Module 14 - Children Adolescents and Adults
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Childhood
time between 2nd birthday and puberty
What happens to nutrient needs during childhood
nutrient needs increase to support growth and maintenance
Significance of childhood eating habits
lifelong consequences for HEALTH and BEHAVIOUR
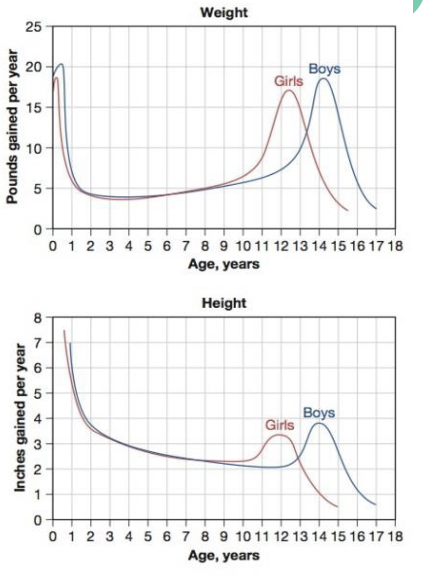
rate of growth
girls tend to gain weight and get taller before boys
height = girls (11 - 13), boys (14 - 15)
weight = girls (11 - 12), boys (14 - 15)
child need for calories depends on which 4 factors
age
body size (weight)
growth rate/ activity level
How does an adequate amount or deficiency in calories effect children
adequate calories and protein support growth
lack of calories slow growth
the amount of needed calories fluctuate during periods of growth
Calories and protein needs per kg body weight per day ____ in intial years of childhood and ____ as child ages
increases; decreases
total calories and protein needs overall increase
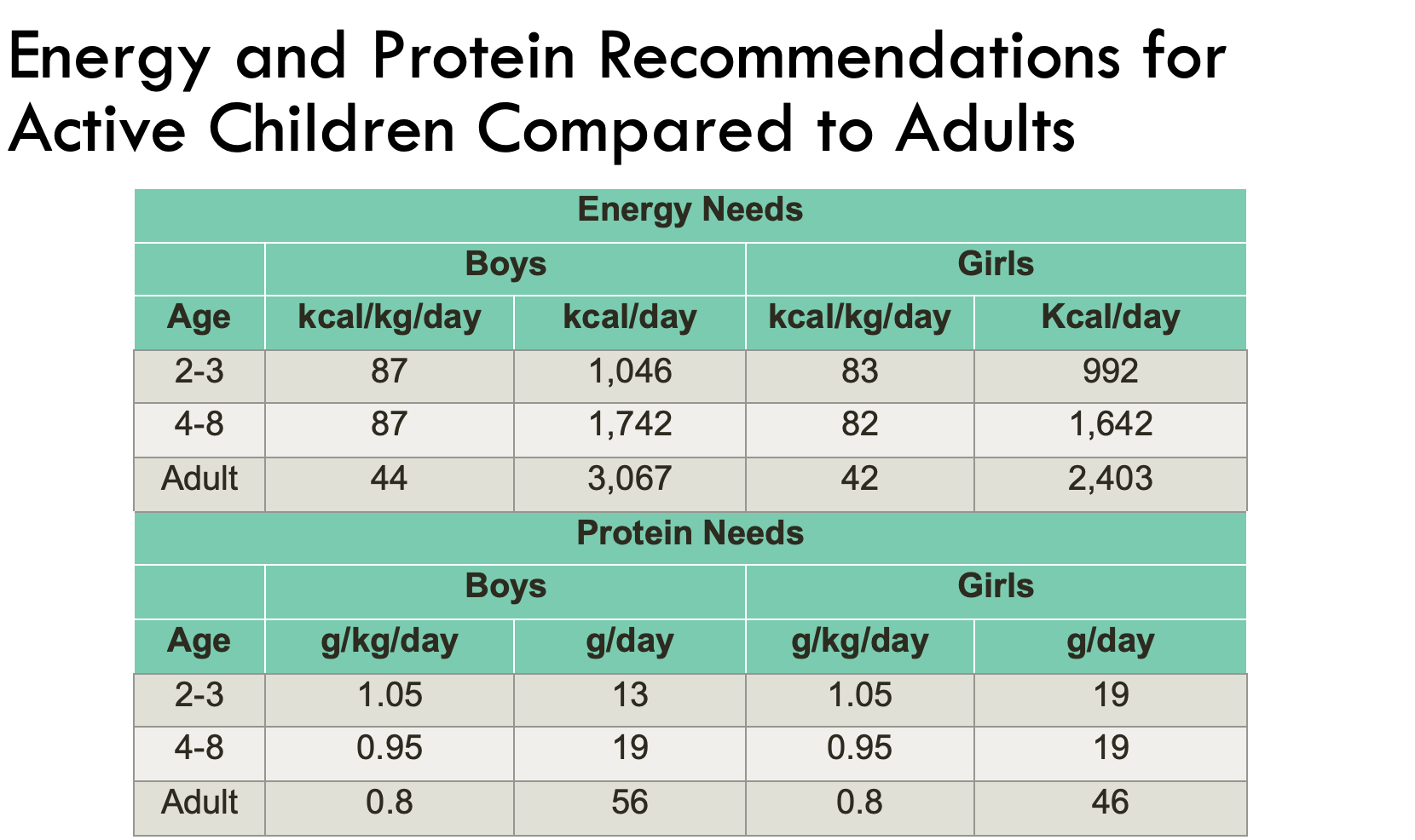
Energy and Protein Recommendations for Active Children Compared to Adults
kcal per kilogram decreases with age, however total amount of kcals per day increase as size increases
MyPlate Recommendations for children
1 cup of fruits
focus on whole fruits
