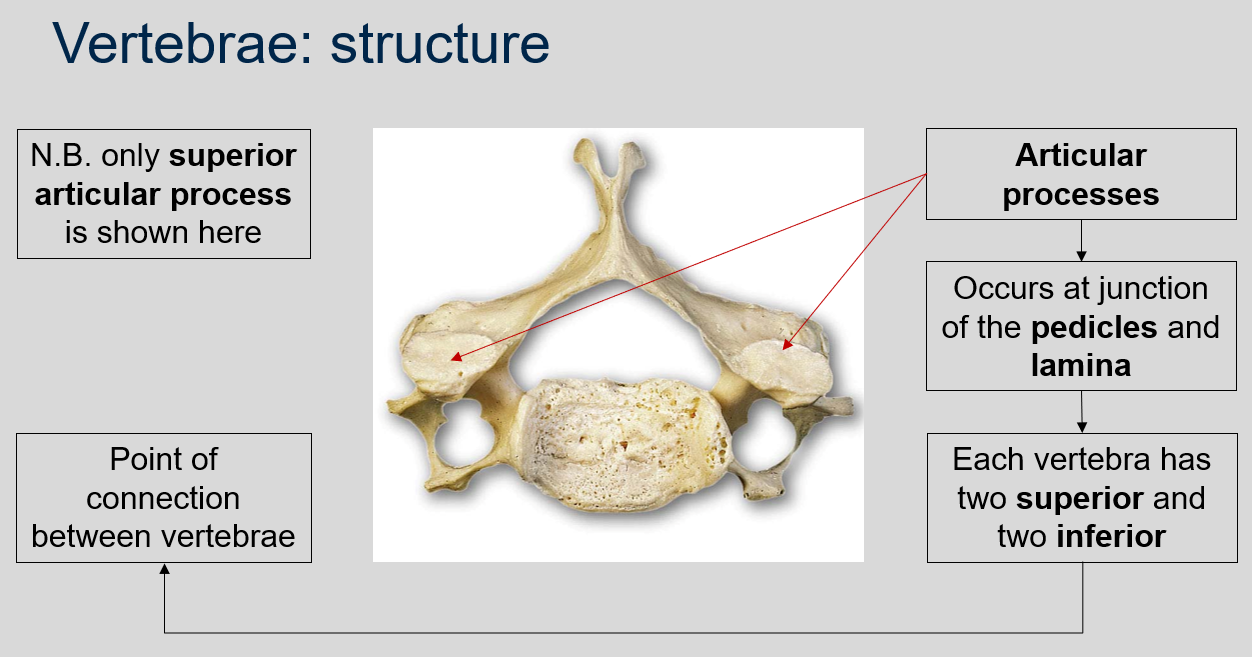
54
New cards
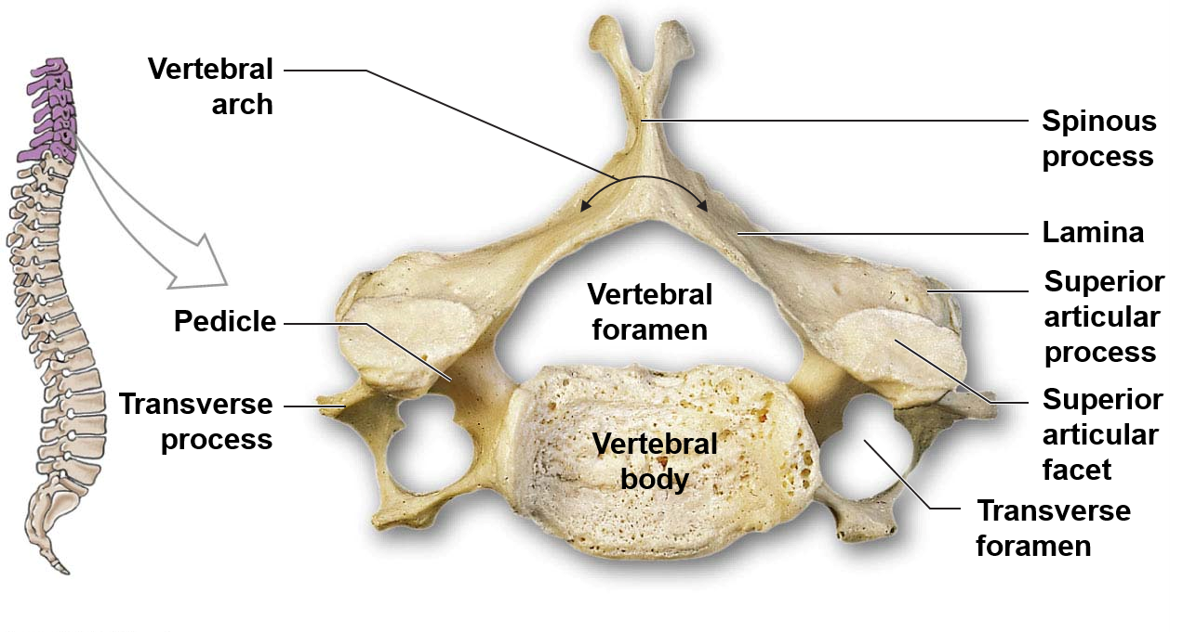
What are articular processes?
The point of connection between vertebrae are the articular processes. Articular processes are bony protrusions that occur at the junction of the pedicles and lamina in each vertebra. Each vertebra has two superior and two inferior articular processes that form joints with adjacent vertebrae, allowing for movement and flexibility of the spine.
55
New cards
Can you name and describe the different structures of vertebrae?
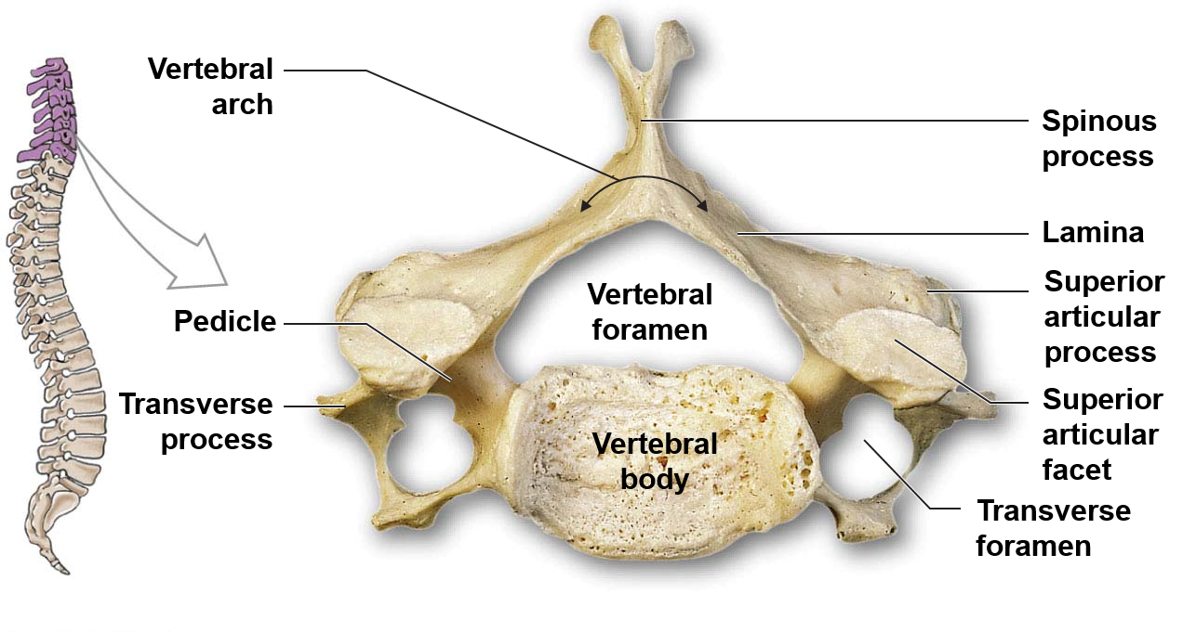
56
New cards
What are the four features of cervical vertebrae?
The four features of cervical vertebrae are an oval and concave vertebral body, a large vertebral foramen, additional transverse foramina for blood vessels to the brain, and a spinous process with a V-shaped tip.
57
New cards
What is C1?
C1 is called atlas. It articulates with the occipital bone, and the connection facilitates nodding.
58
New cards
What is C2 also known as, and what is its additional feature?
C2 is also known as axis. Its additional feature is a dens, which facilitates rotation (head shaking).
59
New cards
Why can't humans move their head without special articulation between the skull, C1, and C2?
Without the special articulation between the skull, C1 and C2, the head would not be able to rotate, nod or shake.
60
New cards
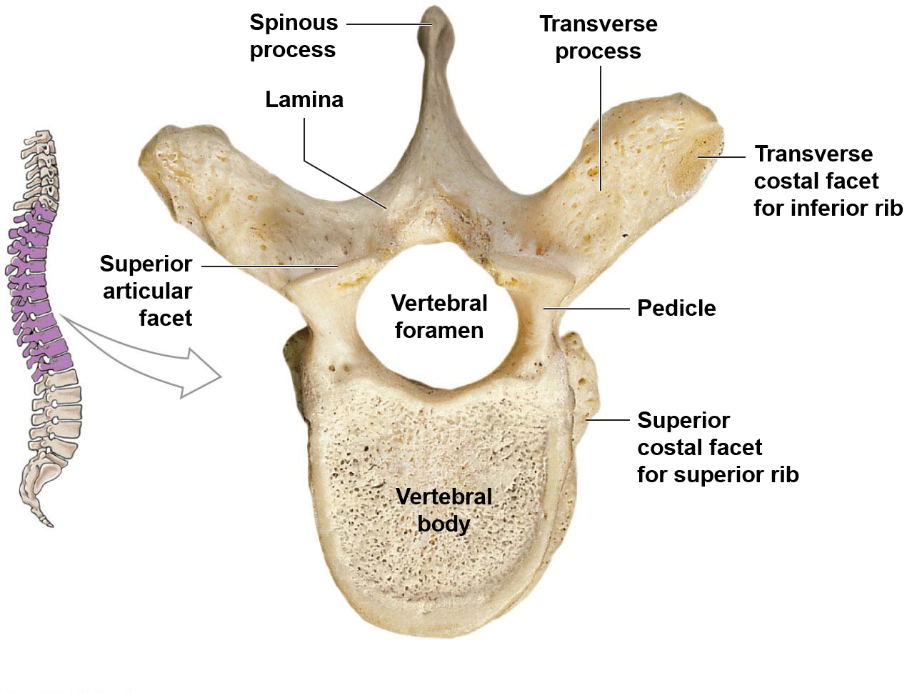
What happens inferiorly from T1 in thoracic vertebrae?
The spinal column width decreases, the vertebral foramina decrease in size, and the vertebral bodies increase in size.
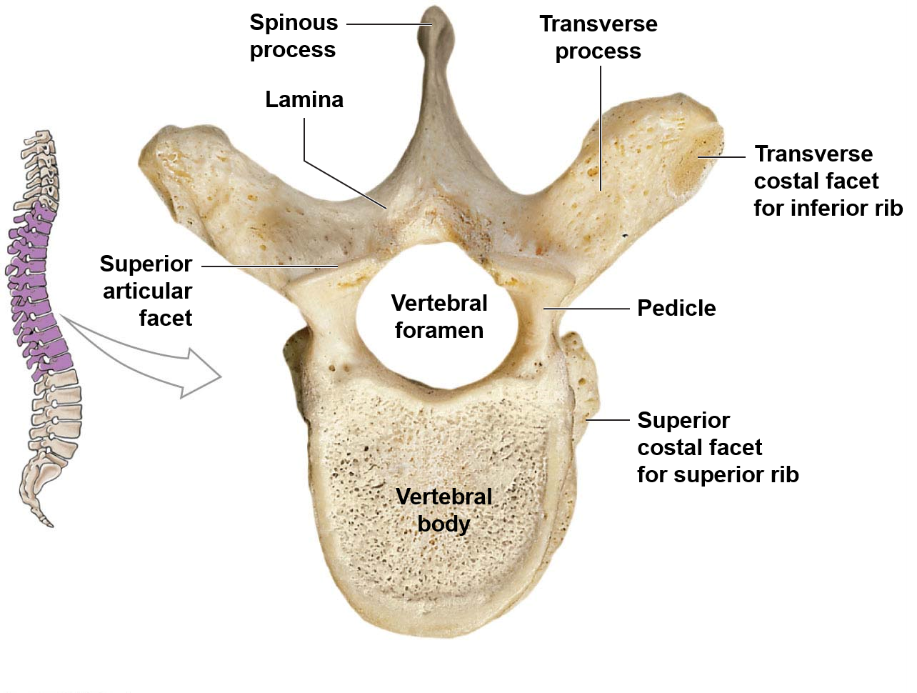
61
New cards
What are the features of thoracic vertebrae?
