Horticulture exam 1
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What is horticulture?
Horticulture is the cultivation and management of plants for practical and aesthetic purposes. Activities include planting, pruning, fertilizing, and harvesting, as well as studying plant diseases and improving growth.
Dicot: Flowering plant with two seed leaves, net-like veins, ring-shaped vascular bundles, taproots, and floral parts in multiples of four or five.
monocot vs dicot leaf?
monocot= straight and long, dicot= complex and veiny
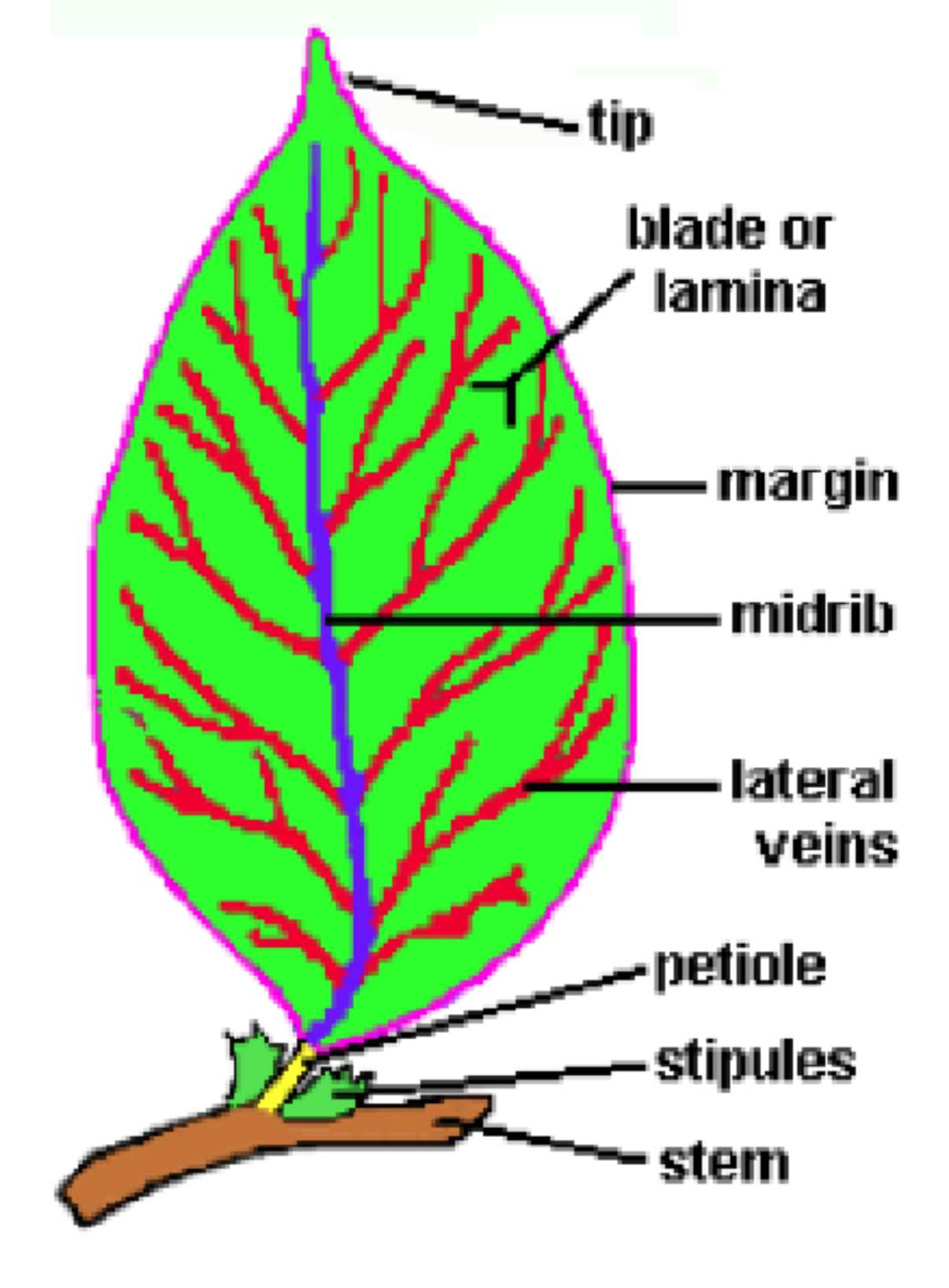
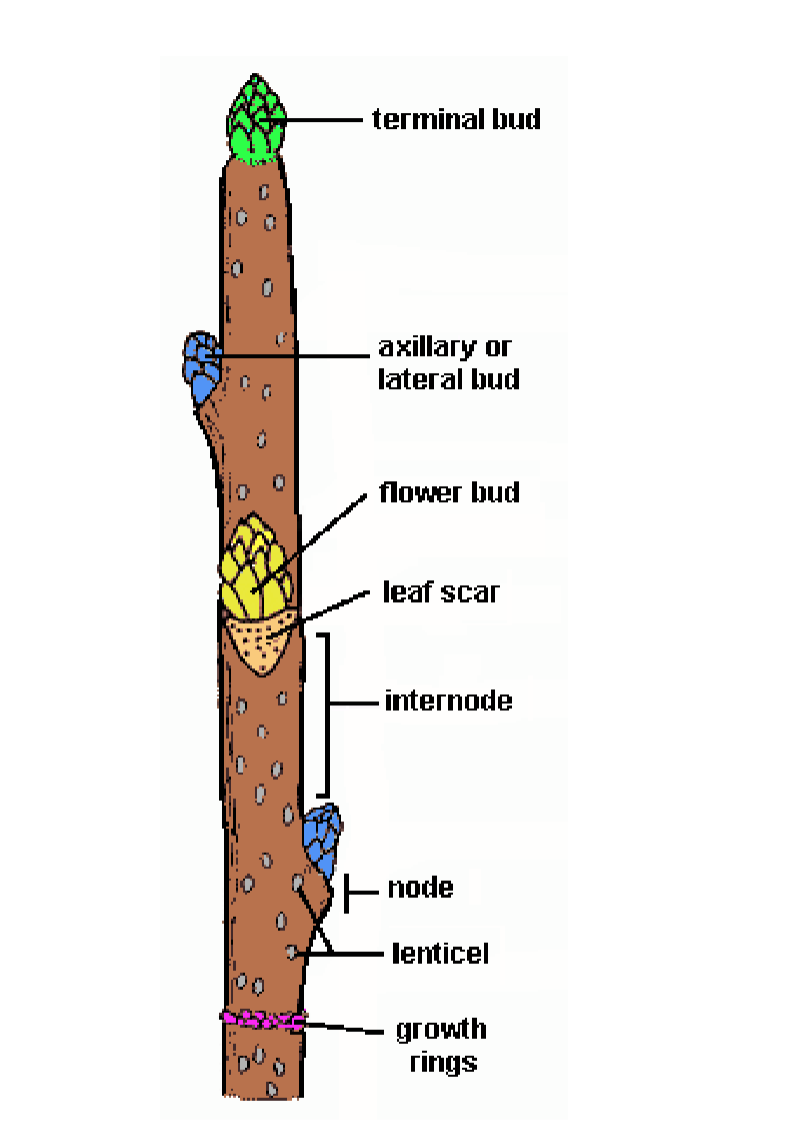
tap root vs fibrous root
tap = one large root (carrot), fibrous = lots of roots and produce is above ground
root hairs and where they arise from?
tubular extensions of epidermal cells that increase surface area of root
where are vascular bundles?
inside cortex and epidermis
levels of taxonomic classifications =
domain, kingdom, phylum/ division, class, order, family, genus, species
who invented the system of binomial nomenclature?
Carl Von Linne/ Linnaeus
what is the difference between a variety and a cultivar?
varieties occur naturally and cultivars are man-made
study this flower diagram!!
