Functional Human Anatomy Exam 2
1/121
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Rutgers University FHA, specifically Rudy's Content (incomplete)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
31
the number of spinal nerve pairs
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
different groups of spinal nerves
1-8
number of cervical spinal nerve pairs
1-12
number of thoracic spinal nerve pairs
1-5 (superior)
number of lumbar spinal nerve pairs
1-5 inferior
number of sacral spinal nerve pairs
1
number of coccygeal spinal nerve pairs
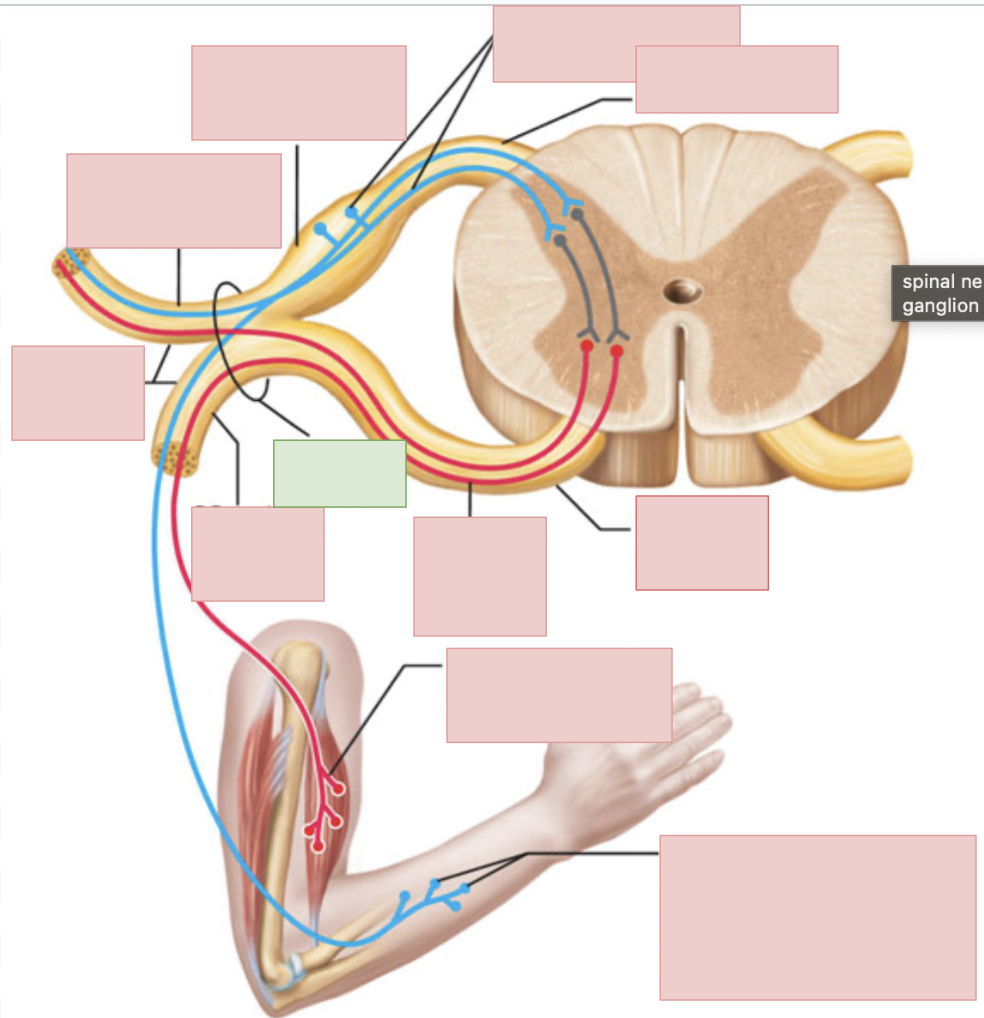
dorsal root
sensory fibers only
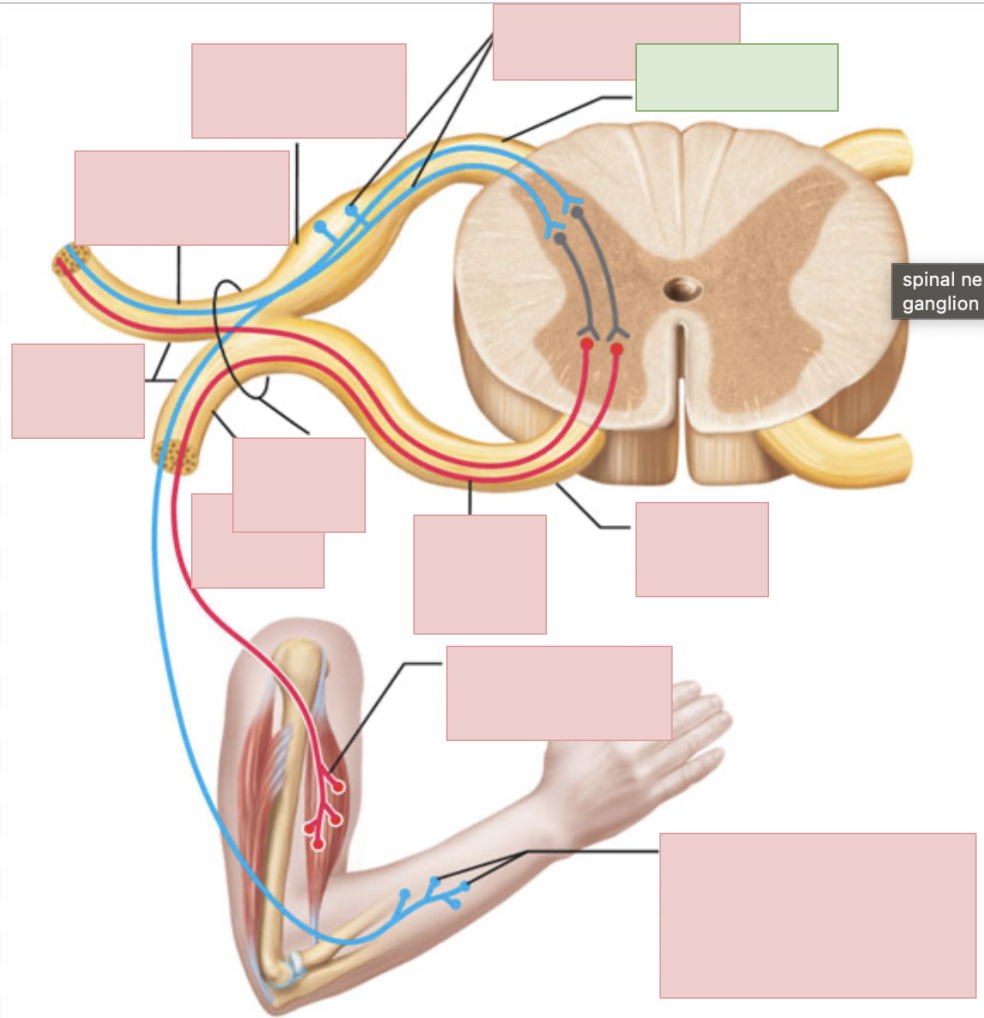
ventral root
motor fibers only
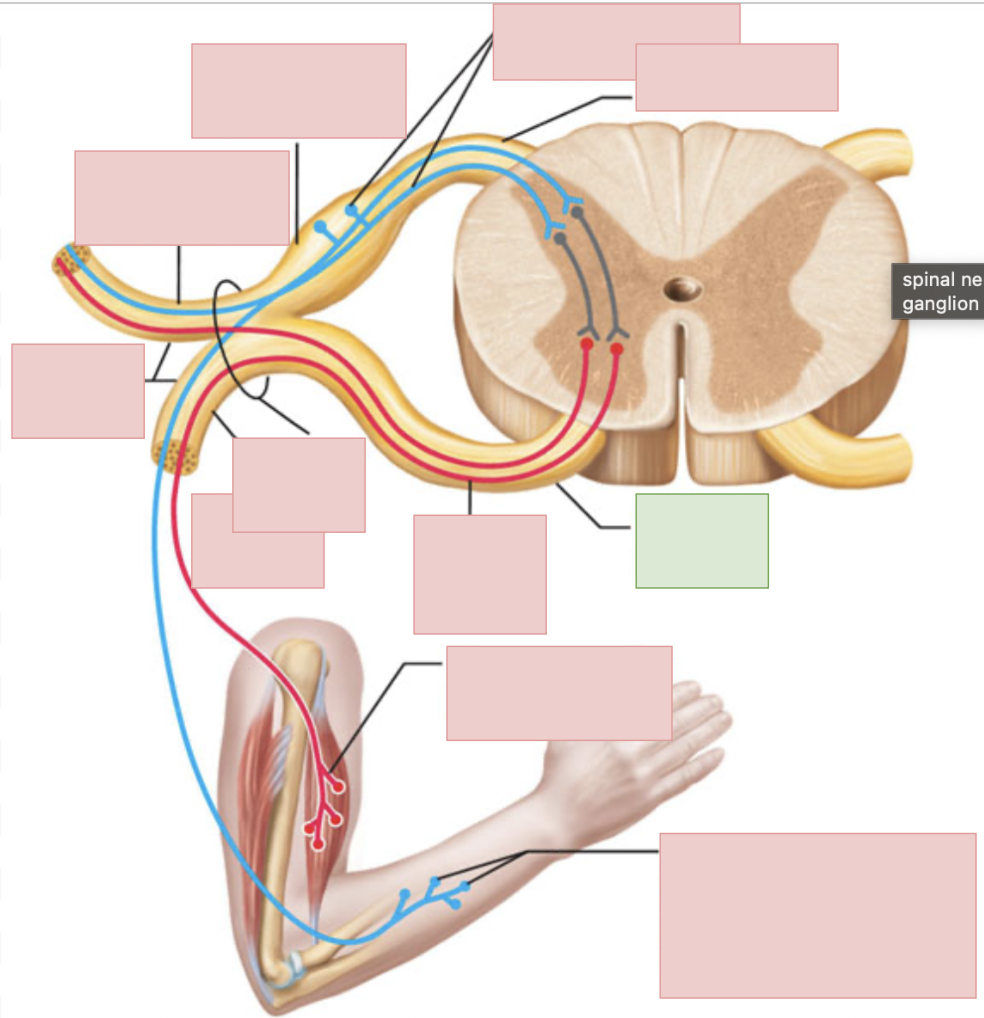
dorsal ramus of spinal nerve
sends outgoing motor signals to the back and brings in sensory information from the skin of the back, deep muscles of the back, and the joints between adjacent vertebrae
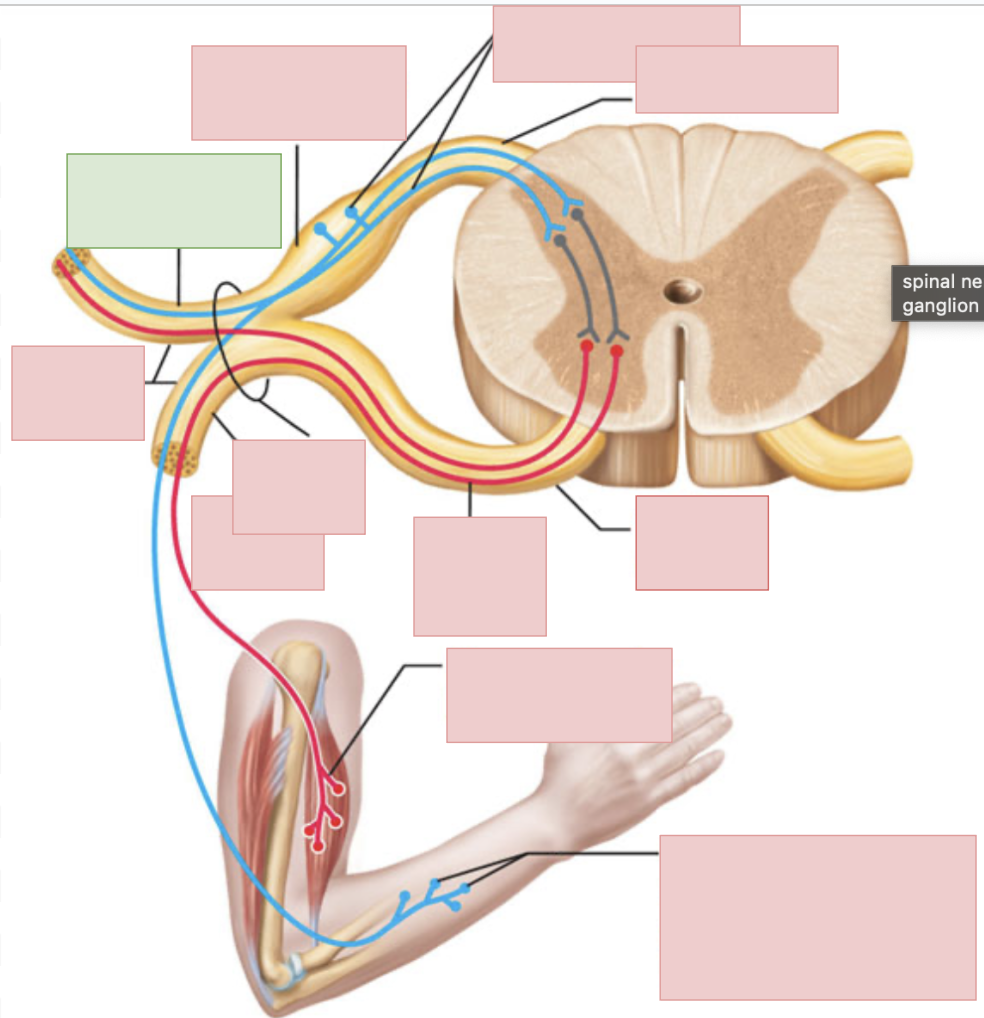
ventral ramus of spinal nerve
sends outgoing motor neuron messages and brings in sensory information (to everywhere but the posterior side of body); they form the nerve plexuses
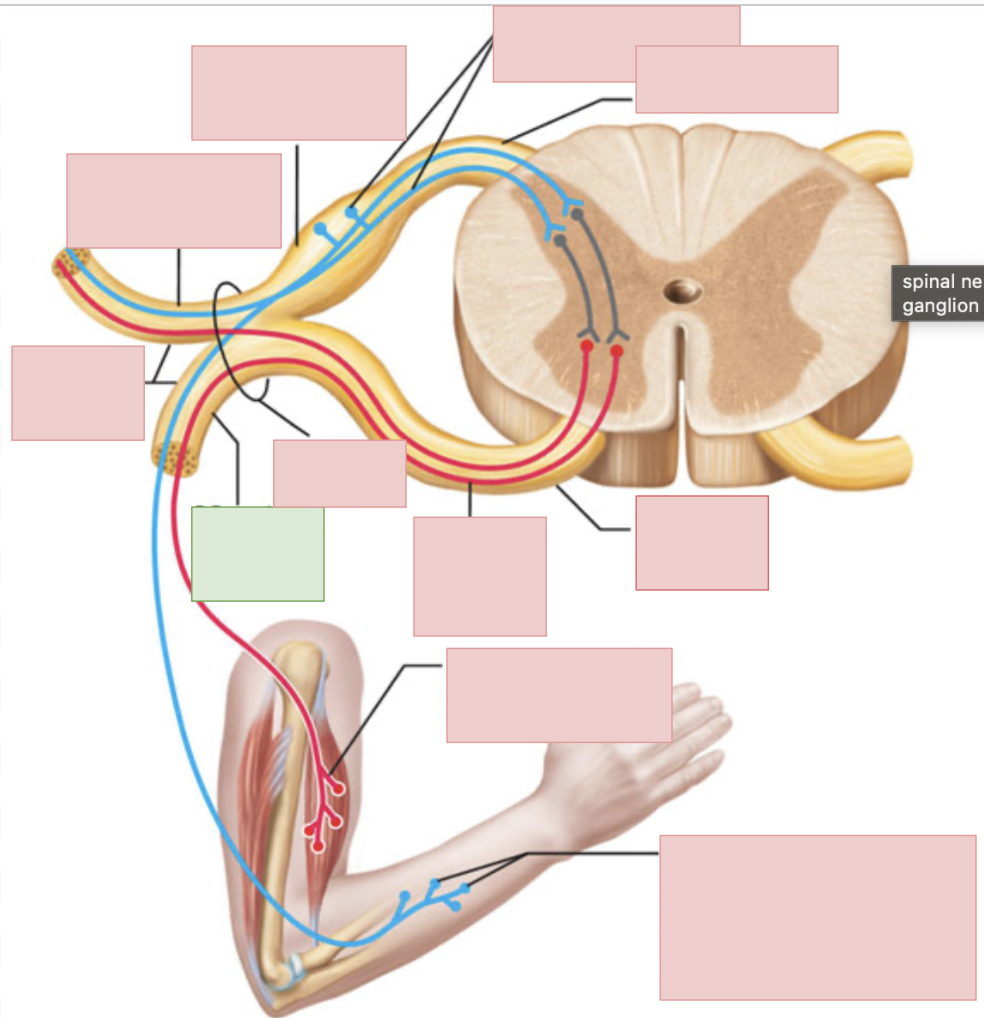
spinal nerves
contains both sensory and motor fibers, ventral + dorsal root come together to form
