Chapter 4 Test Prep
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
electromagnetic
An x-ray photon is a quantum of __________ energy?
Amplitude
__________ is one half the range from crest to valley over which the sine wave varies?
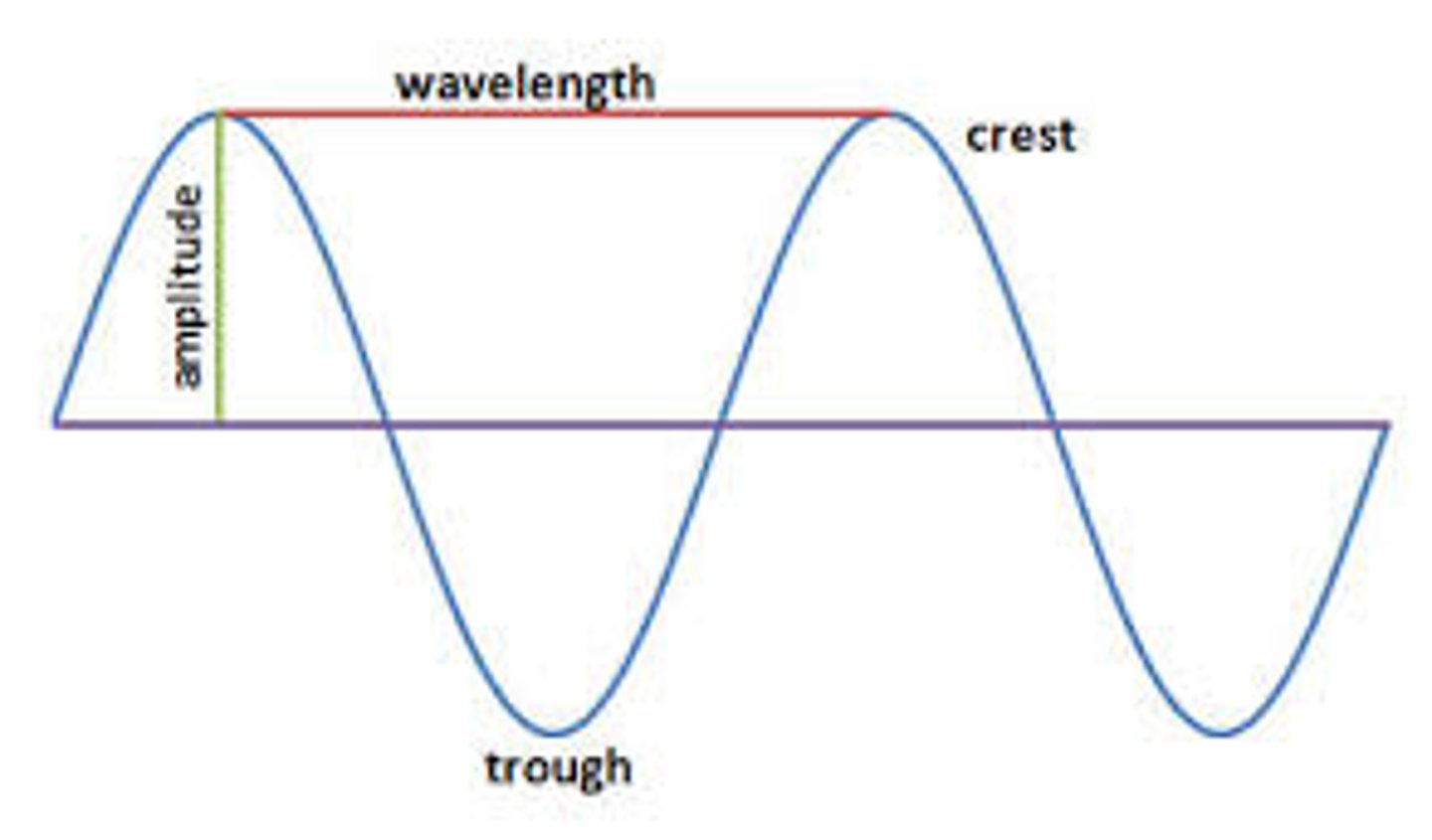
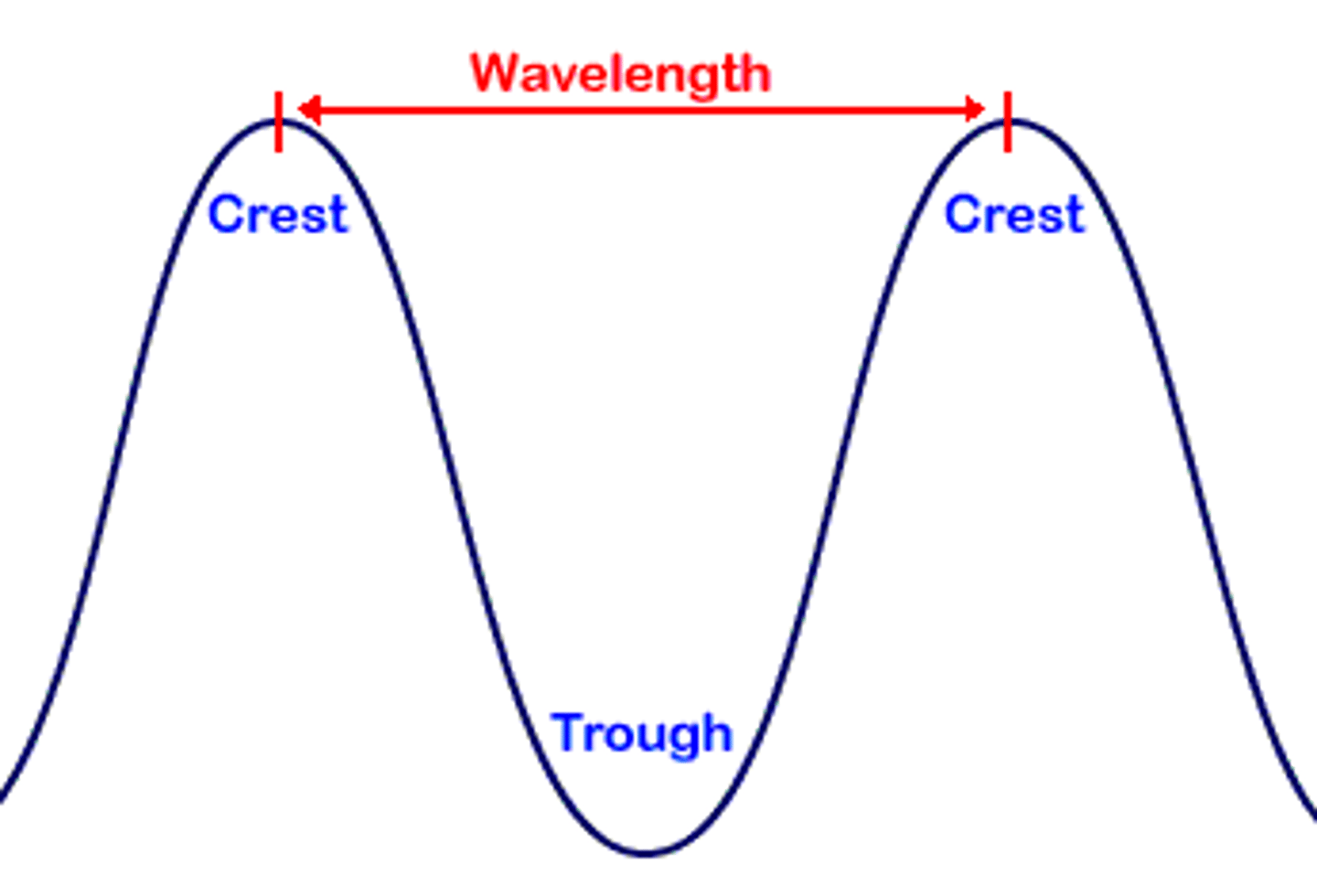
Wavelength
__________ is the distance from one crest to another, from one valley to another, or from any point on the sine wave to the next corresponding point?
inversely