Heart-shaped vertebral body, thin spinous process, costal facets to articulate with ribs.
62
New cards
What is the function of lumbar vertebrae?
Lumbar vertebrae support the most weight and operate as shock absorbers.
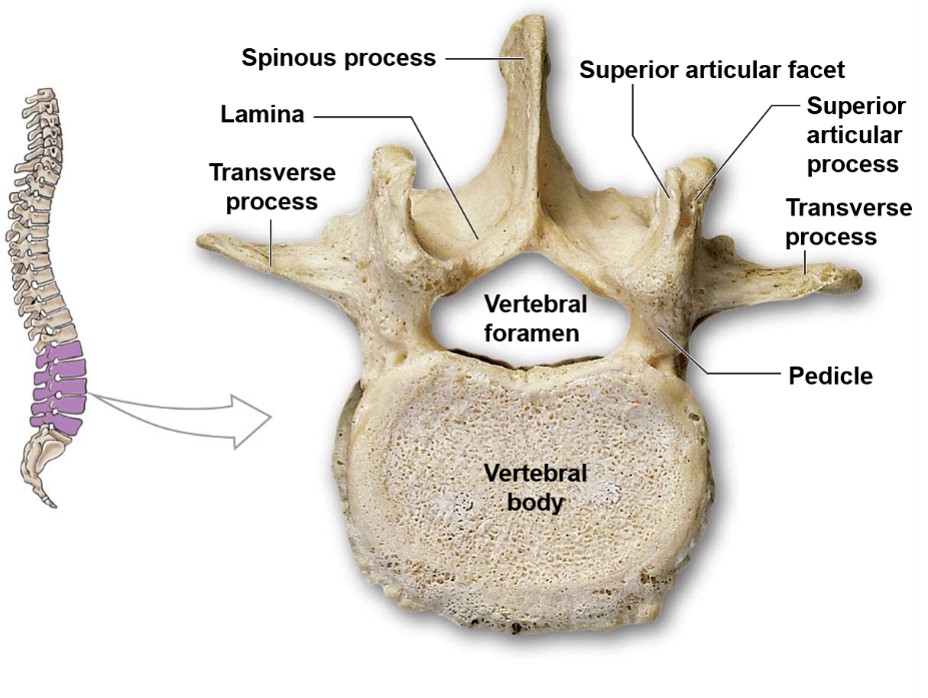
63
New cards
What are the distinctive features of lumbar vertebrae?
Lumbar vertebrae are characterized by a thick and oval vertebral body, a large and thick spinous process, and sharp transverse processes.
64
New cards
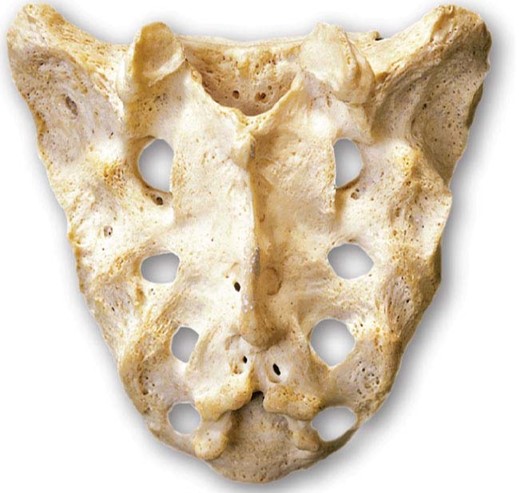
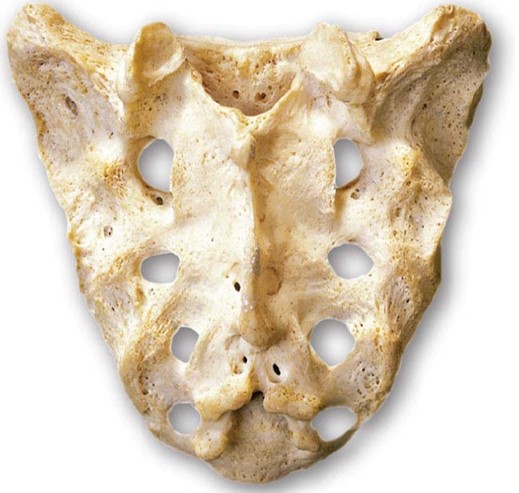
What is the sacrum and what happens during its development?
The sacrum is comprised of five vertebrae that fuse during development (by the age of 25-30). Sacral crests form during fusion.
65
New cards
What are the three important functions of the sacrum?
The three important functions of the sacrum are:
1. Protects the reproductive, digestive and secretory organs
2. Attaches the axial and appendicular skeletons via the pelvic girdle
3. Provides surface area for muscle attachment for leg movement
1. Protects the reproductive, digestive and secretory organs
2. Attaches the axial and appendicular skeletons via the pelvic girdle
3. Provides surface area for muscle attachment for leg movement
66
New cards
What is the coccyx made up of and when does fusion occur?
The coccyx is comprised of 3-5 vertebrae that fuse late in adulthood. In the elderly, the sacrum and coccyx may fuse.
67
New cards
What is the main function of the coccyx?
The main function of the coccyx is to provide surface area for muscles that control the anal opening.
68
New cards
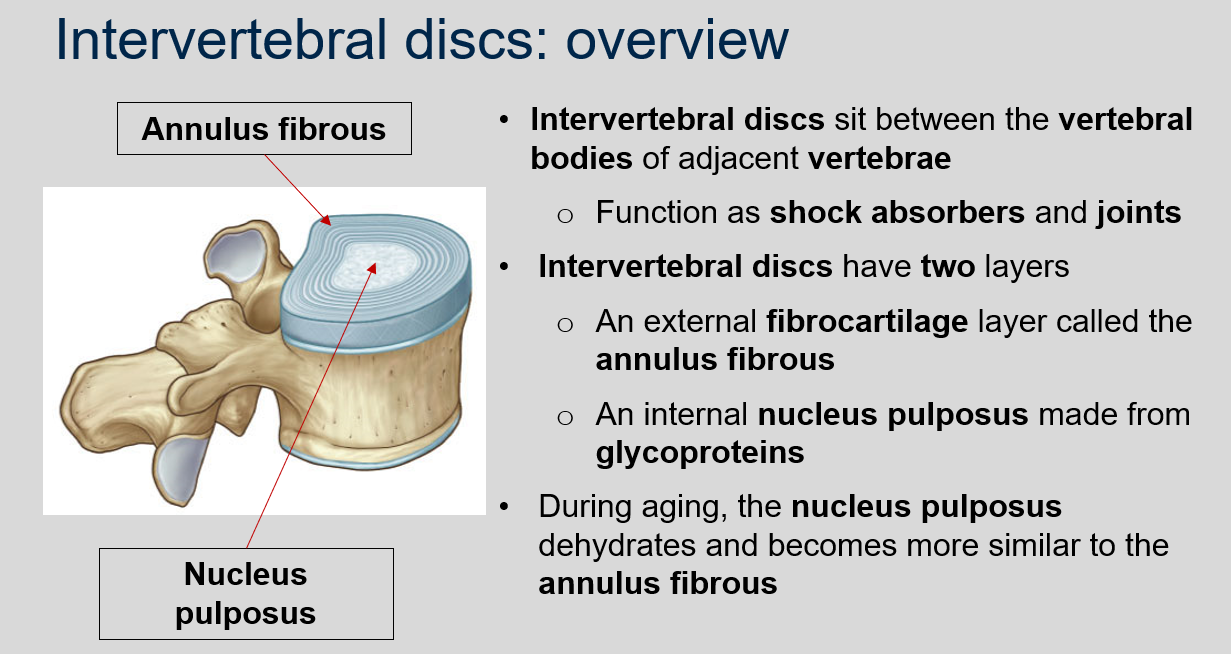
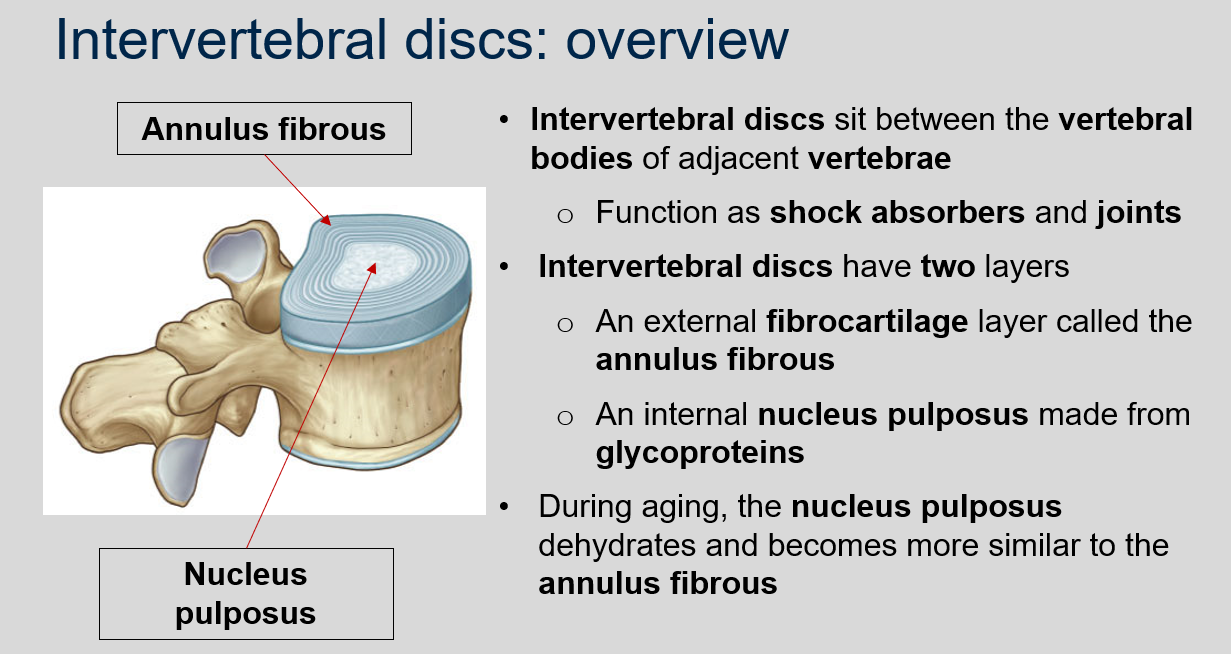
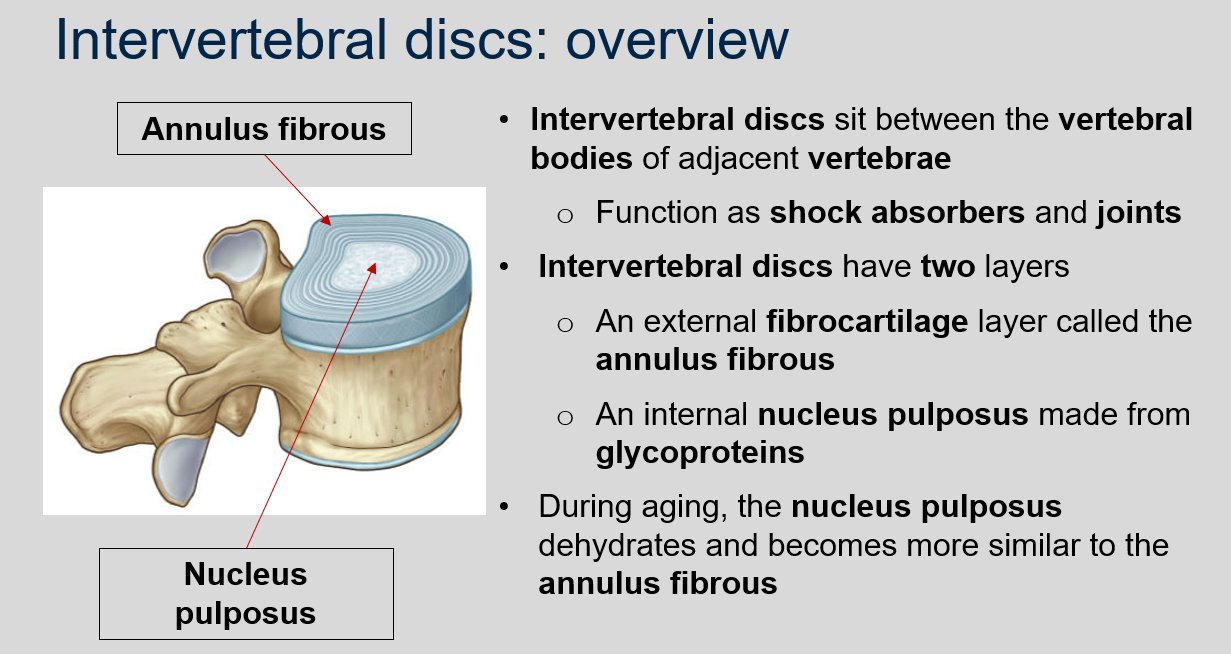
What is the function of intervertebral discs?