nerve plexuses
networks of nerves originating from ventral rami of spinal nerves, contain both motor and sensory nerves
cervical plexus
C1-C4
lesser occipital nerve
apart of cervical plexus
greater auricular nerve
apart of cervical plexus
supraclavicular nerve
apart of cervical plexus
cranial nerves
apart of cervical plexus; as the number increases they become more posterior and inferior
transverse cervical nerve
apart of cervical plexus
ansa cervalis
apart of cervical plexus
phrenic nerve
apart of cervical plexus; provides sensory info from and innervates the diaphragm (from C4)
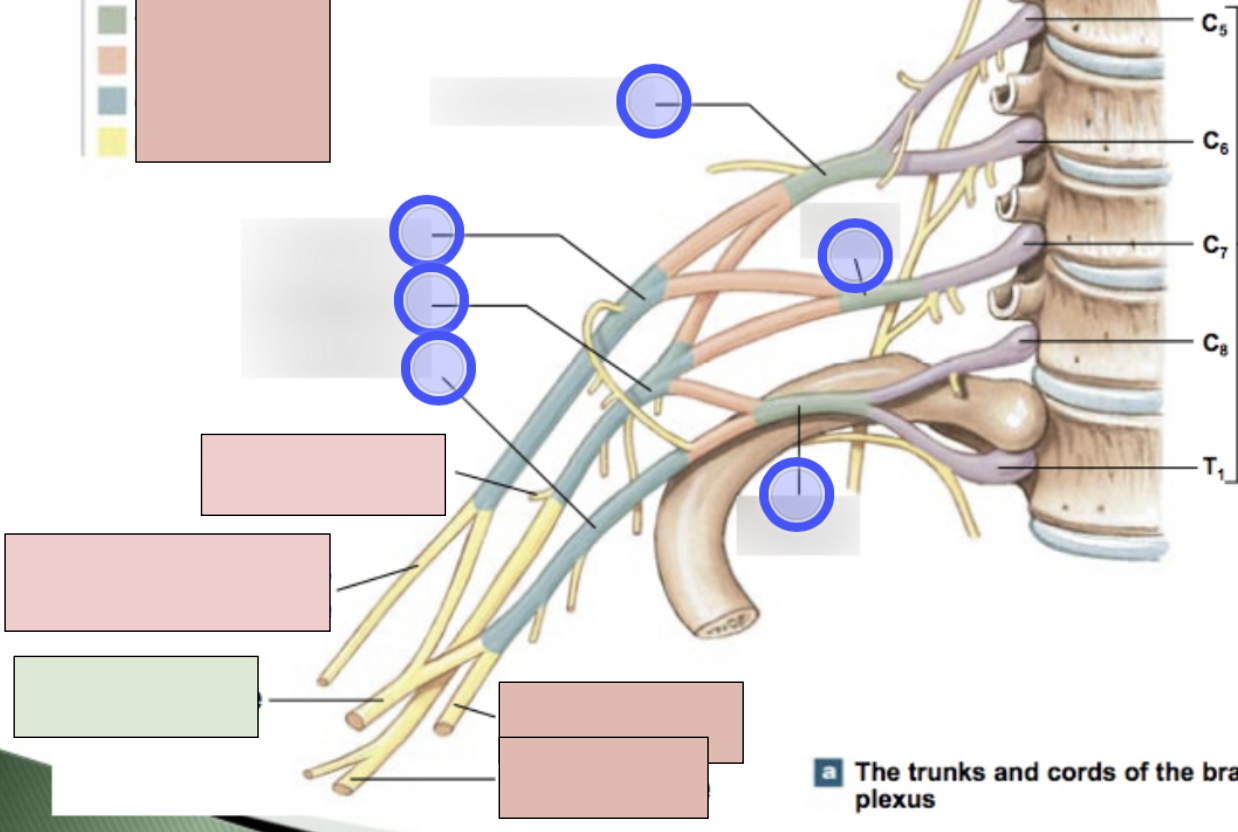
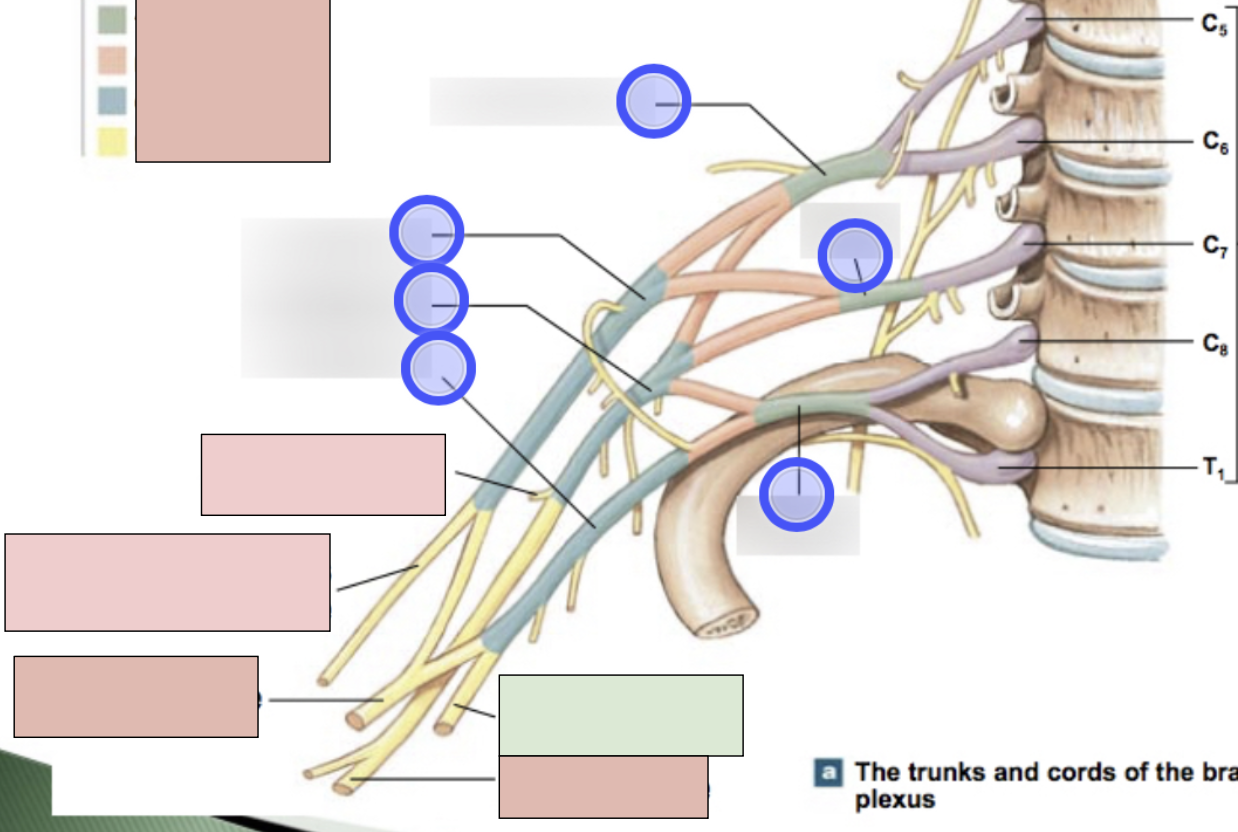
brachial plexus
C5-T1 (don’t forget there is a C8); provides motor innervation to muscles of arm + sensory innervation to the skin of the arm; parts- roots, trunks, divisions, cords, nerves
roots, trunks, divisions, cords, nerves
parts of brachial plexus (medial to lateral)
roots
C5-T1 (5)
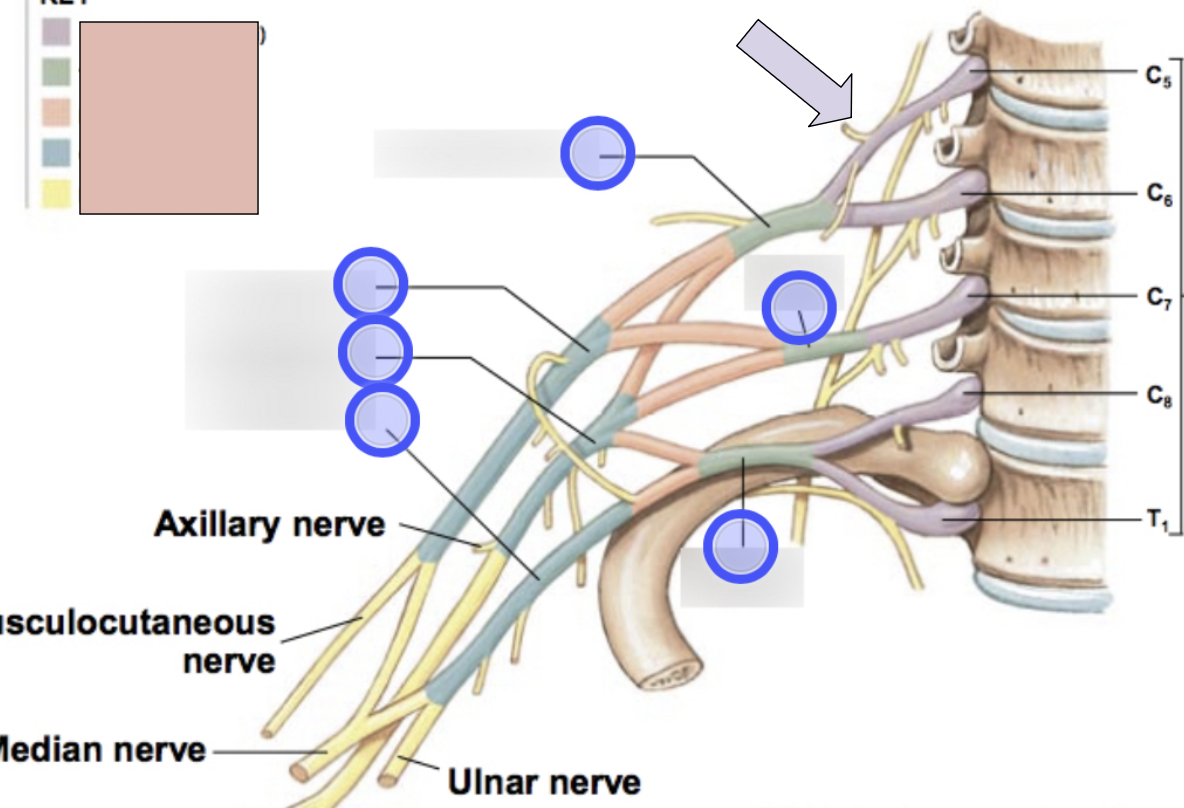
trunks
superior, middle, inferior
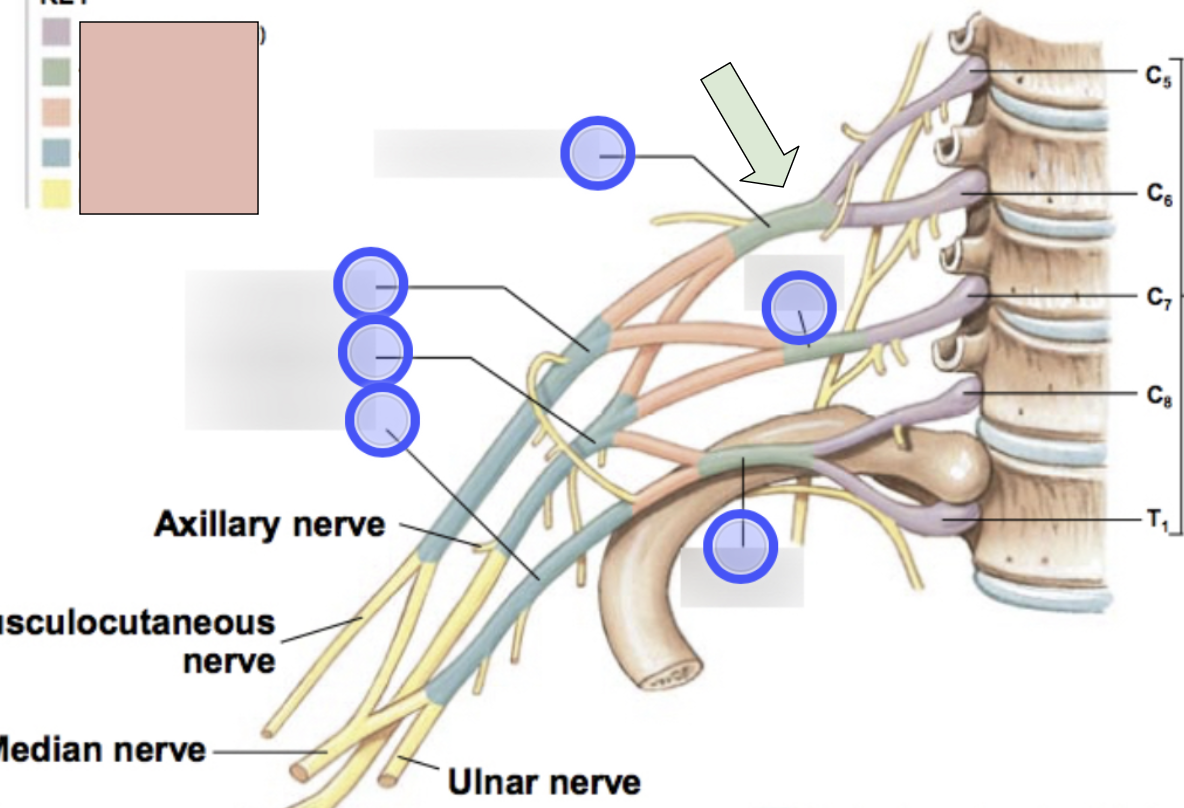
divisions
anterior + posterior for each (6 total)
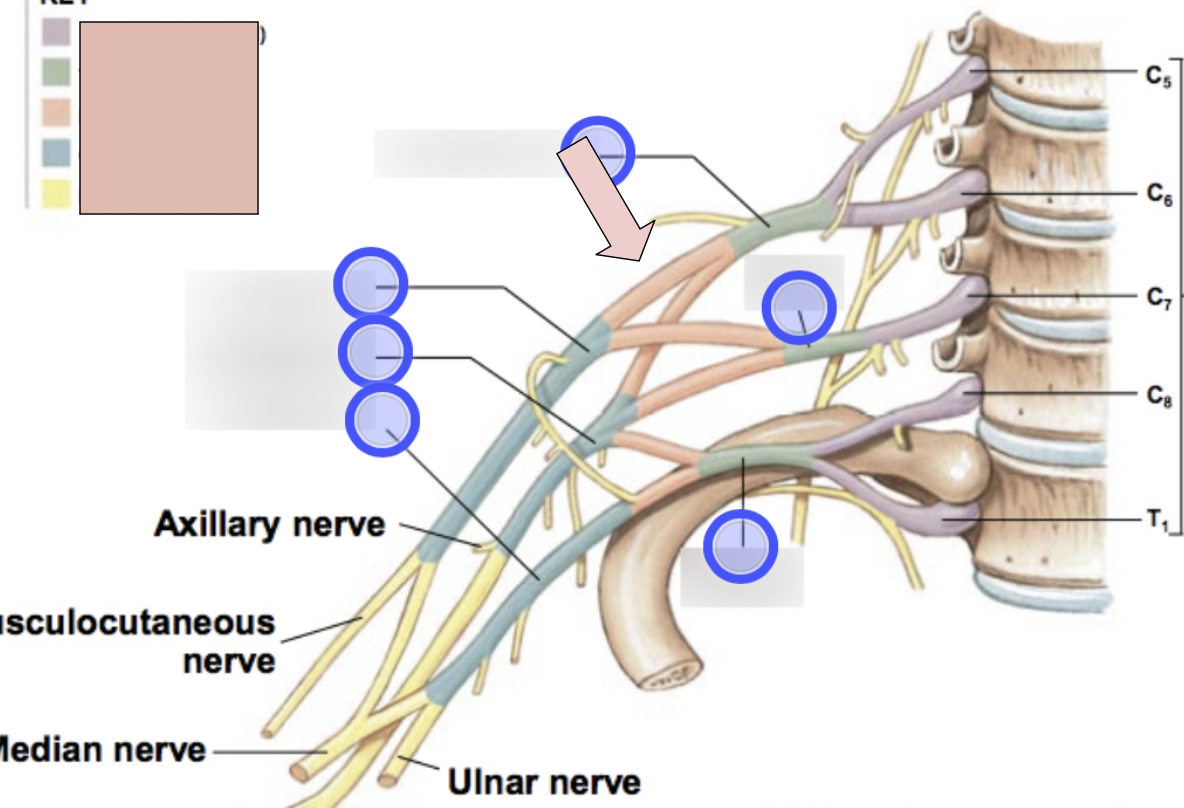
cords
lateral, posterior, medial (3 total)
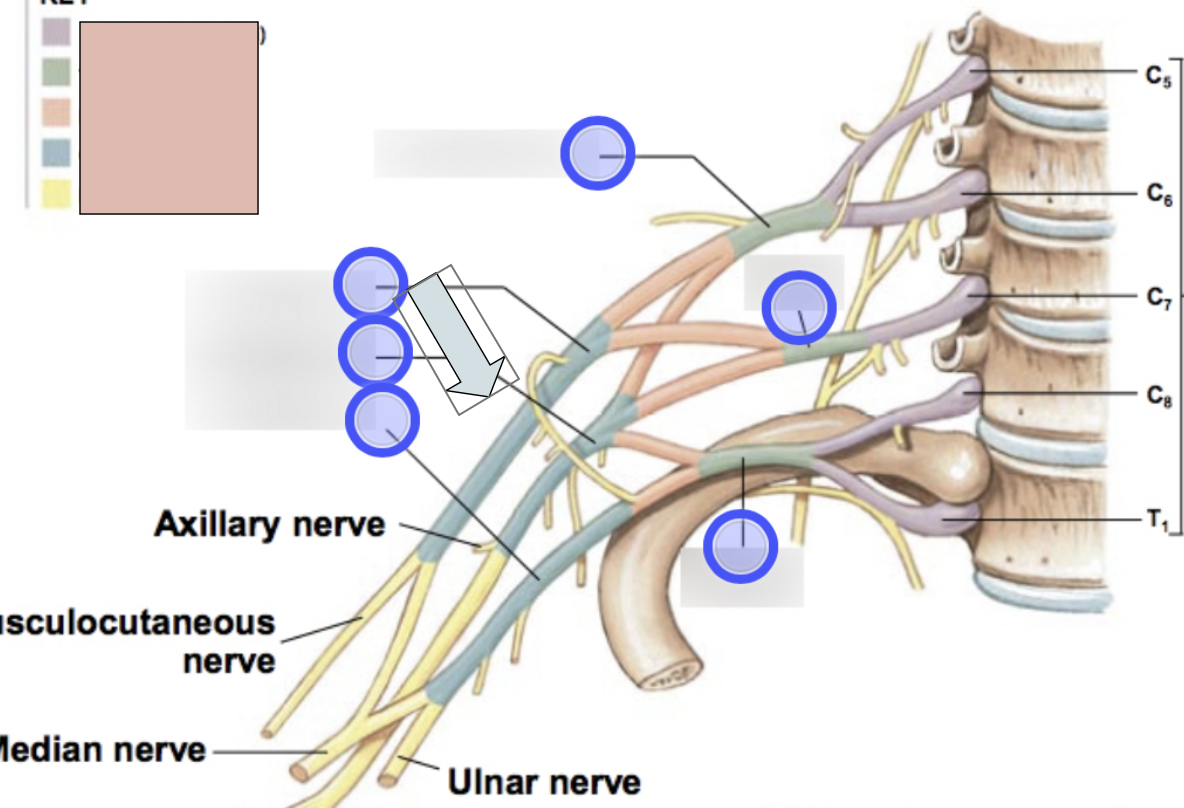
axillary nerve