At a given velocity, wavelength and frequency are _____________ proportional?
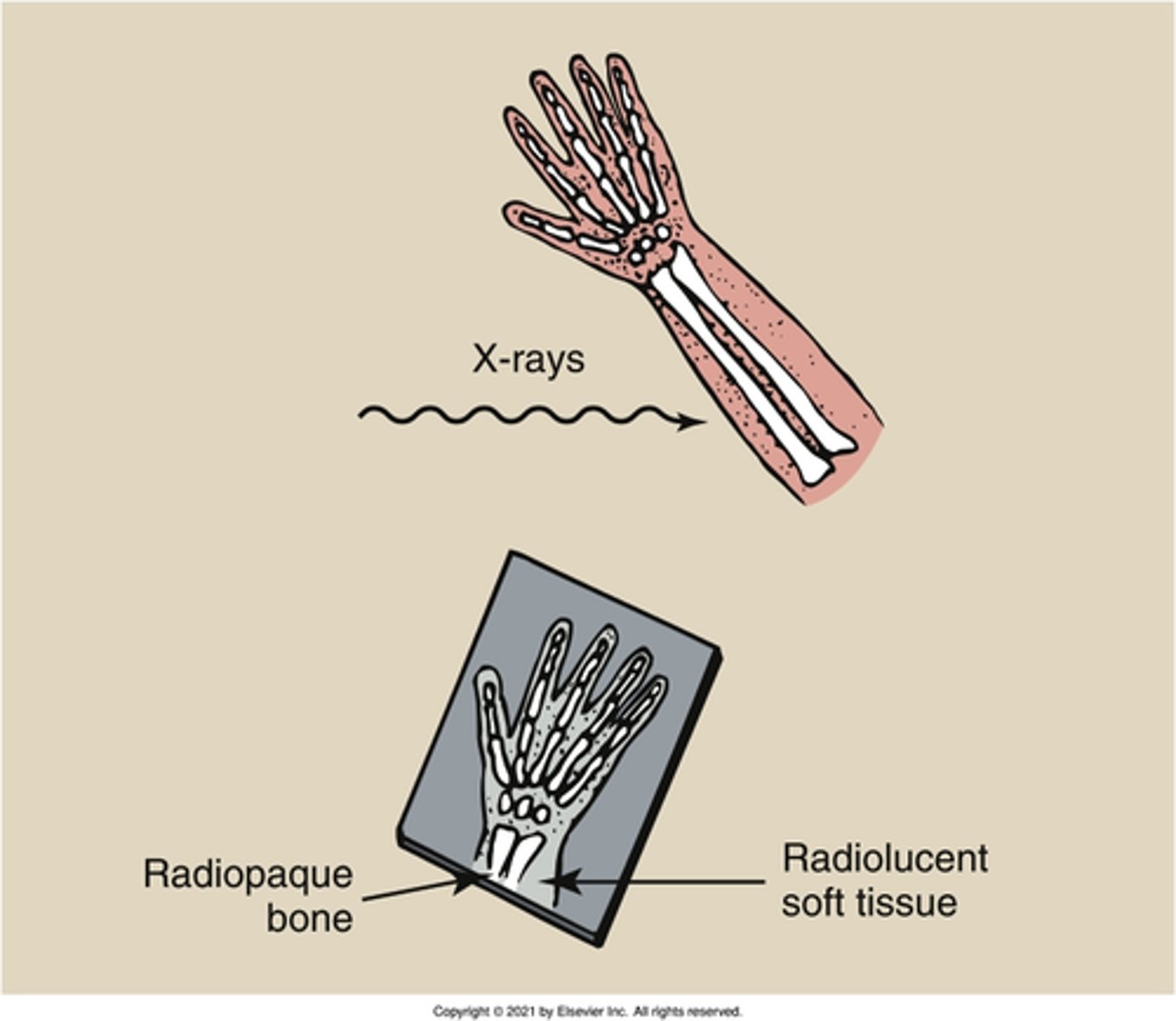
radiopaque; radiolucent
Structures that absorb x-rays are ______________ and structures that transmit x-rays are __________?
frequency
Planck's constant, symbolized h, relates the energy in one quantum (photon) of electromagnetic radiation to the ______________ of that radiation?