Intervertebral discs sit between the vertebral bodies of adjacent vertebrae and function as shock absorbers and joints.
69
New cards
What are the two layers of intervertebral discs?
An external fibrocartilage layer called the annulus fibrous and an internal nucleus pulposus made from glycoproteins.
70
New cards
What happens to the nucleus pulposus during aging?
The nucleus pulposus dehydrates and becomes more similar to the annulus fibrous.
71
New cards
Can you describe what disk generation looks like by comparing a young person to an older person?
72
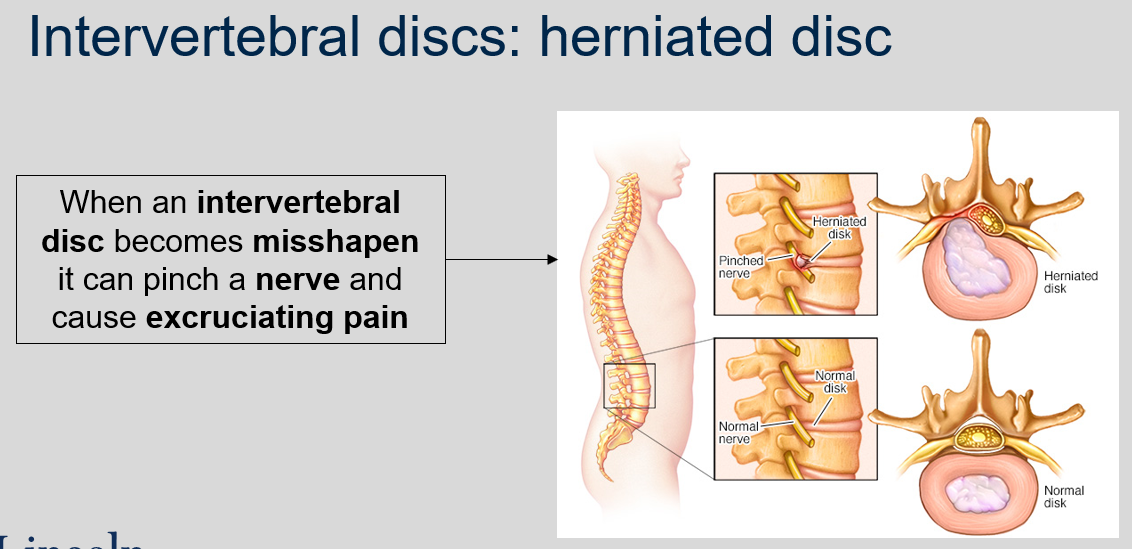
New cards
What happens when an intervertebral disc becomes misshapen?
It can pinch a nerve and cause excruciating pain.
73
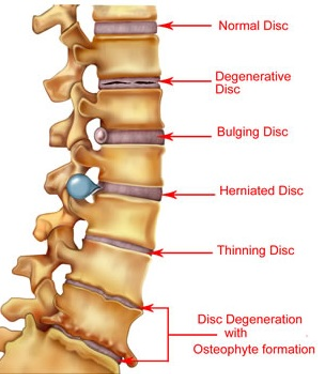
New cards
Can you compare different types of intervertebral discs?
74
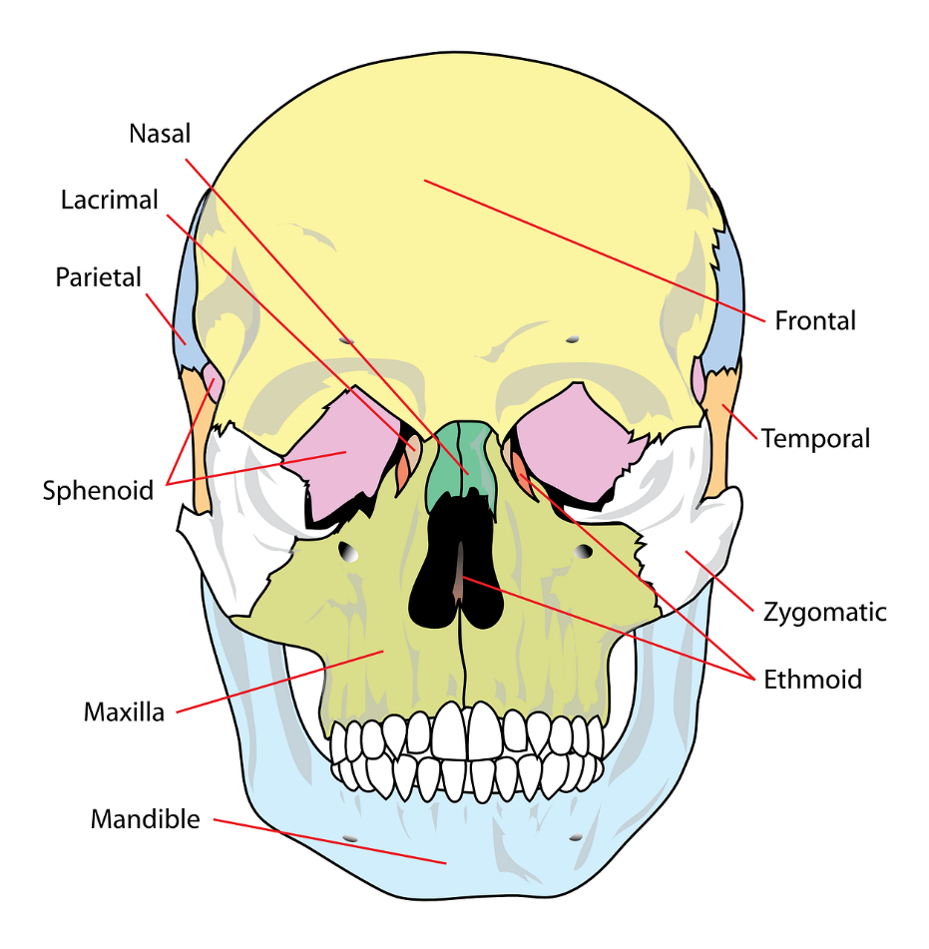
New cards
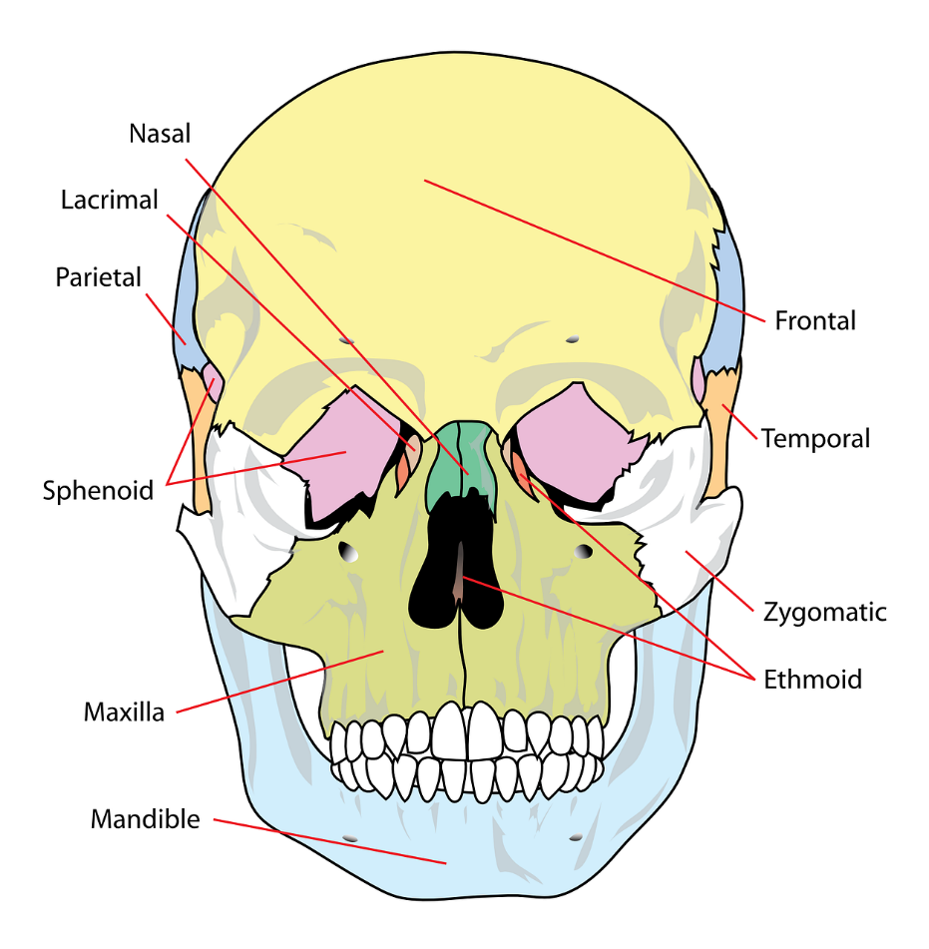
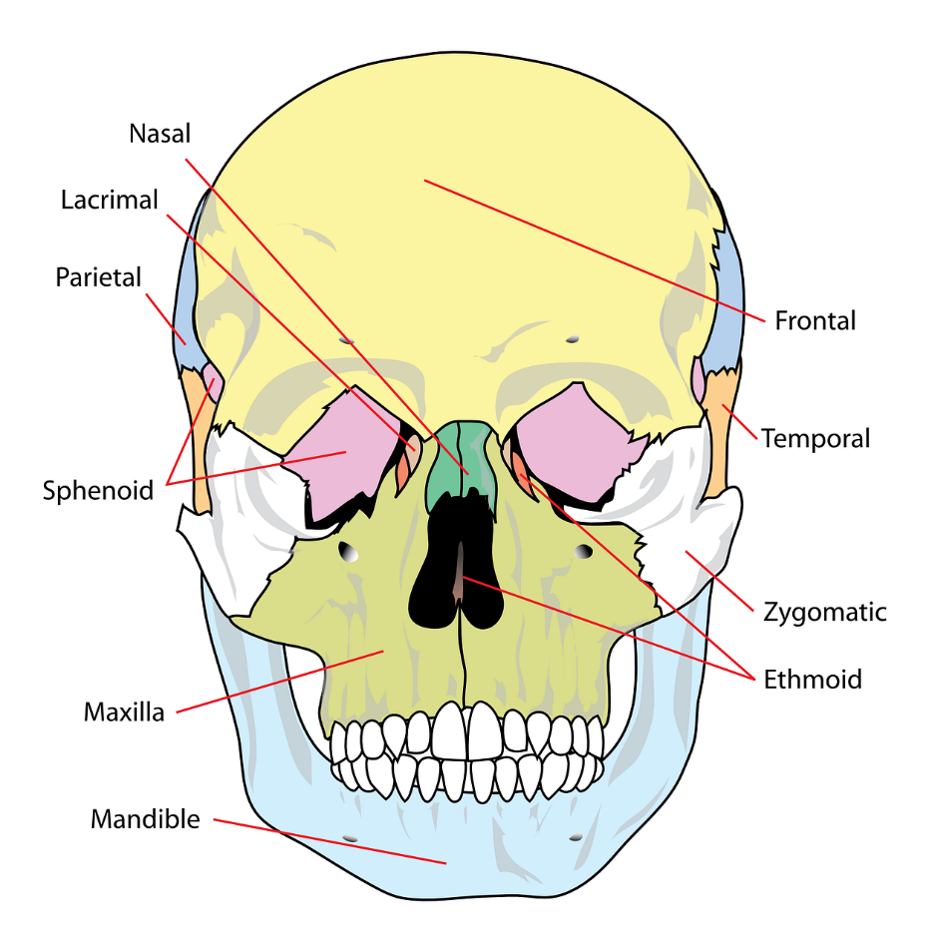
What are the two sections the skull divides into and how many bones does each section consist of?