C5, C6, motor for deltoid and teres minor; sensory from skin of shoulder; roots from posterior cord
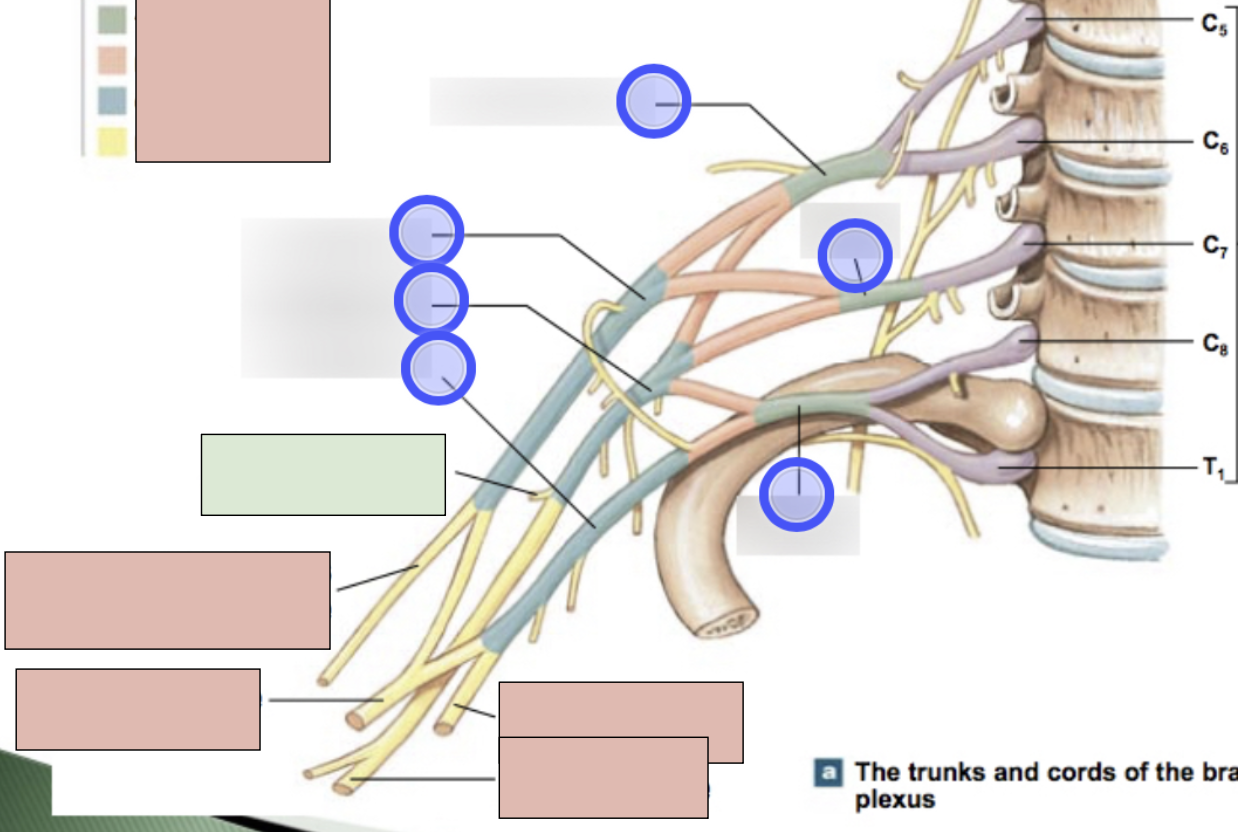
radial nerve
C5-T1, motor for extensor muscles of arm and forearm (triceps brachii, anconeus, extensor carpi radialis, extensor carpi ulnaris, brachioradialis, supinator digital, extensor muscle, abductor pollicis); sensory from skin over the posterolateral surface of the limb; roots from posterior cord
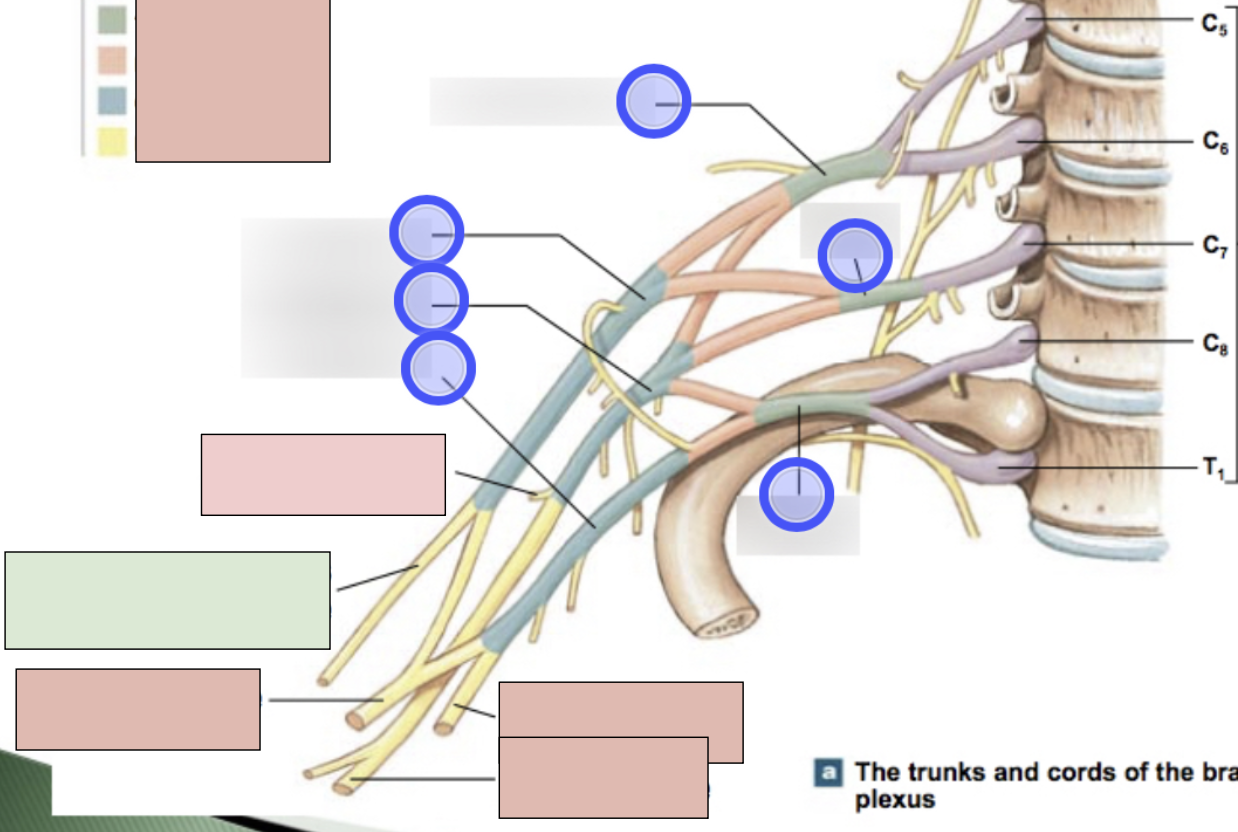
musculocataneous nerve
C5-C7, motor for flexor muscles of the arm; sensory from skin over lateral surface of the forearm; roots from lateral cord
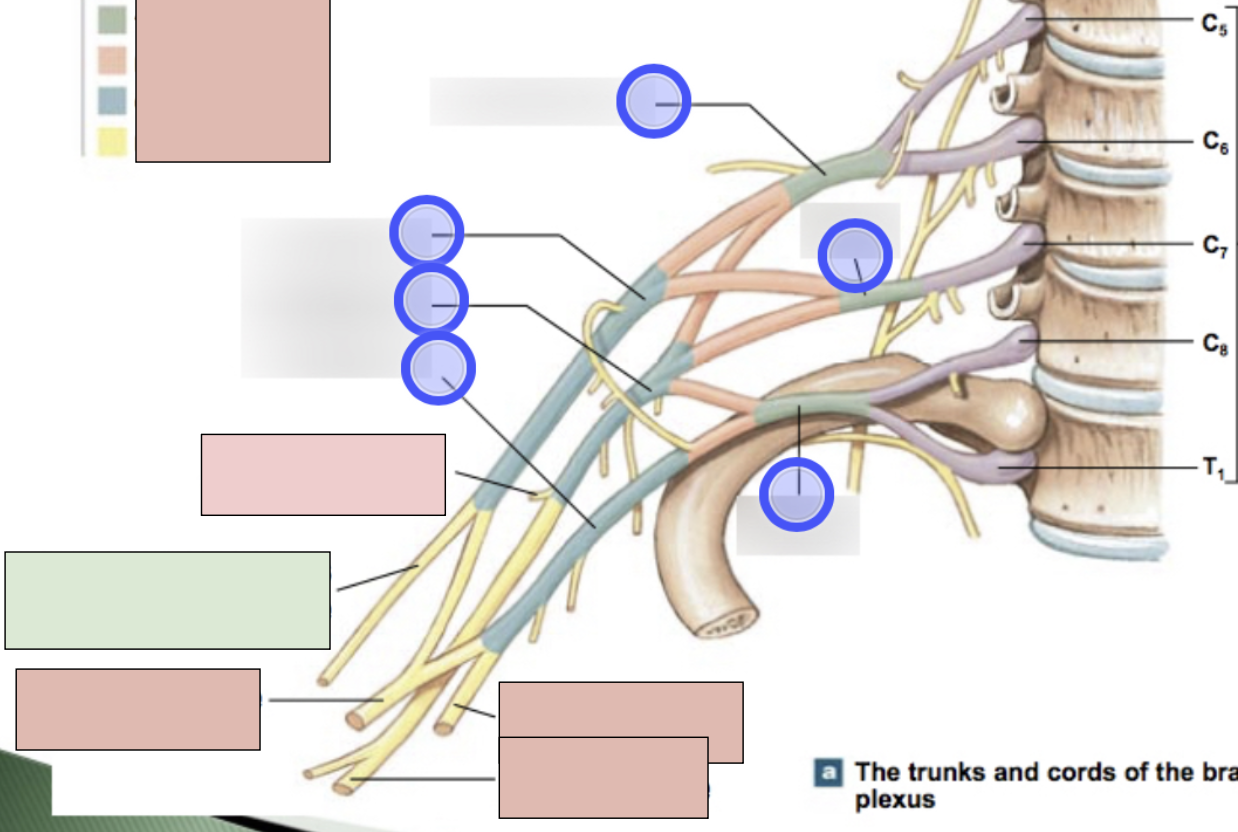
median nerve
C6-T1, motor for flexor muscles of the forearm (flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus/pronator quadratus, pronatus teres, radial half of flexor digitorum profundus, digital flexors); sensory from skin over anterolateral surface of the hand; roots from lateral + medial cord
ulnar nerve
C8-T1, motor for flexor carpi ulnaris, ulnar half of of flexor digitorum profundus, adductor pollicis, and small digital muscle through deep branch; sensory from skin over medial surface of the hand through the superficial branch; roots from medial cord
nerve to subclavius
apart of brachial plexus