1 ½ cups of vegetables
vary vegetables
4 ounces of grains
half of grains should be whole grains
3 ounces of protein
vary protein
2 ½ cups of dairy
move to low fat or fat free milk or yoghurt
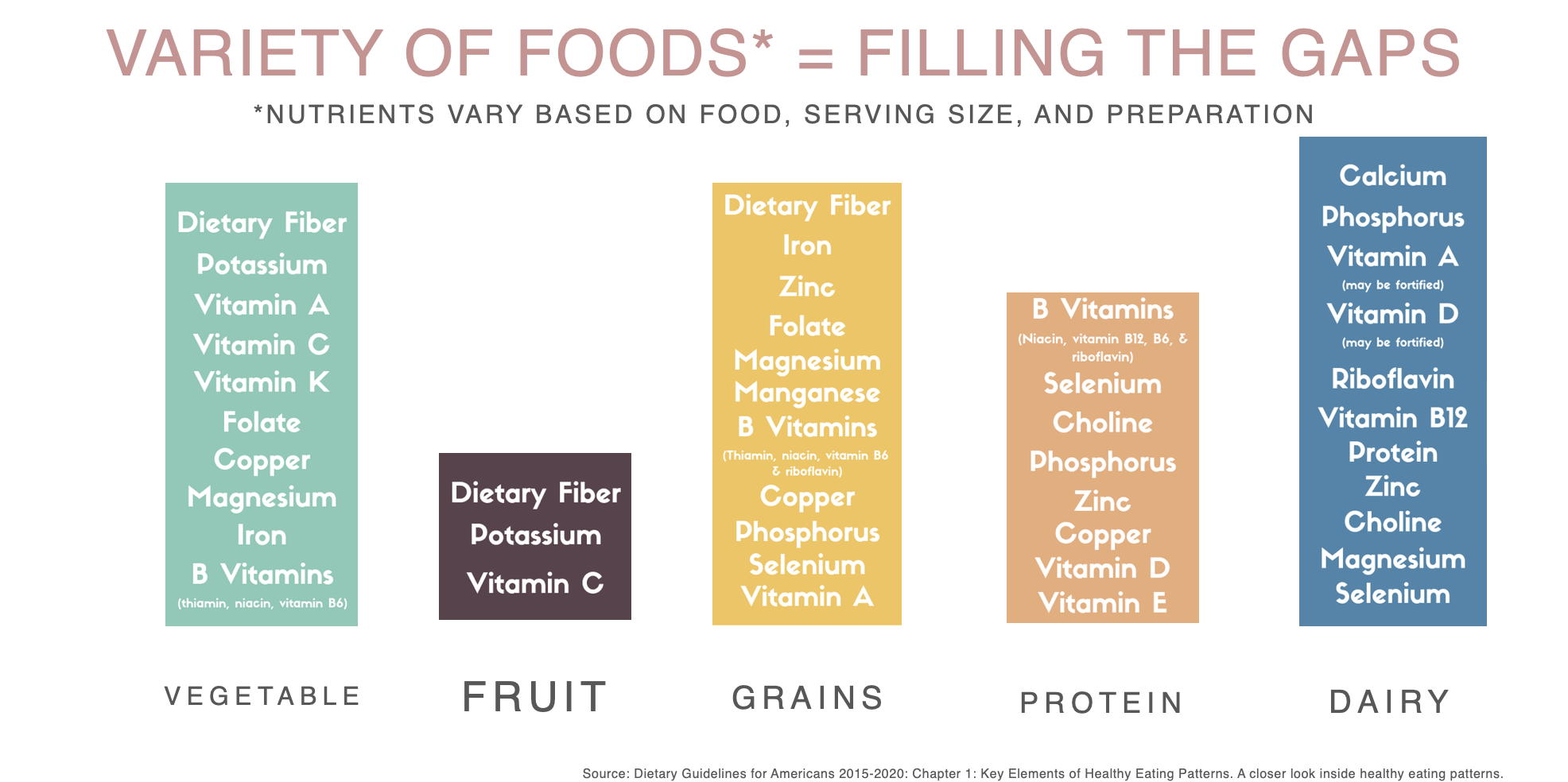
What does “variety of foods = fill the gap” mean?
A balanced diet that includes all food groups “fills the gaps” and helps ensure adequate intake of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and protein.
True or False: younger children have ability to monitor calorie intake
True
children good at understanding and responding to hunger and fullness cues
Six factors that influence acceptance of new foods in children
colour, flavour, texture, temperature, serving size
attitude of server/ preparer
Division of Responsibility for Caregiver/ Parent (what, when, where)
provide regular meals and snacks
when; provide regular meals/ snacks at defined times to aid in body fullness cues - toddlers (2-3hrs), preschoolers (3-4hrs)
choose and prepare foods
what; prepare foods with a variety of options
lead by example
what; show how to behave at meals - include how you eat, what and how you relate to foos
provide the right location
where; make meals pleasant, with a positive environment and limit distractions
Division of Responsibility for Child (how much and whether)
determine how much
child will eat based on fullness cues
provide appropriate amount to reduce food waste
grow through observation
observe caregivers food behaviours
make mealtime fun
eat in a positive environment where child’s feelings are accepted
Risk and Implication of Iron Deficiency Anemia in Children
greatest risk
children in low income homes
implications of iron deficiency
influence on mood and attention span
may impair learning
Sources of Iron
lean meat, peanut butter, fortified breakfast cereals and grains, apricots
Why does lead toxicity cause anemia
inhibits iron absorption
inhibits enzyme needed to synthesize hemoglobin
Causes of anemia
iron deficiency
lead toxicity
sources of lead
paint in older homes
lead pipes in plumbing
possible some imported eating utensils and toys
Lead exposure and risk in children
developing brains are sensitive to even low levels of lead
early lead exposure may increase the risk of lifelong learning diabilities
Obesity in Children (incidence)
incidence in U.S has more than tripled since the 1960s
Obesity in Children Causes
physical inactivity
more time with video games, TV and computer
larger portion sizes
food advertising directed to children
widespread availability of food
use of food as a reward
How id obesity measured in children?