The skull divides into two sections, the cranium, which is made up of 8 bones, and the face, which is made up of 14 bones. Additionally, there are 7 bones that associate with the skull but are not considered here.
75
New cards
What is the name of the joint where bones of the skull articulate?
Sutures.
76
New cards
What is the function of foramina in the skull?
Foramina facilitate passage of nerves and blood vessels.
77
New cards
What are the two main functions of the cranium?
The interior surface maintains brain position, while the exterior surface allows muscle attachment.
78
New cards
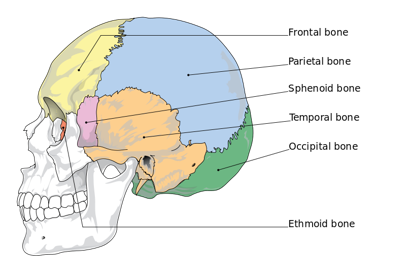
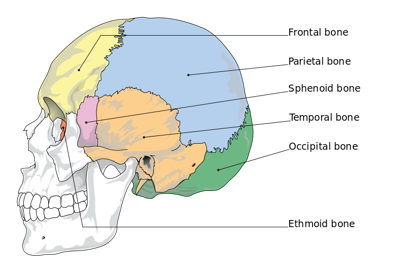
What are the 8 bones of the cranium?
The 8 bones of the cranium are the frontal bone, parietal bones (x2), temporal bones (x2), occipital bone, sphenoid bone, and ethmoid bone.
79
New cards
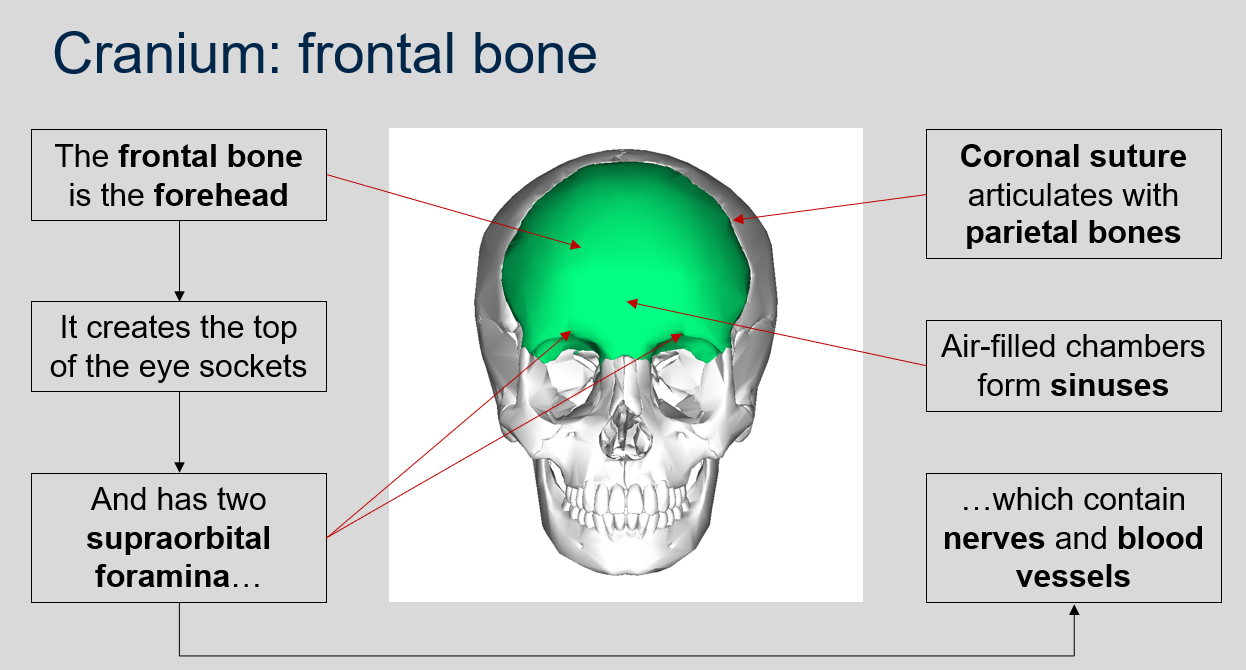
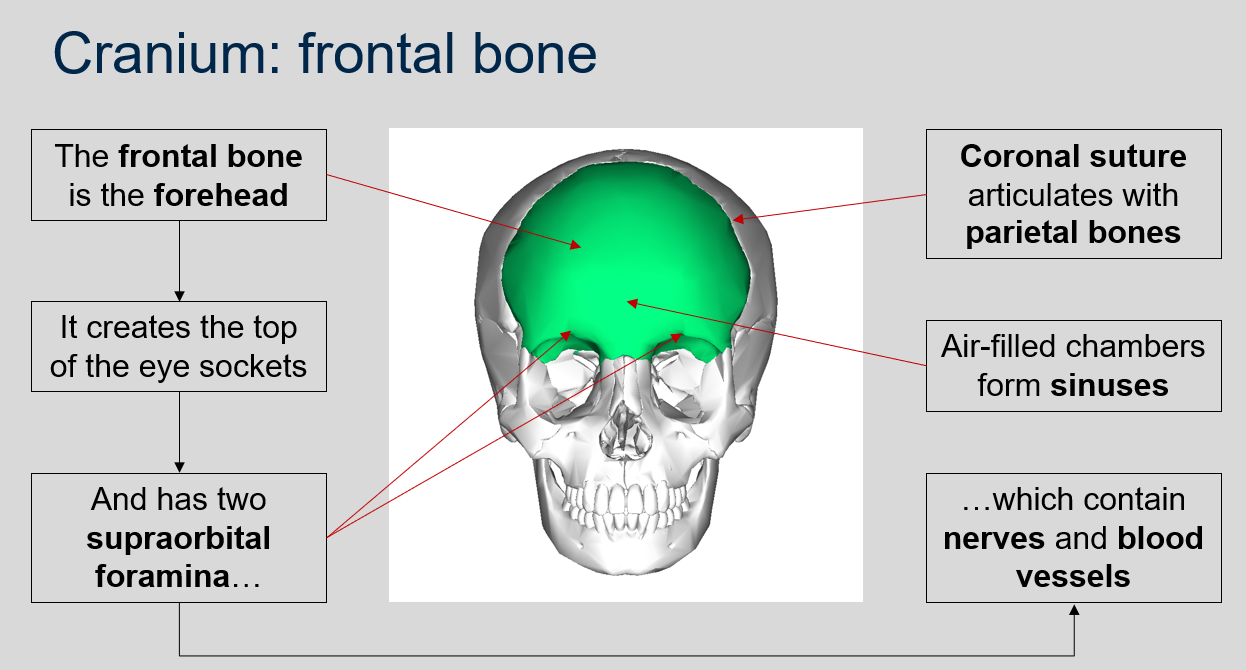
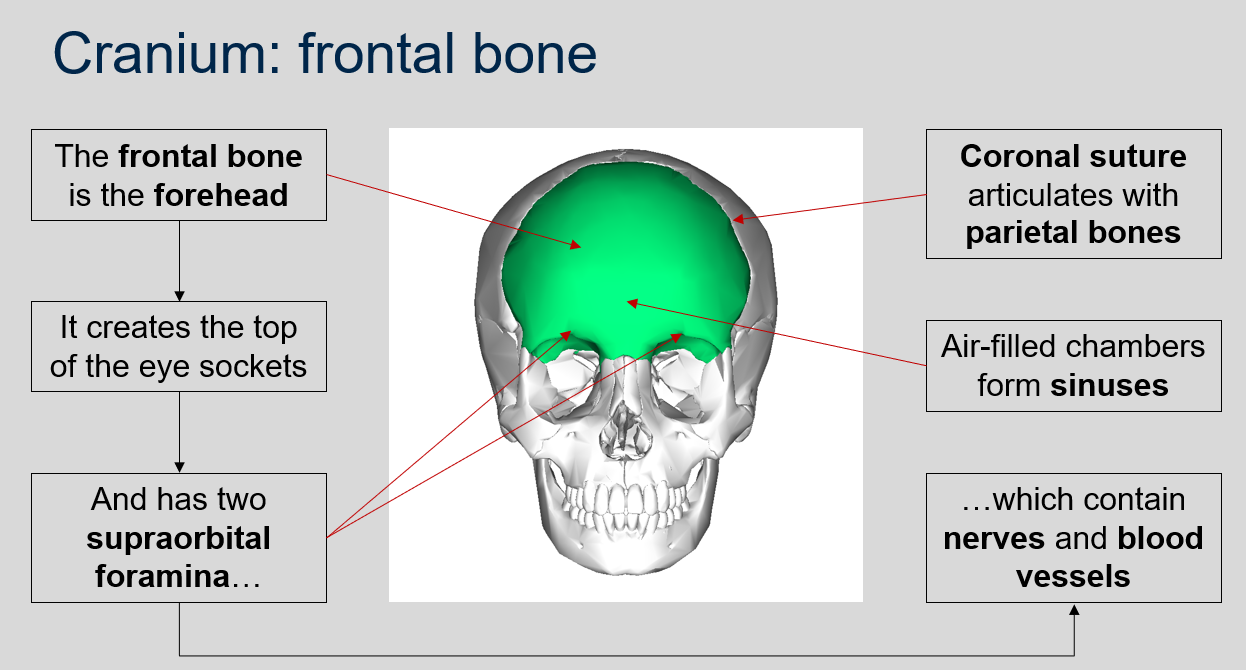
What are the features of the frontal bone?
The frontal bone forms the forehead, creates the top of the eye sockets, and has two supraorbital foramina which contain nerves and blood vessels.
80
New cards
What suture articulates with the parietal bones?
Coronal suture.
81
New cards
What forms sinuses in the cranium?
Air-filled chambers.
82
New cards
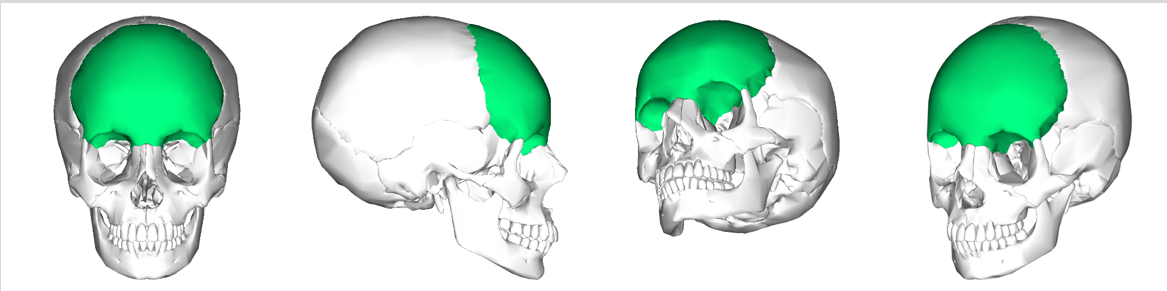
Can you name what each view is of the frontal bone of the cranium?