dorsal scapular nerve
apart of brachial plexus
long thoracic nerve
apart of brachial plexus
suprascapular nerve
apart of brachial plexus
pectoral nerve
apart of brachial plexus; has medial and lateral
subscapular
apart of brachial plexus
thoracordorsal nerve
apart of brachial plexus
lumbar plexus
T12-L4
illiohypogastric nerve
apart of lumbar plexus
illio-inguinal nerve
apart of lumbar plexus
lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
apart of lumbar plexus
genitofemoral nerve
apart of lumbar plexus
femoral nerve
apart of lumbar plexus; L2-L4, motor for quadriceps, sartorius, pectineus, and iliopsoas
obturator nerve
apart of lumbar plexus; L2-L4; motor for gracilis, obturator externus, and adductor magnus
sacral plexus
L4-S4
superior gluteal nerve
apart of sacral plexus
inferior gluteal nerve
apart of sacral plexus
posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
apart of sacral plexus
pudenal nerve
apart of sacral plexus
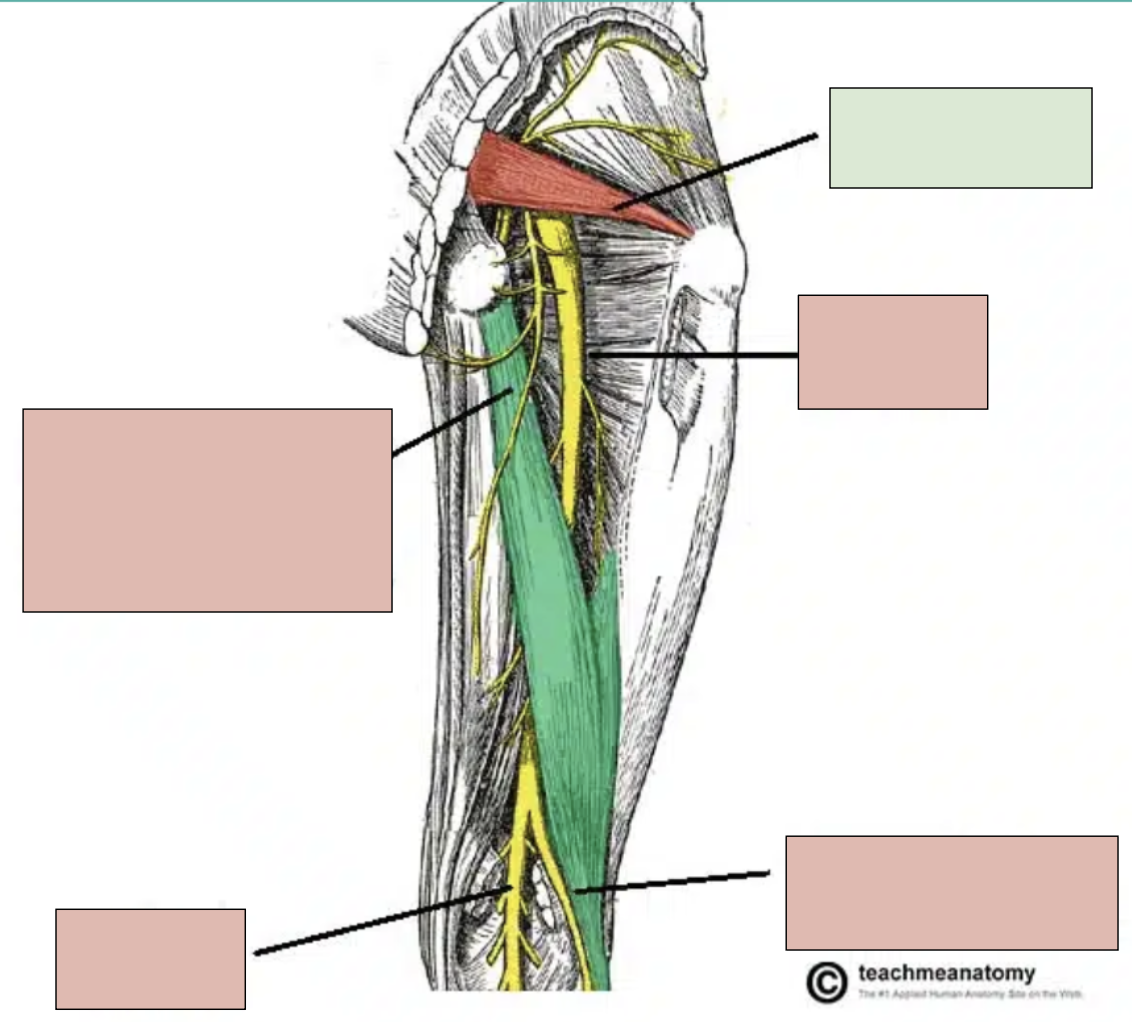
sciatic nerve
motor innervation of muscles in the foot, leg, and posterior thigh and sensory for these areas; branches into tibial nerve and fibular nerve at popliteal fossa
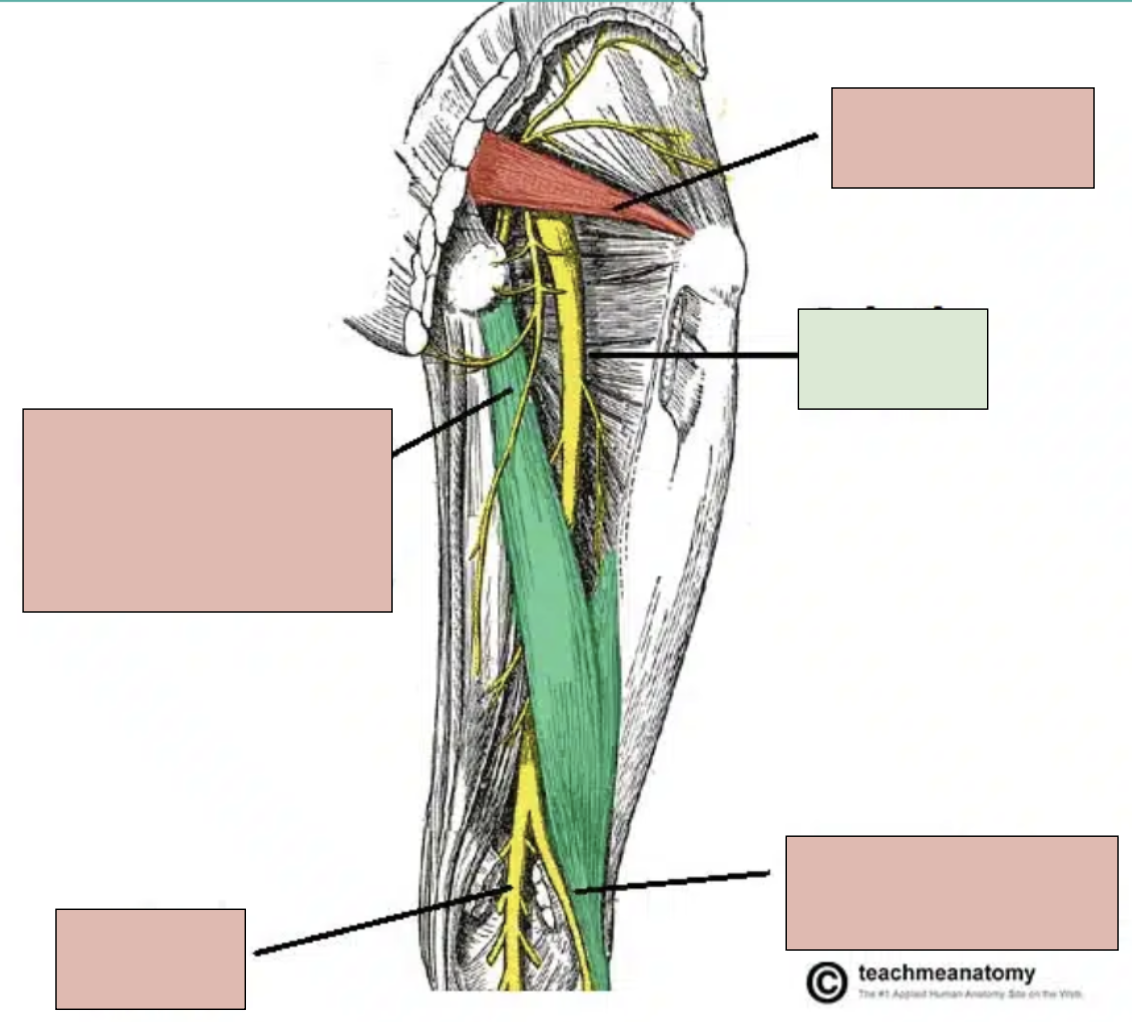
tibial nerve
branch of sciatic nerve; innervates bottom of foot and posterior compartment of leg