BMI for age growth chart
Calculate BMI for children
plot on growth chart for BMI for age
done for ages 2 to 20 years
compare to national standards
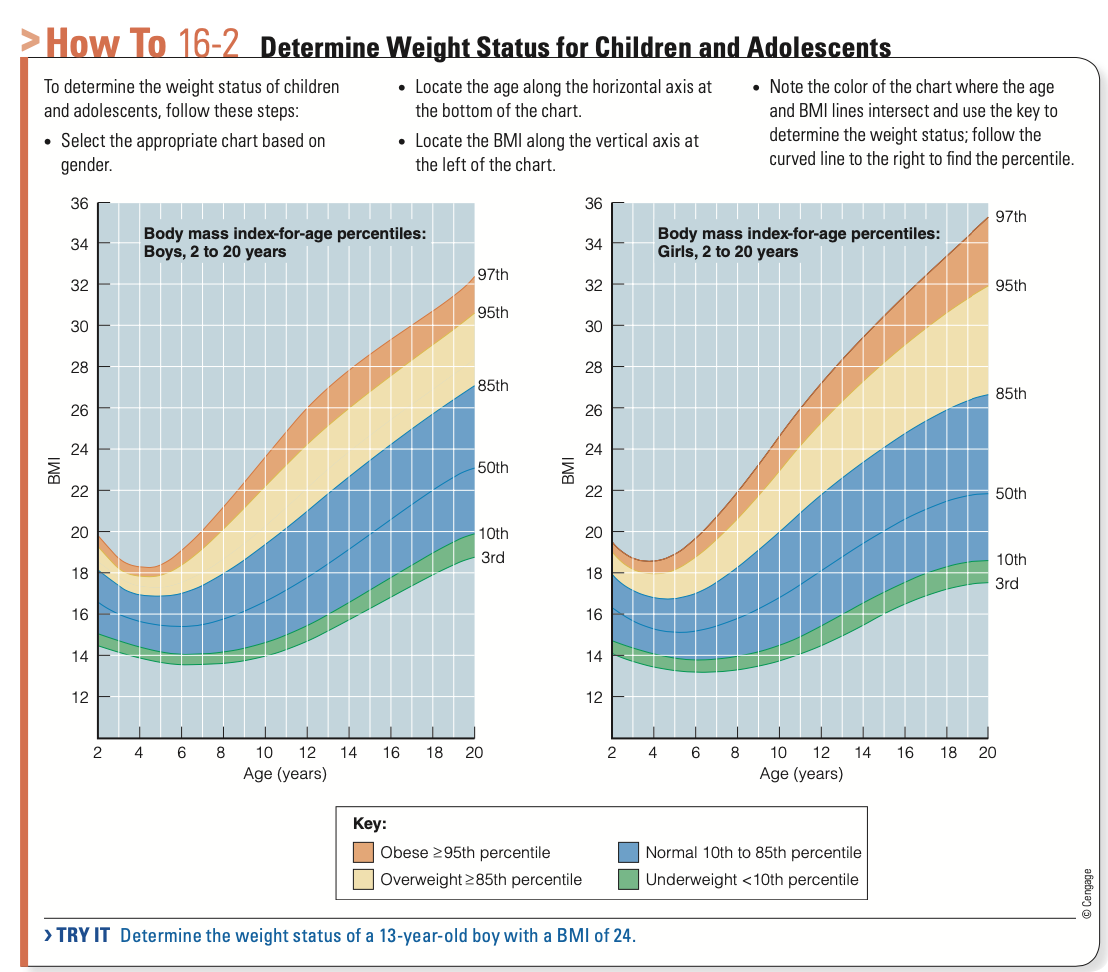
BMI for Age (What are the percentiles)
Overweight
Obese
Underweight
Overweight = 85th to 95th percentile
Obese = 95th percentile or greater
Underweight = less than 5th percentile
Food Allergies Definition
condition in which the body produces antibodies against particular protein in food
Physical Symptoms of Allergies
skin rashes
intestinal upset
diarrhea and vomiting
difficulty in breathing
severe reactions may result in anaphylactic shock
Anaphylactic Shock
condition in which blood pressure is very low and breathing is shallow
The Big 9
common foods for allergic reactions
required by law to be declared on labels

What is a new factor that contributes to overall body growth and development in Adolescent years