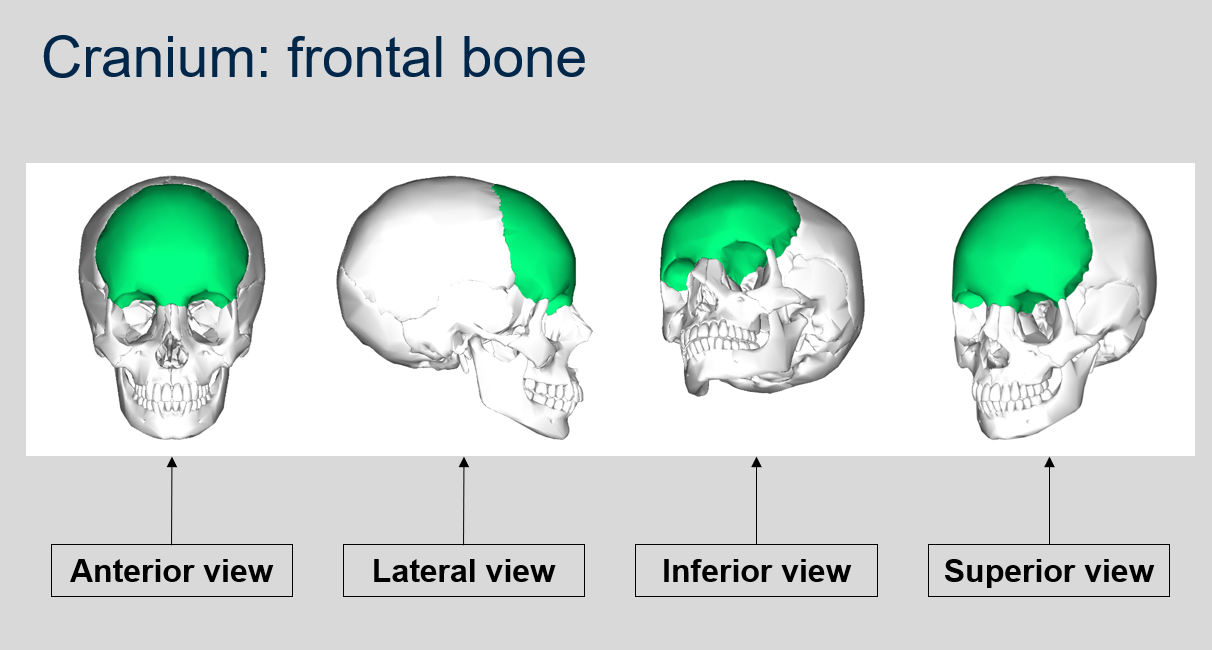
83
New cards
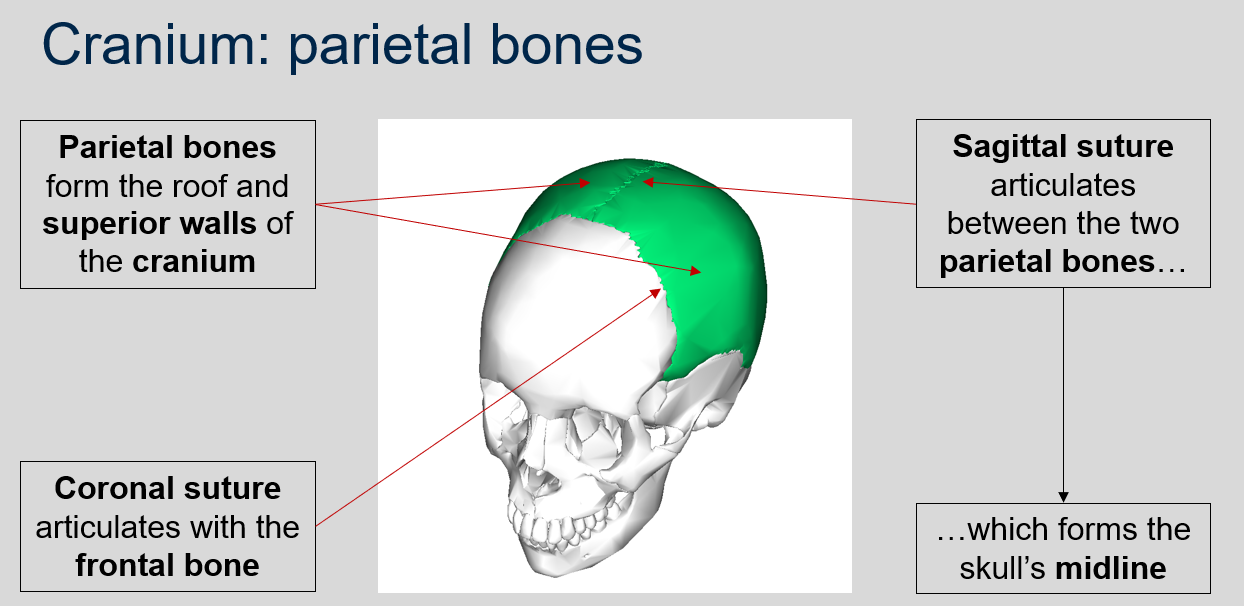
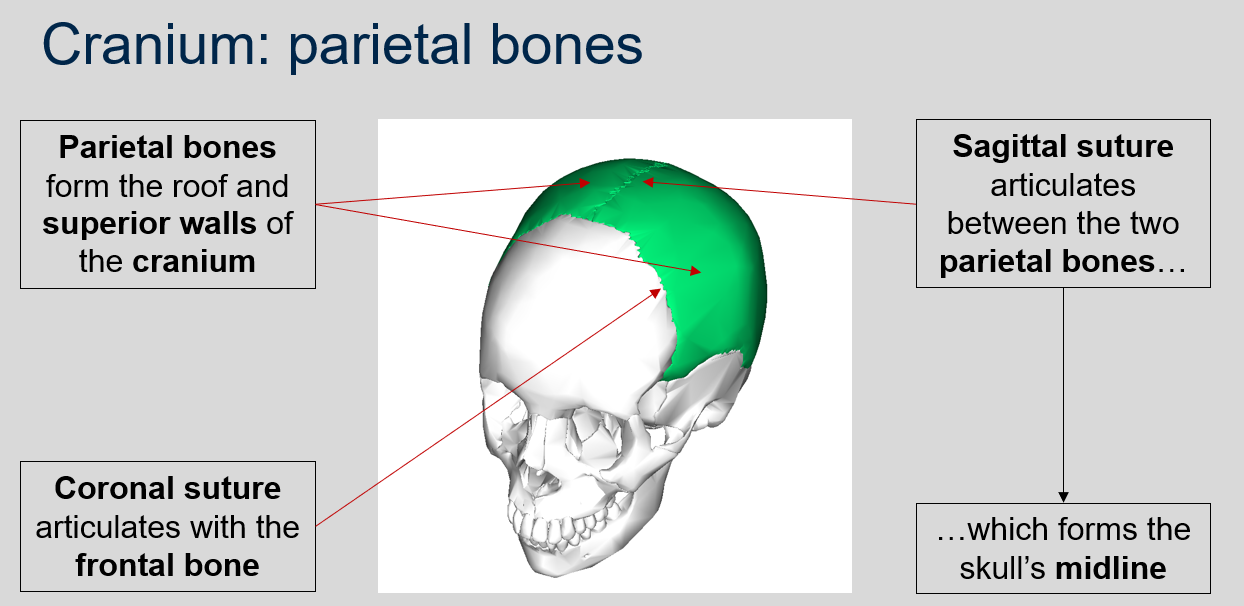
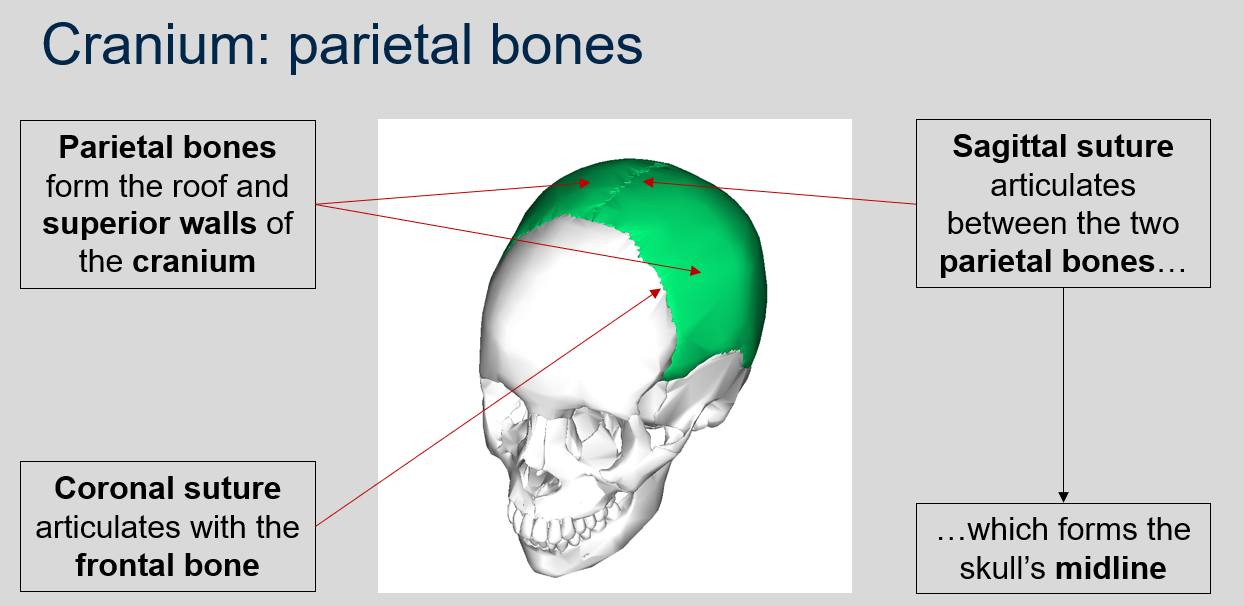
What is the function of the parietal bones in the cranium?
The parietal bones form the roof and superior walls of the cranium.
84
New cards
What does the sagittal suture articulate between?
The sagittal suture articulates between the two parietal bones, forming the skull's midline.
85
New cards
What suture articulates with the frontal bone?
The coronal suture articulates with the frontal bone.
86
New cards
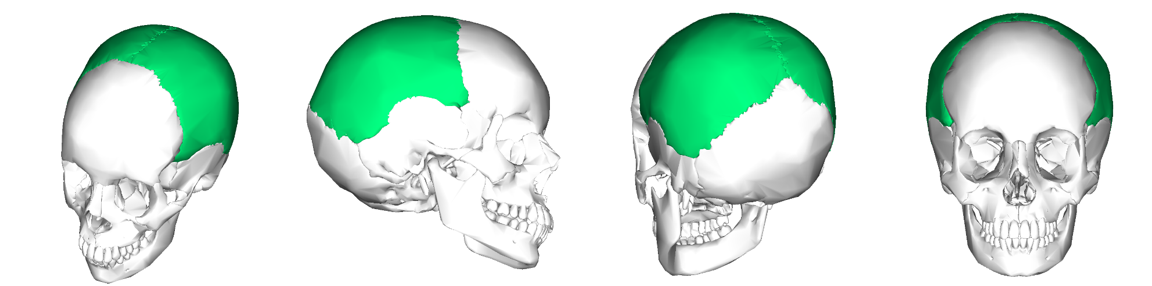
Can you name what each view is of the parietal bones of the cranium?
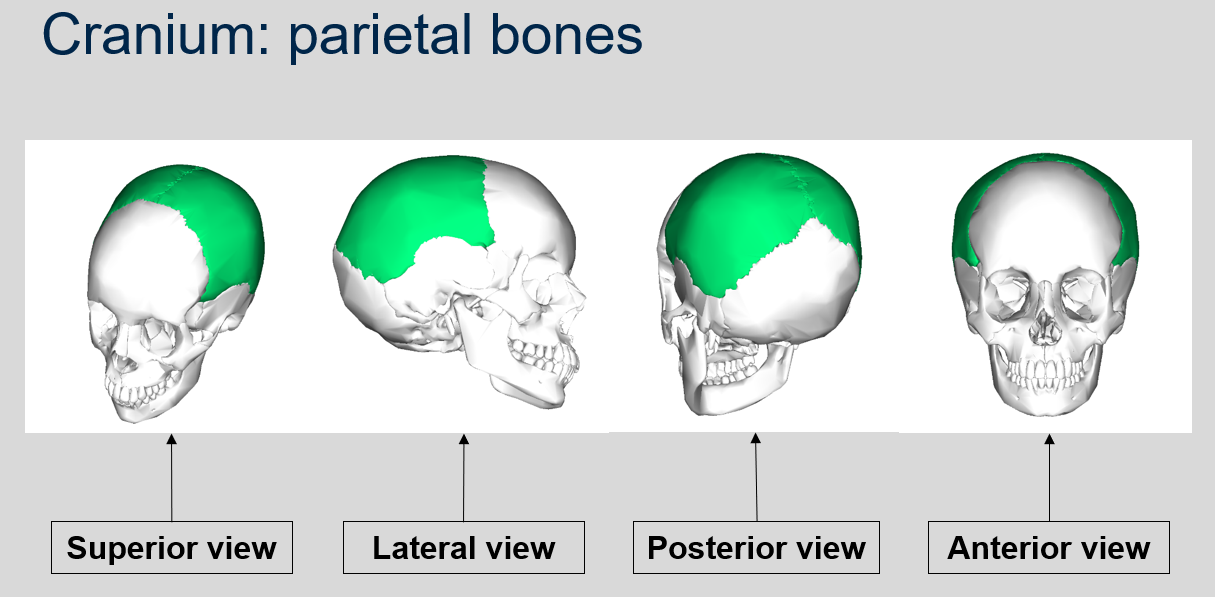
87
New cards
What bones form the inferior walls of the cranium?