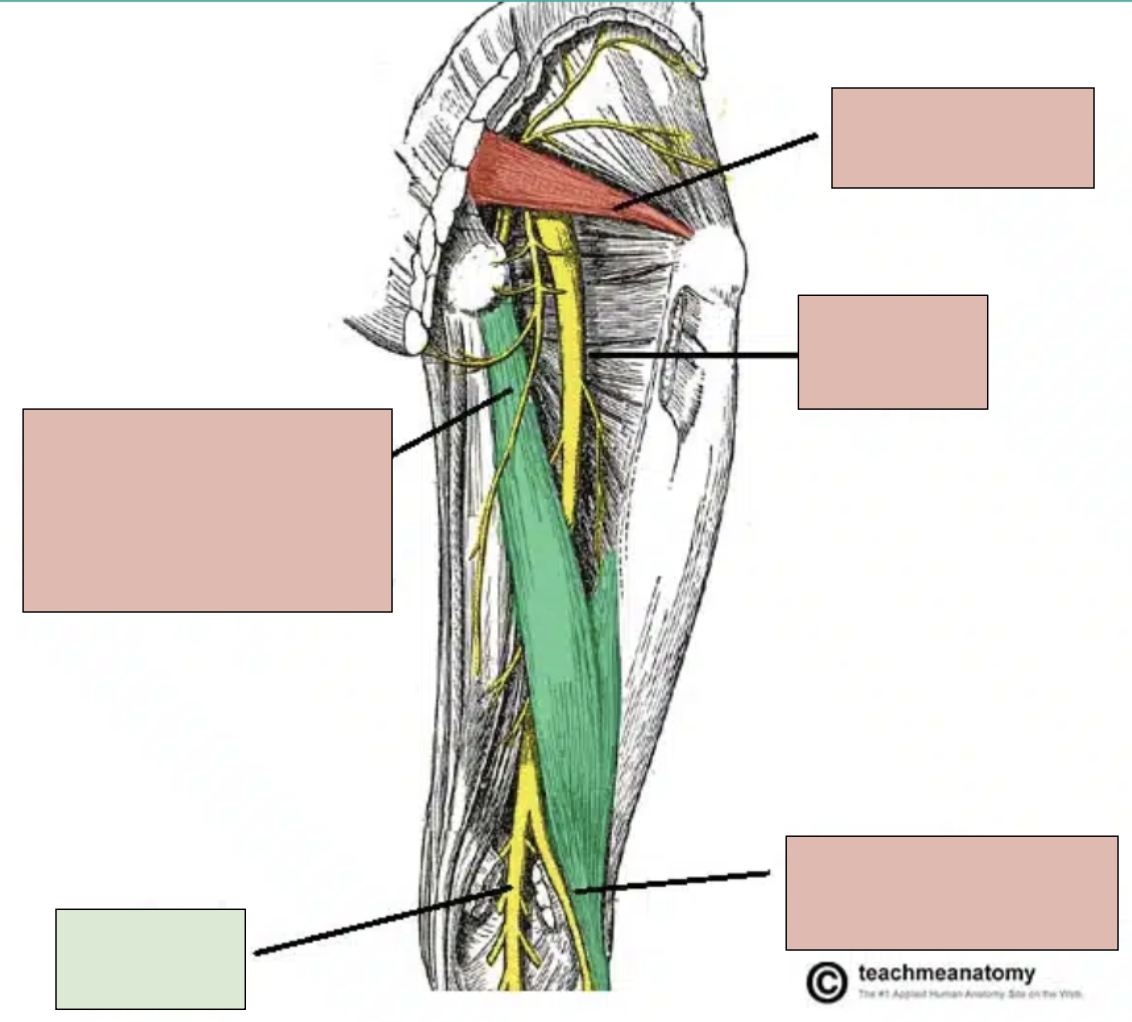
fibular nerve
branch of sciatic nerve; innervates top of foot and anterior compartment of leg
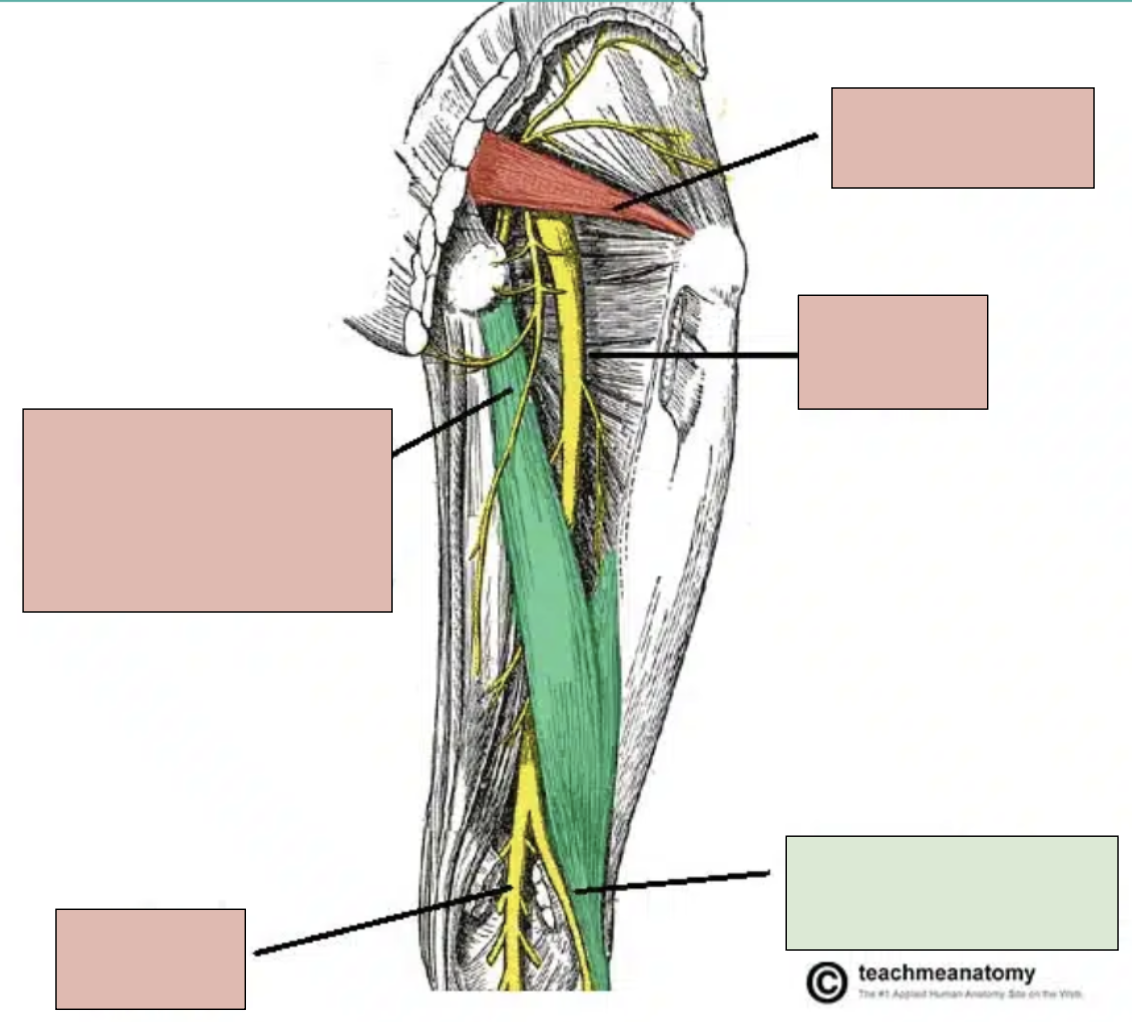
popliteal fossa
where the sciatic nerve branches into tibial and fibular parts
piriformis
small deep muscle in gluteal region that can compress sciatic nerve
sciatica
impingement of sciatic nerve, causes a numbness, pain, and weakening in leg
dermatomes
an area of skin supplied by a single sensory nerve; there are significant overlaps between adjacent ones
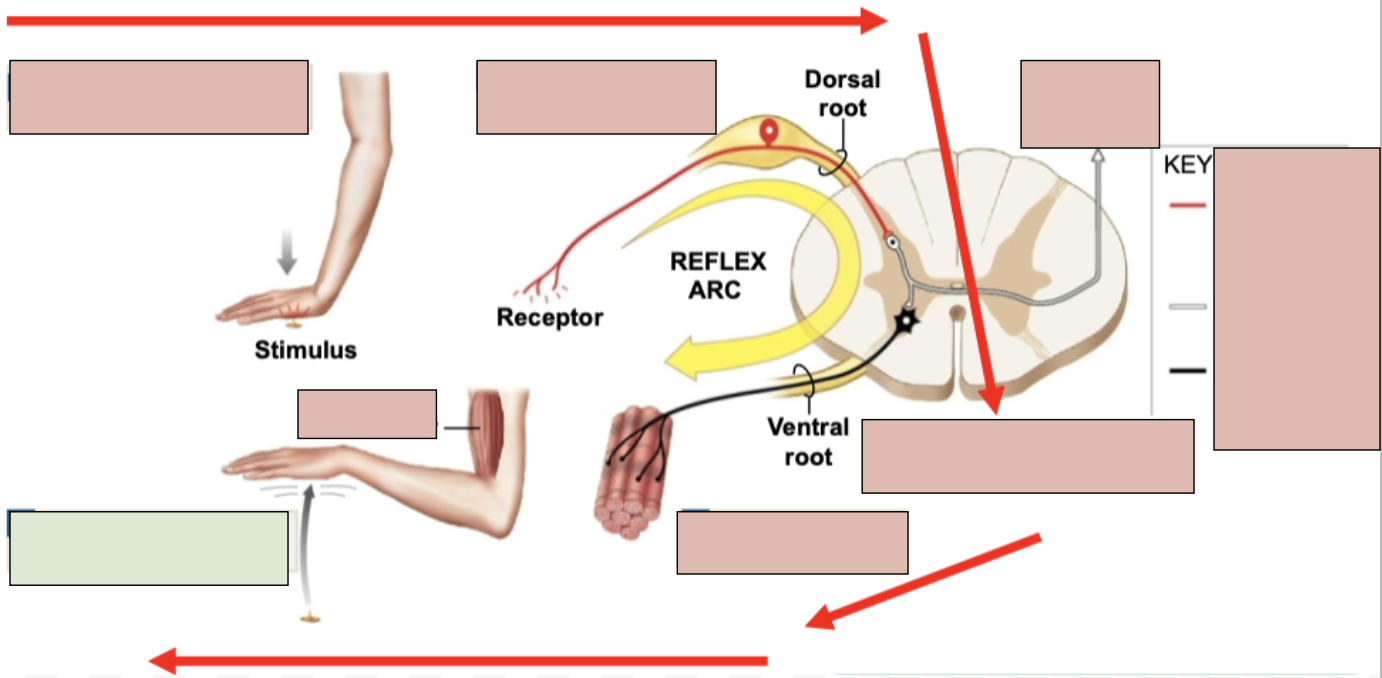
reflex
an immediate involuntary motor action response
1st Step of Reflex Arc
stimulation and activation of receptor
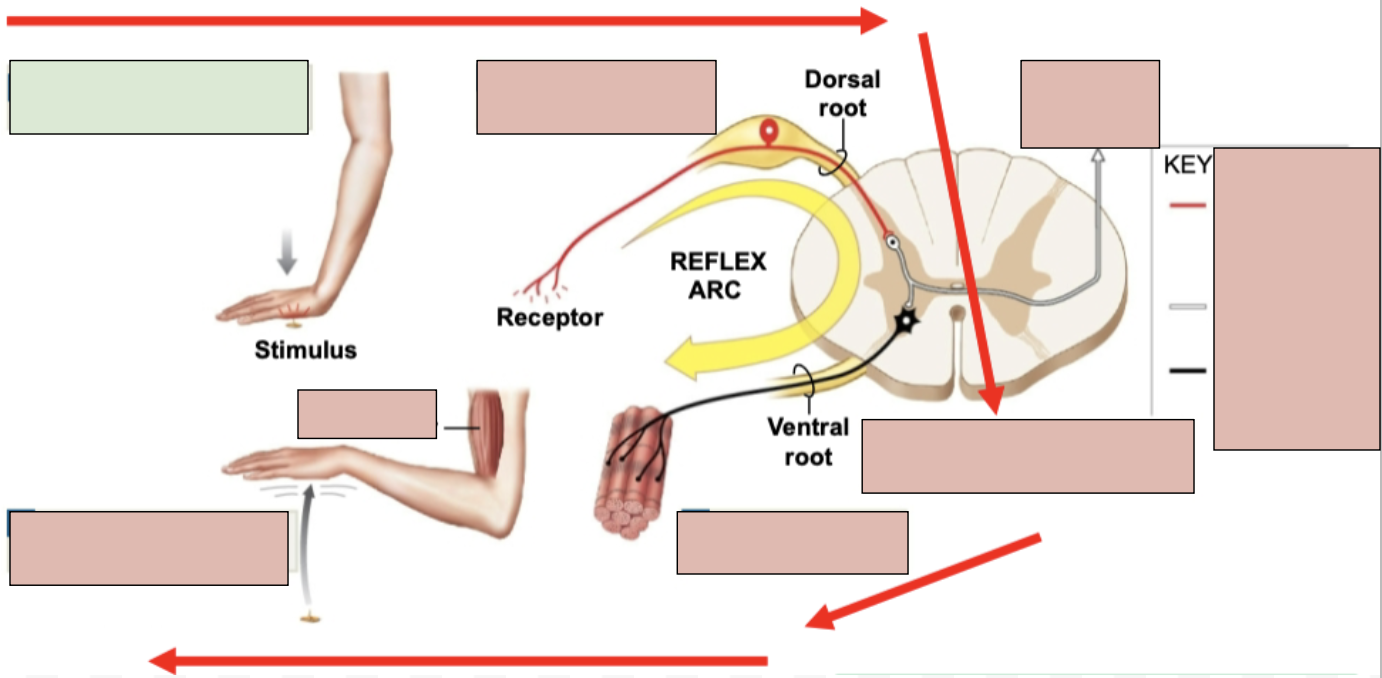
2nd Step of Reflex Arc
Activation of a sensory neuron
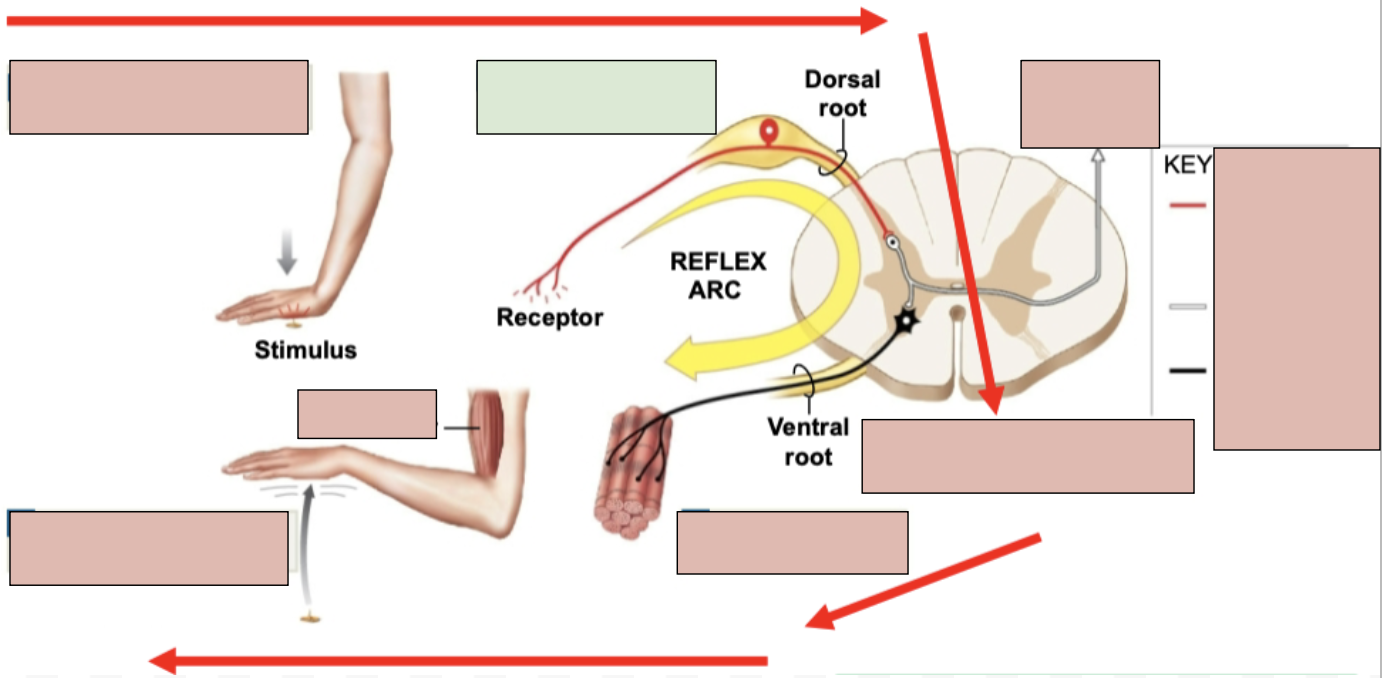
3rd Step of Reflex Arc
information processing in CNA (in spinal cord)
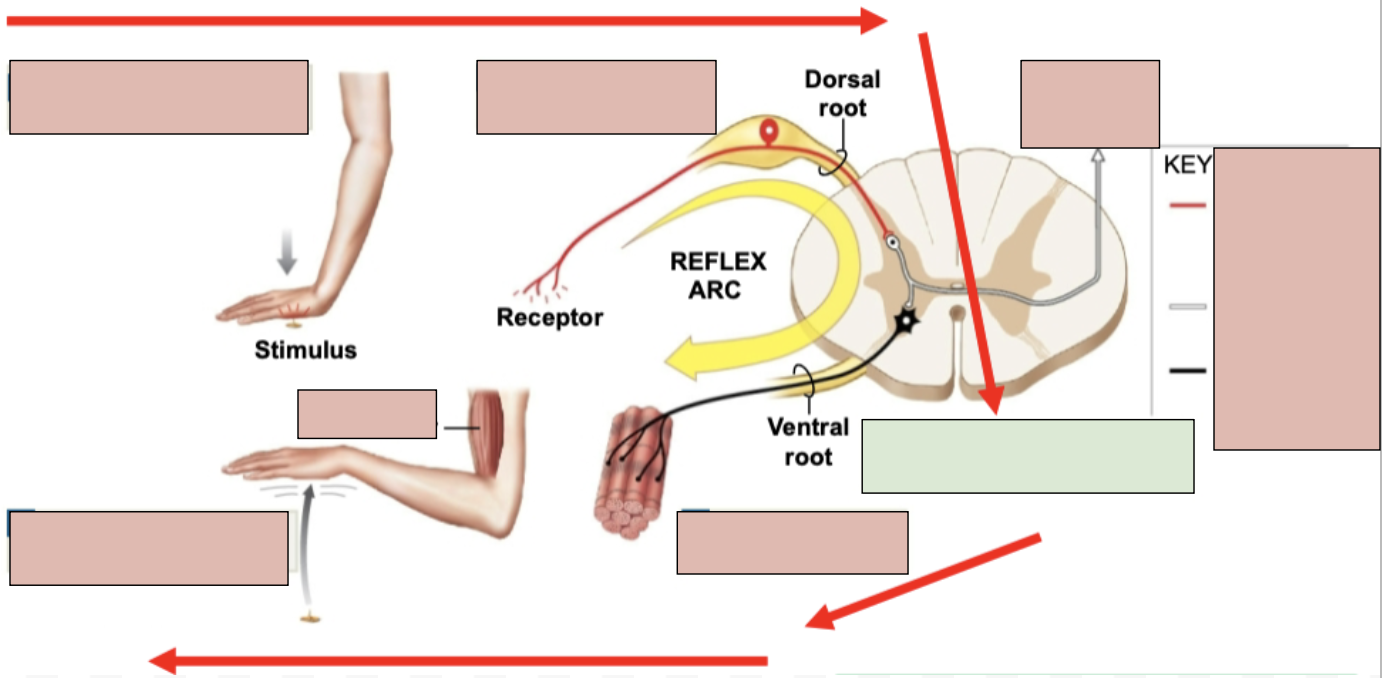
4th Step of Reflex Arc
activation of a motor neuron
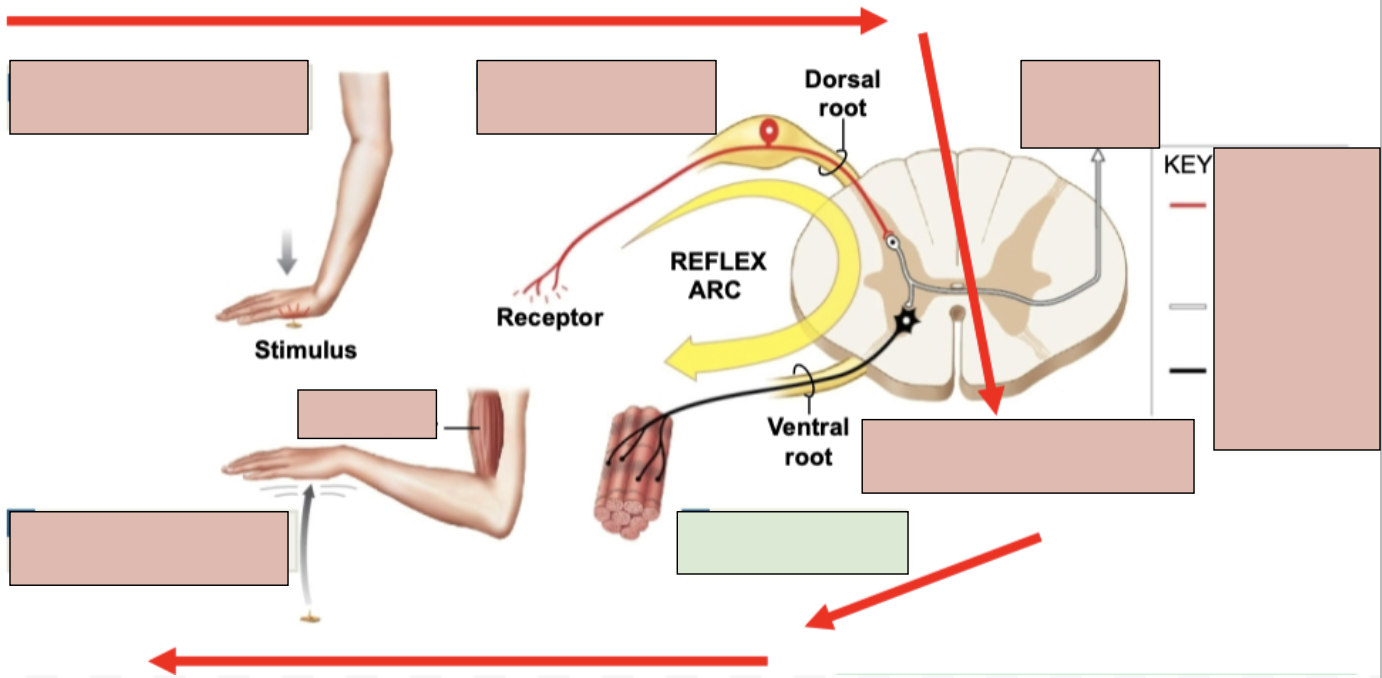
5th Step of Reflex Arc
response by effector (typically skeletal muscle)
Stretch Reflexes
occurs when a muscle is stretched and creates an involuntary motor response; a form of a reflex; initiated by muscle spindles
muscle spindles