hormonal changes
Ages of Growth Spurts in Girls and Boys
Girls (10 - 11 years)
Boys (12 - 13 years)
What does the TIMING of growth spurts rely on for adolescents
reaching a certain critical weight
In United States, this is ~66lb, and a body fat of ~10%
Puberty
period of sexual maturation that occurs until sexual
reproduction is possible
sex hormones are produced
Puberty in Boys
gain proportionately more lean muscle mass
related to increase in testosterone
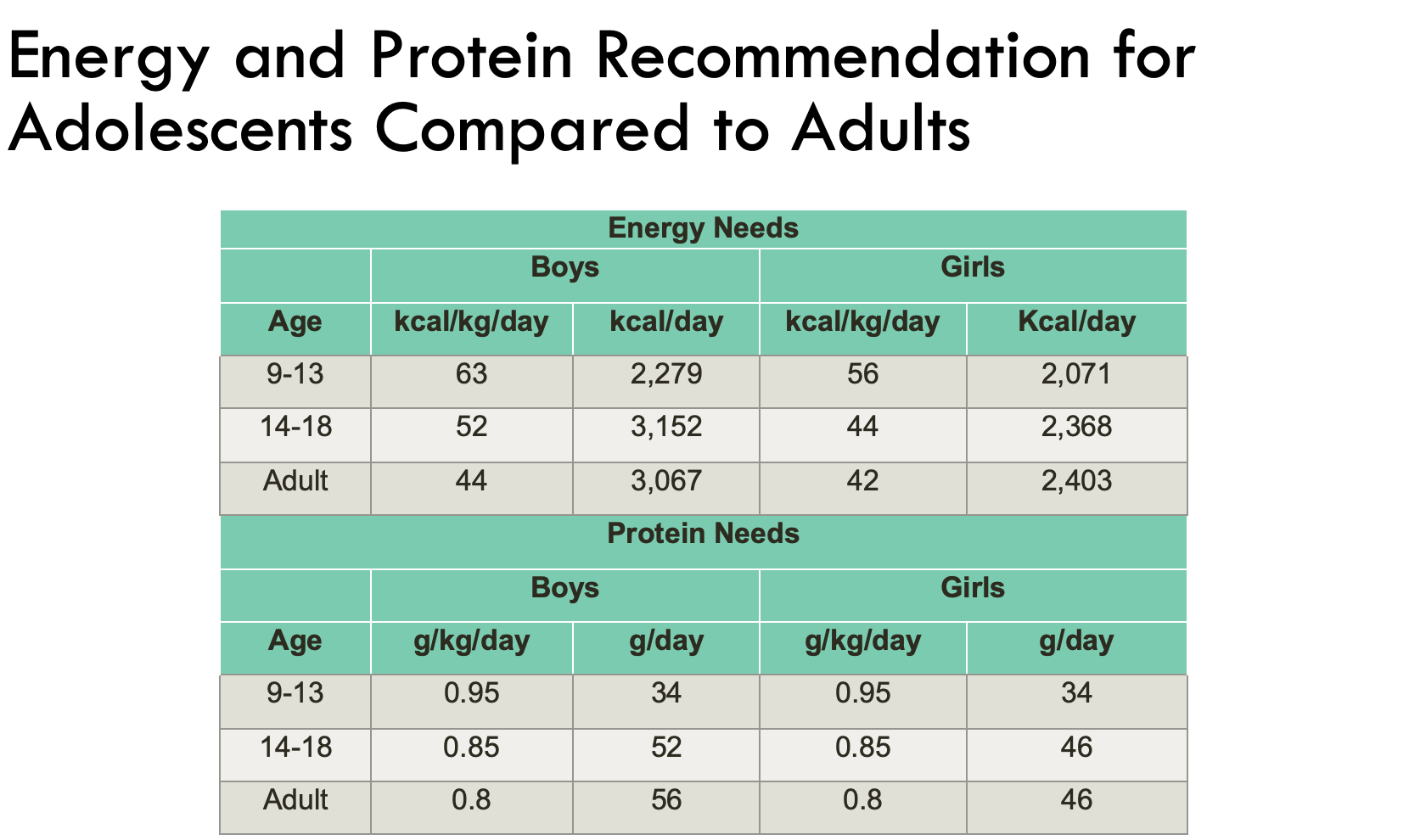
Energy and Protein Recommendation for Adolescents Compared to Adults
starting to see the kcal/ kg decrease with age
furthermore the k/cal per day increase from 14-18 increase in boys and then decreases for adulthood
Why is it very important for adult to have accumulated an adequate amount of calcium during adolescence?