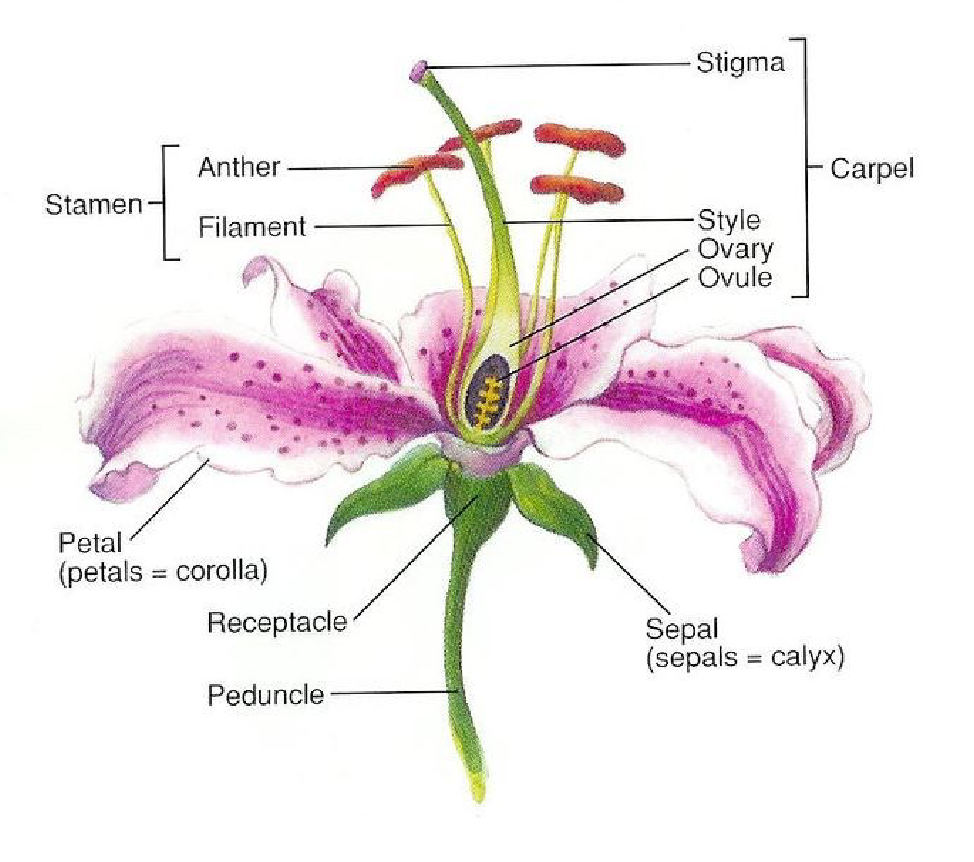
what is the difference between a male and female flower?
female flowers grow fruits and male flowers produce pollen. females have an ovary, style, and stigma. males have an anther and filament
perfect and imperfect flowers
perfect= both male and female parts = either male or female
complete and incomplete flowers
no stamens = incomplete, yes stamens = complete
monoecious and dioecious?
monoecious = both staminate and pistilate occur on the same plant, dioecious = two separate plants
monocot and dicot flowers physical differences
monocot = flower petals divisible by 3, dicot = flower petals divisible by 5
how do flowers fruit and seed?
once pollen gets to the ovary within the flower, the ovary develops into a fruit. the ovules inside the ovary develop into seeds inside of the fruit
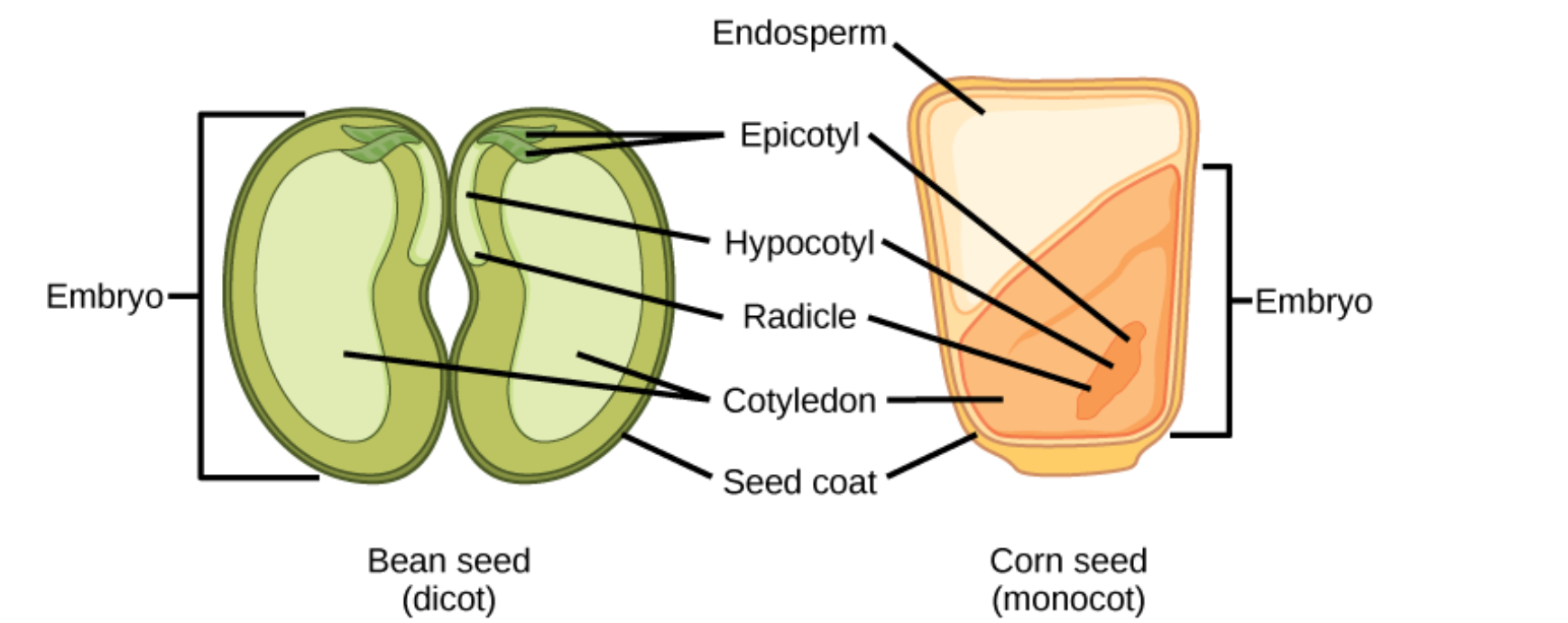
study this diagram about monocot vs dicot seeds!!