sensory receptors inside of our muscles that detect when a muscle is stretched; they help prevent overstretching of a muscle and help main posture of body
dura mater
most superficial layer of meninges
arachnoid mater
middle layer of meninges
pia mater
most deep layer of meninges
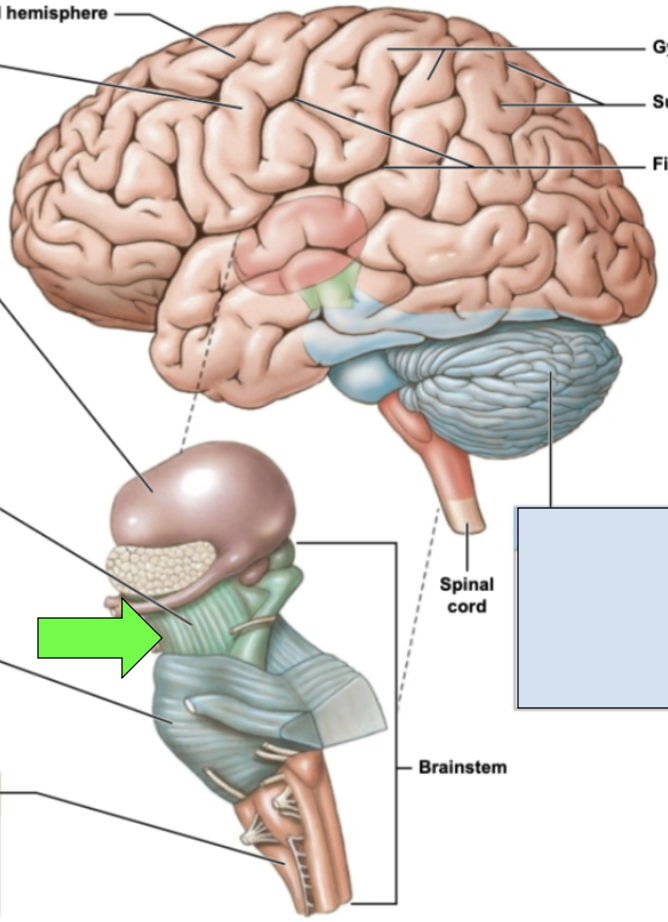
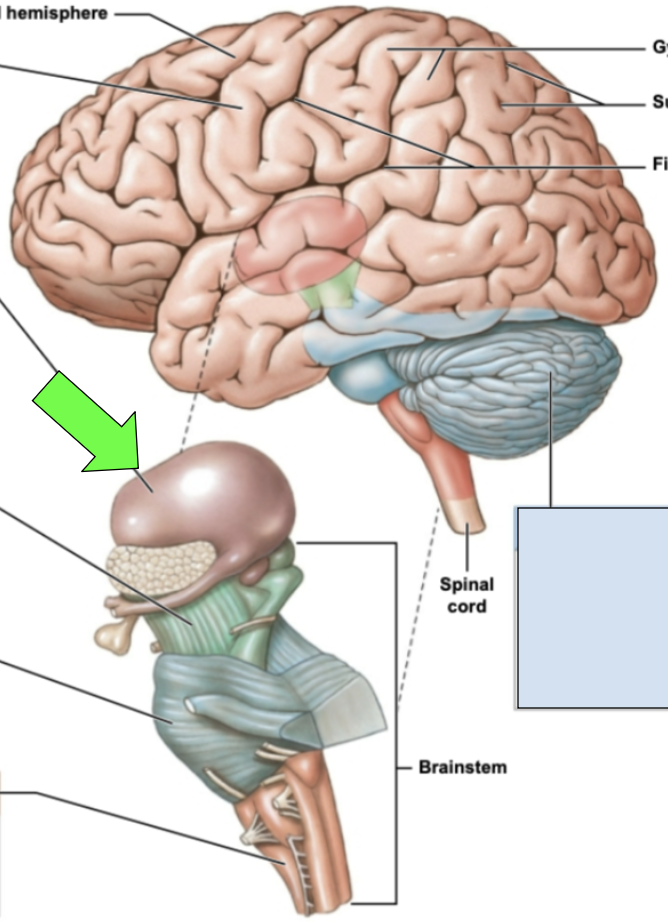
cerebrum
control of skeletal muscles, logic, reasoning, planning, vision/speech/hearing/sensation processing
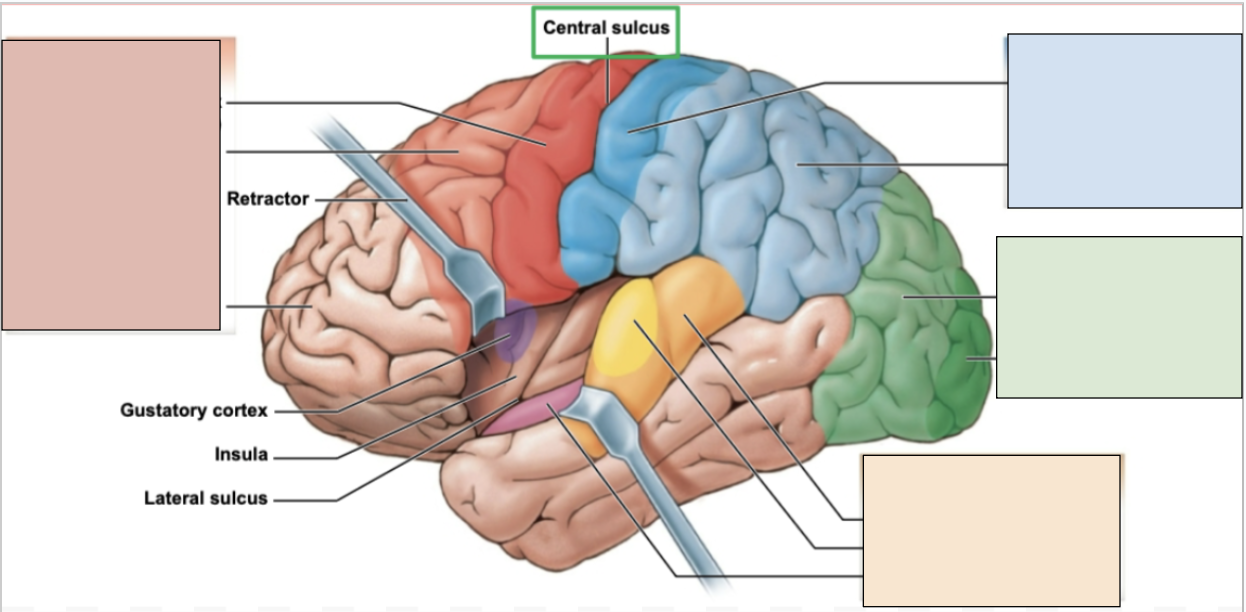
frontal lobe
controls memory, reasoning, planning, voluntary movements, and higher cognitive functioning; contains primary motor cortex
red region
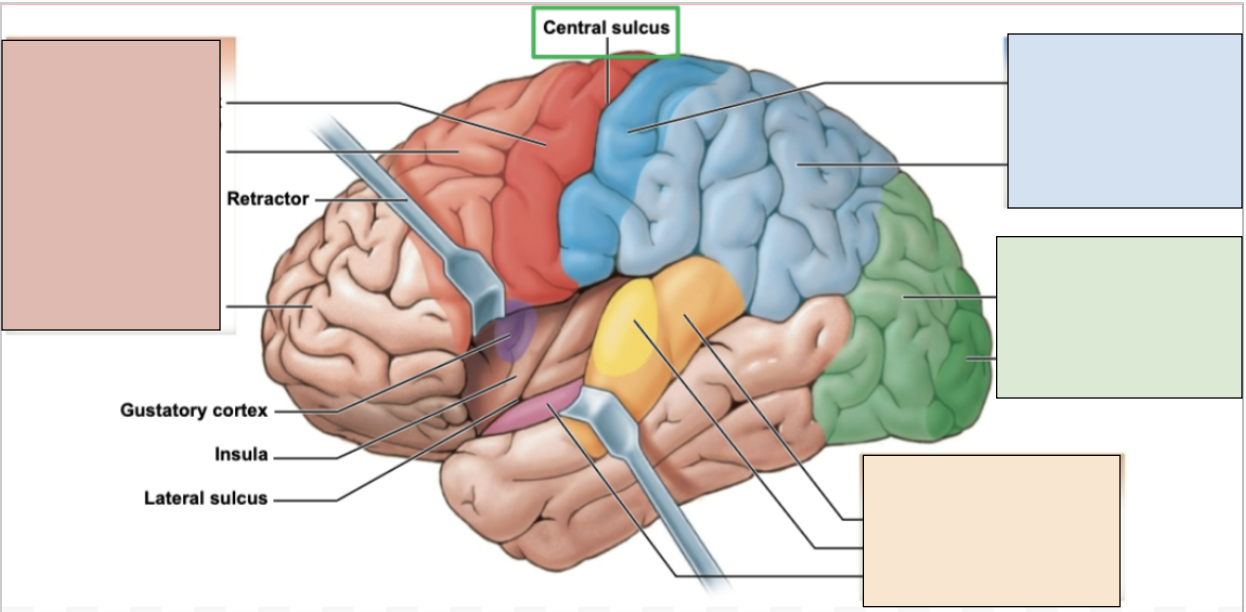
parietal lobe
processes sensory information like touch; constraints primary somatosensory cortex
blue region
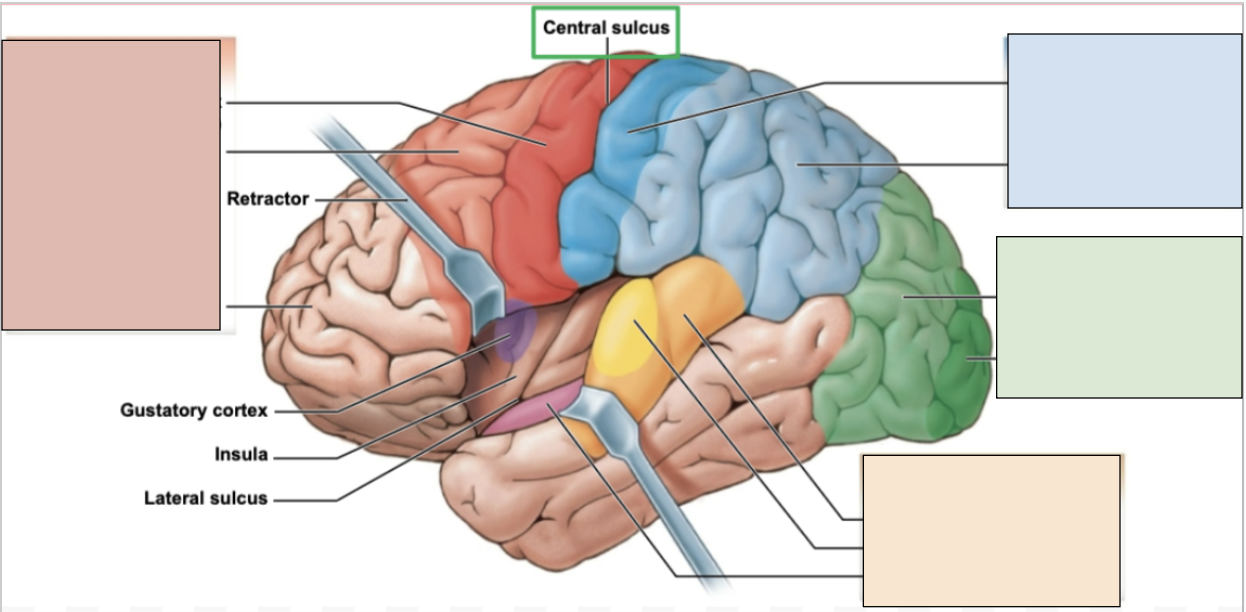
occipital lobe
controls visual information; constraints visual cortex
green region
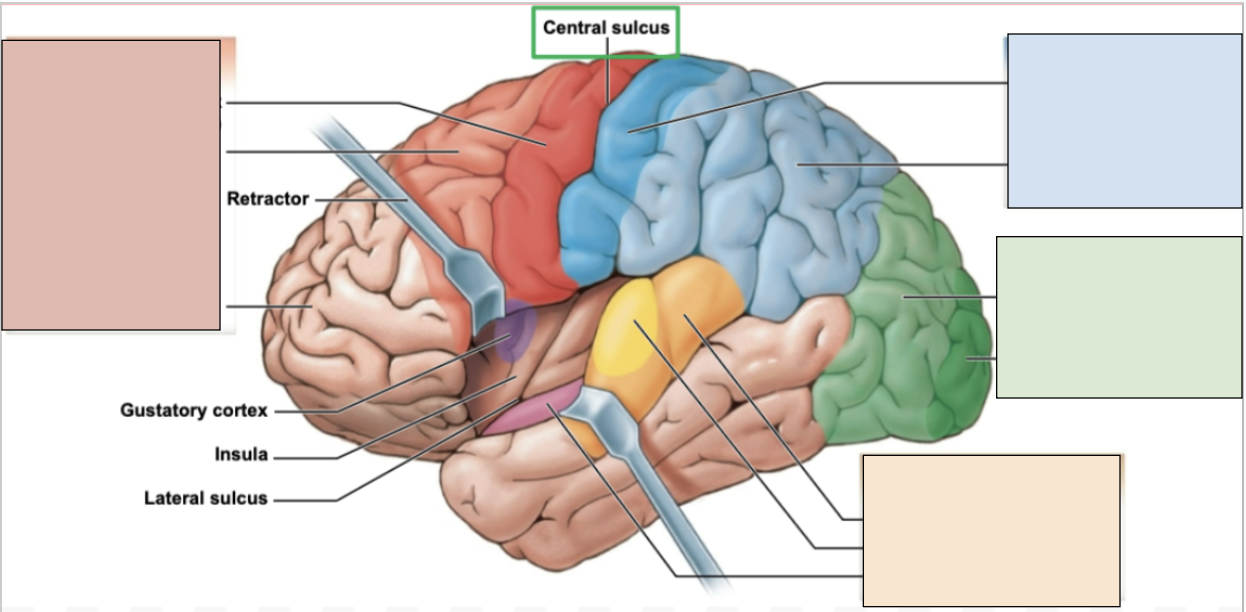
temporal lobe
controls language, auditory, and smell; has auditory and olfactory cortexes
orange region
cerebral hemisphers
the 2 major halves of the brain; contralateral (the left side controls the right side of body)
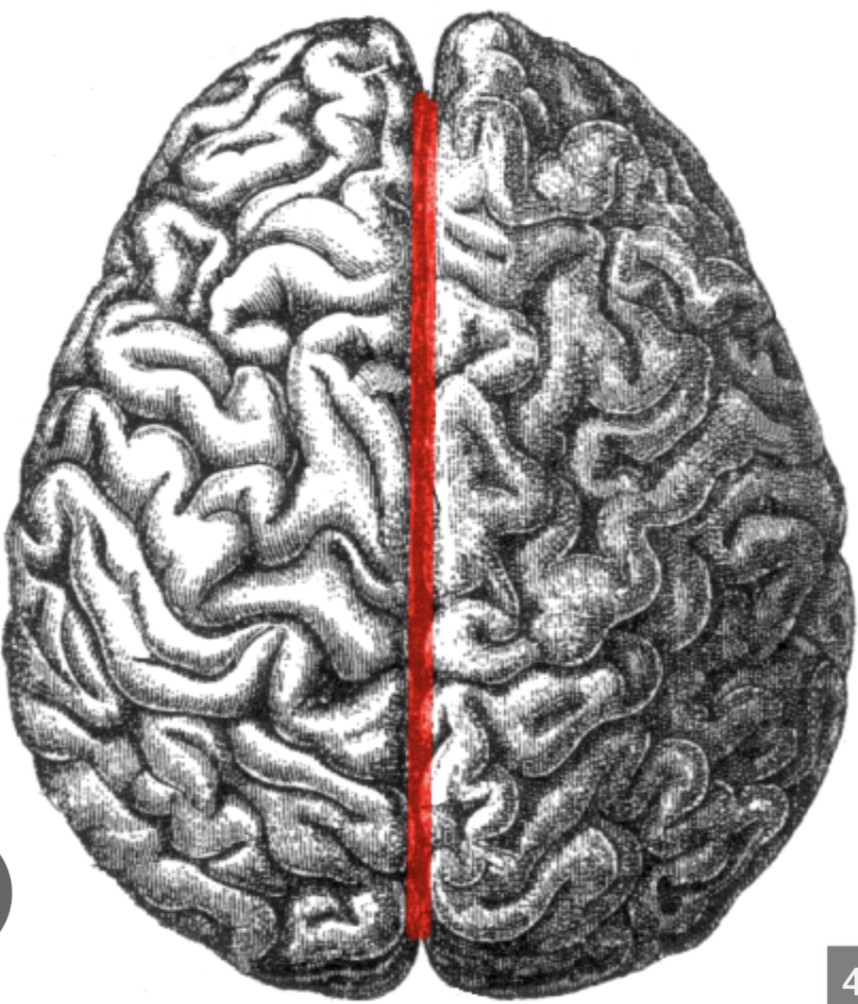
longitudinal fissure
big separation between the cerebral hemispheres