Frequency
________ is the number of wavelengths that pass a point of observation per second?
directly
The energy of a photon is ________________ proportional to its frequency?
wavelength; energy
Visible light is identified by __________ and x-rays are identified by ___________?
inversely; square
The inverse square law states that the intensity of electromagnetic radiation is ________ related to the ______ of the distance from the source?
a quantum of electromagnetic energy and is the smallest quantity of any type of electromagnetic radiation (EM radiation).
What is a photon?
both electric and magnetic
Electromagnetic radiation has what properties?
no
Do photons have mass or energy?
the wave form of electromagnetic energy, the wave having regular characteristics such as a constant amplitude and wavelength
What is a sine wave?
c = λf
What is the wave equation for velocity?
inversely related
How are wavelength and frequency related?
inversely related
How are energy and wavelength related?
directly related
How are energy and frequency related?
E=hf
What is the equation for energy?
frequency
The energy of electromagnetic radiation is directly proportional to its...?
400 nm
What is the wavelength for violet?
700 nm
What is the wavelength for red?
E = mc²
What is the mass-energy equivalence equation?
m= hf/c^2
What is the equation for the effective mass of a photon?
Radiation exhibits both wave-like and particle-like properties.
What is the wave-particle duality of radiation?
the intensity of radiation is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source of radiation
What is the inverse square law?
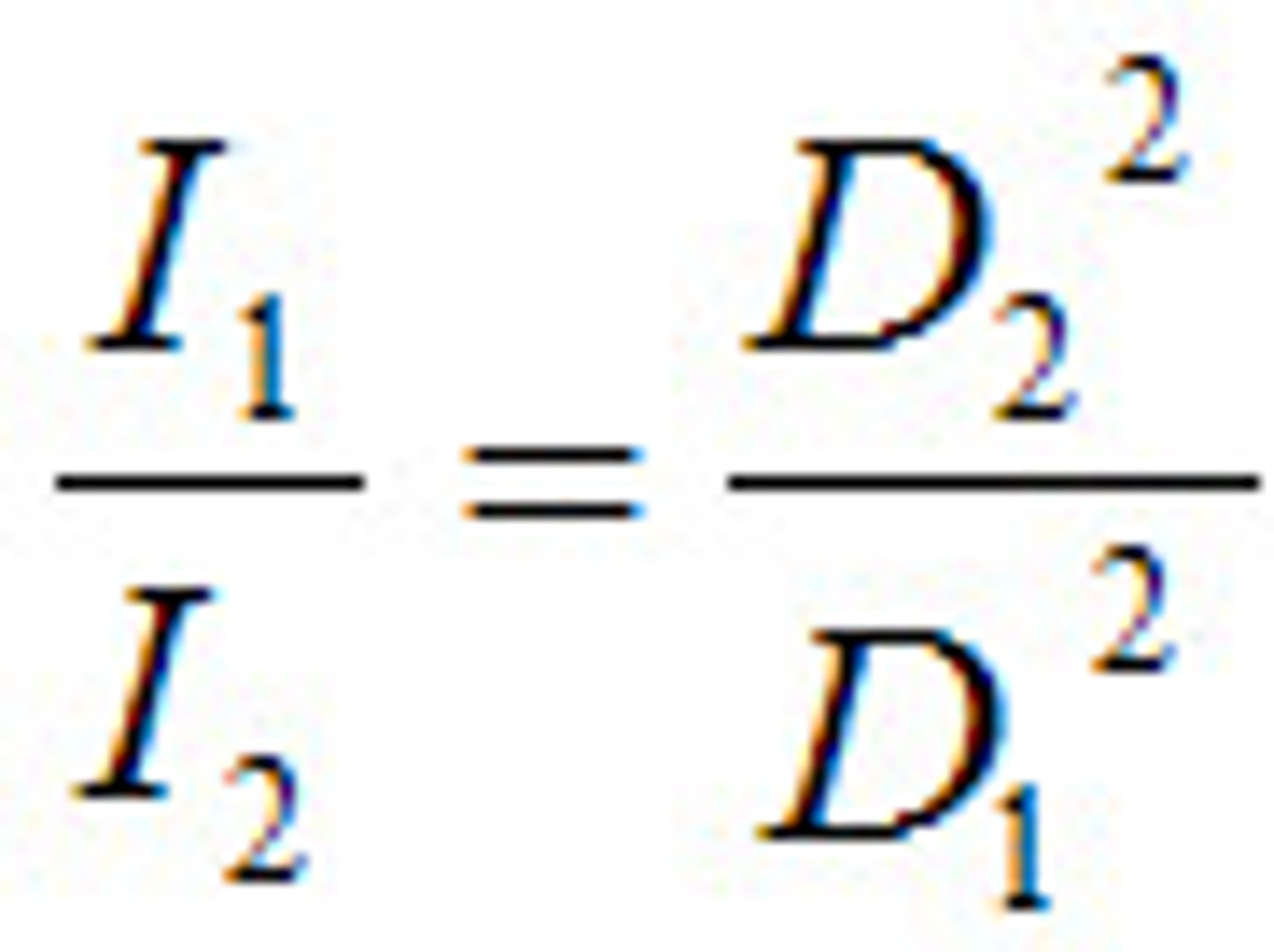
10^6
Mega (M)
10^3
Kilo (k)
10^-2
Centi (c)
10^-3
Mili (m)
10^-6
Micro (μ)
10^-9
Nano (n)
3 x 10^8 m/s
What is the speed of light?
shorter wavelengths (higher photon energy)
What type of wavelengths are used for imaging thick patients?
after meeting a magnetic or electric field
How are photons deflected?
TRUE
T/F: Everything has a wavelength?
TRUE
T/F: Radiation interacts most effectively with matter that is approximately the same size as its wavelength?
electromagnetic energy
Ever present all around us is a state of energy called?
quantum of electromagnetic energy
What is an X-ray photon?