Temporal bones. A mnemonic to remember this is that "temporal" sounds like "temple," and the temporal bones are inferior to the temples.
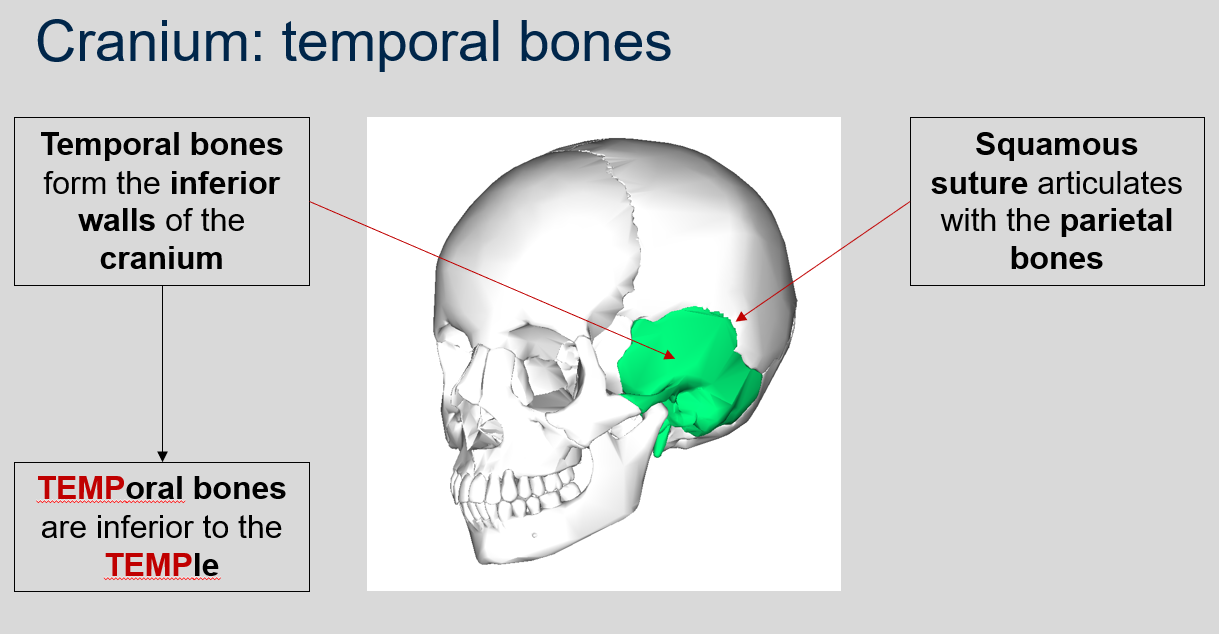
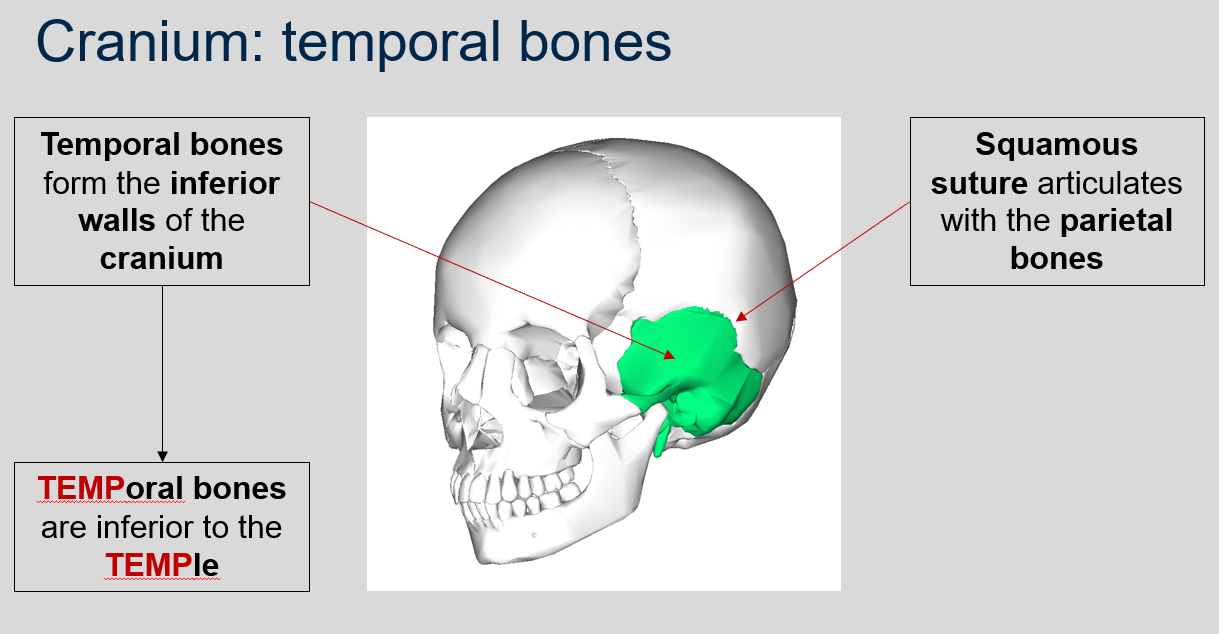
88
New cards
What does the squamous suture articulate with?
The squamous suture articulates with the parietal bones.
89
New cards
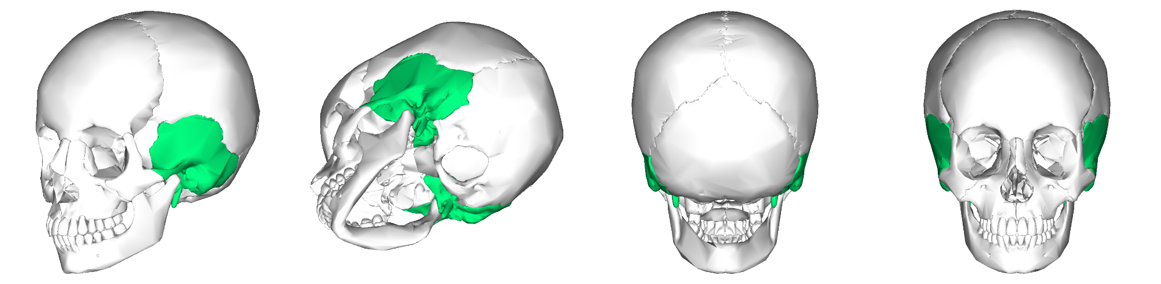
Can you name what each view is of the temporal bones of the cranium?
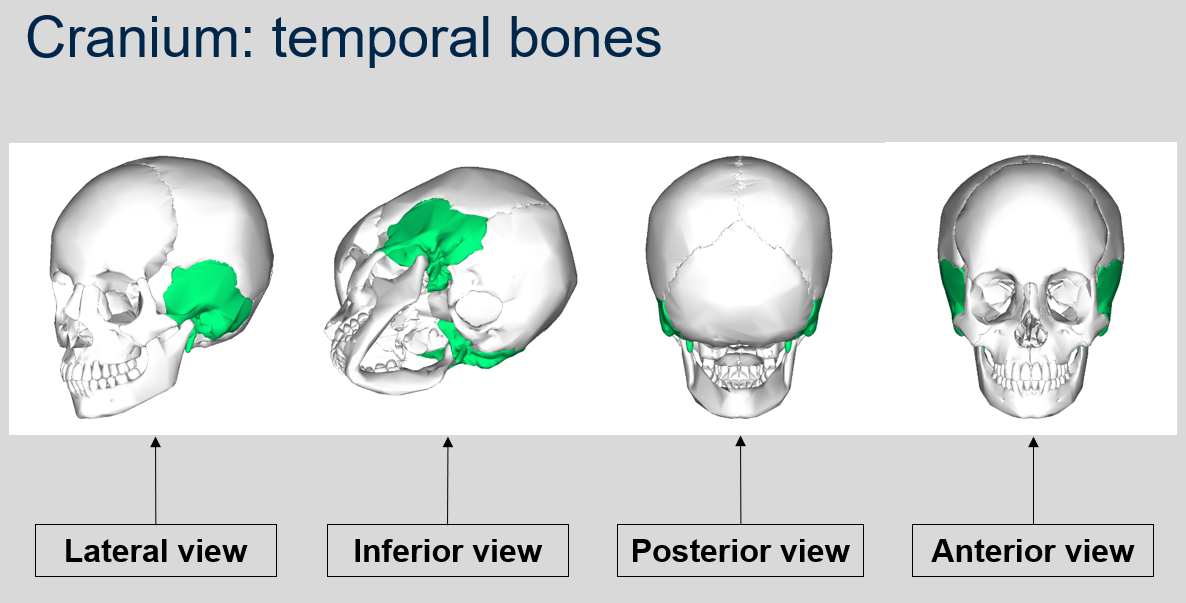
90
New cards
What are the distinctive features of the temporal bones in the cranium?
The temporal bones in the cranium contain the external auditory meatus, which creates the ear canal. This canal connects the outer ear to the ear drum and auditory ossicles.
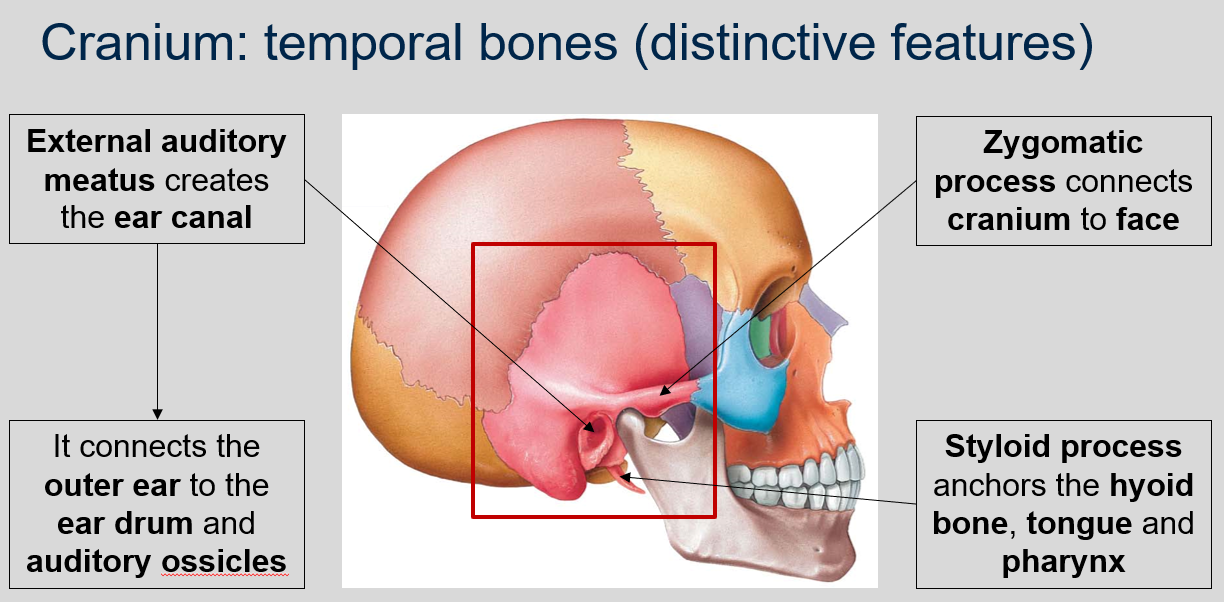
91
New cards
What is the function of the zygomatic process in the temporal bones of the cranium?
The zygomatic process connects the cranium to the face.