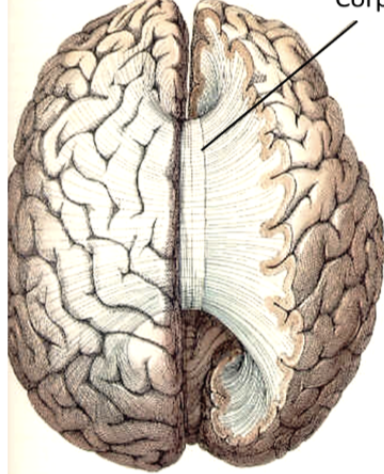
corpus callosum
joins the two cerebral hemispheres together; bundles of fibers and white matter
cortex
gray matter, constraints neuronal cell bodies; outer layer of brain that covers the cerebrum
sulci
indents/groove/fissures
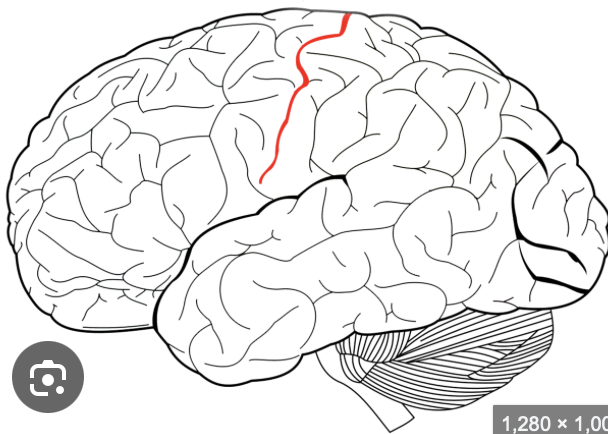
central sulcus
the boundary separating the frontal and parietal lobe
gyri
hills/rounded portions/raised parts
cerebellum
aka the “little brain”; controls balance, coordination and movement
mesencephalon/midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
parts of brainstem
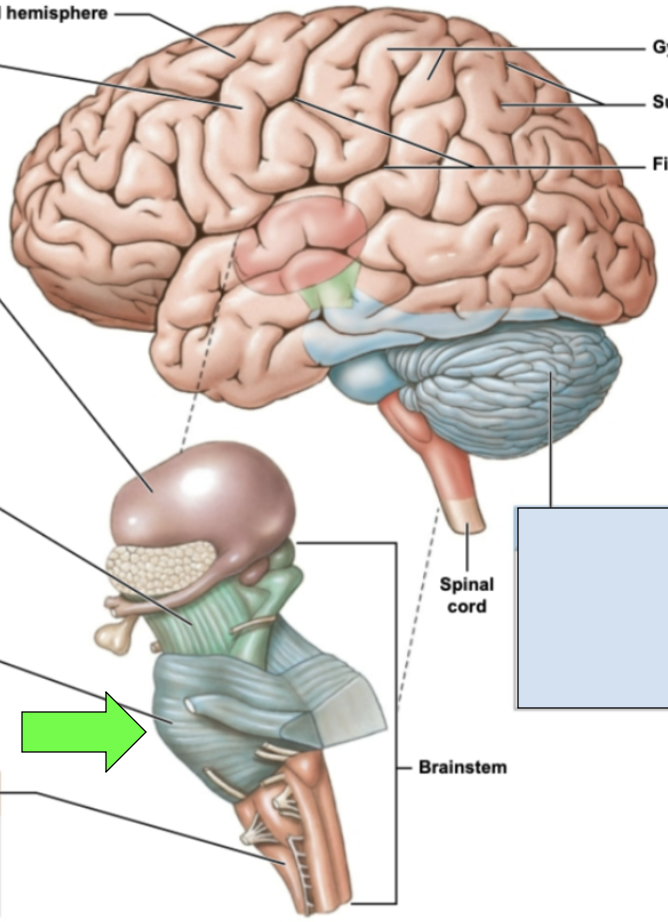
pons
several cranial nerves emerge here; allows for communication between cerebrum and cerebellum; middle portion of brainstem
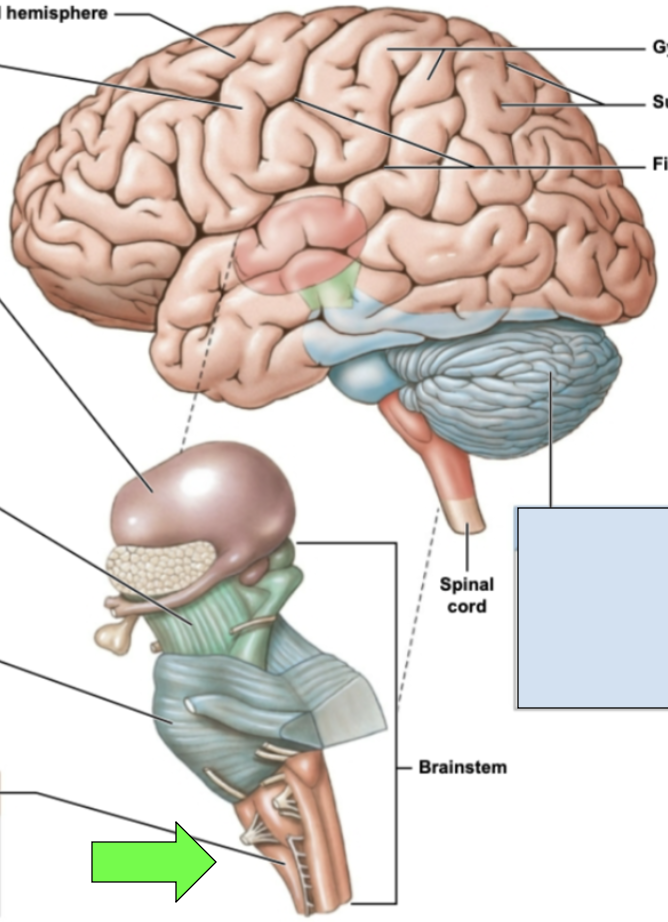
medulla oblongata
most inferior portion of brainstem; processes essential to cervical especially cardiovascular system impulses; joins brainstem to spinal cord
mesencephalon/midbrain
motor pathways, alertness, vision and hearing regulation; most superior part of brainstem
diencephalon
epithalamus, thalamus, hypothalamus
epithalamus
includes pineal gland, limbic system connection to other brain regions; apart of diencephalon
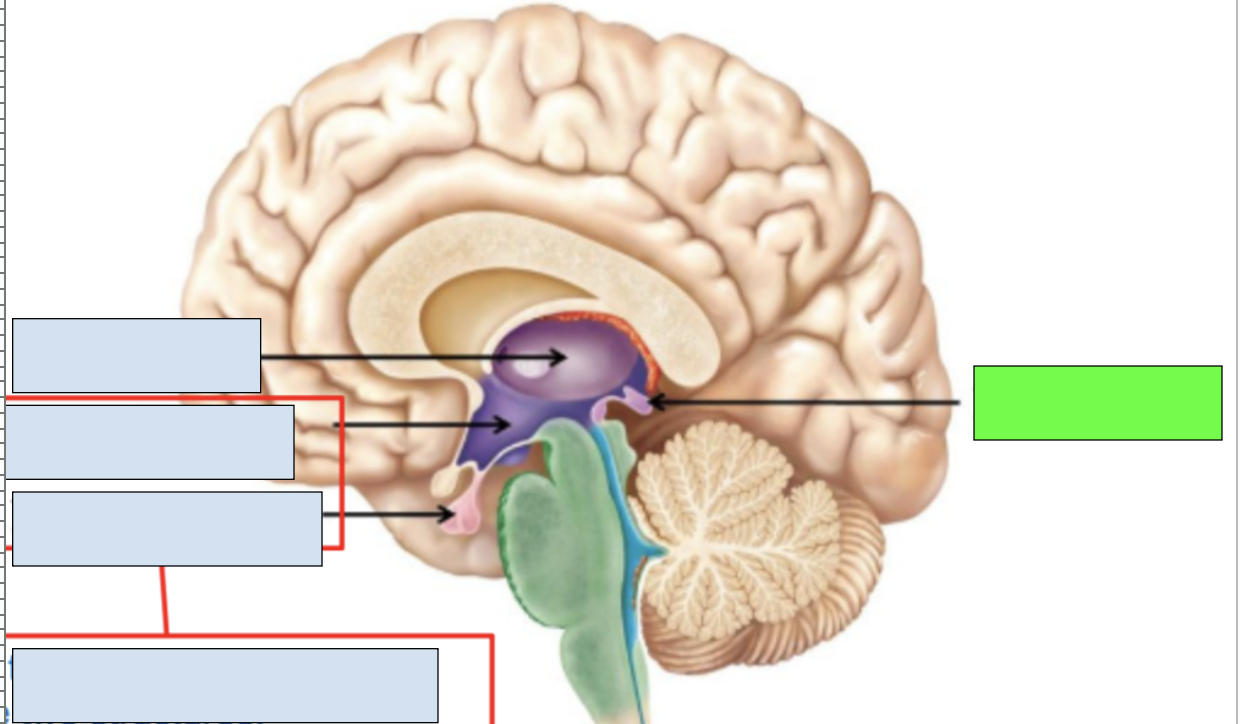