TRUE
T/F: Photons are continuously changing in a sinusoidal fashion?
one half the range from crest to valley (trough) over which the sine wave varies
What is amplitude?
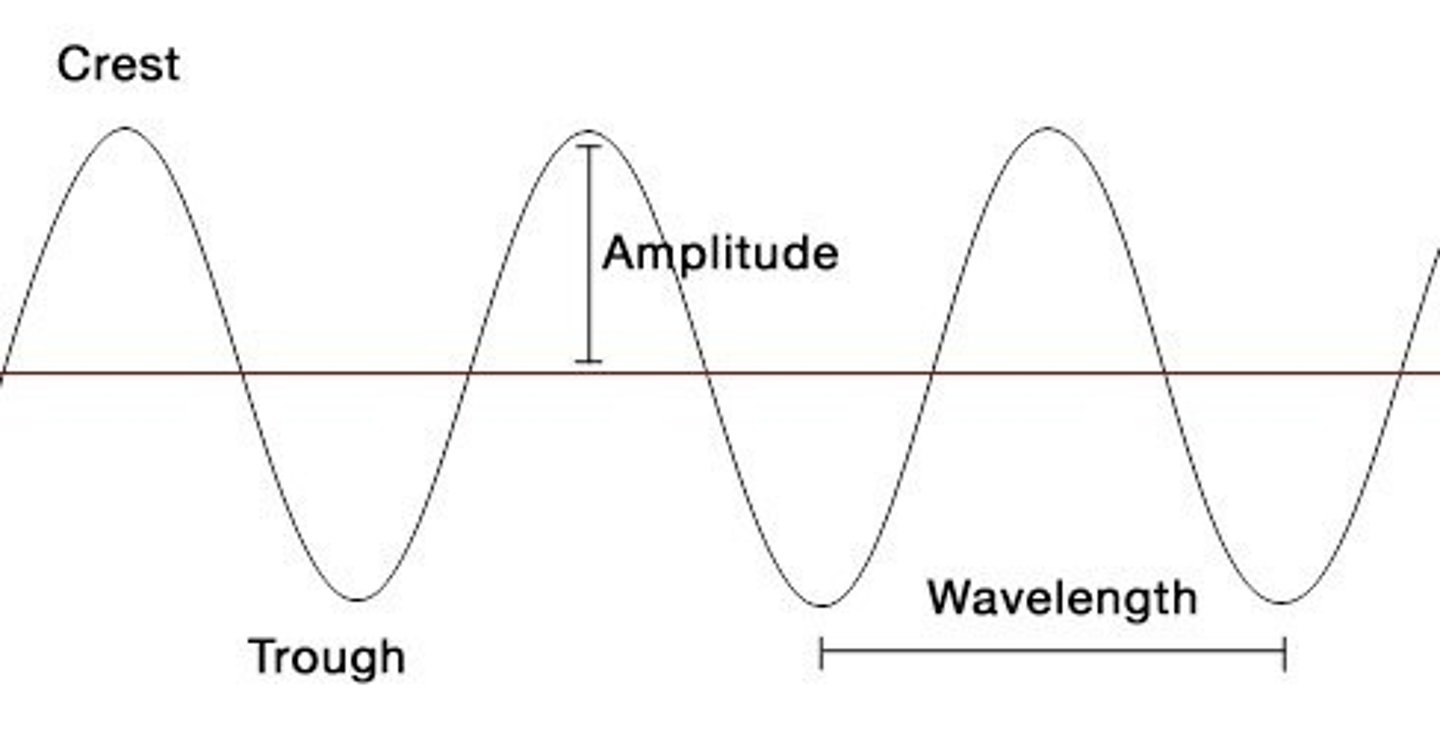
amplitude
What is the height of the wave termed?
TRUE
T/F: A wave with a large amplitude is generally stronger than a wave with a small amplitude?
the number of waves that go by in a second
What is frequency?
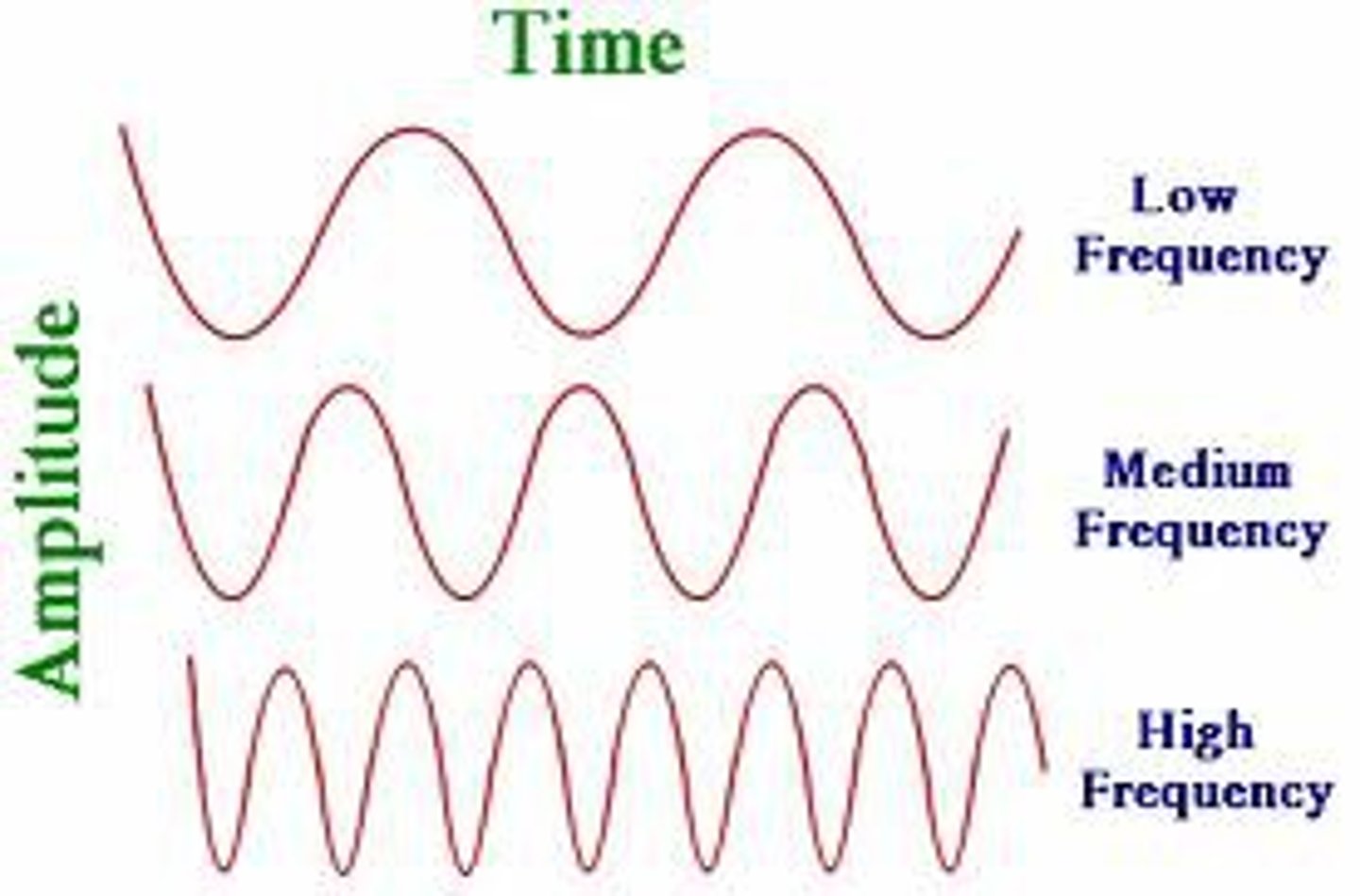
the SI unit of measurement for frequency
What is Hertz (Hz)?
