Physical Agents - Ch. 5 Tone Abnormalities
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
muscle tone
the underlying tension in the muscle that serves as a background for contraction
what muscle tone revealed as
stiffness or slackness of muscles
what does muscle tone include
involuntary resistance generated by neurally activated muscle fiber and passive tension
when is tone considered abnormal
when it affects function or causes pain
example of high tone in quadriceps muscle
getting down in start position for a race
example of low tone in quadriceps muscle
relaxing after running a race
True or False: muscle tone is on a spectrum, not a point
true
Hypotonicity (low tone)
decreased resistance to stretch compared with normal muscles
Flaccidity
total lack of tone (within mid-range of muscle length)
What is the difference between flaccidity and paralysis
paralysis is a movement disorder while flaccidity is a descriptor of tone
paralysis
complete loss of voluntary muscle contraction
Hypertonicity (high tone)
increased resistance to stretch compared to normal muscles
rigidity
hypertonicity in which the muscles are stiff or immovable regardless of velocity of movement
akinesia
loss or impairment of the power of voluntary movement
how does akinesia differ from hypertonicity
akinesia is a movement disorder, not a descriptor of rigidity
spasticity
velocity-dependent resistance to stretch; resistance increases as velocity increases
clonus
multiple oscillations or beats of muscle contractions in response to quick stretch
clasp-knife phenomenon
initial resistance followed by a sudden release of resistance
posture
an observation assessment
dyskinesia
abnormal movement that is involuntary and has no purpose
chorea
dancelike, jerky movements
ballismus
ballistic, throwing-like movements
tremor
low amplitude, high frequency oscillations
athetoid
writhing or wormlike
dystonia
sustained muscle contractions usually resulting in abnormal postures or repetitive twisting movements
which part of the body does dystonia usually involve
dystonia
why are dyskinesia movement patterns exhausting for individuals
it is a constant expenditure of energy
when measuring tone, keep in mind:
avoid generalizing the results of single or multiple tests to all conditions of the muscle
include measures of movement or function to obtain a more complete picture of the subjects ability to use muscle tone appropriately
quantitative measure of muscle tone
dynamometer/myometer
isokinetic testing systems
Near-Infrared spectroscopy (NIRS)
Shear-Wave Ultrasound Elastography
Electromyography (EMG)
Pendulum test
How does NIRS work?
It measures the amount of blood flow to muscle to determine the amount of metabolism needed for muscle activity
How does a shear-wave ultrasound elastography quantify tone?
Measures viscoelastic properties of the muscle via tissue deformation after dynamic stress to a muscle is applied
What could be a problem with using Shear-Wave Ultrasound Elastography to quantify tone?
It cannot differentiate between biomechanical and neurological sources of stretch resistance
Advantages of using Electromyography to quantify tone
measures low level muscle activity
assesses timing
biofeedback
How do you perform a pendulum test
Passively hold a limb and then release it for a quick stretch
0 on clinical tone scale
no tone
1 on clinical tone scale
hypotonicity
2 on clinical tone scale
normal tone
3 on clinical tone scale
moderate hypertonicity
4 on clinical tone scale
sever hypertonicity
0 on modified ashworth scale for grading spasticity
no increase in muscle tone
1 on Modified Ashworth Scale for grading spasticity
slight increase in muscle tone manifested by a catch and release or by minimal resistance at the end of the ROM when the affected part is moved in FLEX or EXT
1+ on modified ashworth scale for grading spasticity
slight increase in muscle tone manifested by a catch, followed by minimal resistance throughout the remainder (less than half) of the ROM
2 on modified ashworth scale for grading spasticity
more marked increase in muscle tone through most of the ROM, but affected part easily moved
3 on modified ashworth scale for grading spasticity
considerable increase in muscle tone, passive movement difficult
4 on modified ashworth scale for grading spasticity
affected part rigid in flexion or extension

what reflex is this?
Asymmetrical Tonic Reflex
what should you document when measuring muscle tone
Position of limb, body, neck, and head to one another and to gravity
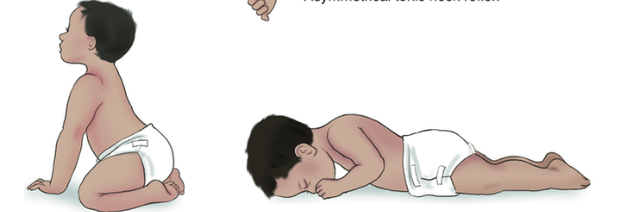
what reflex is this?
Symmetrical tonic neck reflex
What type of touch increases tone
light touch
What type of touch decreases tone
firm touch
Which position is most accurate for the measuring of muscle tone?
midrange