pineal gland
secretes melatonin to regulate sleep cycle
thalamus
sensory information relayed here; apart of diencephalon and limbic system
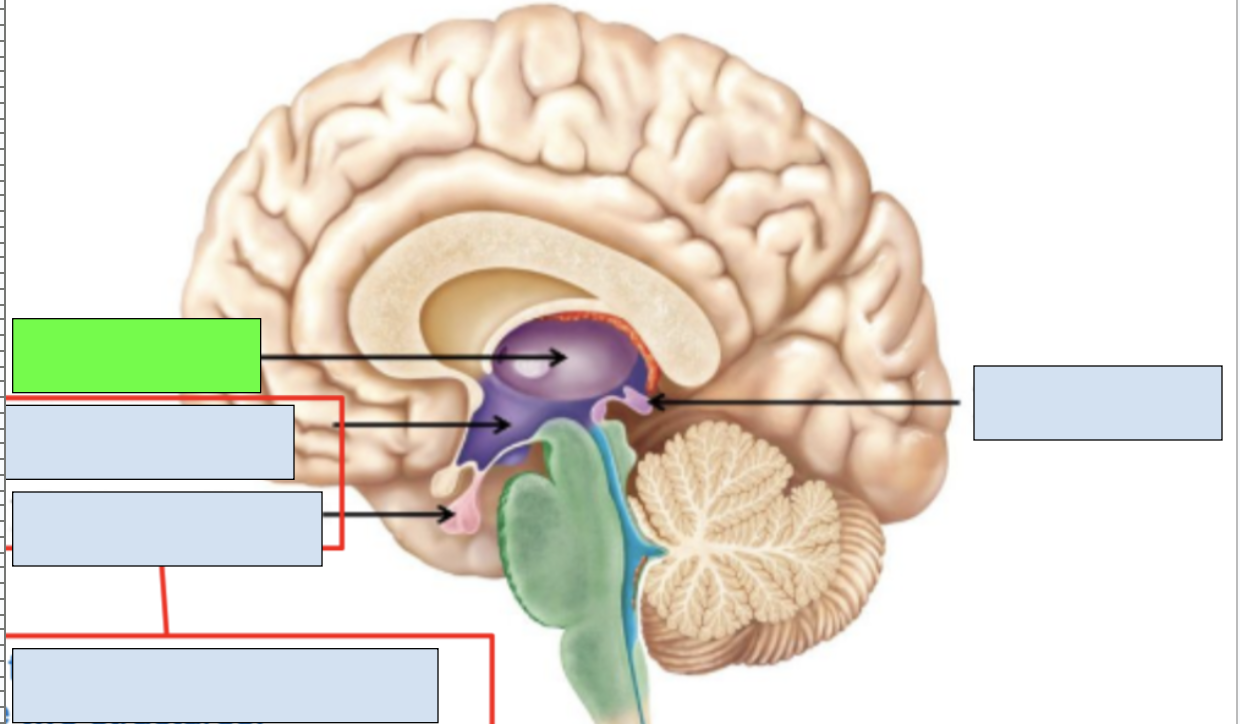
hypothalamus
hormonal release, connection between nervous and endocrine systems; works with pituitary gland; apart of diencephalon and limbic system
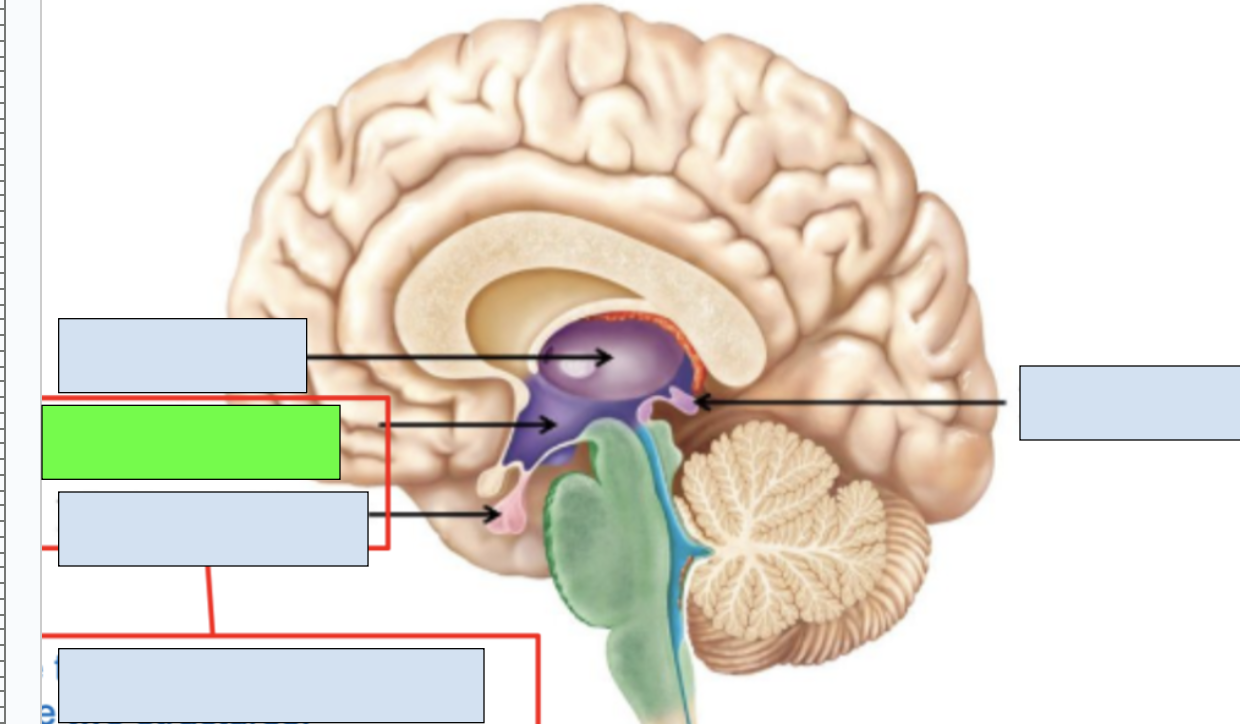
pituitary gland
works with hypothalamus to send out regulating signals for endocrine system
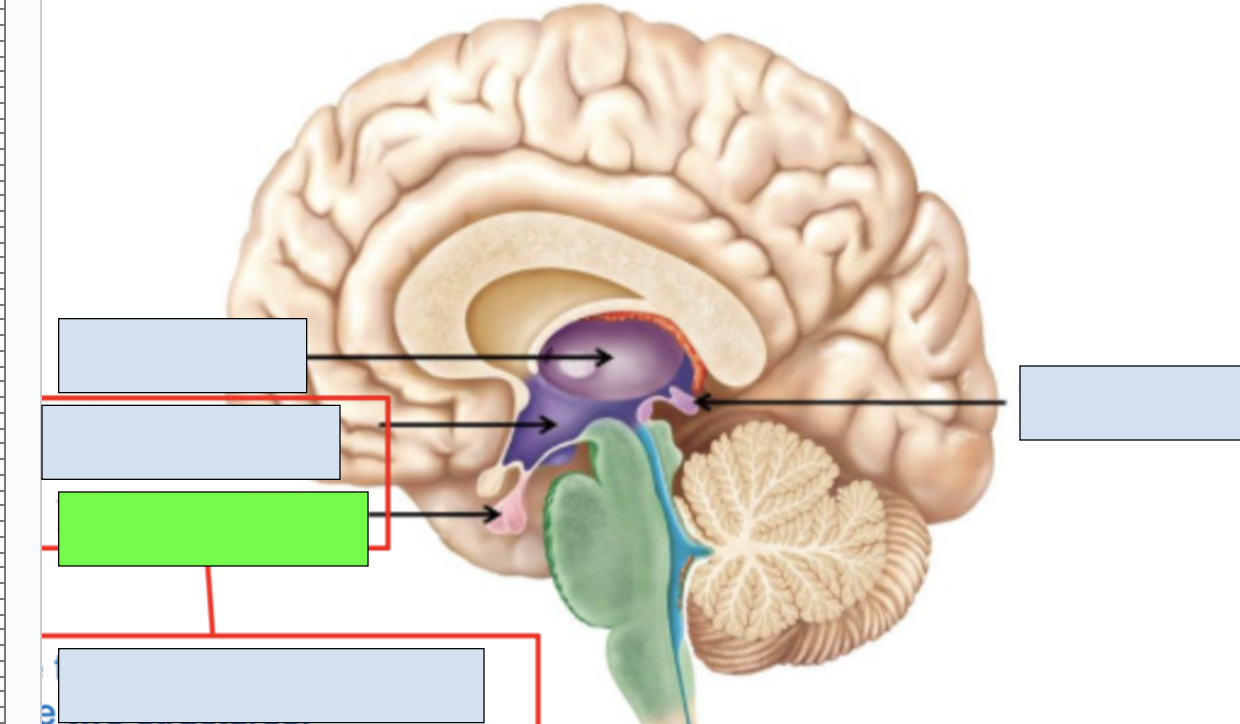
basal ganglia
a series of deeply located brain structures that coordinate movement in the body; beneath the cerebral cortex
limbic system
group of structures that regulate emotions; contains nuclei and cortical structures
thalamus, hypothalamus, hippocampus, amygdala, olfactory bulb
structures of limbic system
hippocampus
important for memory and learning; apart of limbic system
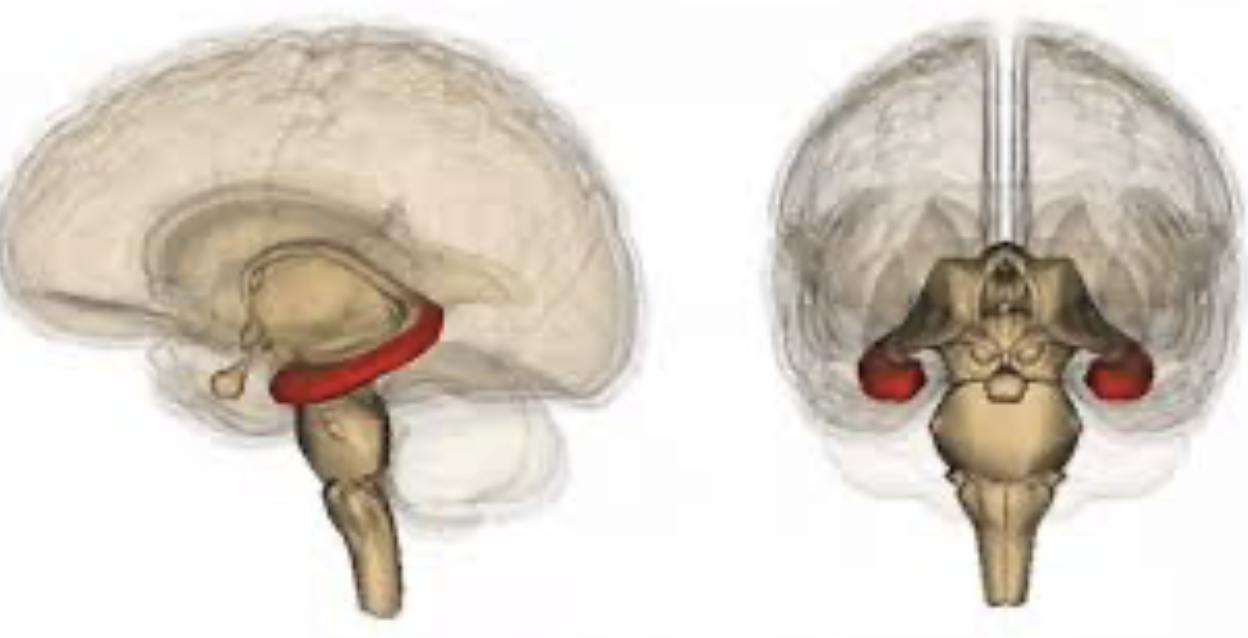
amygdala
important for memory, decision making, and emotions; a part of limbic system
olfactory bulb
important for sense of smell; apart of limbic system
thalamus, hypothalamus, mesencephalon, pons, cerebellum, medulla oblongata
structures visible in midsagittal section of brain
pons, cerebellum, medulla oblongata
structures visible in coronal cut of brain