One wave or cycle per second
What is one Hz?
pure energy, rather than particles with mass. The term is used because rays of electromagnetic energy have properties of both electrical energy and magnetic energy
What is electromagnetic energy?
the range of electromagnetic energy in wavelengths, frequency or energy. It is a continuum of every possible frequency. Radio waves, light and x-rays are all terms for different ranges on this spectrum
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
inversely proportional
At a given velocity, wavelength and frequency have what relationship?
FALSE
T/F: Diagnostic ultrasound is a part of the electromagnetic spectrum?
directly proportional
What is the relationship between the energy of a photon and its frequency?
the "bending" of light photons as they pass through one clear medium to another
What is refraction?

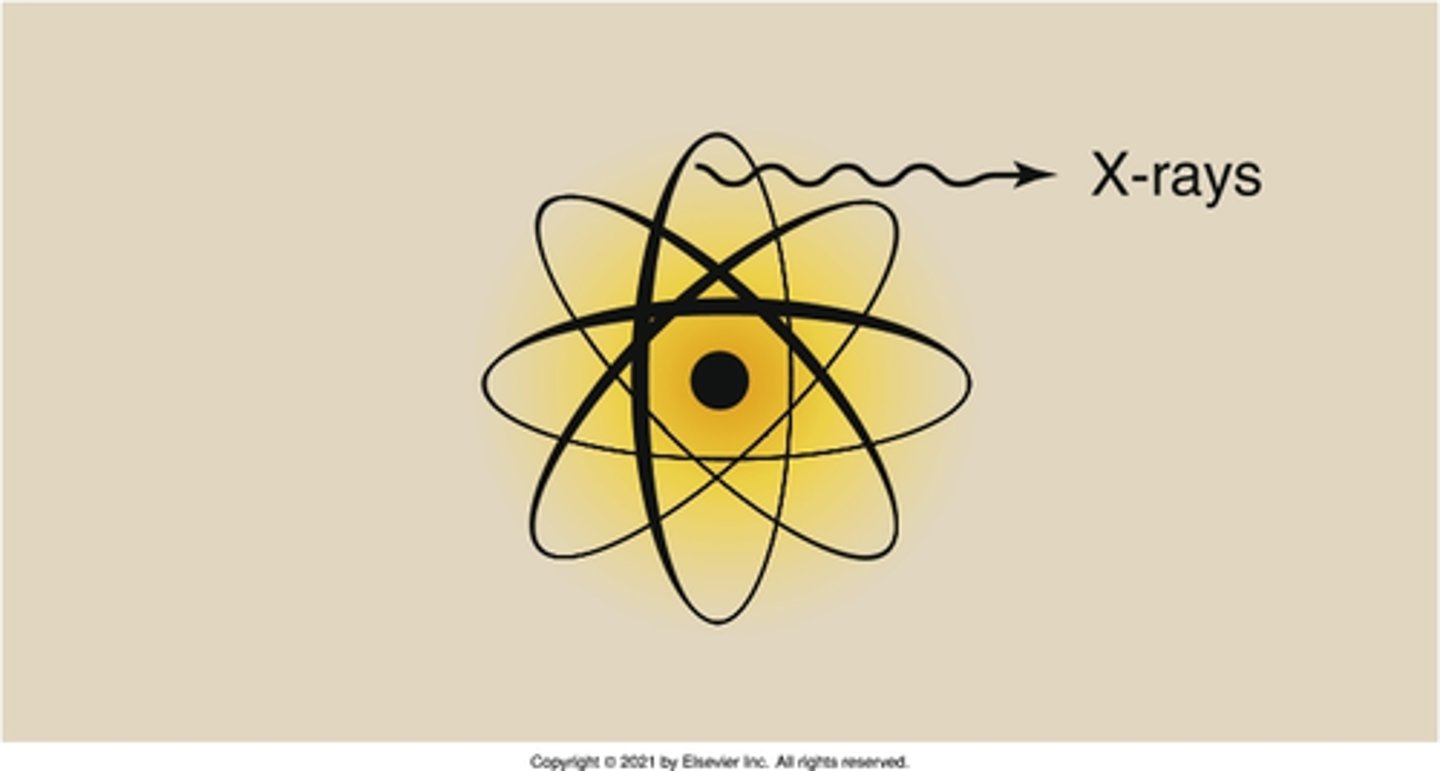
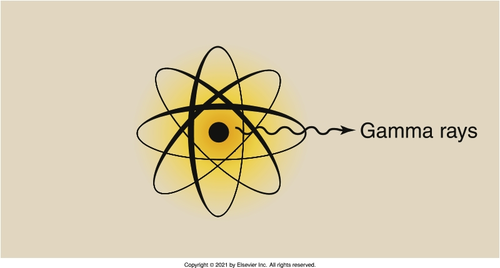
their origin
What is the difference between X-rays and gamma rays?
electron cloud
Where do X-rays originate from?
the nucleus of a radioactive atom
Where do gamma rays originate from?
wavelength
What is visible light identified by?
frequency
Radiofrequency is identified by what?
energy
What are X-rays identified by?