spike inflorescence
flowers form along a single stem in a line
raceme inflorescence
each flower has its own stem and is organized and equal on each side
panicle inflorescence
flowers form on their own stems and have smaller pedicels branching off where the flowers form
corymb inflorescence
flowers grow in bunches at the top of each stem
cyme inflorescence
usually broad and flat topped, usually growing in 3’s
umbel inflorescence
flowers grow in spherical bundles on the top of the stem
difference between meristematic and non-meristematic tissues?
meristematic= cell division becoming permanent growth, non-meristematic= no cell division growth
what are the 3 non-meristematic tissues?
dermal, vascular, ground/ fundamental
where is dermal tissue and what purpose does it serve?
found on the outer layer of stems, roots, and leaves. protects plant from infection, environment, and mechanical stress. it also regulates water and gas exchange. ex.) epidermis and periderm
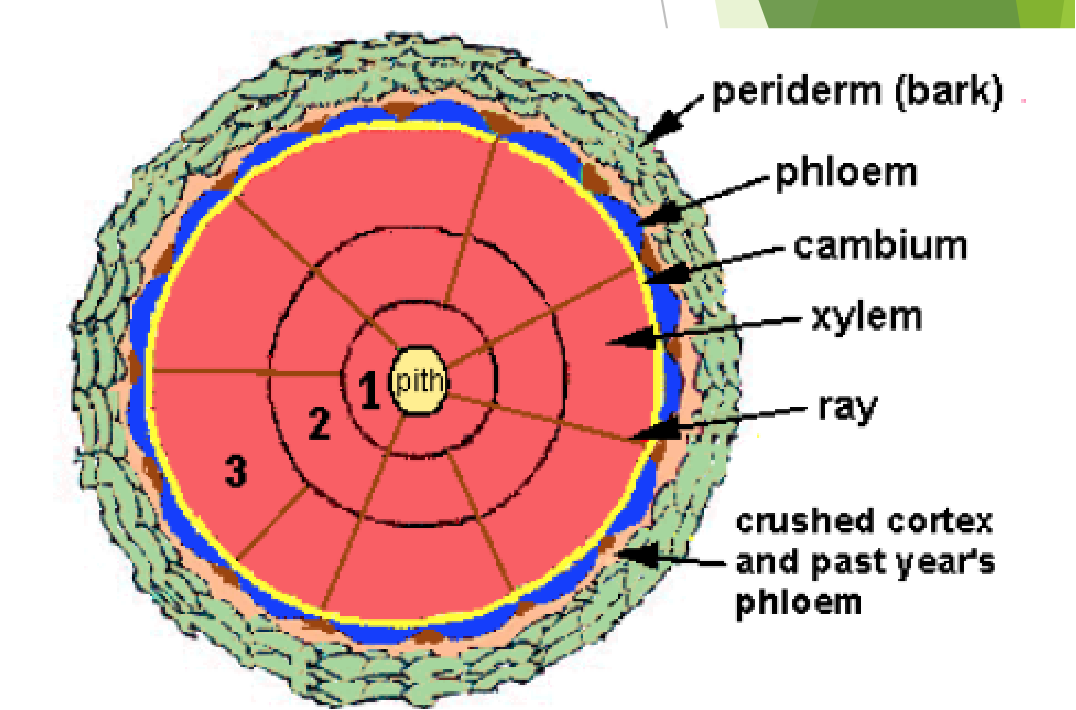
what is the vascular tissue system?
plumbing system of the plant and allows water, minerals and dissolved sugars from photosynthesis to pass through roots, stems, leaves and other parts. ex.) veins on leaves, vascular bundles in stems, vascular stele in roots
what are the differences between xylem and phloem in plants?
the xylem system distributes water and dissolves minerals upward through the plant, from the roots to the leaves. The phloem carries food downward from the leaves to the roots
what is ground/ fundamental tissue?
Tissues not considered dermal or vascular are notes as ground tissue. function- storage, support, filler tissue and site of photosynthesis