45% of calcium used for adult peak bone mass is gradually acquired during adolescence
Mineral needed to support bone health in adolescence
calcium
Good sources of Calcium
dairy products and fortified foods
What can be used to help adolescence that do not require an adequate amount of calcium?
Supplementation
can help achieve greater bone mass
Eating habits in Adolescents that increase risk of deficiency
skipping meals
inadequate consumption of calcium rich foods
nutrient poor food selection away from home
dieting due to body image issues
alcohol use
Why are girls more vulnerable to iron anemia during adolescence
blood loss during regular menstrual cycles
adolescent girls may consume less meat
often diet for weight loss
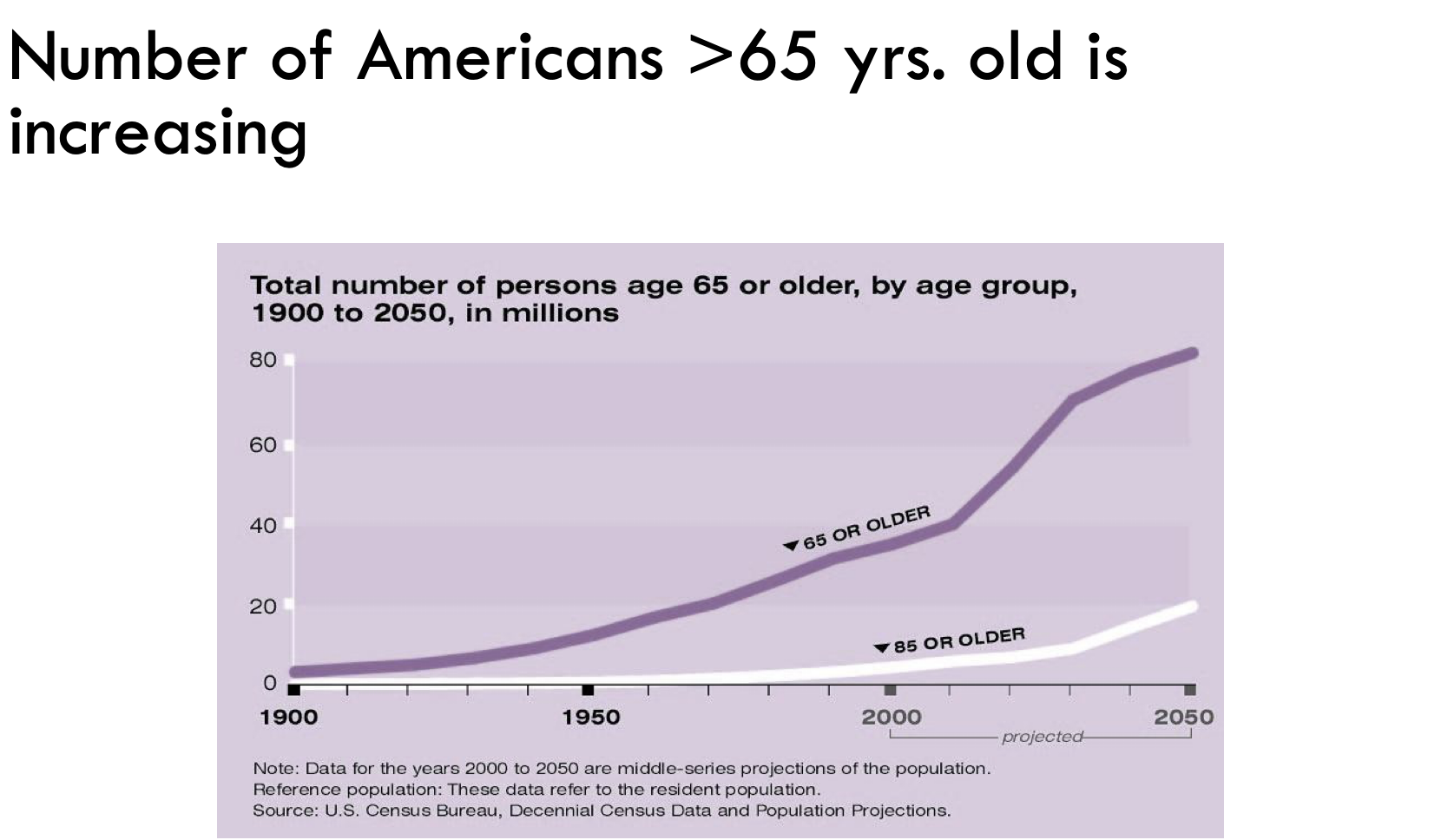
Are the number of elderly Americans (>65) increasing or decreasing?