TRUE
T/F: X-rays behave as though they are particles?
TRUE
T/F: visible light behaves like a wave?
absorption
What is the condition of light when the light photons are stopped by a substance?
attenuation
What is the condition of light when some of the photons are absorbed, but some are transmitted through a substance?
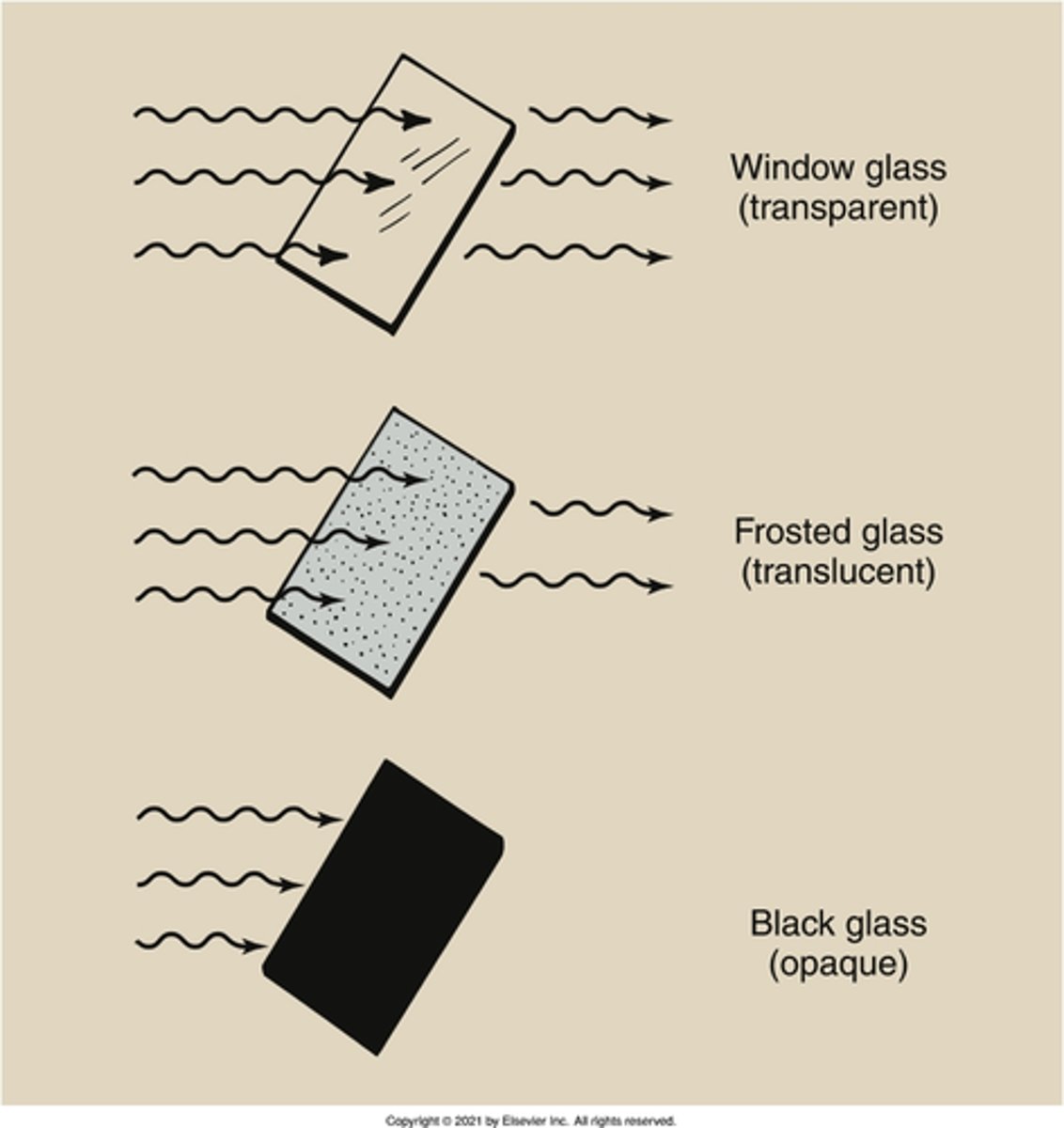
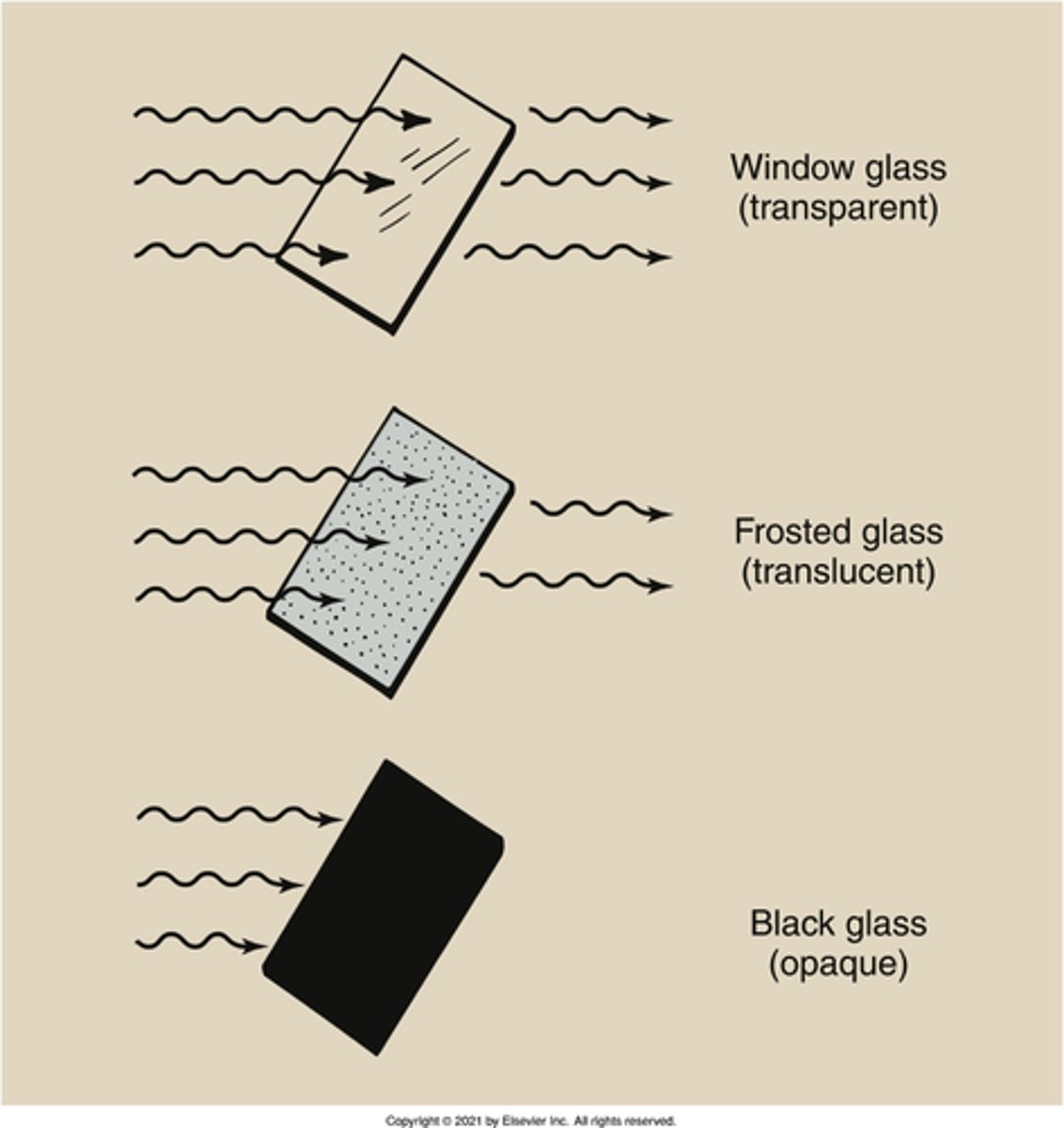
transparent
What is the state of light photons that have passed through a substance such as air, clear glass, or the near vacuum of space?
Ultraviolet light
What is the energy at a higher frequency in the visible light spectrum that can interact with molecules in one's skin and cause sunburn or skin cancer (Light less than 400 nm)?