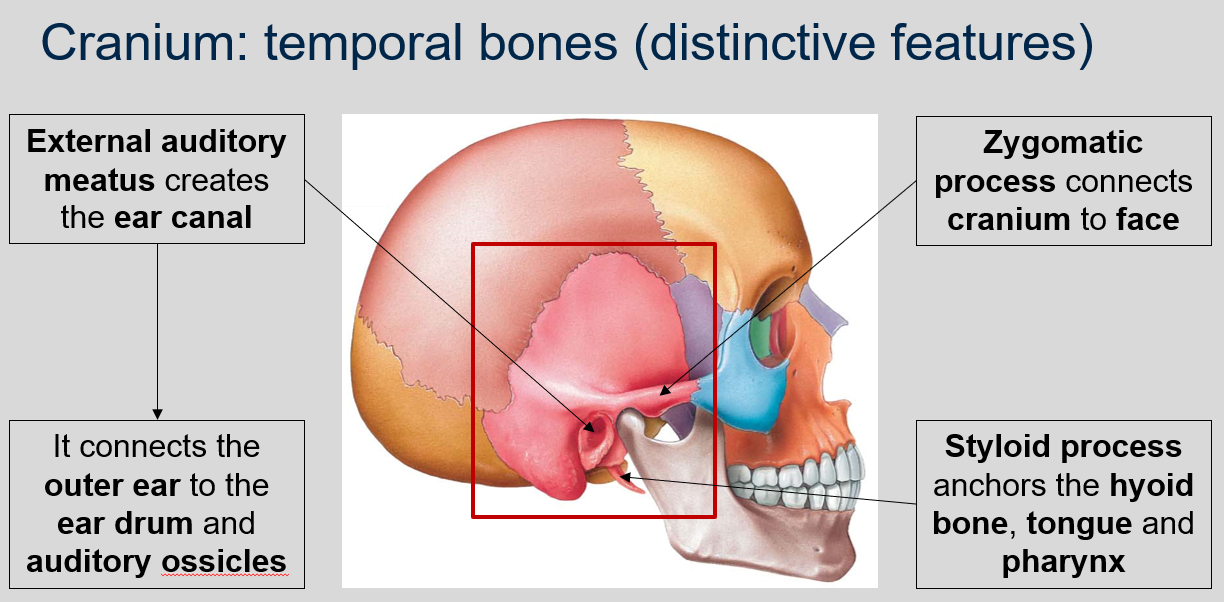
92
New cards
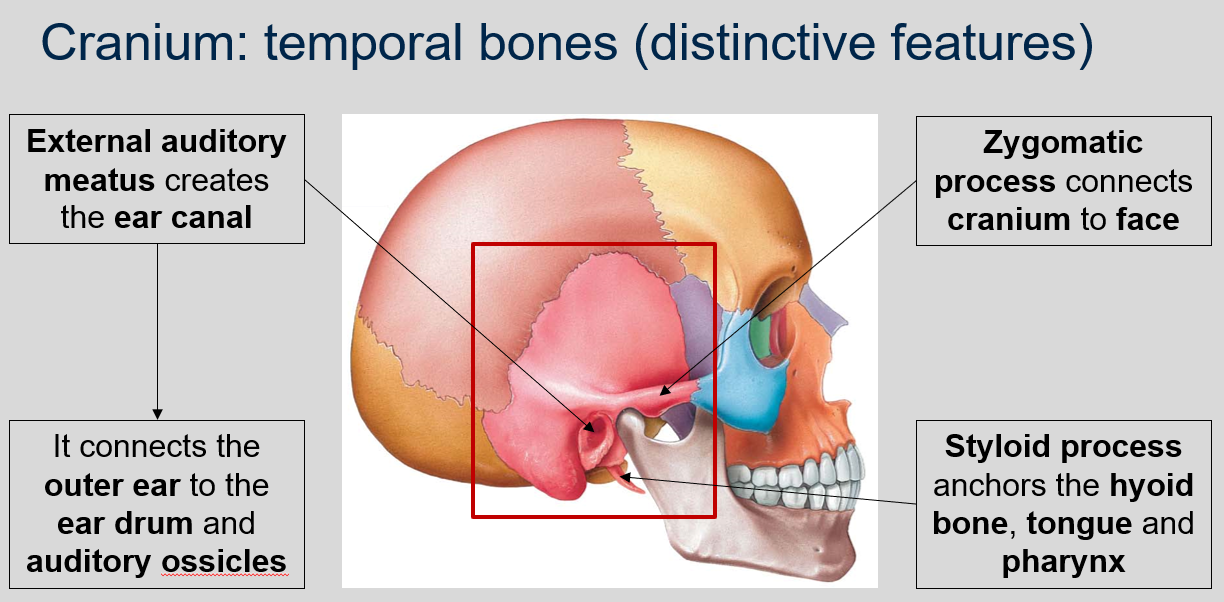
What is the function of the styloid process in the temporal bones of the cranium ?
The styloid process anchors the hyoid bone, tongue, and pharynx.
93
New cards
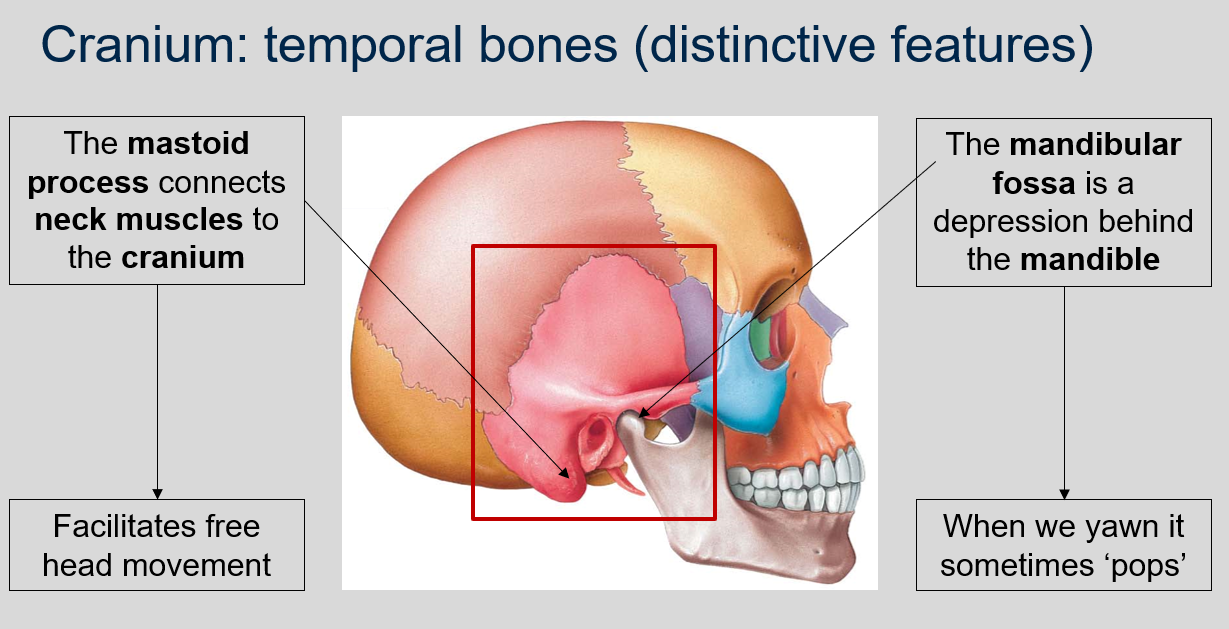
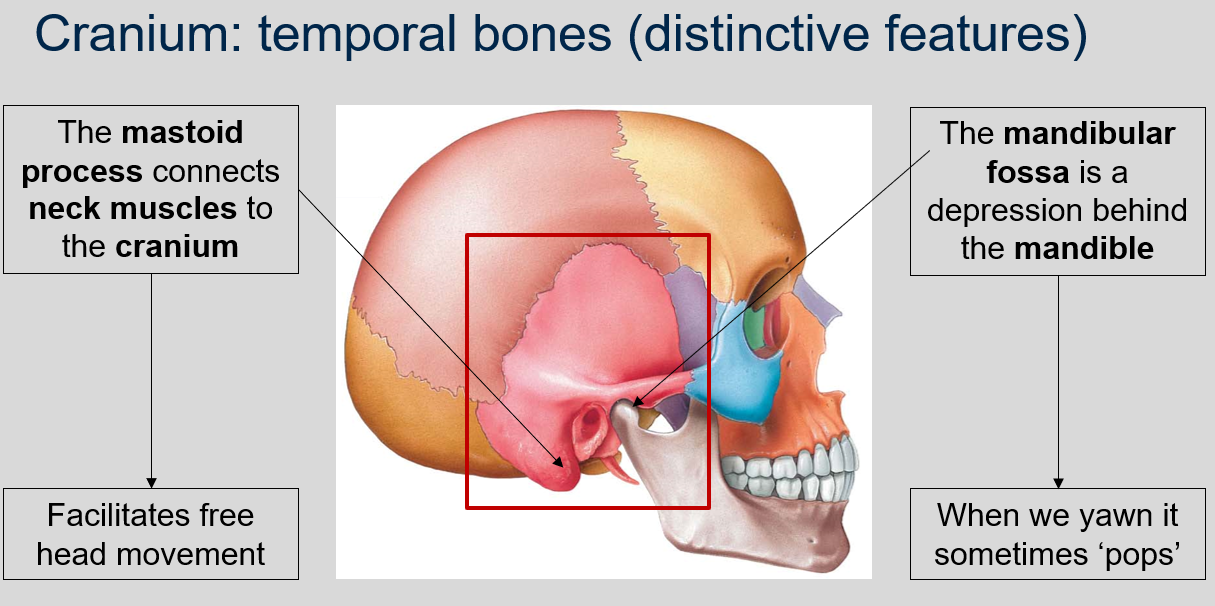
What is the function of the mastoid process in the temporal bones of the cranium?
The mastoid process connects neck muscles to the cranium, which facilitates free head movement.
94
New cards
What is the mandibular fossa in the temporal bones of the cranium and what happens to it when we yawn?
The mandibular fossa is a depression located behind the mandible in the temporal bones of the cranium. It serves as the point of articulation for the mandible, allowing for movement of the lower jaw. When we yawn, the mandible may sometimes 'pop' as it moves within the mandibular fossa.
95
New cards
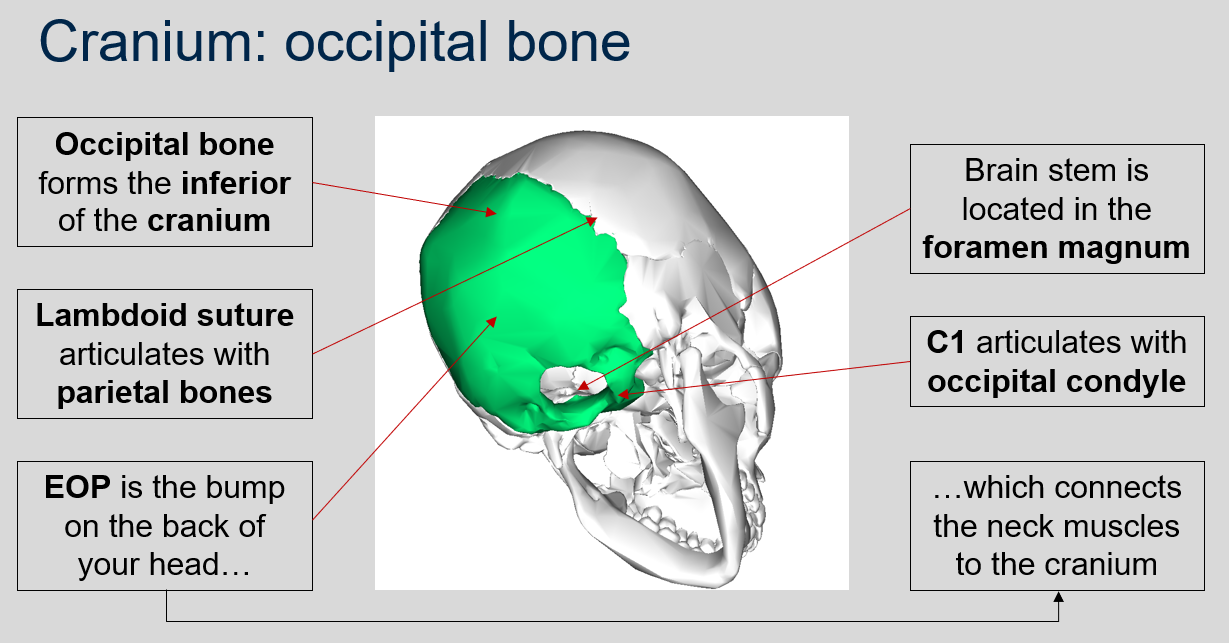
What is the role of the occipital bone in the cranium?