INCREASING
Social and Psychological Aspects of Aging (LEAD)
living alone
lack of motivation to cook meals
depression
overeating or undereating
anxiety
reduction in digestive secretions
economic constraints
Eight Physical and Physiological Function Decline with Aging (How it affects food)
Decreased secretion of digestive enzymes
decreased micronutrient absorption
Slowing of gastric motility
constipation
loss of neuromuscular coordination
cooking and feeding oneself is difficult
Diminished senses of taste and smell
loss of teeth and xerostomia (dry mouth)
difficulty chewing and swallowing
impaired hearing and vision
age related macular degeneration
loss of muscle mass
reduced basal metabolism and calorie needs
Arthritis
Alzheimers
abnormal deterioration of the brain
Nutrients associated with reducing risk of Alzheimers (start early -20/30s)
antioxidants foods (berries)
omega -3 fatty acids
Nutrients of concern for aging
water
energy
fiber
protein
Vitamin B12
Vitamin D
calcium
iron
zinc
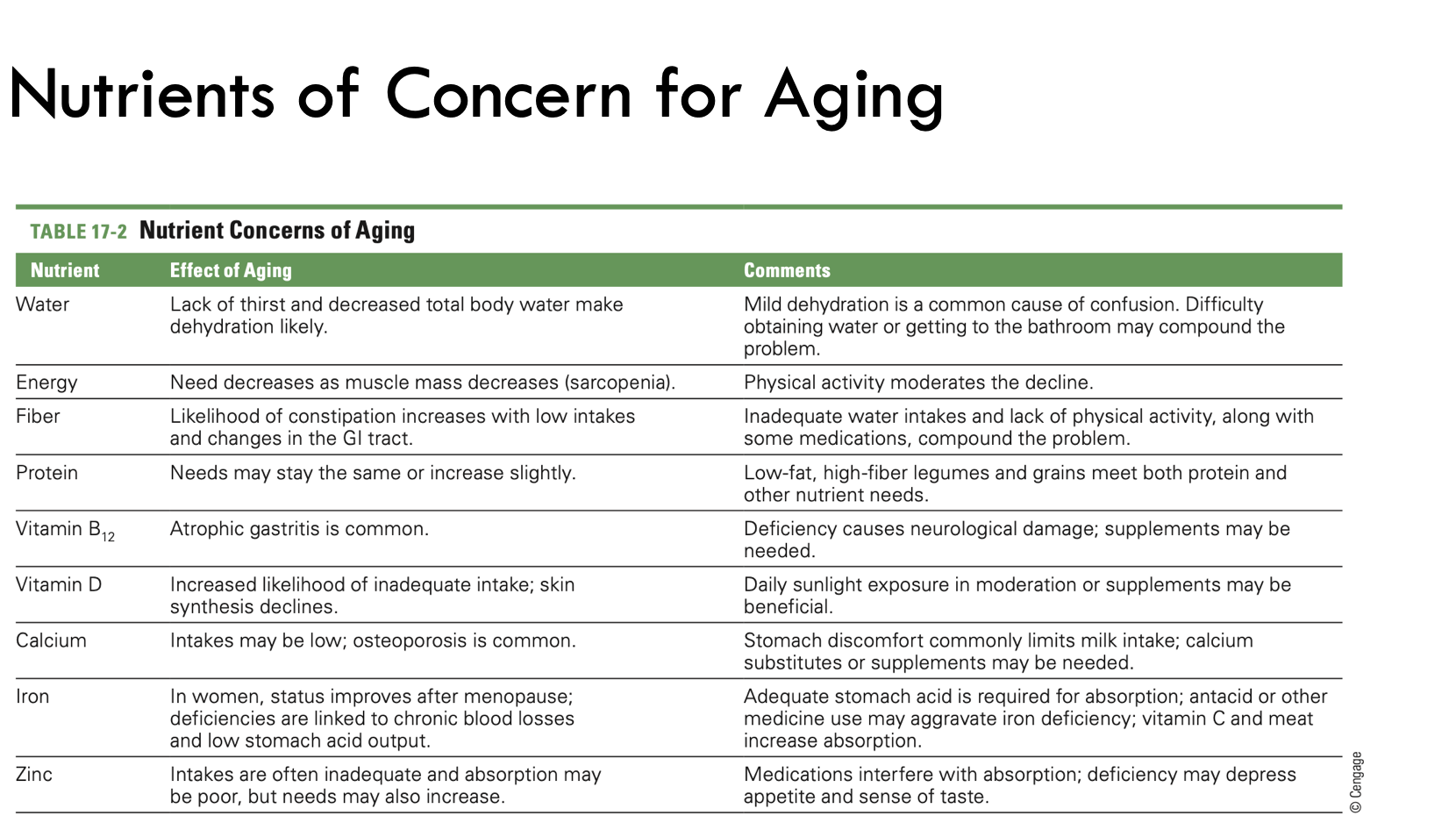
Effect of aging on water
lack of thirst and decreased total body water intake makes dehydration likely
dehydration can cause confusion
Effect of aging on energy
need decreases as muscle mass decreases
physical activity moderates the decline
Effect of aging on fiber
likelihood of constipation increases with low intakes and changes in the GI tract
can be affected by inadequate water intake, lack of physical activity along with some medication
Effect of aging on protein
needs may stay the same or increase slightly
low fat and high fiber legumes and grains meet both protein and other nutrient needs
Effect of aging on Vitamin B12