visible light
What is the range of light that humans can see?
FALSE
T/F: The total range of visible light is more than a millionth of 1% of the electromagnetic spectrum?
visible light spectrum
What is a continuum of visible light that includes the frequency ranges of the various colors (Each color of the spectrum, as a prism or rainbow, is a different frequency) ?
infrared light
What is a type of heat radiation?
opaque
What is the property of a substance that totally absorbs light rays?
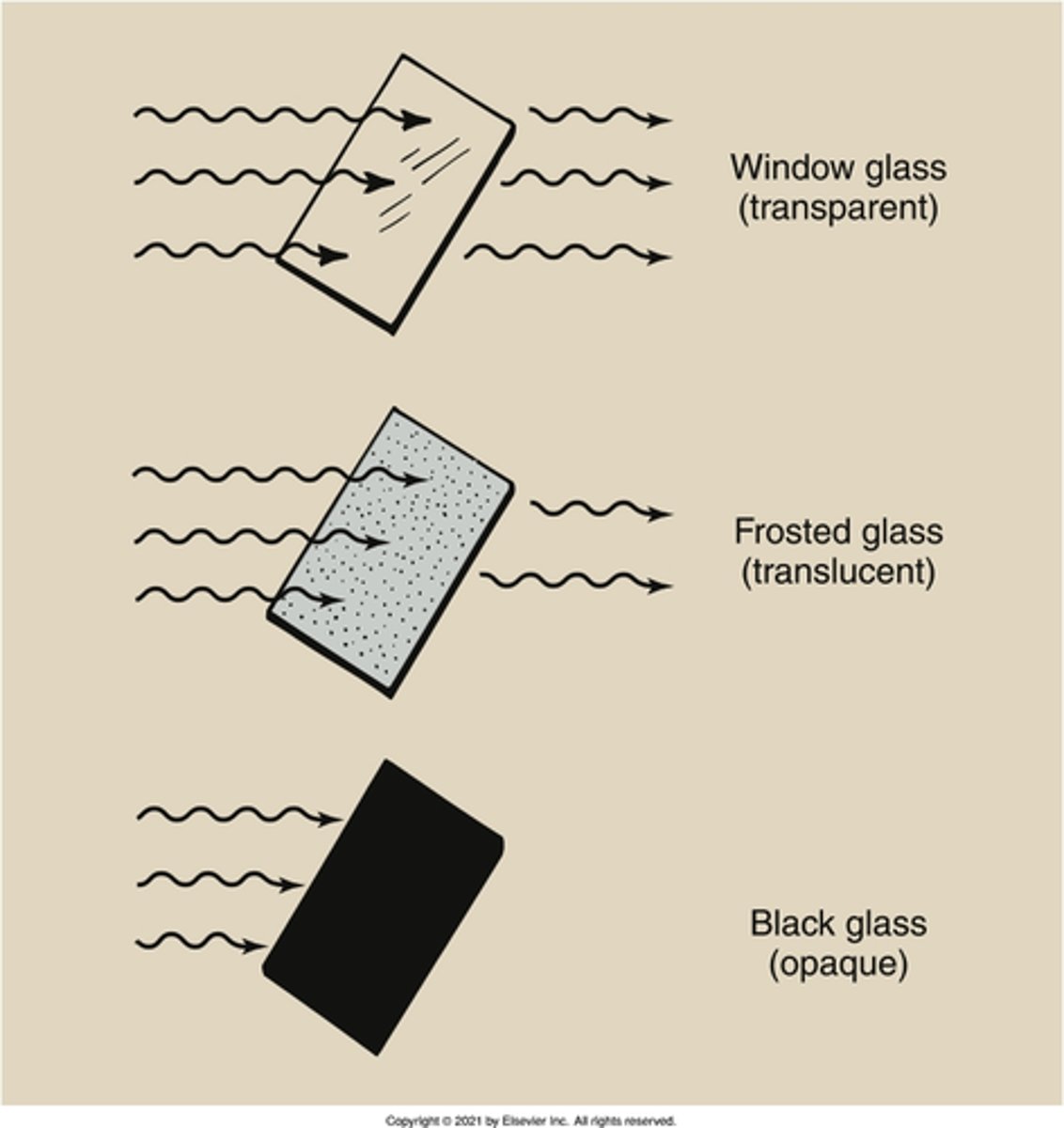
translucent
What is the property of a substance that partially absorbs, or attenuates, light rays?