The occipital bone forms the inferior (bottom) portion of the cranium.
96
New cards
What is the function of the lambdoid suture in the occipital bone of the cranium?
The lambdoid suture in the occipital bone articulates with the parietal bones of the cranium.
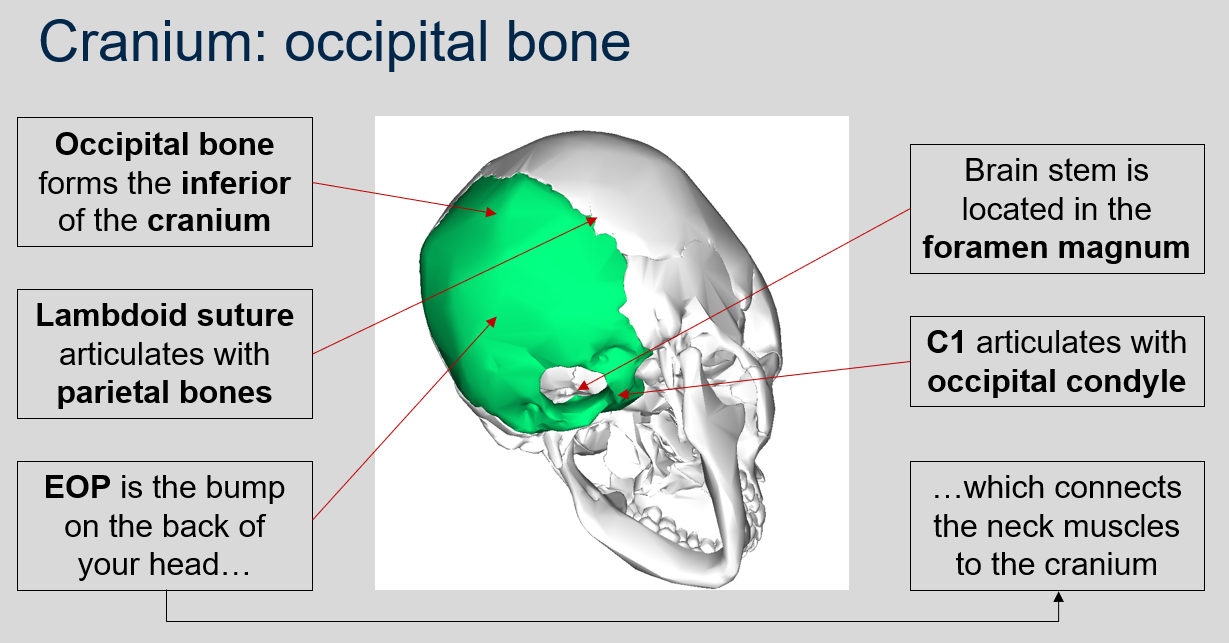
97
New cards
What is the function of the EOP in the occipital bone of the cranium?
The EOP (External Occipital Protuberance) is the bump on the back of your head and it connects the neck muscles to the cranium.
98
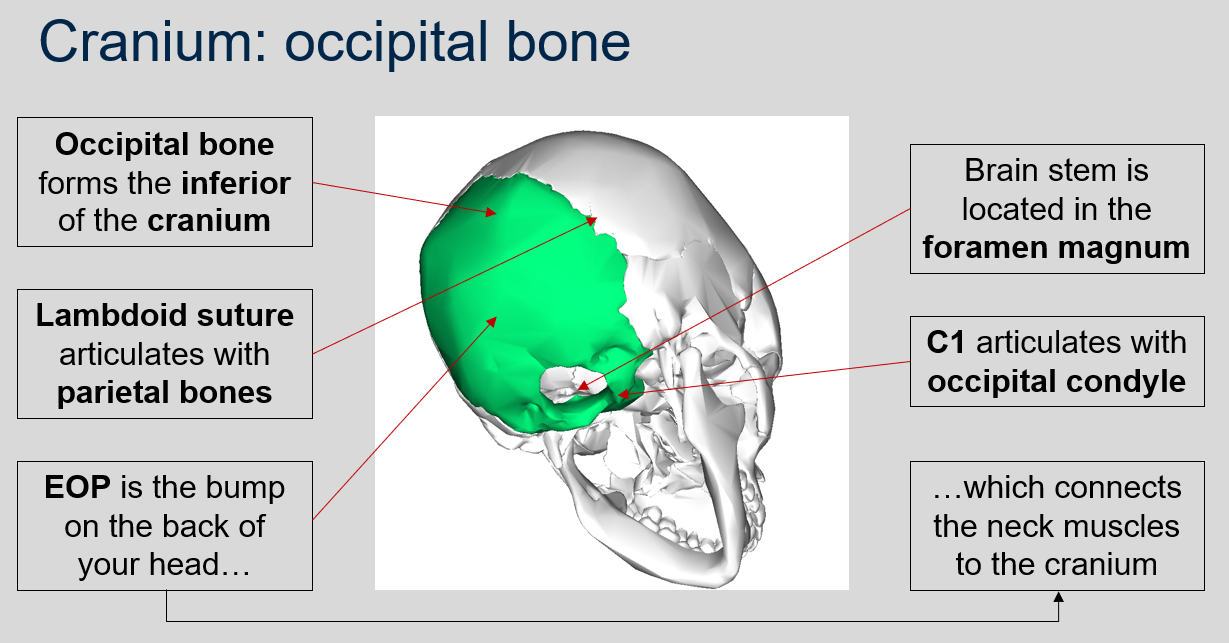
New cards
Where is the brain stem located in the skull?
The brain stem is located in the foramen magnum, a large opening at the base of the skull.
99
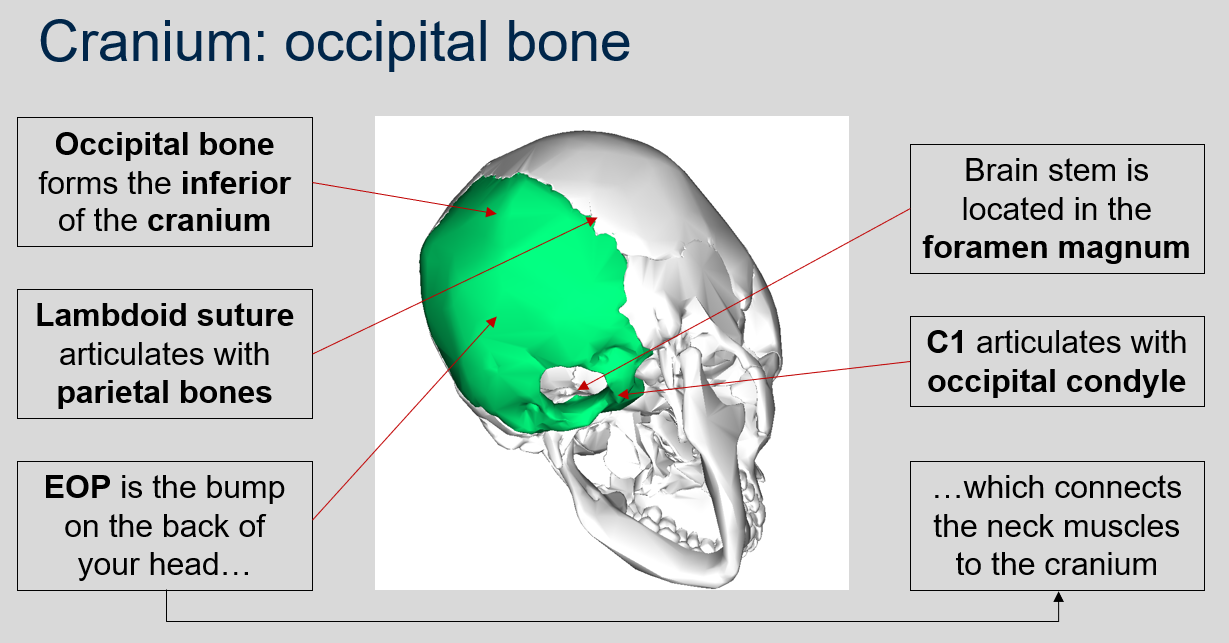
New cards
What does C1 articulate with in the skull?
C1, also known as the atlas vertebra, articulates with the occipital condyle of the skull.
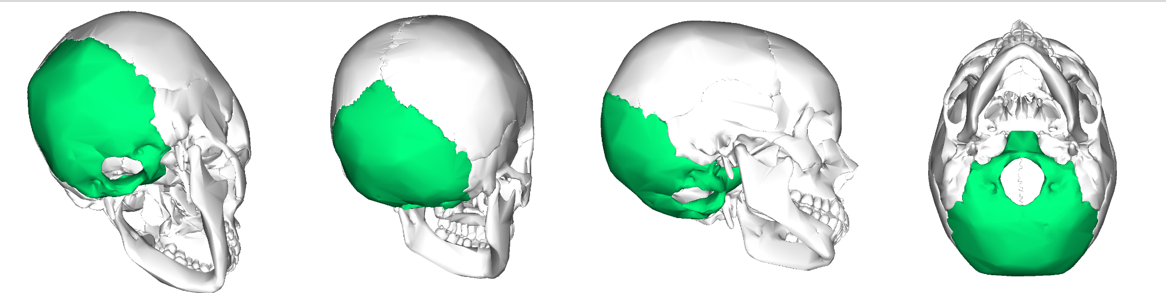
100
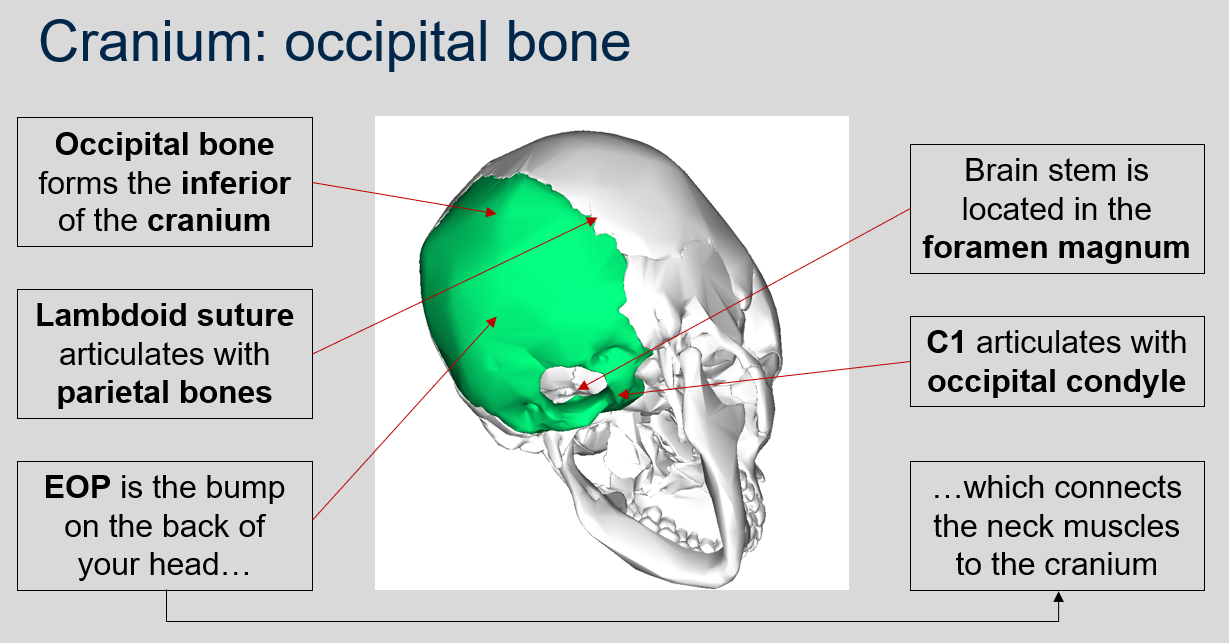
New cards
Can you name what each view is of the occipital bone of the cranium?