Unit 2: Macromolecules
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Most organic molecules contain what that is associated with LIVING ORGANISMS
Carbon
Dehydration synthesis is used to
build or create macromolecules (WATER TAKEN OUT)
Hydrolysis is used to
BREAKDOWN a macromolecule (WATER ADDED)
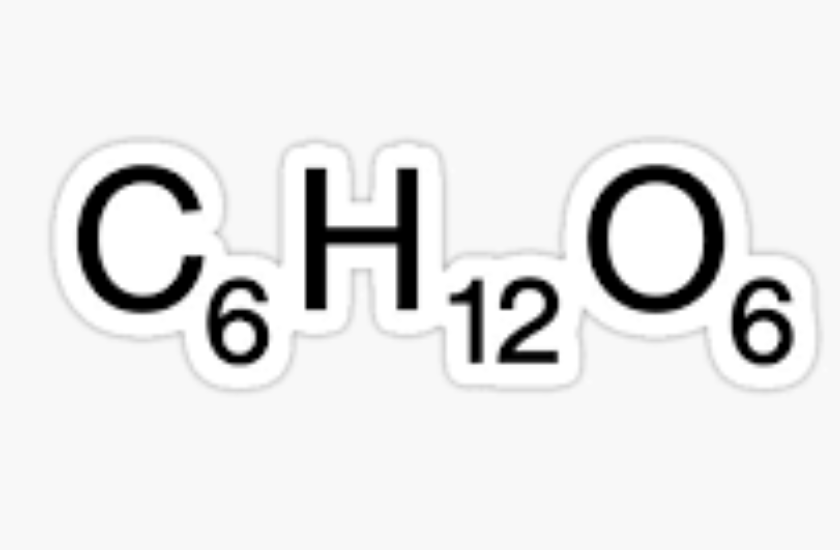
This is the CHEMICAL FORMULA for
Glucose
What elements make up CARBOHYDRATES?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
What ratio does CARBS have?
1:2:1
What is the monomer of CARBS
Monosaccharide
CARBS function: (anything that ends in ose)
Short terms energy
CARBS plant structure; formed out of
CELLULOSE ( cell wall )
Exoskeleton is made of
CHITIN
Plants store glucose in the form of
Starch
Animals store glucose in the form of
Glycogen
Monomers of CARBS
Galactose, Glucose, fructose
Polymers of CARBS
Cellulose (plant structure), Glycogen and Starch
What elements make up LIPIDS?
Carbon, Hydrogen,Oxygen (FEWER O THAN C)
LIPIDS-insoluble to water ( they are )
FATS
Monomer of LIPIDS
fatty acids and glycerol
Function of LIPIDS
Long term energy storage
LIPIDS can
Cushion, insulation, protection (fat or adipose tissue)
LIPIDS structure
cell membrane made of phospholipids
POLYMER EX of lipids
Triglycerides or Fats ( body fats )
Phospholipids are what type of examples
Lipids POLYMER
Control the fluidity of the cell membrane
Cholesterol
Sex hormones regulate processes in the body ( such as pregnancy ) CHEMICAL MESSENGERS
Hormones
Supports metabolism and cell processes
Vitamins function
Saturated fats are Liquid or Solid at room temp
SOLID
SATURATED fats are good or bad for u
BAD
Saturated fats have what type of carbon bonds
Single
Unsaturated fats are solid or liquid
Liquid
Unsaturated fats are good or bad for u
Good
Unsaturated fats have what type of carbon bond
Double
Examples of Saturated fats are
Butter
Examples of Unsaturated fats
Vegetable oil
Unsaturated fats (ones with double bonds) LOOK LIKE
bent over; Unsaturated fats (double-bond) are bent
Phospholipid head is
Polar (hydrophilic); water loving
Phospholipid tail is
Non-polar (hydrophobic); water fearing
Polar means
Water loving
Non-polar means
Water fearing
Protein is the
most diverse group
Protein are made up of what elements
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen
Monomer of Protein
ONE of 20 different AMINO ACIDS
Polymer of PROTEIN
Polypeptide
FUNCTIONS of protein
Structure ( hair, muscles, collagen, keratin )
catalysts ( enzymes )
Examples of Protein
usually end in en most of the time
EX of Protein
Enzymes, hair, muscle, Hemoglobin (transports oxygen in the blood and stores iron), collagen
Enzymes are ( end in -ase )
protein ( that speed up chemical reactions )
Enzymes LOWER the activation energy which means
Lowering the activation energy speeds it up
Can an enzyme have multiple substrates?
No; substrates fit like a puzzle piece; The enyme is made specifically for one substrate
Can an enzyme be used over and over?
YES
Shape of the protein matter because
SHAPE=FUNCTION
3 things that can cause a enzyme to denature
PH, TEMP, Concentration
Optimum means
BEST
Organic molecules means
compounds that contain 2 or more carbons
inorganic molecules means
Compounds that do not contain carbon
What elements make up Nucleic acids?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorous
What is the monomer of nucleic acids?
Nucleotides
What are Nucleotides made up of?
base, sugar, and phosphate
What is the function of Nucleic Acids?
Store genetic information, control cell activities, makes proteins
Polymer examples of NUCLEIC ACIDS?
DNA, RNA, ATP (energy)
DNA is
double-stranded ( DOUBLE-Helix )
how is RNA stranded
single-stranded
DNA is made up of
DEOXYRIBOSE sugar, phosphate, and base
RNA is made up of
RIBOSE sugar, phosphate, and base
DNA bases pair up….
A=T C=G
RNA
A=U C=G
in Lipids what is the Monomer’s structure made of
Glycerol backbone and 3 fatty acids