radiolucent
What is the property of a substance that allows X-rays to partially pass through it?
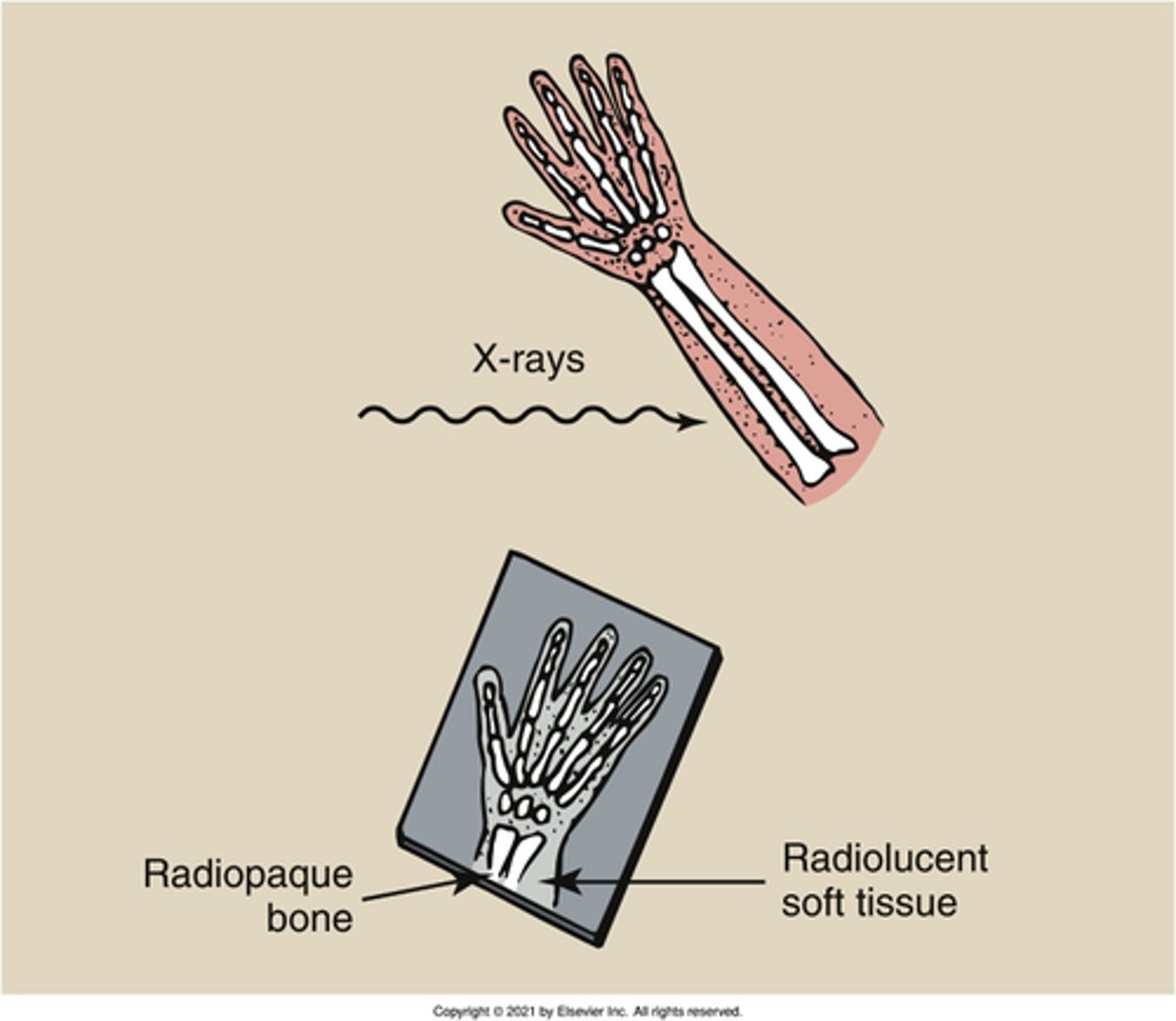
radiopaque
What is the property of a substance that does not allow X-rays to pass through?
the square of the distance from the source
The intensity of electromagnetic radiation is inversely related to what?
1/3 of kV
If you used 110 kVp in an x-ray tube, what would be the energy levels of the x-rays?
TRUE
T/F: At 4 meters from a source of electromagnetic radiation, the field intensity is 1/4 that found at 2 meters from the source?
TRUE
T/F: Given an X-ray and a gamma ray of equal energy, one could not tell them apart.
Frequency increases
The amount of energy carried in a wave increases as the:
FALSE
T/F: Gamma rays can have a higher energy photon than ALL x-rays produced
eV
What is the unit for energy?
m
What is the unit for wavelength?
Hz
What is the unit for frequency?