atrophic gastritis is common
deficiency causes neurological damage, supplements may be needed
Effect of aging on Vitamin D
increased likelihood of inadequate intake - skin synthesis declines
Daily sunlight exposure and supplements may be helpful
Effects of aging on calcium
intakes may be low - osteoporosis is common
stomach discomfort commonly limits milk intake
calcium supplements may be helpful
Effects of Aging on Iron
in women status improves after menopause
deficiencies are linked to chronic blood loss and low stomach acid output
vitamin C and meat increase absorption
Effects of Aging on Zinc
intakes are often inadequate and absorption may be poor, but needs may also increase
medications interfere with absorption
deficiency may depress appetite and sense of taste
Why do iron requirements decrease for postmenopausal women
iron requirements decrease
Causes of anemia in older women that are postmenopausal
tends not to be iron deficiency if women are postmenopausal
They tend to be from
gastric ulcers and related ailments leading to blood loss over time
reduce absorption of Vitamin B12
Undernutrition in Elderly populations
older adults who are hospitalized are often malnourished
Conditions that most commonly cause undernutrition in Elderly populations
little or no appetite
problems with chewing or swallowing
consuming inadequate amounts of nutrients
eating fewer than two meals a day
Drug-Nutrient Interaction (risk factors for elderly)
polypharmacy
multiple drugs by an individual
Negative nutritional impacts of drugs in older adults include
reduced appetite
decreased absorption and utilization of some nutrients
Increase nutrient excretion